A Novel Symmetrical Inertial Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers with Proximal Term for Nonconvex Optimization with Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- Building upon the inertial update step due to [33], we introduce an additional inertial update for y and incorporate into the x-subproblem update; this form of inertial update ensures that the primal variables are treated equally, and thereby we achieve faster acceleration. In addition, we introduce two distinct inertial parameters to avoid the differentiated feedback effect that a single inertial parameter may impose on different inertial terms.
- (ii)
- To simplify the computation of the subproblems, we introduce an approximation term in the x-subproblem, which under appropriate conditions, a closed-form solution can be obtained in practical applications.
- (iii)
- Under reasonable assumptions, we prove that any cluster point of the sequence generated by NIP-ADMM belongs to the set of critical points of the augmented Lagrangian function. Furthermore, under the condition that the auxiliary function satisfies Kurdyka–Łojasiewicz property (KLP), we further establish that the sequence generated by NIP-ADMM converges to a stationary point of the augmented Lagrangian function.
- (iv)
- Since function g in (4) is convex, this ensures that g is well-defined, and enables us to abandon the traditional ADMM update scheme and instead adopt a gradient descent approach. This method requires only the computation of gradients at each iteration, and significantly reduces computational complexity. Consequently, it offers substantial advantages when handling high-dimensional or large-scale datasets.
2. Preliminaries
- (i)
- Frechet sub-differential of χ at is denoted by and defined as:Among others, we set when .
- (ii)
- The limiting sub-differential of χ at is written as and defined by
- (i)
- From Definition 3, which implies that holds for all , and given that is a closed set, is also a closed set.
- (ii)
- Suppose that is a sequence that converges to , and converges to with . Then, by the definition of the sub-differential, we have .
- (iii)
- If is a local minimum of χ, then it follows that .
- (vi)
- Assuming that is a continuously differentiable function, we can derive:
