Symmetry-Informed Optimization and Verification of Loader Working Device Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model
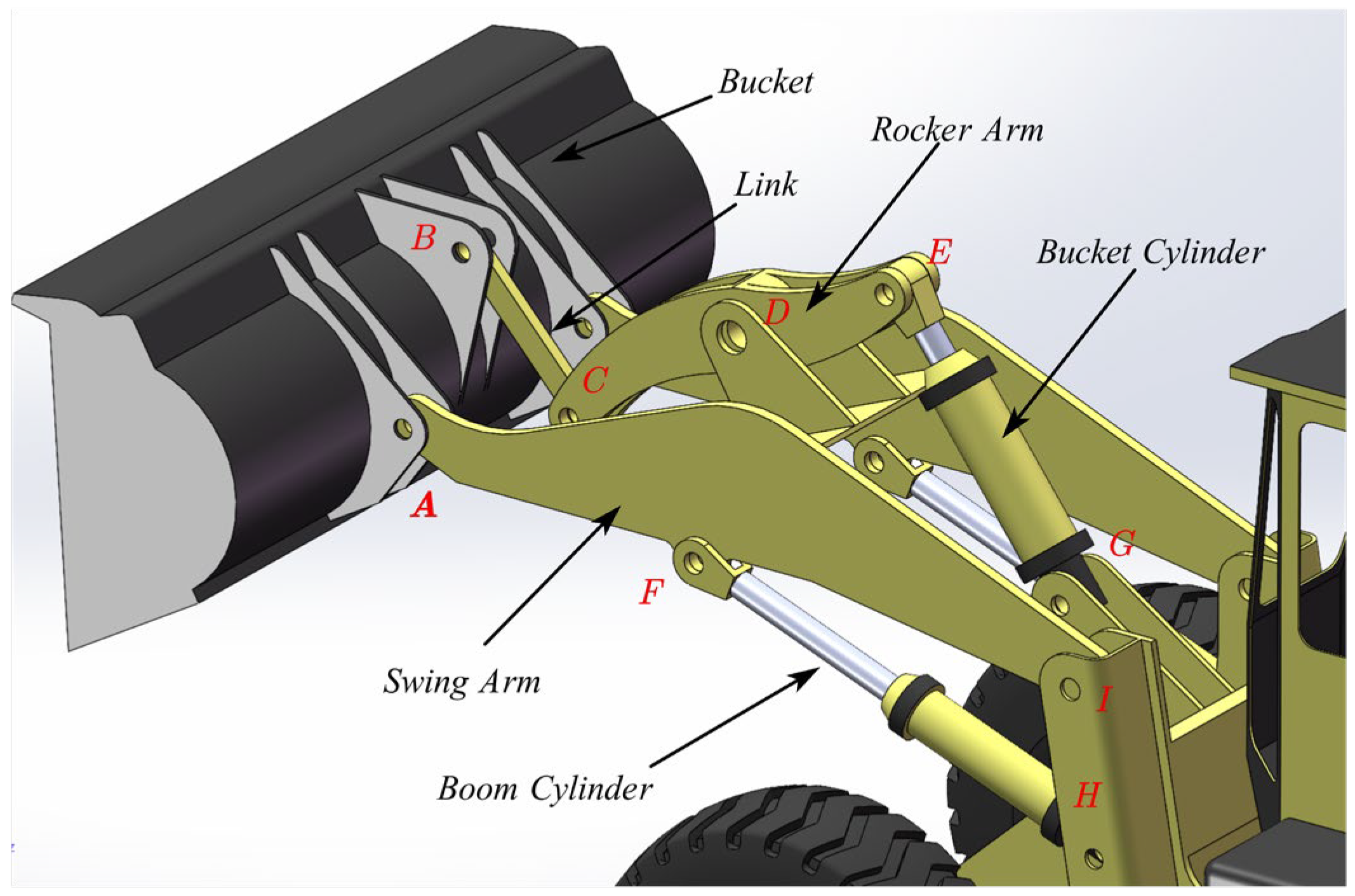
2.1. Problem Description
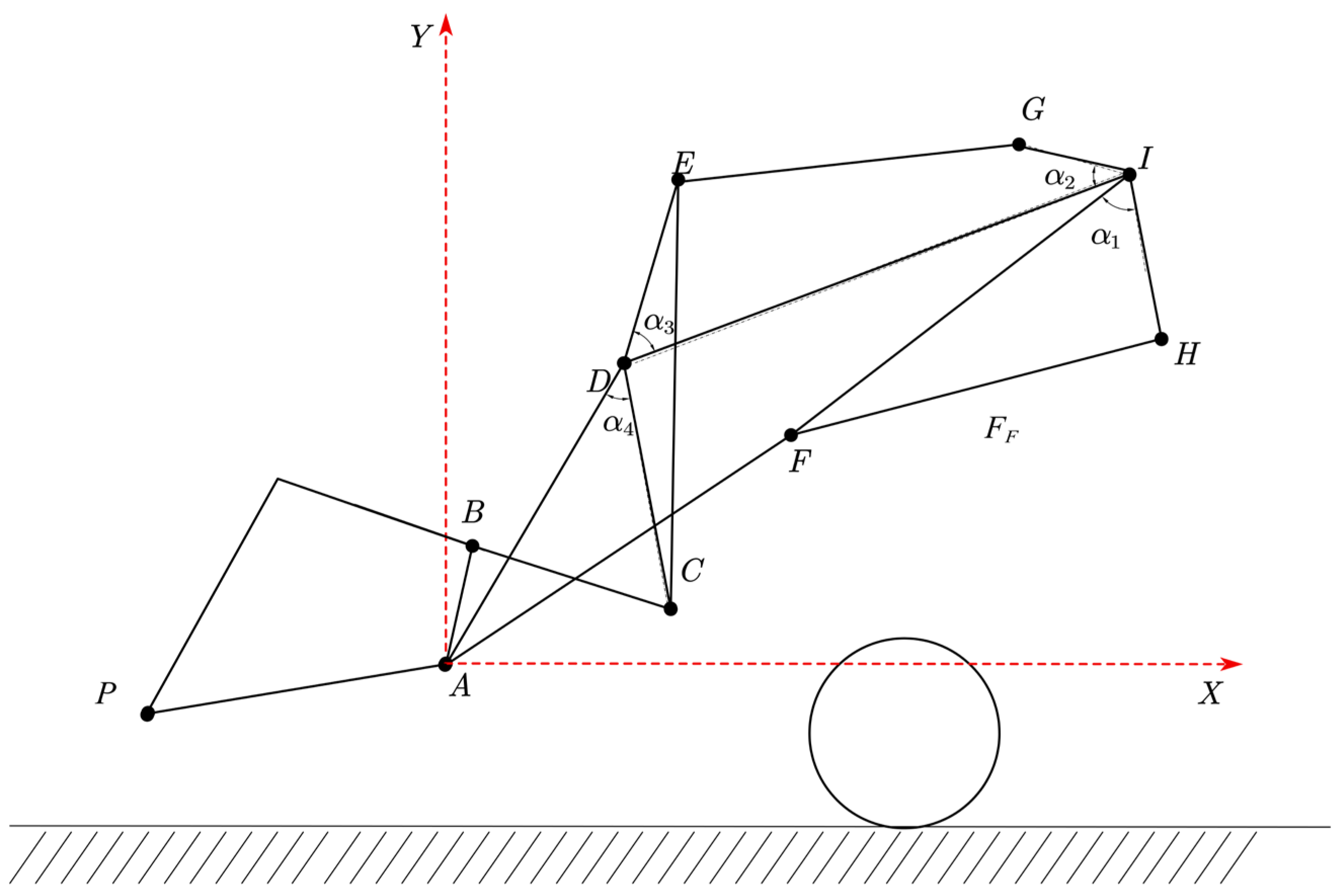
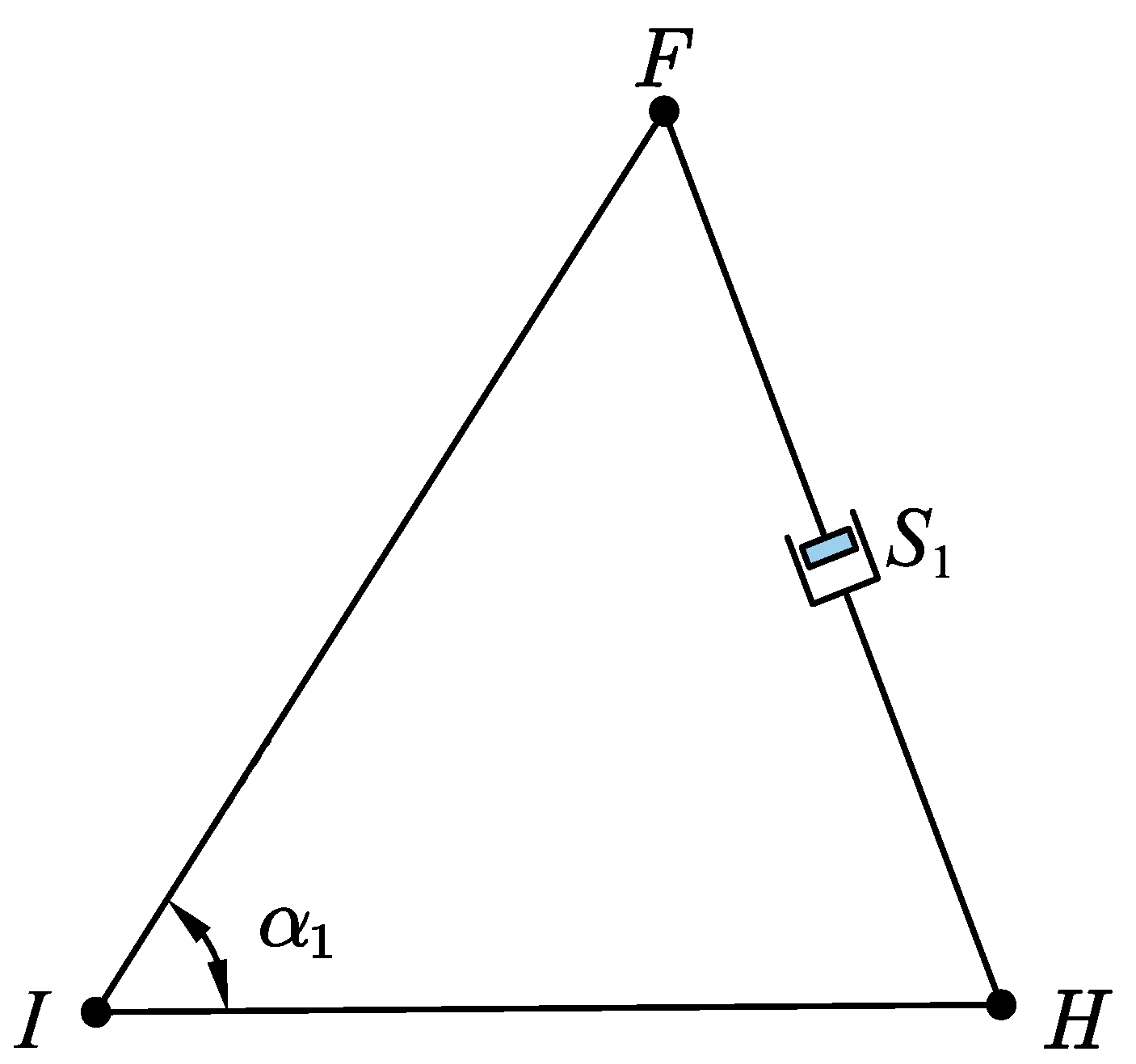
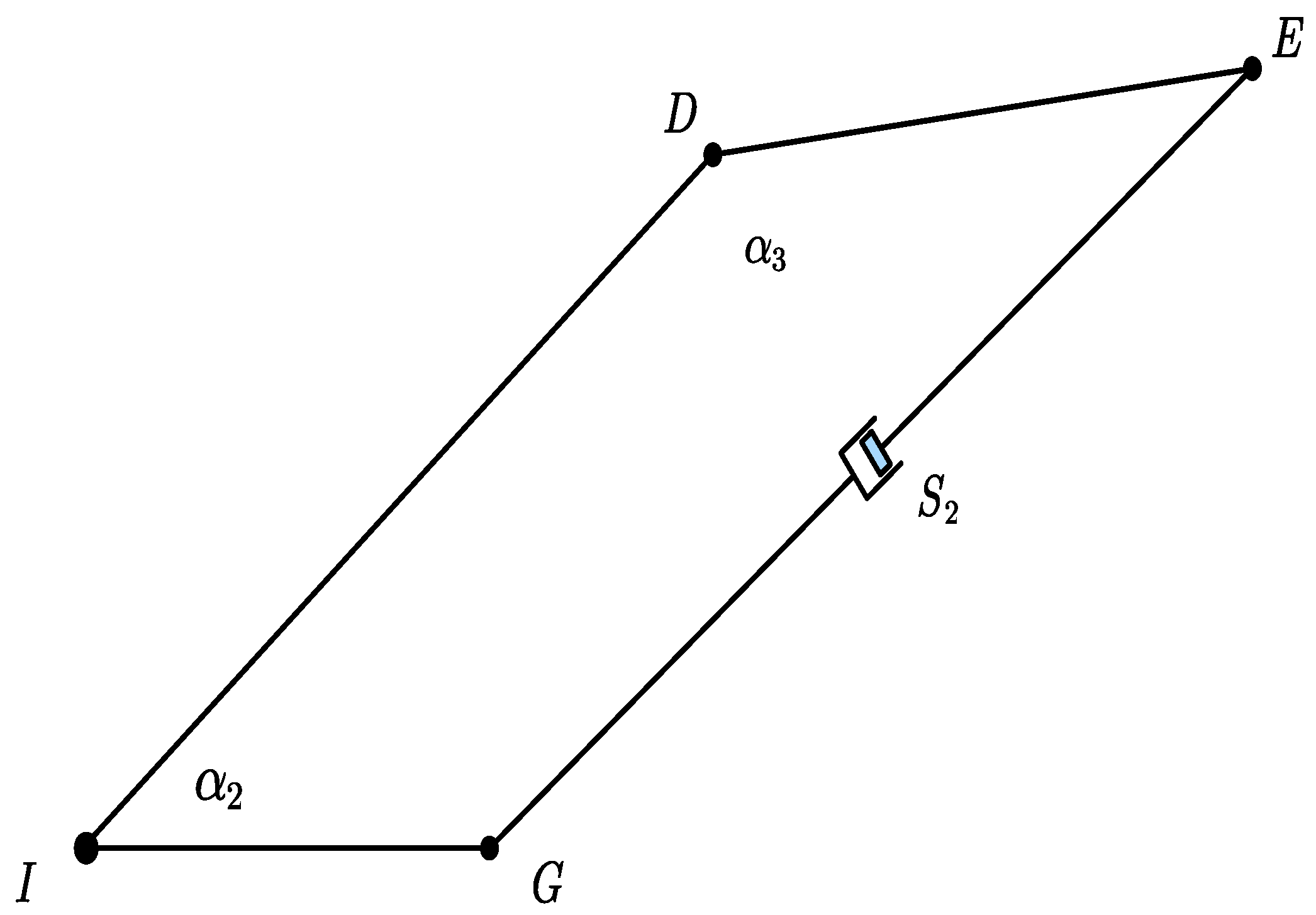
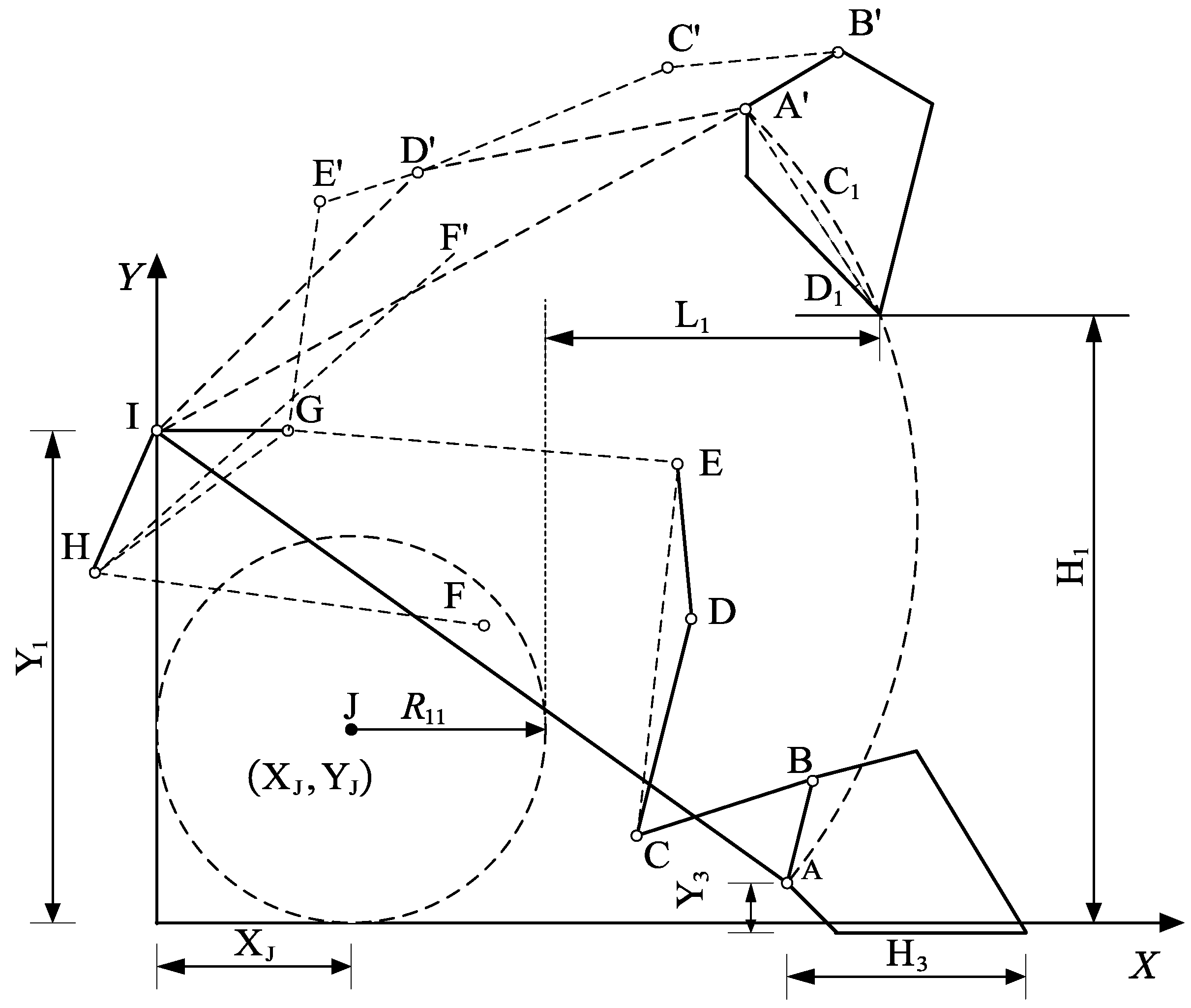
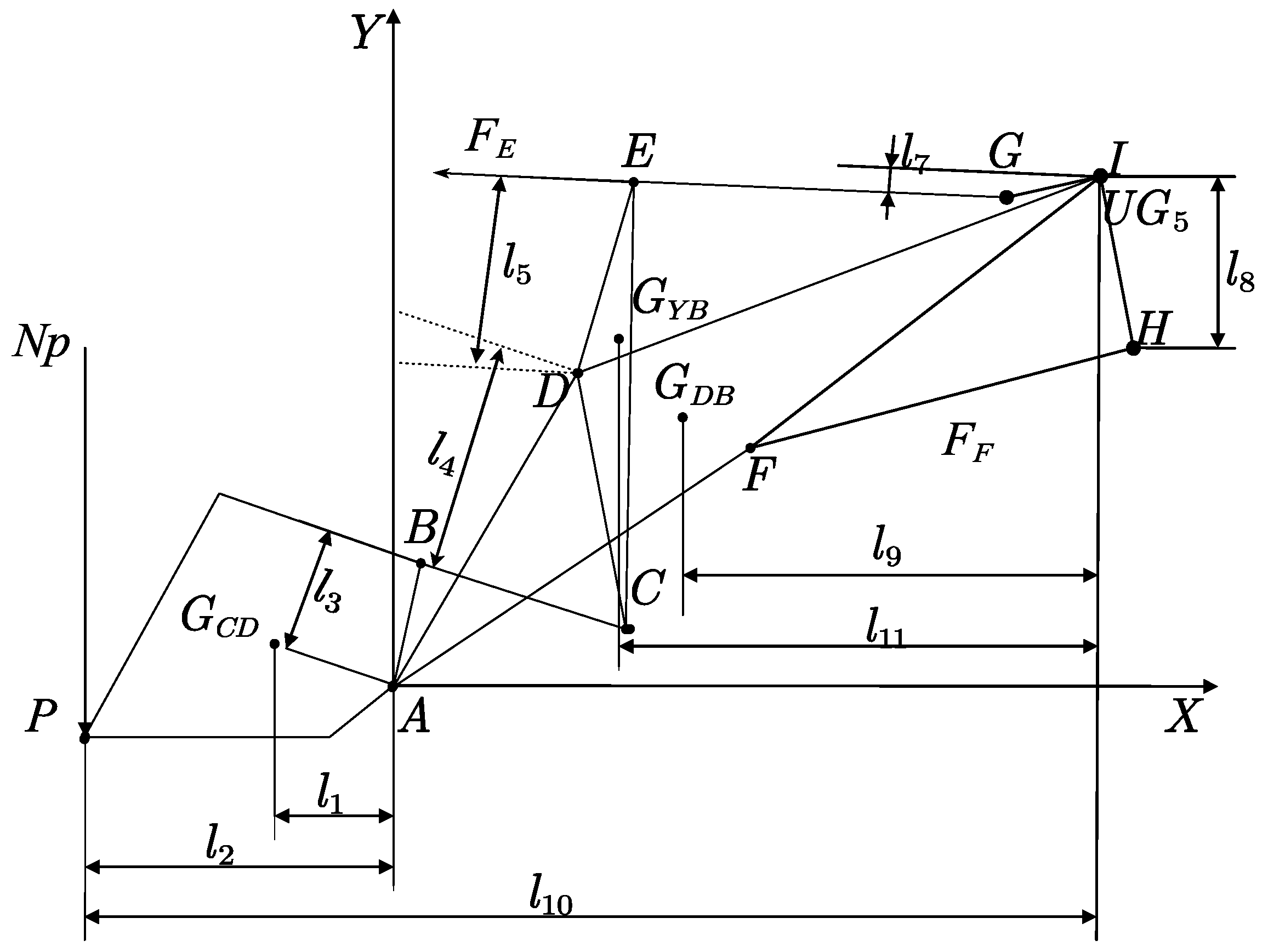
2.2. Kinematic Model
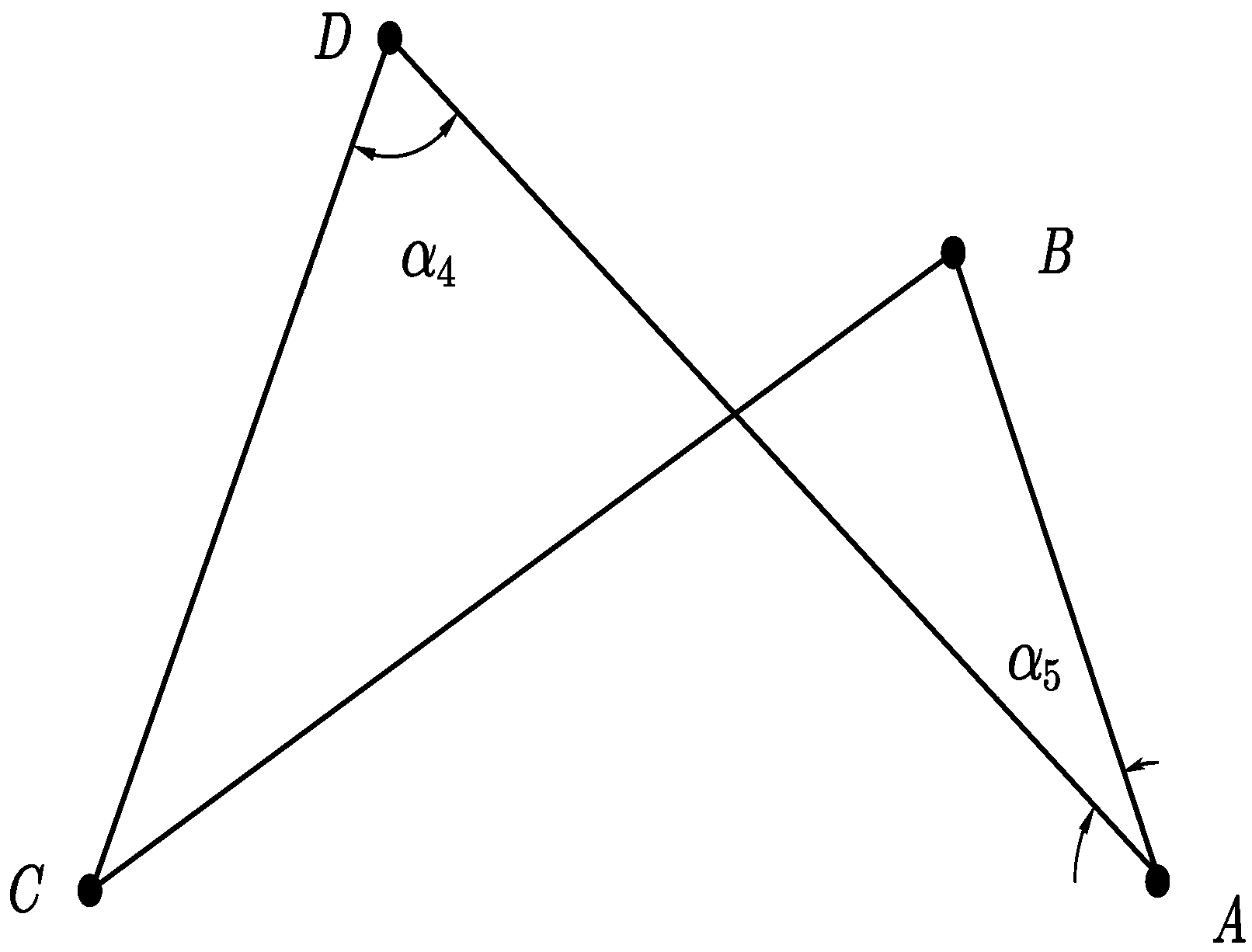
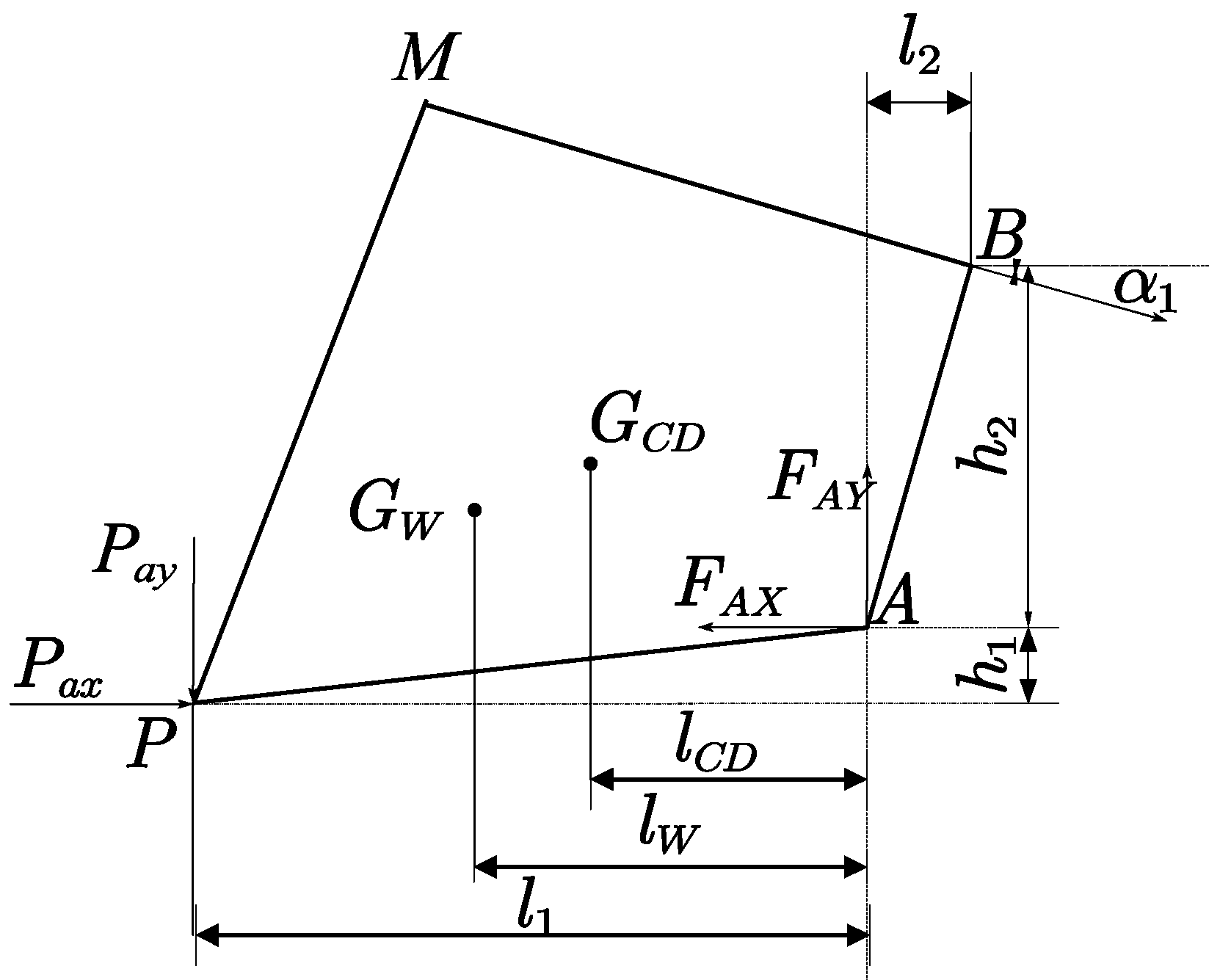
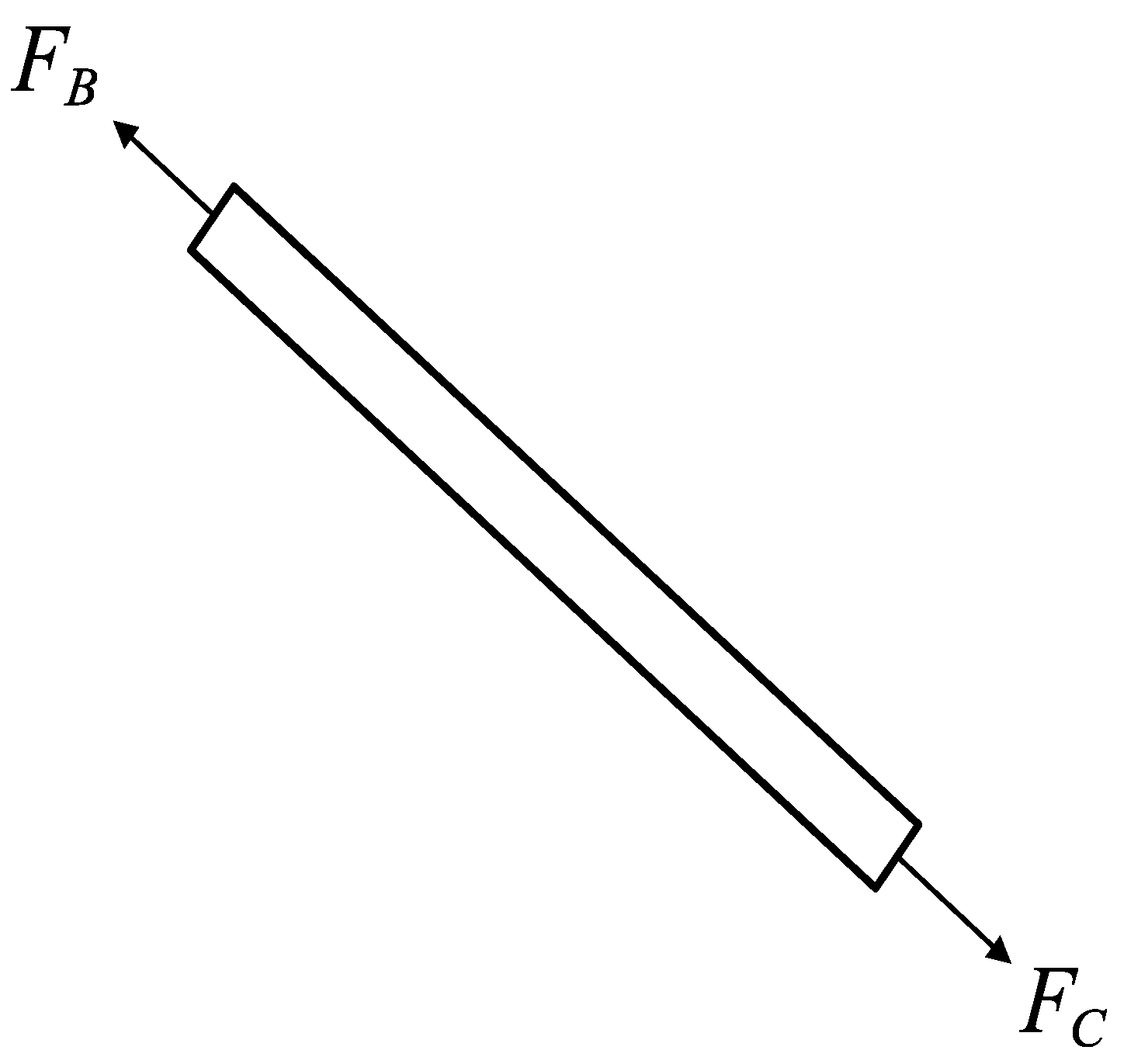
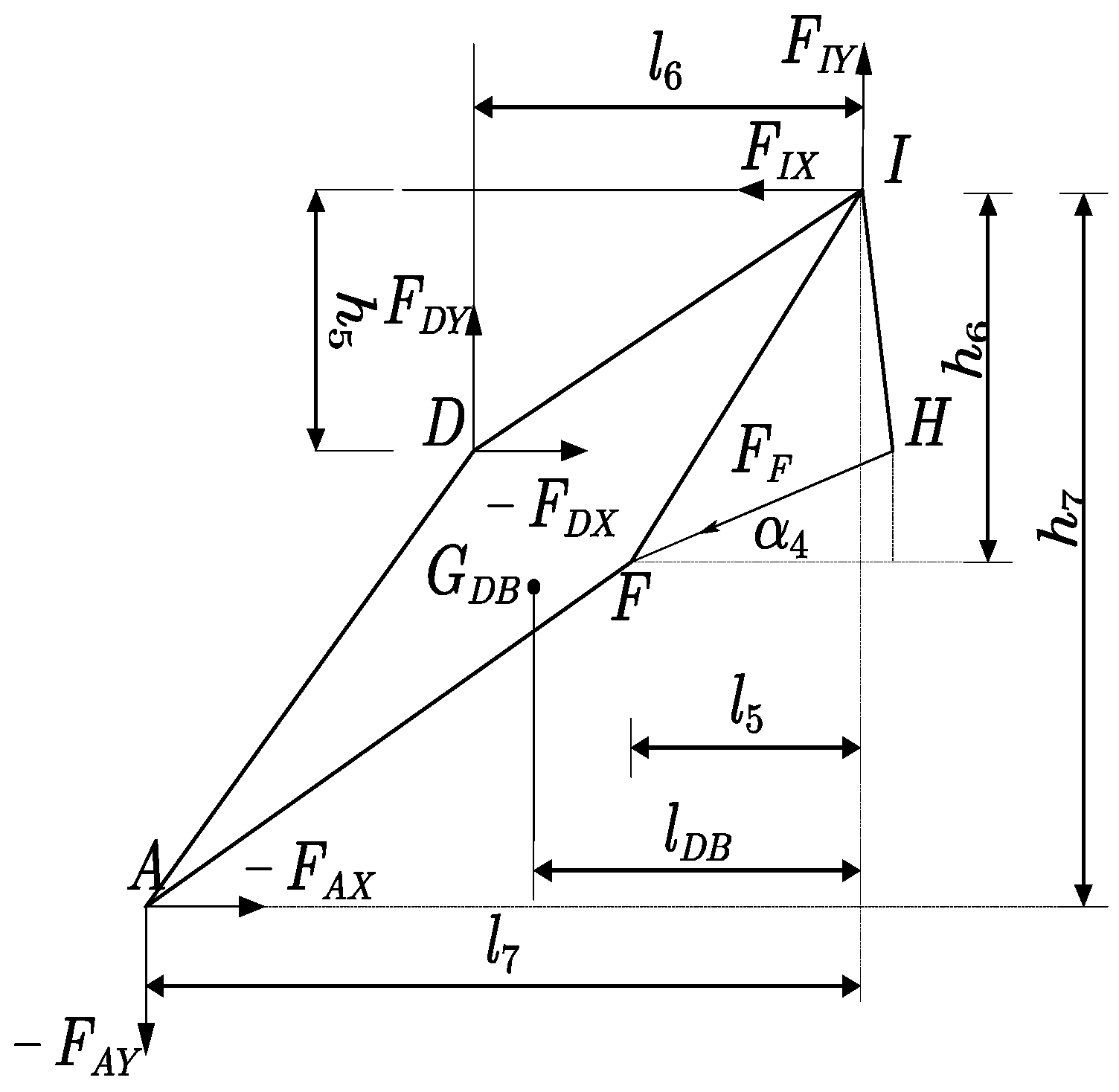
2.3. Force Analysis
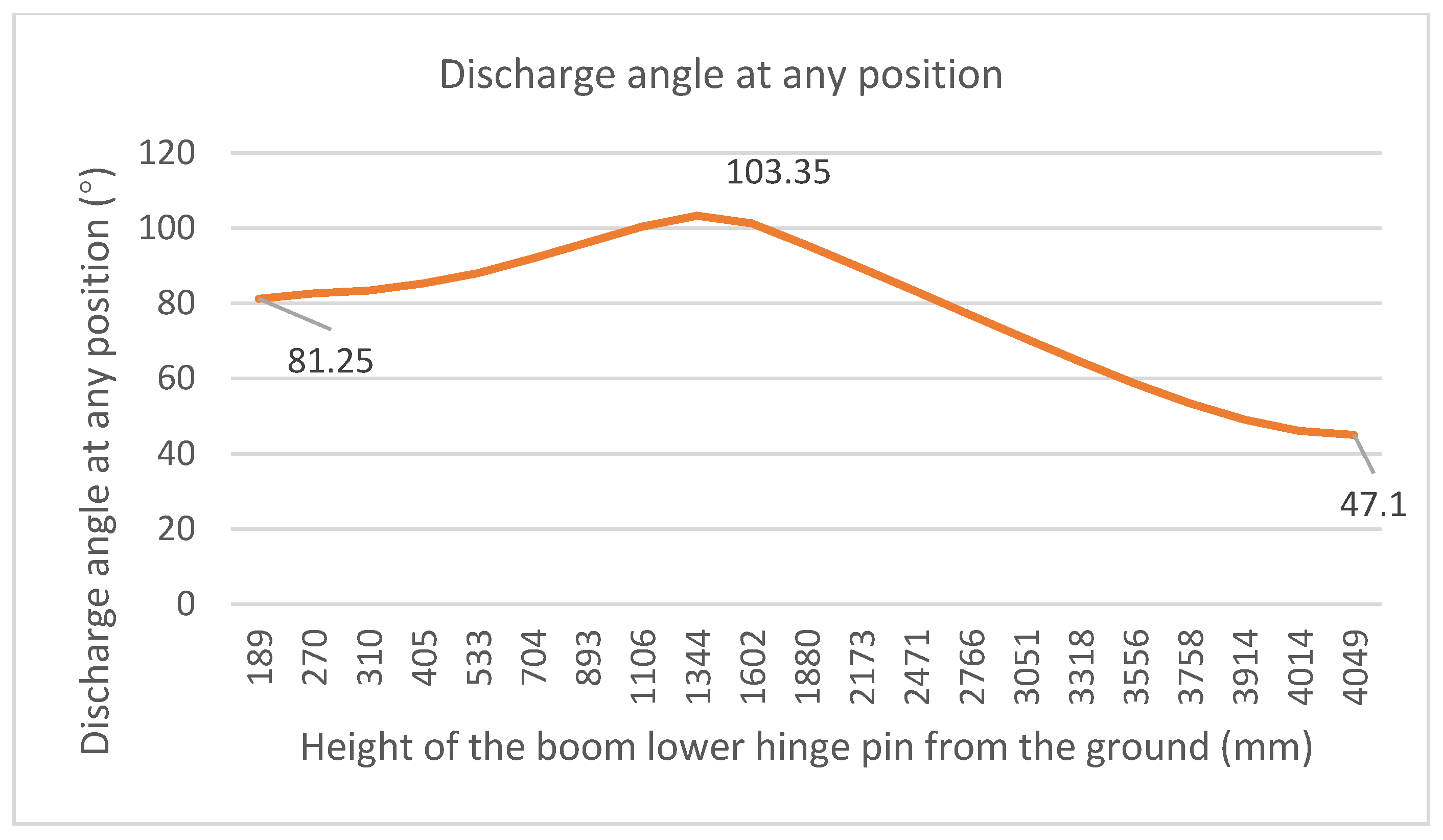
2.4. Performance Model
3. Multi-Objective Optimization Design of the Working Device
3.1. Selection of the Design Variables
3.2. Objective Function and Constraints
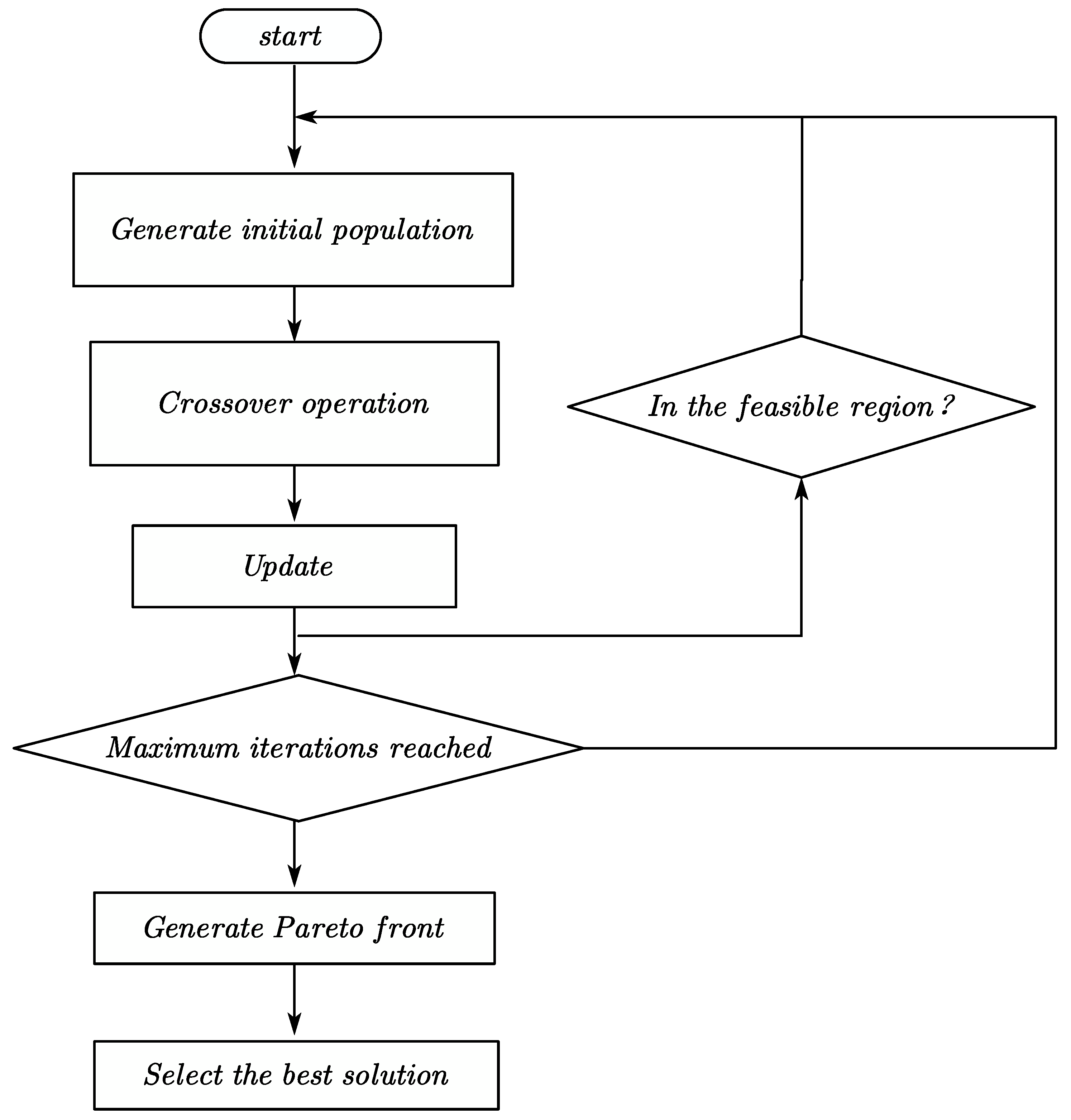
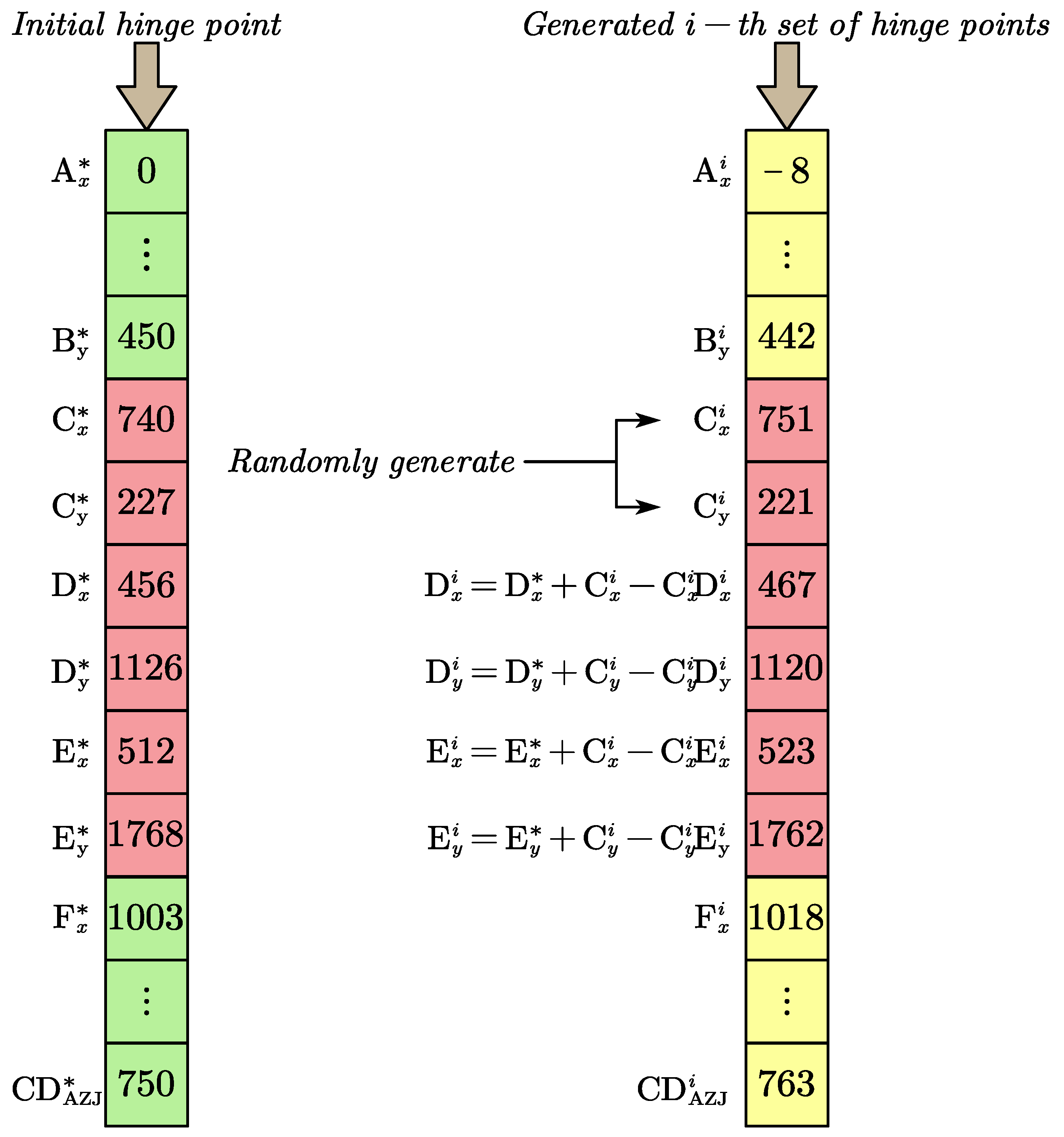
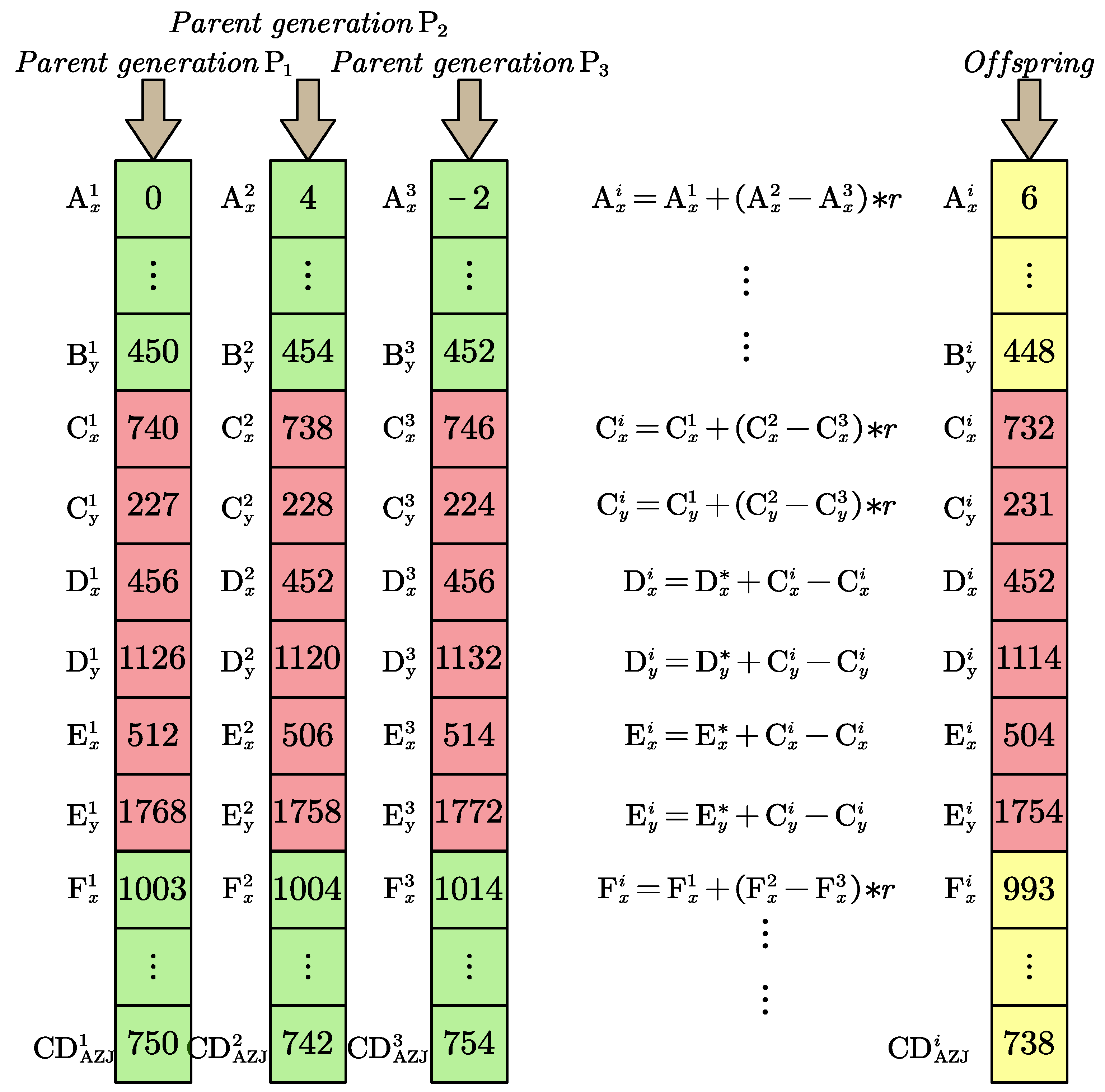
3.3. Improvement of the Optimization Algorithm
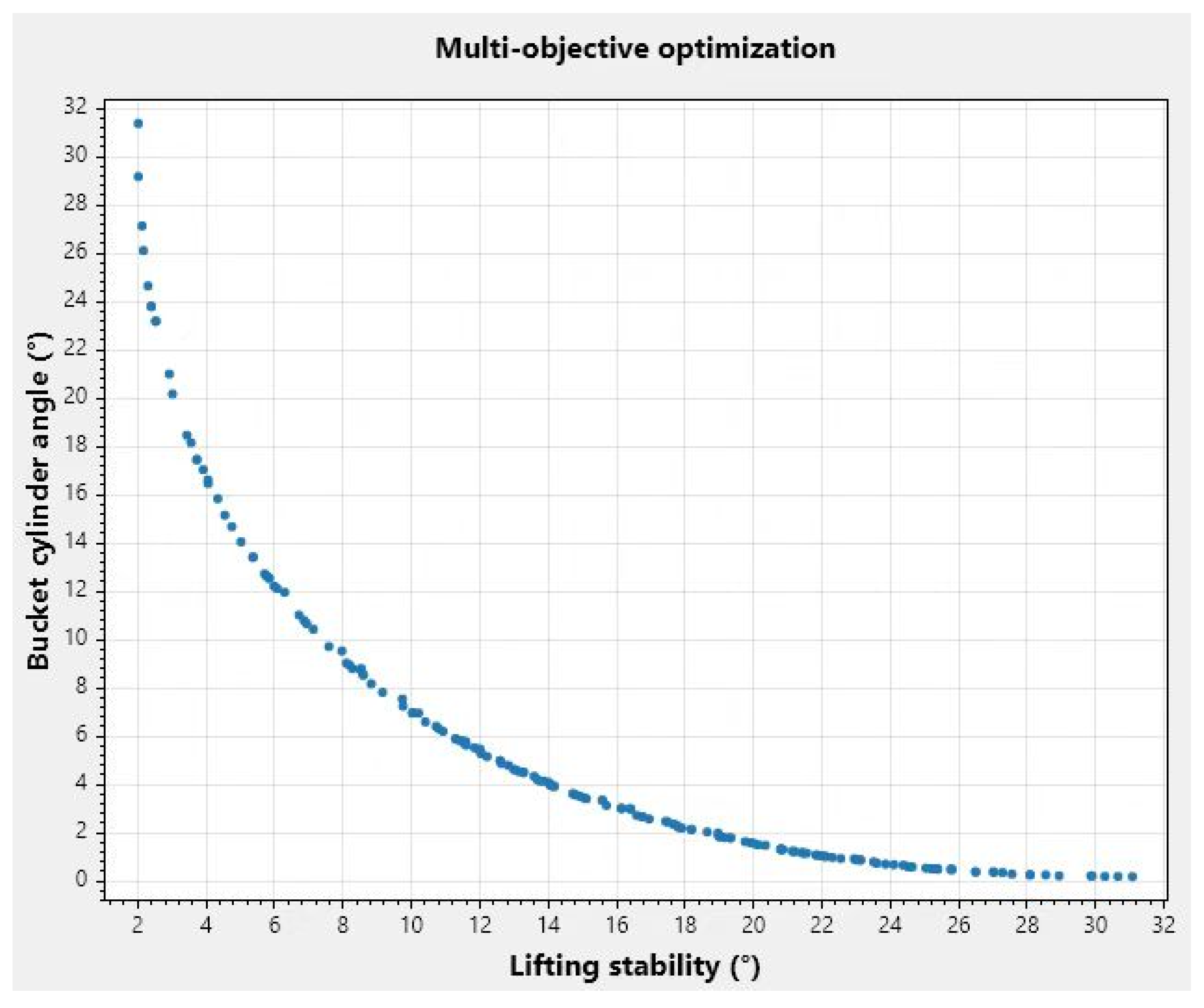
