Research on Coordinated Control of Multi-PMSM for Shaftless Overprinting System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Establishment of the Model for the Shaftless Overprint System
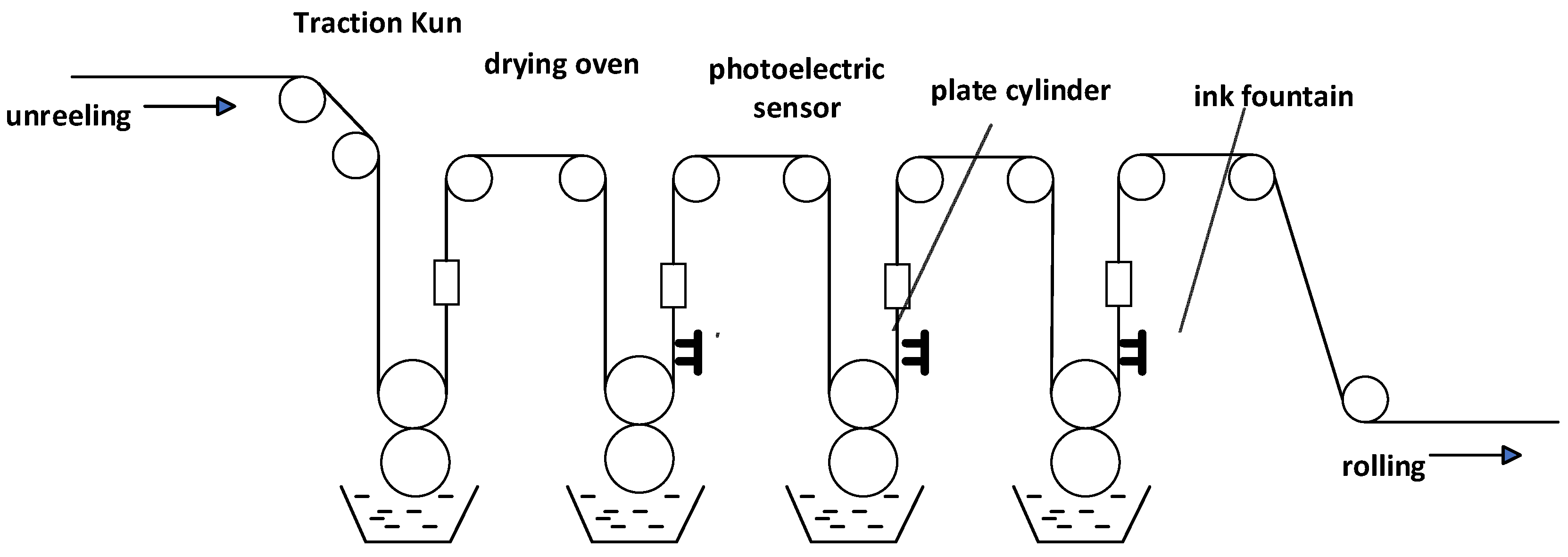
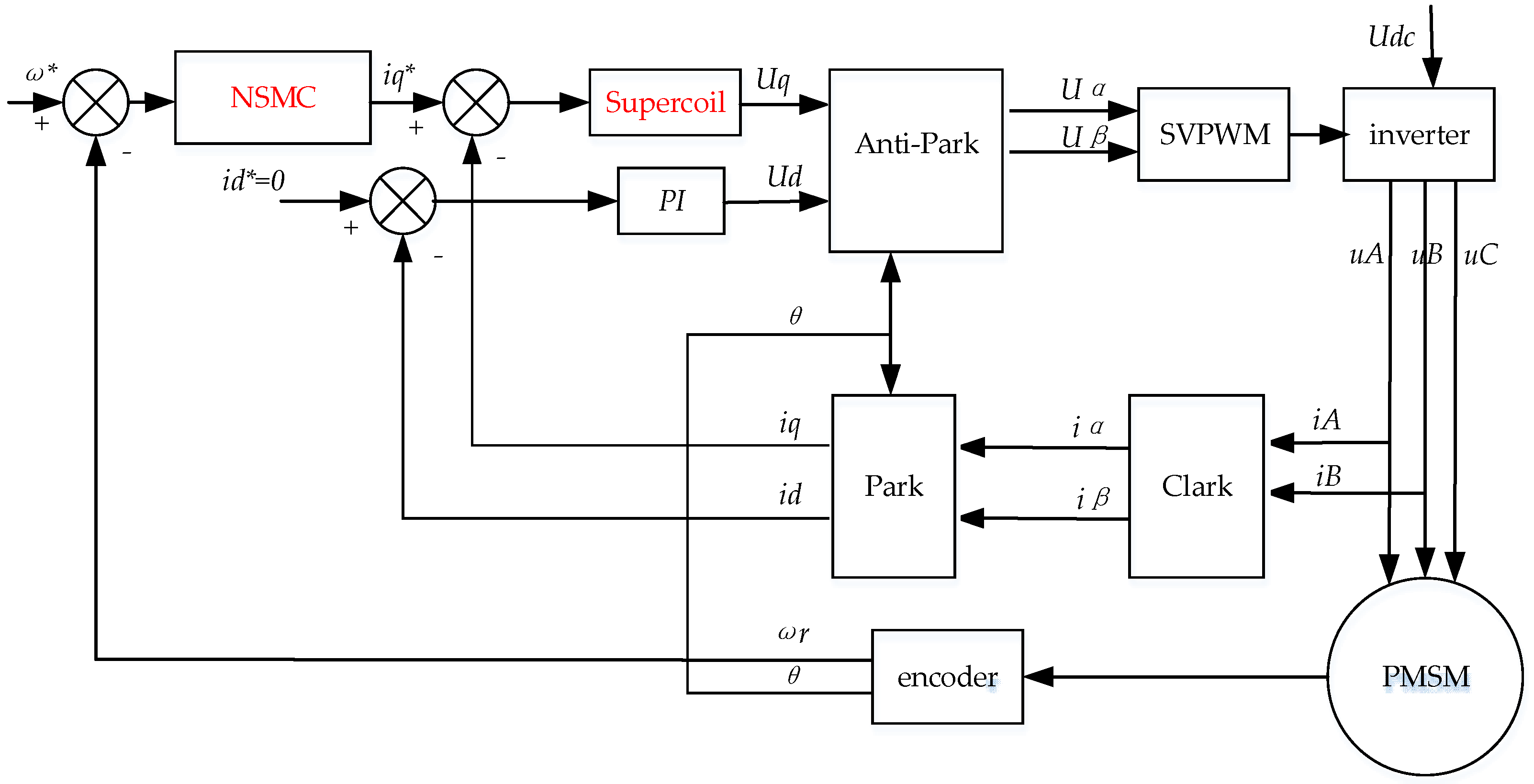
2.1. Multi-Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive System Scheme
2.2. Mathematical Model of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
- (1)
- Disregard core saturation effects and iron loss mechanisms;
- (2)
- Exclude rotor damping circuits;
- (3)
- Assume sinusoidal flux density in the air gap.