3. Novel Algorithm and Convergence Analysis
| Algorithm 1 NIP-ADMM |
|
- (ii)
- The update scheme in of Algorithm 1 for y-subproblem adopts the gradient descent method, where is the gradient of the function with respect to y, and γ is called the learning rate.
- (iii)
- The inertial structure adopted in Algorithm 1 employs a structurally balanced acceleration strategy. This update strategy is mathematically symmetric with the only distinction for the values of the parameters η and θ.
- (ii)
- S is a positive semidefinite matrix.
- (iii)
- For convenience, we introduce the following symbols:
- (iv)
- To analyze the monotonicity of , we set .
- (i)
- M and are two non-empty compact sets. As , it follows that and .
- (ii)
- .
- (iii)
- .
- (iv)
- The sequence converges, and .
4. Numerical Simulations
4.1. Signal Recovery
4.2. SCAD Penalty Problem
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.J.; Koh, K.; Lustig, M.; Boyd, S.; Gorinevsky, D. An interior-point method for large-scale ℓ1-regularized least Squares. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2007, 1, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartrand, R.; Staneva, V. Restricted isometry properties and nonconvex compressive sensing. Inverse Probl. 2008, 24, 035020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.S.; Lin, S.B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.B. L1/2 regularization: Convergence of iterative half thresholding algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 2317–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostmohammadian, M.; Gabidullina, Z.R.; Rabiee, H.R. Nonlinear perturbation-based non-convex optimization over time-varying networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 6461–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Selesnick, I.W. Group-sparse signal denoising: Non-convex regularization, convex optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 3464–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.L. Sparse Bayesian learning for sparse signal recovery using ℓ1/2-norm. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 207, 109340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yan, M.; Rahimi, Y.; Lou, Y.F. Accelerated schemes for the L1/L2 minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 2660–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.R.; Wang, Q.H.; Zhang, B.X.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.L.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Z.G.; Feng, B.; Yu, T.Y. Cauchy non-convex sparse feature selection method for the high-dimensional small-sample problem in motor imagery EEG decoding. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1292724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiddeman, B.; Ghahremani, M. Principal component wavelet networks for solving linear inverse problems. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.C.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Jiang, H.J. Distributed nonconvex optimization subject to globally coupled constraints via collaborative neurodynamic optimization. Neural Netw. 2025, 184, 107027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Fu, H.; Liu, Y.F. High-dimensional cost-constrained regression via nonconvex optimization. Technometrics 2021, 64, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merzbacher, C.; Mac Aodha, O.; Oyarzun, D.A. Bayesian optimization for design of multiscale biological circuits. ACS Synth. Biol. 2023, 12, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.C.; Zhang, H.C.; Li, J.C. A parameterized proximal point algorithm for separable convex optimization. Optim. Lett. 2018, 12, 1589–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Liu, P.L.; Liu, Y.P.; Qiu, R.C.; Yu, W.X. Robust sparse recovery in impulsive noise via ℓp-ℓ1 optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Gao, J.B.; Qian, J.J.; Yang, J.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, B. Linear regression problem relaxations solved by nonconvex ADMM with convergence analysis. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, B.P.W.; Hong, M.Y. Alternating direction method of multipliers for penalized zero-variance discriminant analysis. Comput. Optim. Appl. 2016, 64, 725–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietlow, C.; Lindner, J.K.N. ADMM-TGV image restoration for scientific applications with unbiased parameter choice. Numer. Algorithms 2024, 97, 1481–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, F.M.; Liang, J.W.; Zhang, X.Q. A stochastic alternating direction method of multipliers for non-smooth and non-convex optimization. Inverse Probl. 