Dynamic Modeling and Modal Analysis of Rectangular Plates with Edge Symmetric Periodic Acoustic Black Holes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dynamic Model of Acoustic Black Hole Symmetric Periodic Boundary Rectangular Plate
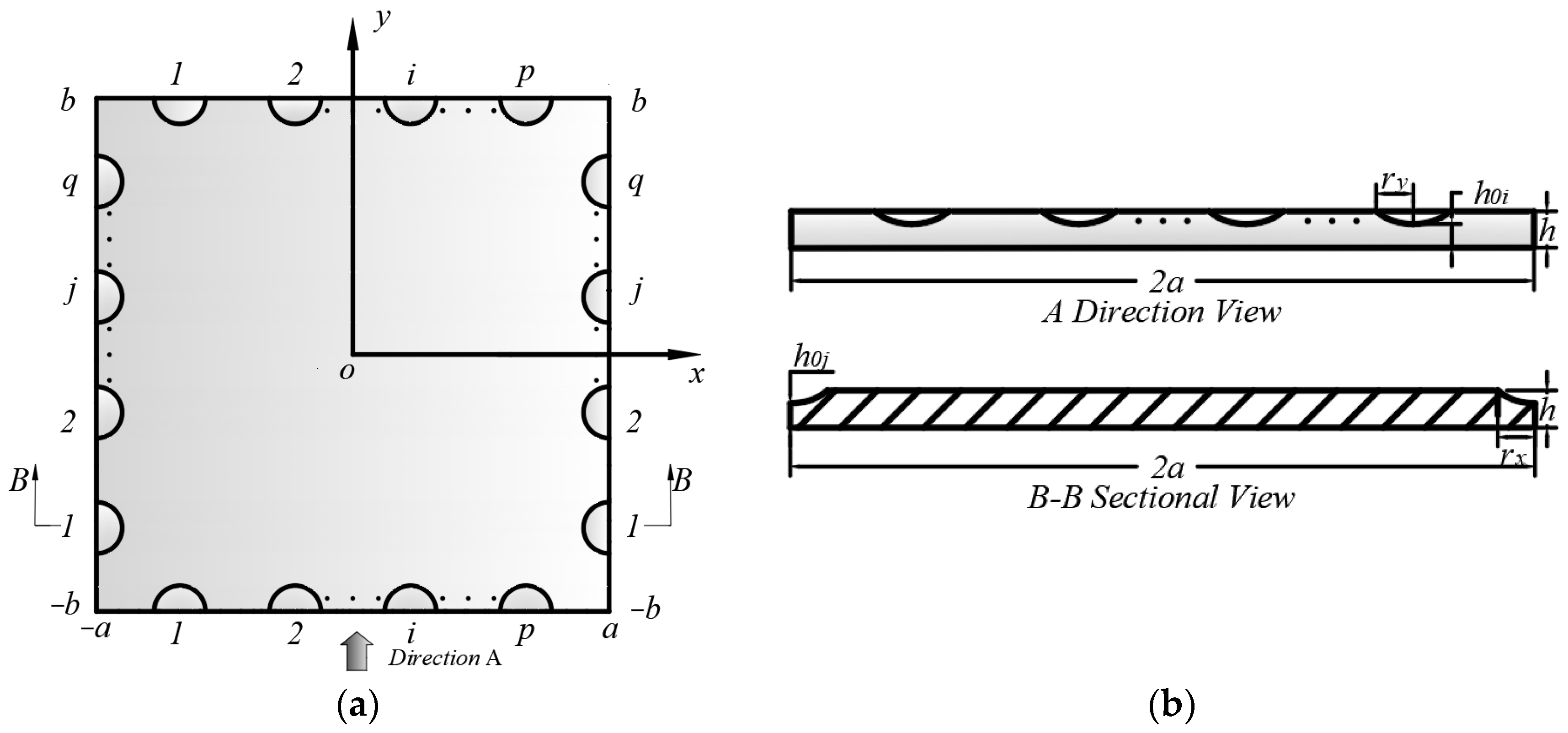
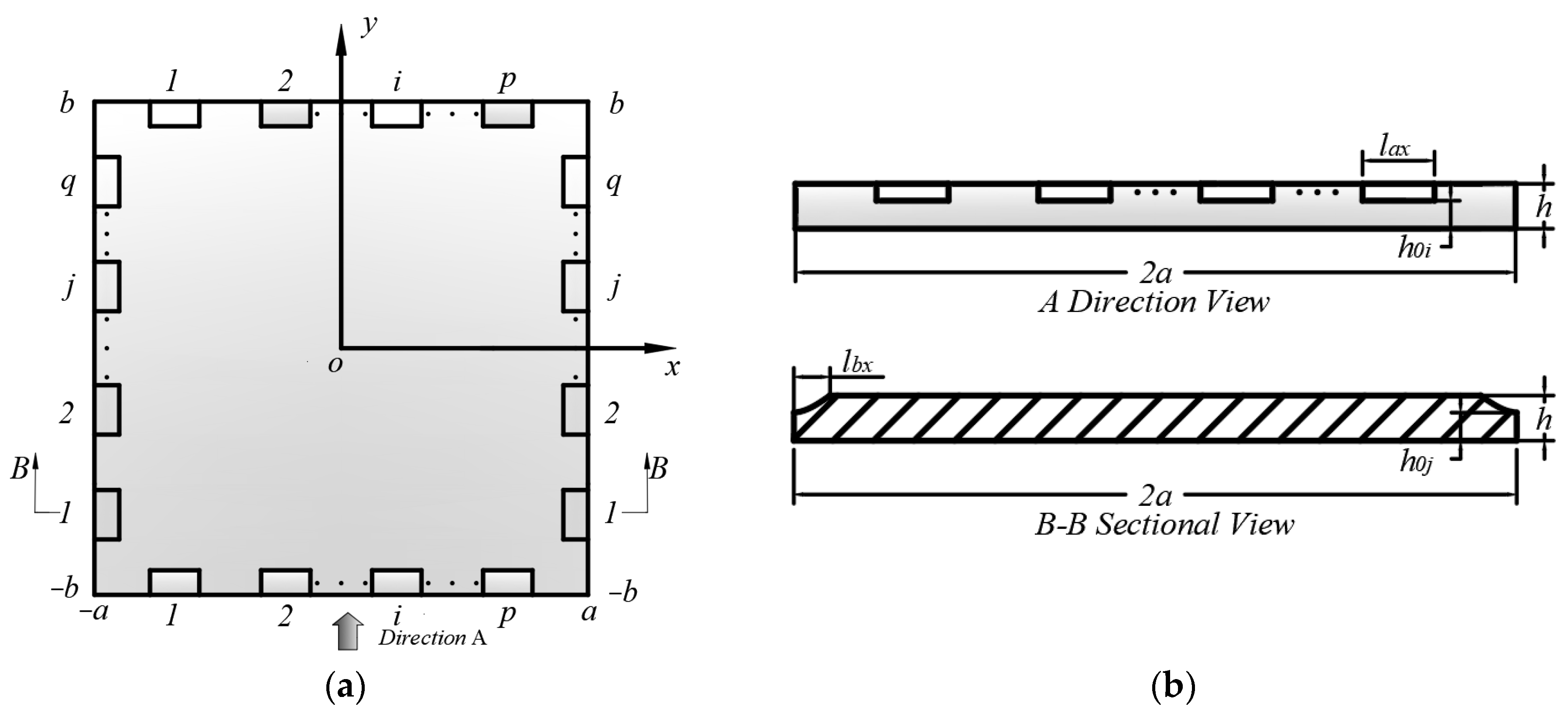
2.1. Geometric Configuration and Mathematical Description of the Edge of a Rectangular Plate Periodic ABH