- (4)
- Perfect symmetry in stator windings and phase currents
3. Design of Sliding Mode Speed Controller
3.1. Basic Ideas of Synovial Control
- (1)
- Function Substitution Method
- (2)
- Reaching Law Optimization
- (3)
- Observer method
3.2. Synovial Controller Design
- (1)
- Design a switching function that conforms to the system and a reasonable sliding mode approach law.
- (2)
- Ensure that the system has good response capability and generates sliding modes.
- (3)
- Make the system tend to stabilize near the sliding surface.
3.2.1. Design of Index Synovial Controller
3.2.2. Design of Improved Index Synovial Velocity Controller
- (1)
- Finite-time convergence through homogeneous scaling;
- (2)
- Chattering suppression via smooth switching;
- (3)
- Disturbance rejection enhancement through state-coupled gain adjustment, ultimately suppressing steady-state errors below 0.05% in experimental validation.
3.3. Design of Super Spiral Structure
3.3.1. Definition of Sliding Surface
3.3.2. Design a Super Spiral Control Law
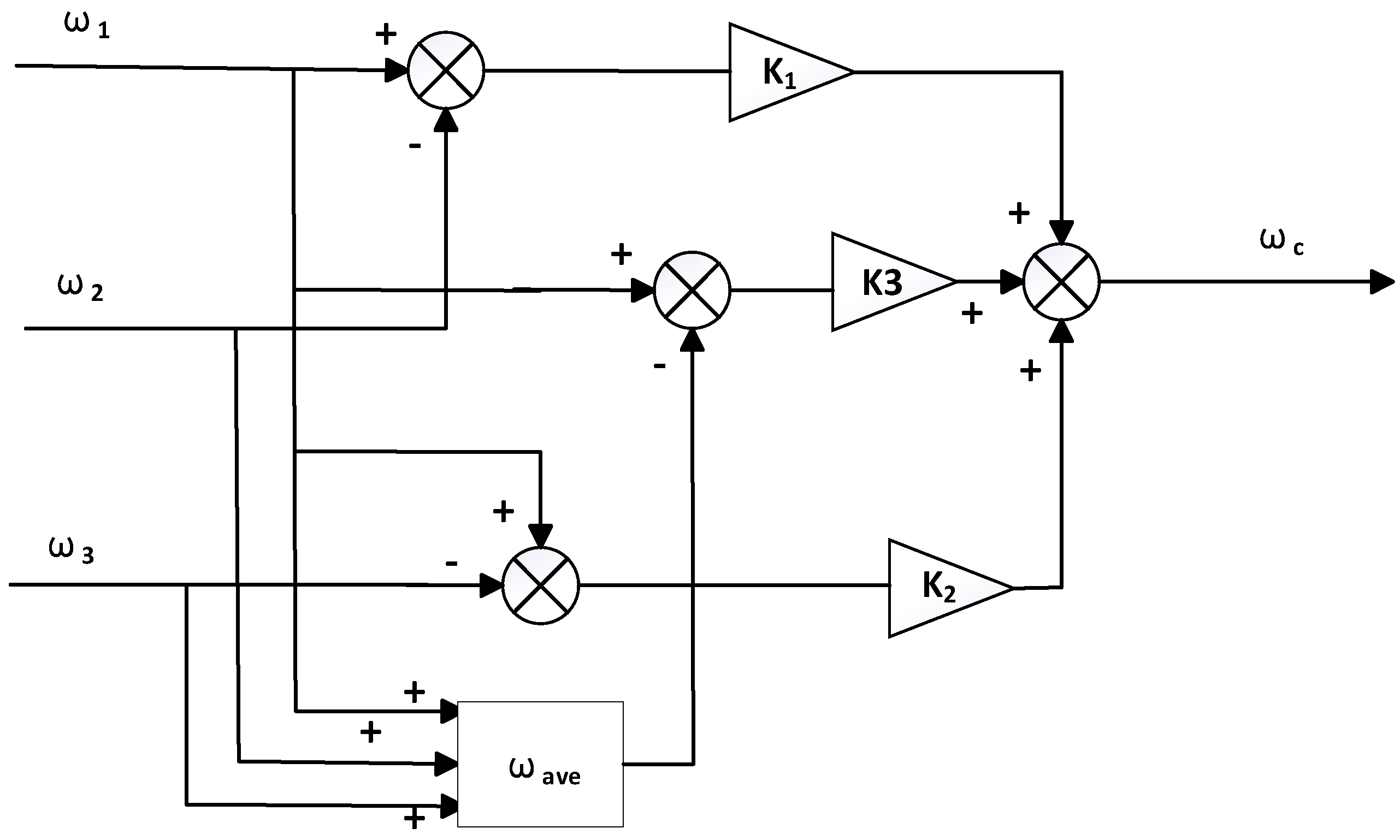
4. Design of a New Compensator Based on Deviation Coupling
4.1. Principle of Deviation Coupling Control
4.2. Improvement of Deviation Coupling Control
4.3. Stability Analysis of Improved Deviation Coupling Control
5. Symmetry Analysis
5.1. Symmetry Maintenance Mechanisms
5.2. Dynamic Utilization of Symmetry
5.3. Symmetry Recovery Strategy
6. Simulation Experiments and Result Analysis
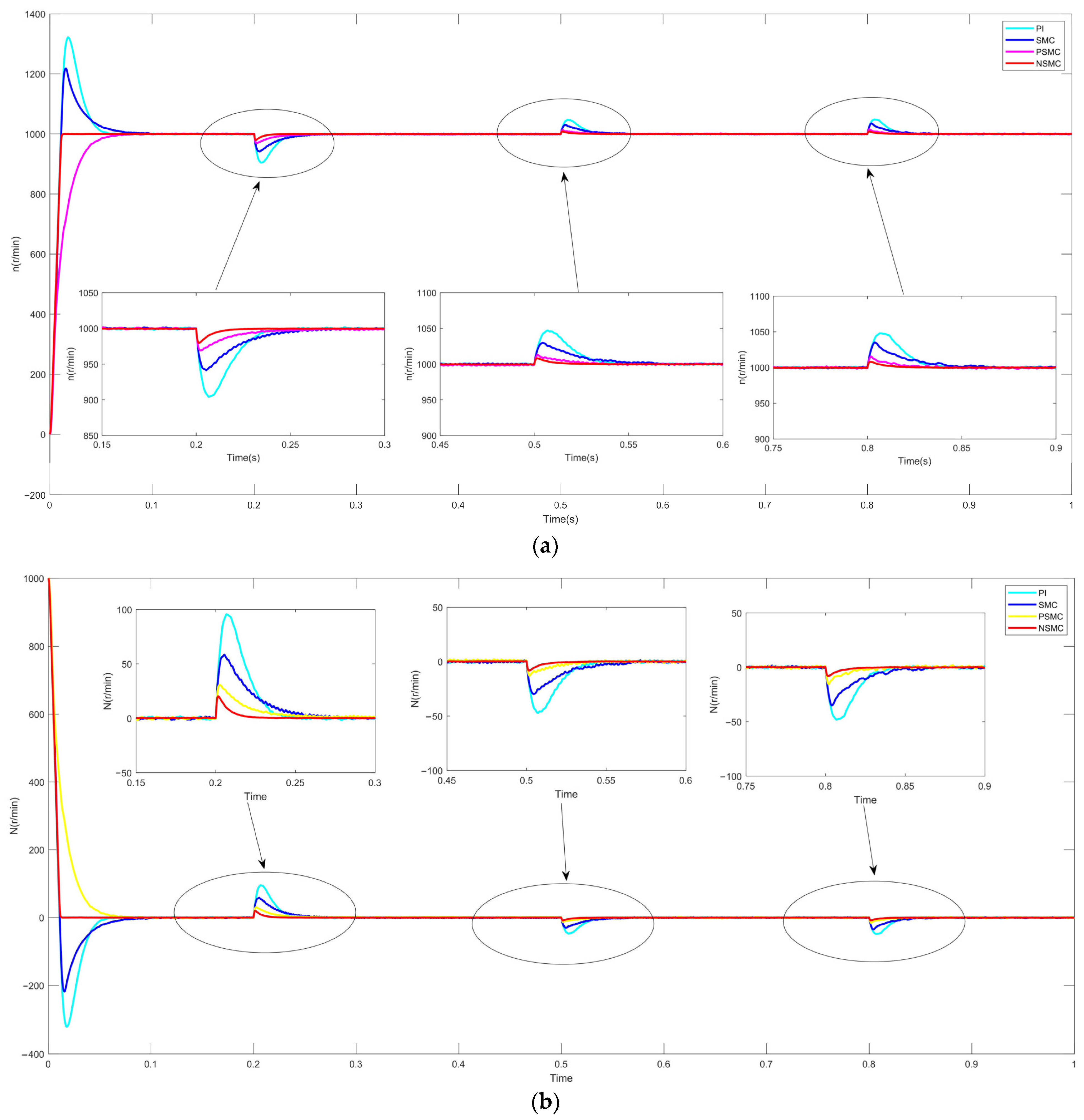
6.1. Single-Motor Control Simulation
