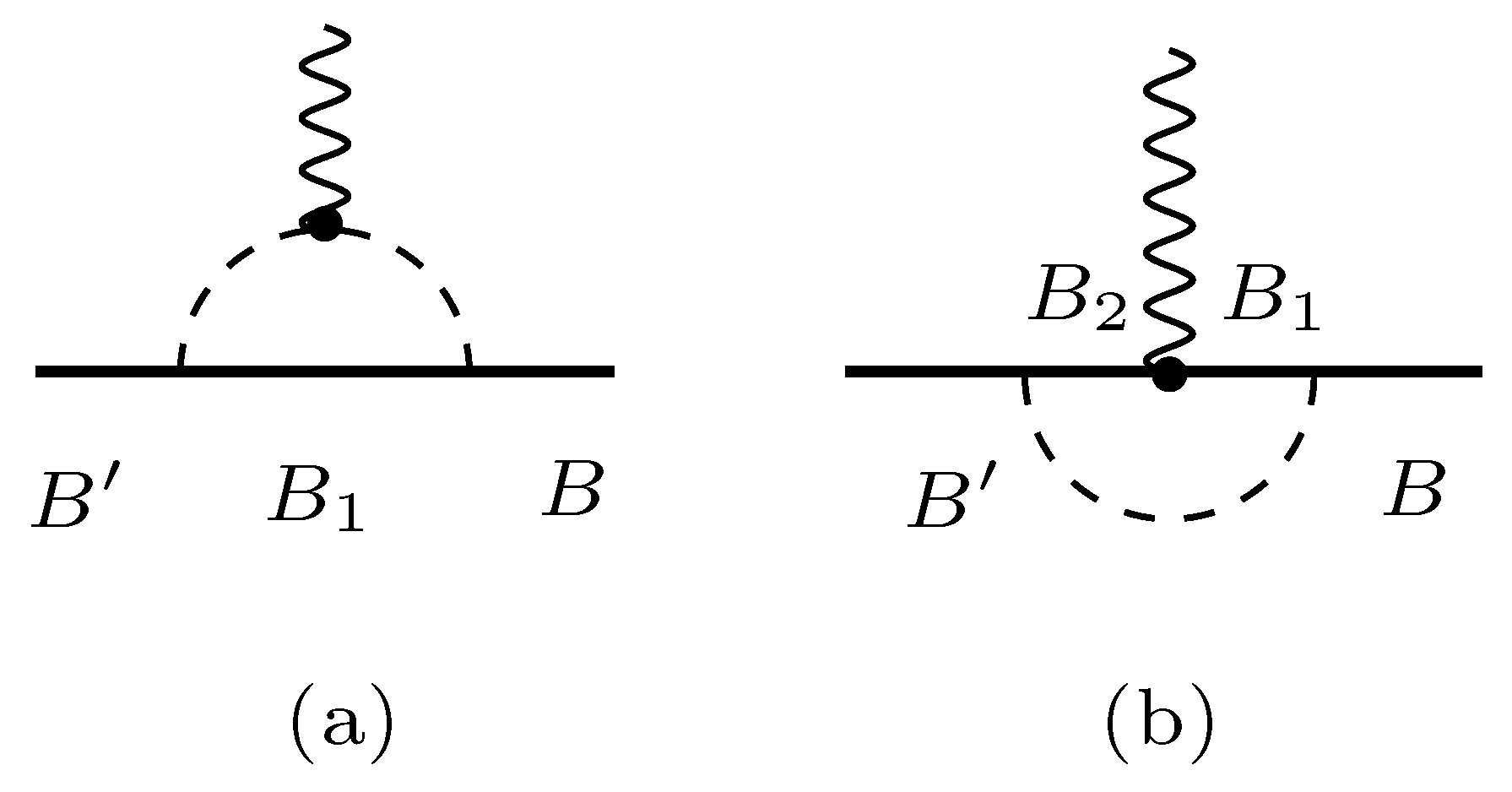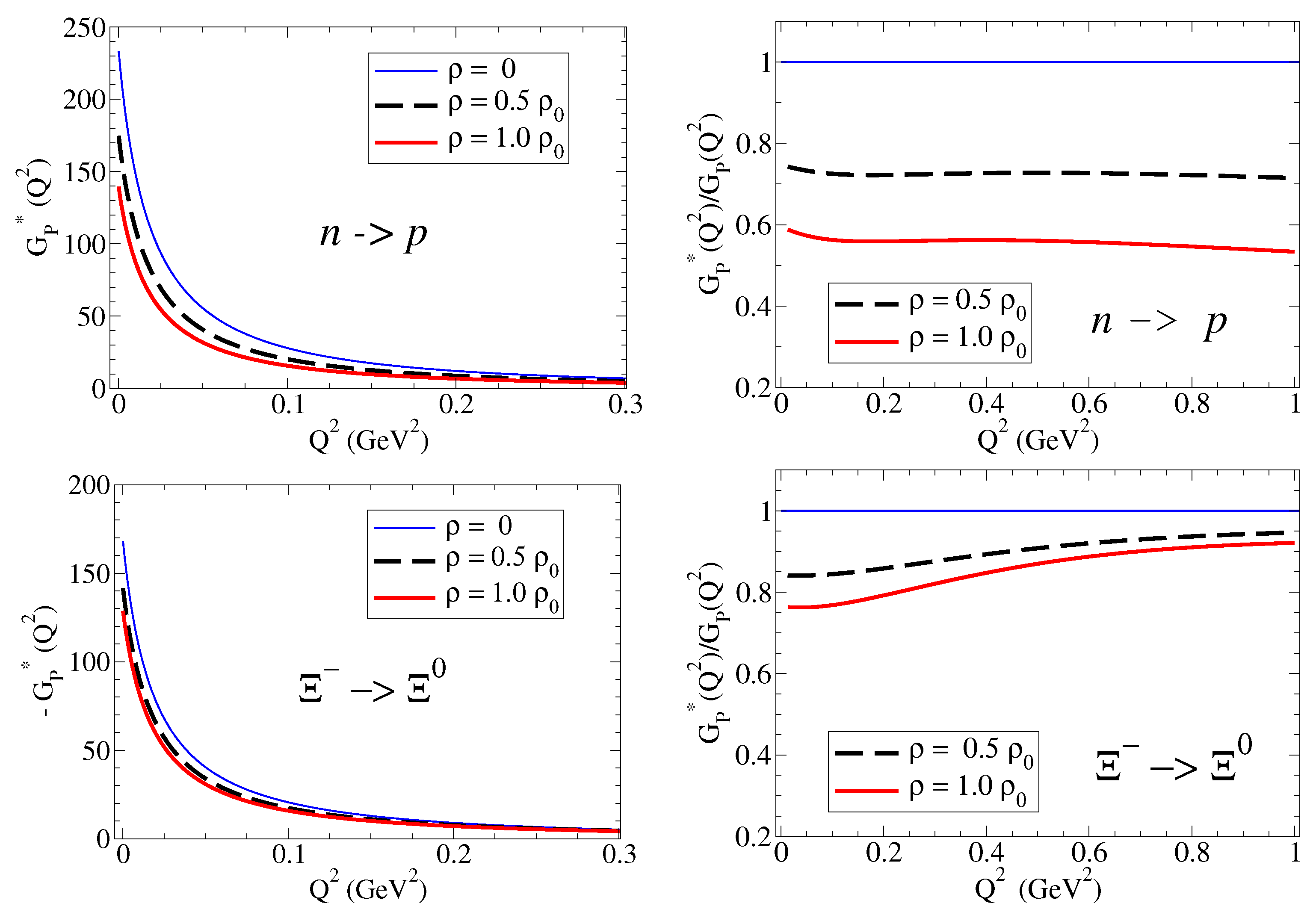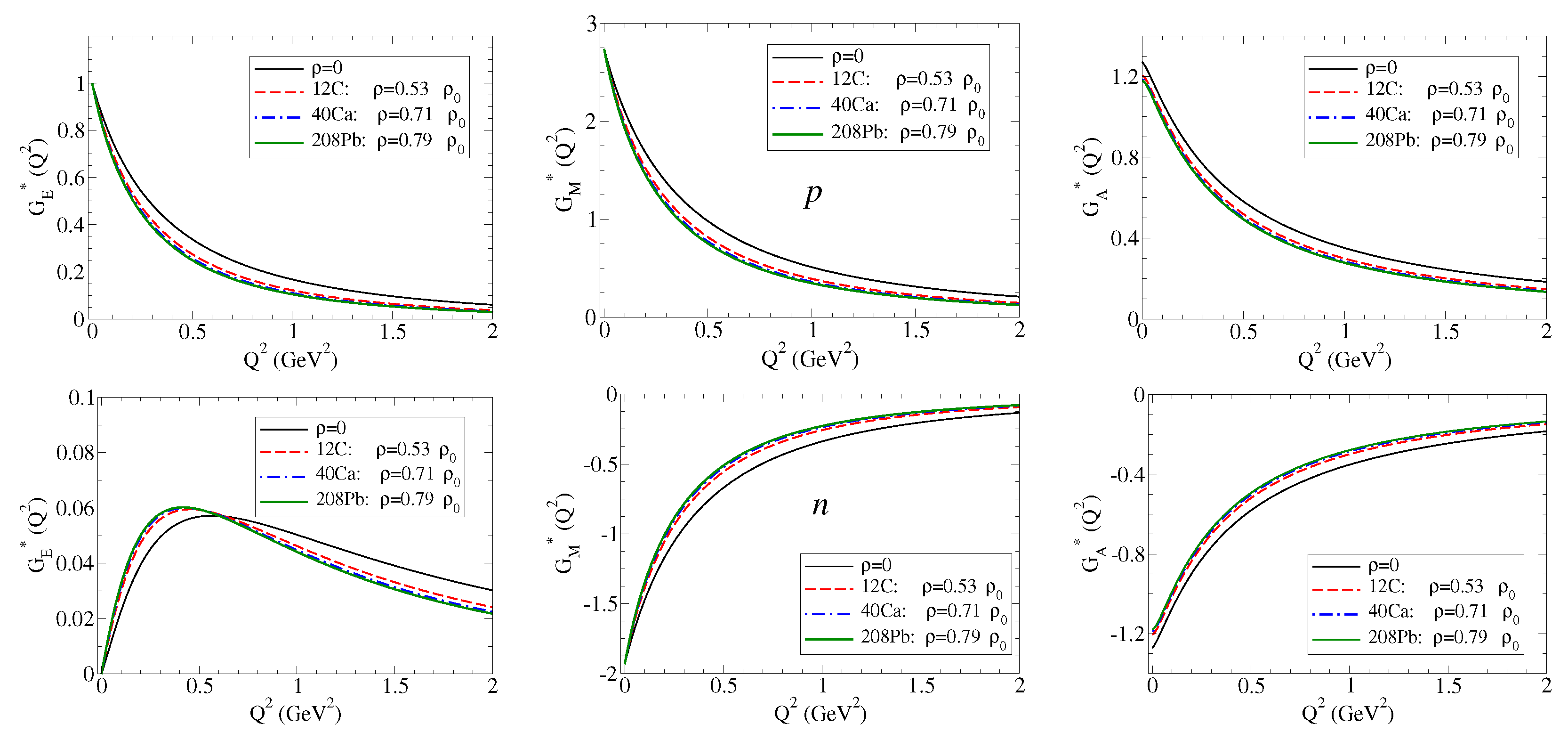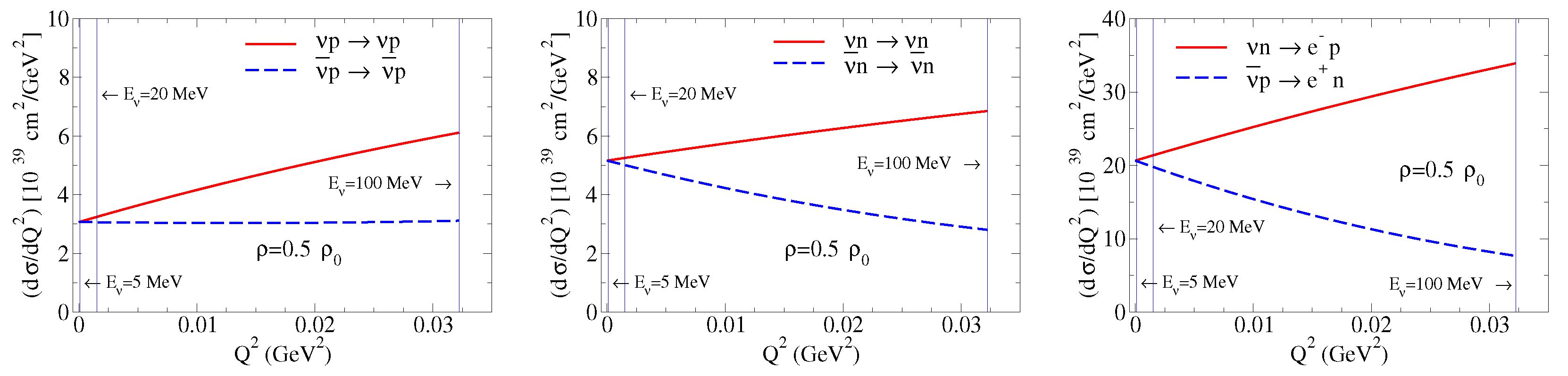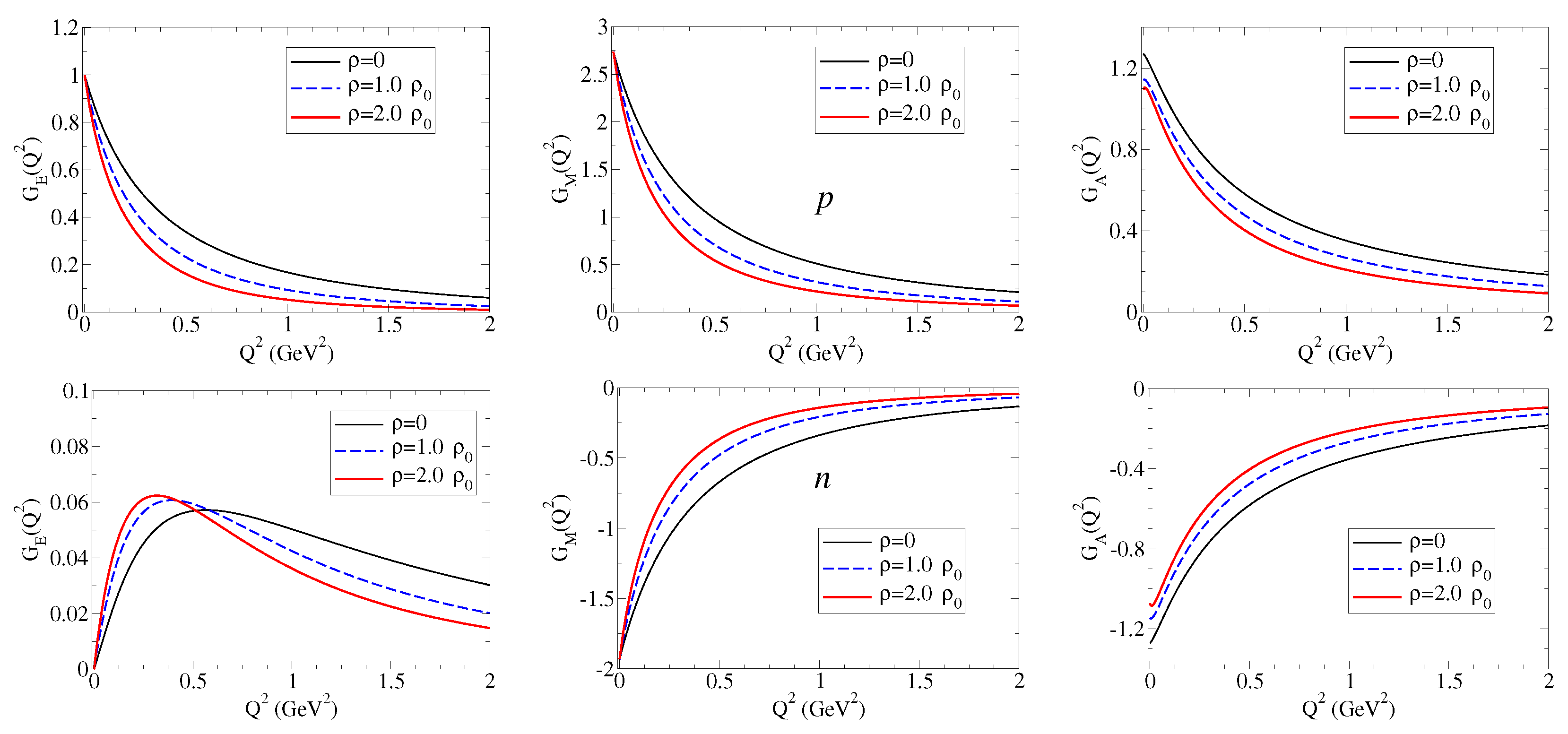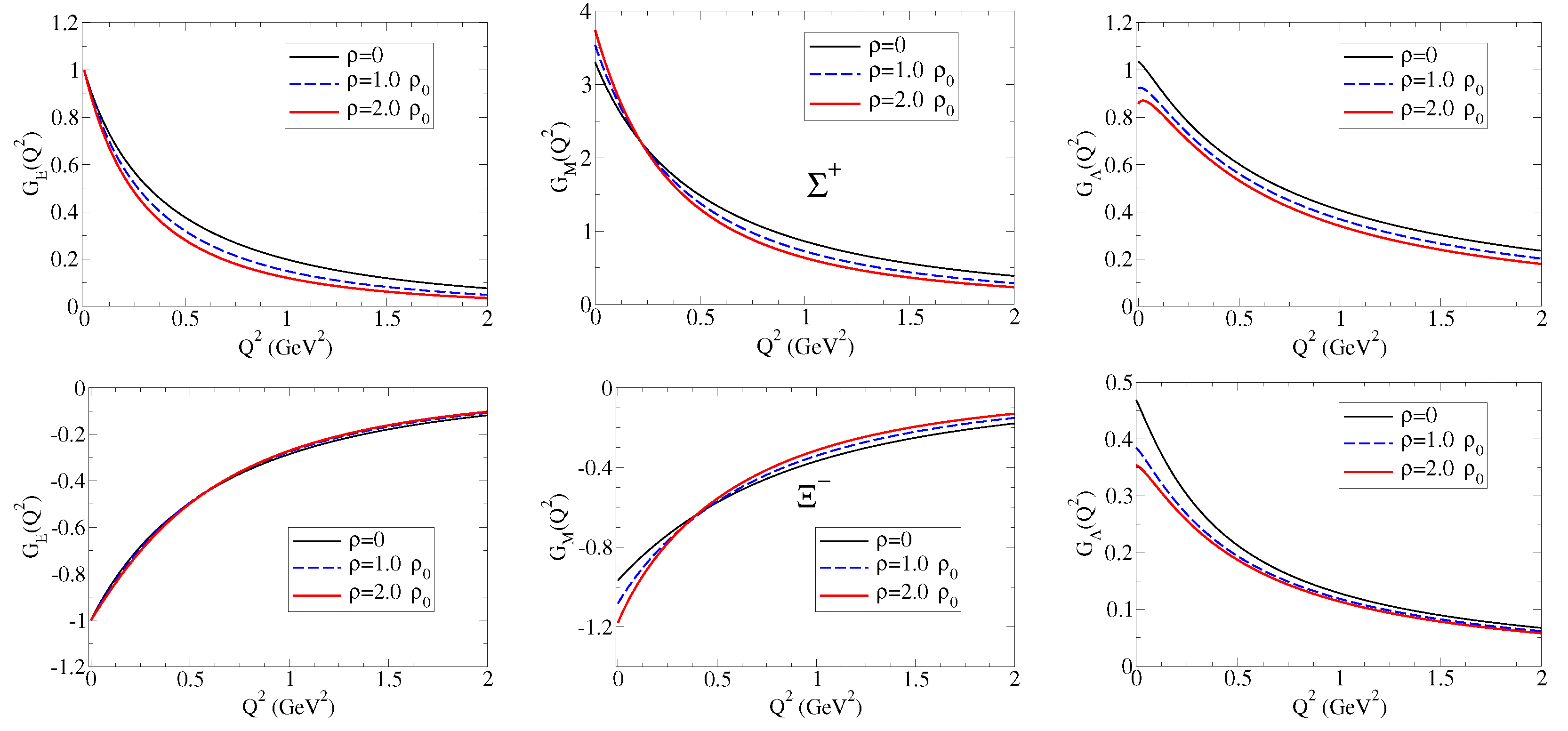Abstract
There is evidence that the properties of hadrons are modified in a nuclear medium. Information about the medium modifications of the internal structure of hadrons is fundamental for the study of dense nuclear matter and high-energy processes, including heavy-ion and nucleus–nucleus collisions. At the moment, however, empirical information about medium modifications of hadrons is limited; therefore, theoretical studies are essential for progress in the field. In the present work, we review theoretical studies of the electromagnetic and axial form factors of octet baryons in symmetric nuclear matter. The calculations are based on a model that takes into account the degrees of freedom revealed in experimental studies of low and intermediate square transfer momentum : valence quarks and meson cloud excitations of baryon cores. The formalism combines a covariant constituent quark model, developed for a free space (vacuum) with the quark–meson coupling model for extension to the nuclear medium. We conclude that the nuclear medium modifies the baryon properties differently according to the flavor content of the baryons and the medium density. The effects of the medium increase with density and are stronger (quenched or enhanced) for light baryons than for heavy baryons. In particular, the in-medium neutrino–nucleon and antineutrino–nucleon cross-sections are reduced compared to the values in free space. The proposed formalism can be extended to densities above the normal nuclear density and applied to neutrino–hyperon and antineutrino–hyperon scattering in dense nuclear matter.