- (1)
- A rectangular plate on the edge of a semicircular annular ABH
- (2)
- A rectangular plate on the edge of a rectangular block-shaped ABH
2.2. Dynamic Model of Rectangular Plate with Periodic ABH Boundary
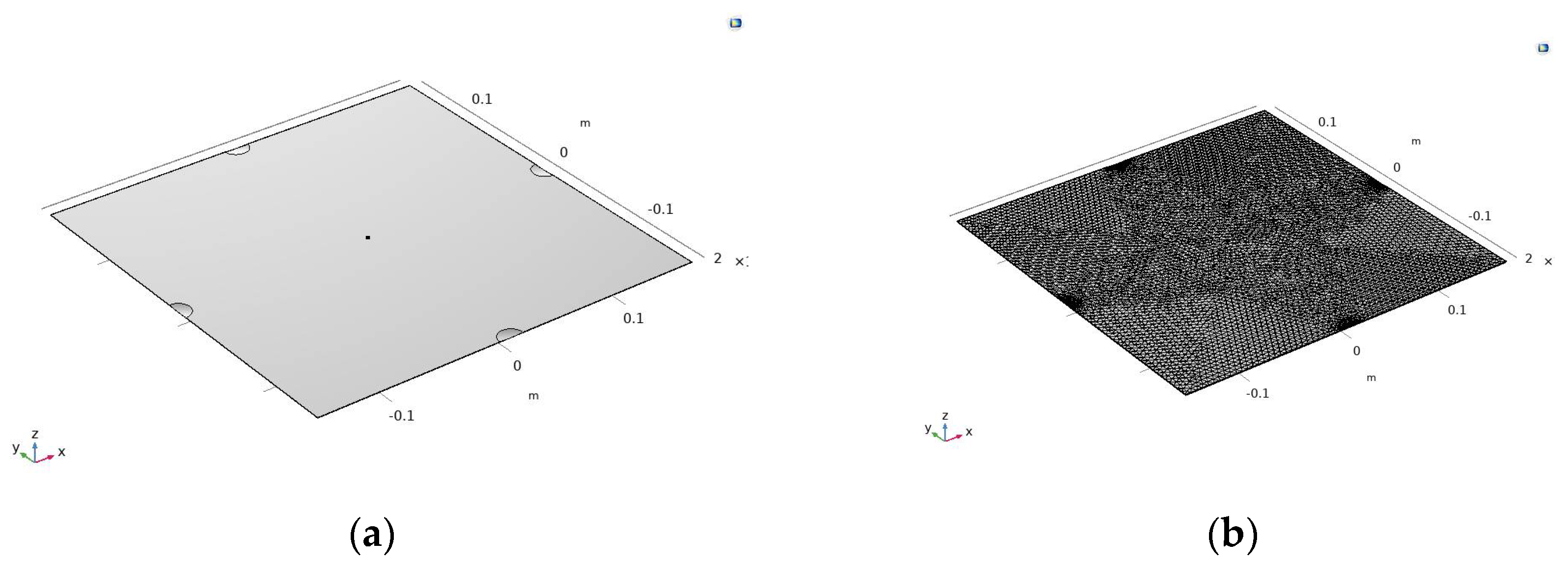
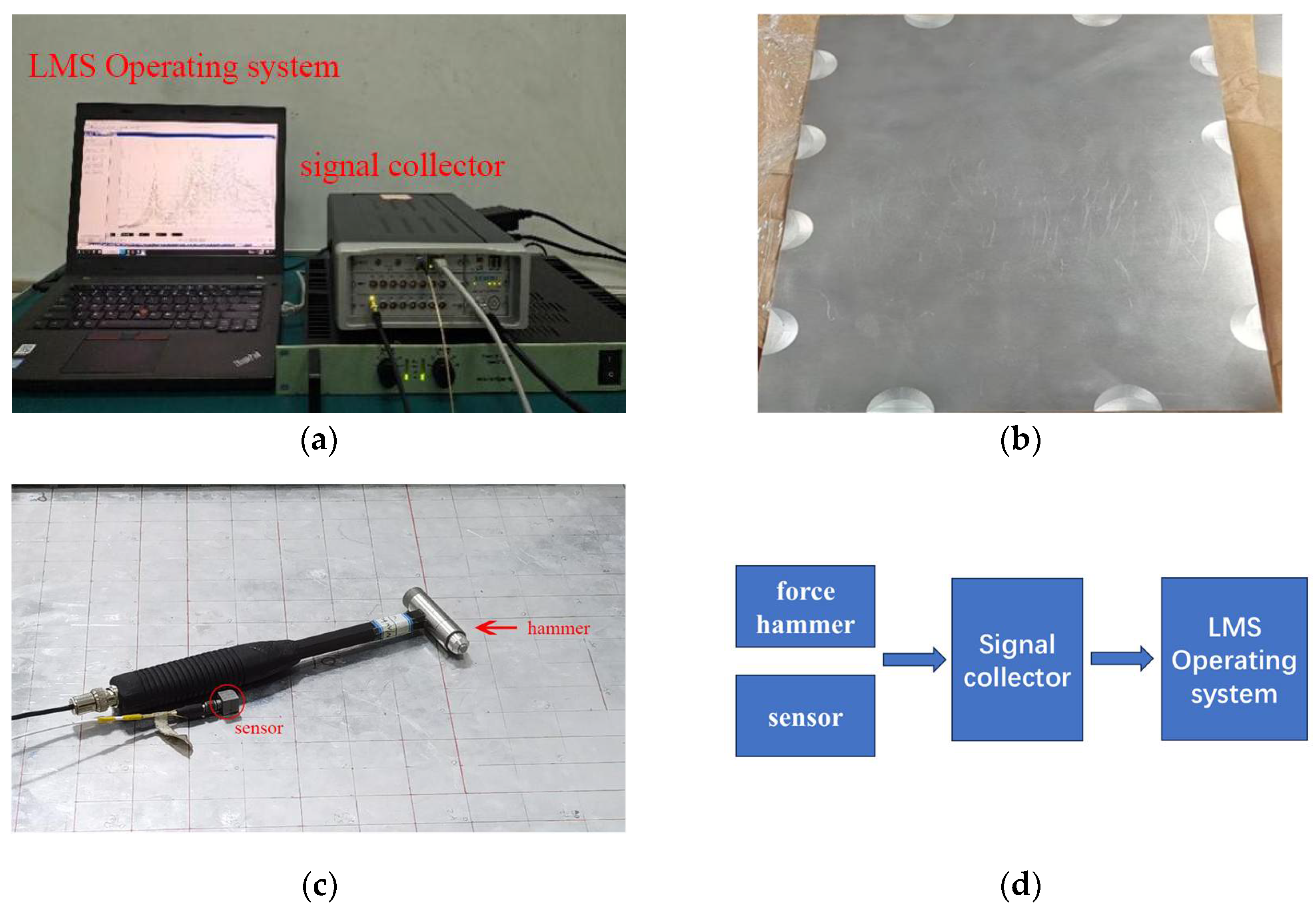
2.3. Model Validation
3. Modal Characteristics of Rectangular Plate with Periodic Boundary of ABHs
