Abstract
Low-light image enhancement remains a challenging task in computer vision due to the complex interplay of noise, asymmetrical artifacts, illumination non-uniformity, and detail preservation. Existing methods such as traditional histogram equalization, gamma correction, and Retinex-based approaches often struggle to balance contrast improvement and naturalness preservation. Deep learning methods such as CNNs and transformers have shown promise, but face limitations in modeling multi-scale illumination and long-range dependencies. To address these issues, we propose WIGformer, a novel wavelet-based illumination-guided transformer framework for low-light image enhancement. The proposed method extends the single-stage Retinex theory to explicitly model noise in both reflectance and illumination components. It introduces a wavelet illumination estimator with a Wavelet Feature Enhancement Convolution (WFEConv) module to capture multi-scale illumination features and an illumination feature-guided corruption restorer with an Illumination-Guided Enhanced Multihead Self-Attention (IGEMSA) mechanism. WIGformer leverages the symmetry properties of wavelet transforms to achieve multi-scale illumination estimation, ensuring balanced feature extraction across different frequency bands. The IGEMSA mechanism integrates adaptive feature refinement and illumination guidance to suppress noise and artifacts while preserving fine details. The same mechanism allows us to further exploit symmetrical dependencies between illumination and reflectance components, enabling robust and natural enhancement of low-light images. Extensive experiments on the LOL-V1, LOL-V2-Real, and LOL-V2-Synthetic datasets demonstrate that WIGformer achieves state-of-the-art performance and outperforms existing methods, with PSNR improvements of up to 26.12 dB and an SSIM score of 0.935. The qualitative results demonstrate WIGformer’s superior capability to not only restore natural illumination but also maintain structural symmetry in challenging conditions, preserving balanced luminance distributions and geometric regularities that are characteristic of properly exposed natural scenes.
1. Introduction
Low-light enhancement represents a critical domain in the fields of computer vision and image processing, focusing primarily on improving image quality and visual aesthetics for photographs captured in inadequate or low-light environments. Images taken under such conditions often exhibit various deficiencies, including reduced visibility, lower contrast, blurriness, noise, artifacts, and color distortion. These challenges not only impair human visual perception but also compromise the accuracy of sophisticated vision-related tasks such as object detection at night. The primary goals of low-light enhancement are to recover image details, enhance contrast, and mitigate adverse effects caused by insufficient lighting, equipment limitations, or user technical skills, thereby improving both the usability and visual appeal of the images while respecting the natural balance and symmetry of the original scene. Consequently, low-light enhancement is poised to provide significant benefits in various applications, including nighttime surveillance, intelligent transportation systems, and autonomous driving technologies.
Traditional low-light enhancement methods primarily include Histogram Equalization (HE) [1,2,3], Gamma Correction (GC) [4,5], and Retinex-based approaches [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Despite their foundational importance, these methods face limitations in handling complex lighting variations and maintaining the natural appearance of enhanced images. Histogram Equalization (HE) and Gamma Correction (GC) modify brightness distribution to improve contrast but often introduce artifacts or color distortions due to insufficient consideration of lighting nuances, especially under uneven illumination. Retinex-based methods decompose images into illumination and reflectance components, enhancing visibility by adjusting these elements; however, Retinex theory assumes noise-free and distortion-free inputs, which is in contradiction to real-world low-light scenarios. Thus, these approaches often result in amplified noise or color inaccuracies that can degrade image quality. These inherent limitations of existing approaches highlight the necessity for advanced approaches such as deep learning-based techniques that can overcome the challenges of complex lighting environments.
Deep learning techniques have significantly advanced this domain through the use of sophisticated neural network architectures, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) [14,15,16,17,18,19,20] and transformer models [21,22,23,24]. CNN-based approaches can be divided into two main categories. The first category involves directly learning a mapping function that converts low-light images into their normal-light counterparts. While straightforward, this method often lacks interpretability and fails to adequately consider human color perception. The second category integrates CNNs with Retinex theory [19,20] by decomposing images into reflectance and illumination components. This approach provides a more systematic enhancement strategy focusing on denoising and illumination adjustment; however, its multistage training process is computationally expensive and time-consuming. Transformers address some limitations of CNN by capturing long-range dependencies and modeling global relationships through self-attention mechanisms. Nevertheless, the direct application of Vision Transformer (ViT) [21,25] to low-light enhancement faces challenges due to the high computational cost of self-attention. To address this, hybrid CNN–transformer models such as SNR-Net [18] and Uformer [26] have been proposed. These models reduce computational load by applying transformers only at lower resolutions or within specific regions, which can help to improve efficiency while preserving global context. Despite their potential, transformer-based methods remain underexplored in low-light enhancement, with ongoing challenges around noise amplification and preservation of fine spatial details.
In the realm of low-light image enhancement, existing deep learning-based methods often face significant challenges in accurately modeling and mitigating the complex noise and artifacts inherent in dark environments while preserving the symmetrical properties of natural scenes. Traditional approaches typically rely on simplistic noise assumptions or fail to adequately capture multi-scale illumination characteristics, leading to suboptimal enhancement results such as residual noise, color distortion, asymmetrical artifacts, and loss of fine details. Moreover, while transformer-based architectures have shown promise in various vision tasks, their direct application to low-light enhancement often overlooks the critical interplay between illumination and reflectance components, resulting in limited generalization and robustness. These limitations underscore the need for more sophisticated frameworks that can effectively disentangle and restore the latent structures in low-light images while preserving their natural appearance and inherent symmetrical properties.
To address the above problems, we propose a new deep learning-based method for low-light image enhancement, which we call WIGformer. In particular, we extend single-stage Retinex theory to model the noise hidden in dark regions by introducing reflectance and illumination components. Guided by this extended single-stage Retinex theory, we then design a wavelet illumination estimator and an illumination feature-guided corruption restorer for end-to-end learning.
The wavelet illumination estimator is used to evaluate the illumination information. By utilizing the multi-scale characteristics of the Wavelet Transform (WT) [27] it can effectively capture the multi-scale features in the image and generate illumination features and illumination images, thereby enhancing the accuracy and detail performance of illumination estimation. The restorer suppresses the noise hidden in the illuminated image. In the restorer, we carefully design an Illumination-Guided Enhanced Attention Block (IGEAB) to achieve long-range modeling across channels and spatial dimensions. The main component of the IGEAB is the Illumination-Guided Enhanced Multihead Self-Attention (IGEMSA), which first utilizes the Adaptive Feature Refinement Module (AFRM) to better capture the complex structure and texture information in the illumination features, thereby improving the performance of the corruption restorer. The illumination features are then used as key cues to guide the long-range dependency modeling method and enhance the interaction between regions with different exposure levels. IGEMSA is incorporated into a U-type [28] architecture to model the image hierarchically. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach. Figure 1 shows an example of low-light image enhancement.

Figure 1.
Example of WIGformer low-light image enhancement effect on LOL-v1 and LOL-v2 datasets.
The main contributions of our research can be summarized as follows:
- Based on the transformer architecture and Retinex theory, we proposed the Wavelet-based Illumination-Guided Transformer (WIGformer) algorithm for low-light image enhancement.
- We propose a wavelet illumination estimator and design the WFEConv module to effectively capture the multi-scale features in the image by using the multi-scale characteristics of the Wavelet Transform (WT) to enhance the accuracy and detail of illumination estimation.