1. Introduction
The structure of hadrons and their interactions are described by Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) in terms of quarks and gluons, the QCD degrees of freedom. It is then natural to assume that, in the presence of a strong mean field pervading nuclear matter, the motion of quarks and gluons inside hadrons is modified. Modifications due to the medium are expected to be reflected on the electromagnetic and weak structure functions of the nucleon and other other baryons when compared with the structure functions in free space [1,2,3].
Information about the medium properties of hadrons is important for understanding environments with dense nuclear matter from high-energy nucleus–nucleus collisions to the cores of compact stars [3,4,5]. At the moment, however, due to the complexity of experiments with nuclear matter, the experimental information about the structure form factors of baryons in nuclear medium is limited, and theoretical studies are fundamental for the progress in the field.
Modifications of the properties of baryons in the nucleus have been observed regarding the European Muon Collaboration (EMC effect) in the deep inelastic structure functions of the nucleus [3,6,7,8]. In the present work, however, we focus on the electromagnetic and weak form factors of octet baryons and study their dependence on transfer momentum and medium density.
Evidence of the modification of the electromagnetic properties of baryons in a nuclear matter has been reported for the proton based on measurements in polarized scattering on different targets at MAMI and Jefferson Lab (JLab) [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. The measurements indicate an enhancement of the ratio between the electric and magnetic form factors of the bound proton when compared with the free space ratio, a clear manifestation of the in-medium modifications of the electromagnetic structure of the proton. This interpretation is consistent with theoretical calculations based on different frameworks [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. At the moment, the experimental study of the in-medium modifications of baryons other than the proton is more challenging, but there are some proposals for measurements on the in-medium neutron electromagnetic form factors [30]. Model estimations for the proton predict a suppression (quenching) for the ratio between the electric and magnetic form factors [17,20,22,23,26,27,28]. For the remaining members of the baryon octet, one can expect enhancement or quenching of the ratio depending on the flavor content of the baryon [18].
The experimental information about the in-medium modifications of the axial-vector form factor of baryons in general and the nucleon in particular is very scarce. Experiments related to the beta decay of heavy nuclei suggest the quenching of the nucleon axial-vector coupling constant [31,32]. Model calculations based on the MIT bag model [33] and quark–meson coupling (QMC) model [3,34] and Skyrme and soliton models [29,32,35,36,37,38,39] are consistent with the reduction in the nucleon axial-vector form factor in nuclear matter.
There is then a strong motivation to develop formalisms that can be used to estimate structure functions of baryons at relatively high densities and moderate and large based on the degrees of freedom manifest in the vacuum: valence quarks and meson cloud excitations of baryon cores. Model calculations based on Effective Field Theory, Skyrme and quark–soliton models, and the QMC model that take into account the effective medium modification of the quarks and hadron masses are particularly appropriate for the study of the properties of baryons immersed in a nuclear medium [20,35,37,38]. In the present work, we review recent calculations of the electromagnetic and axial form factors for the baryon octet in a symmetric nuclear matter based on a covariant quark model combined with the QMC model [5,17,18]. We assume that the nuclear matter is distributed by a large volume, and that the interactions between baryons with the medium can be simulated by mean-field one-body currents, and also that the final state interactions are small [3,5,17]. The octet baryon form factors are calculated in terms of and the medium density in the interval between (free space) and , where is the normal nuclear matter density, characterized by fm−3.
In the free space, there is an extensive body of literature related to the electromagnetic and axial structure of baryons. For a review, see Refs. [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. In the study of the electromagnetic and axial structure of octet baryons, we consider an extension of the covariant spectator quark model [49,50,51,52,53], developed for the study of baryons in free space [44,54,55,56]. In the covariant spectator quark model, the electroweak interactions with the baryon systems are described in relativistic impulse approximation using parametrizations of the quark currents and radial wave functions, determined in previous studies of the nucleon, octet baryons, and decuplet baryons [17,44,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68]. We also consider effective parametrizations of the meson cloud contributions motivated by theoretical principles for a better description of the low- region [17,44,54,63,68]. The extension of the formalism to the nuclear medium takes into account the modifications of the properties of hadrons in the medium (masses and coupling constants), as determined by the QMC model [3,5,17,20,26,69]. The combination of formalisms is justified because there is a correspondence between the quark effective electromagnetic structure of the MIT bag model/cloudy bag model (CBM) [24,33,34,70,71,72,73,74,75] and the covariant spectator quark model [56,63,67,68].
In the covariant spectator quark model, the baryon cores are described as systems of three quarks that interact with electroweak probes under the relativistic impulse approximation (additive quark model). The quarks have their own internal structure (constituent quarks) that simulates dressing by gluons and quark–antiquark pairs, consistently with chiral symmetry in the confining limit [51]. This complex structure is taken into account considering a vector meson dominance structure for electroweak quark currents. This representation of the quark structure is consistent with the picture discussed within the Dyson–Schwinger framework and visualized in lattice QCD simulations, associated with dynamical chiral symmetry breaking that leads to massive extended quarks at low energies [76,77,78]. The quark internal structure and quark masses can then be regraded as a manifestation of the dynamical chiral symmetry breaking.
Using the proposed formalism, we calculate the elastic electromagnetic octet baryon form factors (electric and magnetic ) and the axial form factors (axial-vector and induced pseudoscalar ) associated with the allowed transitions between octet baryon states and discuss the impact of the medium effects in terms of the nuclear medium density. The study of the transitions includes transitions (conversion ), transitions (conversion ), and neutral current transitions (). The impact of the medium on the electromagnetic form factors depends on the flavor content (charged baryons, neutral baryons, and number of strange quarks). In general, and are suppressed in a nuclear medium, but the magnitude of the suppression depends on the type of the transition ( and ) and on the mass of the baryons.
We use the numerical results to study reactions of neutrinos/antineutrinos with nuclei and reactions of neutrinos/antineutrinos with hyperons in dense nuclear matter for different densities. The methods developed here for the octet baryons can be extended in the future to other baryon systems, like decuplet baryons and transitions between octet baryons and decuplet baryons, as well as for densities larger than the normal nuclear matter. There is also the possibility of generalization to asymmetric nuclear matter.
The present article is organized as follows: In the next section, we introduce the structure functions used in the study of electromagnetic and axial interactions with octet baryons and transitions between octet baryon states. In Section 3, we explain the theoretical formalism used in the calculation of the octet baryon electromagnetic and axial form factors in free space and in the nuclear medium. Numerical calculations of octet baryon electroweak form factors in the nuclear medium for different nuclear matter densities are presented and discussed in Section 4. In Section 5, we discuss the applications of the numerical calculations for nucleons bound to nuclei, the calculation of neutrino–nucleon and antineutrino–nucleon cross-sections for bound nucleons, and the extension of the formalism for nuclear matter densities above the normal nuclear matter (). It is the first time that octet baryon form factors are being calculated for densities larger than the normal nuclear matter within our framework. The limitations and possible improvements of the formalism are discussed in Section 6. The outlook and conclusions are provided in Section 7.
2. Octet Baryon Electromagnetic and Axial Form Factors
We focus our attention now on octet baryons. The octet baryons are characterized by spin and positive parity (): in a compact notation. The baryon octet includes the nucleons N (proton p and neutron n), the , the baryons (, , and ), and the baryons ( and ).
We will use the label B to represent properties associated with the baryon B (masses, charges, magnetic moments, etc.). The elastic form factors associated with the interaction with an octet baryon member are also labeled by the index B.
As for the axial transitions, related to the weak interaction, we need to consider different labels (B and ) for the transitions. For simplicity, we avoid the representation , where for beta decays, or for inverse beta decays, with (electron, muon, or tau), since the properties of the current are independent of the lepton family.
The axial transitions can be divided into three different types: change in isospin (like the beta decay), change in strangeness (like ), and neutral current transitions. The first two types (charged transitions) are mediated by the bosons ; the neutral current transitions are mediated by the boson . The list of possible transitions is included in Table 1.

Table 1.
Axial transitions between octet baryon members: , and neutral current transitions [44]. There are no contributions to the transition. The axial flavor operators X associated with (), () and () are defined in Appendix A and discussed in the next section.
These transitions are classified according to the kinematic of the free space. The decays of to and to are kinetically allowed due to the magnitude of their masses. Notice that the order of the decays can be inverted when the baryons are excited by interaction with the nuclear medium. In nuclear medium, one can have for instance the transitions , and .
We discuss now the formalism associated with the electromagnetic transitions and weak axial transitions between octet baryon members.
For the studies in nuclear medium, we use * to label the properties in medium (masses , form factors, etc.).
2.1. Electromagnetic Transitions
We consider first the electromagnetic interactions with an octet baryon: , where is the transfer momentum. The electromagnetic current associated with the transition can be written as [17,54,55]
where , and are the final and initial Dirac spinors, respectively. The functions and are the Dirac and Pauli form factors, respectively.
The current defines the baryon B elastic form factors. In this discussion, we exclude the kinetically allowed transition between octet baryon members: transition [62]. This transition has properties that differ from the octet baryon elastic transitions and has similarities with the inelastic transitions [40].
Using and , we define the Sachs form factors, electric and magnetic [54,64],
At , one has , where is the baryon charge, and is the baryon B anomalous magnetic moment. The function represents the magnetic moment in natural units , where e is the elementary electric charge
The comparison of magnetic moments is usually conducted in units of nuclear magneton (), corresponding to the nucleon natural units in the free space, , where is the physical nucleon mass. We can then write [17,18]
where is the numerical value of in nuclear magneton. We can also represent the anomalous magnetic moment in nuclear magneton.
From the expression for , we can conclude that, for neutral baryons, should vanish for since the charge is zero. This condition is expressed by , leading also to the analytic relation , near .
In the nuclear medium, we redefine the Dirac and Pauli form factors as and , respectively. As a consequence, the electric and the magnetic form factors take the form
where is the in-medium baryon mass.
In the nuclear medium, the baryon masses are modified (to ). In these conditions, the comparison with the magnetic moments in free space must take into account the units in vacuum. Taking the nucleon as an example, in the nuclear medium, the nucleon mass is modified to , and the magnetic moment in the nuclear medium () is
To obtain the magnetic form factor in units of the nuclear magneton, we need then to multiply (the magnetic form factor in natural units) by the factor . In other words, in units of the nuclear magneton, the magnetic moment is corrected by the factor .
2.2. Weak Transitions and Axial Form Factors
We consider now the transition , where x represents the weak transition mediator ( or bosons). We include the double direction arrow to take into account all possible transitions, including decays (beta or muon) and inverse decays [5,45].
The weak transition current can be represented as [46,47]
and defines the axial-vector and the induced pseudoscalar form factors, and is the average between the mass of the initial state () and the final state (), and . As before, . The factor is included to be consistent with the nucleon case ( beta decay). For simplicity, we omitted the indexes B and from the representation of the form factors.
The expression (9) is obtained after a proper projection in the flavor space. The axial flavor operators can be represented in terms of the Gell–Mann matrices () [45], as given in Appendix A. The allowed transitions correspond to the operators: (neutral current transitions), (increases/decreases the isospin projection), and (decreases/increases the number of strange quarks).
In the nuclear medium, the current (9) is replaced by in-medium equivalents, including the in-medium effective masses , that define , and the axial form factors and .
3. Covariant Quark Model for the Free Space and Nuclear Medium
In the present section, we review the formalism associated with the covariant spectator quark model used in the description of the electromagnetic and axial structure of baryons in the free space and discuss how the formalism can be extended to the nuclear medium. The extension is obtained from a consistent combination of the covariant spectator quark model with the CBM and with the QMC model [56,63,67,68].
We start by discussing the model at the microscopic level, how the baryon wave functions are defined in terms of the quark flavor and spin properties, and how the electroweak interactions with the quarks are described. In the covariant spectator quark model, the quarks have an internal structure that is a consequence of the quark dressing (gluons and quark–antiquark pairs). In the interaction with electroweak probes, we can reduce the probe–quark interactions to a coupling with a single quark in a quark–diquark system. In this formalism, the wave functions of the baryons are not determined by a dynamical wave equation but are instead built in terms of the quark spin-flavor structure with radial wave functions determined phenomenologically for a few ground state baryons. The motivation of the formalism is not to determine the baryon mass spectrum but to describe the structure functions of the baryons. In the numerical calculations, we consider then the experimental masses of the baryons.
Within the covariant spectator quark model, the particular form used for the quark–diquark radial wave functions and for the quark currents is employed in a first stage, in the extension of the formalism to a lattice QCD regime associated with a defined pion mass, and in a second stage in the extension to the nuclear medium. These extensions are discussed below.
It is worth mentioning, however, that the consideration of the quark degrees of freedom exclusively is not sufficient to describe the electromagnetic and axial structure of the baryons and transitions between baryon states at low . In that regime, there are excitations that cannot be described only in terms of valence quark effects, and excitations related to quark–antiquark or meson states may have relevant contributions. Those processes can be regarded as a meson cloud dressing at the hadronic level and can be interpreted as interactions between different quarks inside the baryon (not quark self-dressing) [17,54,55,63,67,68]. Since the meson cloud dressing at the hadronic level differs from the quark self-dressing, there is no double counting.
We consider then that, in the electroweak interactions, the elastic and transition form factors can be decomposed into a valence quark contribution and a contribution associated with the electromagnetic and axial interaction with the bare core dressed by meson cloud, hereafter mentioned as the meson cloud contribution (see Figure 1). The separation between valence and meson cloud contributions is naturally model-dependent. The model dependence is a consequence of the differences in the calibration of the background and in the identification of the bare states [79,80,81,82,83]. It is expected that the impact of the model dependence is reduced in our formalism since the bare parameters of the model are determined by lattice QCD simulations associated with large pion masses. Although lattice QCD simulations include some meson cloud effects, their effects are reduced when the pion mass is large [83,84].
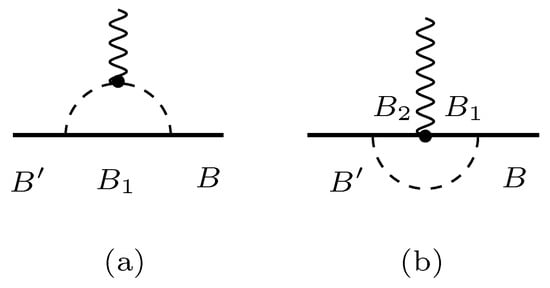
Figure 1.
Electroweak interactions with a baryon B within the one-meson-loop level. (a) Interaction with meson. (b) Interaction with intermediate baryons. differs from B in the inelastic transition (weak axial transitions). The states and represent generic intermediate states.
The masses of the octet baryons are not calculated within the quark model formalism. In the calculations in the free space, we consider the averages of the experimental values of the masses of the different octet baryon families (N, , , and ). The values for the effective masses in medium are discussed next (see Section 3.3).
The covariant spectator quark model has been used successfully in the study of the transitions for the nucleon resonances , , , and [49,50,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95], among others [96,97,98]. The formalism has also been applied to the Dalitz decay of nucleon resonances and other baryons () [67,68,99,100,101,102], to the study of the elastic electromagnetic form factors of baryons in the spacelike region [53,54,57,58,59,60], in the timelike region [64,65,66], and to the nucleon deep inelastic scattering [51,103].
We start by discussing the valence quark component of the model. Next, we consider the contributions associated with the meson cloud dressing. At the end, we explain how the formalism is naturally extended to the nuclear medium.
3.1. Model for the Valence Quark Contributions
The covariant spectator quark model is a constituent quark model derived from the covariant spectator theory [51,104,105]. In the model, the baryons are regarded as three-constituent quark systems, where a quark is free to interact with electroweak fields in relativistic impulse approximation while the two quarks are spectators [5,44,49,51,52,53,106]. Integrating over the degrees of freedom of the two spectator quarks, we reduce the baryon system to a quark–diquark configuration, where the diquark can be represented as an on-shell particle with effective mass . The effective quark–diquark wave function simulates the effect of confinement and is consistent with the chiral symmetry in the limit when the mass of the quarks vanishes [51,52,107,108].
The interaction of the probe with the quarks is described in terms of quark electromagnetic and axial form factors that simulate the structure associated with the gluon and quark–antiquark dressing of the quarks. These constituent quark form factors are parametrized using a vector meson dominance form calibrated in the study of the electromagnetic structure of the nucleon and baryon decuplet [44,51,53].
The baryon wave functions are derived from the spin-flavor-orbital SU(6)⊗O(3) symmetry associated with the quark–diquark spin-flavor and radial configurations. The radial wave functions are determined phenomenologically from experimental data or lattice QCD data associated with some ground state systems. In the model, the effect of the SU(3) quark flavor symmetry-breaking is reflected at the level of the baryon radial wave functions, considering different range parameters for the systems, according to the quark flavor content.
We discuss now the structure of the wave functions of the octet baryons. Following Refs. [5,17], we consider the octet baryon wave functions composed of a mixture of quark–diquark configurations in an S-state and a P-state
where P is the momentum of the baryon, k is the diquark momentum, is the P-state admixture, and . Based on the studies of the electromagnetic structure of the nucleon and the baryon octet, we expect the S-state to yield the dominant contribution [51,54,55].
The S- and P-components of the wave functions are defined as [5,44]
where are the spin wave functions labeled by the diquark spin (), and are the mixed symmetric (S) and mixed anti-symmetric (A) flavor states in the exchange of quarks 1 and 2 [51,53,54]. The functions and are the radial wave functions, and (recall that for on-shell baryon states). In the notation for and , we omit for the simplicity the labels associated with the spin of baryon B. The explicit expressions for the flavor are presented in Appendix B.
