Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy at Aqueous Electrochemical Interfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
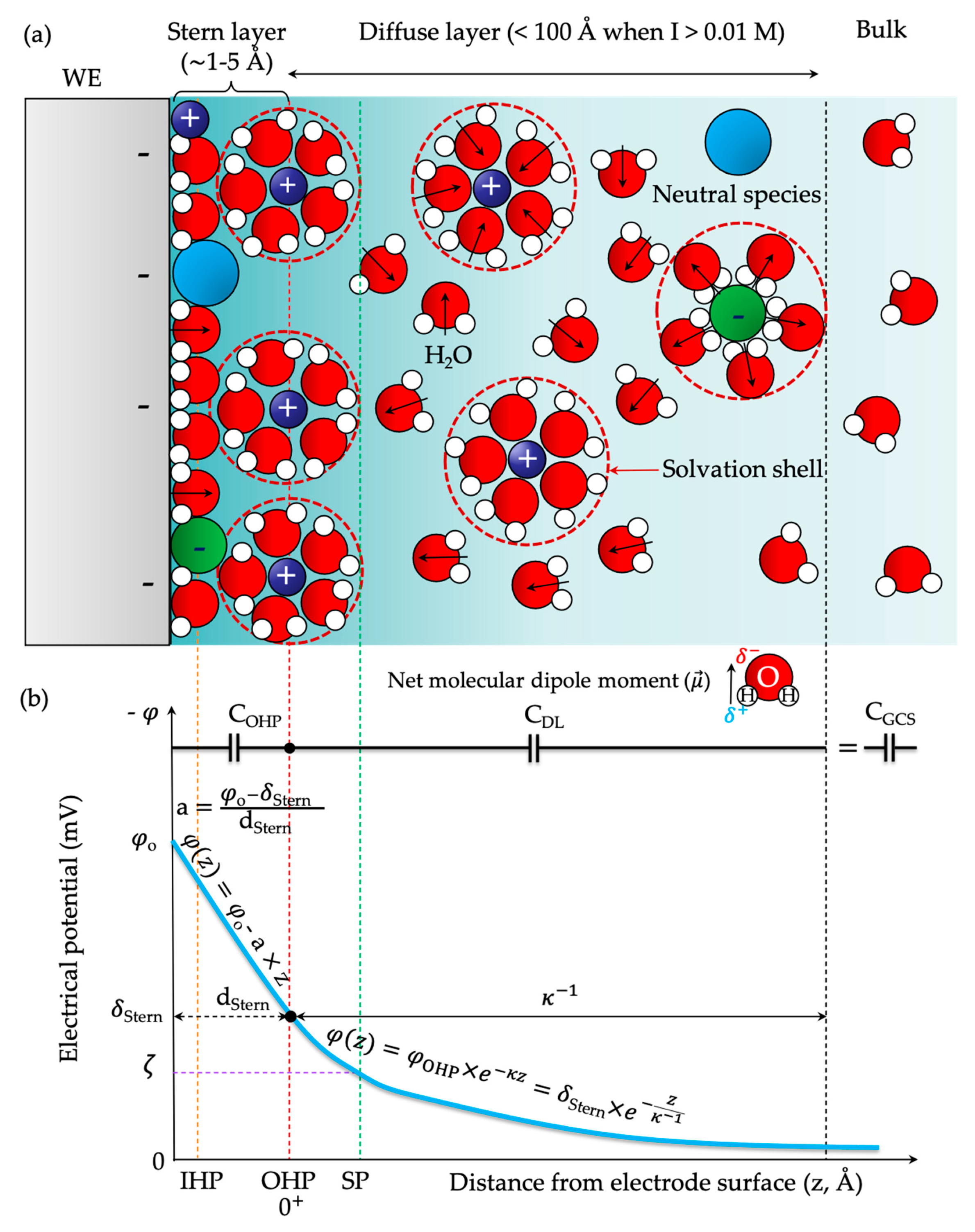
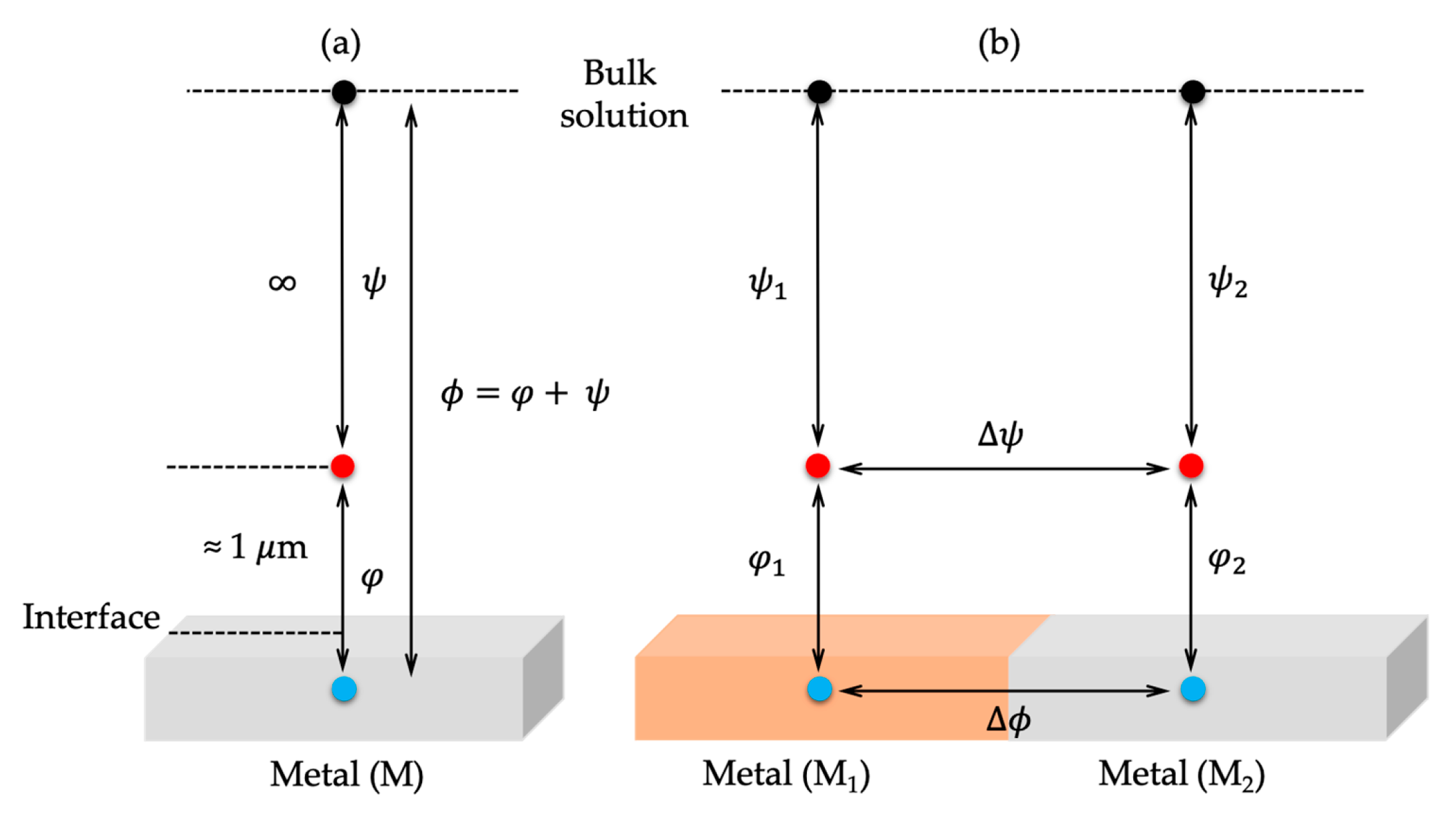
2. Descriptive Models of the Electrical Double Layer and Its Mean-Field Theory
3. Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy at Electrochemical Interfaces
3.1. Fundamentals of Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy
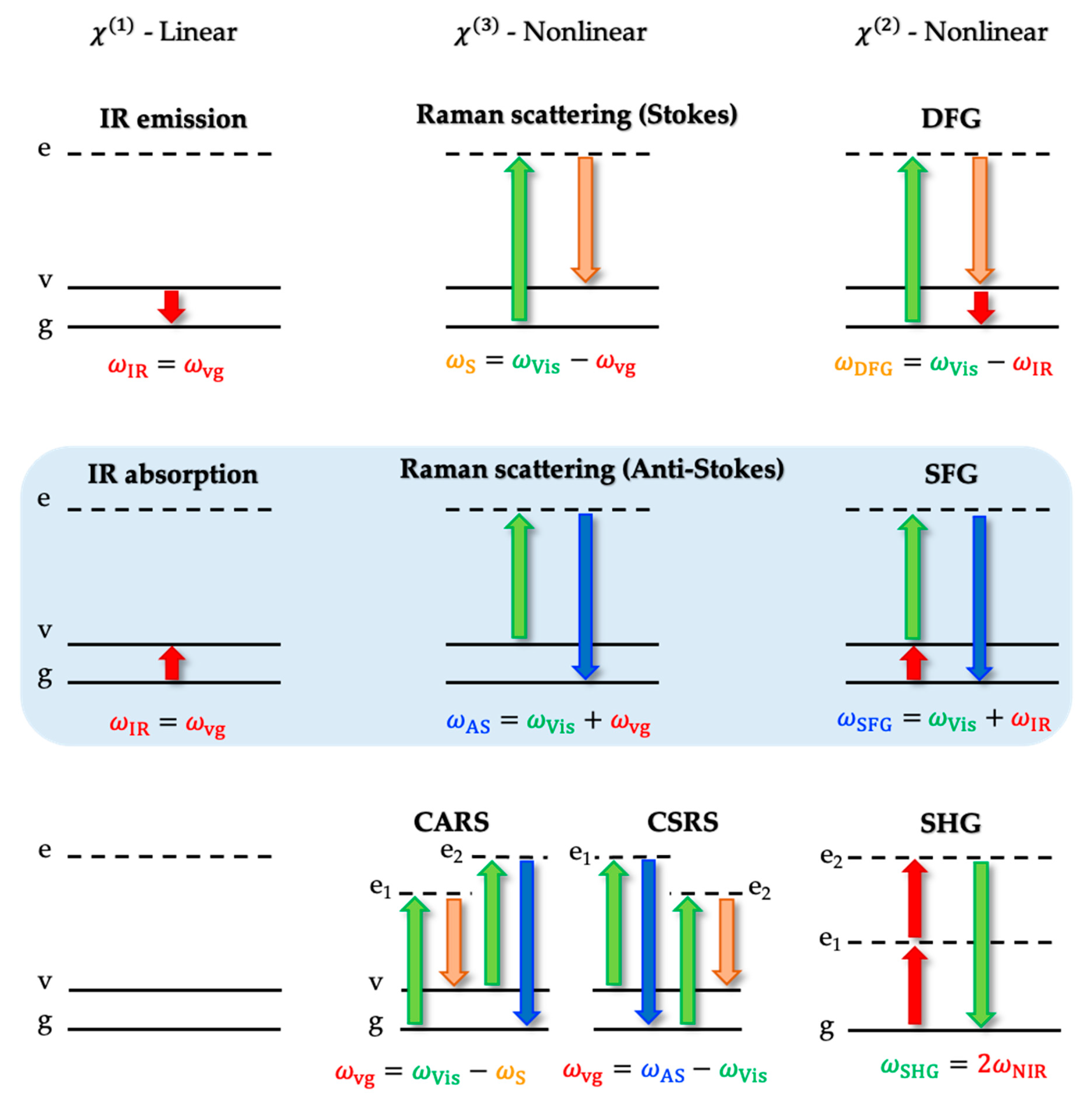
3.2. The Electric Field-Dependent Vibrational Stark Effect at Electrochemical Interfaces
3.3. Potential-Dependent Sum-Frequency Generation (SFG) Spectroscopy
- (i)
- If , meaning that the coherence length (usually between 20 and 50 nm depending on the optical configurations) of the SFG process is much bigger than the effective thickness of the diffuse layer. In other words, the Debye length is much smaller than the coherence length. This is the case for very high electrolyte concentration (I > 10−1 M) and is predominant ( and ). This leads to the exponential phase matching term close to a unity , then
- (ii)
- When (), the Debye length is bigger than the coherence length thick, which corresponds to very low electrolyte concentration (I < 10−4 M) and the significant term is thus with small value since and . This complete destructive interference results in the sole dependence of SFG intensity on contribution [104].
- (iii)
- Otherwise, the coherence length is comparable to the Debye screening length ( when I ≈ 10−3–10−4 M), so the total term remains as a complex value with both contributions from the real and imaginary terms.
3.4. Some Controversial Issues Using the Definition of Surface Potential in the SFG Measurements
3.5. Experimental Considerations on Spectroelectrochemical Cells Adapted to Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy
3.5.1. Sum-Frequency Generation Experimental Setups
3.5.2. Hyphenated Spectroelectrochemical Cell Configurations
4. SFG at Aqueous Electrochemical Interfaces
4.1. Interfacial Water Molecules on Electrode Surfaces
4.2. Interfacial Charged Adsorbates on Electrode Surfaces (Electrolytes)
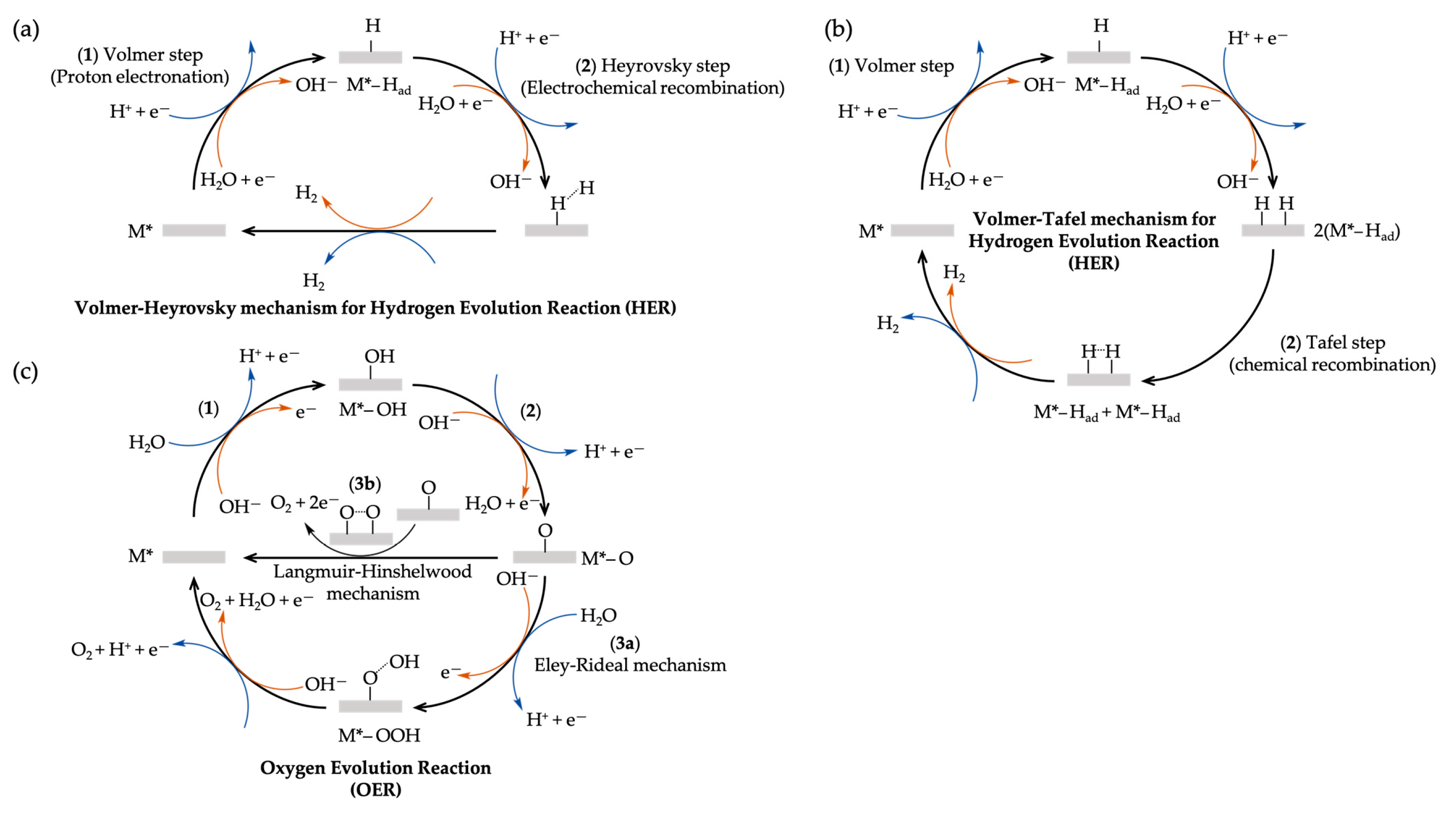
 ) of (bi)sulfate anions where the intense band is detected (Figure 19a–c). A second dramatic augment in SFG intensity is observed at E > 0.5 V (Figure 19a–c) and ascribed to the surface hydroxyl (Pt-OH) formation from co-absorbed water molecules via: 2H2O(l) + Pt → Pt-OHad + e− + H3O+(aq). This weaker hydrogen-bonding of Pt-OH in relation to the hydrogen network of co-adsorbed H2O with sulfate absorbate (at the PtOx formation region in Figure 16) and the released hydronium cations incorporated in the double layer cause the decrease of interfacial electric field and a blue-shift of the vibrational band (reduction of the electrical Stark shift) (Figure 19b–d). One of the intriguing angles in terms of the potential-dependent shift in (bi)sulfate center frequency and intensity that Zwaschka et al. pursued to comprehend experimentally and theoretically is the dipole–dipole interaction. They emphasized the alterations of macroscopic external bias, which linearly change the local field sensed by individual adsorbates dipole–dipole coupling (molecular polarizability), could induce the nonlinearity of the SFG frequency and intensity [267].