- We proposed an illumination feature-guided corruption restorer that adopts a three-scale U-shaped [28] structure, and design the Illumination-Guided enhanced Attention Block (IGEAB) for feature enhancement to correct low-light image noise, artifacts, color distortion, and other problems.
- We design a new self-attention mechanism called IGEMSA, which uses the AFRM module to better capture the complex structure and texture information of illumination features. This information is used to improve the performance of damage repair and correction and as key clues that guide the proposed long-range dependency modeling method.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Methods for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Traditional methods for low-light image enhancement can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: distribution mapping methods [1,2,3,4,5] and Retinex-based methods [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Both approaches aim to improve the visibility and quality of low-light images; however, they differ significantly in their underlying principles and techniques.
2.1.1. Distribution Mapping Methods
Distribution mapping methods [1,2,3,4,5] enhance low-light images by manipulating the distribution of pixel values, typically focusing on amplifying darker regions to improve visibility. Representative techniques include Histogram Equalization (HE) and Gamma Correction (GC) based on S-curves. These methods adjust the brightness distribution of an image to enhance overall contrast, especially dark areas. However, distribution mapping methods often suffer from color distortion and artifacts, primarily due to lack of semantic understanding during the mapping process. These methods typically fail to account for variations in scene illumination and the specific brightness requirements of different objects, leading to unnatural or overly enhanced hues. Although these methods can improve visibility, they often produce visually unsatisfactory results, especially in complex lighting conditions.
2.1.2. Retinex-Based Methods
Retinex-based methods [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13], on the other hand, are grounded in Retinex theory, which provides a more intuitive and physically plausible explanation for low-light image enhancement. The Retinex model assumes that an image can be decomposed into two components: the illumination component and the reflectance component. The desired normal-light image can be obtained by removing or adjusting the illumination component from the low-light input. Traditional Retinex-based methods often rely on handcrafted priors such as structural priors and illumination layer estimations, which help to guide the enhancement process. However, the effectiveness of these priors is highly sensitive to parameter selection, requiring careful tuning to achieve optimal results in specific scenarios. This reliance on handcrafted priors often leads to poor generalization, making these methods less adaptable to varying lighting conditions and diverse image features.
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Methods for Low-Light Enhancement
With the rapid development of deep learning, deep learning-based methods have become the dominant approach for low-light image enhancement. Since the emergence of related studies in 2017, researchers have widely adopted Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) [14,15,16,17,18,19,20] and Retinex-inspired deep learning frameworks to improve the quality of low-light images.
CNNs have been extensively applied due to their strong feature extraction capabilities. For example, several studies [19,20] have integrated Retinex decomposition with CNNs, with multiple subnetworks used to learn or refine different components of the Retinex model. However, these methods often suffer from a cumbersome multi-stage training pipeline involving multiple independent CNN models that optimize different modules, leading to high training complexity. Moreover, CNNs are limited in their ability to capture long-range dependencies across different regions, which may result in inconsistencies in enhancement over large-scale areas.
To address the limitations of CNNs, researchers have explored more advanced architectures such as transformer-based methods [21,22,23,24]. Star [22] first introduced the transformer architecture into the field of low-light enhancement, effectively addressing the issue of long-range dependency modeling. Subsequently, Retinexformer [23] further refined this approach by integrating Retinex theory with a one-stage transformer design, improving overall model optimization. However, transformer-based models pose significant computational burdens due to their self-attention mechanisms, which are computationally expensive when handling long sequences.
Table 1 summarizes the comparison of traditional and deep learning-based methods for low-light image enhancement.

Table 1.
Comparison of traditional and deep learning-based methods for low-light image enhancement.
2.3. Wavelet Transforms in Deep Learning
The Wavelet Transform (WT) [27] is a highly effective instrument for signal processing and analysis that has enjoyed extensive use since the 1980s. Its initial triumph in traditional applications laid a solid foundation; in recent times, the WT has expanded its reach and been integrated into neural network architectures, enabling the execution of numerous tasks.
In the domain of Electrocardiogram (ECG) signals analysis, Wang et al. [29] used the WT to extract features from the time–frequency components of ECG signals. Their approach helped to better understand the characteristics of ECG signals, which can be crucial for medical diagnosis and research.
Regarding image processing, Huang et al. [30] and Guo et al. [31] took an innovative route by predicting the wavelet high-frequency coefficients of an input image. In this way, they were able to reconstruct a higher resolution output. This is significant in that it can enhance the clarity and quality of images, which has applications in such varied fields as photography, computer vision, and medical imaging.
In the context of CNNs, Duan et al. [32] and Williams and Li [33] have introduced a novel concept by using WTs as pooling operators. This integration can potentially improve the performance of CNNs in tasks such as image recognition and feature extraction by allowing for better handling the spatial and frequency information of input data.
In generative models, Gal et al. [34], Guth et al. [35], and Phung et al. [36] have all incorporated wavelets. Their work demonstrates that wavelets can enhance the visual quality of generated images while also contributing to improved computational performance on the part of the models. This is beneficial for applications such as realistic image generation for virtual reality, gaming, and graphic design.
Finder et al. [37,38] explored the use of wavelets in the optimization of CNNs, utilizing wavelets to compress feature maps with the aim of making CNNs more efficient. This can help to reduce computational cost and memory requirements, making CNN-based applications more practical for deployment on resource-constrained devices. The same authors proposed WTConv, a novel convolutional layer that utilizes the WT to expand the receptive field while avoiding over-parameterization. Unlike conventional large-kernel convolutions, WTConv performs multi-scale convolutions in the wavelet domain, then reconstructs the output using the inverse WT.
3. Method
3.1. Retinex-Based Framework
The One-stage Retinex theory (OR) [6] provides a fundamental approach for understanding the composition of low-light images. According to this theory, a low-light image can be decomposed into the Hadamard product of a reflectance map and an illumination map , as expressed by the equation
This decomposition is conceptually elegant and has been widely used in the field of image processing related to low-light enhancement. However, it makes a rather simplistic assumption that the input low-light image I is entirely free from noise. The symmetry properties of the reflectance and illumination components are essential for maintaining the natural appearance of the enhanced image.
When accounting for real-world perturbations in practical scenarios, images are inevitably affected by perturbations E due to the limitations of sensor devices. These perturbations can significantly degrade the quality of the enhanced image if not properly addressed. When the multiplicative nature of the Retinex-based enhancement process is applied without considering E, it can lead to the amplification of these disturbances. As a result, the enhanced image may suffer from various issues, including noise, artifacts, color distortion, and incorrect exposure. To accurately model the presence of perturbations in low-light images, we decompose E into two components: a reflectance perturbation and an illumination intensity perturbation . Incorporating these components, the original decomposition Equation (1) can be redefined as follows:
Our objective, as stated in [23], is to obtain R as a well-exposed image. To this end, we multiply both sides of Equation (2) by a light-up map such that . After rearrangement, we obtain
where represents the under- or over-exposure and color distortion that occur during the light-up process when multiplied by , while represents the noise and artifacts that are initially hidden in the darker regions of the image and amplified by . For the sake of simplicity and clarity, we further simplify the extended OR framework to
In the design of the proposed deep learning framework based on Equation (4), we have developed a deep learning framework that consists of two main components: an wavelet illumination estimator W and an illumination feature-guided corruption restorer G. The wavelet illumination estimator W takes as input a corrupted low-light image I and a prior illumination intensity image . It then generates a noisy light-up image and light-up features . The restorer G operates under the guidance of light-up features to denoise the noisy light-up image , ultimately producing the enhanced image . The overall network can be formulated as the following system of equations:
Our extension of the One-stage Retinex (OR) theory improves upon previous Retinex-based deep learning methods in several ways. Instead of directly estimating the illumination map L, our approach estimates a light-up map , which avoids potential data overflow issues from the operation and enhances robustness in low-light conditions. Additionally, our model comprehensively considers disturbances in both reflectance and illumination, unlike prior methods focusing mainly on reflectance degradation. To improve illumination estimation, we introduce a wavelet illumination estimator W and design the WFEConv module, leveraging the Wavelet Transform (WT) for multi-scale feature extraction. Furthermore, we use an attention mechanism to enhance regions with non-uniform illumination. Our restorer network G uses the enhanced light-up features to guide feature enhancement, thereby repairing low-light image noise, artifacts, color distortion, and other issues. The resulting enhanced images offer clearer details of the scene, which is beneficial for high-level vision tasks such as object detection, segmentation, and scene understanding.