3.4. Multi-Objective Optimization
- (1)
- Pareto optimality
- (2)
- Multi-criteria decision-making
- (3)
- The weighted standardized decision matrix, denoted as W, is calculated as
- (4)
- Solution scoring
4. Simulation Optimization
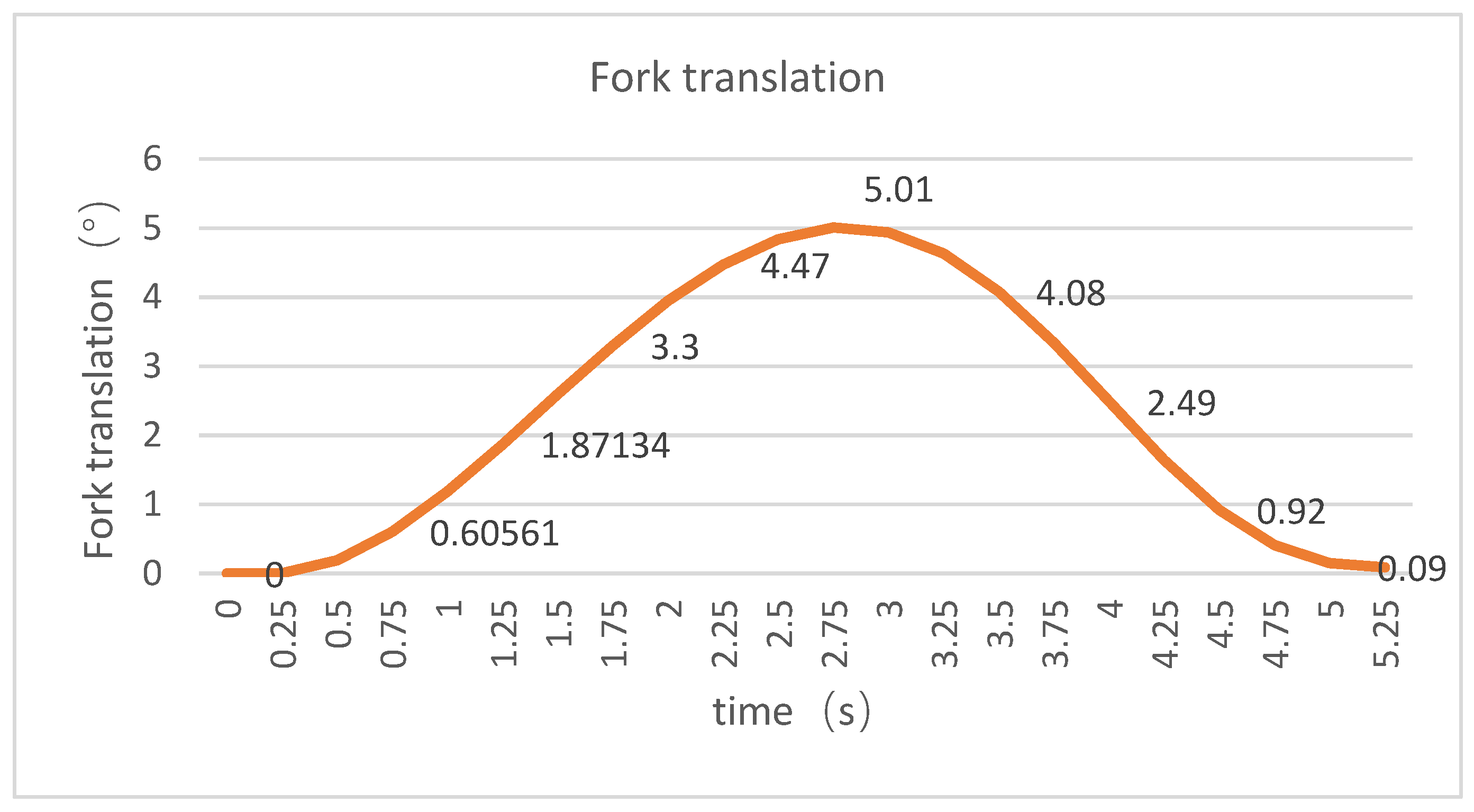
5. Experimental Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, S. Fatigue Performance Study of Hydraulic Forming High-Strength Steel Wheel Rim D; Shenyang University of Technology: Shenyang, China, 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. Kinematic Analysis and Optimization Design of Loader Working Device D; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2017; pp. 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, H.E.; Fang, Z.; Zhu, D. Optimal Design of the Working Device for Loader Based on Virtual Prototype Technology. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics, Beijing, China, 21 October 2009; pp. 45–63. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Su, S.; Xu, K. Dynamics Modeling and Simulation of Loader Working Device Under Unloading Condition. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Engineering Applications, Hong Kong, China, 12–13 November 2016; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Gao, G.; Zhang, T. Optimization Design of Loader Working Device Based on Composite Forming Method. Agric. Equip. Veh. Eng. 2013, 51, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.; Lin, S. Parameter Optimization Design of Excavator Working Device Based on Elite Ant Colony Algorithm. J. Sanming Univ. 2011, 28, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Qu, T. Research on Integrated Optimization of Excavator Working Device Parameters Based on Hybrid Algorithm. Mech. Transm. 2016, 40, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, G.; Miao, S. Optimal Design of a Hydraulic Excavator Working Device Based on Parallel Particle Swarm Optimization. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2017, 39, 3793–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Niu, Q. Optimization Design of Working Device of ZL-80 Loader Based on Adams. Int. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 2013, 50, 264–271. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.M.; Xiao, G.X.; Chen, R. Comprehensive Optimal Design of Working Device of Loader Based on Sensitivity. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 490, 3027–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.C.; Pang, H.T. Motion Simulation and Optimization of Loader Working Device. Constr. Mach. Maint. 2023, 6, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, R.; Liu, C.; Liu, H.B. Performance Optimization of Stone Fork Working Device of Loader Based on Kinematics Simulation. Constr. Mach. 2024, 55, 131–135+10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z. Motion Analysis of Loader Working Device Construction Process Based on Matlab. Equip. Manag. Maint. 