The operator is included to generate a P-state wave function. In the numerical calculations, we correlate the P-state radial wave function with the S-state radial wave function using for simplicity (notice that by construction) [5,44,52]. In these conditions, compared with the S-state model (), no extra momentum range parameters are included in the model.
3.1.1. Radial Wave Functions
In the covariant spectator quark model, the radial wave functions of a baryon B are represented in terms of the dimensionless variable
The S-state radial wave functions take the Hulthen form [51,85,108]
where is a normalization constant, and (N), ( and ), or () are momentum range parameters determined in the study of the electromagnetic structure of the octet baryon in free space from the analysis of the lattice QCD data [17,109]. We consider here the parametrization from Ref. [17]: , , , and . We obtain then the order expected from the natural size of the baryons. Systems with more strange quarks are more compact than systems with more light quarks. The normalization constant is determined by the condition when . The integral on k is defined below.
The form used for the radial wave functions (14) is motivated by simplicity, by the asymptotic falloff induced in the electromagnetic form factors, and by the possibility of breaking the SU(3) symmetry in the simple form, as mentioned already [5,51,53,54]. The presence of the factor in the definition of the radial wave functions implies that the form factors are independent of the value of diquark mass [51,85]. This approximation is justified by the effective parametrization of the radial wave functions, and by phenomenological determination of the values of the momentum range parameters ().
3.1.2. Electromagnetic Interaction with Quarks
The electromagnetic transition current associated with the interaction with a baryon B can be calculated in impulse approximation using [17,51,52,54]
where are the quark–diquark wave function described above, is the quark current operator, and factor 3 takes into account the contributions of all diquark pairs. Hereafter, we use the subscript 0 to label functions related to the bare contributions. In the calculation, we consider the sum into the intermediate diquark polarizations , including the scalar diquark (s) and the vectorial diquark polarization , and integrate on the on-shell diquark momentum using
which is the diquark energy.
The relativistic impulse approximation current (15) is based on a single quark operator (i.e., no exchange or interaction currents) and is valid when we consider an effective quark–diquark wave function with phenomenological radial wave functions [5,51,53].
The quark current operator in Equation (15) has the general structure [17,51,54]
where are SU(3) flavor operators acting on the third quark of the and states. The quark current (17) includes an implicit connection with the quark mass expressed by the dependence on the nucleon mass on the Pauli term.
The operators () can be decomposed into a sum of operators acting on quark 3 in the SU(3) space [53,54]
where , , and are the flavor space operators [see Appendix A]. These operators act on the wave functions in the flavor space .
The functions () are normalized by , , and , . In this notation, and are the isoscalar and isovector quark anomalous magnetic moments and the strange quark anomalous magnetic moment. The quark form factors are parametrized in terms of a vector meson dominance form that includes contributions from the , , and meson poles plus an effective vector meson pole that simulates the short range structure.
The explicit expressions and parameters related to the quark current and the radial wave functions are included in Appendix B. The isoscalar and isovector magnetic moments can be expressed in terms of quarks u and d regarding anomalous magnetic moments ( and ) [see Appendix B.1].
The evaluation of the transition current (15) with the octet baryon wave functions (11) leads to the following expressions for the electromagnetic form factors as defined by Equation (1) [17,54]
where
and
are the projections of the quark current operators on the mixed anti-symmetric (A) and mixed symmetric (S) states.
The flavor structure of the octet baryons is encoded in the coefficients and . These coefficients are presented in Appendix B.1. The radial structure of the baryons is included in the overlap integral of the radial wave functions , normalized as . The present expressions are based on a model that includes only the S-state contribution to the octet baryons [17,54].
The electric and magnetic form factors are calculated using Equations (19) and (20). The previous relations take into account only the valence quark contribution to the electromagnetic form factors. For the discussion of dressed form factors that take into account the meson cloud dressing, discussed above, we consider the compact notation
Using this notation, we can calculate the valence quark contribution to the electric and magnetic form factors
The combination of bare and meson cloud effects to the electromagnetic form factors is discussed in Section 3.2.1.
3.1.3. Weak Interaction with Quarks
In the covariant spectator quark model, the weak transition current associated with the transitions is determined in relativistic impulse approximation using [44,51,52,53]
where is the quark axial current operator. We follow here the notation used for the electromagnetic transition current (15). The quark axial current operator includes the axial flavor operators associated with the hadronic transition , as discussed next. The current (25) can be used to calculate the axial form factors based on the general form (9).
The possible transitions (allowed kinematically) between the octet baryon members are presented in Table 1. We can divide the transitions into 3 kinds, depending on the flavor transition operator X: transitions associated with the variation in isospin (, operator ), transitions associated with the variation in strangeness (, operator ), and neutral current transitions ().
In the weak axial interaction with the baryons, we consider the quark axial current operator
where () are the Gell–Mann matrices. In the previous equation, and are the quark axial-vector and quark-induced pseudoscalar form factors, respectively. The flavor operators act on the quark flavor states (), and the Lorentz operators act on the baryon spin states. The explicit expressions for and are presented in Appendix B.2.
As for the quark electromagnetic current , the current is defined in terms of the nucleon mass for convenience. For , we assume that the function is equivalent to the Dirac isovector form factor due to its isovector character [44].
The induced pseudoscalar form factor can be decomposed in the bare and pole contributions [44]
where the pole contribution takes the form
where is the bare contribution to , and is the mass of the meson related to the weak transition (the pion for transitions and neutral current transitions, and the kaon for the transitions).
The bare contributions to the axial transitions can be expressed in the form [44]
where is a coefficient dependent on the baryon flavor, determined by
The expressions for and are presented in Appendix B.2.
In Equations (29) and (30), and the functions () are overlap integrals of the radial functions and . The normalization of the radial wave function leads to . The integrals () are defined in Appendix B.2.
In the calculation of the octet baryon axial form factors, we use the radial wave functions and the Dirac isovector form factor determined by the study of the octet baryon electromagnetic form factors [17]. The free parameters of our model of the axial form factors: the admixture parameter and the parameters of [see Appendix B.2] are determined by the fit to lattice QCD results for the nucleon axial form factors from Ref. [110].
The meson cloud contributions to the the axial form factors are discussed in Section 3.2.2.
3.1.4. Extension of the Model to the Lattice QCD Regime
The quark model, discussed in the previous sections for baryons in the free space, can be extended to lattice QCD regimes associated with a given pion mass. The extension of the formalism to the lattice QCD regime is based on the properties of the radial wave functions and the vector meson dominance form of the electromagnetic quark currents [5,17,44,54].
The determination of the parameters of the model by with the lattice QCD data with large pion masses provides a clear estimate of the pure valence quark degrees of freedom since meson cloud effects are suppressed for large pion masses [17,53,54,86,87].
The radial wave functions presented in Section 3.1.1, in terms of the mass of the baryon (), are determined in the lattice QCD regime replacing the baryon mass by the baryon mass in lattice. As for the quark electromagnetic and axial currents defined in terms of vector meson poles, they are redefined in lattice QCD in terms of the vector mass poles associated with the lattice QCD regime (labeled by the pion mass of the simulation). In the second term of the currents, we also replace the nucleon mass by the nucleon mass in lattice. The coefficients associated with the vector meson dominance parametrizations are kept unchanged in the lattice QCD regime. The quark electromagnetic and axial currents are discussed in Section 3.1.2 and Section 3.1.3, and in Appendices Appendix B.1 and Appendix B.2.
With this procedure, we have a method that can be used to calculate elastic and electromagnetic transition form factors, which can be compared with numerical results form lattice QCD simulations. We expect the comparison to be accurate for simulations associated with large pion masses since the effects of the meson cloud excitations are small. The formalism has been tested successfully in the comparison with nucleons, nucleon to transitions, and nucleon to transitions [87,90].
More recently, the extension of the model to lattice QCD has been used to determine the parameters associated with the valence quark properties of the systems using fits of the radial wave functions of the [86,88,89], of the octet baryons, and of the decuplet baryons [5,17,53,54].
Our study of the octet baryon electromagnetic structure was based on the lattice QCD results from Lin et al. [109]. Reference [109] includes lattice QCD data for p, n, , , , and from the range 350–700 MeV, a range appropriated for the calibration of the model.
Our study of the octet baryon axial form factors was based on the results from Ref. [110]. Reference [110] includes a systematic study of the and nucleon form factors with several sets of pion masses in the range of –470 MeV that can be used for an accurate calibration of the unknown parameters in range –2 GeV2. There has been significant progress in lattice QCD simulations for the octet baryon axial form factors and octet baryons axial coupling constants using different methods and pion mass ranges [110,111,112,113,114,115]. Lattice QCD simulations near the physical limit are in agreement with the experimental value of the nucleon axial-vector coupling . For finite , however, there are still discrepancies between lattice QCD simulations and experimental data [116,117]. Combined studies of the experimental data and lattice simulations suggest that the octet baryon weak axial-vector form factors can be described by a dominant contribution associated with the valence quark and a component associated with the meson cloud dressing of the baryon cores [44,118].
Once the parameters of the model are calibrated by the lattice QCD data, one can calculate the valence quark contributions to the electromagnetic and form factors in the physical limit (using the physical masses) and combine the bare contributions with the meson cloud contributions to obtain the final result for the electromagnetic and axial form factors [17,44,53,54,86,87].
3.2. Meson Cloud Contributions
The physical baryon state can, in general, be represented as a combination of a bare three-quark state and term associated with the meson cloud excitations [5,17,44,54,55]
In this representation, takes into account the pure valence quark contributions discussed in the previous sections, and represents the baryon–meson state associated with the meson cloud dressing. The coefficient is determined by the normalization , assuming that is normalized to unity.
The factor provides the probability of finding the state in the physical baryon state. The probability of being associated with the meson cloud component is then , in general a small fraction of the probability associated with the three-quark state. The meson cloud terms are associated with baryon–meson states like , , , , etc. The corrections associated with baryon–meson–meson states are usually very small [5,17].
We recall that the separation between valence quark and meson cloud effects is intrinsically model-dependent. In our applications, we try to reduce the model dependence using the comparison with lattice QCD simulations with large pion masses (reduce meson cloud effects) to determine parameters of the model associated with the valence quark physics [17,44,54].
3.2.1. Electromagnetic Transitions
In the first studies of the octet baryon electromagnetic structure [17,54,55], we look for the more relevant meson cloud contributions to the nucleon system. According to the chiral perturbation theory, the pion, the lightest meson, has the largest contribution to the meson cloud [24,70,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126]. It is possible, however, in some transitions between baryon states, that the pion cloud contributions are small, and that the next meson contribution, the kaon cloud, became important. It has been shown that the kaon cloud contributions are relevant, in particular, for the octet baryon to decuplet baryon transitions [63,67,68]. In the first approximation, we consider for simplicity that the pion has the more relevant contribution to the meson cloud and to the nucleon and to the octet baryon and restrict the calculation to the pion cloud.
The electromagnetic interaction with the valence quarks was discussed in Section 3.1. The processes associated with the pion cloud contributions can be decomposed into the two processes displayed in Figure 1: the direct photon interaction with the pion and interaction with the baryon when the pion is “on the air”. The transition current can then be expressed in the form
where stands for the direct interaction with the quark core (15) and can be written as
describes the coupling with the pion, and the coupling with the intermediate baryon states. The factor is a normalization constant defined by Equation (32).
For the photon interaction with the pion–baryon states, we consider [17,55]
where , , , , , and are phenomenological functions of , and , , and are the operators acting on the SU(3) baryon–meson space. take into account the photon–pion interaction, while and describe the Dirac and Pauli couplings, respectively, with the intermediate baryon.
The currents (34)–(36) are constrained by the octet baryon charges. As a consequence, and . See Refs. [17,54,55] for a discussion on the subject.
The operators , , and are defined by SU(3) operators [55]. In an SU(3) model, the product of the functions , , and with the operators , , and can be represented as a product of the ratios and -dependent functions associated with the baryon–meson loop integrals. In the calculations, we use factors , , , and ( by construction) [17,54].
The falloffs of the functions , , , , , and are adjusted to a form consistent with the result expected from pQCD and valence quark sum rules, leading to suppression of in comparison with the leading order contribution [17]. In addition, the dependence of the functions and takes into account chiral constraints on the Dirac and Pauli square radii near the chiral limit [127,128].
The numerical values of couplings , , , and are calculated using an SU(3) baryon–meson symmetry model. Combining the different terms of the current (33), we can write
where the bare contributions are defined by Equations (19), (20), and (23), and the coefficients () are presented in Appendix C.1. The argument is omitted in the coefficients for simplicity.
Notice that the functions include combinations of the bare electromagnetic form factors , . Notice also that the coefficients are the same for and .
The values of the constants and the explicit parametrizations of the functions , and () are presented in Appendix C.1.
The normalization constants are determined by the constants and the by value of , associated with the octet baryon self-energies [55]:
The parameters associated with the bare contributions (radial wave function momentum range parameters , ) are determined by the fit to the lattice QCD form factor data from Ref. [109]. The remaining parameters of the model associated with the pion/meson cloud for the free space are then adjusted using
- the proton electromagnetic form factor data [129,130,131,132,133] and the neutron electromagnetic form factor data [134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148], including the proton and neutron magnetic moments;
- the octet baryon magnetic moments of the , , , , and [149];
- the nucleon square electric and magnetic radii, and the square electric radius [149,150].
The numerical results for the octet baryon electromagnetic form factors are presented in Section 4.1.
3.2.2. Axial Transitions
The meson cloud contributions are also relevant for the axial transitions. In the first studies of the axial transitions, we considered a simplified form for the meson cloud contributions, associated with the axial coupling with the intermediate baryons (in the elastic electromagnetic transitions, we need to take into account the two diagrams from Figure 1 in order to reproduce the charge of the baryon within a baryon–meson system. For the charged current axial transitions, we need to take into account that the diagrams include two baryon–meson couplings proportional to the factor ) [diagram (b) from Figure 1].
Similarly to the electromagnetic case, we represent the combination of the valence and meson cloud contributions to the axial form factor in the form
where is determined by
where is the parametrization of the meson cloud contribution to the nucleon axial form factor ( transition) and is an SU(3) coefficient associated with the transition. The function is defined by the relative contribution to the axial form factor (), and the cutoff is GeV. The falloff of is compatible with the expected falloff of a baryon system with 5 constituents [44]. A similar value for can be used to parametrize the nucleon axial form factor . The details of the parametrization are presented in Appendix C.2.
For large , we can write [44]
This relation can be used to estimate the constants and the impact of the meson cloud dressing in the axial form factors.
Also, the induced pseudoscalar form factor has contributions associated with the meson cloud
where
Notice that meson cloud contribution for has no adjustable parameters because it is determined directly from .
The parametrizations for and can be regarded as the global contribution of the meson cloud, not just the pion since they are estimated by empirical data (all meson cloud effects included).
The parametrizations of the meson cloud are determined from the study of the lattice QCD data for the nucleon, as discussed in Section 3.1.3, and from the empirical data for the nucleon axial form factors and the axial-vector coupling constant. The parameters involved are [related to ] and two coefficients included in [see Appendix C.2]. The value of or is determined using the relation (42) applied to the parametrization , while the coefficients in are adjusted to the , , , and experimental axial-vector coupling constants [149].
The model calculations for are in agreement with the experimental data for the axial form factor [44,46,151,152]. Also, the calculations for are in agreement with the data obtained at very low by muon capture and from pion electroproduction [46,153]. Notice that, apart from the valence quark contributions for , estimated from lattice QCD data (small relative contributions), the model calculations of are predictions.
3.3. Extension of the Model to the Nuclear Medium
The formalism discussed in the previous sections can be extended from the free space to nuclear matter. We consider here the simplest case, the symmetric nuclear matter associated with a medium with equal density of protons and neutrons.
In symmetric nuclear matter, the hadrons behave like free particles with effective masses ( for mesons and for baryons) modified by the interaction with the nuclear medium and modified baryon–meson couplings. These medium modifications are calculated using the QMC model, where the interaction with the medium is described using the self-consistent interaction with Lorentz–scalar–isoscalar and Lorentz–vector–isovector fields. The calculations of the baryon–meson coupling constants, discussed below, use the MIT bag model/QMC model bare axial couplings [34], meaning that they take into account only the valence quark contributions. The effective masses of the mesons and baryons are calculated using the QMC model [3,154,155]. The values for the densities , , and are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Meson and baryon masses are in GeV [154,155].
The calculations of the coupling constants are based on the Goldberger–Treiman relation [17,156]:
where represent the baryon B bare axial coupling [bare contribution to in medium], and is the in-medium pion decay constant (units of energy). In the second equation, we approximate . In Equation (45), we consider the diagonal case (), but the case can be calculated with minor modifications [17].
The constant depends on , and it is calculated using a chiral perturbation theory expression derived in Ref. [157], assuming also that the pion mass is almost unchanged in medium (), where is the mass of the pion in free space.
The extension of the covariant spectator quark model to nuclear matter takes into account the medium modifications determined by the QMC model. In the valence quark component of the model, we consider the medium modifications in the hadron masses in the quark current and the baryon mass modification () in the radial wave function . As for the meson cloud component, we consider the modifications on the baryon–meson coupling constants as presented in Table 3. In the table, we use and for simplicity.

Table 3.
Ratios , and coupling constant ratios (no dimensions). We use and . The values for are from Ref. [34], and the values for are from Ref. [157].
In the electromagnetic transitions, we take into account the modification in [17]
where the power 2 takes into account the double pion–baryon coupling of the processes from Figure 1.
In the axial transitions, we take advantage of the fact that the different baryon–meson couplings can be represented as linear combinations of to write [5]
where the medium modifications on cutoff are neglected in the first approximation. A consequence of the relation (47) is that the meson cloud function is also modified in medium, and
The medium variation in implies that the normalization factors of the wave functions due to the meson cloud are also modified in the form
where the coefficients are determined by Equation (39).
The values of are calculated in Refs. [5,44]
For each density, the value of is determined imposing that for consistency, with the QMC model used in the calculation of in-medium masses and coupling constants [5].
3.4. Summary of the Formalism
In the previous sections, we reviewed the formalism associated with the calculation of the electromagnetic and axial form factors of octet baryons in free space and in nuclear matter. The contributions to the form factors are decomposed into valence quarks and meson cloud contributions. For the calculations in nuclear matter, we combine the covariant quark model and the QMC model to take into account the medium modifications associated with the hadron masses and baryon–meson coupling constants and calculate the electromagnetic and axial form factors in terms of the medium density.
The formalism discussed is mainly based on Refs. [5,17,18,44,54]. The electromagnetic and axial form factors of the octet baryons are first studied in free space in Refs. [44,54]. The study of the electromagnetic form factors is then extended to nuclear matter in Refs. [17,18]. The in-medium axial form factors are discussed in Ref. [5]. The present work is the first time that the electromagnetic and axial form factors of the octet baryons are discussed in a combined form.
The covariant spectator quark model was originally developed for the study of the nucleon electromagnetic form factors and nucleon parton distribution functions in deep inelastic scattering [51,52,103] and has since been extended to the study of the electromagnetic structure of baryons based on the SU(3) flavor-symmetry [53,55], as well as a significant number of nucleon resonances [40,49] in different spacelike and timelike regions. Details of the formalism and references to different applications of models can be found in Section 1 and Section 3.
The motivation to the extension of the covariant spectator quark model formalism to the nuclear medium has been the development of tools that can be used in the study of electromagnetic and weak interactions of baryons in dense nuclear matter based on the observable degrees of freedom in free space.
In the next section, we present and discuss numerical calculations of the electromagnetic and axial form factors in free space and in nuclear medium for the octet baryons and transitions between octet baryon states.