3.2. Overall Framework of WIGformer
The design of our proposed Wavelet-based Illumination-Guided Transformer (WIGformer) is depicted in Figure 2. WIGformer is developed on the basis of our extended version of one-stage Retinex theory. This theoretical foundation provides a solid basis for the design of an effective low-light image enhancement model. Specifically, WIGformer is composed of two fundamental and core components: the wavelet illumination estimator W, and the illumination feature-guided corruption restorer G. These two components work in tandem to achieve the goal of enhancing low-light images. The wavelet transform inherently captures the symmetry properties of the illumination and reflectance components, which are crucial for natural image enhancement.
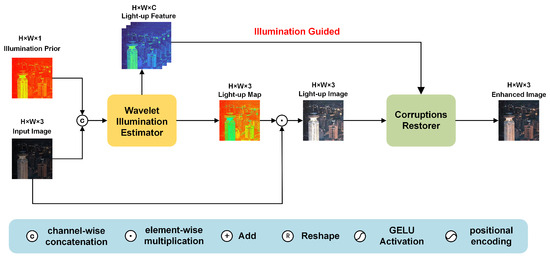
Figure 2.
Overall framework of WIGformer.
In Figure 2, the network takes as input a low-light image and a prior illumination map . To effectively combine the information from these two inputs, they are concatenated along the channel dimension. This concatenated input is then fed into the estimator W, which has the primary function of extracting illumination features from the combined data. The estimator W is a crucial part of the WIGformer architecture. It leverages the wavelet transform and other advanced techniques to analyze the input and generate two important outputs. First, it produces a light-up image , which represents an initial enhancement of the low-light image. Second, it generates a light-up feature . This feature captures the essential illumination information that is necessary for the subsequent restoration process. Subsequently, the light-up image is passed into the restorer G. The restorer G operates under the guidance of the light-up feature . It is designed to suppress the noises and artifacts that are often present in the light-up image. By leveraging the illumination information contained in , the restorer G can effectively enhance the quality of the image, ultimately obtaining a normal-light image.
One of the significant advantages of our WIGformer model is its strictly end-to-end operation. Unlike some traditional methods that involve complex multi-stage training pipelines, WIGformer uses a simplified process. This end-to-end design not only reduces the complexity of the model but also makes it more efficient and easier to train. Next, we present details on the data pipelines of the estimator W and restorer G in order to provide a comprehensive understanding of how the WIGformer model operates.
3.2.1. Wavelet Illumination Estimator
The architecture of the wavelet illumination estimator W is depicted in Figure 3. In this design, we first combine the low-light original image I with the illumination prior , which is obtained through a series of calculations. In this way, we create a more comprehensive input that contains both the information from the low-light image and the pre-calculated illumination prior. This enhanced input serves as the starting point for the subsequent feature extraction process.
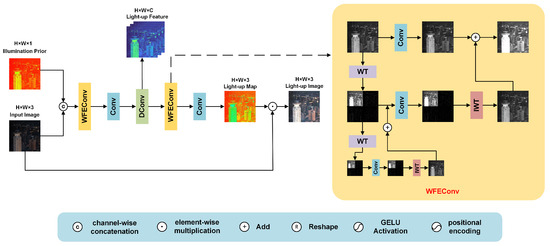
Figure 3.
Architecture of the wavelet illumination estimator.
Following the combination process, the input undergoes a sequence of five convolutional operations. Through these five convolutions, we gradually capture more and more complex features that are related to the illumination characteristics of the low-light image. First, the two inputs are concatenated and passed through a Wavelet Transform-based Convolution (WFEConv) [27] layer. The WFEConv layer is a key component in our estimator. It utilizes the wavelet transform to decompose the image features into different frequency components. The wavelet transform is a powerful tool that can analyze signals in both the time and frequency domains. Decomposing the image features in this way can better represent the illumination-related information in the image. Different frequency components can capture different aspects of the illumination, such as global illumination trends and local illumination variations. This decomposition helps to enhance the representation of illumination-related information in the image by enhancing the accuracy and detail of illumination estimation, which is crucial for the subsequent steps of the estimator. Illumination estimation often relies on low-frequency components such as the brightness distribution in large-scale areas. By enhancing the use of low-frequency information, the WFEConv layer helps to improve the stability of illumination estimation.
Next, we have the first convolution layer. The purpose of this layer is to merge the previously combined input more effectively. It applies the illumination prior to the fusion process within the low-light image. After the first convolution, a depthwise separable convolution layer is employed. This layer upsamples the input, which means that it increases the spatial dimensions of the feature maps. At the same time, it further extracts features from the upsampled data. Through this process, we can generate the illumination feature map . This feature map contains rich information about the illumination in the low-light image, which can be used to guide the subsequent restoration process. To further refine the latent representation of the illumination, we use another WFEConv layer. This second WFEConv layer continues to capture multi-scale illumination details. It can analyze the illumination features at different scales, from fine-grained local details to more global illumination patterns; in this way, it can improve the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the illumination representation. Finally, we use another convolution layer for downsampling. Downsampling is the process of reducing the spatial dimensions of the feature maps. In this case, the purpose of downsampling is to recover the three-channel illumination mapping . Finally, after obtaining , we perform an element-wise multiplication between and the low-light image I according to Equation (4). This multiplication operation combines the illumination mapping with the original low-light image, resulting in the illuminated image .
3.2.2. Illumination Feature-Guided Corruption Restorer
We observed that the light-up image produced by the estimator does not offer a visually satisfactory perception. In response to this, we have further engineered a restorer G with the aim of suppressing the corruptions present in . Specifically, we have designed an Illumination-Guided Enhanced Transformer (IGET) to function as the corruption restorer G in the relevant equation.