6.2. Multi-Motor Simulation Results
- (1)
- (2)
- rotational speed error analysis (Figure 9),
- (3)
- (4)
- comparative torque characteristics (Figure 12),
- comprehensively illustrating system behavior under dynamic load variation scenarios.
| Time | Operating Condition | Load Torque (M1)TL | Load Torque (M2)TL | Load Torque (M3)TL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–0.2 s | No load | 0 N·m | 0 N·m | 0 N·m |
| 0.2–0.5 s | Heavy load | 0 N·m | 12 N·m | 10 N·m |
| 0.5–0.8 s | Light load | 0 N·m | 6 N·m | 5 N·m |
| 0.8–1 s | No load | 0 N·m | 0 N·m | 0 N·m |
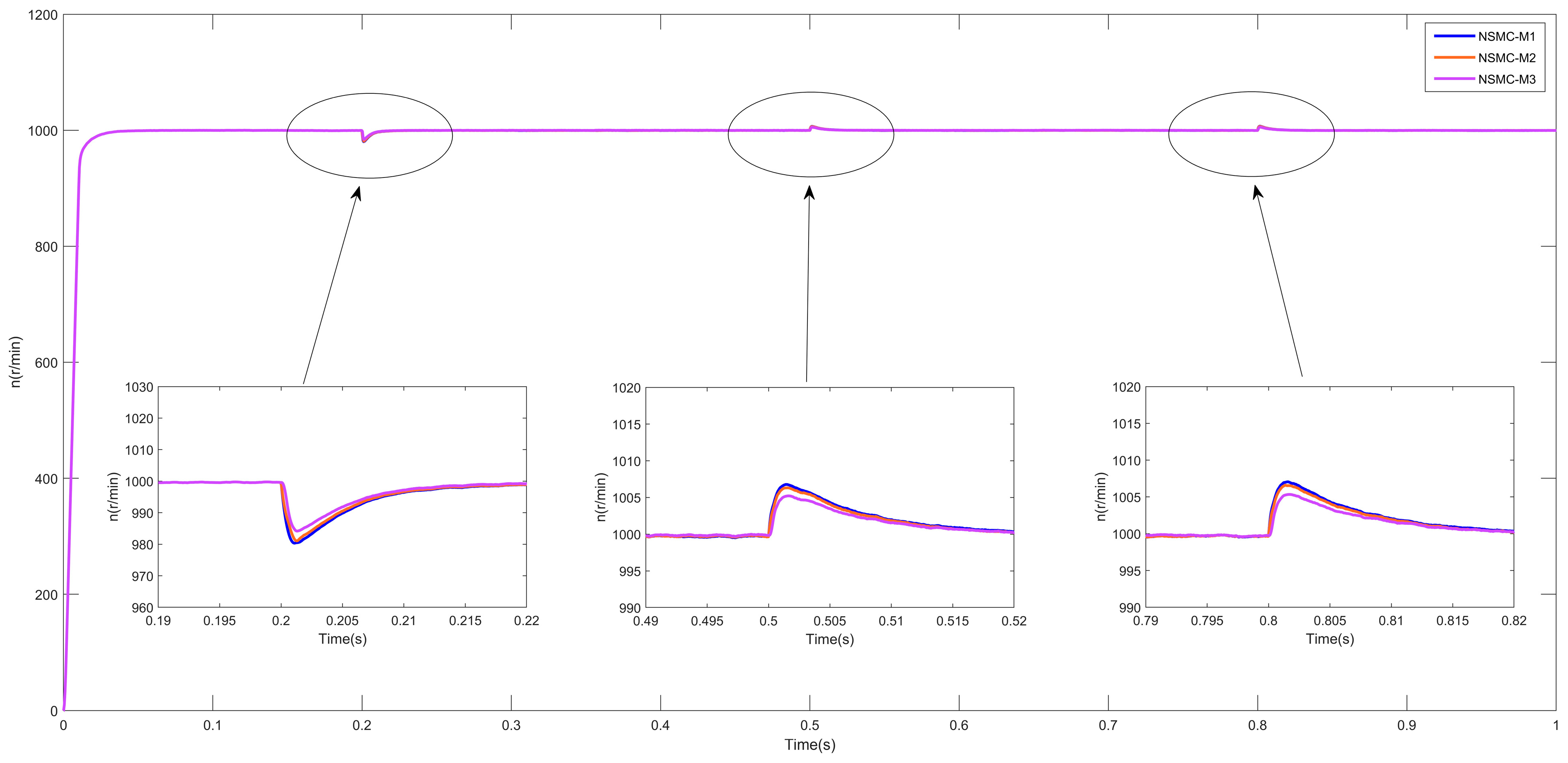

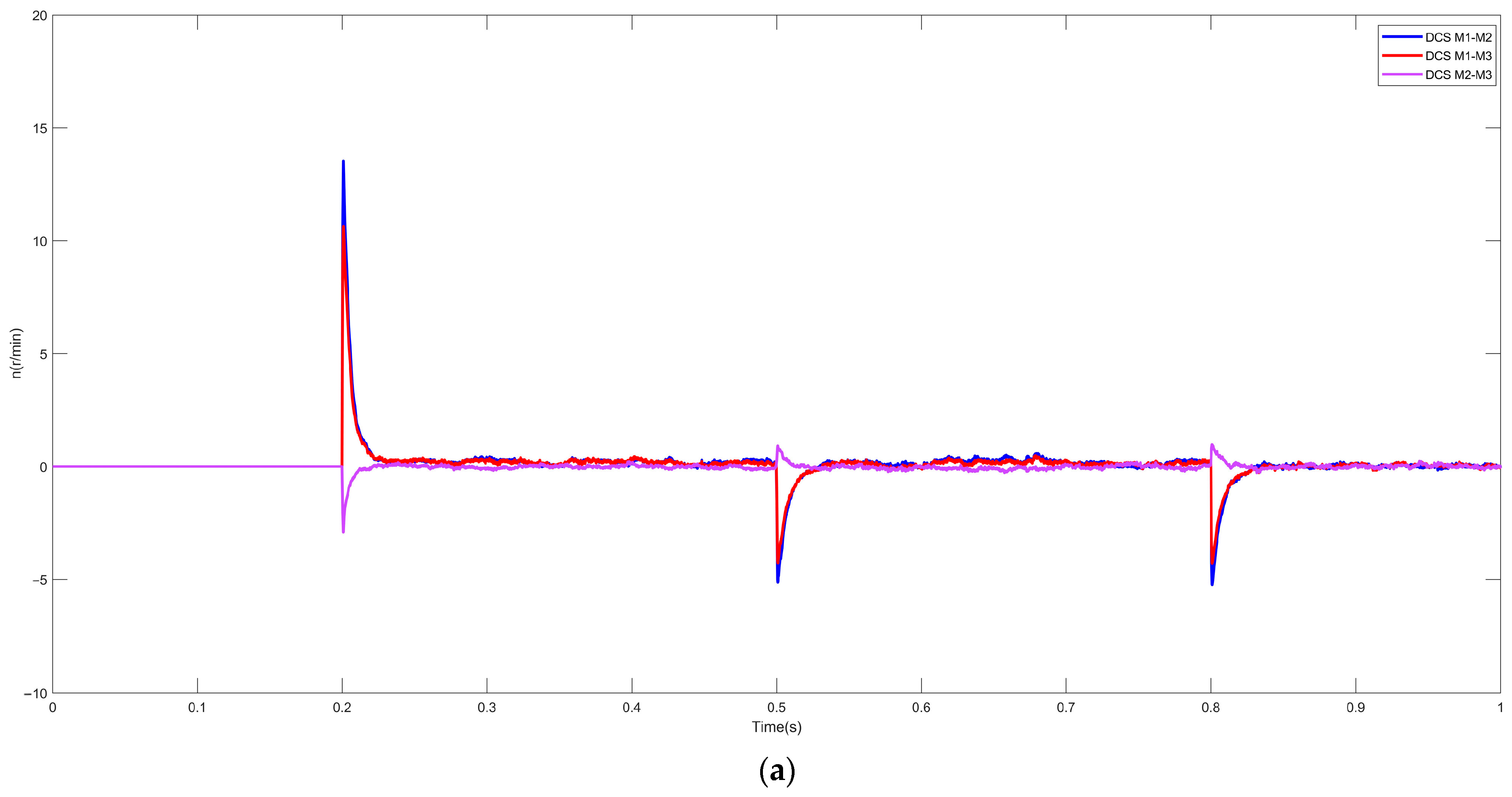
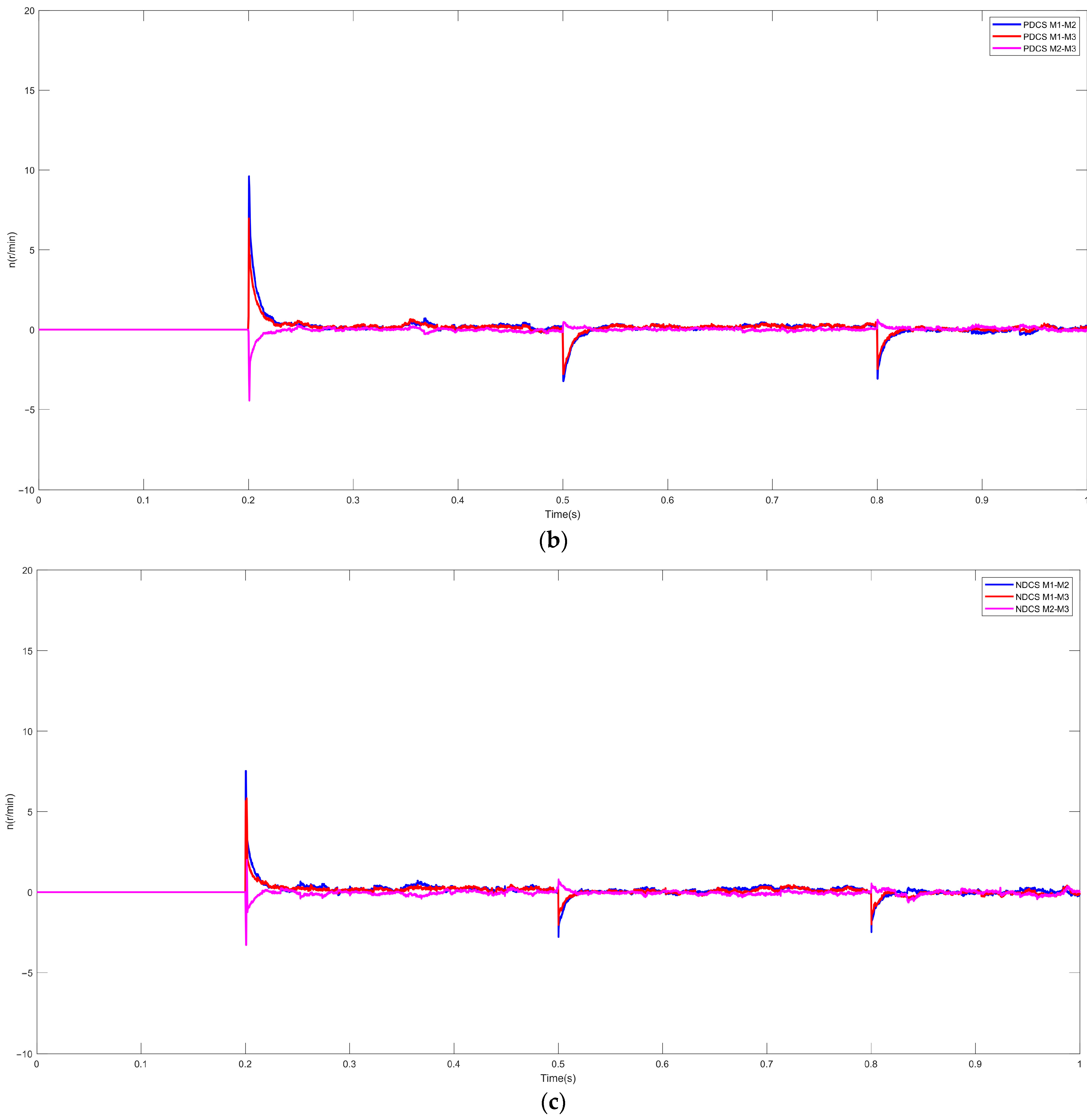
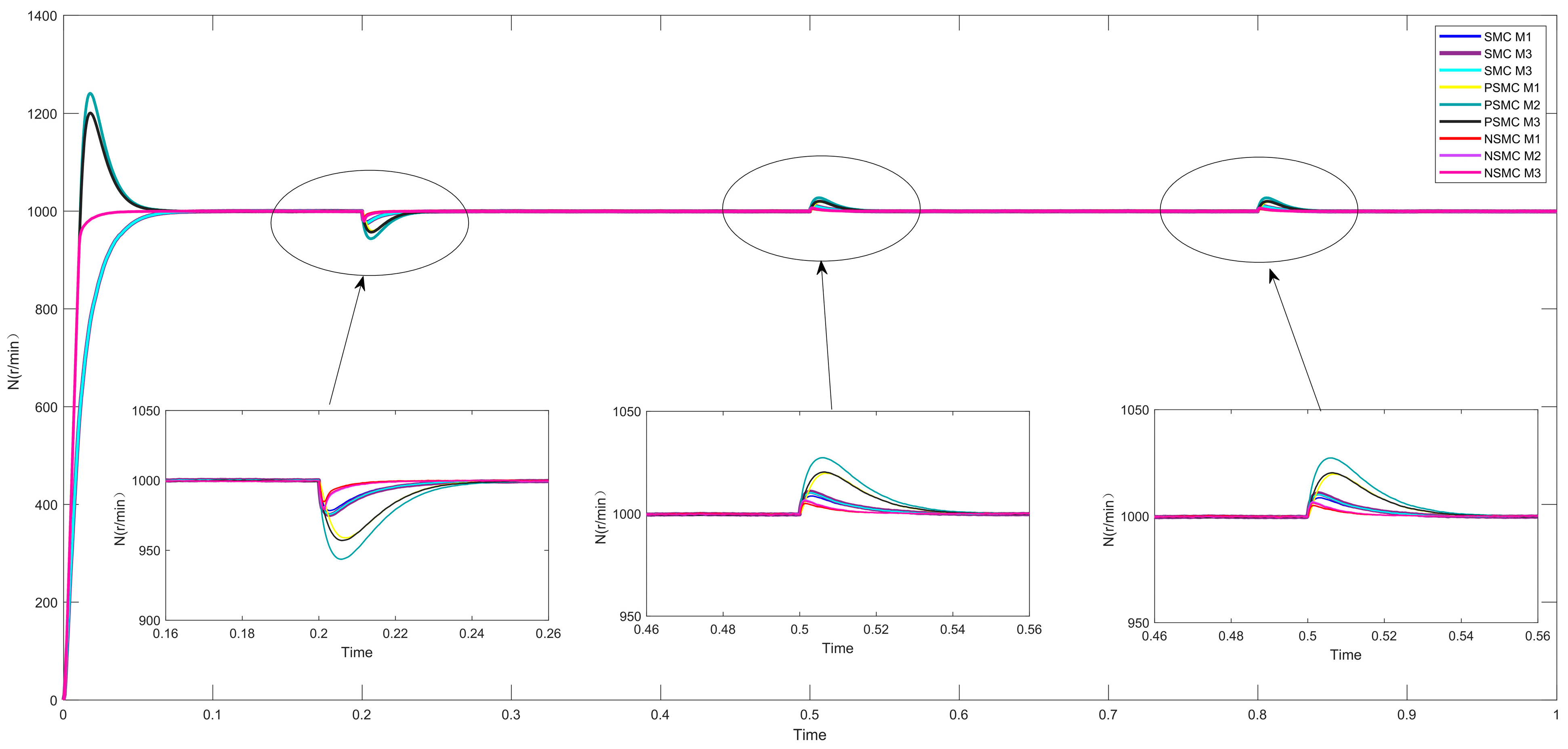
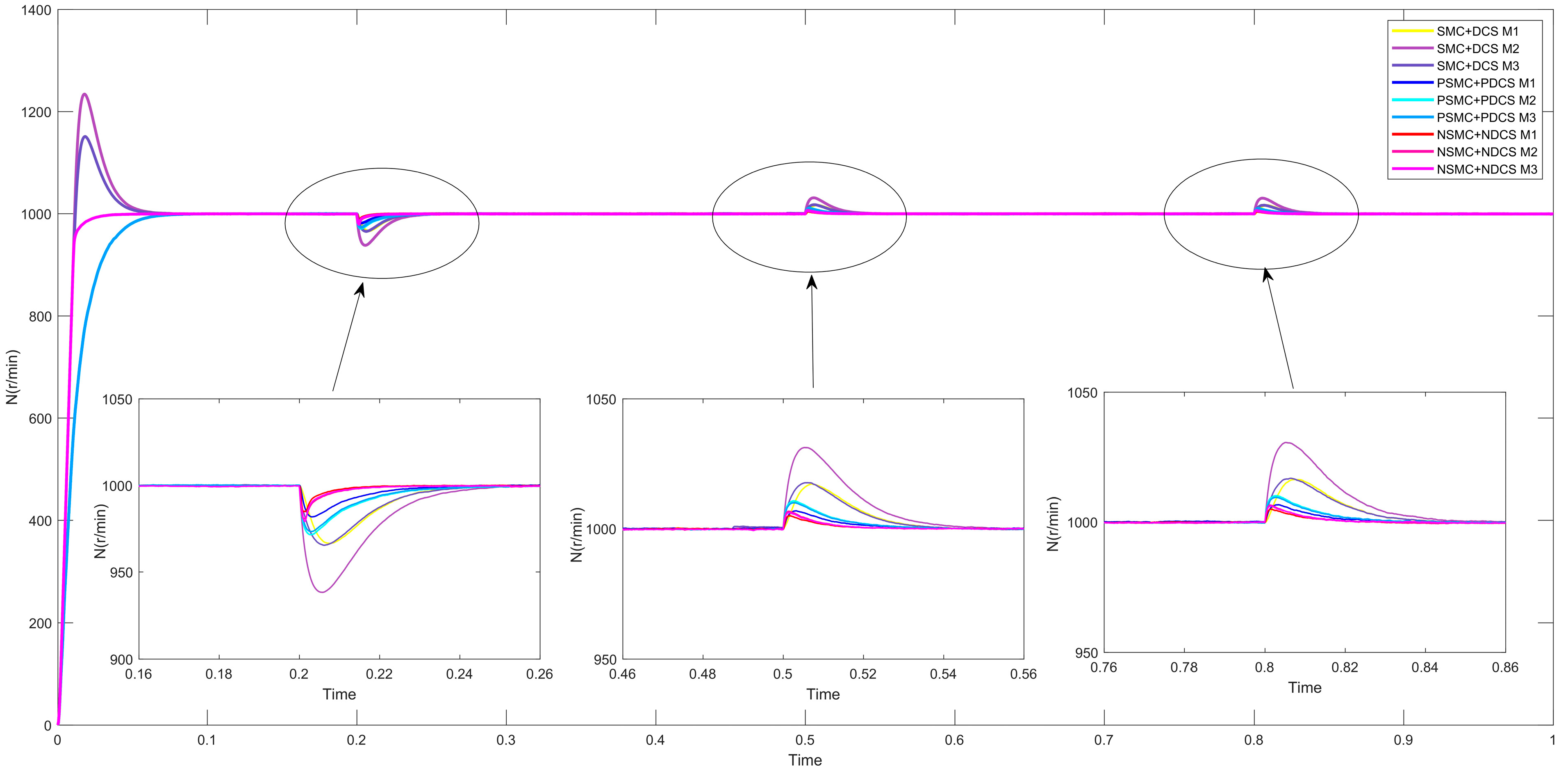
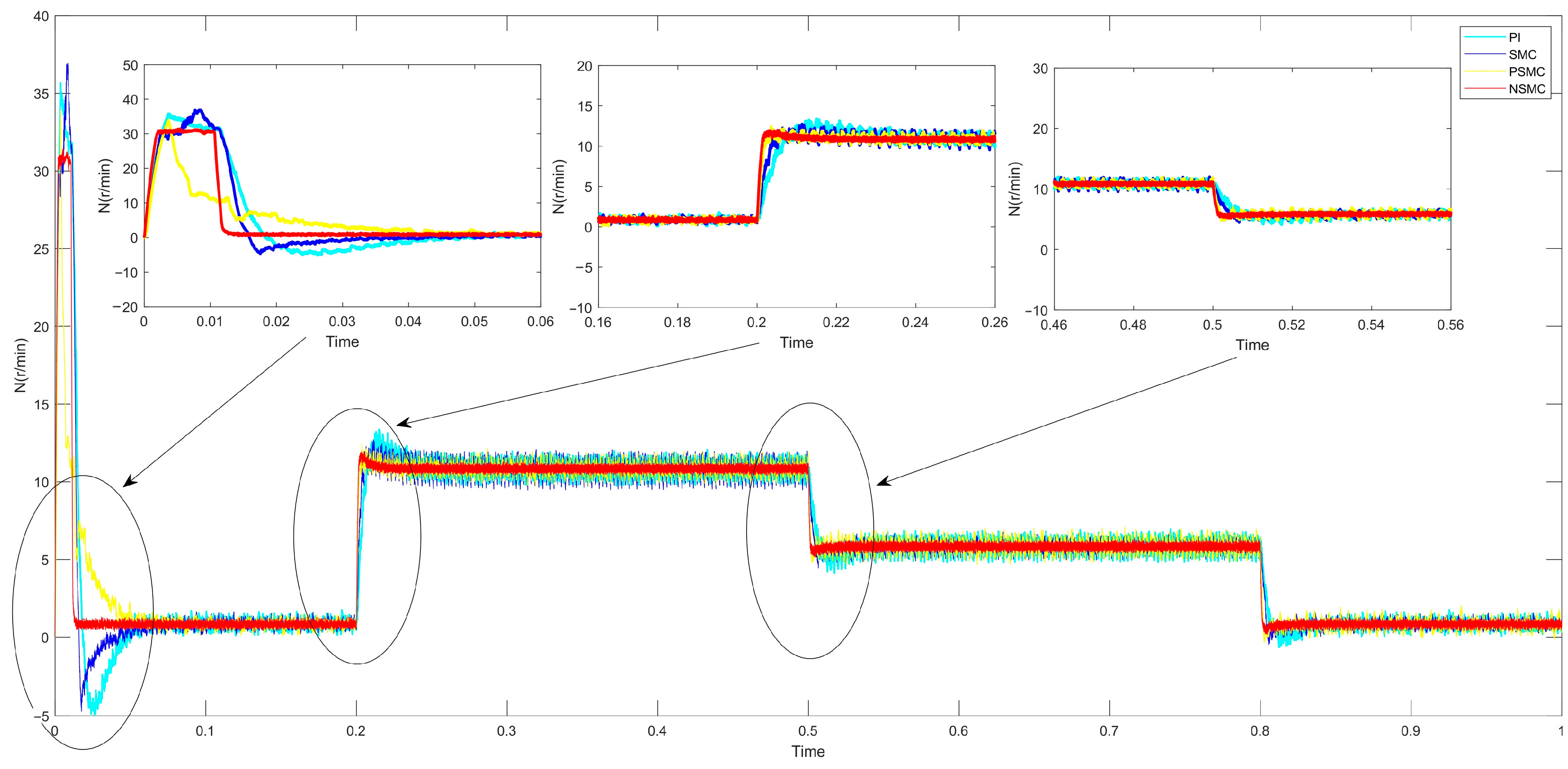
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- Based on the improved sliding mode control, the PMSM deviation coupling control strategy has achieved smooth operation at high speed and high torque. Moreover, the motor has a faster response speed, smaller overshoot, stronger disturbance resistance, better dynamic responsiveness, and improved ability to follow the reference speed.
- (2)
- The new synchronous speed compensator has better synchronization performance compared to traditional speed compensators and reduces synchronization errors between motors, thereby reducing motor losses and extending their lifespan.