In Section 5, we discuss the extension of the formalism for densities above the normal nuclear matter and explain how the baryon form factors can be used to calculate neutrino/antineutrino–baryon cross-sections in terms of the neutrino energies and the square transfer momentum.
The discussion about the advantages and limitations of the formalism, the contribution of the present work to the field, and future developments will be presented in Section 6.
4. Electroweak Form Factors in Nuclear Medium
The formalism discussed in the previous section has been used in the calculation of the octet baryon electromagnetic form factors in the nuclear medium [17] and the weak axial transition form factors between octet baryon members in the nuclear medium [5]. In the calculations, we used the densities and in comparison with calculations in free space ().
In the study of the electromagnetic form factors, we consider the simplest approximation, when the octet baryon structure is represented by a quark–diquark S-state [17,54] [based on Equation (11)]. In the study of the axial form factors, we consider a combination of S- and P-states since it was demonstrated that the inclusion of a quark–diquark P-state is necessary for an accurate description of the nucleon axial transition form factors [5,44].
In this section, we omit the discussion of the results for the neutral baryons, except for the neutron, because in these cases we cannot expect very accurate estimates for the electromagnetic and axial form factors. Recall that the electric form factors of neutral baryons are proportional to near . The limitations in the electromagnetic form factors are a consequence of the lack of lattice data for and . As for axial form factors, the and axial-vector form factors are dominated by the meson cloud contribution (poorly constrained by the data) since the valence quark contributions vanish [5,44].
For the comparison with the in-medium experimental data, it is important to know the uncertainties associated with the model calculations in nuclear matter. The precision of our calculations is determined by the precision of the QMC parametrizations of the hadron masses and baryon–meson couplings. Based on the parametrizations of the hadron masses [154,155], we can estimate the uncertainties of the model calculations as better than 2%, assuming a similar precision for the axial-vector couplings. The same relative precision should be expected for calculations of form factors at finite due to the dominance of the linear terms for small variations in the input parameters.
4.1. Electromagnetic Form Factors
We now review the calculations of the electromagnetic form factors of the octet baryons from Ref. [17]. The electromagnetic form factors include the valence quark and the pion cloud contributions. In general, the valence quarks provide the dominant contribution, with more than 80% of the total, while the pion cloud contributions are at most 10%. In the nuclear medium, the valence quark contributions are more modified than the pion cloud contributions [5]. The exceptions to these conclusions are the results for the electric form factors of neutral baryons (neutron, , , and ) that have in general smaller magnitudes than the charged baryons.
We start by discussing the medium modifications on the form factors and . Since the in-medium form factors and cannot be directly measured at the moment [18], in a second stage, we discuss the medium effects on the ratio .
4.1.1. Electromagnetic Ratios and
As mentioned already, a simple way to study the impact of the medium effects on the form factors is the calculation of the ratios between the functions ( and ) in medium and in vacuum for the same value of .
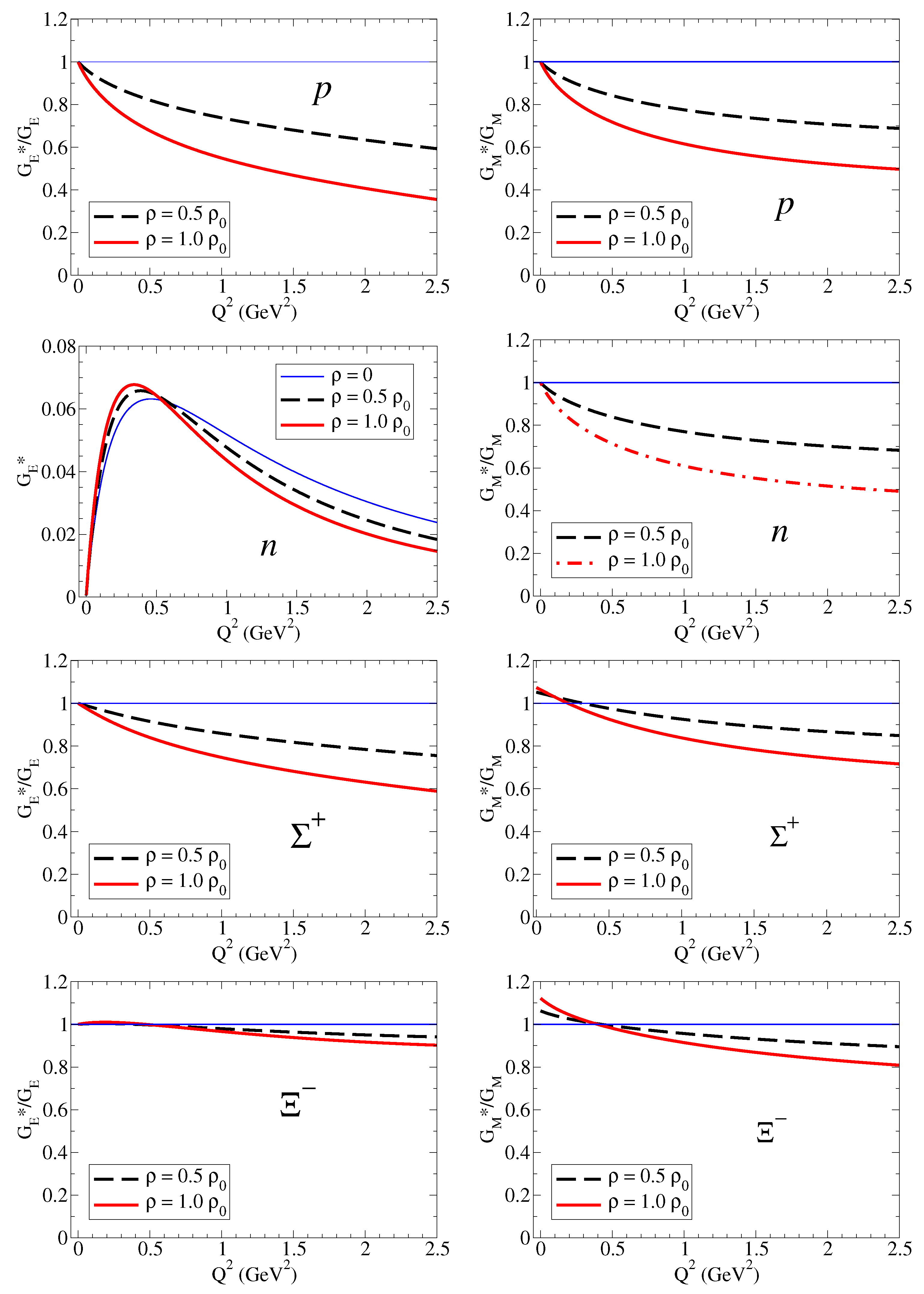
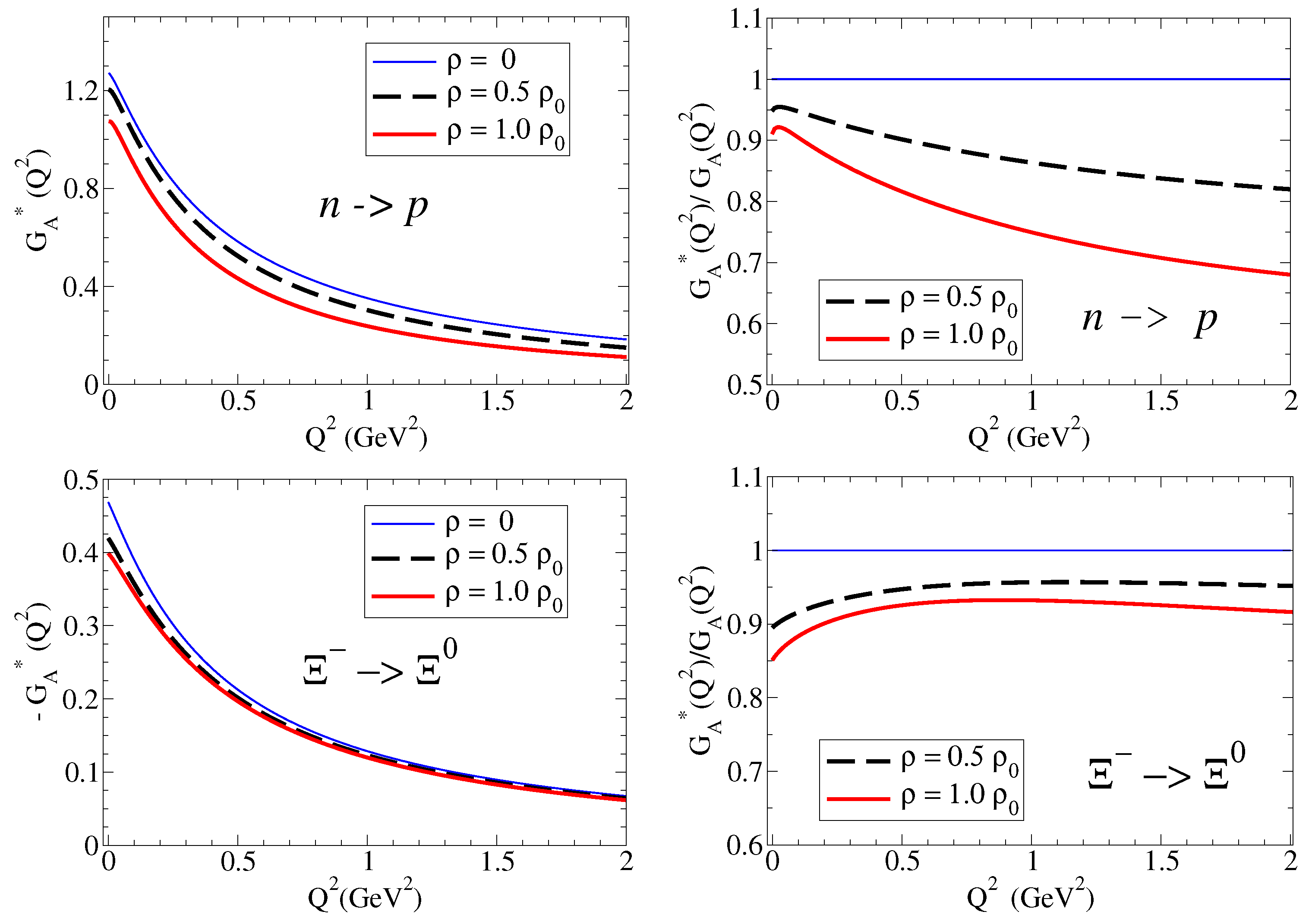
We then calculate the ratios and for the baryon B: proton, neutron, , and for the densities and . Later on, we discuss the similarities with the remaining cases. The numerical results are presented in Figure 2 on the left side for and on the right side for . In the case of the neutron, due to the small magnitude and the particular dependence on , it is more appropriate to compare the magnitudes of the form factors directly. In the case of the and (neutral particles), we may observe the divergence of due to zero of the electric form factors in free space. See Ref. [18] for a more detailed discussion.
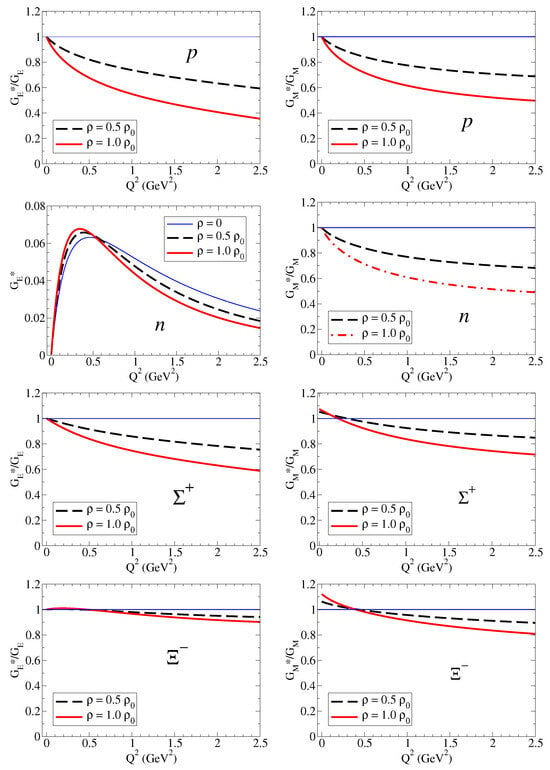
Figure 2.
Electric and magnetic form factor ratios for the nucleon: proton, neutron, , and . The magnetic form factors are in natural units ( and ). The horizontal line is included to represent the ratio in free space. In the case of the neutron, we display instead of the ratio for a cleaner comparison.
From the results for the ratio , we can conclude that the form factors for p, , and are suppressed in the nuclear medium, and also that the suppression increases with the density. We can also conclude that suppression with is more effective for systems with light quarks than for systems with one or two strange quarks. In the case of the , the ratio is almost the unity.
From the results for for the neutron, the main conclusions are that the magnitudes of are small compared to the charged cases (), and the variations due to the medium are small in magnitude. One can also conclude that is reduced in medium below GeV2. We can understand this result noticing that, at low , one has . As a consequence, , where and are the neutron square charge radius in medium and in vacuum, respectively.
The results for the ratio , displayed on the right side of Figure 2 show a trend similar to that observed for . Differently from Ref. [17], we represent here the magnetic form factors in natural units [see Equation (7)]. The ratios for and are similar to the ratio for . There are also similarities between the cases and and and . These similarities are a consequence of the approximated SU(3) symmetry in the expressions for the bare and meson cloud contributions.
The results from Figure 2 for the for the proton, , and are interpreted as the enhancement of the absolute value of the charge radius in medium (). The results for the proton and neutron magnetic moments can also be interpreted as an enhancement of the magnetic radius in medium (). We follow here the interpretation of Ref. [22]. A more detailed discussion of the octet baryon electric and magnetic ratios can be found in Ref. [17].
The ratios and for the nucleon have been calculated using Skyrme and quark–soliton models [21,25,29,38,39], QMC models [20,21,26,27,28], Nambu–Jona–Lasinio, and light front quark models [19,22,23,35]. In general, one observes a reduction in both and in the nuclear medium at low . As in our model calculations, the suppression is more significant for than for , increases with the density, and with up to GeV2. See for instance Refs. [19,20,21,25,26,39]. In the case of the neutron, an enhancement of the electric form factor [22,23] is expected. The magnitude and shape of the functions and depend on the specific nucleus and on the considered orbital states [20]. In the case of bag and QMC models, the trend of the ratios changes after a certain value of (0.5 or 1 GeV2) [20,26].
It is worth mentioning that, when we convert for the nucleon to units of nuclear magneton, the numerical results are modified by the factor (see Section 2.1). In that case, we expect to obtain, at , a ratio larger than unity (enhancement of magnetic moment in medium). This enhancement of the magnetic moment in medium [in units ] has been reported using different frameworks dominated by the valence quark degrees of freedom [22].
4.1.2. Electromagnetic Double Ratios of Octet Baryons
Since the measurements at JLab of the ratio between the electric and magnetic form factors using the polarization transfer method for the proton [128,129,130,131,132,158,159,160,161] and for the neutron [141], there is the perspective that the method may be extended to other baryons and to baryons bound to a nucleus. The interaction with baryons bound to a nucleus can be regarded as the interaction with a baryon immersed in a nuclear medium (quasi-elastic reaction) [18]. At the moment, there are only complete measurements of the ratio for protons on 4He targets [9,10,11,12,13]. There is the possibility that the experiments can be extended for 2H, 8O, and 12C targets [14,15,16]. Under study are extension of the experiments that measure the ratio for bound neutrons [30].
Experiments at JLab and MAMI measured the ratios for bound protons () and for free protons (). The ratio between the medium and vacuum
can be used to measure the effect of the nuclear medium on the ratio . If , there are no medium effects. If , the ratio is reduced in nuclear medium (quenching effect). If , the ratio is enhanced in nuclear medium.
The medium effects on the magnetic moments are usually discussed and measured in units of nuclear magneton, as discussed in Section 2.1. For that reason, in the following, we convert the double ratios from Equation (51) into units of nuclear magneton in vacuum . In the conversion of magnetic form factors from natural units to nuclear magneton, we multiply by the factor in free space and by in the medium. The overall conversion for the double ratio is then . We then use the factor in the conversion of to nuclear magneton.
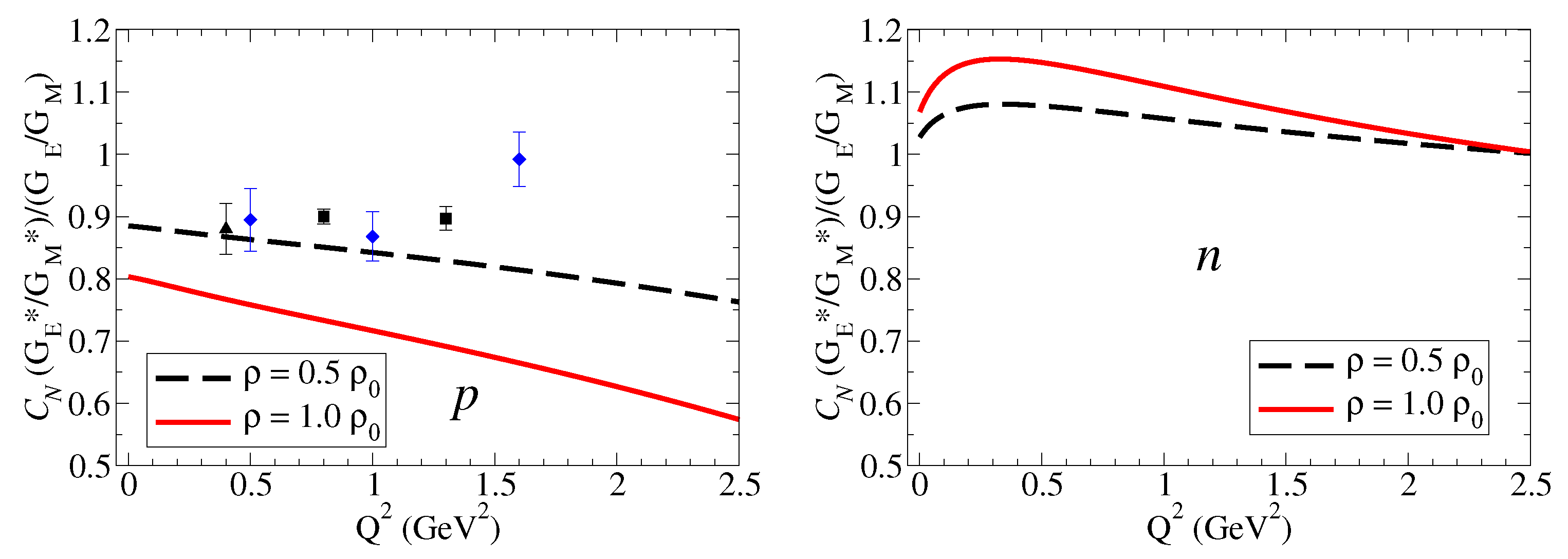
Our calculations of the double ratios for the nucleon and and , converted to nuclear magneton, are presented Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively. As before, we consider the densities and .
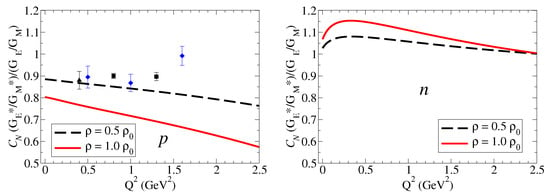
Figure 3.
Proton and neutron double ratios in units of nuclear magneton. . The proton data are from MAMI [9] (black) and JLab [10] (blue).