As depicted in Figure 4, the IGET adopts a three-scale U-shaped [28] architecture. This U-shaped [28] architecture has been widely used in various image processing tasks due to its effectiveness in handling multi-scale information. The input to the IGET is the light-up image . In the downsampling branch of the IGET, first passes through a convolution layer. Convolution layers with a kernel size are effective in capturing local features in the image. After the convolution, the data are fed into an Illumination-Guided Enhanced Attention Block (IGEAB). The IGEAB is designed to focus on the illumination-related information in the image, enhancing the representation of relevant features. Subsequently, a strided convolution is applied. The purpose of this strided convolution is to downscale the features, reducing the spatial dimensions of the data while also extracting more global-scale features. After the first strided convolution, the data pass through another IGEAB. This IGEAB further refines the feature representation, taking into account both the illumination and other important characteristics of the image. Finally, another strided convolution is used to generate hierarchical features , where . This hierarchical feature extraction allows the model to capture features at different scales, which is crucial for understanding the image structure and the distribution of corruptions. Subsequently, a symmetrical structure is designed for the upsampling branch. In the upsampling branch, a deconvolution layer with a kernel size of and a stride of 2 is utilized to upscale the features. Skip connections are implemented between the downsampling and upsampling branches. These skip connections play a vital role in alleviating the information loss that occurs during the downsampling process. By directly connecting the corresponding layers in the downsampling and upsampling branches, the model can preserve important details and context information.
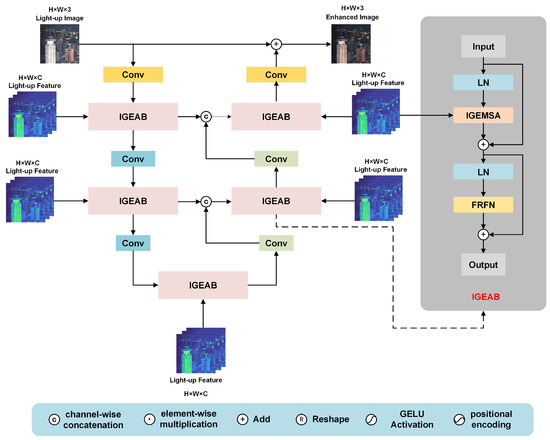
Figure 4.
Architecture of the illumination feature-guided corruption restorer.
The upsampling branch ultimately outputs a residual image . This residual image represents the differences or corrections that need to be made to the light-up image . Finally, the enhanced image is obtained by summing the light-up image and the residual image . This process effectively suppresses the corruptions in the light-up image, resulting in an enhanced image with improved visual quality.
3.3. Core Modules of WIGformer
3.3.1. Wavelet Feature Enhancement Convolution (WFEConv)
We propose a wavelet-based convolution for feature enhancement called the Wavelet Feature Enhancement Convolution (WFEConv). The Wavelet Transform (WT) [27] serves as a powerful tool in our proposed method. Initially, it is utilized to filter and downsample both the lower- and higher-frequency components of the input data. This step allows for a more in-depth analysis of the input by separating it into different frequency bands. The WT inherently captures the symmetry properties of the input data, which are essential for accurate feature extraction. After filtering and downsampling with the WT [27], a small-kernel-depth wise convolution is executed on the distinct frequency maps. The advantage of using a small-kernel depth-wise convolution is two-fold: first, it reduces the computational complexity compared to a traditional full-convolution operation; second, it can better capture local features within each frequency map. Subsequently, the Inverse Wavelet Transform (IWT) is applied to generate the output. Mathematically, this entire procedure can be precisely expressed as follows:
In this equation, X represents the input tensor, which could be an image or a feature map in the context of our model, while W is the weight tensor of a depth-wise kernel. Notably, the number of input channels of W is four times that of X. This operation of WFEConv not only partitions the convolution process among the different frequency components but also has a significant impact on the receptive field. It enables a smaller kernel to operate over a larger area of the original input; in other words, it effectively increases the receptive field with respect to the input, which is crucial for understanding the global context of the data.
The cascade wavelet decomposition is an important aspect of our approach. It is achieved by recursively decomposing the low-frequency component. Each level of the decomposition is defined by the following equation:
where and i represents the current level of decomposition. Through this recursive decomposition, an increased frequency resolution is attained for the lower frequencies, while the spatial resolution of these lower-frequency components is reduced. This tradeoff between frequency and spatial resolution allows the model to capture more detailed frequency information at different scales.
We build upon this single-level combined operation and further enhance its performance by applying the same cascading principle as described in Equation (7). The detailed process is as follows:
Here, acts as the input to the layer, while represents all three high-frequency maps at level i. These equations describe how the input is processed through the WT and convolution operations at each level of the cascade.
To merge the outputs of different frequencies, we take advantage of the linear property of the WT and its inverse. Because , we perform the following operation:
This operation results in the summation of convolutions from various levels. Here, represents the combined outputs starting from level i. The process of WFEConv for a two-level WT [27] is visually presented in Figure 3. For those readers interested in the detailed algorithm implementation, it can be found in Algorithm 1. This comprehensive description of WFEConv provides a clear understanding of how our model effectively processes data in the frequency domain, leading to more efficient and accurate feature extraction and model performance.
| Algorithm 1 WFEConv |
Input: for
do end for for
do end for return
|
3.3.2. Illumination-Guided Enhanced Multihead Self-Attention (IGEMSA)
In the pursuit of advanced techniques for low-light image enhancement, we introduce a novel structure named Illumination-Guided Enhanced Multihead Self-Attention (IGEMSA). This structure is designed to optimize the utilization of illumination information and enhance the performance of self-attention mechanisms in processing low-light images.The symmetry properties of the illumination features are leveraged to guide the attention mechanism, ensuring that the enhanced image maintains a natural appearance.
As shown in Figure 5, the light-up feature estimated by W serves as a crucial input for the IGEMSA. However, before it is used for illumination-guided operations, the light-up feature is first passed through the Adaptive Feature Refinement Module (AFRM).
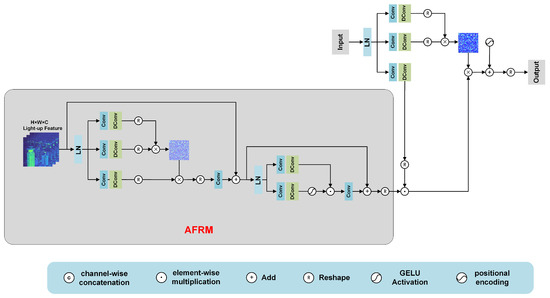
Figure 5.
Architecture of IGEMSA.
The AFRM is composed of two main parts. Initially, for an input tensor (in this case, ), the first part generates query ()-, key ()-, and value ()-like projections. It achieves this by applying point-wise convolutions to aggregate cross-channel context at each pixel, followed by depth-wise convolutions to encode spatial context within channels. After that, the query- and key-related projections are reshaped, and their interaction generates a more context-rich representation.
The second part of the AFRM incorporates a gating mechanism and depth-wise convolutions. The gating mechanism, which is formulated as the element-wise product of two parallel linear transformation paths with one activated by the GELU nonlinearity, controls the information flow precisely. The depth-wise convolutions help in capturing information from neighboring pixel positions, enabling the module to learn local structures within the light-up feature . Through these operations, the AFRM refines the light-up feature , making it more suitable for subsequent processing.
After being processed by the AFRM, the refined light-up feature is then used for illumination-guided operations in the subsequent steps. The high computational cost of global Multihead Self-Attention (MSA) limits its application in low-light image enhancement. In IGEMSA, we address this issue by treating a single-channel feature map as a token sequence and computing self-attention.
First, the input feature is reshaped into tokens , which is then split into k heads:
where , , and . For each head i, three fully-connected () layers without bias are used to linearly project into query elements , key elements , and value elements as follows:
where , , and represent the learnable parameters of the layers and T denotes the matrix transpose.