) of (bi)sulfate anions where the intense band is detected (Figure 19a–c). A second dramatic augment in SFG intensity is observed at E > 0.5 V (Figure 19a–c) and ascribed to the surface hydroxyl (Pt-OH) formation from co-absorbed water molecules via: 2H2O(l) + Pt → Pt-OHad + e− + H3O+(aq). This weaker hydrogen-bonding of Pt-OH in relation to the hydrogen network of co-adsorbed H2O with sulfate absorbate (at the PtOx formation region in Figure 16) and the released hydronium cations incorporated in the double layer cause the decrease of interfacial electric field and a blue-shift of the vibrational band (reduction of the electrical Stark shift) (Figure 19b–d). One of the intriguing angles in terms of the potential-dependent shift in (bi)sulfate center frequency and intensity that Zwaschka et al. pursued to comprehend experimentally and theoretically is the dipole–dipole interaction. They emphasized the alterations of macroscopic external bias, which linearly change the local field sensed by individual adsorbates dipole–dipole coupling (molecular polarizability), could induce the nonlinearity of the SFG frequency and intensity [267].4.3. Interfacial Uncharged Adsorbates and Fuel-Generated Oxidation on Electrode Surfaces (Molecules)
| (−) Pt-Ru alloy|C2H5OH(l), OH−/H+(aq)|AEM/PEM|OH−/H+(aq), O2(g)|Pt-Ru alloy (+) | |
| Anode (−): | C2H5OH(l) + 3H2O(l) ⇄ 2CO2(g) + 12H+(aq) + 12e− in PEM |
| C2H5OH(l) + 12OH−(aq) ⇄ 2CO2(g) + 9H2O(l) + 12e− in AEM | |
| Cathode (+): | 3O2(g) + 12H+(aq) + 12e− ⇄ 6H2O(l) in PEM |
| 3O2(g) + 6H2O(l) + 12e− ⇄ 12OH−(aq) in AEM | |
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Universal gas constant | R = 8.314 J∙mol–1∙K–1 = 0.08314 L∙bar∙mol–1∙K–1 = 0.08205 atm∙L∙K–1∙mol–1 |
| Faraday’s constant | F = 96,500 C∙mol–1 |
| Avogadro’s constant | NA = 6.0221 × 1023 mol–1 |
| The elementary charge | e = 1.6021 × 10−19 C |
| Speed of light | c = 2.998 × 108 m∙s–1 |
| Planck’s constant | h = 6.626 × 10–34 J∙s |
| Boltzmann constant | kB = 1.3807 × 10–23 J∙K–1 |
| Zero of the Celsius scale | 0 °C = 273.15 K |
| Standard pressure | p° = 1 bar = 105 Pa |
| Atmospheric pressure | 1 atm = 1.013 bar = 1.013 × 105 Pa = 760 mm Hg = 760 Torr |
| Electron-volt | 1 eV = 1.6022∙10−19 J |
| Euler’s number | e = 2.7183 |
| Conversion | 1 pm = 10–12 m; 1 Å = 10−10 m; 1 nm = 10–9 m |
| Planck–Einstein relation | [cm−1] |
| Relation between standard Gibbs (free) energy, equilibrium constant, and standard cell potential (electromotive force) | ∆G° = −RTlnK = −nE°F or K = at 25 °C and ln(x) = 2.303log(x) |
| Relation between Gibbs energy and reaction quotient for a reaction | aA(aq) + bB(aq) cC(aq) + dD(aq) (a is the activity of species M), |
| Nernst equation | Eox/red = = of species M is 1), E = E° + = E + at 25 °C |
| Henderson–Hasselbalch equation | pH = pKa when Ka, Kb>> Kw = 1) |
| where pKa = −logKa; pKsp = −logKsp; pKw = −logKw = 14 at 25 °C. |
References
- Stamenkovic, V.R.; Strmcnik, D.; Lopes, P.P.; Markovic, N.M. Energy and fuels from electrochemical interfaces. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millet, P. Fundamentals of Water Electrolysis. In Hydrogen Production; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 33–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden, J.C.; Trussell, R.R.; Hand, D.W.; Howe, K.J.; Tchobanoglous, G. Physical and Chemical Quality of Water. In MWH’s Water Treatment: Principles and Design, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 17–71. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Lopez, M.F.; Francisco, J.S.; Martins-Costa, M.T.C.; Anglada, J.M. Molecular reactions at aqueous interfaces. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, X.; Shi, L.; Zhao, Z.; Min, W. Probing the structure of water in individual living cells. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarun, O.B.; Okur, H.I.; Rangamani, P.; Roke, S. Transient domains of ordered water induced by divalent ions lead to lipid membrane curvature fluctuations. Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhai, T.; Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Jono, R.; Mao, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. The effect of water on colloidal quantum dot solar cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
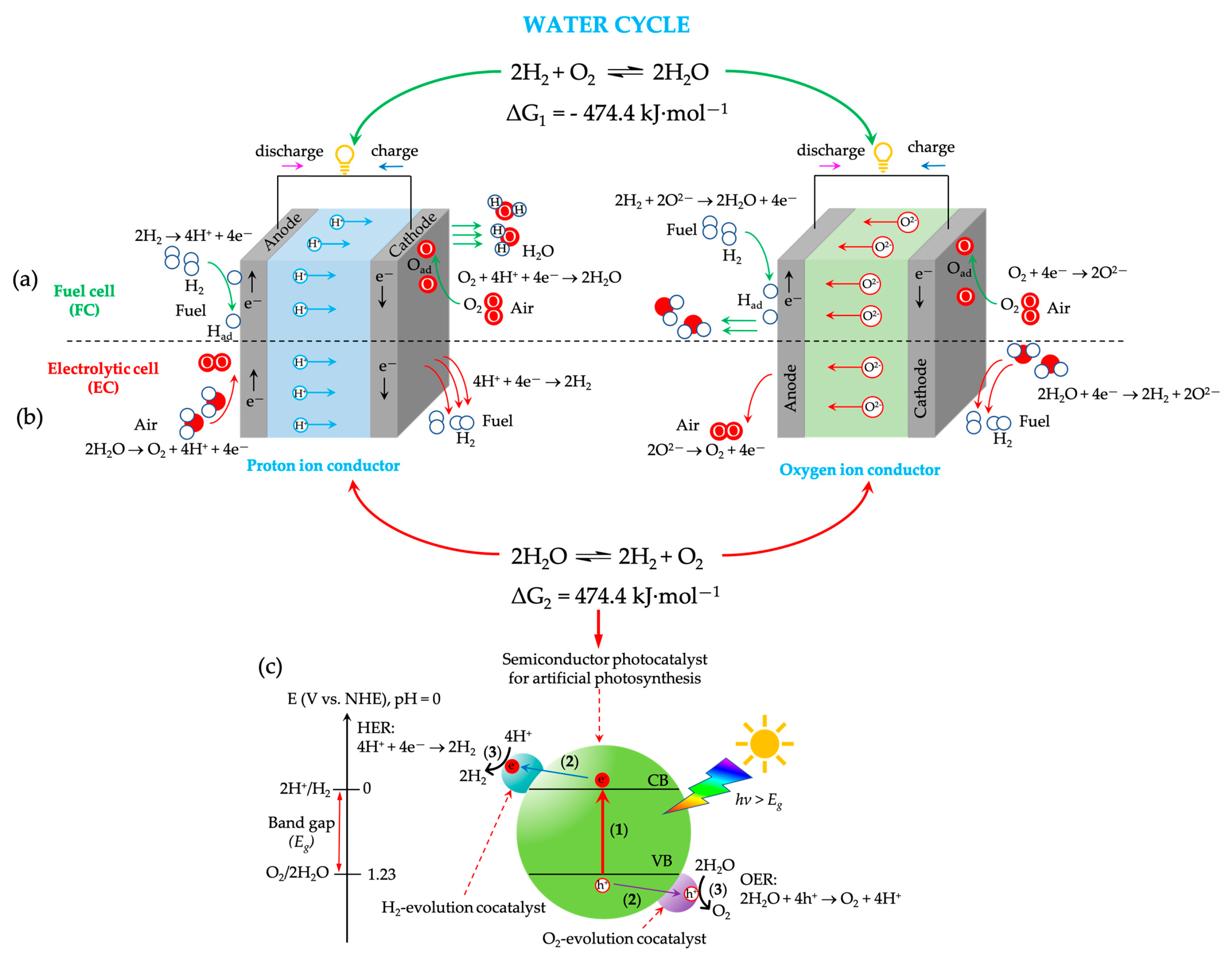
- Chen, S.; Takata, T.; Domen, K. Particulate photocatalysts for overall water splitting. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Kee, R.; Zhu, H.; Sullivan, N.; Zhu, L.; Bian, L.; Jennings, D.; O’Hayre, R. Highly efficient reversible protonic ceramic electrochemical cells for power generation and fuel production. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.; Lu, Y.; Akbar, M.; Lei, L.; Jing, S.; Tao, Y. Advances in solid oxide fuel cell technologies: Lowering the operating temperatures through material innovations. Mater. Today Energy 2024, 44, 101633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonella, G.; Backus, E.H.G.; Nagata, Y.; Bonthuis, D.J.; Loche, P.; Schlaich, A.; Netz, R.R.; Kühnle, A.; McCrum, I.T.; Koper, M.T.M.; et al. Water at charged interfaces. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 466–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-J.; Kim, D.H.; Bae, G.; Ringe, S.; Choi, H.; Lim, H.-K.; Choi, C.H.; Kim, H. On the importance of the electric double layer structure in aqueous electrocatalysis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, H.-J.; Graf, K.; Kappl, M. The Electric Double Layer. In Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 42–56. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, D.C. Chapter 16. Electroanalytical techniques. In Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 8th ed.; W.H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chatenet, M.; Pollet, B.G.; Dekel, D.R.; Dionigi, F.; Deseure, J.; Millet, P.; Braatz, R.D.; Bazant, M.Z.; Eikerling, M.; Staffell, I.; et al. Water electrolysis: From textbook knowledge to the latest scientific strategies and industrial developments. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 4583–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, D. Chapter 11. Electrochemical Methods. In Modern Analytical Chemistry; McGraw-Hill Companies: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 2.1, p. 1122. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor, E.; Lian, Z.; Xia, L.; Ecija, D.; Galán-Mascarós, J.R.; Barja, S.; Giménez, S.; Arbiol, J.; López, N.; García de Arquer, F.P. Complementary probes for the electrochemical interface. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2024, 8, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Kuang, P.; Yu, J. Introductory chapter: Fundamentals of photocatalysis and electrocatalysis. In Graphene Oxide-Metal Oxide and Other Graphene Oxide-Based Composites in Photocatalysis and Electrocatalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Millet, P. Chapter 2—Fundamentals of water electrolysis. In Electrochemical Power Sources: Fundamentals, Systems, and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 37–62. [Google Scholar]
- Santana Santos, C.; Jaato, B.N.; Sanjuán, I.; Schuhmann, W.; Andronescu, C. Operando Scanning Electrochemical Probe Microscopy during Electrocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 4972–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Abruna, H.D.; Chidsey, C.E.; Faulkner, L.R.; Feldberg, S.W.; Itaya, K.; Majda, M.; Melroy, O.; Murray, R.W. The electrode/electrolyte interface—A status report. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 7147–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Skaanvik, S.A.; Xiong, X.; Wang, S.; Dong, M. Scanning probe microscopy for electrocatalysis. Matter 2021, 4, 3483–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-Z.; Shen, Z.-Z.; Wen, R.; Wan, L.-J. Recent advances in the application of scanning probe microscopy in interfacial electroanalytical chemistry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 938, 117443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-X.; Sun, C.; Huang, S.-L.; Kang, B.; Chen, H.-Y.; Xu, J.-J. Single-Particle Imaging Reveals the Electrical Double-Layer Modulated Ion Dynamics at Crowded Interface. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 9743–9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaro, M.; Jeong, B.; Ross, P.N.; Yano, J.; Hussain, Z.; Liu, Z.; Crumlin, E.J. Unravelling the electrochemical double layer by direct probing of the solid/liquid interface. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Velez, J.J.; Pfeifer, V.; Hävecker, M.; Weatherup, R.S.; Arrigo, R.; Chuang, C.-H.; Stotz, E.; Weinberg, G.; Salmeron, M.; Schlögl, R.; et al. Photoelectron Spectroscopy at the Graphene–Liquid Interface Reveals the Electronic Structure of an Electrodeposited Cobalt/Graphene Electrocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14554–14558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaro, M.; Drisdell, W.S.; Marcus, M.A.; Gregoire, J.M.; Crumlin, E.J.; Haber, J.A.; Yano, J. An Operando Investigation of (Ni–Fe–Co–Ce)Ox System as Highly Efficient Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Evolution Reaction. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Velez, J.-J.; Wu, C.H.; Pascal, T.A.; Wan, L.F.; Guo, J.; Prendergast, D.; Salmeron, M. The structure of interfacial water on gold electrodes studied by X-Ray absorption spectroscopy. Science 2014, 346, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grespi, A.; Larsson, A.; Abbondanza, G.; Eidhagen, J.; Gajdek, D.; Manidi, J.; Tayal, A.; Pan, J.; Merte, L.R.; Lundgren, E. Probing the electrode-liquid interface using operando total-reflection X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Surf. Sci. 2024, 748, 122538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.K.; Maier, S.; Verdaguer, A.; Velasco-Velez, J.-J.; Salmeron, M. Water at surfaces and interfaces: From molecules to ice and bulk liquid. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2018, 93, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, M.; Hendra, P.J.; Hill, I.R.; Pemble, M.E. Enhanced Raman spectra from species formed by the coadsorption of halide ions and water molecules on silver electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1981, 117, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamekye, C.K.A.; Bobbitt, J.M.; Zhu, Q.; Smith, E.A. The evolution of total internal reflection Raman spectroscopy for the chemical characterization of thin films and interfaces. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 6009–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, D.A.; Bain, C.D. Total internal reflection Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2012, 137, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiling, M.; Pfeiffer, F.; Baghernejad, M. Vibrational Spectroscopy Insight into the Electrode|electrolyte Interface/Interphase in Lithium Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2202504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Pemberton, J.E. Investigation of trace interfacial water at silver electrodes in a series of normal alcohols using surface enhanced Raman scattering. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 5677–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Liu, Z.; Duan, S.; Wu, D.-Y.; Ren, B.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Zou, S.-Z. Orientation Change of Adsorbed Pyrazine on Roughened Rhodium Electrodes as Probed by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 17597–17602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Sabanés, N.; Ohto, T.; Andrienko, D.; Nagata, Y.; Domke, K.F. Electrochemical TERS Elucidates Potential-Induced Molecular Reorientation of Adenine/Au(111). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9796–9801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P. Tip-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: Technique and Recent Advances. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6447–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataka, K.-I.; Yotsuyanagi, T.; Osawa, M. Potential-Dependent Reorientation of Water Molecules at an Electrode/Electrolyte Interface Studied by Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 10664–10672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandlowski, T.; Ataka, K.; Pronkin, S.; Diesing, D. Surface enhanced infrared spectroscopy—Au(111-20nm)/sulphuric acid—New aspects and challenges. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 1233–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, A. ATR-SEIRAS for time-resolved studies of electrode–electrolyte interfaces. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 35, 101041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Kato, H.; Hoshi, N. Infrared Spectroscopy of Water Adsorbed on M(111) (M = Pt, Pd, Rh, Au, Cu) Electrodes in Sulfuric Acid Solution. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 9458–9463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, M.; Tsushima, M.; Mogami, H.; Samjeské, G.; Yamakata, A. Structure of Water at the Electrified Platinum−Water Interface: A Study by Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 4248–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Xu, B.; Lu, Q. Influence of electric double layer rigidity on CO adsorption and electroreduction rate. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Huang, B.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, D.; Hong, J.; Cao, D.; Wang, E.; Xu, L.; Shao-Horn, Y.; et al. Effect of ion-specific water structures at metal surfaces on hydrogen production. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Huang, Y.F.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Li, S.B.; Zhou, X.S.; Fan, F.R.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Wu, D.Y.; et al. Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 2010, 464, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-Y.; Le, J.-B.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chen, S.; Yang, Z.-L.; Li, J.-F.; Cheng, J.; Tian, Z.-Q. In situ probing electrified interfacial water structures at atomically flat surfaces. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, S.; Lu, X.; Meng, J.; Yan, J.; Abruña, H.D.; Feng, G.; Lian, T. Unconventional interfacial water structure of highly concentrated aqueous electrolytes at negative electrode polarizations. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Zheng, S.; Yang, W.-M.; Zhou, R.-Y.; He, Q.-F.; Radjenovic, P.; Dong, J.-C.; Li, S.; Zheng, J.; Yang, Z.-L.; et al. In situ Raman spectroscopy reveals the structure and dissociation of interfacial water. Nature 2021, 600, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic, S.; Jakes, P.; Merz, S.; Daniel, D.T.; Eichel, R.-A.; Granwehr, J. In operando NMR investigations of the aqueous electrolyte chemistry during electrolytic CO2 reduction. Commun. Chem. 2023, 6, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Jerschow, A. In situ and operando magnetic resonance imaging of electrochemical cells: A perspective. J. Magn. Reson. 2019, 308, 106600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.M.; Forse, A.C.; Tsai, W.-Y.; Taberna, P.-L.; Simon, P.; Grey, C.P. In situ NMR and electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance techniques reveal the structure of the electrical double layer in supercapacitors. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Malveau, C.; Rochefort, D. Solid-state NMR and electrochemical dilatometry study of charge storage in supercapacitor with redox ionic liquid electrolyte. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 20, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bols, M.L.; Ma, J.; Rammal, F.; Plessers, D.; Wu, X.; Navarro-Jaén, S.; Heyer, A.J.; Sels, B.F.; Solomon, E.I.; Schoonheydt, R.A. In Situ UV–Vis–NIR Absorption Spectroscopy and Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 2352–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pool, R.E.; Versluis, J.; Backus, E.H.G.; Bonn, M. Comparative Study of Direct and Phase-Specific Vibrational Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy: Advantages and Limitations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 15362–15369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiopkin, I.V.; Jayathilake, H.D.; Bordenyuk, A.N.; Benderskii, A.V. Heterodyne-Detected Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2271–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayama, A.; Nihonyanagi, S.; Ohshima, Y.; Tahara, T. In situ observation of the potential-dependent structure of an electrolyte/electrode interface by heterodyne-detected vibrational sum frequency generation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 2580–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Doan, L.C.; Lou, D.; Wen, C.; Vinh, N.Q. Interfacial layers between ion and water detected by terahertz spectroscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 2022, 157, 054501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemes, C.T.; Swierk, J.R.; Schmuttenmaer, C.A. A Terahertz-Transparent Electrochemical Cell for In Situ Terahertz Spectroelectrochemistry. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4389–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogai, T.; Uranagase, M.; Motobayashi, K.; Ogata, S.; Ikeda, K. Probing collective terahertz vibrations of a hydrogen-bonded water network at buried electrochemical interfaces. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 6531–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmholtz, H. Uber einige Gesetze der Vertheilung elektrischer Strome in korperlichen Leitem mit Anwendung auf die thierisch-elektrischen Versuche. Ann. Phys. Chem. 1853, 89, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmholtz, H Studien über electrische Grenzschichten. Ann. Phys. Chem. 1879, 243, 337–382. [CrossRef]