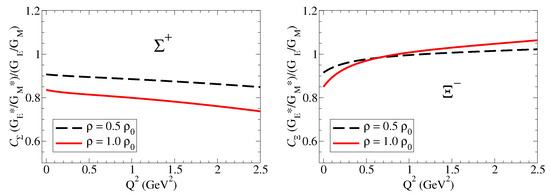
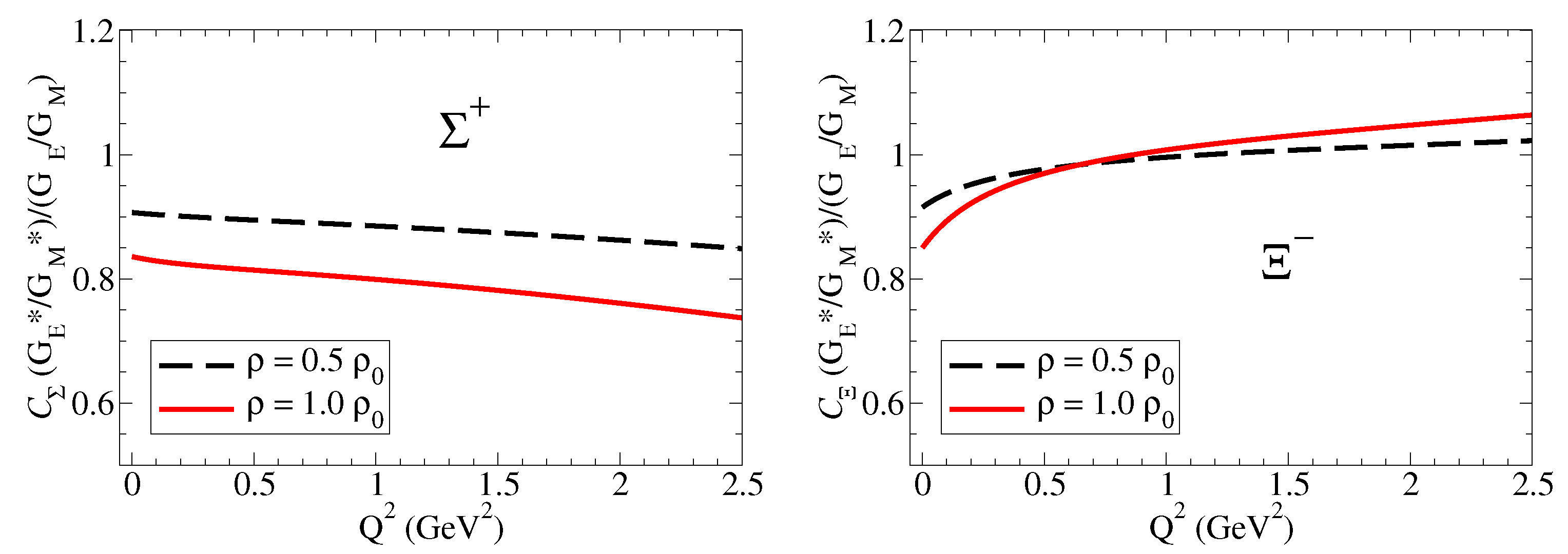
Figure 4.
and double ratios in units of nuclear magneton. and .
On the right side of Figure 3, the model calculations for the proton are compared with the experimental results from MAMI and JLab [9,10]. The calculations of the proton double ratio, presented on the right side of Figure 3, suggest that is suppressed in the nuclear medium. Noticing that the double ratio can also be written as , we can then conclude that the suppression of is a consequence of the stronger suppression of comparatively to . A more detailed analysis [18] shows that is suppressed in the nuclear medium because both the electric square radius and the magnetic square radius are enhanced in the nuclear medium, but dominate over (in the low- region, we can write [22]). From the comparison of the model calculations with the data, we conclude that the 4He data are better described by a calculation with a smaller density () than the calculation with dense nuclear matter (). The uncertainty of the data (about 5%) is in the present case larger than the model uncertainty (about 2%). The difference in the double ratio predictions for the two densities (about 10%) suggests that future experiments may distinguish the double ratios for low dense nucleus () from more dense nucleus ().
The predictions for the neutron contrast with the model calculations for the proton (quenched effect). According to the results from left side of Figure 3, we expect now an enhancement of for the neutron for GeV2. We can understand this trend by recalling that . The enhancement of in medium is then a consequence of the enhancement of in medium, an effect that dominates over the multiplicative factor . When increases, however, the enhancement effect is reduced, and one may expect a suppression of the double ratio for GeV2.
From the analysis of the model calculations of the neutron double ratio, we can conclude that a maximum is expected for the region –0.5 GeV2. We can also conclude that the difference between the two calculations (about 7%) is maximal in the same region. The maximum on the double ratios is a consequence of the enhancement of in the nuclear medium in the region, as shown in Figure 2 for the neutron combined with the suppression of . Above GeV2, and are enhanced with similar rates with dominance of , leading to a smooth convergence to the unity (almost no medium effect) near GeV2. In principle, measurements of double ratios for nuclei with intermediate density () can be distinguished from double ratios of nuclei with higher densities () when the precision of the measurements is closer to the model accuracy (2%). In general, we can expect to measure an enhancement of about 10% near GeV2 for a nucleus of intermediate density ().
To summarize the results for nucleon double ratio: In the case of the proton, and are both reduced in the nuclear medium, but there is a dominance of (stronger suppression). In the case of the neutron, is enhanced, is enhanced, and, as a consequence, the double ratio is positive ( is enhanced in units of nuclear magneton).
The double ratio for the nucleon has been calculated using the QMC model [20], quark–soliton model [21], and light front quark models [22,23]. Model calculations predict in general the quenching of the ratio for the proton in the range of 5% to 10% at low depending on the density [21,22,23]. As for the neutron, Refs. [22,23] predict, as our model, an enhancement of for GeV2. Calculations based on light front quark model and Nambu–Jonas–Lasinio model, with manifest dominance of the valence quark effects, lead to the conclusion that, near , the neutron double ratio can be estimated by , corresponding to an enhancement of about 20% [22].
The model calculations for and double ratios are presented in Figure 4. The results for the (right side) are similar to the results for the proton, except for the slower falloff with . We can understand these results noticing that we should expect slower falloffs comparatively to the case of the proton for both and as a consequence of the reductions in and compared to the proton, as expected from a system with a strange quark (more compact system).
The analyses of the results for , on left side of Figure 4, require some care. At low , the quenched effect is a consequence of the near independence of in medium (notice in Figure 2 that ) and the enhancement of . At large , one can notice a very slow increment regarding the double ratio, very close to unity, the signature of the smooth medium variations, as expected in a system dominated by strange quarks.
A more detailed discussion of the double ratios, including the neutral baryons (, , and ) is presented in Ref. [18].
4.2. Axial Form Factors
We discuss now the calculations of the axial form factors and in nuclear medium based on the formalism from Section 3. These calculations use the model developed in Ref. [44] for the octet baryon axial form factors in free space. The valence quark contributions are calculated using the expressions presented in Section 3.1.3, where the quark axial form factors are determined by the analyses of the lattice QCD data for the nucleon from Ref. [110], while meson cloud contributions are estimated using the nucleon form factor data for and the octet baryon axial couplings (see Section 3.2.2).
As mentioned already, there are 12 possible transitions associated with charged currents between octet baryon members: 6 associated with transitions, and 6 associated with transitions (see Table 1). There are also 8 elastic transitions associated with neutral currents. We focus here on the inelastic transitions (charged currents) since the elastic form factors can also be related to the transition form factors.
It is also worth noticing that, in our formalism, the form factors associated with the and transitions differ by a sign, and the form factors associated with the and are identical. There are then only 4 independent transitions to discuss.
The discussion about the magnitude and shape of the 10 independent axial transition form factors is simplified when we consider a few typical cases associated with each channel ( or ), depending on the baryon masses. Notice that the mass increases with the number of strange quarks of the baryon.
The extension of the calculations of the octet baryon axial form factors from the free space to the nuclear medium was motivated by the quality of the description of the nucleon lattice QCD and the nucleon physical data for and , combined with a fair description of the , , and axial couplings [5,44].
4.2.1. Axial-Vector Form Factor
A detailed discussion of the axial-vector form factors in vacuum can be found in Refs. [5,44]. Here, we mention only the general properties. The available free space data are well described by a combination of valence quark and meson cloud contributions. The magnitude of the axial-vector form factors varies with the transition under discussion. At , the absolute values of are between 0.2 and 1.3. The valence quark contributions are dominant, but the inclusion of the processes associated with meson cloud helps to improve the description of the physical data.
The calculations for the nucleon axial-vector form factor ( transition) are in agreement with the known data for the axial-vector form factor in the regions –1 GeV2 and –4 GeV2 [46,48,151].
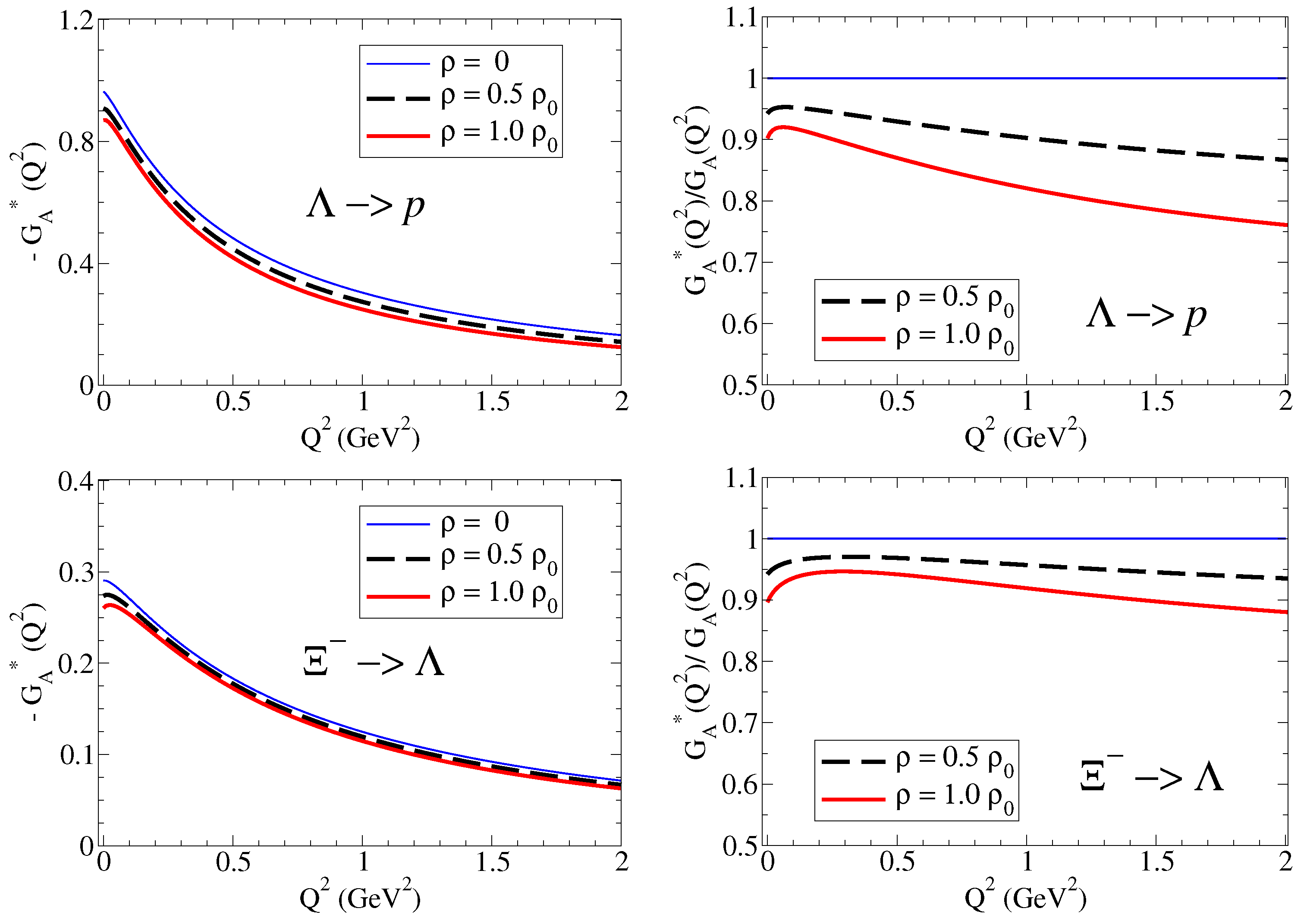
Calculations of transitions and transitions are presented in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively, for the vacuum (), , and . On the left side, we present the explicit form factors; on the right side, we consider the ratio .
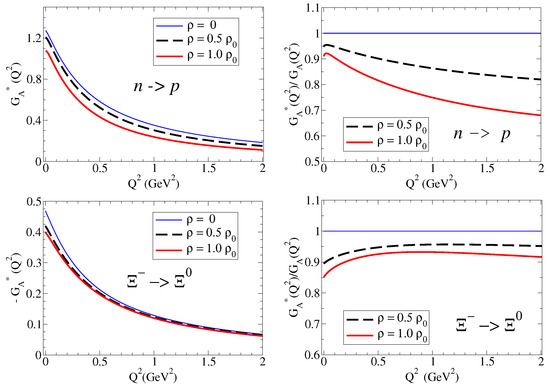
Figure 5.
and axial form factors in nuclear medium ( transitions). We use for the negative functions for an easy comparison of magnitudes. The horizontal line () is included to represent the ratio in free space.
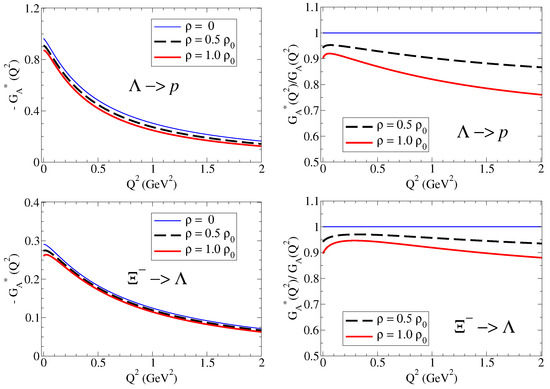
Figure 6.
and axial-vector form factors in nuclear medium ( transitions). We use for the negative functions for an easy comparison of magnitudes. The horizontal line () is included to represent the ratio in free space.
From Figure 5 and Figure 6, we can conclude that transitions associated with the lighter baryons ( and ) are strongly suppressed in nuclear medium. In contrast, in the transitions associated with heavier baryons ( and ), the impact of the medium is milder, and the suppression is less significant. Notice that the lines became flatter for larger values of . The suppression increases with , particularly for transitions with lighter baryons. As expected, the medium effects are more noticeable for more dense nuclear media, represented here by . For the normal nuclear matter (), the suppression for GeV2 can be about 30% for lighter baryons ( transition) and about 15% for heavier baryons ( transition).
Overall, the valence quark and meson cloud contributions are suppressed in medium but in different proportions. The suppression of the meson cloud contribution is more noticeable at low . The impact of the medium on the bare contributions is more visible at large , when the meson cloud contributions are almost irrelevant, and the falloffs of the form factors are regulated by quark power counting rules.
For the axial-vector form factors associated with the remaining transitions, not presented here, we can observe an intermediate suppression in medium.
The calculations presented here for the nuclear medium are based on the QMC model and the bag model [34]. We use the QMC estimates for the nucleon axial-vector coupling constant associated with the density (see Section 3.3 and Table 3). The QMC model predicts, at , the quenching of 5% for the density , and 10% for the normal nuclear matter (). Similar proportions are obtained in our final results when we take into account the contributions from the meson cloud.
We discuss now the literature about the nucleon axial-vector form factor in nuclear medium.
Measurements of beta decay rates in heavy nuclei, more than 50 years ago, showed that the axial-vector of the nucleon is reduced by about 25% [31,32], providing evidence that the axial-vector form factors are quenched in nuclear medium.
Calculations based on the effective theory that take into account two-body interactions [32] are consistent with the quenched effect of 0.75, observed on nucleon beta-decay rates of heavy nuclei [31].
Skyrme, soliton, and quark–soliton models [35,36,38,39] are particularly useful to estimate the medium effects on the axial-vector of baryons in general and the nucleon in particular because the reduction in in-medium quark mass can be taken into account in a simple form. In the leading order, the calculation underestimates the observed nucleon axial-vector coupling, but more accurate results are obtained when higher-order corrections are taken into account [35,38,39]. Skyrme and soliton model calculations also predict the quenching of the axial-vector coupling constant and the function . Explicit calculations can be found in Refs. [35,36] for different densities.
To finish our discussion, we compare our estimates with the QMC model [34,162,163] used in the calibration of our model (ratio . The main difference between the calculations is that we include a contribution for the meson cloud. Apart from small differences at low , the calculation differs in the shape of the ratio . In the bag model, the ratio decreases until –1 GeV2 and starts to increase after that value, displaying an enhancement for larger values of , due to the relativistic Lorentz contraction effect. In our calculations, the quenching effect increases with .
4.2.2. Induced Pseudoscalar Form Factor
The literature about the induced pseudoscalar form factor is scarce because it is hard to measure since the contributions to the neutrino/antineutrino cross-sections are suppressed by a factor , where is the lepton mass associated with the weak transition [46,47,164]. The available data for the nucleon came from pion electroproduction experiments and muon capture by nucleons [46,153].
The results of the induced pseudoscalar form factor differ significantly in magnitude for the channels and . This result is a consequence of the pole term (28), which dominates the function near , leading to , where for and for .
Calculations of the induced pseudoscalar form factors of the octet baryons based on the covariant spectator formalism in vacuum are discussed in Refs. [5,44]. The results for the transitions are, in general, dominated by the pole term, although the meson cloud contribution (no adjustable parameters) is also relevant to the agreement of the model with the experimental data for the transition. As for the transitions, the magnitude of the form factors is significantly reduced, and the dominance of the pole term is less effective. In that case, the bare term has a larger relative contribution and cancels parts of the pole and meson cloud terms [44]. These general properties are also observed in the nuclear medium [5].
The calculations of for the transition are in good agreement with the electroproduction data extracted with low-energy theorem [153] and with the muon capture data [46] in the range –0.2 GeV2. The model calculations are also in close agreement with the lattice QCD simulations for pion masses in the range –265 MeV for GeV2 [111]. These results are discussed in detail in Ref. [44].