3.1. Influence of Power Law Exponent m of ABH on Modal Frequency of Rectangular Plate
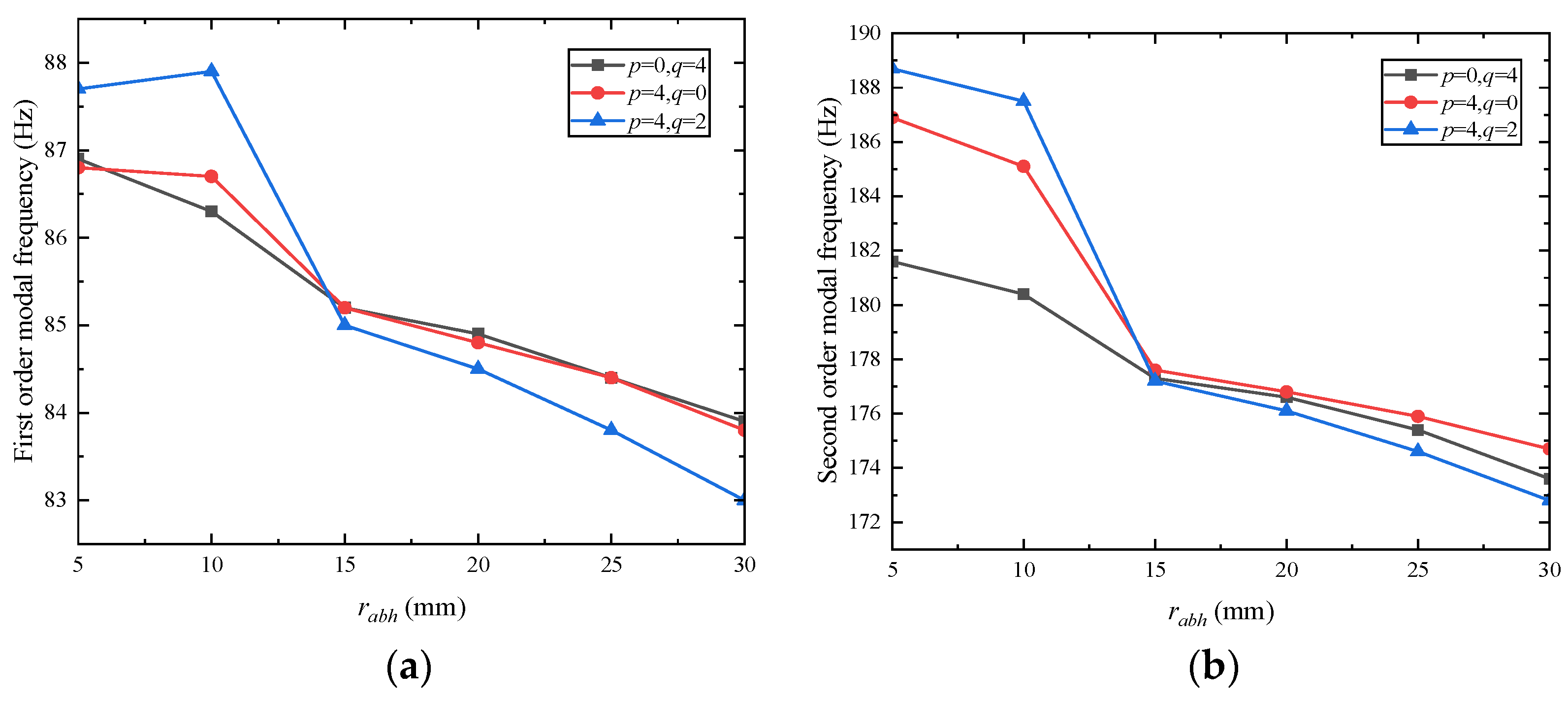
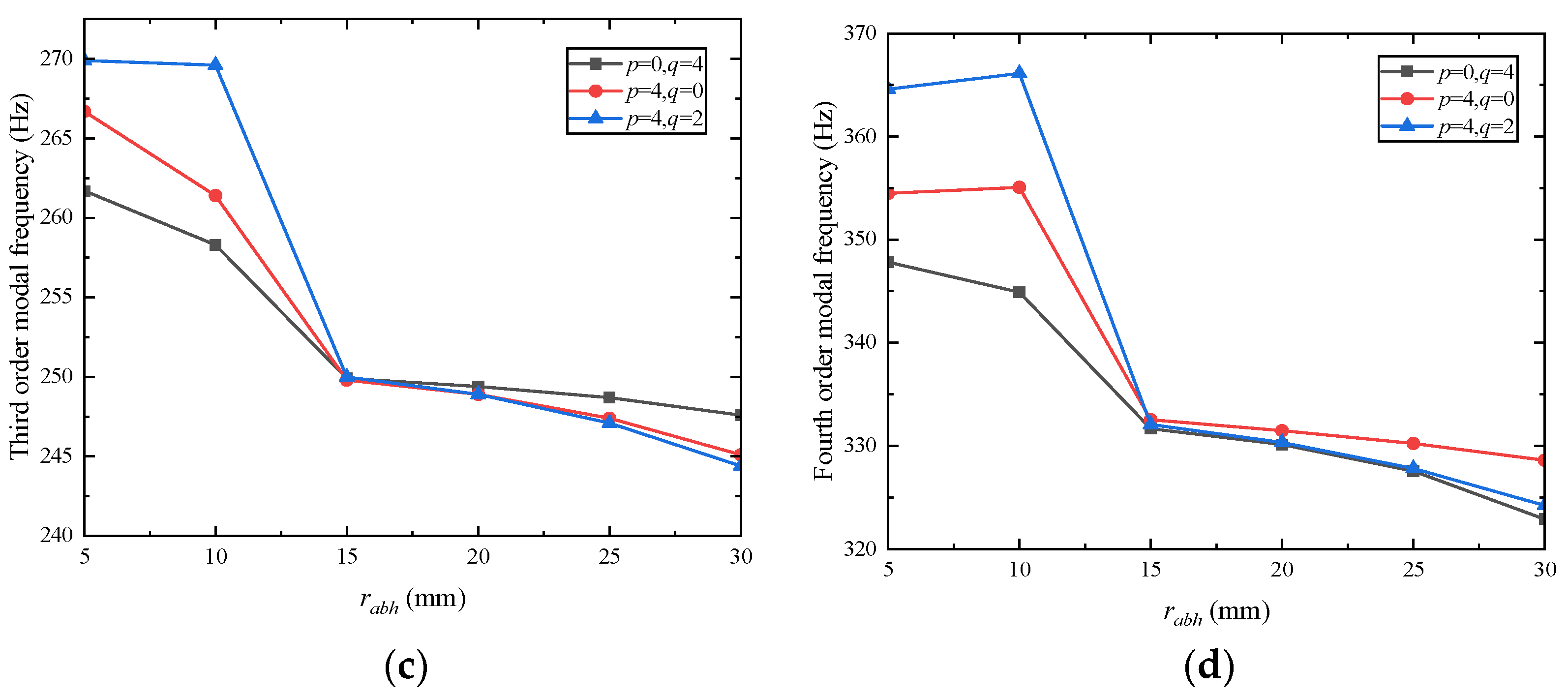
3.2. Influence of Radius of ABH on Modal Frequency of Rectangular Plate
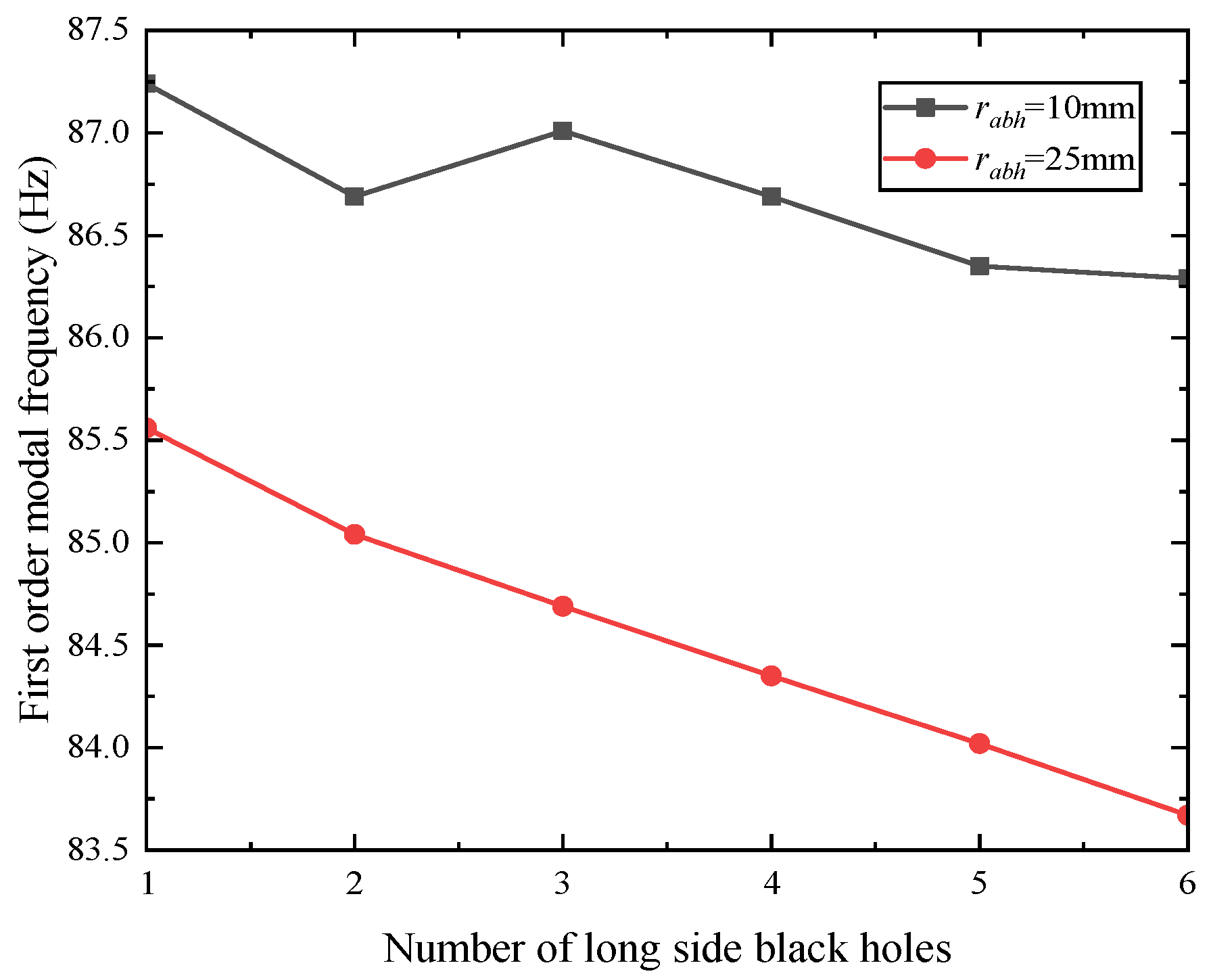
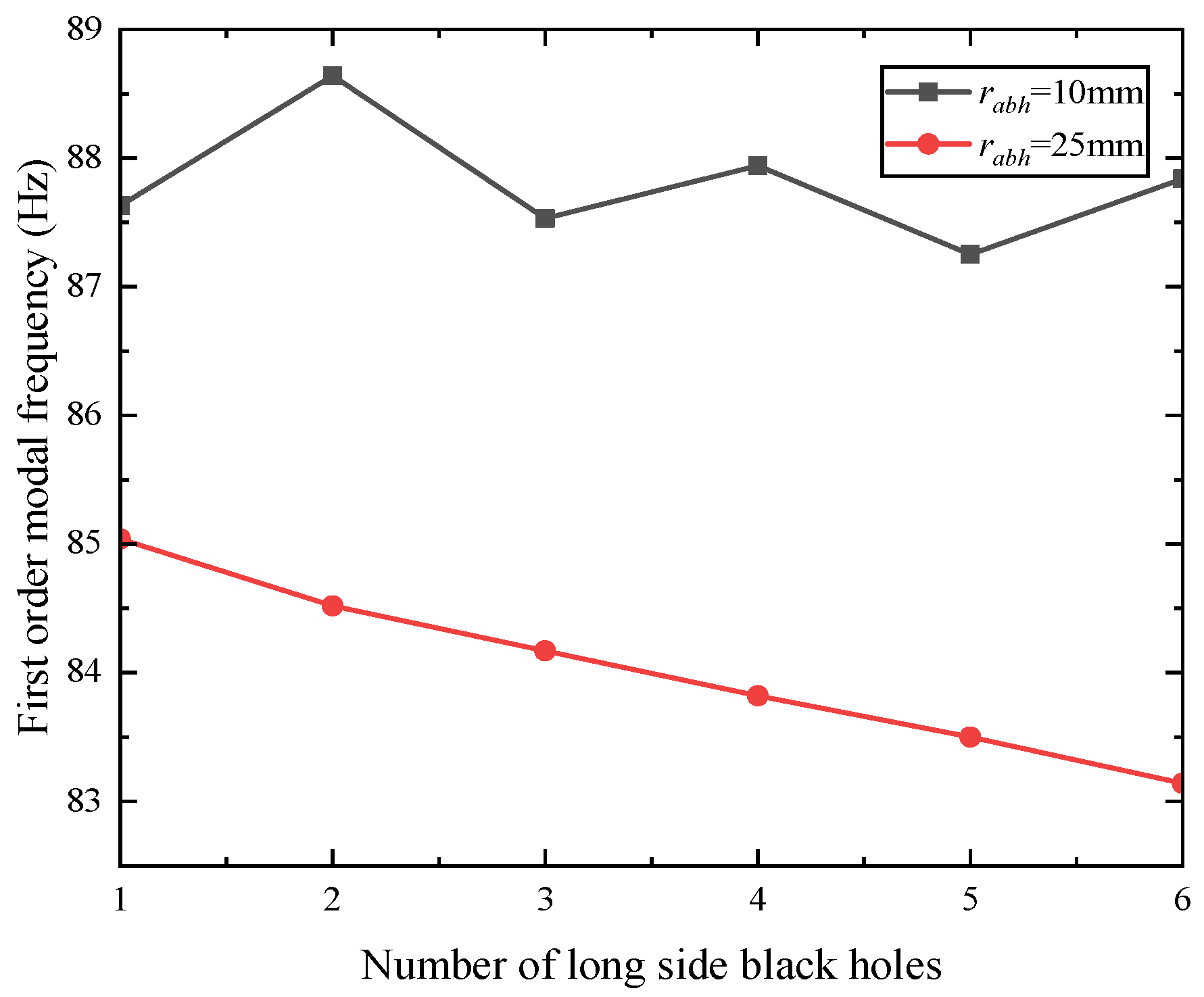
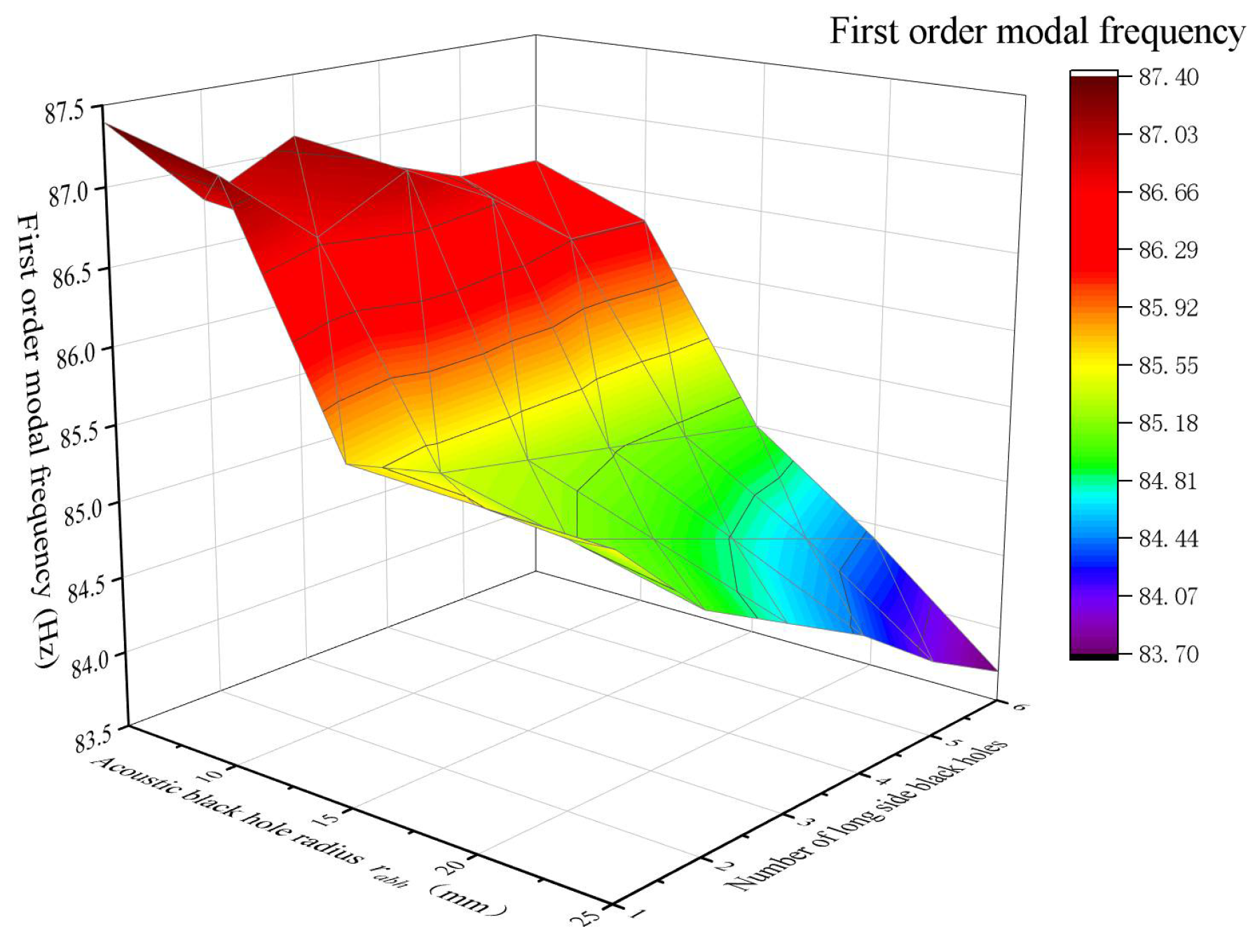
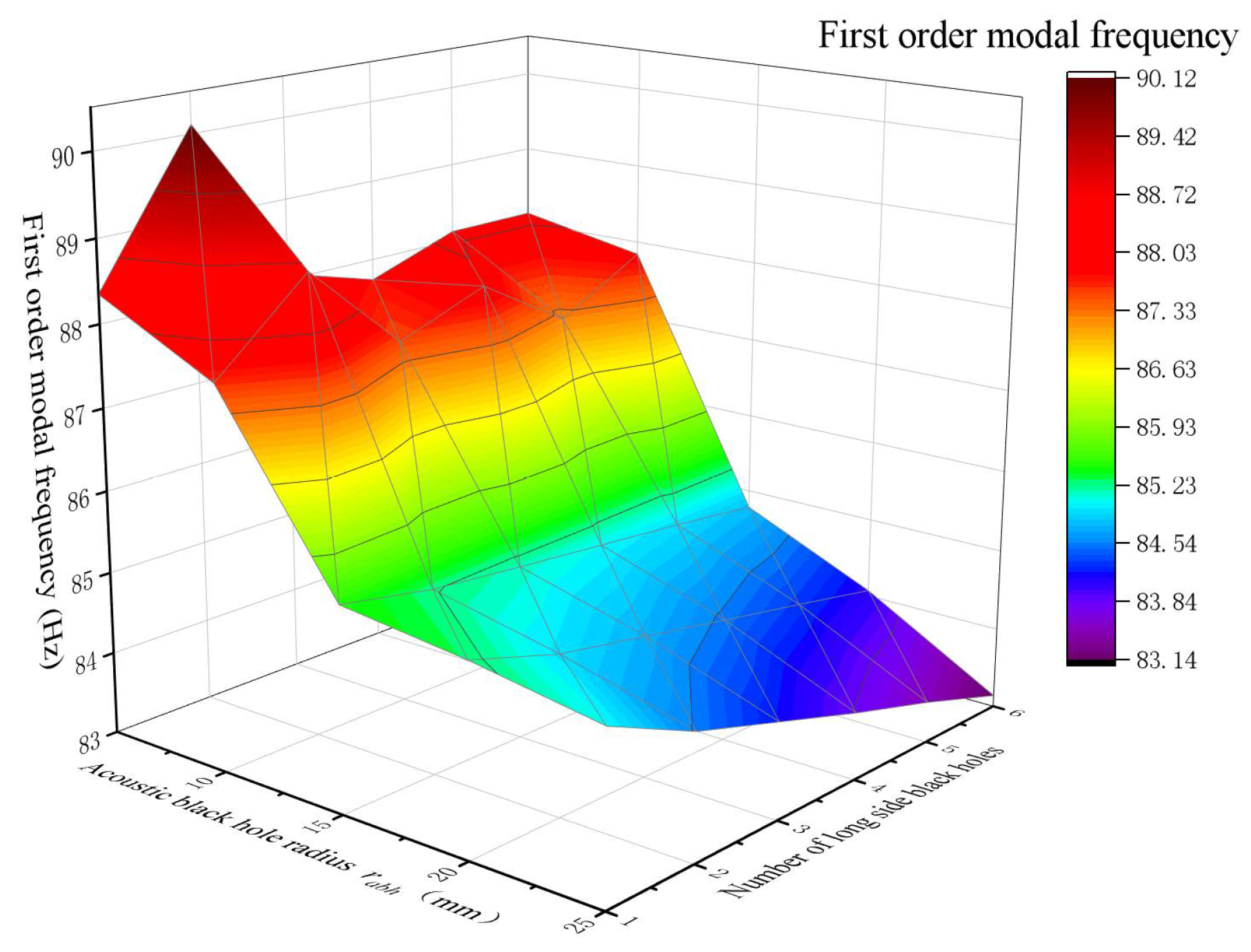