8. Prospects for Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. PI Control Strategy for Electric Vehicle Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on SVPWM. Intern. Combust. Engine Accessories 2020, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hu, H.; Cai, S.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Wei, C. Design of autonomous flight system for biomimetic flapping wing aircraft based on PID algorithm. South. Agric. Mach. 2024, 134–137. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, Q.; He, Z.; Tan, T.; Chen, C. Performance Study of Fractional Order Fuzzy Backstepping Controller for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Manuf. Technol. Mach. Tool 2024, 1–14. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19287/j.mtmt.1005-2402.2025.04.014 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Liu, F.; Xie, C. Adaptive Tracking Control of Locomotive PMSM Traction Transmission System. Autom. Technol. Appl. 2024, 1–8. Available online: https://cstj.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=7108409788&from=Qikan_Search_Index (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Tang, R.; Chen, J. Predefined Time Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for Flexible Space Robots. J. Zhejiang Univ. Eng. Sci. 2024, 1–11. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/33.1245.T.20241217.1450.008.html (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Sun, C.; Liu, J.; Li, J. Nonlinear Integral Sliding Mode Variable Structure Control of Electro-Hydraulic Servo System. J. Chongqing Univ. Technol. Nat. Sci. 2024, 1–7. Available online: http://clgzk.qks.cqut.