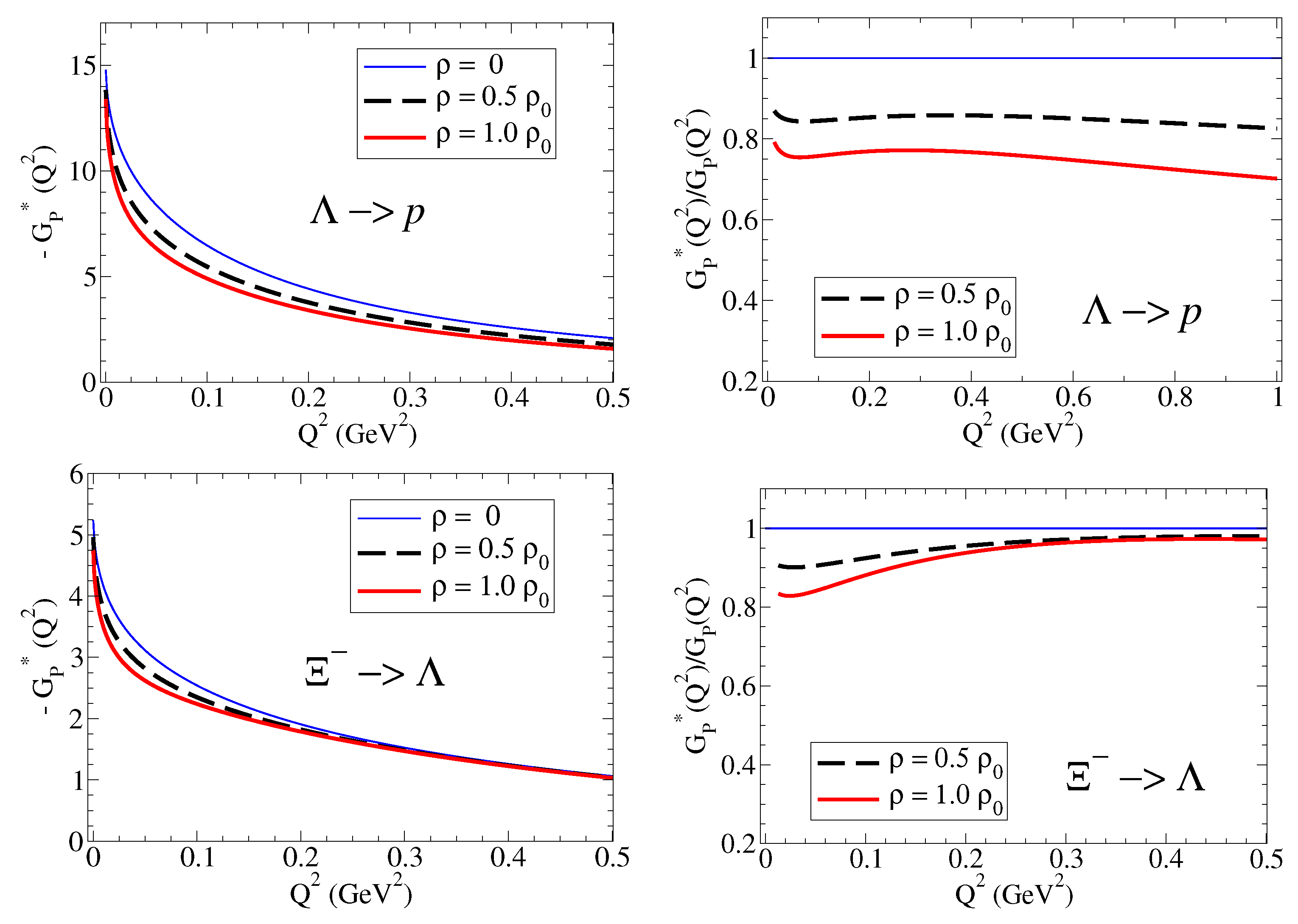
Calculations of for the transitions: and in vacuum and in medium are presented in Figure 7. Calculations for the transitions: and are presented in Figure 8. The results for the form factors are on the left side, and the ratios to the vacuum () are on the right side. Notice the difference of about an order of magnitude for between the or channels.
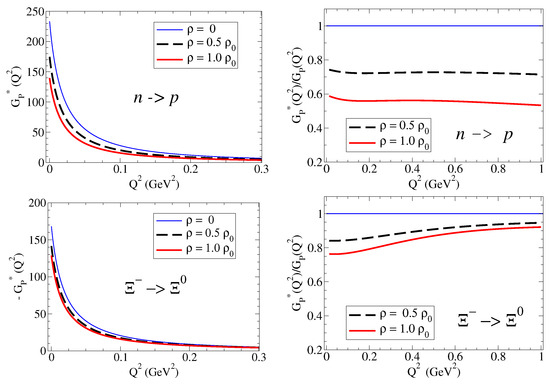
Figure 7.
form factors for the and transitions () in nuclear medium. For an easy comparison of magnitudes, we use for the negative functions. The horizontal line () is included to represent the ratio in free space.
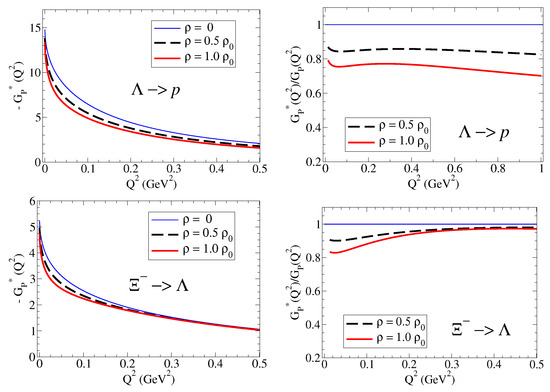
Figure 8.
form factors for the and transitions () in nuclear medium. For an easy comparison of magnitudes, we use for the negative functions. The horizontal line () is included to represent the ratio in free space.
In both cases, one can observe the reduction in the function in nuclear medium. The difference in magnitudes of the two channels is clear in the figures. The values for are about an order of magnitude larger for transitions than for transitions.
The calculations for the transitions (Figure 7) show a significant suppression in the nuclear medium. This result is mainly a consequence of the dominance of the pole contribution discussed above. Using this property, we can write . The reduction in the masses in medium (power 2) and the suppression of in medium both contribute to the significant suppression of the function at low . Notice that the suppression is more significant for light baryons () than for heavy baryons (). For heavy baryons, the more significant suppression at low is a consequence of the meson cloud effects on .
In the case of the transitions (Figure 8), one can notice, apart the difference in magnitudes mentioned above, the slower falloff of with , a consequence of the dependence of pole term on the mass of the kaon.
In the low- region, the suppression of in nuclear medium is clear. This result is a consequence of the suppression on the meson cloud contribution, included in , and the dominance of the pole term , where the impact of the baryon mass reduction in medium is partially canceled by the reduction in the in-medium kaon mass.
In the large- region, the effect of the kaon mass is irrelevant, and we recover the result , where and are well approximated by their bare results. As a consequence, there is a significant reduction in compared with unity (reduction due to the in-medium baryon mass reduction and the in-medium reduction in ) for transitions associated with light baryons, like for , or almost no medium modifications for transitions associated with heavy baryons, like for .
For the remaining transitions, the magnitude of the suppression is between the magnitudes discussed here [5].
5. Applications
We consider now two useful extensions of the formalism discussed in the previous sections. First, we consider calculations of the nucleon form factors for intermediate densities, below the normal nuclear matter density (). After that, we look for the extension of the calculations of the octet baryon form factors for more dense nuclear matter (). The first application can be used in the study of protons and neutrons bound to a nucleus. The second application is suitable for studies of heavy-ion collisions and cores of compact stars.
5.1. Nucleon Bound to a Nucleus
The study of the electromagnetic and axial structure of nucleons bound to a nucleus can be conducted considering the parametrizations of the hadron masses (baryons and mesons) and the values of baryon–meson coupling constants for the nucleus average density . In practice, we obtain a value between free space () and the normal nuclear matter (). We follow the method discussed in Section 3.3 and calculate the hadron masses and the coupling constants for the average densities of some nuclei. The average densities calculated by the QMC model [69] are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Average densities of nucleus calculated by the QMC model [69].
In the discussion, we consider three typical cases: 12C (12C), 40Ca (40Ca), and 208Pb (208Pb). The form factors , , and are presented in Figure 9. For the axial-vector form factors, we use the relations and , following Table 1.
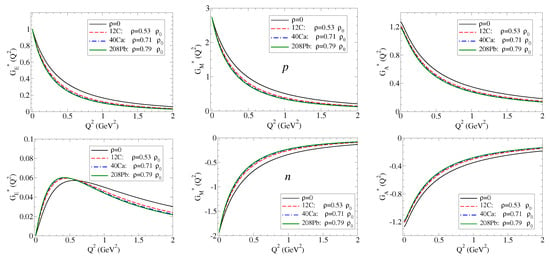
Figure 9.
, , and form factors for the nucleon bound to a nucleus.
From the results in Figure 9, we can conclude that the proton and the neutron electromagnetic and axial form factors are in general reduced in the nuclear medium compared to the free space (). The conclusion is exact for . The exceptions are the results for and at . The value of is the same in medium and in vacuum because the charge is preserved in medium. The result for is approximately the same in medium and in vacuum due to the dominance of the valence quark contribution [18]. The explicit expressions for the bare contribution to are presented in Table A3/Appendix B.1.
Our model calculations for n and p form factors for and have been used in the calculation of the , , and single-differential cross-sections, as well as the and single-differential cross-sections [5,162,163]. Here, represents the electron neutrino. From the calculations, one can conclude that the in-medium single-differential cross-sections are suppressed compared with the free space, and that the the suppression increases with the density [5].
The numerical calculations for the neutrino energy of MeV, a typical energy for neutrinos ( GeV2), for a density are presented in Figure 10. Higher neutrino energies are achieved in experiments with KDAR neutrinos, muon neutrinos generated by kaon decay, where the neutrino energy is MeV ( GeV2) [165]. Within our framework the electroweak form factor calculations can be extended to larger neutrino energies , corresponding to larger values (in the massless neutrino limit, the maximum value of is determined by , where M is the nucleon effective mass) [5].
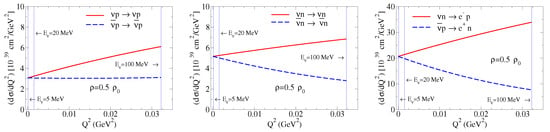
Figure 10.
Single-differential cross-sections in terms of [5]. Comparison between and (left); and (center); and and (right) for the neutrino/antineutrino energy MeV. The nuclear matter density is . The vertical lines indicate the upper limit in for MeV, MeV, and MeV.
The comparison between and cross-sections presented in Figure 10 is consistent with the well-known dominance of the neutrino–nucleon cross-section dominance over the antineutrino–nucleon cross-sections observed in BNL and other experiments [162,163,166,167,168].
The numerical calculations of nucleons , , and form factors can also be used in the calculation of the coherent neutrino scattering on nucleus, in the low- limit, defined by , where R is radius of the nucleus [168,169,170,171,172,173,174,175].
5.2. Hyperons in Dense Nuclear Matter
We now discuss calculations for the electromagnetic and axial-vector form factors of the octet baryon members for densities larger than . We follow the formalism from Section 3.3, with an alternative model for the pion-decay constant , where the original expression derived from perturbation theory [157] is modified for , in order to saturate at a certain value of near [176]. As an example, we consider calculations up to .
The calculations for the nucleon (p and n) are presented in Figure 11, and the calculations for the and are presented in Figure 12. For the last case, we used and (see Table 1). Similar relations can be derived for and .
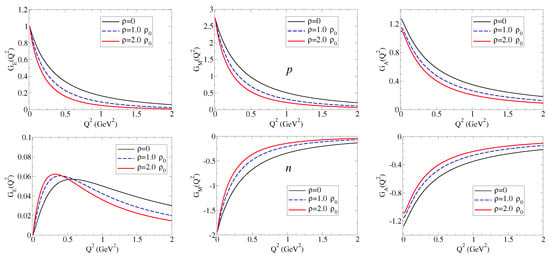
Figure 11.
, , and form factors for the nucleon bound to a nucleus ().
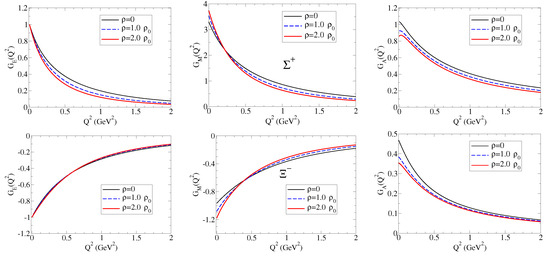
Figure 12.
, , and form factors for and bound to a nucleus.
From the results for the nucleon (Figure 11), one can confirm the trend observed for . Except for the electric form factor of the neutron, the form factors are reduced (quenched) in the nuclear medium.
In Figure 11, one can notice that the electric form factor of the neutron is suppressed for GeV2 when compared with the function in free space. The same happens to the proton and form factors and to the neutron form factor. These results are a consequence of the dominance of the valence quark contributions on the nucleon electromagnetic form factors for large . In these conditions, the electromagnetic form factors are determined by the quark form factors, parametrized in a vector meson dominance form in terms of vector meson poles in nuclear medium (see Appendix B.1). The suppression of the form factors in medium is then the consequence of the reduction in the vector meson masses in medium. The functions associated with lower masses (higher densities) are suppressed relative to the functions associated with larger masses (lower densities).
As for the hyperons (Figure 12), one has a similar reduction in form factors, except for the magnetic form factors, which are enhanced at low and suppressed at large . In the present model, the enhancement of is a consequence of the dominance of bare contribution to near . Near , the bare contribution to is enhanced if the mass of the baryon B in medium () is larger than the nucleon mass in medium (). The explicit expressions for the bare contributions to are presented in Table A3/Appendix B.1. The trend changes for larger values of , as can be observed in the figures.
The medium effects on and for and can be inferred from the results for and using the SU(3) symmetry, a good approximation in these cases. Notice for in Figure 12 the very mild dependence of the electric form factor in . Systems with more strange quarks tend to be less affected in nuclear medium.
The discussion of changes when we convert the results to nuclear magneton units in the free space. In that case, is, in general, enhanced at low [18].
The present formalism, combined with model parametrizations of the neutrino/anti-neutrino flux, can be used to calculate differential cross-sections for neutrino/antineutrino–baryon scattering in nuclear medium in terms of , as well as the neutrino and antineutrino mean free paths in dense nuclear matter (densities above the normal nuclear matter) [162,163,166,168,177].
The conclusion of this section is that the neutrino/antineutrino–nucleon cross-sections are in general reduced in the nuclear medium. Under study is the impact of the hyperon form factors on the neutrino/antineutrino–hyperon cross-sections, and other interactions with neutrinos in a nuclear medium [176].
6. Discussion
The results presented in Section 4 and Section 5 correspond to two different applications of the covariant spectator quark model to symmetric nuclear matter. The model for the electromagnetic form factors [17] is based on the simplest model for the quark–diquark system based on an S-state wave function. In the study of the axial structure, it was concluded that the S-state model was insufficient to describe the observed experimental data as well as the lattice QCD data for the nucleon axial form factors, and the model was improved with the inclusion of a P-state [5,44]. In the future, we should consider a combined analysis of the electromagnetic and axial structure of octet baryons. New lattice QCD simulations for electromagnetic and axial transitions with accurate data for neutral baryons (neutron, , and ) can also help to improve the description of the octet baryon form factor data in the free space.
The model description of the physics associated with meson cloud dressing can be improved. The contributions of the kaon cloud that have been proven to be relevant for some electromagnetic transitions should be taken into account in more detailed studies of the electromagnetic and axial structure of octet baryons. The inclusion of a kaon cloud component automatically improves the description of the axial-vector coupling due to the correction of the normalization constant [reduction in ] [5]. The effect of the kaon cloud will also improve the description of the baryon octet electromagnetic form factors since the coupling with the kaon is expected to be stronger for the and systems [17]. Concerning the meson cloud contributions to the axial form factors, there is also the opportunity of improving the model considering a more theoretically motivated parametrization of the meson cloud, taking into account the explicitly pion and kaon cloud contributions weighted by explicit SU(3) baryon–meson coupling.
In our studies, we also provide calculations of the induced pseudoscalar form factor , seldom discussed in the literature. These calculations are predictions of the model since no free parameters are adjusted in the calculations, except for small bare contributions, determined by the analysis of the lattice QCD data for the nucleon.
From the experimental side, we expect that, in the near future, the proton in-medium form factors will be measured for several nuclei. There is the hope that new experiments based on the polarization transfer method may provide information about the ratio for the neutron or hyperons bound to a nucleus. Concerning the axial structure of baryons, we expect that new and accurate measurements of beta decays of heavy nuclei may improve our knowledge on the quenching of the nucleon axial-vector coupling in nuclear matter.
The calculations of the electromagnetic and axial-vector form factors are used to study neutrino–nucleon and antineutrino–nucleon single-differential cross-sections in terms of the neutrino energy . The model calculations can be used in the near future for the study of the neutrino–hyperon and antineutrino–hyperon scattering in dense nuclear matter, generalizing the studies on neutrino/antineutrino–nucleon scattering [162,163,166]. The extension of the model for higher densities expands the range of application of the model to studies with astrophysical implications, including neutrino scattering off nuclear targets, high-energy nucleus–nucleon collisions, and cores of compact stars. The study of the neutrino/antineutrino mean free paths in dense nuclear matter is an example of a direct application of the present model. For more realistic applications, we need to consider the case of asymmetric nuclear matter in order to study nuclear systems with different numbers of protons and neutrons.
7. Outlook and Conclusions
The literature regarding the properties of baryons in a nuclear medium is scarce. Theoretical studies on the subject are very important for the study of hadrons in extreme conditions, including nucleus–nucleus and hyperon–nucleons collisions, neutrino and antineutrino propagation in dense matter, neutrino–baryon and antineutrino–baryon in-medium interactions, and cores of compact stars, among other processes.
Models based on the degrees of freedom observed in free space measurements, involving valence quarks and the meson cloud excitations of baryon cores, are particularly useful because they can help in the interpretation of the results based on the physical processes associated with empirical data (vacuum/free space).
The formalism used in the in-medium calculations was tested in previous works in free space, including physical systems and lattice QCD simulations. The latter are important to disentangle the physical mechanisms associated with valence quarks, within our model the interpretation of valence/meson cloud contributions.
We conclude that the electromagnetic and axial structure of octet baryons is modified in the nuclear medium. The impact of the medium effects increases with medium density.
For charged baryons, the absolute values of the electric and axial-vector form factors are in general suppressed in the nuclear medium. As for the magnetic form factor, in general, the absolute value of is reduced in medium above a certain value of in natural units (in units of nuclear magneton in free space, is enhanced at low and suppressed for larger values of ). For neutral baryons, and have small magnitudes and milder in-medium modifications. The magnetic form factors of neutral baryons have properties similar to charged baryons (suppression for finite ). A consequence of these medium modifications is the reduction in the single-differential neutrino/antineutrino cross-sections in medium in neutral-current and charged-current reactions.
The calculations presented here can be used in the study of reactions of neutrinos/antineutrinos with nuclei and reactions of neutrinos/antineutrinos with hyperons in dense nuclear matter (above the normal nuclear matter density). The numerical results for , , and can be used to calculate the single-differential cross-sections for neutrino/antineutrino–baryon scattering in a nuclear medium, and using model parametrizations of neutrino flux to calculate the neutrino/antineutrino–baryon differential cross-sections, as well as the free neutrino/antineutrino mean free paths in dense nuclear matter.
In the future, the methods discussed in the present work for octet baryons can be extended to other baryon systems, like decuplet baryons and transitions between octet baryons and decuplet baryons, as well as for densities larger than normal nuclear matter. For applications to problems with astrophysical implications, we also consider the generalization of the formalism to asymmetric nuclear matter.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, G.R.; writing—review and editing, K.T. and M.-K.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
G.R. and M.-K.C. were supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant No. RS-2021-NR060129). K.T. was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, Brazil), Processes No. 313063/2018-4, No. 426150/2018-0, and No. 014199/2022-2, and FAPESP Processes No. 2019/00763-0 and No. 2023/07313-6, and his work was also part of the project Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia—Nuclear Physics and Applications (INCT-FNA), Brazil, Process No. 464898/2014-5.
Data Availability Statement
The experimental data presented here are available in the literature (references included). The tables with numerical values used in the figures can be supplied upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Gell–Mann Matrices
The Gell–Mann matrices are used in the definition of the octet baryon axial transitions (Section 2) and on the quark electromagnetic and axial currents (Section 3.1.2 and Section 3.1.3). We use here the standard definition [45]
We can also define .
The neutral current transitions ( and ) are associated with the operator
The transitions that increase/decrease the isospin () are defined by
The transitions associated with transitions () are represented by the operator
For the discussion of the quark electromagnetic current, we also define
which can also be written as
where is the SU(3) generalization of the SU(2) unitary matrix.