2025, 3, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Wang, H.; Liang, G. Multi-objective Optimization of the Flip Mechanism of Mobile Garbage Compression Device. Mech. Transm. 2024, 48, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Deng, M.Y.; Li, K.J. Hinge Point Optimization of Boom Lifting Mechanism of Multi-functional Operation Vehicle in Forest Land. Mech. Des. 2024, 41, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
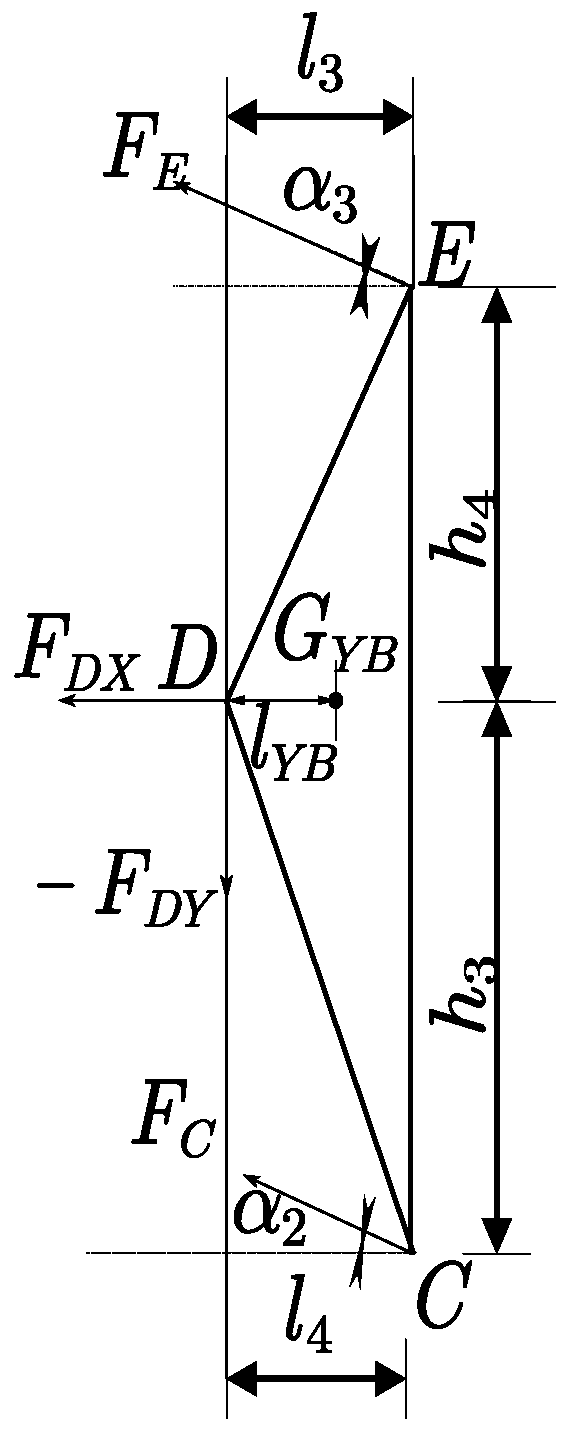

| Performance Parameter Name | Solution 1 | Solution 2 | Solution 3 | Solution 4 | Solution 5 | Solution 6 | Solution 7 | Solution 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High transmission angle (°) | 15.3 | 14.8 | 15.9 | 14.2 | 16.1 | 15.6 | 15.7 | 15.2 |
| Automatic leveling (°) | 14.2 | 14.5 | 14.8 | 15.2 | 15.7 | 14.6 | 16.3 | 15.9 |
| Unloading height (mm) | 4350 | 4350 | 4350 | 4350 | 4350 | 4350 | 4350 | 4350 |
| Unloading distance (mm) | 412 | 412 | 412 | 412 | 412 | 412 | 412 | 412 |
| High position angle of the bucket (°) | 61.2 | 62.3 | 64.4 | 63.8 | 64.1 | 64.2 | 63.9 | 64.0 |