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract7228.shtml (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Xi, L.; Ma, J.; Ao, B. Design of Improved Sliding Mode Composite Controller for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Manuf. Technol. Mach. Tool 2024, 1–11. Available online: https://1951.mtmt.com.cn/cn/article/id/b5946240-b022-4085-81ba-0ac2d9c41a62 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Jia, L.; Hou, M. Sliding mode control of robotic arm based on adaptive parameter convergence law. Mach. Tools Hydraul. 2024, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.; Yue, Y.; Liu, D. Multi motor synchronous control based on improved deviation coupling. Comb. Mach. Tools Autom. Mach. Technol. 2023, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Jiang, J.; Liu, A. Research on Multi motor Synchronous Control Strategy of Flexographic Printing Machine. Inf. Technol. Informatiz. 2020, 6, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J. Fuzzy Self Regulating Deviation Coupled Multi Motor Synchronous Control; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2017; pp. 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Li, K. Multi motor synchronous control strategy with improved adjacent coupling error. Autom. Instrum. 2014, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wang, J. Adaptive fault-tolerant control of quadcopter unmanned aerial vehicle based on novel sliding mode approach law. Syst. Sci. Technol. 2024, 1–18. Available online: https://sysmath.cjoe.ac.cn/jweb_xtkxysx/CN/lexeme/showArticleByLexeme.do?articleID=54393 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Huang, H.; Peng, Y.; Huang, X. Improved Adaptive Sensor Less Control of Sliding Mode Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on SPWM. 2024, pp. 1–11. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=v1PGZ9hyqdsmfwKt_wVnpwGXeMA-hqUCJFJ6TqaZJMJV7lNoj4W-SUvGrEfN-vQ7yeA_CbdqsvJ5IFe8SbUdHndgv74e7DRUoEsmDil74UTd81JQPRUYGr7CINjpklu_9D8bsKReYgZpLxptF0zhPOvY9FHwoOW7HKfBtsthwTN9jwDTU3aGmrIRbqukwkFG5jZ91xKsuuk=&uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Adaptive Super Spiral Sliding Mode Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Control Eng. 2025, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F. Research on Coupled Synchronous Control of Multi Motor Servo System; Zhejiang University of Technology: Hangzhou, China, 2018; pp. 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Peng, F.; Huang, Y. Overview of Multi motor Synchronous Motion Control Technology. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2021, 16, 2922–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Wang, H.; Hu, H. Improving the Coordinated Control of Multiple Motors with Circular Coupling Structure. J. Chang. Univ. Technol. 2022, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandro, B.; Lorenzo, C.; Simone, C. Surface Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors’ Passive Sensor less Control: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 7747. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, C.; Zhang, Z. A Review on Position/Speed Sensor less Control for Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine-Based Wind Energy Conversion Systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2013, 1, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Song, C.; Du, M. Research on self-coupling PID for multi-driven synchronization control with ring adjacent compensation. Meas. Control 2024, 57, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardila, M.Z.; Saad, M.; Mubin, M. Robust Speed Control of PMSM Using Sliding Mode Control (SMC)—A Review. Energies 2019, 12, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changlin, Z.; Qunzhang, T.; Chengming, J.; Ming, P.; Hao, H.; Zhiwen, T. Deviation Coupling Control for Multimotor System via Global Fast Terminal Sliding Mode. Control Adv. Math. Phys. 2021, 2021, 9200267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Qi, L.; Sun, M.; Han, W. An Improved Deviation Coupling Control Method for Speed Synchronization of Multi-Motor Systems. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q. Multi-Motor Cooperative Control Strategy for Speed Synchronous Control of Construction Platform. Electronics 2022, 11, 4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
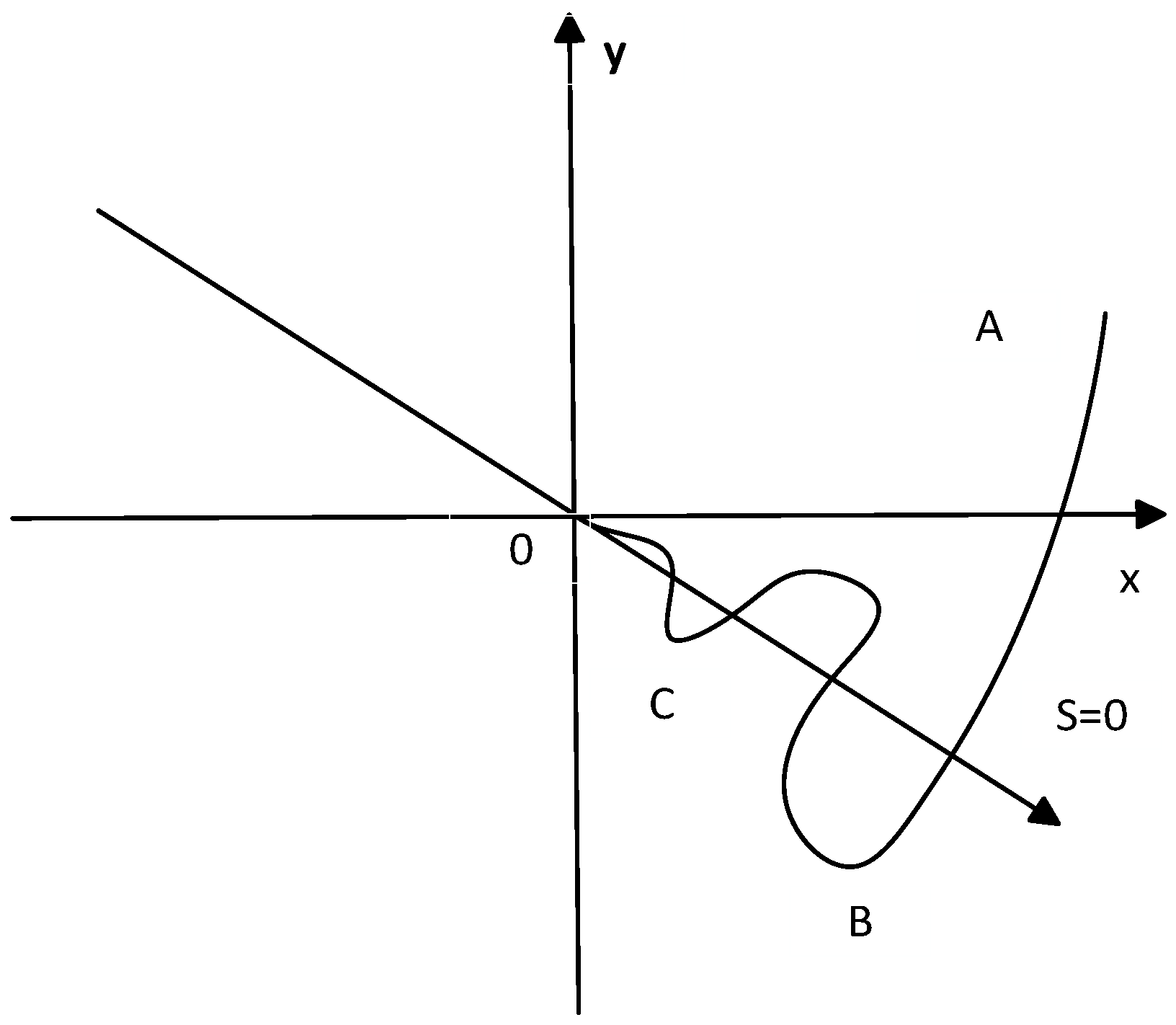


| Parameter | Parameter Size | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Number of pole pairs Pn | 4 | |
| Stator resistance R | 2.8 | Ω |
| Stator d, q-axis inductance Ld Lq | 8.5 | mH |
| Rotor moment of inertia J | 8.25 × 10−3 | Kg∙m2 |