- Gouy, M. Sur la constitution de la charge électrique à la surface d’un électrolyte. J. Phys. Theor. Appl. 1910, 9, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.L. A contribution to the theory of electrocapillarity. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1913, 25, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housecroft, C.E.; Sharpe, A.G. Inorganic Chemistry, 5th ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Harlow, England, 2018; p. 1137. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, I.; Cvitas, T.; Homann, K.; Kallay, N.; Kuchitsu, K. Electric dipole moment. In Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry, 2nd ed.; International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC): Zürich, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.-C.; Zha, S.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Guo, P.; Shi, G.; Fang, H.; Shen, Y.R.; Tian, C. Unveiling Microscopic Structures of Charged Water Interfaces by Surface-Specific Vibrational Spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 016101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, N.G.; Dlott, D.D. Studies of electrochemical interfaces by broadband sum frequency generation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 800, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beranek, R. (Photo)electrochemical Methods for the Determination of the Band Edge Positions of TiO2-Based Nanomaterials. Adv. Phys. Chem. 2011, 2011, 786759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Abbas, Z.; Kleibert, A.; Green, R.G.; Goel, A.; May, S.; Squires, T.M. Determination of Surface Potential and Electrical Double-Layer Structure at the Aqueous Electrolyte-Nanoparticle Interface. Phys. Rev. X 2016, 6, 011007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Miyazaki, K.; Hwang, J.; Yamamoto, T.; Sakuda, A. Electrode Potentials Part 1: Fundamentals and Aqueous Systems. Electrochemistry 2022, 90, 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debye, P.H.E.; Zur Theorie der Elektrolyte, I. Gefrierpunktserniedrigung und verwandte Erscheinungen. Phys. Z. 1923, 24, 185–206. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, O. Zur theorie der elektrolytischen doppelschicht. Z. Für Elektrochem. Und Angew. Phys. Chem. 1924, 30, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahame, D.C. The Electrical Double Layer and the Theory of Electrocapillarity. Chem. Rev. 1947, 41, 441–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockris, J.O.; Devanathan, M.A.V.; Müller, K. On the structure of charged interfaces. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1963, 274, 55–79. [Google Scholar]
- Limaye, A.; Suvlu, D.; Willard, A.P. Water molecules mute the dependence of the double-layer potential profile on ionic strength. Faraday Discuss. 2024, 249, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornyshev, A.A.; Spohr, E.; Vorotyntsev, M.A. Electrochemical Interfaces: At the Border Line. In Encyclopedia of Electrochemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baldelli, S. Probing Electric Fields at the Ionic Liquid−Electrode Interface Using Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy and Electrochemistry. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 13049–13051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafie, L.A. Vibrational optical activity: From discovery and development to future challenges. Chirality 2020, 32, 667–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, T.-a.; Okuno, M. Chapter 9—Heterodyne-detected chiral vibrational sum frequency generation spectroscopy of bulk and interfacial samples. In Molecular and Laser Spectroscopy; Gupta, V.P., Ozaki, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 315–348. [Google Scholar]
- Molloy, K.C. Group Theory for Chemists: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 2nd ed.; Horwood: Chichester, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- McQuarrie, D.A.; Simon, J.D. Physical Chemistry: A Molecular Approach; University Science Books: Sausalito, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Humbert, C.; Noblet, T. A Unified Mathematical Formalism for First to Third Order Dielectric Response of Matter: Application to Surface-Specific Two-Colour Vibrational Optical Spectroscopy. Symmetry 2021, 13, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, C.; Noblet, T.; Dalstein, L.; Busson, B.; Barbillon, G. Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy of Plasmonic Nanomaterials: A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, C.; Pluchery, O.; Lacaze, E.; Busson, B.; Tadjeddine, A. Two-Colour Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy Coupled to Plasmonics with the CLIO Free Electron Laser. Photonics 2022, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblet, T.; Dreesen, L.; Boujday, S.; Méthivier, C.; Busson, B.; Tadjeddine, A.; Humbert, C. Semiconductor quantum dots reveal dipolar coupling from exciton to ligand vibration. Commun. Chem. 2018, 1, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.G.; Davies, P.B.; Neivandt, D.J. Implementing the Theory of Sum Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy: A Tutorial Review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2005, 40, 103–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblet, T.; Boujday, S.; Méthivier, C.; Erard, M.; Hottechamps, J.; Busson, B.; Humbert, C. Two-Dimensional Layers of Colloidal CdTe Quantum Dots: Assembly, Optical Properties, and Vibroelectronic Coupling. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 25873–25883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.L.; Piard, A.; Erard, M.; Gayral, A.; Noblet, T.; Dreesen, L.; Humbert, C. Quantum efficiency of excitonic enhancement in nanosensors by rainbow nonlinear optical spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the French, Swiss and German Conference on Photochemistry, Photophysics and Photosciences CP2P’23, Mulhouse, France, 15–17 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Takashima, K.; Furukawa, Y. Vibrational Stark effect (VSE) on the infrared spectrum of a poly(methyl methacrylate) thin film. Vib. Spectrosc. 2015, 78, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Boxer, S.G. Vibrational Stark Effects of Nitriles, I. Methods and Experimental Results. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 11853–11863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D.K. Vibrational Stark effect of adsorbates at electrochemical interfaces. Electrochim. Acta 1996, 41, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.J.; Rohwer, E.J.; Rohrbach, D.; Zyaee, E.; Akbarimoosavi, M.; Ollmann, Z.; Sorohhov, G.; Borgoo, A.; Cascella, M.; Cannizzo, A.; et al. Time-resolved THz Stark spectroscopy of molecules in solution. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hush, N.S.; Reimers, J.R. Vibrational Stark Spectroscopy. 1. Basic Theory and Application to the CO Stretch. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 15798–15805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fica-Contreras, S.M.; Charnay, A.P.; Pan, J.; Fayer, M.D. Rethinking Vibrational Stark Spectroscopy: Peak Shifts, Line Widths, and the Role of Non-Stark Solvent Coupling. J. Phys. Chem. B 2023, 127, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorenson, S.A.; Patrow, J.G.; Dawlaty, J.M. Solvation Reaction Field at the Interface Measured by Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2369–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Rey, N.; Dlott, D.D. Effects of water on low-overpotential CO2 reduction in ionic liquid studied by sum-frequency generation spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 10491–10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.; Tao, Y.; Zou, W.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Freindorf, M.; Kraka, E. A Critical Evaluation of Vibrational Stark Effect (VSE) Probes with the Local Vibrational Mode Theory. Sensors 2020, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, D.; Videla, P.E.; Cattaneo, M.; Batista, V.S.; Lian, T.; Kubiak, C.P. Vibrational Stark shift spectroscopy of catalysts under the influence of electric fields at electrode–solution interfaces. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 10131–10149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, A.; Videla, P.E.; Lee, G.L.; Rudshteyn, B.; Song, J.; Kubiak, C.P.; Batista, V.S.; Lian, T. Interfacial Structure and Electric Field Probed by in Situ Electrochemical Vibrational Stark Effect Spectroscopy and Computational Modeling. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 18674–18682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.; Zhao, X.; Eisenthal, K.B. Polarization of water molecules at a charged interface: Second harmonic studies of the silica/water interface. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1992, 191, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ong, S.; Eisenthal, K.B. Polarization of water molecules at a charged interface. Second harmonic studies of charged monolayers at the air/water interface. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1993, 202, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonella, G.; Lütgebaucks, C.; de Beer, A.G.F.; Roke, S. Second Harmonic and Sum-Frequency Generation from Aqueous Interfaces Is Modulated by Interference. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 9165–9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, Y.; Mukamel, S. Electrical Double Layer Probed by Surface-Specific Vibrational Technique. Chem 2018, 4, 1484–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalstein, L.; Chiang, K.-Y.; Wen, Y.-C. Surface Potential at Electrolyte/Air Interfaces: A Quantitative Analysis via Sum-Frequency Vibrational Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2023, 127, 4915–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, P.E.; Wang, H.-f.; Geiger, F.M. Second-order spectral lineshapes from charged interfaces. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-F. Sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy (SFG-VS) for complex molecular surfaces and interfaces: Spectral lineshape measurement and analysis plus some controversial issues. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2016, 91, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buessler, M.; Maruyama, S.; Zelenka, M.; Onishi, H.; Backus, E.H.G. Unravelling the interfacial water structure at the photocatalyst strontium titanate by sum frequency generation spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 31471–31480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, A.; Dutta, C.; Mammetkuliev, M.; Shi, H.; Hou, B.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Zhao, B.; Cronin, S.B.; Benderskii, A.V. Asymmetric response of interfacial water to applied electric fields. Nature 2021, 594, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darlington, A.M.; Jarisz, T.A.; DeWalt-Kerian, E.L.; Roy, S.; Kim, S.; Azam, M.S.; Hore, D.K.; Gibbs, J.M. Separating the pH-Dependent Behavior of Water in the Stern and Diffuse Layers with Varying Salt Concentration. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 20229–20241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Chiang, K.-Y.; Yu, C.-C.; Yu, X.; Okuno, M.; Hunger, J.; Nagata, Y.; Bonn, M. The Bending Mode of Water: A Powerful Probe for Hydrogen Bond Structure of Aqueous Systems. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 8459–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Sun, S.; Zhong, K.; Yu, C.-C.; Machel, K.; Dreier, L.B.; Backus, E.H.G.; Bonn, M.; Nagata, Y. Unveiling Heterogeneity of Interfacial Water through the Water Bending Mode. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 6936–6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, P.E.; Saslow, S.A.; Wang, H.-F.; Geiger, F.M.; Eisenthal, K.B. Phase-referenced nonlinear spectroscopy of the α-quartz/water interface. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Ye, S. Determination of the Thickness of Interfacial Water by Time-Resolved Sum-Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy. Langmuir 2023, 39, 18573–18580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.M.; Azam, M.S.; Hore, D.K. Variable-Angle Surface Spectroscopy Reveals the Water Structure in the Stern Layer at Charged Aqueous Interfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 11756–11763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Goel, A.; Abbas, Z. Effect of Electrolyte Concentration on the Stern Layer Thickness at a Charged Interface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3790–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehl, B.; Ma, E.; Parshotam, S.; DeWalt-Kerian, E.L.; Liu, T.; Geiger, F.M.; Gibbs, J.M. Water Structure in the Electrical Double Layer and the Contributions to the Total Interfacial Potential at Different Surface Charge Densities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 16338–16349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, C.; Busson, B.; Tadjeddine, A. Enhanced Stability of a Carbon Monoxide Monolayer Adsorbed on Platinum under Electrochemical Control Probed by Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 16211–16220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; von Rueden, A.D.; Schimmenti, R.; Mavrikakis, M.; Suntivich, J. Optical method for quantifying the potential of zero charge at the platinum–water electrochemical interface. Nat. Mater. 2023, 22, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auer, A.; Ding, X.; Bandarenka, A.S.; Kunze-Liebhäuser, J. The Potential of Zero Charge and the Electrochemical Interface Structure of Cu(111) in Alkaline Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 5020–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohandas, N.; Bawari, S.; Shibuya, J.J.T.; Ghosh, S.; Mondal, J.; Narayanan, T.N.; Cuesta, A. Understanding electrochemical interfaces through comparing experimental and computational charge density–potential curves. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 6643–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-S.; Solla-Gullón, J.; Sun, S.-G.; Feliu, J.M. The potential of zero total charge of Pt nanoparticles and polycrystalline electrodes with different surface structure: The role of anion adsorption in fundamental electrocatalysis. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 7982–7994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, A. Measurement of the surface charge density of CO-saturated Pt(111) electrodes as a function of potential: The potential of zero charge of Pt(111). Surf. Sci. 2004, 572, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Malek, A.; Zhang, J.; Eikerling, M.H. Non-monotonic Surface Charging Behavior of Platinum: A Paradigm Change. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 13587–13595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Huang, A.; Suntivich, J. Phase-Sensitive Second-Harmonic Generation of Electrochemical Interfaces. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 8216–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastián-Pascual, P.; Sarabia, F.J.; Climent, V.; Feliu, J.M.; Escudero-Escribano, M. Elucidating the Structure of the Cu-Alkaline Electrochemical Interface with the Laser-Induced Temperature Jump Method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 23253–23259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Sarpey, T.K.; Hou, S.; Garlyyev, B.; Li, W.; Fischer, R.A.; Bandarenka, A.S. Prospects of Using the Laser-Induced Temperature Jump Techniques for Characterisation of Electrochemical Systems. ChemElectroChem 2022, 9, e202101175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledezma-Yanez, I.; Wallace, W.D.Z.; Sebastián-Pascual, P.; Climent, V.; Feliu, J.M.; Koper, M.T.M. Interfacial water reorganization as a pH-dependent descriptor of the hydrogen evolution rate on platinum electrodes. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganassin, A.; Sebastián, P.; Climent, V.; Schuhmann, W.; Bandarenka, A.S.; Feliu, J. On the pH Dependence of the Potential of Maximum Entropy of Ir(111) Electrodes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollar, L.; Intikhab, S.; Zhang, S.; Deng, H.; Zeng, Z.; Snyder, J.D.; Tang, M.H. On the relationship between potential of zero charge and solvent dynamics in the reversible hydrogen electrode. J. Catal. 2021, 398, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, G.A.; Ahmadi, A. Anion—Surface interactions Part 3. N2O reduction as a chemical probe of the local potential of zero total charge. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1995, 389, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ong, S.; Wang, H.; Eisenthal, K.B. New method for determination of surface pKa using second harmonic generation. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1993, 214, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gragson, D.E.; McCarty, B.M.; Richmond, G.L. Ordering of Interfacial Water Molecules at the Charged Air/Water Interface Observed by Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 6144–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodopyanov, K.L. Mid-IR by Nonlinear Optical Frequency Conversion. In Laser-Based Mid-Infrared Sources and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 109–188. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, R.W. Nonlinear Optics, 4th ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; p. 634. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal, F.; Tadjeddine, A. Sum-frequency generation spectroscopy of interfaces. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadjeddine, A.; Vidal, F. Chapter 9—Vibrational and Electronic Spectroscopic Investigation of the Electrochemical Interface using IR-Visible Sum-Frequency Generation and Related Nonlinear Optical Techniques. In In-Situ Spectroscopic Studies of Adsorption at the Electrode and Electrocatalysis; Sun, S.-G., Christensen, P.A., Wieckowski, A., Eds.; Elsevier Science, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 273–298. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, L.J.; Petralli-Mallow, T.P.; Stephenson, J.C. Vibrationally resolved sum-frequency generation with broad-bandwidth infrared pulses. Opt. Lett. 1998, 23, 1594–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, N.; Ostroverkhov, V.; Chen, C.-Y.; Shen, Y.-R. Phase-Sensitive Sum-Frequency Vibrational Spectroscopy and Its Application to Studies of Interfacial Alkyl Chains. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10056–10057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Tahara, T. Heterodyne-detected electronic sum frequency generation: “Up” versus “down” alignment of interfacial molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihonyanagi, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Tahara, T. Direct evidence for orientational flip-flop of water molecules at charged interfaces: A heterodyne-detected vibrational sum frequency generation study. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 204704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perakis, F.; De Marco, L.; Shalit, A.; Tang, F.; Kann, Z.R.; Kühne, T.D.; Torre, R.; Bonn, M.; Nagata, Y. Vibrational Spectroscopy and Dynamics of Water. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7590–7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Rupprechter, G. Sum frequency generation (SFG) spectroscopy at surfaces and interfaces: Adsorbate structure and molecular bond orientation. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2024, 79, 100645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-R. Second Harmonic and Sum-Frequency Spectroscopy; World Scientific Publishing: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, A.M.; Saeed, K.H.; Cowan, A.J. Vibrational sum-frequency generation spectroscopy of electrode surfaces: Studying the mechanisms of sustainable fuel generation and utilisation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 12067–12086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Seki, T.; Yu, C.-C.; Nagata, Y. Microscopic Structure of Ice Surface Viewed through Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy. In Chemistry in the Cryosphere; World Scientific Publishing: London, UK, 2022; pp. 139–171. [Google Scholar]
- Guyot-Sionnest, P.; Tadjeddine, A. Spectroscopic investigations of adsorbates at the metal—Electrolyte interface using sum frequency generation. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1990, 172, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, D. Calcium Fluoride and Barium Fluoride Crystals in Optics. Opt. Photonik 2014, 9, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Dao, T.P.D. Analytical Chemistry, Questions and Problems in Ionic Equilibrium in Aqueous Solutions; Hanoi National University of Education Publishers: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2005; p. 363. [Google Scholar]
- Miessler, G.L.; Fischer, P.J.; Tarr, D.A. Inorganic Chemistry, 5th ed.; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2021; pp. xiv, 682p. [Google Scholar]
- León, L.; Mozo, J.D. Designing spectroelectrochemical cells: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-Y.; Tian, Z.-Q. Sixty years of electrochemical optical spectroscopy: A retrospective. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 3579–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, A.; Inoue, K.-I.; Ye, S. Probing the electrode–solution interfaces in rechargeable batteries by sum-frequency generation spectroscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 170902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beden, B.; Lamy, C.; Bewick, A.; Kunimatsu, K. Electrosorption of methanol on a platinum electrode. IR spectroscopic evidence for adsorbed CO species. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1981, 121, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, N.; Motto, S.; Kunimatsu, K. Vibrational spectroscopy on platinum single-crystal electrodes: Part, I. In-situ infrared spectroscopic studies of the adsorption and oxidation of CO on Pt (111) in sulphuric acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1988, 239, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallentine, S.; Bandaranayake, S.; Biswas, S.; Baker, L.R. Plasmon-Resonant Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation of Electrochemical Interfaces: Direct Observation of Carbon Dioxide Electroreduction on Gold. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 124, 8057–8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-T.; Shen, Y.R. In situ sum-frequency vibrational spectroscopy of electrochemical interfaces with surface plasmon resonance. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 111, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H.; Okada, T.; Uosaki, K. Molecular structure at electrode/electrolyte solution interfaces related to electrocatalysis. Faraday Discuss. 2009, 140, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, Y.; Han, H.-L.; Soto, F.A.; Ralston, W.T.; Balbuena, P.B.; Somorjai, G.A. Fluoroethylene Carbonate as a Directing Agent in Amorphous Silicon Anodes: Electrolyte Interface Structure Probed by Sum Frequency Vibrational Spectroscopy and Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.X.; Miki, A.; Ye, S.; Sakai, H.; Osawa, M. Formate, an Active Intermediate for Direct Oxidation of Methanol on Pt Electrode. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3680–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, R.; Dietzek-Ivanšić, B. A Happy Get-Together—Probing Electrochemical Interfaces by Non-Linear Vibrational Spectroscopy. Chem. Eur. J. 2022, 28, e202200407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.L.; Horowitz, Y.; Somorjai, G.A. A Review on In Situ Sum Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy Studies of Liquid–Solid Interfaces in Electrochemical Systems. In Encyclopedia of Interfacial Chemistry; Wandelt, K., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Iwahashi, T.; Miwa, Y.; Zhou, W.; Sakai, Y.; Yamagata, M.; Ishikawa, M.; Kim, D.; Ouchi, Y. IV-SFG studies on the effect of Li+ in extending the electrochemical window at the Pt|[C2mim][FSA] interface. Electrochem. Commun. 2016, 72, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Xu, Y.; Ouchi, Y. Hysteresis Effects in the In Situ SFG and Differential Capacitance Measurements on Metal Electrode/Ionic Liquids Interface. ECS Trans. 2013, 50, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Inoue, S.; Iwahashi, T.; Kanai, K.; Seki, K.; Miyamae, T.; Kim, D.; Katayama, Y.; Ouchi, Y. Electrochemical Double-Layer Structure of Pt Electrode/Ionic Liquids Interface Studied by in situ IR-visible Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy. ECS Trans. 2009, 16, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldelli, S. Surface Structure at the Ionic Liquid−Electrified Metal Interface. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakhtemanian, L.; Duwadi, A.; Baldelli, S.; Ghatee, M.H. Simulating the ionic liquid mixing with organic-solvent clarifies the mixture’s SFG spectral behavior and the specific surface region originating SFG. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, A.U.; Muralidharan, N.; Daniel, C.; Amin, R.; Belharouak, I. Probing the electrolyte/electrode interface with vibrational sum frequency generation spectroscopy: A review. J. Power Sources 2021, 506, 230173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, Y.; Han, H.-L.; Ross, P.N.; Somorjai, G.A. In Situ Potentiodynamic Analysis of the Electrolyte/Silicon Electrodes Interface Reactions—A Sum Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 726–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Lagutchev, A.; Dlott, D.D. In Situ Probing of Solid-Electrolyte Interfaces with Nonlinear Coherent Vibrational Spectroscopy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björneholm, O.; Hansen, M.H.; Hodgson, A.; Liu, L.-M.; Limmer, D.T.; Michaelides, A.; Pedevilla, P.; Rossmeisl, J.; Shen, H.; Tocci, G.; et al. Water at Interfaces. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7698–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J. Understanding the Electric Double-Layer Structure, Capacitance, and Charging Dynamics. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 10821–10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-H.; Singer, S.J. Molecular Dynamics Study of the Electric Double Layer and Nonlinear Spectroscopy at the Amorphous Silica–Water Interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 6364–6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joutsuka, T.; Morita, A. Electrolyte and Temperature Effects on Third-Order Susceptibility in Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy of Aqueous Salt Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 11407–11413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groß, A.; Sakong, S. Ab Initio Simulations of Water/Metal Interfaces. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 10746–10776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnussen, O.M.; Groß, A. Toward an Atomic-Scale Understanding of Electrochemical Interface Structure and Dynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4777–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, T.; Imamura, T.; Morita, A. Theoretical Studies of Structures and Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation Spectra at Aqueous Interfaces. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8447–8470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litman, Y.; Lan, J.; Nagata, Y.; Wilkins, D.M. Fully First-Principles Surface Spectroscopy with Machine Learning. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 8175–8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungerer, M.J.; Santos-Carballal, D.; Cadi-Essadek, A.; van Sittert, C.G.C.E.; de Leeuw, N.H. Interaction of H2O with the Platinum Pt(001), (011), and (111) Surfaces: A Density Functional Theory Study with Long-Range Dispersion Corrections. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 27465–27476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, K.; Sundararaman, R. The electrochemical interface in first-principles calculations. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2020, 75, 100492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, J.-F.; Hynes, J.T.; Laage, D. Water dynamics and sum-frequency generation spectra at electrode/aqueous electrolyte interfaces. Faraday Discuss. 2024, 249, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souna, A.J.; Motevaselian, M.H.; Polster, J.W.; Tran, J.D.; Siwy, Z.S.; Aluru, N.R.; Fourkas, J.T. Beyond the electrical double layer model: Ion-dependent effects in nanoscale solvent organization. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 6726–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulpizi, M.; Salanne, M.; Sprik, M.; Gaigeot, M.-P. Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy of the Water Liquid–Vapor Interface from Density Functional Theory-Based Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, R.; Backus, E.H.G.; Bonn, M.; Perez-Haro, M.-J.; Gaigeot, M.-P.; Sulpizi, M. Water orientation and hydrogen-bond structure at the fluorite/water interface. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Brigiano, F.S.; Pezzotti, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Lin, X.; Zheng, W.; et al. Unconventional structural evolution of an oxide surface in water unveiled by in situ sum-frequency spectroscopy. Nat. Chem. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzotti, S.; Galimberti, D.R.; Shen, Y.R.; Gaigeot, M.P. Structural definition of the BIL and DL: A new universal methodology to rationalize non-linear χ(2)(ω) SFG signals at charged interfaces, including χ(3)(ω) contributions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 5190–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verreault, D.; Kurz, V.; Howell, C.; Koelsch, P. Sample cells for probing solid/liquid interfaces with broadband sum-frequency-generation spectroscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2010, 81, 063111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becraft, K.A.; Richmond, G.L. In Situ Vibrational Spectroscopic Studies of the CaF2/H2O Interface. Langmuir 2001, 17, 7721–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becraft, K.A.; Moore, F.G.; Richmond, G.L. In-situ spectroscopic investigations of surfactant adsorption and water structure at the CaF2/aqueous solution interface. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2004, 6, 1880–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödle, S.; Moore, F.G.; Richmond, G.L. Surface Speciation at Solid/Liquid Interfaces: A Vibrational Sum-Frequency Study of Acetate Adsorption at the Fluorite/Water Interface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 10088–10094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, P.; Boon, W.Q.; Dijkstra, M.; Backus, E.H.G.; van Roij, R.; Bonn, M. Liquid flow reversibly creates a macroscopic surface charge gradient. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis, D.; Backus, E.H.G.; Hunger, J.; Parekh, S.H.; Bonn, M. Liquid flow along a solid surface reversibly alters interfacial chemistry. Science 2014, 344, 1138–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesnicki, D.; Zhang, Z.; Bonn, M.; Sulpizi, M.; Backus, E.H.G. Surface Charges at the CaF2/Water Interface Allow Very Fast Intermolecular Vibrational-Energy Transfer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13116–13121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.R.; Ostroverkhov, V. Sum-Frequency Vibrational Spectroscopy on Water Interfaces: Polar Orientation of Water Molecules at Interfaces. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostroverkhov, V.; Waychunas, G.A.; Shen, Y.R. New Information on Water Interfacial Structure Revealed by Phase-Sensitive Surface Spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 046102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myalitsin, A.; Urashima, S.-H.; Nihonyanagi, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Tahara, T. Water Structure at the Buried Silica/Aqueous Interface Studied by Heterodyne-Detected Vibrational Sum-Frequency Generation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 9357–9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urashima, S.-h.; Myalitsin, A.; Nihonyanagi, S.; Tahara, T. The Topmost Water Structure at a Charged Silica/Aqueous Interface Revealed by Heterodyne-Detected Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 4109–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostroverkhov, V.; Waychunas, G.A.; Shen, Y.R. Vibrational spectra of water at water/α-quartz (0001) interface. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 386, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Freysz, E.; Shen, Y.R. Vibrational spectra of water molecules at quartz/water interfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 72, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalstein, L.; Potapova, E.; Tyrode, E. The elusive silica/water interface: Isolated silanols under water as revealed by vibrational sum frequency spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 10343–10349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeganeh, M.S.; Dougal, S.M.; Pink, H.S. Vibrational Spectroscopy of Water at Liquid/Solid Interfaces: Crossing the Isoelectric Point of a Solid Surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tian, C.; Waychunas, G.A.; Shen, Y.R. Structures and Charging of α-Alumina (0001)/Water Interfaces Studied by Sum-Frequency Vibrational Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7686–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, S.; Gurau, M.C.; Albertorio, F.; Holden, M.A.; Lim, S.-M.; Yang, R.D.; Cremer, P.S. Investigation of Water Structure at the TiO2/Aqueous Interface. Langmuir 2004, 20, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, S.J.; Hosseinpour, S.; Gebhard, M.; Devi, A.; Bonn, M.; Backus, E.H.G. How water flips at charged titanium dioxide: An SFG-study on the water–TiO2 interface. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 8956–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, S.; Tang, F.; Wang, F.; Livingstone, R.A.; Schlegel, S.J.; Ohto, T.; Bonn, M.; Nagata, Y.; Backus, E.H.G. Chemisorbed and Physisorbed Water at the TiO2/Water Interface. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 2195–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuladhar, A.; Chase, Z.A.; Baer, M.D.; Legg, B.A.; Tao, J.; Zhang, S.; Winkelman, A.D.; Wang, Z.; Mundy, C.J.; De Yoreo, J.J.; et al. Direct Observation of the Orientational Anisotropy of Buried Hydroxyl Groups inside Muscovite Mica. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nihonyanagi, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Tahara, T. Water Hydrogen Bond Structure near Highly Charged Interfaces Is Not Like Ice. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6867–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, C.; Mammetkuliyev, M.; Benderskii, A.V. Re-orientation of water molecules in response to surface charge at surfactant interfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 151, 034703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.-C.; Zha, S.; Tian, C.; Shen, Y.R. Surface pH and Ion Affinity at the Alcohol-Monolayer/Water Interface Studied by Sum-Frequency Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 15224–15229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, J.A.; Nihonyanagi, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Tahara, T. Structure and Orientation of Water at Charged Lipid Monolayer/Water Interfaces Probed by Heterodyne-Detected Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10656–10657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, J.A.; Nihonyanagi, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Tahara, T. Three Distinct Water Structures at a Zwitterionic Lipid/Water Interface Revealed by Heterodyne-Detected Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7842–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hua, W.; Huang, Z.; Allen, H.C. Interfacial Water Structure Associated with Phospholipid Membranes Studied by Phase-Sensitive Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 11336–11342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sovago, M.; Vartiainen, E.; Bonn, M. Observation of buried water molecules in phospholipid membranes by surface sum-frequency generation spectroscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131, 161107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubb, A.M.; Hua, W.; Allen, H.C. Environmental Chemistry at Vapor/Water Interfaces: Insights from Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2012, 63, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasatti, S. Electrochemical Theory | Oxygen Evolution. In Encyclopedia of Electrochemical Power Sources; Garche, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Philipossian, A.; Mustapha, L. Tribological Attributes of Post-CMP Brush Scrubbing. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, G456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J. Hydrolysis and condensation of silicates: Effects on structure. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1988, 100, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Chatzitakis, A.; Aarholt, T.; Sun, X.; Negri, C.; Norby, T. Facet-engineered TiO2 nanomaterials reveal the role of water–oxide interactions in surface protonic conduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Gubbins, K.E.; Li, L.; Lu, X. Water on Titanium Dioxide Surface: A Revisiting by Reactive Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Langmuir 2014, 30, 14832–14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasulo, F.; Piccini, G.; Muñoz-García, A.B.; Pavone, M.; Parrinello, M. Dynamics of Water Dissociative Adsorption on TiO2 Anatase (101) at Monolayer Coverage and Below. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 15752–15758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Tu, K.-J.; Deng, J.-P.; Lo, Y.-S.; Wu, C.-H. Markedly Enhanced Surface Hydroxyl Groups of TiO2 Nanoparticles with Superior Water-Dispersibility for Photocatalysis. Materials 2017, 10, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanawa, T. Biofunctionalization of Metallic Materials: Creation of Biosis–Abiosis Intelligent Interface. In Proceedings of the Interface Oral Health Science, Tokyo, Japan, 20–21 January 2014; pp. 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, L.; Lei, E.; Hu, C.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, W.; Guo, Z.; Huang, D. A facile hydrothermal synthesis and properties of TiO2 nanosheet array films. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.J.; Baldelli, S.; Schnitzer, C.; Simonelli, D. Aqueous Solution/Air Interfaces Probed with Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 5313–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litman, Y.; Chiang, K.-Y.; Seki, T.; Nagata, Y.; Bonn, M. Surface stratification determines the interfacial water structure of simple electrolyte solutions. Nat. Chem. 2024, 16, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nihonyanagi, S.; Ishiyama, T.; Lee, T.-k.; Yamaguchi, S.; Bonn, M.; Morita, A.; Tahara, T. Unified Molecular View of the Air/Water Interface Based on Experimental and Theoretical χ(2) Spectra of an Isotopically Diluted Water Surface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 16875–16880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, W.J.; Tang, F.; Nagata, Y.; Sánchez, M.A.; Hasegawa, T.; Backus, E.H.G.; Bonn, M.; Bakker, H.J. Observation and Identification of a New OH Stretch Vibrational Band at the Surface of Ice. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 3656–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaigeot, M.-P.; Sprik, M.; Sulpizi, M. Oxide/water interfaces: How the surface chemistry modifies interfacial water properties. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2012, 24, 124106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaienko, O.; Borguet, E. Hydrophobicity of Hydroxylated Amorphous Fused Silica Surfaces. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7885–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-y.; Groenzin, H.; Shultz, M.J. Molecular Species on Nanoparticulate Anatase TiO2 Film Detected by Sum Frequency Generation: Trace Hydrocarbons and Hydroxyl Groups. Langmuir 2003, 19, 7330–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-C.; Chiang, K.-Y.; Okuno, M.; Seki, T.; Ohto, T.; Yu, X.; Korepanov, V.; Hamaguchi, H.-o.; Bonn, M.; Hunger, J.; et al. Vibrational couplings and energy transfer pathways of water’s bending mode. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qian, L. Role of interfacial water in adhesion, friction, and wear—A critical review. Friction 2021, 9, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasojevic, I.; Verdaguer, A.; Catalan, G.; Domingo, N. Effect of Humidity on the Writing Speed and Domain Wall Dynamics of Ferroelectric Domains. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2022, 8, 2100650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovering, K.A.; Bertram, A.K.; Chou, K.C. New Information on the Ion-Identity-Dependent Structure of Stern Layer Revealed by Sum Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 18099–18104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhtemanian, L.; Dashti, N.; Ghatee, M.H. A singular behavior at the electrolytes solution surfaces: Experimental and simulation investigation over an extended range of temperature. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2022, 555, 113347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshotam, S.; Rehl, B.; Busse, F.; Brown, A.; Gibbs, J.M. Influence of the Hydrogen-Bonding Environment on Vibrational Coupling in the Electrical Double Layer at the Silica/Aqueous Interface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 21734–21744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peremans, A.; Tadjeddine, A. Electrochemical deposition of hydrogen on platinum single crystals studied by infrared-visible sum-frequency generation. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 7197–7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Tadjeddine, A. Adsorption processes and structure of water molecules on Pt(110) electrodes in perchloric solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 13096–13099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.Q.; Pluchery, O.; Tadjeddine, A. SFG study of platinum electrodes in perchloric acid solutions. Surf. Sci. 2002, 502–503, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piontek, S.M.; Naujoks, D.; Tabassum, T.; DelloStritto, M.J.; Jaugstetter, M.; Hosseini, P.; Corva, M.; Ludwig, A.; Tschulik, K.; Klein, M.L.; et al. Probing the Gold/Water Interface with Surface-Specific Spectroscopy. ACS Phys. Chem. Au 2023, 3, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backus, E.H.G.; Garcia-Araez, N.; Bonn, M.; Bakker, H.J. On the Role of Fresnel Factors in Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy of Metal–Water and Metal-Oxide–Water Interfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 23351–23361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Nihonyanagi, S.; Fujishima, K.; Uosaki, K. Conformational Order of Octadecanethiol (ODT) Monolayer at Gold/Solution Interface: Internal Reflection Sum Frequency Generation (SFG) Study. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Iwasawa, Y., Oyama, N., Kunieda, H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 132, pp. 705–710. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.-T. Coherent Vibrational Spectroscopy of Electrochemical Interfaces with Plasmonic Nanogratings. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihonyanagi, S.; Ye, S.; Uosaki, K.; Dreesen, L.; Humbert, C.; Thiry, P.; Peremans, A. Potential-dependent structure of the interfacial water on the gold electrode. Surf. Sci. 2004, 573, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fang, J.; Huang, X. Different behaviors between interband and intraband transitions generated hot carriers on g-C3N4/Au for photocatalytic H2 production. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 513, 145830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, Z.D.; Shaw, S.K.; Gewirth, A.A. Potential Dependent Organization of Water at the Electrified Metal−Liquid Interface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15916–15922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petek, H.; Zhao, J. Ultrafast Interfacial Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 7082–7099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H.; Okada, T.; Uosaki, K. SFG study on potential-dependent structure of water at Pt electrode/electrolyte solution interface. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 6841–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, M.; Michely, T.; Comsa, G. Anisotropy in the adsorption of H2O at low coordination sites on Pt(111). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikemiya, N.; Gewirth, A.A. Initial stages of water adsorption on Au surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 9919–9920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagutchev, A.; Hambir, S.A.; Dlott, D.D. Nonresonant Background Suppression in Broadband Vibrational Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 13645–13647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagutchev, A.; Lozano, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Hambir, S.A.; Dlott, D.D. Compact broadband vibrational sum-frequency generation spectrometer with nonresonant suppression. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 75, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Lapointe, F.; Thämer, M.; Wolf, M.; Campen, R.K. Hydrophobic Water Probed Experimentally at the Gold Electrode/Aqueous Interface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4211–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreier, L.B.; Liu, Z.; Narita, A.; van Zadel, M.J.; Müllen, K.; Tielrooij, K.J.; Backus, E.H.G.; Bonn, M. Surface-Specific Spectroscopy of Water at a Potentiostatically Controlled Supported Graphene Monolayer. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 24031–24038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sovago, M.; Campen, R.K.; Wurpel, G.W.H.; Müller, M.; Bakker, H.J.; Bonn, M. Vibrational Response of Hydrogen-Bonded Interfacial Water is Dominated by Intramolecular Coupling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 173901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Seki, T.; Yu, X.; Yu, C.-C.; Chiang, K.-Y.; Domke, K.F.; Hunger, J.; Chen, Y.; Nagata, Y.; Bonn, M. Chemistry governs water organization at a graphene electrode. Nature 2023, 615, E1–E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Seki, T.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Yu, C.-C.; Domke, K.F.; Hunger, J.; Koper, M.T.M.; Chen, Y.; Nagata, Y.; et al. Surface-specific vibrational spectroscopy of interfacial water reveals large pH change near graphene electrode at low current densities. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.02532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadjeddine, A.; Guyot-Sionnest, P. Spectroscopic investigation of adsorbed cyanide and thiocyanate on platinum using sum frequency generation. Electrochim. Acta 1991, 36, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daum, W.; Friedrich, K.A.; Klünker, C.; Knabben, D.; Stimming, U.; Ibach, H. Sum-frequency generation at electrochemical interfaces: Cyanide vibrations on Pt(111) and Pt(110). Appl. Phys. A Solids Surf. 1994, 59, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadjeddine, A.; Peremans, A.; Guyot-Sionnest, P. Vibrational spectroscopy of the electrochemical interface by visible-infrared sum-frequency generation. Surf. Sci. 1995, 335, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altowyan, M.S.; Fathalla, E.M.; Albering, J.H.; Abu-Youssef, M.A.M.; Kassem, T.S.; Barakat, A.; Haukka, M.; Badr, A.M.A.; Soliman, S.M. Synthesis, X-ray Structures and Hirshfeld Analysis of Two Novel Thiocyanate-Bridged Ag(I) Coordination Polymers. Inorganics 2023, 11, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Huangfu, Z.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, Z. Observation of gold electrode surface response to the adsorption and oxidation of thiocyanate in acidic electrolyte with broadband sum-frequency generation spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 2016, 85, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.F.; Bergamaski, K.; Pinto, M.F.S.; Miranda, P.B. Reaction intermediates of ethanol electro-oxidation on platinum investigated by SFG spectroscopy. J. Catal. 2013, 302, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbaraman, R.; Strmcnik, D.; Stamenkovic, V.; Markovic, N.M. Three Phase Interfaces at Electrified Metal−Solid Electrolyte Systems 1. Study of the Pt(hkl)−Nafion Interface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 8414–8422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunschweig, B.; Mukherjee, P.; Dlott, D.D.; Wieckowski, A. Real-Time Investigations of Pt(111) Surface Transformations in Sulfuric Acid Solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14036–14038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwaschka, G.; Wolf, M.; Campen, R.K.; Tong, Y. A Microscopic Model of the Electrochemical Vibrational Stark Effect: Understanding VSF Spectroscopy of (bi)Sulfate on Pt(111). Surf. Sci. 2018, 678, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, Z. Sharaf and Mehmet F. Orhan, An overview of fuel cell technology: Fundamentals and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 810–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Abdulrahman, G.A.Q. A Recent Comprehensive Review of Fuel Cells: History, Types, and Applications. Int. J. Energy Res. 2024, 2024, 7271748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadjeddine, A.; Peremans, A. Vibrational spectroscopy of the electrochemical interface by visible infrared sum-frequency generation. Surf. Sci. 1996, 368, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayden, J.; Greeves, N.; Warren, S. Organic Chemistry; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, S. Phosphine supported metal-dihydrogen complexes: Elongation of H−H bond to reversible release of H2. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2011, 14, 1029–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo, R.; Herrero, E.; Climent, V.; Feliu, J.M. On the nature of adsorbed species on platinum single-crystal electrodes. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2023, 38, 101240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo, R.; Fernández-Vidal, J.; Hardwick, L.J.; Attard, G.A.; Vidal-Iglesias, F.J.; Climent, V.; Herrero, E.; Feliu, J.M. Investigating the presence of adsorbed species on Pt steps at low potentials. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Noguchi, H.; Uosaki, K. Electronic Structure of the CO/Pt(111) Electrode Interface Probed by Potential-Dependent IR/Visible Double Resonance Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 26056–26063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, F.; Busson, B.; Six, C.; Pluchery, O.; Tadjeddine, A. SFG study of methanol dissociative adsorption at Pt(100), Pt(110) and Pt(111) electrodes surfaces. Surf. Sci. 2002, 502–503, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutz, R.B.; Braunschweig, B.; Mukherjee, P.; Behrens, R.L.; Dlott, D.D.; Wieckowski, A. Reaction pathways of ethanol electrooxidation on polycrystalline platinum catalysts in acidic electrolytes. J. Catal. 2011, 278, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.Q.; Lagutchev, A.; Dlott, D.D.; Wieckowski, A. Quantitative vibrational sum-frequency generation spectroscopy of thin layer electrochemistry: CO on a Pt electrode. Surf. Sci. 2005, 585, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H.; Ishimaru, T.; Uosaki, K. Potential and time dependent broad band sum frequency generation spectroscopic study on electrochemical oxidation of adsorbed CO on Pt(111) electrode surface in pre-peak region in alkaline solution. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 896, 115478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peremans, A.; Tadjeddine, A. Spectroscopic investigation of electrochemical interfaces at overpotential by infrared-visible sum-frequency generation: Platinum in bare and methanol-containing electrolyte. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1995, 395, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, F.; Busson, B.; Six, C.; Tadjeddine, A.; Dreesen, L.; Humbert, C.; Peremans, A.; Thiry, P. Methanol dissociative adsorption on Pt(100) as studied by nonlinear vibrational spectroscopy. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 1, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, F.; Tadjeddine, A.; Humbert, C.; Dreesen, L.; Peremans, A.; Thiry, P.A.; Busson, B. The influence of surface defects in methanol dissociative adsorption and CO oxidation on Pt(110) probed by nonlinear vibrational SFG spectroscopy. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 672, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Bellamkonda, S. Chapter 10—Oxygen reduction reaction in ethanol fuel cells. In Oxygen Reduction Reaction; Sengupta, K., Chatterjee, S., Dutta, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 337–378. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Soto, F.A.; Li, D.; Deng, T.; Hu, E.; Lu, X.; Cullen, D.A.; Eidson, N.; Yang, X.-Q.; He, K.; et al. Pd-Ru pair on Pt surface for promoting hydrogen oxidation and evolution in alkaline media. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunschweig, B.; Mukherjee, P.; Kutz, R.B.; Rumpel, A.; Engelhardt, K.; Peukert, W.; Dlott, D.D.; Wieckowski, A. Spectroscopy of Electrified Interfaces with Broadband Sum Frequency Generation: From Electrocatalysis to Protein Foams. In Vibrational Spectroscopy at Electrified Interfaces; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 120–150. [Google Scholar]
- Braunschweig, B.; Wieckowski, A. Surface spectroscopy of Pt(111) single-crystal electrolyte interfaces with broadband sum-frequency generation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 716, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunschweig, B.; Mukherjee, P.; Kutz, R.B.; Wieckowski, A.; Dlott, D.D. Sum-frequency generation of acetate adsorption on Au and Pt surfaces: Molecular structure effects. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 133, 234702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, P.; Chen, L. CO2 electrolysis: Advances and challenges in electrocatalyst engineering and reactor design. Mater. Rep. Energy 2023, 3, 100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birdja, Y.Y.; Pérez-Gallent, E.; Figueiredo, M.C.; Göttle, A.J.; Calle-Vallejo, F.; Koper, M.T.M. Advances and challenges in understanding the electrocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide to fuels. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Niu, Z.; Kim, D.; Li, M.; Yang, P. Surface and Interface Control in Nanoparticle Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1184–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Gong, J.; Dewangan, N.; Hidajat, K.; Gates, B.C.; Kawi, S. Core–shell structured catalysts for thermocatalytic, photocatalytic, and electrocatalytic conversion of CO2. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 2937–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang-fu, Z.-C.; Song, Q.-T.; He, Y.-H.; Wang, J.-J.; Ye, J.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Sun, S.-G.; Wang, Z.-H. Electrochemical CO2 reduction on Cu and Au electrodes studied using in situ sum frequency generation spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 25047–25053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, C.; Dattila, F.; Rettenmaier, C.; Herzog, A.; Herran, M.; Wagner, T.; Scholten, F.; Bergmann, A.; López, N.; Roldan Cuenya, B. Key intermediates and Cu active sites for CO2 electroreduction to ethylene and ethanol. Nat. Energy 2024, 9, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Song, Q.; Huang, H.; He, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, Z. Direct Observation of Surface-Bound Intermediates in CO/CO2 Reduction on a Polycrystalline Cu Electrode Using Broad-Band SFG Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 23675–23686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, H.; He, Z.; Long, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, P.; et al. Surface modification of metal materials for high-performance electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction. Matter 2021, 4, 888–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Srivastava, R. Utilization of bio-inspired catalyst for CO2 reduction into green fuels: Recent advancement and future perspectives. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 53, 101748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.-M.; Zhu, Y.-P.; Chen, P.; Ma, T.-Y. Recent Advances in Transition-Metal-Mediated Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction: From Homogeneous to Heterogeneous Systems. Catalysts 2017, 7, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallentine, S.; Bandaranayake, S.; Biswas, S.; Baker, L.R. Direct Observation of Carbon Dioxide Electroreduction on Gold: Site Blocking by the Stern Layer Controls CO2 Adsorption Kinetics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 8307–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.-H.; Zhu, Q.; Rebstock, J.; Neves-Garcia, T.; Baker, L.R. Direct observation of bicarbonate and water reduction on gold: Understanding the potential dependent proton source during hydrogen evolution. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 4523–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, C.; Busson, B.; Six, C.; Gayral, A.; Gruselle, M.; Villain, F.; Tadjeddine, A. Sum-frequency generation as a vibrational and electronic probe of the electrochemical interface and thin films. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2008, 621, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldelli, S.; Mailhot, G.; Ross, P.N.; Somorjai, G.A. Potential-Dependent Vibrational Spectroscopy of Solvent Molecules at the Pt(111) Electrode in a Water/Acetonitrile Mixture Studied by Sum Frequency Generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 7697–7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluchery, O.; Tadjeddine, A. Investigation of the adsorption of 4-cyanopyridine on Au(111) by in situ visible–infrared sum frequency generation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 500, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rille, A.; Tadjeddine, A.; Zheng, W.Q.; Peremans, A. Vibrational spectroscopy of a Au(hkl)-electrolyte interface by in situ visible-infrared difference frequency generation. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1997, 271, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelici, R.J.; Lazar, M. Isocyanide Ligands Adsorbed on Metal Surfaces: Applications in Catalysis, Nanochemistry, and Molecular Electronics. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 9155–9165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, S.A.; McClain, R.; Lovejoy, K.S.; Alamdari, N.B.; Hamilton, J.S.; Scott, J.C. Self-Assembled Diisocyanide Monolayer Films on Gold and Palladium. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5034–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, Z.D.; Gewirth, A.A. Potential-Dependent Adsorption and Orientation of a Small Zwitterion: p-Aminobenzoic Acid on Ag(111). Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 7373–7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 NH3+ is the protonated form of APTES (EtO)3Si-(CH2)3-NH2 (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane and
NH3+ is the protonated form of APTES (EtO)3Si-(CH2)3-NH2 (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane and  COO− represents the carboxylate form of mercaptocarboxylic acids HS-(CH2)n-COOH (n 3).
COO− represents the carboxylate form of mercaptocarboxylic acids HS-(CH2)n-COOH (n 3).  denotes the vibro-electronic dipolar coupling of the exciton (electron–hole pair) of QDs to the vibrational resonances of surrounding ligands. From geometry investigation, the optimized angles for Visible and Infrared photons are 55o and 65o, respectively. The polarization scheme is (S:SP) for the SFG, Vis, and IR beams, where the polarization plane of P(x,0,z) and S(0,y,0) is illustrated. Light can be polarized parallel (P polarization) or perpendicular (S polarization) to the plane of incidence (Oxz plane). This figure is inspired by references [87,89,90].
denotes the vibro-electronic dipolar coupling of the exciton (electron–hole pair) of QDs to the vibrational resonances of surrounding ligands. From geometry investigation, the optimized angles for Visible and Infrared photons are 55o and 65o, respectively. The polarization scheme is (S:SP) for the SFG, Vis, and IR beams, where the polarization plane of P(x,0,z) and S(0,y,0) is illustrated. Light can be polarized parallel (P polarization) or perpendicular (S polarization) to the plane of incidence (Oxz plane). This figure is inspired by references [87,89,90].
 NH3+ is the protonated form of APTES (EtO)3Si-(CH2)3-NH2 (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane and
NH3+ is the protonated form of APTES (EtO)3Si-(CH2)3-NH2 (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane and  COO− represents the carboxylate form of mercaptocarboxylic acids HS-(CH2)n-COOH (n 3).
COO− represents the carboxylate form of mercaptocarboxylic acids HS-(CH2)n-COOH (n 3).  denotes the vibro-electronic dipolar coupling of the exciton (electron–hole pair) of QDs to the vibrational resonances of surrounding ligands. From geometry investigation, the optimized angles for Visible and Infrared photons are 55o and 65o, respectively. The polarization scheme is (S:SP) for the SFG, Vis, and IR beams, where the polarization plane of P(x,0,z) and S(0,y,0) is illustrated. Light can be polarized parallel (P polarization) or perpendicular (S polarization) to the plane of incidence (Oxz plane). This figure is inspired by references [87,89,90].