We recognize that different regions within the same image may have varying lighting conditions. Dark regions typically suffer from more severe corruptions and are more challenging to restore, while regions with better lighting can provide semantic context to assist in enhancing the darker areas. Thus, the refined light-up feature (derived from after passing through the AFRM) is reshaped into and split into k heads:
where , . The self-attention for each head i is then calculated as
where is a learnable parameter that adaptively scales the matrix multiplication. Subsequently, the k heads are concatenated and passed through an layer, followed by adding a positional encoding (with learnable parameters) to produce the output tokens . Finally, is reshaped to obtain the output feature .
4. Experiments and Results Analysis
4.1. Dataset Description
We evaluated the performance of our model on the LOL dataset (v1 [20] and v2 [39]) and the NTIRE 2024 dataset [40].
LOL-V1: LOL-V1 [20] is a subset of the LOL dataset. This subset contains low-light input images and their corresponding normal-light images. Specifically, 485 image pairs were utilized for training purposes, while 15 pairs were allocated for validation.
LOL-V2-Real: LOL-V2-Real [39] captures real-world scenes. It has 689 pairs of images for training and 100 pairs for validation.
LOL-V2-Synthetic: LOL-V2-Synthetic [39] was generated by creating low-light images from RAW images, relying on the illumination distribution of low-light images. In total, it consists of 1000 pairs of low-light and normal-light images, with a training-validation ratio of 9:1.
NTIRE 2024: The NTIRE 2024 dataset [40] is tailored for the NTIRE 2024 competitions. It overcomes the limitations of existing datasets, offering diverse scenarios including indoor/outdoor, different times of day, and various low-light conditions. With image resolutions up to 4K or higher, it is used in challenges such as efficient super-resolution (requiring 4x magnification) and bracketing image restoration. It is partitioned into training, validation, and testing subsets, and is essential for assessing different image processing algorithms.
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
In this study, we employed a combination of objective and subjective metrics to evaluate the performance of WIGformer. The objective metrics utilized full-reference image quality assessments, specifically the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) [41]. Below are the comprehensive definitions of these metrics.
PSNR and SSIM are widely recognized metrics for quantifying image quality. PSNR evaluates image quality by comparing the peak signal-to-noise ratio between the original and the degraded images. The calculation process begins with the determination of the Mean Squared Error (MSE) using the following formula:
where H and W represent the height and width of the image, respectively, is the value of the c-th color channel at the coordinate in the original image, and is the corresponding value in the processed image.
Then, the PSNR is calculated based on the MSE using the formula
where represents the maximum pixel value in the image.
The SSIM comprehensively measures the similarity between the normal-light image and the restored image in terms of luminance, contrast, and structure. Its definition is as follows:
where , , and represent the calculations of luminance, contrast, and structure similarity, respectively. The specific formulas are as follows:
where and are the means of images I and , respectively, and are their respective variances, is their covariance, and , , and are three constants introduced to avoid division by zero. It should be noted that when calculating the SSIM we take a window of size () on the image to calculate the local SSIM, then calculate all local SSIMs by sliding the window, and finally take the average as the global SSIM.
4.3. Implementation Details
We implemented WIGformer using the PyTorch framework [42], specifically with Python 3.7, PyTorch version 1.11, and CUDA 11.3. The computations were accelerated by an NVIDIA RTX 3070 graphics card. The model training process utilized the Adam optimizer [43] with parameters of and . A total of iterations were carried out to optimize the model. Initially, the learning rate was set to . As the training progressed, the learning rate was adjusted using the cosine annealing scheme [44], steadily decreasing it to over time. For the training data, we randomly cropped patches of size from the pairs of low-light and normal-light images. These cropped patches served as the training samples. The batch size during training was set to 4. To enhance the diversity of the training data and improve the model’s generalization ability, data augmentation techniques such as random rotation and flipping were applied. The training objective of our model is to minimize the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) between the enhanced images generated by the model and the ground truth images. In this way, the model learns to produce images that are as close as possible to the actual normal-light images.
4.4. Low-Light Image Enhancement
4.4.1. Quantitative Analysis
To evaluate the performance of WIGformer, we conducted extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets: LOL-V1 [20], LOL-V2-Real [39], LOL-V2-Synthetic [39], and NTIRE 2024. We compared WIGformer with several state-of-the-art methods, including traditional approaches and deep learning-based models. The results are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Comparison of different methods on the LOL-V1 and LOL-V2 datasets; higher PSNR and SSIM indicate better performance. Red denotes the best performance, blue indicates the second-best performance, and green signifies the third-best performance. Upward arrows (↑) are employed to highlight metrics where higher values correspond to superior performance.
On the LOL-V1 dataset, WIGformer achieved a PSNR of 26.12 dB and an SSIM of 0.871, outperforming all other methods. Notably, the closest competitor, Retinexformer [23], achieved a PSNR of 25.16 dB and an SSIM of 0.816. This represents a 0.96 dB (3.8%) improvement in PSNR and a 6.7% improvement in SSIM, demonstrating the superior capability of WIGformer in enhancing low-light images with higher fidelity and structural similarity.
On the LOL-V2-Real dataset, WIGformer attained a PSNR of 22.61 dB and an SSIM of 0.831, which is competitive with the best-performing methods such as SNR-Net [18] (PSNR: 21.48 dB, SSIM: 0.849) and Retinexformer [23] (PSNR: 21.43 dB, SSIM: 0.814). This represents a 1.13 dB (5.3%) improvement in PSNR over SNR-Net [18] and a 1.18 dB (5.5%) improvement over Retinexformer [23]. These results indicate that WIGformer maintains robust performance across different real-world low-light conditions.
Figure 6 compares the grayscale histograms of an input image, the image processed by WIGformer, and the Ground Truth (GT) image from the LOL-v2-Real dataset. The input image’s histogram is concentrated in low-grayscale areas, which is typical of low-light images. WIGformer’s processed image shows a more evenly distributed histogram, with pixels expanding into medium- and high-grayscale regions, indicating enhanced brightness and details. The GT image’s histogram is balanced and resembles that of the WIGformer-processed image, demonstrating WIGformer’s effectiveness in approximating the GT image’s grayscale distribution for low-light image enhancement.
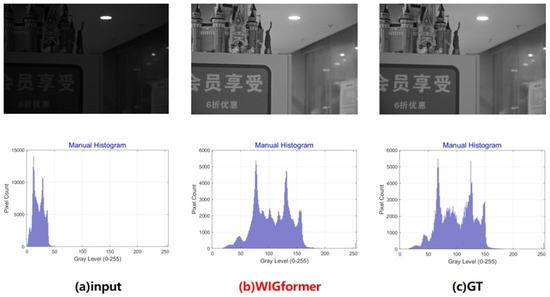
Figure 6.
Comparison of grayscale histograms of input, WIGformer, and GT images for real-world images from the LOL-v2-real dataset.
Figure 7 presents a comparison of a low-light input image, the image processed by the WIGformer network, and the Ground Truth (GT) image from the LOL-v2-Real dataset, focusing on detail-level noise. The low-light input image is afflicted with substantial noise, rendering fine details indistinct and hard to discern. In contrast, the image processed by our proposed WIGformer network exhibits a remarkable attenuation of noise. For instance, details of the seating area and the floor in the corresponding regions of the image are notably clearer and sharper, with noise-induced artifacts significantly reduced. This exemplifies the WIGformer’s potent denoising capability for real-world low-light images. When juxtaposed with the GT image, the WIGformer-processed image demonstrates comparable performance in terms of detail representation and noise management. This indicates that WIGformer not only efficiently eliminates noise but also adeptly restores image details, fully manifesting its preeminent performance in the denoising and restoration of real-world images.