3.3. Influence of Combination of ABH Number and Black Hole Radius on Modal Frequency of Rectangular Plate
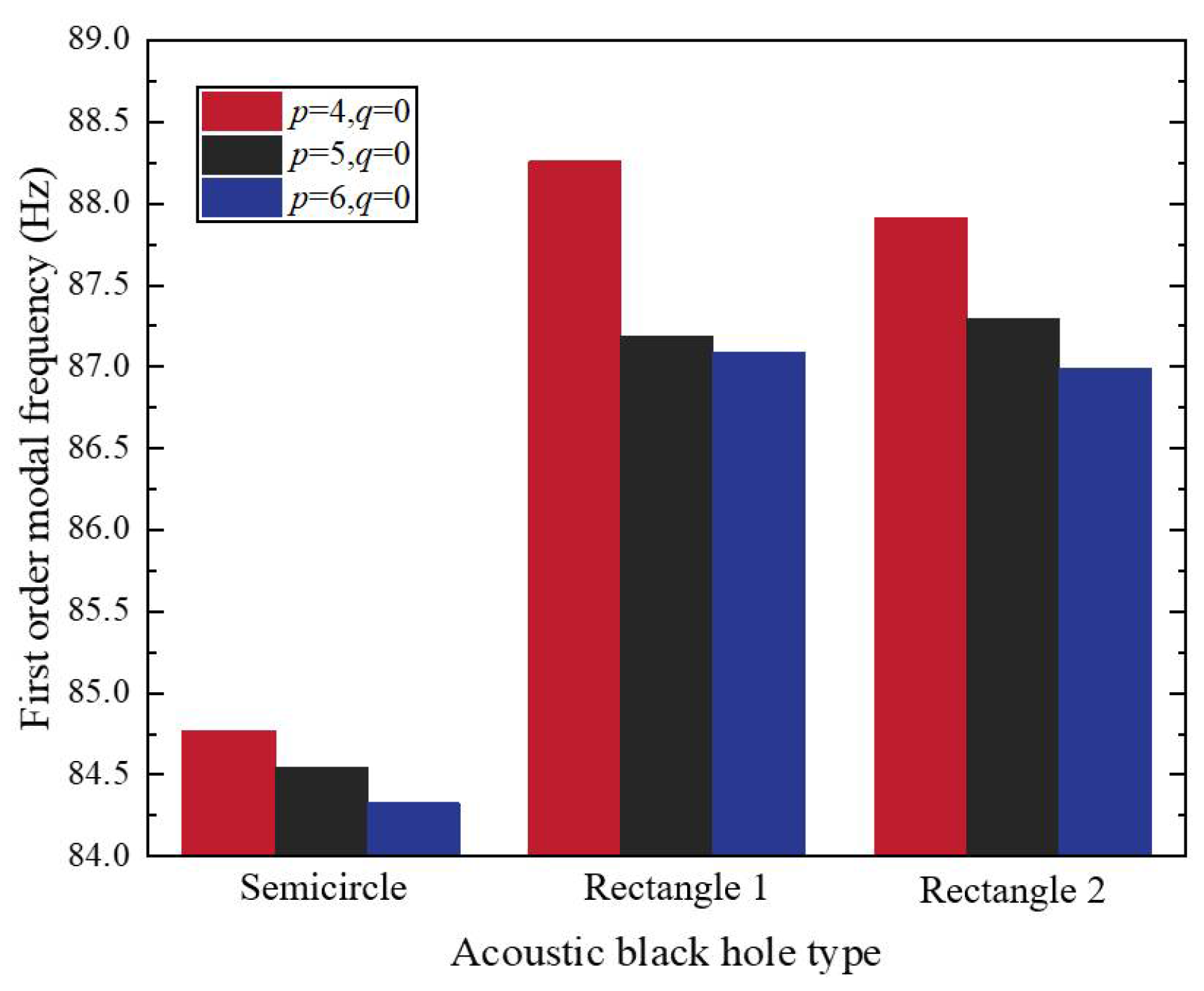
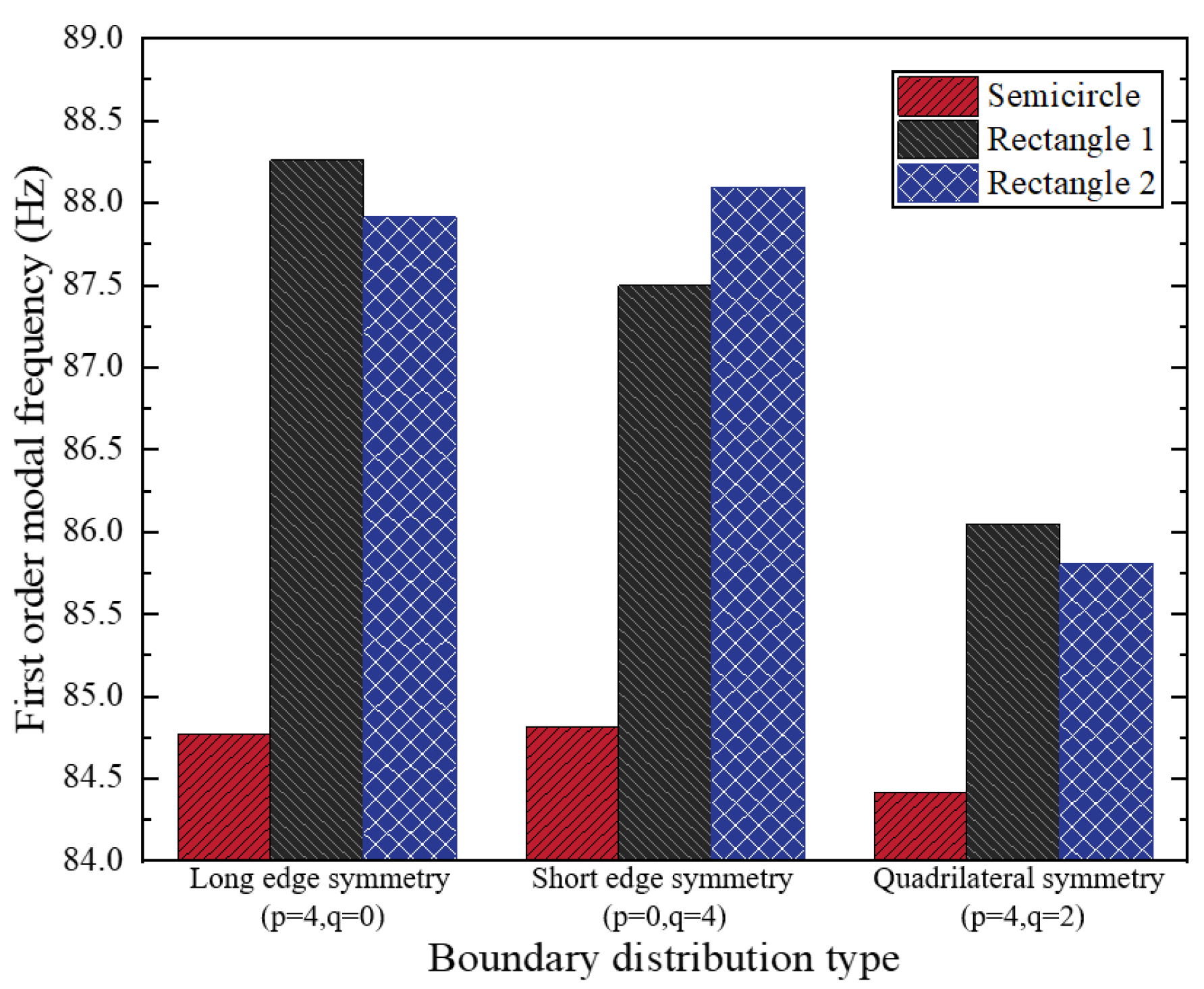
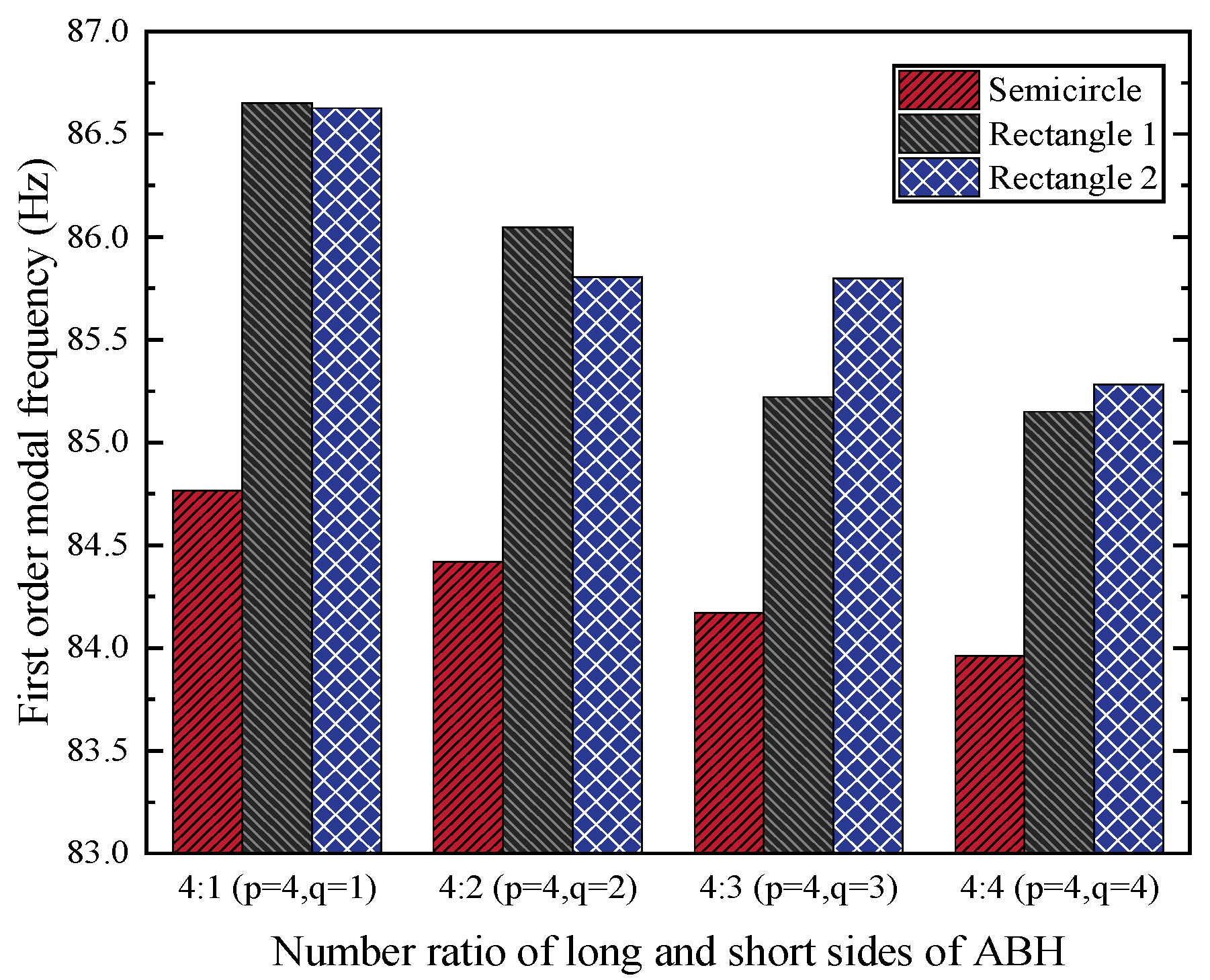
3.4. Influence of ABH Configuration on Modal Frequency of Rectangular Plate
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The “remove-and-fill” substitution method proposed in this paper can effectively resolve the dynamic modeling problems of the rectangular plate with a variable cross-section in the edge ABH by constructing a local energy model of the rectangular plate in the edge ABH. Through selecting the Gaussian function as the shape function, the rapid changes in the ABH region can be captured with fewer terms, which significantly reduces the computational degrees of freedom and improves the computational efficiency and stability of the solution.
- (2)
- The edge parameters of the periodic ABHs, including the radii of the edge ABHs, the number of ABHs, and the periodic distribution of the ABHs, directly affect the overall bending stiffness of the plate structure and significantly influence its modal frequency, which is a key parameter in the regulation of the dynamic properties of the structure. In addition, the configuration of the ABH also has an important effect on the modal frequency of the plate structure, and the modal frequency of the semicircular ABHs is relatively low compared with that of the rectangular wedge-shaped ABHs. The modal frequencies of rectangular plates with four-side symmetric periodic ABHs are lower than those of two-side symmetric rectangular plates.