2021, 37, 075009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Teboulle, M. A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2009, 2, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.Q.; Li, R.Z. Variable selection via nonconcave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties. J. Am. Statist. Assoc. 2001, 96, 1348–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, N.; Boyd, S. Proximal Algorithms; Now Publishers: Braintree, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, M.Y.; Luo, Z.Q.; Razaviyayn, M. Convergence analysis of alternating direction method of multipliers for a family of nonconvex problems. SIAM J. Optim. 2016, 26, 337–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.H.; Xu, Z.B.; Xu, H.K. Convergence of Bregman alternating direction method with multipliers for nonconvex composite problems. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1410.8625. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.; Shang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Fan, Y. Semi-proximal ADMM for primal and dual robust Low-Rank matrix restoration from corrupted observations. Symmetry 2024, 16, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Han, D.R.; Wu, T.T. Convergence of alternating direction method for minimizing sum of two nonconvex functions with linear constraints. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2016, 94, 1653–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, W.T.; Zeng, J.S. Global convergence of ADMM in nonconvex nonsmooth optimization. J. Sci. Comput. 2019, 78, 29–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.H.; Cao, W.F.; Xu, Z.B. Convergence of multi-block Bregman ADMM for nonconvex composite problems. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2018, 61, 122101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, R.F.; Sidky, E.Y. Convergence for nonconvex ADMM, with applications to CT imaging. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2024, 25, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.F.; Yan, J.C.; Jin, B.; Li, W.H. Distributed and parallel ADMM for structured nonconvex optimization problem. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 4540–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.; Attouch, H. An inertial proximal method for maximal monotone operators via discretization of a nonlinear oscillator with damping. Set-Valued Anal. 2001, 9, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.M.; Li, M. General inertial proximal gradient method for a class of nonconvex nonsmooth optimization problems. Comput. Optim. Appl. 2019, 73, 129–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.T.; Zhang, Y.; Jian, J.B. An inertial proximal alternating direction method of multipliers for nonconvex optimization. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2020, 98, 1199–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Shao, H.; Liu, P.J.; Wu, T. An inertial proximal partially symmetric ADMM-based algorithm for linearly constrained multi-block nonconvex optimization problems with applications. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2023, 420, 114821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Chan, R.H.; Ma, S.Q.; Yang, J.F. Inertial proximal ADMM for linearly constrained separable convex optimization. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2015, 8, 2239–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attouch, H.; Bolte, J.; Redont, P.; Soubeyran, A. Proximal alternating minimization and projection methods for nonconvex problems: An approach based on the Kurdyka-Łojasiewicz inequality. Math. Oper. Res. 2010, 35, 438–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockafellar, R.T.; Wets, R.J.B. Variational Analysis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bolte, J.; Sabach, S.; Teboulle, M. Proximal alternating linearized minimization for nonconvex and nonsmooth problems. Math. Program. 2014, 146, 459–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterov, Y. Introductory Lectures on Convex Optimization: A Basic Course; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.B.; Chang, X.Y.; Xu, F.M.; Zhang, H. L1/2 regularization: A thresholding representation theory and a fast solver. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2012, 23, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