| Ground lifting force (kN) | 82.87 | 83.82 | 87.13 | 85.44 | 82.18 | 86.49 | 85.39 | 88.24 |
| Ground digging force (kN) | 111.23 | 107.19 | 105.45 | 108.61 | 112.72 | 110.7 | 108.55 | 107.60 |
| High lifting force (kN) | 51.33 | 50.09 | 52.16 | 50.76 | 51.97 | 53.9 | 54.61 | 54.82 |
| Digging depth (mm) | 185 | 185 | 185 | 185 | 185 | 185 | 185 | 185 |
| Discharge angle at any position (°) | 45.8 | 48.2 | 47.1 | 45.6 | 46.9 | 47.4 | 46.3 | 47.7 |
| Maximum transportation height of the bucket with the guard block in place (mm) | 831 | 836 | 829 | 841 | 836 | 835 | 840 | 837 |
| Lateral movement of the fork lift (°) | 28.31 | 22.07 | 16.79 | 12.48 | 8.73 | 4.92 | 4.02 | 2.01 |
| Bucket cylinder angle (°) | 0.43 | 1.34 | 2.27 | 4.82 | 7.91 | 12.32 | 16.08 | 31.8 |
| Solution | Solution 1 | Solution 2 | Solution 3 | Solution 4 | Solution 5 | Solution 6 | Solution 7 | Solution 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Score | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.09 |