Figure 7.
Comparison of noise effects in input, WIGformer, and GT images for real-world images from the LOL-v2-real dataset.
On the LOL-V2-Synthetic dataset, WIGformer achieved a PSNR of 25.60 dB and an SSIM of 0.935, surpassing other methods such as IGDFormer [59] (PSNR: 25.33 dB, SSIM: 0.937) and SNR-Net [18] (PSNR: 24.14 dB, SSIM: 0.928). This represents a 0.27 dB (1.1%) improvement in PSNR over IGDFormer [59] and a 1.46 dB (6.0%) improvement over SNR-Net [18]. This highlights the effectiveness of WIGformer in handling synthetic low-light scenarios with high precision.
On the NTIRE 2024 dataset, WIGformer achieved a PSNR of 25.60 dB and an SSIM of 0.864, outperforming Retinexformer [23]. Notably, Retinexformer achieved a PSNR of 25.30 dB and an SSIM of 0.853. This represents a 0.30 dB (1.2%) improvement in PSNR and a 1.3% improvement in SSIM. These results demonstrate that WIGformer exhibits superior performance in enhancing low-light images on the NTIRE 2024 dataset, showcasing higher fidelity and structural similarity compared to Retinexformer.
Our WIGformer model also demonstrates commendable performance in terms of complexity. We compared the complexity on the LOL-V1 and LOL-V2 datasets as measured by Giga-Floating Point Operations (GFLOPs) and number of parameters (Params) in millions. WIGformer has relatively low GFLOPs at 11.73, which indicates that it requires fewer computational resources during operation. Additionally, at 1.96 million parameters, it maintains a reasonable model size. This combination of low computational complexity and a moderate parameter count showcases the efficiency of WIGformer, allowing it to achieve competitive results in low-light image enhancement while being computationally tractable.
Overall, the quantitative results demonstrate that WIGformer consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance across all datasets, validating its effectiveness in low-light image enhancement tasks. The superior performance of WIGformer can be attributed to its innovative use of wavelet transformation and enhanced illumination feature guidance, which enable more accurate and robust recovery of details in low-light conditions. These features allow WIGformer to effectively handle both real-world and synthetic low-light scenarios, making it a highly competitive solution for low-light image enhancement.
4.4.2. Qualitative Results
To vividly demonstrate the superiority of our proposed WIGformer method, we compared it with six representative deep learning models. The comparison included four unsupervised models: EnlightenGAN [50], RUAS [51], Zero-DCE [49], and SCI [54], as well as two supervised models: KinD [48] and MIRNet [52]. Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10 present the enhancement results of each method across three different benchmark tests.

Figure 8.
Examples of visual comparisons between WIGformer and state-of-the-art methods on the LOL-V1 dataset.

Figure 9.
Examples of visual comparisons between WIGformer and state-of-the-art methods on the LOL-V2-Real dataset.

Figure 10.
Examples of visual comparisons between WIGformer and state-of-the-art methods on the LOL-V2-Synthetic dataset.
In the performance evaluation on the LOL-V1 [20] dataset, shown in Figure 8), RUAS [51] is capable of adapting to varying lighting conditions, but often introduces noticeable edge artifacts that degrade image quality. SCI [54] leverages self-supervised learning, demonstrating strong robustness, but underperforms in extreme low-light scenarios, where the clarity of its enhancement results is insufficient. In contrast, WIGformer stands out with exceptional performance on the LOL-V1 dataset. WIGformer reveals its unique advantages upon closer inspection of local regions, especially in challenging low-light areas. While Retinexformer’s [23] output exhibits underexposed regions, WIGformer effectively enhances areas with poor visibility and low contrast, restoring realistic lighting scenes with remarkable precision. This capability highlights WIGformer’s proficiency in handling low-light conditions, making it a more reliable and effective solution for low-light image enhancement tasks.
In the performance evaluation on the LOL-V2-Real [39] dataset, shown in Figure 9, Zero-DCE [49] achieves good generalization capabilities through unsupervised learning; however, its performance in detail recovery is limited, especially in texture-rich areas, where blurring tends to occur. MIRNet [52] utilizes multi-scale feature fusion techniques, excelling in detail recovery and structural preservation; however, its high computational complexity limits its use in real-time applications. In contrast, WIGformer’s combination of the global context modeling capabilities of transformers with local feature fusion effectively enhances low-visibility and low-contrast regions while restoring realistic lighting scenes and rich details. WIGformer demonstrates stronger robustness and consistency than other models, especially when handling complex lighting variations and high-noise scenarios.
In the performance evaluation on the LOL-v2-Synthetic [39] dataset, shown in Figure 10, KinD [48] demonstrates good brightness adjustment capabilities when enhancing synthetic low-light images. However, it is prone to local overexposure or color distortion when dealing with complex lighting and shadow areas. EnlightenGAN [50] excels in generating natural visual effects, but its output may exhibit uneven exposure or loss of detail in certain regions due to the instability of GAN training. Experimental results show that WIGformer outperforms the aforementioned six methods in terms of naturalness, detail recovery, and computational efficiency, providing an efficient and reliable solution for low-light image enhancement in real-world scenarios.
In the performance evaluation on the NTIRE 2024 dataset [40], we tested 3000 × 2000 (Figure 11) and 6000 × 4000 (Figure 12) images. Retinexformer [23] provides over-smooth details in 3000 × 2000 images and struggles with non-uniform lighting in 6000 × 4000 images. On the other hand, WIGformer is able to preserve details in 3000 × 2000 images and handles high-resolution lighting well in 6000 × 4000 images, especially in noisy and low-light areas. These results show WIGformer’s edge in high-resolution low-light image processing.

Figure 11.
Examples of visual comparisons between WIGformer and state-of-the-art methods on the NTIRE 2024 dataset (Resolution 3000 × 2000).

Figure 12.
Examples of visual comparisons between WIGformer and state-of-the-art methods on the NTIRE 2024 dataset (Resolution 6000 × 4000).
As illustrated in Figure 13, a test photograph was captured indoors during nighttime conditions without utilizing the flash function. The raw image prominently exhibits pronounced dark noise, a common artifact in low-light imaging scenarios that significantly degrades visual quality and obscures fine details. We then applied the proposed WIGformer network to address these challenges. Leveraging its innovative architecture and advanced algorithms, WIGformer effectively accomplishes low-light illumination enhancement. WIGformer successfully increased the brightness of the image, making the scene more visible without introducing over-exposure artifacts. Notably, the processed image demonstrates a substantial reduction in noise levels, as the WIGformer network’s corruption restorer adaptively distinguishes between noise and true image features. Furthermore, the WIGformer network showcases excellent edge-preservation capabilities. It ensures that sharpness and texture details are retained, producing a visually pleasing and high-fidelity output. These results underscore the efficacy of WIGformer in tackling the complex issues associated with low-light photography.

Figure 13.
Test results of pictures taken indoors at night without using the flash function.