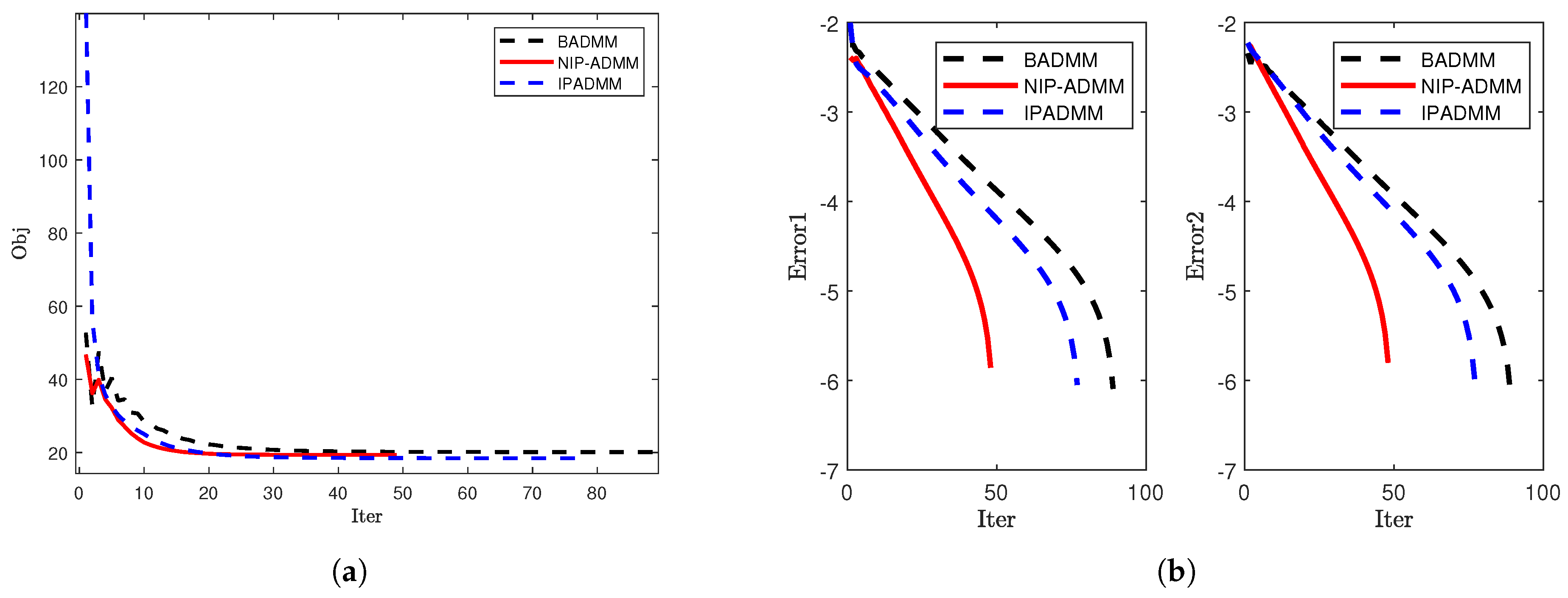
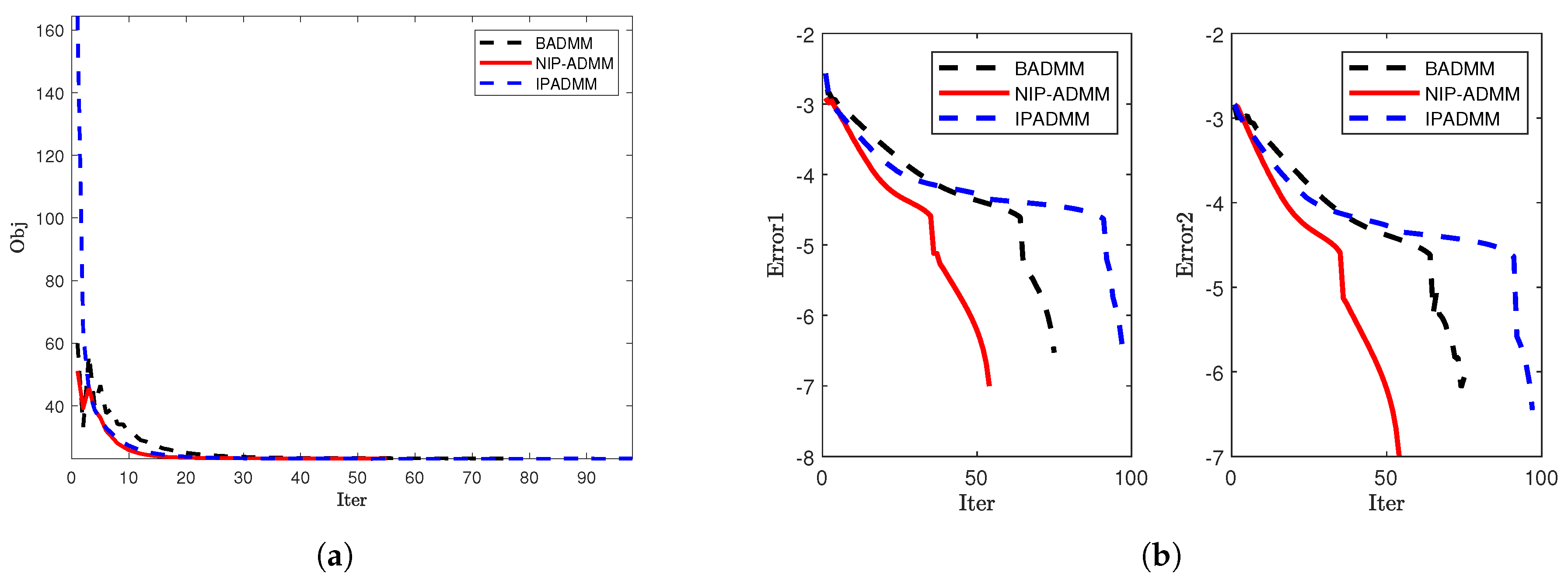
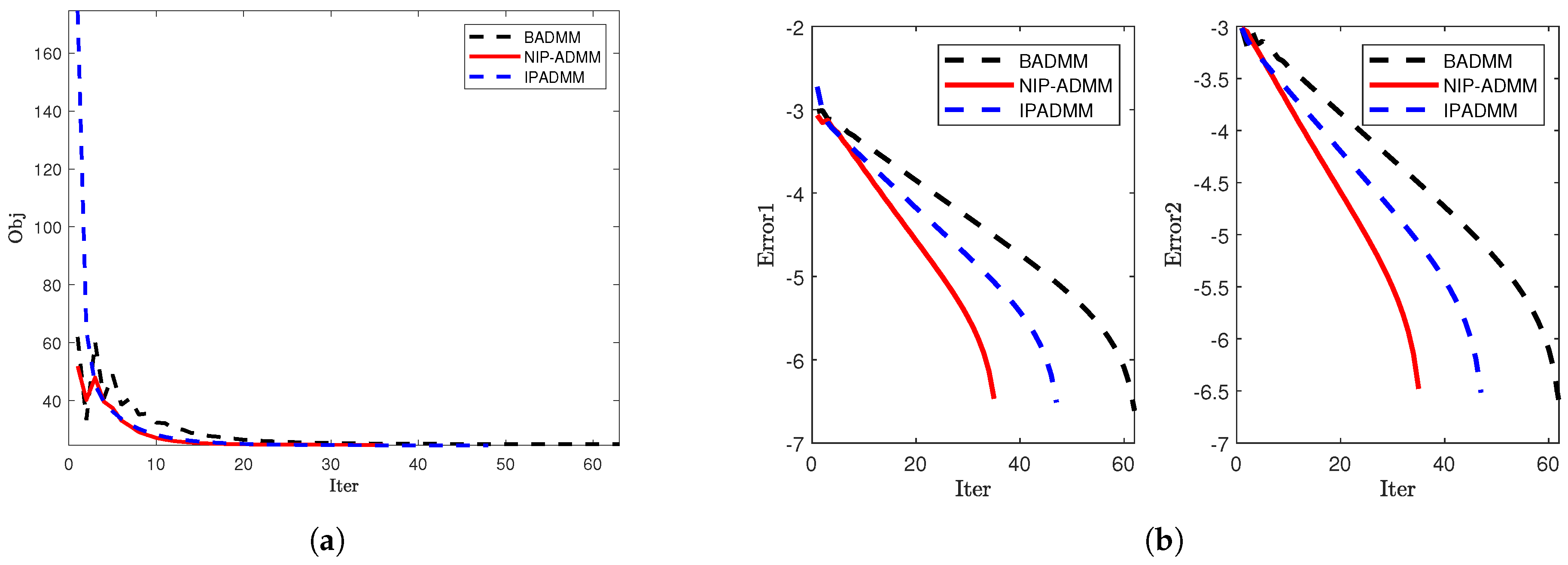

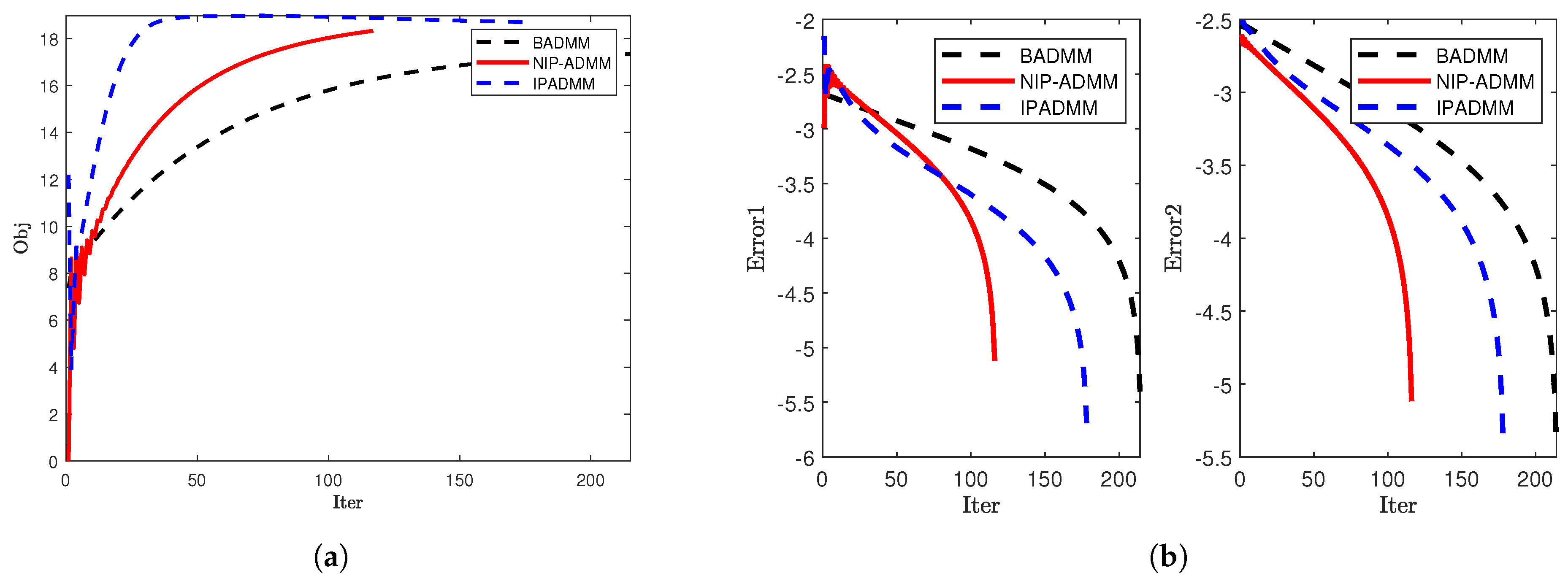
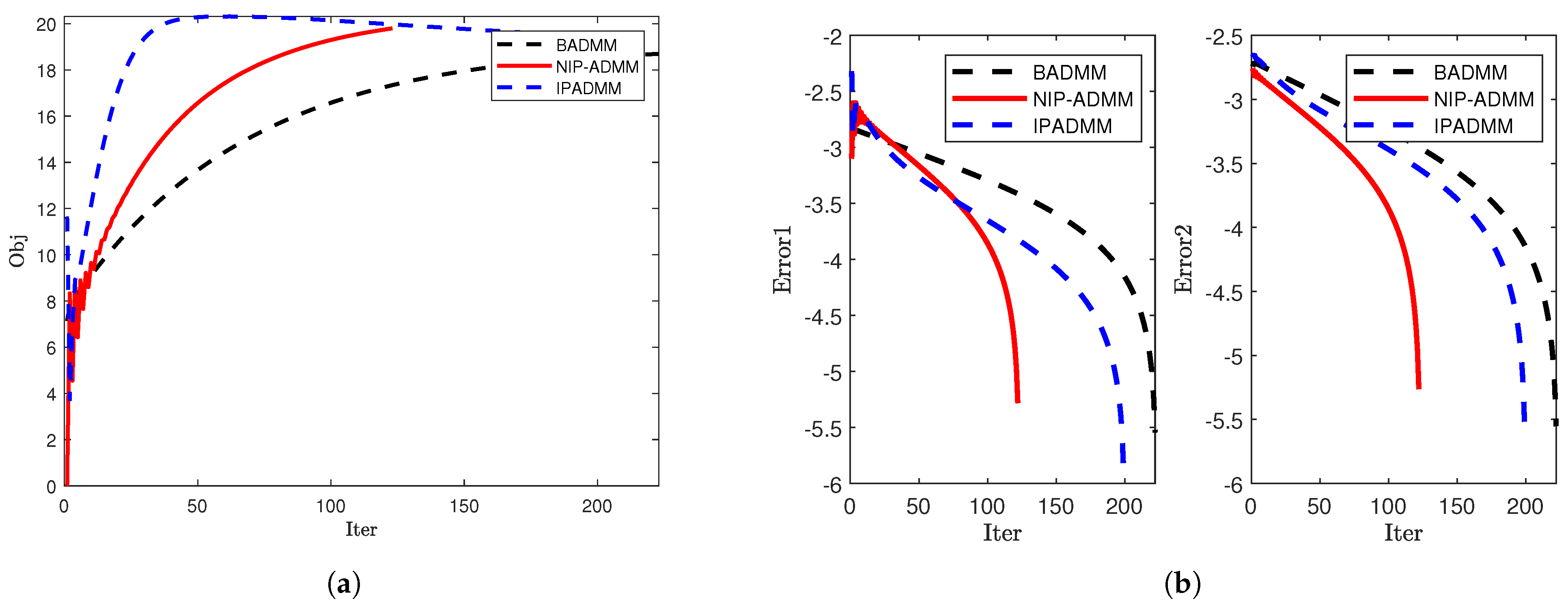
| Iter | CPUT(s) | Iter | CPUT(s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.2 | 75 | 2.2392 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 54 | 1.6014 |
| 0.3 | 0.2 | 78 | 2.3039 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 49 | 1.4583 |
| 0.3 | 0.3 | 69 | 1.9476 | 0.8 | 0.75 | 49 | 1.4309 |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | 60 | 1.7622 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 56 | 1.6445 |
| 0.6 | 0.6 | 56 | 1.6516 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 84 | 2.4614 |
| m | n | NIP-ADMM | IPADMM | BADMM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iter | CPUT(s) | Obj | Iter | CPUT(s) | Obj | Iter | CPUT(s) | Obj | ||
| 1000 | 1000 | 49 | 1.2698 | 19.36 | 78 | 2.1407 | 18.46 | 90 | 2.3407 | 20.14 |
| 1500 | 2000 | 44 | 4.9152 | 23.17 | 72 | 8.4978 | 22.12 | 76 | 8.5387 | 23.69 |
| 3000 | 3000 | 40 | 15.0464 | 21.02 | 57 | 22.3823 | 20.56 | 73 | 27.4115 | 21.18 |
| 3000 | 4000 | 55 | 34.0601 | 23.21 | 98 | 62.8206 | 23.11 | 76 | 48.3825 | 23.22 |
| 4000 | 5000 | 36 | 40.6110 | 24.02 | 53 | 61.7431 | 23.09 | 65 | 74.4521 | 24.03 |
| 4500 | 5500 | 40 | 61.7638 | 24.05 | 45 | 71.7627 | 23.79 | 67 | 102.6028 | 24.06 |
| 6000 | 6000 | 40 | 88.7702 | 24.99 | 48 | 108.3045 | 24.56 | 63 | 135.8133 | 25.00 |
| Iter | CPUT(s) | Iter | CPUT(s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.2 | 196 | 2.0092 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 149 | 1.5017 |
| 0.3 | 0.2 | 187 | 1.9122 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 134 | 1.3693 |
| 0.3 | 0.3 | 181 | 1.8690 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 133 | 1.3503 |
| 0.4 | 0.5 | 170 | 1.7650 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 127 | 1.3467 |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | 159 | 1.6438 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 126 | 1.3100 |
| m | n | NIP-ADMM | IPADMM | BADMM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iter | CPUT(s) | Obj | Iter | CPUT(s) | Obj | Iter | CPUT(s) | Obj | ||