| Performance Parameter Name | Original Model Parameters | Optimized Parameters (Improved Algorithm) | Optimized Parameters (Traditional Algorithm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| High transmission angle (°) | 14.5 | 15.6 | 15.7 |
| Automatic leveling | 17.8 | 14.6 | 13.4 |
| (°) | 4350 | 4350 | 4350 |
| Unloading height | 412 | 412 | 412 |
| (mm) | 58.7 | 64.2 | 63.4 |
| Unloading distance | 80.9 | 86.49 | 84.15 |
| (mm) | 102.4 | 110.7 | 108.2 |
| High bucket angle (°) | 50.6 | 53.9 | 51.7 |
| Ground lifting force | 185 | 185 | 185 |
| (kN) | 45 | 47.4 | 45.8 |
| Ground digging force | 800 | 835 | 837 |
| (kN) | 29.13 | 4.92 | 10.34 |
| High lifting force | 0.23 | 12.32 | 9.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Z.; Meng, L.; Song, D.; Wang, Z.; Gao, P.; Ma, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M. Symmetry-Informed Optimization and Verification of Loader Working Device Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071084
Dong Z, Meng L, Song D, Wang Z, Gao P, Ma L, Sun Y, Liu H, Zhang M. Symmetry-Informed Optimization and Verification of Loader Working Device Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm. Symmetry. 2025; 17(7):1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071084
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Zhikui, Lingchao Meng, Ding Song, Zixian Wang, Peng Gao, Long Ma, Yongkuan Sun, Huibin Liu, and Menglong Zhang. 2025. "Symmetry-Informed Optimization and Verification of Loader Working Device Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm" Symmetry 17, no. 7: 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071084
APA StyleDong, Z., Meng, L., Song, D., Wang, Z., Gao, P., Ma, L., Sun, Y., Liu, H., & Zhang, M. (2025). Symmetry-Informed Optimization and Verification of Loader Working Device Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm. Symmetry, 17(7), 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071084