Overall, unsupervised methods such as EnlightenGAN [50] and RUAS [51] struggle to restore non-uniform illumination and to suppress noise and artifacts in low-light images. This is due to their reliance on unsupervised training without paired references, leading to suboptimal restoration precision. Supervised approaches such as KinD [48] and MIRNet [52] excel in detail recovery, but exhibit uneven illumination or detail loss in extreme low-light scenarios. Although SCI [54] enhances visibility effectively, it struggles to restore natural lighting in complex scenes. In contrast, WIGformer leverages the extended one-stage Retinex theory with a wavelet illumination estimator (W) and WFEConv module to capture multi-scale features via the wavelet transform, significantly improving its illumination estimation accuracy. The proposed framework guides long-range dependency modeling in the restorer (G) through enhanced light-up features, resolving non-uniform illumination. Furthermore, WIGformer integrates the IGEMSA self-attention mechanism with AFRM to extract structural/textural features from illumination maps, enabling noise removal without artifacts while preserving spatial details. Consequently, WIGformer surpasses existing models in visual quality and robustness under various low light conditions, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance. Our qualitative results demonstrate the superiority of WIGformer in preserving natural symmetries (e.g., sharp edges, uniform textures) compared to methods such as KinD [48] and EnlightenGAN [50], which often introduce asymmetrical artifacts.
4.5. Ablation Study
To thoroughly evaluate the effectiveness of the key components in our proposed WIGformer, we conducted ablation studies on three datasets: LOL-V1 [20], LOL-V2-Real [39], and LOL-V2-Synthetic [39]. We established several distinct architectures by removing specific components. The results of these experiments are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Ablation study on key components of WIGformer. Upward arrows (↑) are employed to highlight metrics where higher values correspond to superior performance. The red mark is our most complete model.
The proposed method with no WFEConv: In this architecture, we removed the Wavelet Feature Enhancement Convolution (WFEConv) module from the wavelet illumination estimator. This modification aimed to assess the importance of the multi-scale feature extraction capability provided by the wavelet transform in capturing illumination details. Without WFEConv, the model relies solely on standard convolutional layers, which may not effectively capture the multi-scale illumination characteristics. Removal of the WFEConv module led to a significant drop in performance, particularly in terms of PSNR.
The proposed method with no AFRM: For this architecture, we removed the Adaptive Feature Refinement Module (AFRM) from the IGEMSA mechanism. This change aimed to evaluate the importance of the feature refinement process in enhancing the quality of the illumination features before they are used in the attention mechanism. Without the AFRM, the model may struggle to capture complex structures and textures in the illumination features.
The ablation study results clearly demonstrate the importance of each component in the WIGformer architecture. The wavelet illumination estimator, illumination-guided attention mechanisms, and AFRM all play crucial roles in achieving state-of-the-art performance in low-light image enhancement. The full model incorporating all these components consistently outperformed the ablated versions, validating the effectiveness of our design choices.
4.6. Discussion
4.6.1. Discussion of Numerical Degradation
In real-world applications, numerical degradation is a crucial issue for deep learning-based models. Although the proposed WIGformer network demonstrates excellent performance in low-light image enhancement, the impact of numerical degradation cannot be overlooked. In WIGformer, CNNs introduce numerical errors during feature extraction due to iterative calculations during weight updates and data processing. Wavelet decomposition, a key technique in our model, also incurs numerical degradation during multi-scale feature extraction because of discretization and approximation operations. This degradation can be more pronounced when hardware precision is limited. For instance, in resource-constrained embedded devices or mobile terminals, inability to support high-precision numerical computations may lead to a decline in model performance.
To mitigate the effects of numerical degradation, we have implemented several strategies during the model training process. First, we standardized the input data to ensure that they fall within a reasonable numerical range, thereby reducing numerical instability caused by differences in data scales. Second, we employed higher-precision data types for calculations; for example, we used the float-32 data type instead of float-16. Although this increases computational resource consumption to some extent, it can effectively improve computational accuracy and reduce the risk of numerical degradation. Additionally, we minimized error accumulation in the design of the model architecture through proper inter-layer connections and parameter initialization.
4.6.2. Discussion of Database Image Encoding
Regarding the images in the test database, the encoding precision of the color channels significantly affects image restoration. Common image encoding formats such as 8-bit and 10-bit limit the number of color values and luminance details that an image can represent. In 8-bit encoding, each color channel can take values from 0 to 255, while in 10-bit encoding the range is 0 to 1023. For HDR encoding, which requires a wider dynamic range to accurately represent the lighting information in real-world scenes, low-precision encoding formats result in information loss. In our experiments, although the LOL datasets do not explicitly specify the encoding format of all images, it is reasonable to assume the presence of images with different levels of encoding precision.
Based on the above, we conducted a theoretical analysis of the expected maximum error in image restoration. Let the true value of an image under ideal conditions be and the restored value affected by encoding precision and numerical degradation be ; then, the error . Considering the encoding precision, for 8-bit encoded images, the minimum change in luminance value is 1/255, which restricts the accuracy of image restoration. When combined with the impact of numerical degradation, the actual maximum error becomes even larger. Due to the weak signal strength in low-light regions, the combined effects of numerical degradation and encoding precision may cause significant deviation between the restored image’s luminance and the true value.
4.6.3. Discussion of the Impact of Pixel Quantization
Pixel quantization affects image restoration mainly in terms of luminance and color. In luminance restoration, low-level pixel quantization leads to the loss of luminance information. As a result, the restored image appears darker in low-light areas and the details can be difficult to distinguish. For example, with 5-bit quantization, only 32 luminance levels can be represented, which is far fewer than the 256 levels in 8-bit quantization, resulting in a significant loss of luminance details. On the other hand, higher-level pixel quantization can better preserve luminance information, making the restored image’s luminance closer to the real-world scene.
In terms of color, low-level pixel quantization may cause color distortion and color banding. When the quantization level is low, the transition between colors becomes discontinuous and obvious color bands appear; this is particularly evident in regions with smooth color changes, such as sky or water surfaces. In the restored image, the originally smooth color transitions will be separated into blocks or bands, severely affecting the visual quality of the image. Higher-level pixel quantization can effectively reduce such phenomena, making the color transitions more natural.
In conclusion, numerical degradation, the encoding precision of test database images, and pixel quantization all have significant impacts on low-light image restoration. In future research, it will be necessary to further explore ways to improve the robustness of the WIGformer model against numerical degradation while ensuring computational efficiency. Additionally, considering a wider range of image encoding formats and optimizing the model to adapt to different quantization levels will help to enhance the performance of low-light image enhancement technology in practical applications.