| Permanent magnet magnetic flux φf | 0.175 | Wb |
| Damping coefficient B | 0.001 | N∙m∙s |
| Rated load torque TL | 10 | N∙m |
| Sample time Ts | 1 | s |
| DC Voltage Vdc | 380 | V |
| Rated power | 100 | Kw |
| Parameter | Connotation |
|---|---|
| The stator phase resistance | |
| The d-axis and q-axis voltages | |
| , | The d-axis and q-axis currents |
| , | The d-axis and q-axis inductances |
| The magnetic flux of the permanent magnet | |
| The rotor electrical angular velocity | |
| The polar logarithm | |
| The load torque | |
| The mechanical angle of the rotor |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, Z.; Sun, S.; Cui, Z. Research on Coordinated Control of Multi-PMSM for Shaftless Overprinting System. Symmetry 2025, 17, 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060958
Xu Y, Liu C, Huang Z, Sun S, Cui Z. Research on Coordinated Control of Multi-PMSM for Shaftless Overprinting System. Symmetry. 2025; 17(6):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060958
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yuntao, Cheng Liu, Zihao Huang, Shiyuan Sun, and Zewei Cui. 2025. "Research on Coordinated Control of Multi-PMSM for Shaftless Overprinting System" Symmetry 17, no. 6: 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060958
APA StyleXu, Y., Liu, C., Huang, Z., Sun, S., & Cui, Z. (2025). Research on Coordinated Control of Multi-PMSM for Shaftless Overprinting System. Symmetry, 17(6), 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060958