Appendix B. Information About the Valence Quark Contributions
We consider the octet baryon wave function given by Equations (10)–(12). The flavor wave functions are determined by the SU(3) flavor symmetry as presented in Table A1. The spin wave functions are determined by the covariant spectator quark model [50,51,53,85]
where is the baryon B Dirac spinor in terms of the momentum (P) and spin projection (s), and is the diquark polarization in the fixed-axis representation discussed in Refs. [51,85,106]. The S-state wave function (11) is a generalization of the nonrelativistic wave function [51].

Table A1.
Flavor wave functions of the octet baryons.
Table A1.
Flavor wave functions of the octet baryons.
| B | ||
|---|---|---|
| p | ||
| n | ||
Appendix B.1. Quark Electromagnetic Form Factors
Motivated by the vector meson dominance mechanism, we use the following parametrizations for the quark form factors and ()
where and represent the masses of mesons and , respectively. In this representation, we consider for simplicity the approximation for the isoscalar channels (). The terms with correspond to an effective heavy vector meson that parametrizes the short-range effects. The value of is fixed as [51,87]. Numerically, we use GeV and GeV.

Table A2.
Mixed symmetric () and anti-symmetric () coefficients for the octet baryons defined by Equation (22). The coefficients are used in the calculation of the valence quark contributions to the electromagnetic form factors (19) and (20).
| B | ||
|---|---|---|
| p | ||
| n | ||
In the calculations, we use the quark anomalous magnetic moments
and the parameters
The quark anomalous magnetic moments and were determined by the fit to the nucleon and octet baryon electromagnetic data in Ref. [17], while was determined in the study of the electromagnetic form factors of the decuplet baryons, taking into account the magnetic moment [53]. The renaming parameters were determined in the study of the nucleon and decuplet baryon form factors [51,53].
The form factors () with are related to the flavor form factors ():
where and are the quark charges.
From the previous relations and the normalization of , one can write and .
For the discussion of the magnetic form factors near , we include in Table A3 the valence quark contributions to , in natural units, in terms of in-medium baryon masses.

Table A3.
Explicit expressions for the bare contribution to in terms of the octet baryon mass in medium () and the free space nucleon mass. Values in natural units.
Table A3.
Explicit expressions for the bare contribution to in terms of the octet baryon mass in medium () and the free space nucleon mass. Values in natural units.
| B | |
|---|---|
| p | |
| n | |
Appendix B.2. Quark Axial Form Factors
As discussed in Refs. [5,44], we consider the following parametrizations for the quark axial form factors
where the hadron masses have the same meaning as in the previous section, and
The calculation of the valence quark contributions to the axial form factors and based on Equations (29) and (30) requires the knowledge of the coefficient . These coefficients are determined by the values of , given by Equation (31), and presented in Table A4.

Table A4.
Axial transitions. Coefficients and for the possible axial transitions and the global factor . The column SU(3) is the estimate based on the functions and determined by an SU(3) baryon–meson coupling. For the neutral current transitions: the operators act on the isospin states and for isospin states and act on isospin 1 states (charge operator).
Table A4.
Axial transitions. Coefficients and for the possible axial transitions and the global factor . The column SU(3) is the estimate based on the functions and determined by an SU(3) baryon–meson coupling. For the neutral current transitions: the operators act on the isospin states and for isospin states and act on isospin 1 states (charge operator).
| 1 | |||||
| 0 | |||||
| 0 | |||||
| 0 | |||||
| 0 | |||||
| 1 | |||||
| , | |||||
| 0 |
In the calculation of the overlap integrals, we use the variables
where .
The overlap integrals () are defined as
The integrals take a simpler form at the Breit frame. In the Breit frame,
where is the diquark energy .
The normalization of the radial wave functions, defined in Section 3.1, lead to and . For simplicity, we redefined the integral compared to the previous works [5,44]. Notice, however, that the integrals and are correlated in the limit or according to . The last relation ensures that is finite.
Appendix C. Information About the Meson Cloud Contributions
Appendix C.1. Electromagnetic Transitions
The pion cloud contributions to the octet baryon form actors are calculated based on Equations (37) and (38). The coefficients (), are written in Table A5 in terms of the couplings and the bare functions and .

Table A5.
Pion cloud coefficients for the functions and [17,54,55].
Table A5.
Pion cloud coefficients for the functions and [17,54,55].
| B | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| p | |||
| n | |||
| 0 | |||
| 0 | |||
For the electromagnetic couplings with the meson cloud, we use the values of determined by the SU(6) quark model, defined by [17]:
The functions , , and () are parametrized in terms two generic cutoffs associated with the Dirac () and Pauli () and the values of , , , , and the constant , based on
and
In the last relations, GeV−2, GeV−2, GeV−2, and GeV−2. The values of and are calculated in terms of the pion decay constant GeV and nucleon axial coupling in order to describe the asymptotic properties of the nucleon wave functions at the physical pion mass.
Notice that and that the shape of the function is determined by the constant . The parametrizations for and reproduce the expected chiral expressions for the isovector nucleon charge radius, both Dirac and Pauli, according to chiral perturbation theory [46].
The relevant parameters associated with the pion cloud parametrization are in Table A6.

Table A6.
Pion cloud parameters.
Table A6.
Pion cloud parameters.
| (0) | (0) | (0) | (0) | (GeV2) | (GeV2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0510 | 0.216 | 0.00286 | 0.0821 | 0.618 | 1.281 |
Appendix C.2. Axial Transitions
As discussed in Section 3.2.2, we consider a general parametrization of the meson cloud based on the form of the nucleon axial-vector form factor (41) with [5]
The coefficients are determined by the coefficients from Table A4 for according to
where represents the value of the function for expressed in terms of and . The coefficients from are calculated in terms of
The value of corresponds to the result for the nucleon .
In the extension to the nuclear medium, the denominator () is preserved, while and are modified by the factor .
References
- Brown, G.E.; Rho, M. Scaling effective Lagrangians in a dense medium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 66, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, W.K.; Strauch, S.; Tsushima, K. Medium Modifications of Hadron Properties and Partonic Processes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 299, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Tsushima, K.; Thomas, A.W. Nucleon and hadron structure changes in the nuclear medium and impact on observables. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2007, 58, 1–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatsu, T.; Cheoun, M.K.; Saito, K. Equation of State for Neutron Stars with Hyperons and Quarks in the Relativistic Hartree–fock Approximation. Astrophys. J. 2015, 813, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K.; Cheoun, M.K. Weak interaction axial form factors of the octet baryons in nuclear medium. Phys. Rev. D 2025, 111, 013002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, J.J.; Bassompierre, G.; Becks, K.H.; Best, C.; Bohm, E.; de Bouard, X.; Brasse, F.W.; Broll, C.; Brown, S.; Carr, J.; et al. The ratio of the nucleon structure functions F2n for iron and deuterium. Phys. Lett. B 1983, 123, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, R.G.; Bosted, P.E.; Chang, C.C.; Gomez, J.; Katramatou, A.T.; Petratos, G.; Rahbar, A.A.; Rock, S.; Sill, A.F.; Szalata, Z.M.; et al. Measurements of the a-Dependence of Deep Inelastic electron Scattering from Nuclei. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 52, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hen, O.; Miller, G.A.; Piasetzky, E.; Weinstein, L.B. Nucleon-Nucleon Correlations, Short-lived Excitations, and the Quarks Within. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2017, 89, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, S.; Bartsch, P.; Baumann, D.; Bermuth, J.; Bohinc, K.; Bohm, R.; Bosnar, D.; Derber, S.; Ding, M.; Distler, M.; et al. Polarization transfer in the 4He(e→,e′p→)3H reaction. Phys. Lett. 2001, B500, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauch, S.; Dieterich, S.; Aniol, K.A.; Ann, J.R.; Baker, O.K.; Bertozzi, W.; Boswell, M.; Brash, E.J.; Chai, Z.; Chen, J.P.; et al. Polarization transfer in the 4He(e→,e′p→)3H reaction up to Q2= 2.6 (GeV/c)2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 052301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauch, S. [E93-049 Collaboration]. Medium modification of the proton form-factor. Eur. Phys. J. A 2004, 19, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolone, M.; Malace, S.P.; Strauch, S.; Albayrak, I.; Arrington, J.; Berman, B.L.; Brash, E.J.; Briscoe, B.; Camsonne, A.; Chen, J.P.; et al. Polarization Transfer in the 4He(e,e′p)3H at Q2=0.8 and 1.3 (GeV/c)2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 072001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malace, S.P.; Paolone, M.; Strauch, S.; Albayrak, I.; Arrington, J.; Berman, B.L.; Brash, E.J.; Briscoe, W.J.; Camsonne, A.; Chen, J.P.; et al. A precise extraction of the induced polarization in the 4He(e,e′p)3H reaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 052501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malov, S.; Wijesooriya, K.; Baker, F.T.; Bimbot, L.; Brash, E.J.; Chang, C.C.; Finn, J.M.; Fissum, K.G.; Gao, J.; Gilman, R.; et al. Polarization transfer in the 16O(e→,e′p→)15N reaction. Phys. Rev. C 2000, 62, 057302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izraeli, D.; Brecelj, T.; Achenbach, P.; Ashkenazi, A.; Böhm, R.; Cohen, E.O.; Distler, M.O.; Esser, A.; Gilman, R.; Kolar, T.; et al. Measurement of polarization-transfer to bound protons in carbon and its virtuality dependence. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 781, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, T.; Achenbach, P.; Christmann, M.; Distler, M.O.; Doria, L.; Eckert, P.; Esser, A.; Giusti, C.; Geimer, C.; Gülker, P.; et al. Measurement of polarization transfer in the quasi-elastic 40Ca(e→,e′p→) process. Phys. Lett. B 2023, 847, 138309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K.; Thomas, A.W. Octet Baryon Electromagnetic form Factors in Nuclear Medium. J. Phys. G 2013, 40, 015102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; de Melo, J.P.B.C.; Tsushima, K. Octet baryon electromagnetic form factor double ratios (GE*/GM*)/(GE/GM) in a nuclear medium. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 014030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.R.; Jennings, B.K.; Miller, G.A. The Role of color neutrality in nuclear physics: Modifications of nucleonic wave functions. Phys. Rev. C 1996, 54, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.H.; Tsushima, K.; Thomas, A.W.; Williams, A.G.; Saito, K. Electromagnetic form-factors of the bound nucleon. Phys. Rev. C 1999, 60, 068201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.R.; Miller, G.A. Chiral solitons in nuclei: Electromagnetic form-factors. Phys. Rev. C 2004, 70, 065205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloet, I.C.; Miller, G.A.; Piasetzky, E.; Ron, G. Neutron Properties in the Medium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 082301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, W.R.B.; de Melo, J.P.B.C.; Tsushima, K. Study of the in-medium nucleon electromagnetic form factors using a light-front nucleon wave function combined with the quark-meson coupling model. Nucl. Phys. A 2018, 970, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.A. Light front cloudy bag model: Nucleon electromagnetic form-factors. Phys. Rev. C 2002, 66, 032201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhshiev, U.T.; Meissner, U.G.; Wirzba, A. Electromagnetic form-factors of bound nucleons revisited. Eur. Phys. J. A 2003, 16, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.H.; Thomas, A.W.; Tsushima, K.; Williams, A.G.; Saito, K. In-medium electron-nucleon scattering. Phys. Lett. B 1998, 417, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.H.; Tsushima, K.; Thomas, A.W.; Williams, A.G.; Saito, K. The Neutron charge form-factor in helium-3. Phys. Lett. B 1998, 441, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsushima, K.; Kim, H.; Saito, K. Effect of the bound nucleon form-factors on charged current neutrino nucleus scattering. Phys. Rev. C 2004, 70, 038501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christov, C.V.; Gorski, A.Z.; Goeke, K.; Pobylitsa, P.V. Electromagnetic form-factors of the nucleon in the chiral quark soliton model. Nucl. Phys. A 1995, 592, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letter of Intent to JLab PAC 35. In Neutron Properties in the Nuclear Medium Studied by Polarization Measurements; Gilman, R.; Higinbotham, D.W.; Lichtenstadt, J.; Ron, G.; Strauch, S., Eds. Available online: https://hallaweb.jlab.org/collab/PAC/PAC35/LOI-10-007-Neutron-Modification.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Brown, B.A.; Wildenthal, B.H. Experimental and Theoretical Gamow-Teller Beta-Decay Observables for the sd-Shell Nuclei. Atom. Data Nucl. Data Tabl. 1985, 33, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gysbers, P.; Hagen, G.; Holt, J.D.; Jansen, G.R.; Morris, T.D.; Navrátil, P.; Papenbrock, T.; Quaglioni, S.; Schwenk, A.; Stroberg, S.R.; et al. Discrepancy between experimental and theoretical β-decay rates resolved from first principles. Nat. Phys. 2019, 15, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.W. Chiral Symmetry And The Bag Model: A New Starting Point For Nuclear Physics. Adv. Nucl. Phys. 1984, 13, 1–137. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.H.; Thomas, A.W.; Tsushima, K. Medium modification of the nucleon axial form-factor. arXiv 2001, arXiv:nucl-th/0112001. [Google Scholar]
- Christov, C.V.; Blotz, A.; Kim, H.-C.; Pobylitsa, P.; Watabe, T.; Meissner, T.; Arriola, E.R.; Goeke, K. Baryons as non-topological chiral solitons. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 1996, 37, 91–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhimov, A.M.; Khanna, F.C.; Yakhshiev, U.T.; Musakhanov, M.M. Density dependence of meson nucleon vertices in nuclear matter. Nucl. Phys. A 1998, 643, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, F.; Walliser, H. Quantum corrections to baryon properties in chiral soliton models. Phys. Rept. 1997, 289, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, U.G.; Kaiser, N.; Weise, W. Nucleons as Skyrme Solitons with Vector Mesons: Electromagnetic and Axial Properties. Nucl. Phys. A 1987, 466, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, U.G. Chiral Symmetry and Medium Modifications of Nucleon Properties. Phys. Lett. B 1989, 220, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. Electromagnetic transition form factors of baryon resonances. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2024, 136, 104097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznauryan, I.G.; Bashir, A.; Braun, V.; Brodsky, S.J.; Burkert, V.D.; Chang, L.; Chen, C.h.; El-Bennich, B.; Cloet, I.C.; Cole, P.L.; et al. Studies of Nucleon Resonance Structure in Exclusive Meson Electroproduction. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 2013, 22, 1330015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznauryan, I.G.; Burkert, V.D. Electroexcitation of nucleon resonances. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2012, 67, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichmann, G.; Ramalho, G. Nucleon resonances in Compton scattering. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 093007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K. Axial form factors of the octet baryons in a covariant quark model. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, J.M.; Sauvage, G. Hyperon Beta Decays. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 1984, 34, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, V.; Elouadrhiri, L.; Meissner, U.G. Axial structure of the nucleon: Topical Review. J. Phys. G 2002, 28, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorringe, T.; Fearing, H.W. Induced pseudoscalar coupling of the proton weak interaction. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2004, 76, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, M.R.; Scherer, S. Nucleon Form Factors of the Isovector Axial-Vector Current: Situation of Experiments and Theory. Eur. Phys. J. A 2007, 32, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G. N* Form Factors based on a Covariant Quark Model. Few Body Syst. 2018, 59, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T.; Gross, F. D-state effects in the electromagnetic NΔ transition. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 114017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, F.; Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. A Pure S-wave covariant model for the nucleon. Phys. Rev. C 2008, 77, 015202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, F.; Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. Covariant nucleon wave function with S, D, and P-state components. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 093005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K.; Gross, F. A Relativistic quark model for the Ω− electromagnetic form factors. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 033004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K. Octet baryon electromagnetic form factors in a relativistic quark model. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 054014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, F.; Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K. Using baryon octet magnetic moments and masses to fix the pion cloud contribution. Phys. Lett. B 2010, 690, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K. Octet to decuplet electromagnetic transition in a relativistic quark model. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 093011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. Electromagnetic form factors of the Delta in a S-wave approach. J. Phys. G 2009, 36, 085004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T.; Gross, F. Electromagnetic form factors of the Delta with D-waves. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 113011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T.; Gross, F. Electric quadrupole and magnetic octupole moments of the Delta. Phys. Lett. B 2009, 678, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. Extracting the Ω− electric quadrupole moment from lattice QCD data. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 054011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T.; Stadler, A. The shape of the Δ baryon in a covariant spectator quark model. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 093022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K. Covariant spectator quark model description of the γ*Λ→Σ0 transition. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 114030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K. What is the role of the meson cloud in the Σ*0→γΛ and Σ*→γΣ decays? Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 053002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T.; Tsushima, K. Hyperon electromagnetic timelike elastic form factors at large q2. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 014014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G. Electromagnetic form factors of the Ω− baryon in the spacelike and timelike regions. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 074018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T.; Tsushima, K.; Cheoun, M.K. Electromagnetic |GE/GM| ratios of hyperons at large timelike q2. Phys. Lett. B 2024, 858, 139060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G. Ovariant model for Dalitz decays of decuplet baryons to octet baryons. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 054016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K. Meson cloud contributions to the Dalitz decays of decuplet to octet baryons. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 074019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Tsushima, K.; Thomas, A.W. Selfconsistent description of finite nuclei based on a relativistic quark model. Nucl. Phys. A 1996, 609, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.H.; Yang, S.N.; Thomas, A.W. On the role of the pion cloud in nucleon electromagnetic form-factors. Nucl. Phys. A 2001, 684, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theberge, S.; Thomas, A.W. Magnetic Moments Of The Nucleon Octet Calculated In The Cloudy Bag Model. Nucl. Phys. A 1983, 393, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.H.; Thomas, A.W.; Williams, A.G. Electromagnetic form-factors of the nucleon in an improved quark model. Phys. Rev. C 1998, 57, 2628–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubodera, K.; Kohyama, Y.; Oikawa, K.; Kim, C.W. Weak Interactions Form-factors of the Octet Baryons in the Cloudy Bag Model. Nucl. Phys. A 1985, 439, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Tsushima, K.; Kohyama, Y.; Kubodera, K. Semileptonic Beta Decay Form-factors and Magnetic Moments of Octet Baryons: Recoil Effects and Center-of-mass Corrections in the Cloudy Bag Model Including Gluonic Effects. Nucl. Phys. A 1989, 500, 429. [Google Scholar]