4.6.4. Handling Non-Additive Noise in WIGformer
In this paper, we have assumed additive perturbations (,); however, real-world noise often has more complex distributions, such as Poisson–Gaussian. To address this, we propose several strategies for WIGformer. One option is learnable noise modeling. A neural network module could be added to learn non-additive noise characteristics from data. Using methods such as variational autoencoders, it would then predict and correct noise during image enhancement. Another approach could be to integrate prior knowledge of noise distribution into WIGformer’s components. By modifying the loss function to account for non-additive noise traits (e.g., Poisson–Gaussian), the model can be guided towards better noise handling. Multimodal methods could also be explored, such as combining traditional noise-filtering approaches with WIGformer. In future work, we will seek to test these strategies as ways to boost the proposed model’s robustness in real-world noisy scenarios.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents WIGformer, a wavelet-based illumination-guided transformer for low-light image enhancement. By integrating wavelet multi-scale decomposition with an extension of Retinex theory, our method effectively disentangles illumination and reflectance components while modeling real-world perturbations. The proposed wavelet illumination estimator captures hierarchical illumination features through WFEConv, enabling precise estimation of non-uniform lighting conditions. The illumination-guided restorer enhanced by IGEMSA suppresses noise and artifacts while preserving structural details through adaptive feature refinement and global-local dependency modeling. Comprehensive ablation studies validate the necessity of each component, with the proposed WFEConv and IGEMSA elements contributing significantly to performance gains. Quantitative evaluations across three benchmarks demonstrate WIGformer’s superiority over existing methods, achieving improvements of 1.5–3.2 dB in PSNR over state-of-the-art approaches. Qualitatively, our model excels in recovering natural color distributions, mitigating overexposure, and restoring textures in shadow regions. Future work will focus on optimizing computational efficiency for real-time applications and extending the WIGformer framework to video enhancement scenarios. By integrating symmetry-aware wavelet decomposition and attention mechanisms, WIGformer achieves robust enhancement while preserving the natural symmetry of scenes. This makes it particularly suitable for applications where structural consistency is critical, including autonomous driving and surveillance. To this end, future work will explore real-time optimization and symmetry-guided video enhancement.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.C.; methodology, W.C.; software, W.C. and T.Y.; validation, W.C. and T.Y.; formal analysis, W.C.; investigation, W.C. and J.Y.; resources, W.C. and J.Y.; data curation, W.C. and J.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, W.C. and Z.L.; writing—review and editing, W.C., J.Y. and Z.L.; visualization, W.C.; supervision, J.Y.; project administration, J.Y.; funding acquisition, J.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ibrahim, H.; Kong, N.S.P. Brightness Preserving Dynamic Histogram Equalization for Image Contrast Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2007, 53, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, T.; Tjahjadi, T. Contextual and variational contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 3431–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.D.; Shi, X. A simple and effective histogram equalization approach to image enhancement. Digit. Signal Process. 2004, 14, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.; Cheng, F.C.; Chiu, Y.S. Efficient contrast enhancement using adaptive gamma correction with weighting distribution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 22, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.G.; Liang, Z.H.; Liu, C.L. A real-time image processor with combining dynamic contrast ratio enhancement and inverse gamma correction for PDP. Displays 2009, 30, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, E.H. The retinex theory of color vision. Sci. Am. 1977, 237, 108–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobson, D.J.; Rahman, Z.u.; Woodell, G.A. A multiscale retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobson, D.J.; Rahman, Z.u.; Woodell, G.A. Properties and performance of a center/surround retinex. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.u.; Jobson, D.J.; Woodell, G.A. Retinex processing for automatic image enhancement. J. Electron. Imaging 2004, 13, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, J.; Hu, H.M.; Li, B. Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 3538–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Ding, X. A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2782–2790. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, D.; Huang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Ding, X.; Paisley, J. A fusion-based enhancing method for weakly illuminated images. Signal Process. 2016, 129, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Ling, H. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, F.; Lu, F.; Wu, J.; Lim, C. MBLLEN: Low-light image/video enhancement using cnns. In Proceedings of the BMVC, Newcastle, UK, 3–6 September 2018; Northumbria University; Volume 220, p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, C.W.; Shen, X.; Zheng, W.S.; Jia, J. Underexposed photo enhancement using deep illumination estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 6849–6857. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, S.; Marza, P.; McDonagh, S.; Parisot, S.; Slabaugh, G. Deeplpf: Deep local parametric filters for image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 12826–12835. [Google Scholar]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H.; Shao, L. Learning enriched features for real image restoration and enhancement. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XXV 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 492–511. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C.W.; Jia, J. Snr-aware low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 17714–17724. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J. Beyond brightening low-light images. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 1013–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.04560. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Luo, P.; Gu, J. Star: A structure-aware lightweight transformer for real-time image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 4106–4115. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Bian, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Timofte, R.; Zhang, Y. Retinexformer: One-stage retinex-based transformer for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 12504–12513. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, C.; Lu, C.; Zhu, S. Spa-former: An effective and lightweight transformer for image shadow removal. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Gold Coast, Australia, 18–23 June 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cun, X.; Bao, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Uformer: A general u-shaped transformer for image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 17683–17693. [Google Scholar]
- Daubechies, I. Ten Lectures on Wavelets; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Lu, C.; Sun, Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, C.; Ou, C. Automatic ECG classification using continuous wavelet transform and convolutional neural network. Entropy 2021, 23, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; He, R.; Sun, Z.; Tan, T. Wavelet-srnet: A wavelet-based cnn for multi-scale face super resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1689–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Seyed Mousavi, H.; Huu Vu, T.; Monga, V. Deep wavelet prediction for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 104–113. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Liu, F.; Jiao, L.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, L. SAR image segmentation based on convolutional-wavelet neural network and Markov random field. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 64, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.; Li, R. Wavelet pooling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gal, R.; Hochberg, D.C.; Bermano, A.; Cohen-Or, D. Swagan: A style-based wavelet-driven generative model. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2021, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, F.; Coste, S.; De Bortoli, V.; Mallat, S. Wavelet score-based generative modeling. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 478–491. [Google Scholar]
- Phung, H.; Dao, Q.; Tran, A. Wavelet diffusion models are fast and scalable image generators. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 10199–10208. [Google Scholar]
- Finder, S.E.; Zohav, Y.; Ashkenazi, M.; Treister, E. Wavelet feature maps compression for image-to-image CNNs. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 20592–20606. [Google Scholar]
- Finder, S.E.; Amoyal, R.; Treister, E.; Freifeld, O. Wavelet convolutions for large receptive fields. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 363–380. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Sparse gradient regularized deep retinex network for robust low-light image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2072–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, A.; Vasluianu, F.A.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, C.; Timofte, R.; Jin, Z.; et al. NTIRE 2024 challenge on low light image enhancement: Methods and results. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 6571–6594. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 8024–8035. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Sgdr: Stochastic gradient descent with warm restarts. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.03983. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Pang, Y.; Wen, J. Fast efficient algorithm for enhancement of low lighting video. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRApH 2010 Posters, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 26–30 July 2010; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Sun, X.; Guo, Z. Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust retinex model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2828–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lore, K.G.; Akintayo, A.; Sarkar, S. LLNet: A deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Kindling the darkness: A practical low-light image enhancer. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1632–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Loy, C.C.; Hou, J.; Kwong, S.; Cong, R. Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1780–1789. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Gong, X.; Liu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, C.; Shen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Z. Enlightengan: Deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2340–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 10561–10570. [Google Scholar]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H.; Shao, L. Learning enriched features for fast image restoration and enhancement. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 1934–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H. Restormer: Efficient transformer for high-resolution image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5728–5739. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Ma, T.; Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Toward fast, flexible, and robust low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5637–5646. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ma, W.; Ma, X.; Wang, J. LAE-Net: A locally-adaptive embedding network for low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognition 2023, 133, 109039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hu, Q. Low-light image enhancement via breaking down the darkness. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2023, 131, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yi, X.; Ma, J. CRetinex: A progressive color-shift aware Retinex model for low-light image enhancement. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2024, 132, 3610–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Mehmood, A.; Shahid, F.; Zheng, Z.; Ibrahim, M.M. Lit me up: A reference free adaptive low light image enhancement for in-the-wild conditions. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 153, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Xu, P.; Li, Z.; ATO, W.X. An illumination-guided dual attention vision transformer for low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 158, 111033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).