| 1000 | 1000 | 121 | 1.3366 | 10.91 | 213 | 2.3065 | 10.55 | 182 | 1.9632 | 10.55 |
| 1000 | 1300 | 115 | 1.9246 | 12.96 | 211 | 3.5724 | 12.48 | 174 | 2.9611 | 13.13 |
| 1500 | 1000 | 130 | 1.9270 | 8.92 | 228 | 3.2943 | 8.59 | 172 | 2.4709 | 7.49 |
| 1500 | 1300 | 140 | 3.0474 | 13.38 | 259 | 5.7832 | 12.90 | 215 | 4.7147 | 11.88 |
| 1500 | 1500 | 125 | 3.6104 | 13.43 | 230 | 6.6865 | 12.81 | 196 | 5.4584 | 12.71 |
| 1800 | 1500 | 146 | 4.6432 | 13.47 | 257 | 8.0396 | 12.94 | 209 | 6.1925 | 11.83 |
| 1800 | 2000 | 115 | 5.8341 | 15.00 | 210 | 10.7513 | 14.29 | 182 | 9.1033 | 14.69 |
| 2500 | 2000 | 142 | 8.9043 | 14.95 | 250 | 15.6397 | 14.29 | 201 | 12.2370 | 13.07 |
| 2900 | 2700 | 134 | 15.3647 | 17.70 | 245 | 28.4289 | 16.71 | 203 | 22.9945 | 16.50 |
| 3000 | 3000 | 125 | 17.1686 | 17.20 | 217 | 34.1575 | 16.34 | 188 | 25.0864 | 17.22 |
| 3500 | 3000 | 128 | 20.2808 | 16.87 | 234 | 37.1725 | 15.84 | 194 | 30.6876 | 15.94 |
| 3500 | 3500 | 123 | 24.5455 | 19.80 | 223 | 44.4163 | 18.69 | 200 | 39.2771 | 19.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.-H.; Lan, H.-Y.; Lin, S.-Y. A Novel Symmetrical Inertial Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers with Proximal Term for Nonconvex Optimization with Applications. Symmetry 2025, 17, 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060887
Li J-H, Lan H-Y, Lin S-Y. A Novel Symmetrical Inertial Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers with Proximal Term for Nonconvex Optimization with Applications. Symmetry. 2025; 17(6):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060887
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ji-Hong, Heng-You Lan, and Si-Yuan Lin. 2025. "A Novel Symmetrical Inertial Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers with Proximal Term for Nonconvex Optimization with Applications" Symmetry 17, no. 6: 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060887
APA StyleLi, J.-H., Lan, H.-Y., & Lin, S.-Y. (2025). A Novel Symmetrical Inertial Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers with Proximal Term for Nonconvex Optimization with Applications. Symmetry, 17(6), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060887