- Tsushima, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kohyama, Y.; Kubodera, K. Weak Interaction Form-factors and Magnetic Moments of Octet Baryons: Chiral Bag Model with Gluonic Effects. Nucl. Phys. A 1988, 489, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichmann, G.; Sanchis-Alepuz, H.; Williams, R.; Alkofer, R.; Fischer, C.S. Baryons as relativistic three-quark bound states. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2016, 91, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloet, I.C.; Roberts, C.D. Explanation and Prediction of Observables using Continuum Strong QCD. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2014, 77, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maris, P.; Roberts, C.D. Dyson-Schwinger equations: A Tool for hadron physics. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 2003, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, V.; Fearing, H.W.; Hemmert, T.R.; Meissner, U.G. The form-factors of the nucleon at small momentum transfer. Nucl. Phys. A 1998, 635, 121, Erratum in Nucl. Phys. A 1998, 642, 563.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, H.W.; Drechsel, D.; Meissner, U.G. On the pion cloud of the nucleon. Phys. Lett. B 2004, 586, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, U.G. The Pion cloud of the nucleon: Facts and popular fantasies. AIP Conf. Proc. 2007, 904, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Ronchen, D.; Doring, M.; Huang, F.; Haberzettl, H.; Haidenbauer, J.; Hanhart, C.; Krewald, S.; Meissner, U.G.; Nakayama, K. Coupled-channel dynamics in the reactions πN→πN, ηN, KΛ, KΣ. Eur. Phys. J. A 2013, 49, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascalutsa, V.; Vanderhaeghen, M.; Yang, S.N. Electromagnetic excitation of the Δ(1232)-resonance. Phys. Rept. 2007, 437, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrou, C.; Koutsou, G.; Neff, H.; Negele, J.W.; Schroers, W.; Tsapalis, A. Nucleon to delta electromagnetic transition form factors in lattice QCD. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 085012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T.; Gross, F. A Covariant model for the nucleon and the Delta. Eur. Phys. J. A 2008, 36, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. Valence quark contribution for the γN→Δ quadrupole transition extracted from lattice QCD. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 013008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. Nucleon and γN→Δ lattice form factors in a constituent quark model. J. Phys. G 2009, 36, 115011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G. Parametrizations of the γ*N→Δ(1232) quadrupole form factors and Siegert’s theorem. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 114001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G. New low-Q2 measurements of the γ*N→Δ(1232) Coulomb quadrupole form factor, pion cloud parametrizations and Siegert’s theorem. Eur. Phys. J. A 2018, 54, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K. Valence quark contributions for the γN→P11(1440) form factors. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 074020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K. γ*N→N(1710) transition at high momentum transfer. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 073010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G. Semirelativistic approximation to the γ*N→N(1520) and γ*N→N(1535) transition form factors. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 054008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. A covariant model for the γN→N(1535) transition at high momentum transfer. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 033007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K. A simple relation between the γN→N(1535) helicity amplitudes. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 051301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. γ*N→N*(1520) form factors in the spacelike region. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 094016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G. Using the Single Quark Transition Model to predict nucleon resonance amplitudes. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 033010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Jido, D.; Tsushima, K. Valence quark and meson cloud contributions for the γ*Λ→Λ* and γ*Σ0→Λ* reactions. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 093014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K. A Model for the Δ(1600) resonance and γN→Δ(1600) transition. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 073007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. Covariant model for the Dalitz decay of the N(1535) resonance. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 114008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. γ*N→N*(1520) form factors in the timelike regime. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 014003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T.; Weil, J.; van Hees, H.; Mosel, U. Role of the pion electromagnetic form factor in the Δ(1232)→γ*N timelike transition. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 033004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. Timelike γ*N→Δ form factors and Delta Dalitz decay. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 113014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, F.; Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. Spin and angular momentum in the nucleon. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 093006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, F. Three-Dimensional Covariant Integral Equations For Low-Energy Systems. Phys. Rev. 1969, 186, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, A.; Gross, F.; Frank, M. Covariant equations for the three-body bound state. Phys. Rev. C 1997, 56, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, F.; Ramalho, G.; Peña, M.T. Fixed-axis polarization states: Covariance and comparisons. Phys. Rev. C 2008, 77, 035203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savkli, C.; Gross, F. Quark-antiquark bound states in the relativistic spectator formalism. Phys. Rev. C 2001, 63, 035208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, F.; Agbakpe, P. The Shape of the nucleon. Phys. Rev. C 2006, 73, 015203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.W.; Orginos, K. Strange Baryon Electromagnetic Form Factors and SU(3) Flavor Symmetry Breaking. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 074507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrou, C.; Brinet, M.; Carbonell, J.; Constantinou, M.; Harraud, P.A.; Guichon, P.; Jansen, K.; Korzec, T.; Papinutto, M. Axial Nucleon form factors from lattice QCD. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 045010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrou, C.; Constantinou, M.; Dinter, S.; Drach, V.; Jansen, K.; Kallidonis, C.; Koutsou, G. Nucleon form factors and moments of generalized parton distributions using Nf = 2 + 1 + 1 twisted mass fermions. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 014509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rehim, A.; Alexandrou, C.; Constantinou, M.; Dimopoulos, P.; Frezzotti, R.; Hadjiyiannakou, K.; Jansen, K.; Kallidonis, C.; Kostrzewa, B.; Koutsou, G.; et al. Nucleon and pion structure with lattice QCD simulations at physical value of the pion mass. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 114513, Erratum in Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 039904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.C.; Gupta, R.; Yoon, B.; Bhattacharya, T. Axial Vector Form Factors from Lattice QCD that Satisfy the PCAC Relation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 072002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djukanovic, D.; von Hippel, G.; Koponen, J.; Meyer, H.B.; Ottnad, K.; Schulz, T.; Wittig, H. Isovector axial form factor of the nucleon from lattice QCD. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 074503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, G.S.; Collins, S.; Heybrock, S.; Löffler, M.; Rödl, R.; Söldner, W.; Weishäupl, S. Octet baryon isovector charges from Nf=2+1 lattice QCD. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 034512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Nicholson, A.N.; Rinaldi, E.; Berkowitz, E.; Garron, N.; Brantley, D.A.; Monge-Camacho, H.; Monahan, C.J.; Bouchard, C.; Clark, M.A.; et al. A per-cent-level determination of the nucleon axial coupling from quantum chromodynamics. Nature 2018, 558, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.S.; Walker-Loud, A.; Wilkinson, C. Status of Lattice QCD Determination of Nucleon Form Factors and their Relevance for the Few-GeV Neutrino Program. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2022, 72, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G. Holographic estimate of the meson cloud contribution to nucleon axial form factor. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 073002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, E.E.; Luke, M.E.; Manohar, A.V.; Savage, M.J. Chiral perturbation theory analysis of the baryon magnetic moments. Phys. Lett. B 1993, 302, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, U.G.; Steininger, S. Baryon magnetic moments in chiral perturbation theory. Nucl. Phys. B 1997, 499, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubis, B.; Hemmert, T.R.; Meissner, U.G. Baryon form-factors. Phys. Lett. B 1999, 456, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J. Phenomenological quark model for baryon magnetic moments and beta decay ratios (GA/GV). Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 033010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheedket, S.; Lyubovitskij, V.E.; Gutsche, T.; Faessler, A.; Pumsa-ard, K.; Yan, Y. Electromagnetic form factors of the baryon octet in the perturbative chiral quark modeluark model. Eur. Phys. J. A 2004, 20, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leinweber, D.B.; Boinepalli, S.; Cloet, I.C.; Thomas, A.W.; Williams, A.G.; Young, R.D.; Zanotti, J.M.; Zhang, J.B. Precise determination of the strangeness magnetic moment of the nucleon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 212001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinepalli, S.; Leinweber, D.B.; Williams, A.G.; Zanotti, J.M.; Zhang, J.B. Precision electromagnetic structure of octet baryons in the chiral regime. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 093005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Leinweber, D.B.; Thomas, A.W.; Young, R.D. Chiral extrapolation of octet-baryon charge radii. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 094001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, V.; Kaiser, N.; Meissner, U.G. Chiral dynamics in nucleons and nuclei. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 1995, 4, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdrisat, C.F.; Punjabi, V.; Vanderhaeghen, M. Nucleon Electromagnetic Form Factors. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2007, 59, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.K.; Aniol, K.A.; Baker, F.T.; Berthot, J.; Bertin, P.Y.; Bertozzi, W.; Besson, A.; Bimbot, L.; Boeglin, W.U.; Brash, E.J.; et al. GEp/GMp ratio by polarization transfer in e→p→ep→. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 1398–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayou, O.; Benmokhtar, F.; Bertozzi, W.; Bimbot, L.; Brash, E.J.; Calarco, J.R.; Cavata, C.; Chai, Z.; Chang, C.C.; Chang, T.; et al. Measurement of GEp/GMp in e→p→ep→ to Q2=5.6 GeV2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 092301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckett, A.J.R.; Brash, E.J.; Jones, M.K.; Luo, W.; Meziane, M.; Pentchev, L.; Perdrisat, C.F.; Punjabi, V.; Wesselmann, F.R. and Ahmidouch, A.; et al. Recoil Polarization Measurements of the Proton Electromagnetic Form Factor Ratio to Q2 = 8.5 GeV2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 242301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Allada, K.; Armstrong, D.S.; Arrington, J.; Bertozzi, W.; Boeglin, W.; Chen, J.-P.; Chirapatpimol, K.; Choi, S.; Chudakov, E.; et al. High Precision Measurement of the Proton Elastic Form Factor Ratio μpGE/GM at low Q2. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 705, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrington, J.; Melnitchouk, W.; Tjon, J.A. Global analysis of proton elastic form factor data with two-photon exchange corrections. Phys. Rev. C 2007, 76, 035205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrick, M.; Herberg, C.; Andresen, H.G.; Annand, J.R.M.; Aulenbacher, K.; Becker, J.; Drescher, P.; Eyl, D.; Frey, A.; Grabmayr, P.; et al. Measurement of the neutron electric form factor GE,n in the quasifree 2H(e→,e′p→)p reaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herberg, C.; Ostrick, M.; Andresen, H.G.; Annand, J.R.M.; Aulenbacher, K.; Becker, J.; Drescher, P.; Eyl, D.; Frey, A.; Grabmayr, P.; et al. Determination of the neutron electric form factor in the D(e,e′n)p reaction and the influence of nuclear binding. Eur. Phys. J. A 1999, 5, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, D.I.; Seimetz, M.; Annand, J.R.M.; Arenhövel, H.; Antelo, M.A.; Ayerbe, C.; Bartsch, P.; Baumann, D.; Bermuth, J.; Böhm, R.; et al. Measurement of the Electric Form Factor of the Neutron at Q2=0.3–0.8 (GeV/c)2. Eur. Phys. J. A 2005, 24, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passchier, I.; Alarcon, R.; Bauer, T.S.; Boersma, D.; Brand, J.F.J.v.; Buuren, L.D.v.; Bulten, H.J.; Ferro-Luzzi, M.; Heimberg, P.; Higinbotham, D.W.; et al. The charge form factor of the neutron from the reaction 2H(e→,e′n)p. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eden, T.; Madey, R.; Zhang, W.-M.; Anderson, B.D.; Arenhövel, H.; Baldwin, A.R.; Barkhuff, D.; Beard, K.B.; Bertozzi, W.; Cameron, J.M.; et al. Electric form-factor of the neutron from the 2H(e→,e′n)1H reaction at Q2=0.255 (GeV/c)2. Phys. Rev. C 1994, 50, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Ahmidouch, A.; Anklin, H.; Arenhövel, H.; Armstrong, C.; Bernet, C.; Boeglin, W.; Breuer, H.; Brindza, P.; Brown, D.; et al. A measurement of the electric form-factor of the neutron through d(e→,e′n)p at Q2=0.5 (GeV/c)2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 081801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, G.; Wesselmann, F.; Zhu, H.; McKee, P.; Savvinov, N.; Zeier, M.; Aghalaryan, A.; Ahmidouch, A.; Arenhövel, H.; Asaturyan, R.; et al. Measurement of the electric form factor of the neutron Q2=0.5 (GeV/c)2 and 1.0 (GeV/c)2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 042301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madey, R.; Semenov, A.Y.; Taylor, S.; Plaster, B. Measurements of GEn/GMn from 2H(e→,e′n)1H reaction to Q2=1.45 (GeV/c)2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 122002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Beck, S.M.-T.; Puckett, A.J.R.; Qiang, Y.; Sirca, S.; Zhu, X. Measurements of the Electric Form Factor of the Neutron up to Q2=3.4 GeV2 using the Reaction 3He(e→,e′n)pp. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 262302. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavilla, R.; Sick, I. Neutron charge form factor at large q2. Phys. Rev. C 2001, 64, 041002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosted, P.E. An Empirical fit to the nucleon electromagnetic form-factors. Phys. Rev. C 1995, 51, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubon, G.; Anklin, H.; Bartsch, P.; Baumann, D.; Boeglin, W.U.; Bohinc, K.; Böhm, R.; Distler, M.O.; Ewald, I.; Friedrich, J.; et al. Precise neutron magnetic form factors. Phys. Lett. B 2002, 524, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anklin, H.; deBever, L.J.; Blomqvist, K.I.; Boeglin, W.U.; Böhm, R.; Distler, M.; Edelhoff, R.; Friedrich, J.; Fritschi, D.; Geiges, R.; et al. Precise measurements of the neutron magnetic form factor. Phys. Lett. B 1998, 428, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anklin, H.; Bruins, E.E.W.; Day, D.; Fritschi, D.; Groft, B.; Joosse, F.C.P.; Jourdan, J.; Lichtenstadt, J.; Loppacher, M.; Masson, G.; et al. Precision measurement of the neutron magnetic form-factor. Phys. Lett. B 1994, 336, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachniet, J. et al. [CLAS Collaboration] A Precise Measurement of the Neutron Magnetic Form Factor GMn in the Few-GeV2 Region. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 192001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Particle Data Group. Review of particle physics. J. Phys. G 2010, 37, 075021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschrich, I.; Krüger, H.; Simon, J.; Vorwalter, K.; Alkhazov, G.; Atamantchouk, A.G.; Balatz, M.Y.; Bondar, N.F.; Cooper, P.S.; Dauwe, L.J.; et al. Measurement of the Σ− charge radius by Σ− electron elastic scattering. Phys. Lett. B 2001, 522, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Gothe, R.W.; Adhikari, K.P.; Adikaram, D.; Anghinolfi, M.; Baghdasaryan, H.; Ball, J.; Battaglieri, M.; Batourine, V.; Bedlinskiy, I.; et al. Measurement of the generalized form factors near threshold via γ*p→nπ+ at high Q2. Phys. Rev. C 2012, 85, 035208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Particle Data Group; Workman, R.L.; Burkert, V.D.; Crede, V.; Klempt, E.; Thoma, U.; Tiator, L.; Agashe, K.; Aielli, G.; Allanach, B.C.; et al. Review of Particle Physics. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2022, 2022, 083C01. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.; Duval, M.A.; Elouadrhiri, L.; Estenne, V.; Bardin, G.; Berthot, J.; Bertin, P.Y.; Botton, N.D.; Didelez, J.P.; Fonvieille, H.; et al. Axial and pseudoscalar nucleon form-factors from low-energy pion electroproduction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 71, 3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsushima, K. Magnetic moments of the octet, decuplet, low-lying charm, and low-lying bottom baryons in a nuclear medium. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2022, 2022, 043D02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos-Martínez, J.J.; Tsushima, K.; Krein, G.; Thomas, A.W. ϕ meson mass and decay width in nuclear matter and nuclei. Phys. Lett. B 2017, 771, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberger, M.L.; Treiman, S.B. Decay of the pi meson. Phys. Rev. 1958, 110, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchbach, M.; Wirzba, A. In-medium chiral perturbation theory and pion weak decay in the presence of background matter. Nucl. Phys. A 1997, 616, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christy, M.E.; Ahmidouch, M.E.; Armstrong, C.S.; Arrington, J.; Asaturyan, R.; Avery, S.; Baker, O.K.; Beck, D.H.; Blok, H.P.; Bochna, C.W.; et al. Measurements of electron proton elastic cross-sections for 0.4<Q2<5.5 (GeV/c)2. Phys. Rev. C 2004, 70, 015206. [Google Scholar]
- Punjabi, V.; Perdrisat, C.F.; Aniol, K.A.; Baker, F.T.; Berthot, J.; Bertin, P.Y.; Bertozzi, W.; Besson, A.; Bimbot, L.; Boeglin, W.U.; et al. Proton elastic form-factor ratios to Q2=3.5 GeV2 by polarization transfer. Phys. Rev. C 2005, 71, 055202, Erratum in Phys. Rev. C 2005, 71, 069902.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckett, A.J.R.; Brash, E.J.; Gayou, O.; Jones, M.K.; Pentchev, L.; Perdrisat, C.F.; Punjabi, V.; Aniol, K.A.; Averett, T.; Benmokhtar, F.; et al. Final Analysis of Proton Form Factor Ratio Data at Q2=4.0, 4.8 and 5.6 GeV2. Phys. Rev. C 2012, 85, 045203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckett, A.J.R.; Brash, E.J.; Jones, M.K.; Luo, W.; Meziane, M.; Pentchev, L.; Perdrisat, C.F.; Punjabi, V.; Wesselmann, F.R.; Afanasev, A.; et al. Polarization Transfer Observables in Elastic Electron Proton Scattering at Q2=2.5, 5.2, 6.8, and 8.5 GeV2. Phys. Rev. C 2017, 96, 055203, Erratum in Phys. Rev. C 2018, 98, 019907.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheoun, M.K.; Choi, K.S.; Kim, K.S.; Saito, K.; Kajino, T.; Tsushima, K.; Maruyama, T. Effects of the density-dependent weak form factors on the neutrino reaction via neutral current for the nucleon in nuclear medium and 12C. Phys. Rev. C 2013, 87, 065502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheoun, M.K.; Choi, K.; Kim, K.S.; Saito, K.; Kajino, T.; Tsushima, K.; Maruyama, T. Asymmetry in the neutrino and anti-neutrino reactions in a nuclear medium. Phys. Lett. B 2013, 723, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cai, T.; Moore, M.L.; Olivier, A.; Akhter, S.; Dar, Z.A.; Ansari, V.; Ascencio, M.V.; Bashyal, A.; Bercellie, A.; Betancourt, M.; et al. Measurement of the axial vector form factor from antineutrino-proton scattering. Nature 2023, 614, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The DUNE Collaboration; Abud, A.A.; Abi, B.; Acciarri, R.; Acero, M.A.; Adames, M.R.; Adamov, G.; Adams, D.; Adinolfi, M.; Aduszkiewicz, A.; et al. Searching for solar KDAR with DUNE. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 10, 065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberico, W.M.; Bilenky, S.M.; Maieron, C. Strangeness in the nucleon: Neutrino-nucleon and polarized electron-nucleon scattering. Phys. Rept. 2002, 358, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.A.; Aronson, S.H.; Connolly, P.L.; Gibbard, B.G.; Murtagh, M.J.; Murtagh, S.J.; Terada, S.; White, D.H.; Callas, J.L.; Cutts, D.; et al. Measurement of Neutrino—Proton and anti-neutrino-Proton Elastic Scattering. Phys. Rev. D 1987, 35, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athar, M.S.; Fatima, A.; Singh, S.K. Neutrinos and their interactions with matter. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2023, 129, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruso, L.A.; Ankowski, A.M.; Bacca, S.; Balantekin, A.B.; Carlson, J.; Gardiner, S.; González-Jiménez, R.; Gupta, R.; Hobbs, T.J.; Hoferichter, M.; et al. Theoretical tools for neutrino scattering: Interplay between lattice QCD, EFTs, nuclear physics, phenomenology, and neutrino event generators. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.09030. [Google Scholar]
- Akimov, D.; Alawabdeh, S.; An, P.; Awe, C.; Barbeau, P.S.; Barry, C.; Becker, B.; Belov, V.; Bernardi, I.; Bock, C.; et al. The COHERENT Experimental Program. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.04575. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, D.; Steinberg, N.; Lovato, A.; Meurice, Y.; Rocco, N.; Wagman, M. Form factor and model dependence in neutrino-nucleus cross section predictions. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.02455. [Google Scholar]
- Hoferichter, M.; Menéndez, J.; Schwenk, A. Coherent elastic neutrino-nucleus scattering: EFT analysis and nuclear responses. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 074018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Aristizabal Sierra, D.; Dutta, B.; Strigari, L.E. Coherent Elastic Neutrino-Nucleus Scattering with directional detectors. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 015009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadeddu, M.; Dordei, F.; Giunti, C. A view of coherent elastic neutrino-nucleus scattering. Europhys. Lett. 2023, 143, 34001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondolo, P. Recoil momentum spectrum in directional dark matter detectors. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 103513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, G.; Tsushima, K.; Cheoun, M.K. Soongsil University, Seoul 06978, Republic of Korea, 2025; (manuscript in preparation; to be submitted).
- Hutauruk, P.T.P.; Oh, Y.; Tsushima, K. Impact of medium modifications of the nucleon weak and electromagnetic form factors on the neutrino mean free path in dense matter. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 013009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).