- (3)
- Without changing the main structure, the design and regulation of the structural modal frequency can be realized only through boundary structure design, which has significant engineering value and application prospects in the vibration and noise control of aerospace panels, automobile base plates, and body structures, etc.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mironov, M.A. Propagation of a flexural wave in a plate whose thickness decreases smoothly to zero in a finite interval. Sov. Phys. Acoust. 1988, 34, 318–319. [Google Scholar]
- Mironov, M.A.; Pislyakov, V. One-dimensional acoustic waves in retarding structures with propagation velocity tending to zero. Acoust. Phys. 2002, 48, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feurtado, P.A.; Conlon, S.C.; Semperlotti, F. A normalized wave number variation parameter for acoustic black hole design. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, V.V. New type of vibration dampers utilizing the effect of acoustic black holes. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2004, 90, 830–837. [Google Scholar]
- Krylov, V.V. Propagation of plate bending waves in the vicinity of one-and two-dimensional acoustic black holes. In Proceedings of the ECCOMAS Thematic Conference on Computational Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, Rethymno Crete, Greece, 13–16 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Krylov, V.V.; Winward, R.E.T.B. Experimental investigation of the acoustic black hole effect for flexural waves in tapered plates. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 300, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, V.V. Acoustic black holes: Recent developments in theory and applications. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2014, 61, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, V.B.; Cuenca, J.; Gautier, F.; Simon, L.; Krylov, V.V. Damping of structural vibrations in beams and elliptical plates using the acoustic black hole effect. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 2497–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, V.; Pelat, A.; Gautier, F.; Elie, B. Modal overlap factor of a beam with an acoustic black hole termination. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 2475–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Jeon, W. Vibration damping using a spiral acoustic black hole. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Jeon, W. Exact solution of Euler-Bernoulli equation for acoustic black holes via generalized hypergeometric differential equation. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 452, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.L.; Cheng, L.; Ji, H.L.; Qiu, J.H. Characterization of acoustic black hole effect using a one-dimensional fully coupled and wavelet-decomposed semi-analytical model. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 374, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Du, J.T.; Cheng, L. Power flow and structural intensity analyses of Acoustic Black Hole beams. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 131, 538–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zheng, L.; Guasch, O. Elliptical acoustic black holes for flexural wave lensing in plates. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 174, 107744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Guasch, O. On the bandgap mechanism of periodic acoustic black holes. J. Sound Vib. 2024, 579, 118379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.T.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, Y. Vibration behavior and power transmission of coupled plate structures with embedded acoustic black holes joined at an arbitrary angle. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 197, 111565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azbaid El Ouahabi, A.; Krylov, V.V.; O’Boy, D.J. Investigation of the acoustic black hole termination for sound waves propagating in cylindrical waveguides. In Proceedings of the International Conference ‘InterNoise 2015’, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–12 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Guasch, O.; Arnela, M.; Sánchez-Martín, P. Transfer matrices to characterize linear and quadratic acoustic black holes in duct terminations. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 395, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Cheng, L. Broadband and low frequency sound absorption by Sonic black holes with Micro-perforated boundaries. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 512, 116401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; He, N.W.; Cheng, L.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.K.; Hu, F.C. Sound absorption in sonic black holes: Wave retarding effect with broadband cavity resonance. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 221, 110007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Huang, W.; Ji, H.L.; Qiu, J.H. Acoustic black hole effect of composite sheet structures. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2023, 44, 426–453. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.K.; Liu, X.D.; Liu, Y.T.; Shan, Y.C.; He, T. Study on energy focusing effects of two-dimensional acoustic black holes on flexural waves in composite plate structures. In Proceedings of the INTER—NOISE and NOISE—CON Congress and Conference Proceedings, Beijing, China, 30 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.L.; Bai, J.B.; Liu, Y.M.; Tian, W.Q.; Tian, D.H.; Liu, L.W. Vibration Reduction Design and Performance Research of Bearing Plate of Undersea Vehicle Based on Acoustic Black Hole. J. Unmanned Undersea Syst. 2023, 31, 934–941. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.M.; Gao, K.; Liu, X.D. Parameter Optimization of ABH and Energy Focalization Analysis of ABH Array of Plate Embedded Structures. Noise Vib. Control 2022, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.L.; Cheng, L. Impaired sound radiation in plates with periodic tunneled Acoustic Black Holes. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 135, 106410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.A.; Jeon, W. Concave-shaped acoustic black holes with asymmetric arrangement for suppression and amplification of structural vibration. J. Sound Vib. 2025, 600, 118885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, M.; Pislyakov, V. One-dimensional sonic black holes: Exact analytical solution and experiments. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 473, 115223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelat, A.; Gautier, F.; Semperlotti, F.; Conlon, S.C. Passive control of vibrations using Acoustic Black Holes. In Proceedings of the 46th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering: Taming Noise and Moving Quiet, INTER-NOISE, Hong Kong, China, 27–30 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.H.; Prasad, M.G. Acoustic Black Holes in Structural Design for Vibration and Noise Control. Acoustics 2019, 1, 220–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Liu, X.D.; Tai, J.F.; He, T.; Shan, Y.C. A novel method of reducing the acoustic emission wave reflected by boundary based on acoustic black hole. Ultrasonics 2019, 94, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Ding, Q. Novel vibration self-suppression of periodic pipes conveying fluid based on acoustic black hole effect. J. Sound Vib. 2023, 567, 118077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, T.; Ding, Q.; Li, Y. Novel vibration suppression of spinning periodically acoustic black hole pipes based on the band-gap mechanism. Thin-Walled Struct. 2025, 212, 113198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Chen, D.; Yang, T.; Ding, Q. Novel vibration self-attenuation design of drill-string-like pipes transporting fluid with the enhancement of acoustic black hole effect. Ocean. Eng. 2025, 335, 121694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zheng, L.; Guasch, O. Gaussian expansion for the vibration analysis of plates with multiple acoustic black holes indentations. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 131, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Geometric Parameters | Material Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Length and width of plate a × b | 0.16 m × 0.16 m | 0.40 m × 0.30 m | Steel |
| Thickness of plate | 2 mm | 5 mm | ρ1 = 7800 kg/m3 |
| Number of black holes, long side p, short side q | p = 1, q = 1 | p = 4, q = 2 | E1 = 210 GPa |
| Power law exponent of black hole m | 2 | 2 | |
| Radius of black hole | 10 mm | 20 mm | ν1 = 0.3 |
| Boundary condition | Quadrilateral freedom | Quadrilateral freedom | |
| Modal Order | Theory ft (Hz) | Simulation fs (Hz) | Relative Error a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1,1) | 25.75 | 25.83 | 0.31 |
| (1,2) | 79.61 | 80.27 | 0.83 |
| (2,2) | 150.53 | 153.24 | 1.80 |
| (1,3) | 160.36 | 161.57 | 0.75 |
| (2,3) | 221.81 | 220.78 | 0.46 |
| (1,4) | 259.45 | 260.46 | 0.39 |
| Modal Order | Experiment ft (Hz) | Simulation fs (Hz) | Relative Error a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1,1) | 137.23 | 139.05 | 1.01 |
| (2,1) | 164.14 | 166.46 | 1.41 |
| (1,2) | 310.31 | 312.19 | 0.61 |
| (3,1) | 325.88 | 328.79 | 0.89 |
| (2,2) | 481.21 | 485.84 | 0.96 |
| Modal Order | Power Law Exponent m | 2.5 | 3.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | |||
| (1,1) | 84.50 | 84.42 | 84.35 |
| (2,1) | 176.08 | 175.90 | 175.73 |
| (1,2) | 248.93 | 248.65 | 248.48 |
| (3,1) | 330.33 | 329.99 | 429.69 |
| (2,2) | 339.48 | 338.97 | 338.55 |
| (3,2) | 492.61 | 491.75 | 490.96 |
| Geometric Parameter | Semicircular Section | Rectangular Section 1 | Rectangular Section 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| m | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| h | 2 mm | 2 mm | 2 mm |
| a | 400 mm | 400 mm | 400 mm |
| b | 300 mm | 300 mm | 300 mm |
| 0.5 mm | 0.5 mm | 0.5 mm | |
| 20 mm | - | - | |
| - | 40 mm | 16 mm | |
| - | 16 mm | 40 mm | |
| 4.87481/m | 4.87481/m | 4.87481/m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Q.; Wang, X.; Huang, Q.; Peng, J. Dynamic Modeling and Modal Analysis of Rectangular Plates with Edge Symmetric Periodic Acoustic Black Holes. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071031
Shi Y, Liu Z, Fan Q, Wang X, Huang Q, Peng J. Dynamic Modeling and Modal Analysis of Rectangular Plates with Edge Symmetric Periodic Acoustic Black Holes. Symmetry. 2025; 17(7):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071031
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yuanyuan, Ziyi Liu, Qiyuan Fan, Xiao Wang, Qibai Huang, and Jiangying Peng. 2025. "Dynamic Modeling and Modal Analysis of Rectangular Plates with Edge Symmetric Periodic Acoustic Black Holes" Symmetry 17, no. 7: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071031
APA StyleShi, Y., Liu, Z., Fan, Q., Wang, X., Huang, Q., & Peng, J. (2025). Dynamic Modeling and Modal Analysis of Rectangular Plates with Edge Symmetric Periodic Acoustic Black Holes. Symmetry, 17(7), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071031