denotes the vibro-electronic dipolar coupling of the exciton (electron–hole pair) of QDs to the vibrational resonances of surrounding ligands. From geometry investigation, the optimized angles for Visible and Infrared photons are 55o and 65o, respectively. The polarization scheme is (S:SP) for the SFG, Vis, and IR beams, where the polarization plane of P(x,0,z) and S(0,y,0) is illustrated. Light can be polarized parallel (P polarization) or perpendicular (S polarization) to the plane of incidence (Oxz plane). This figure is inspired by references [87,89,90].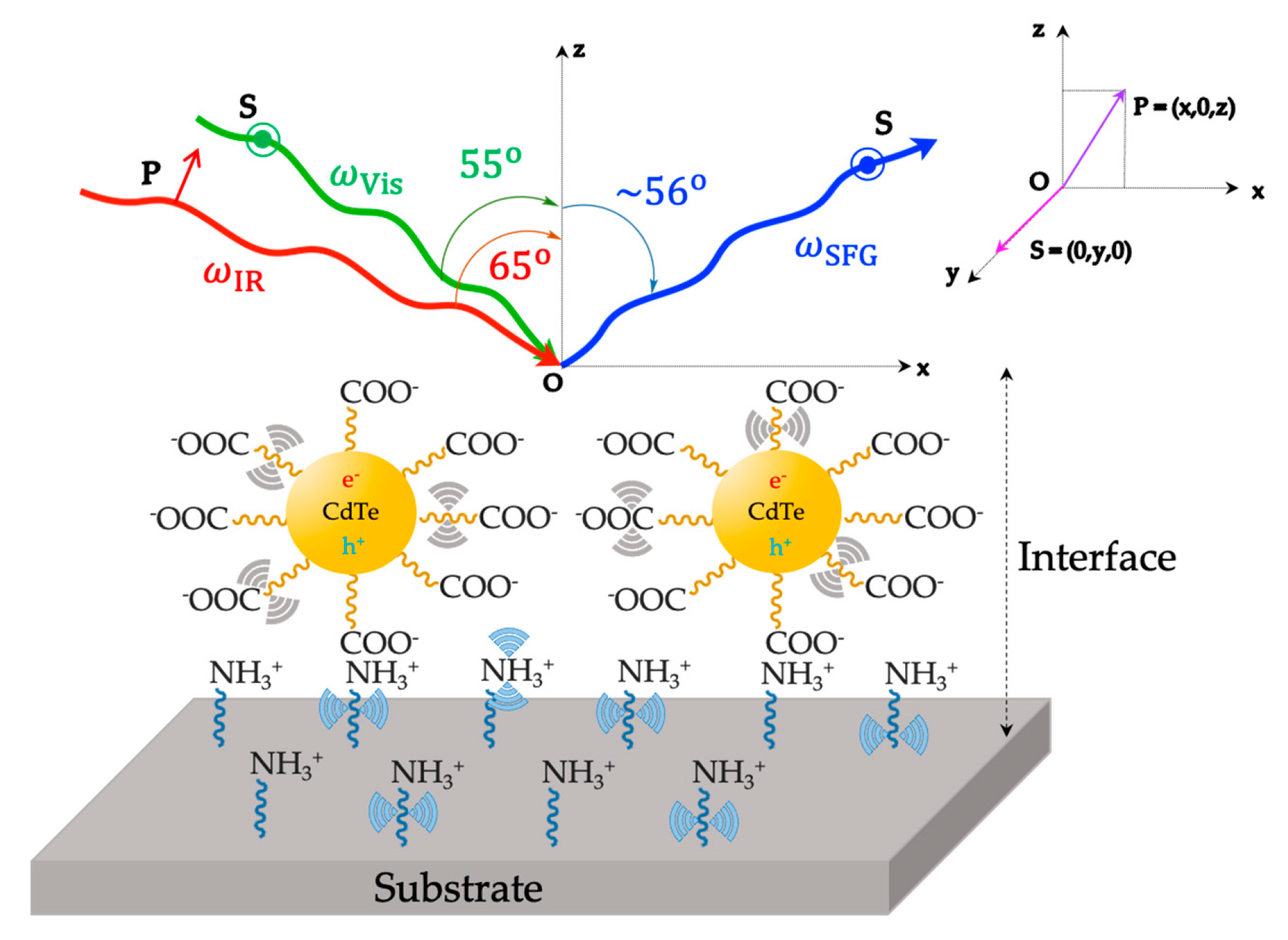
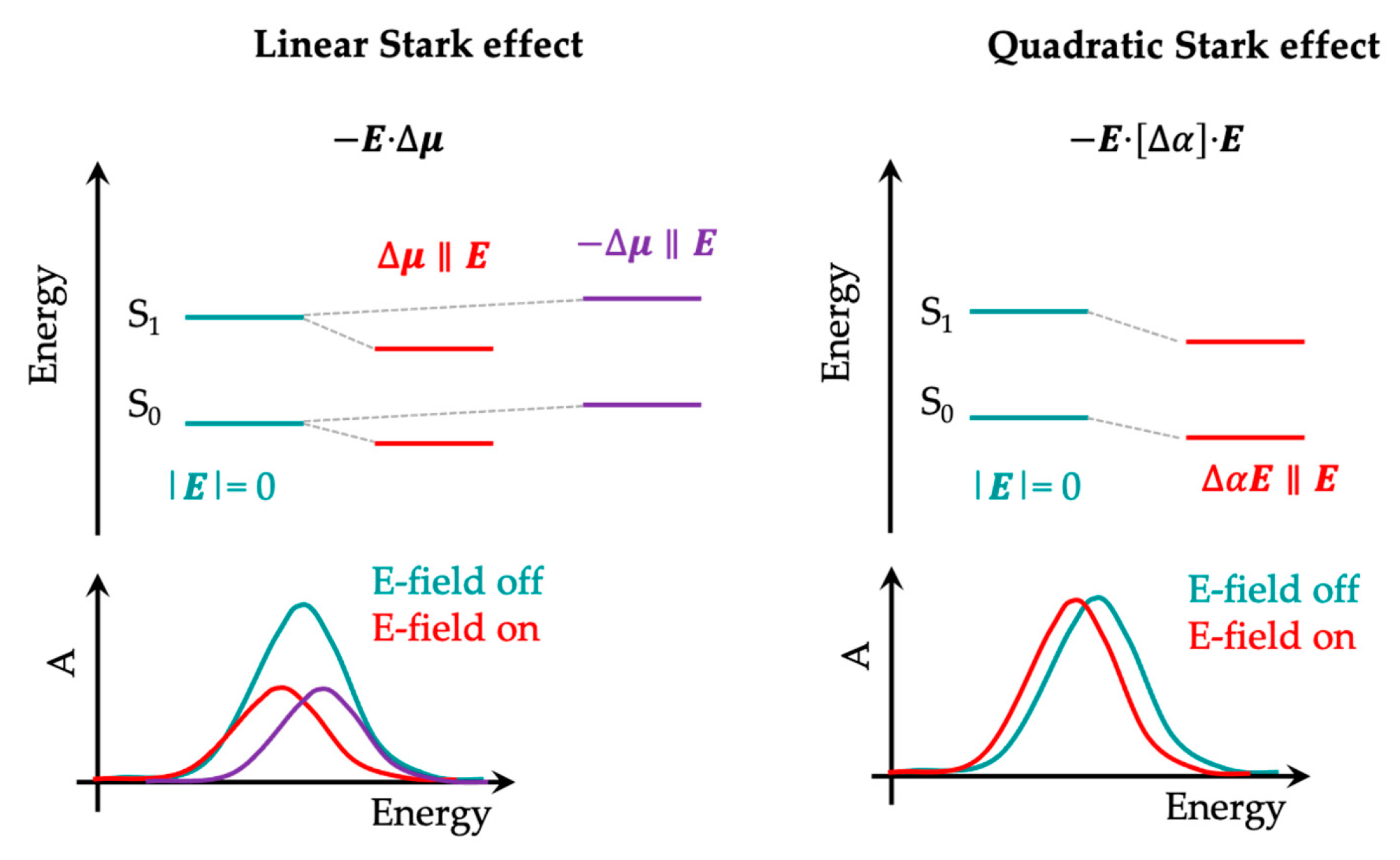


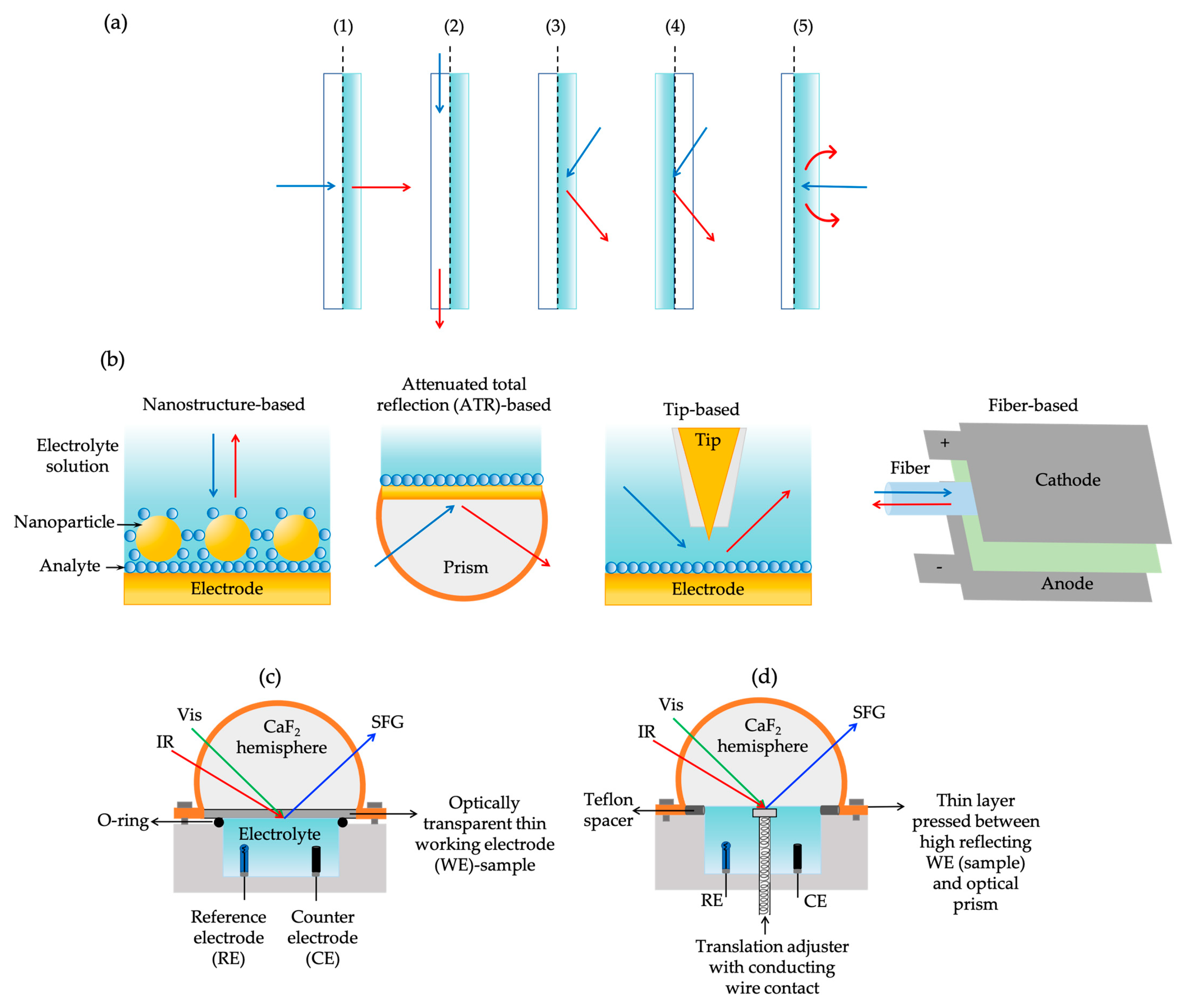


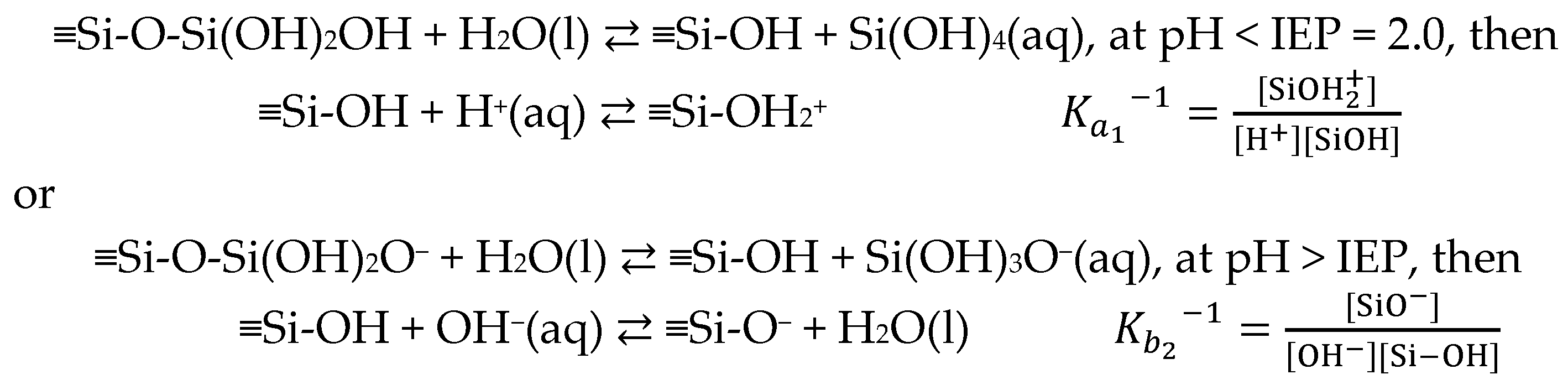
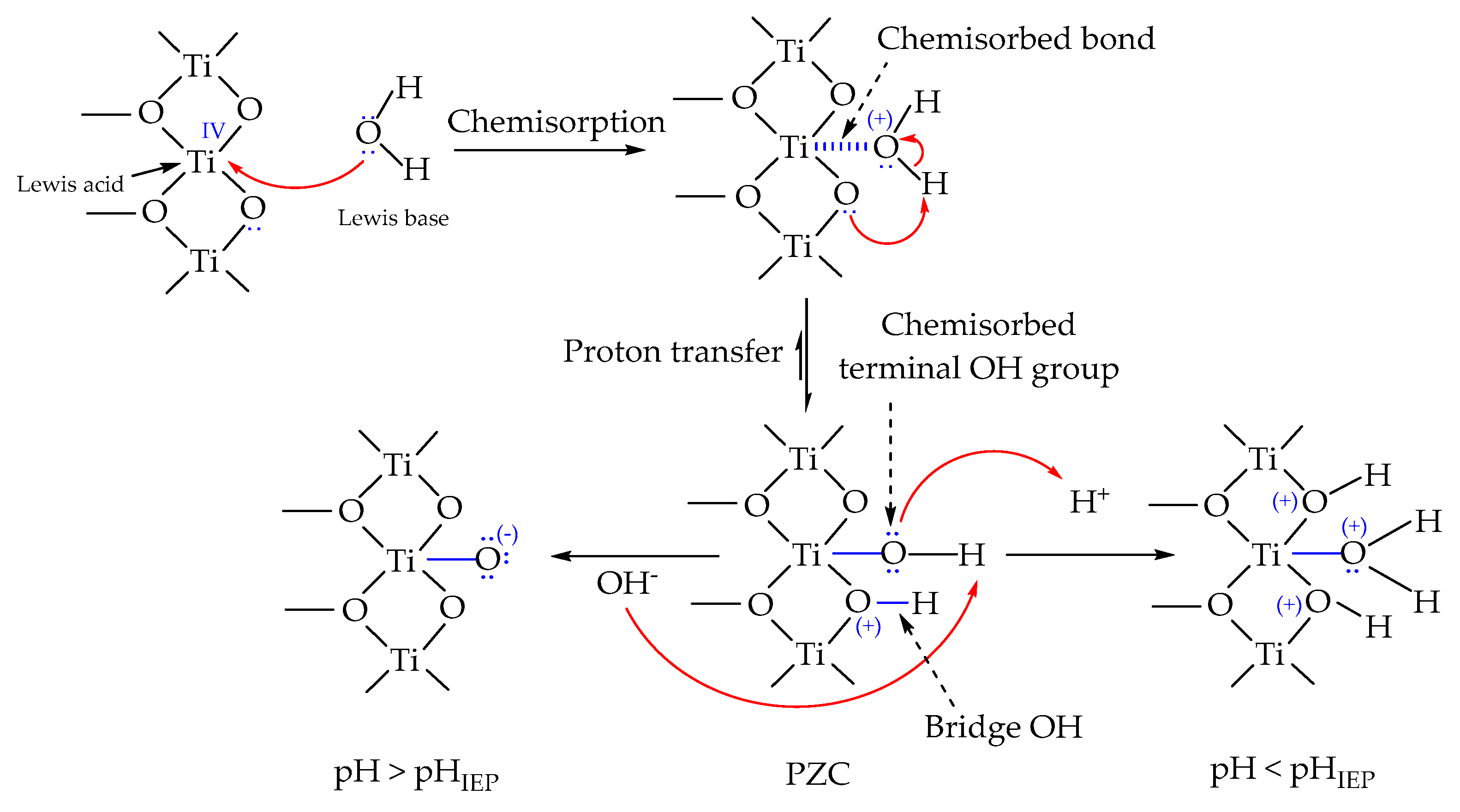
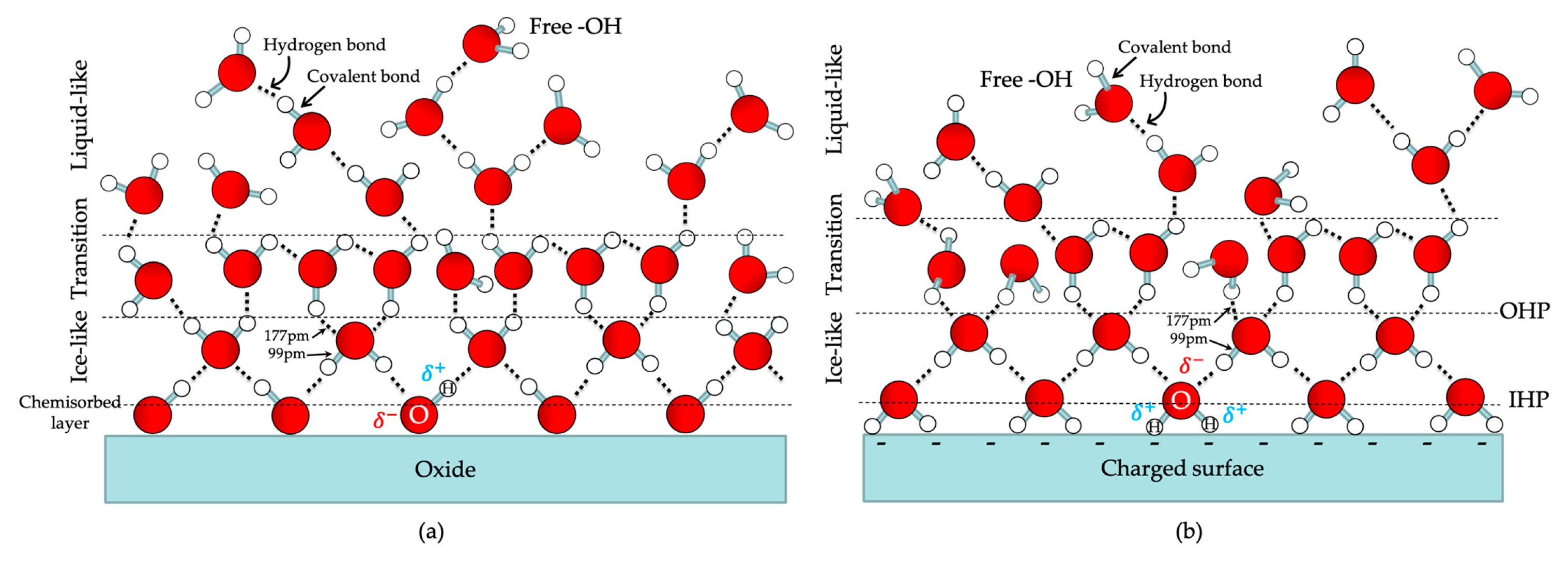
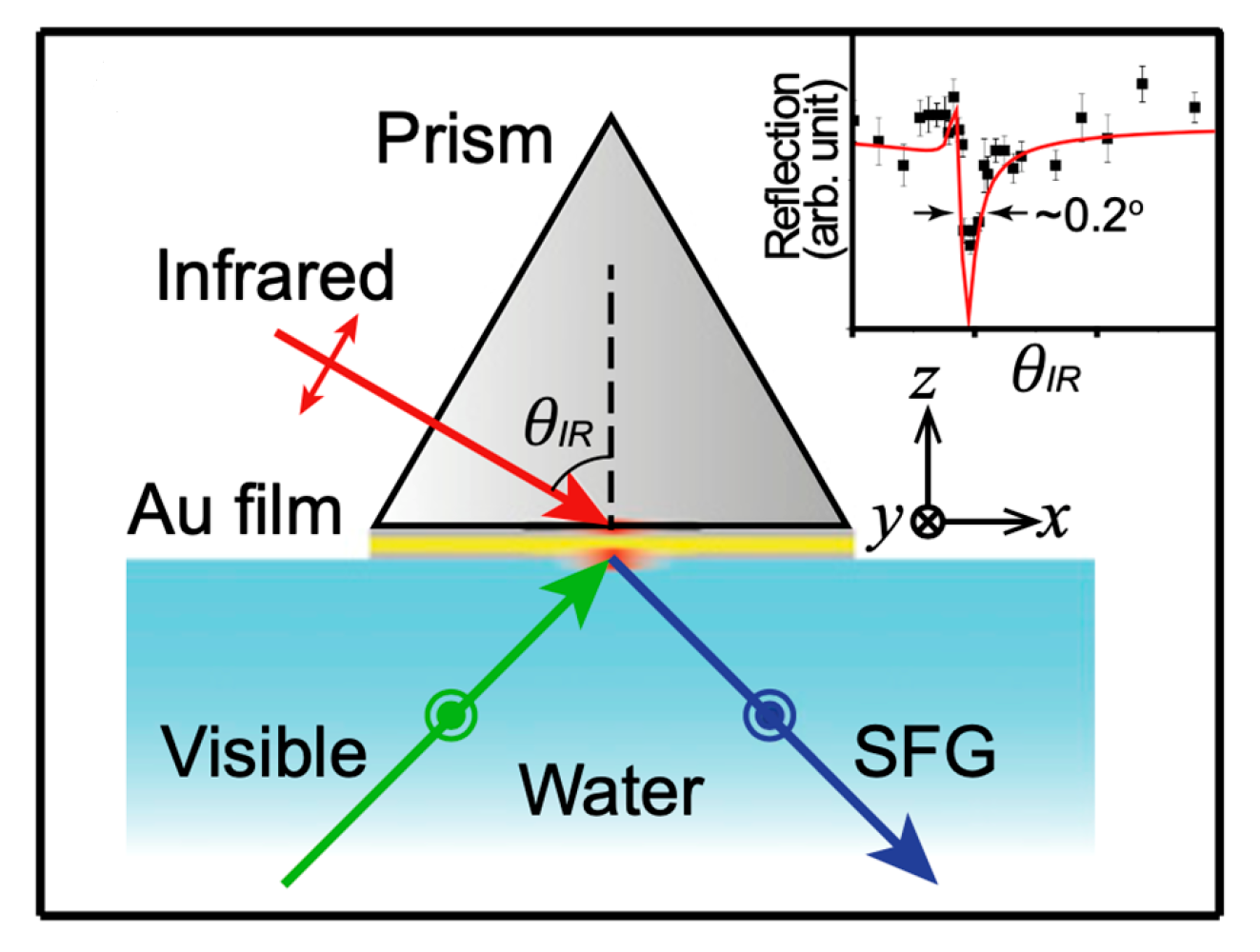
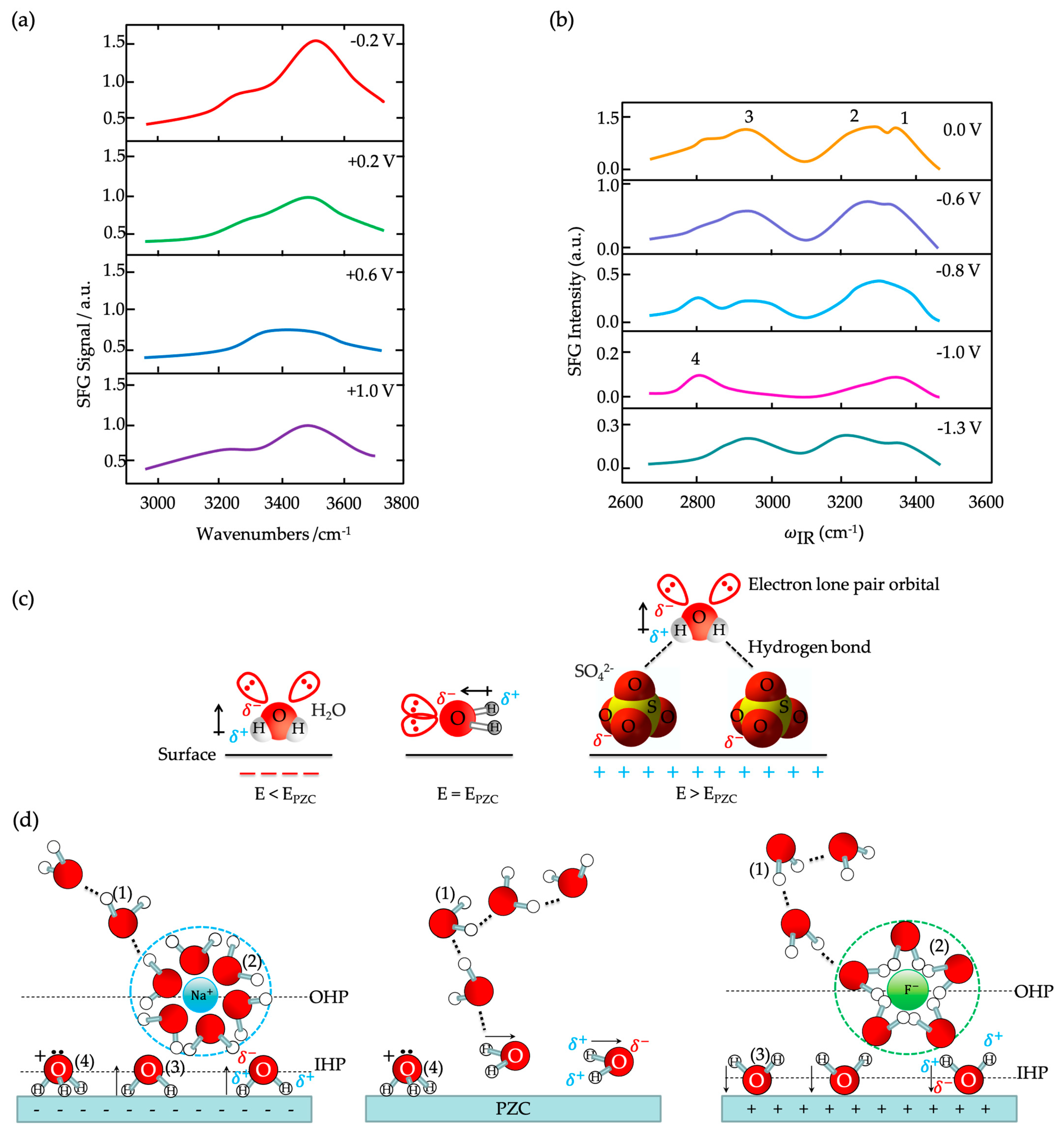
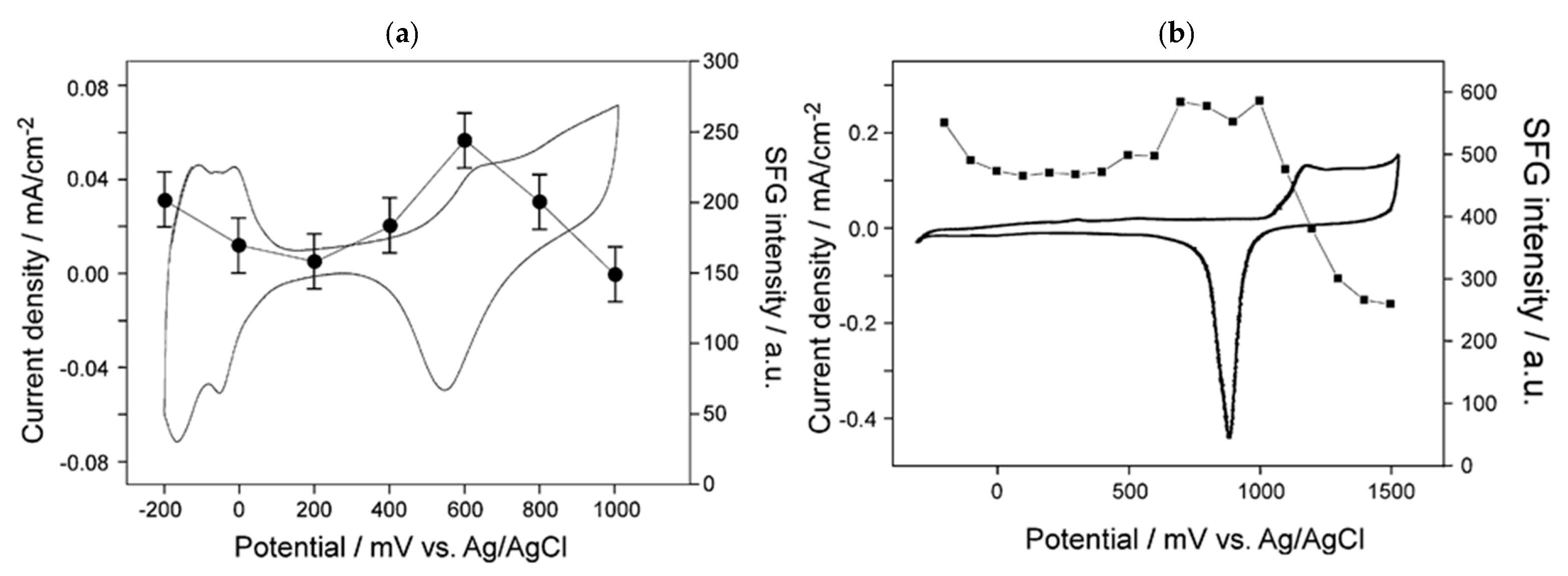
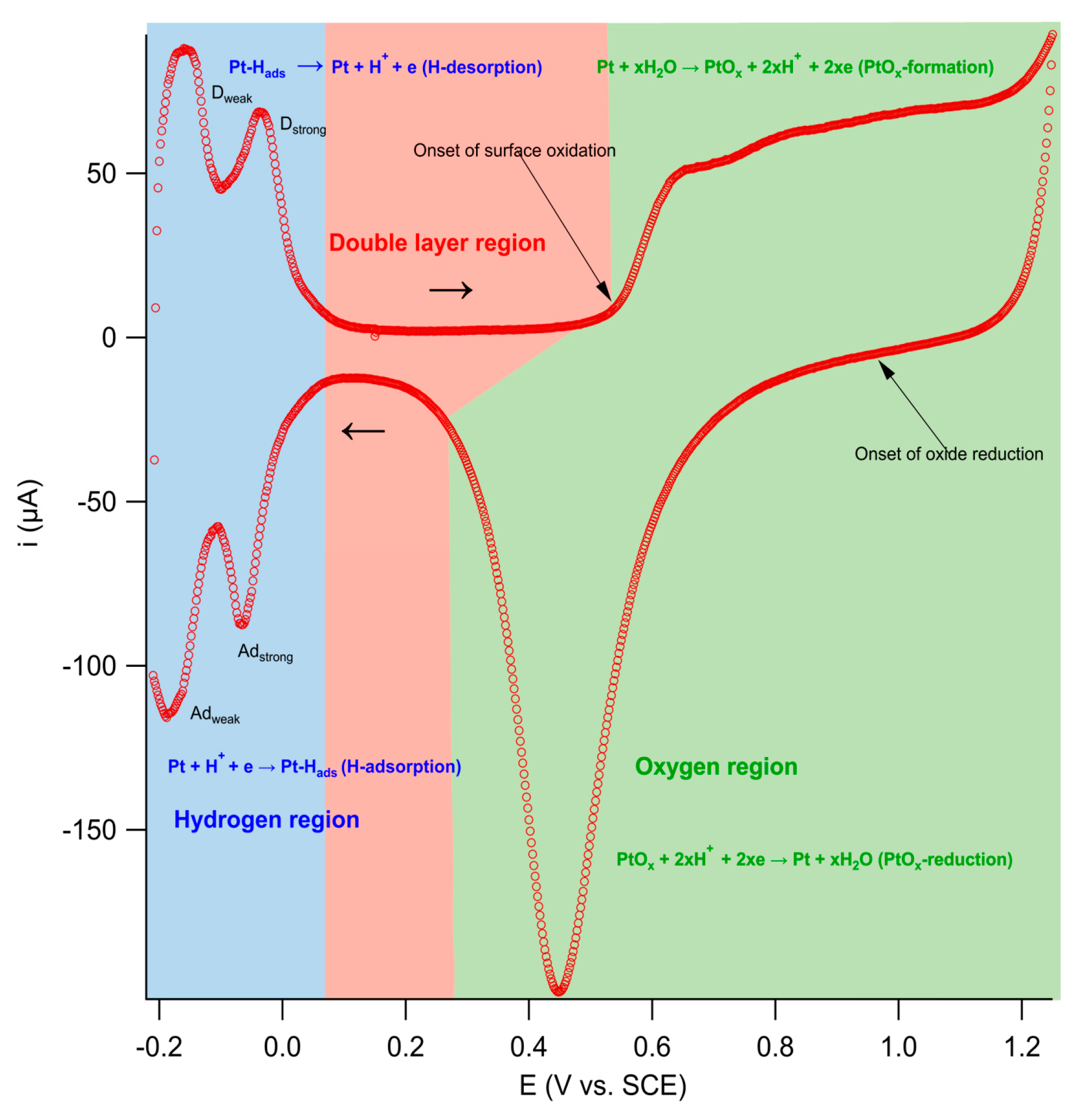

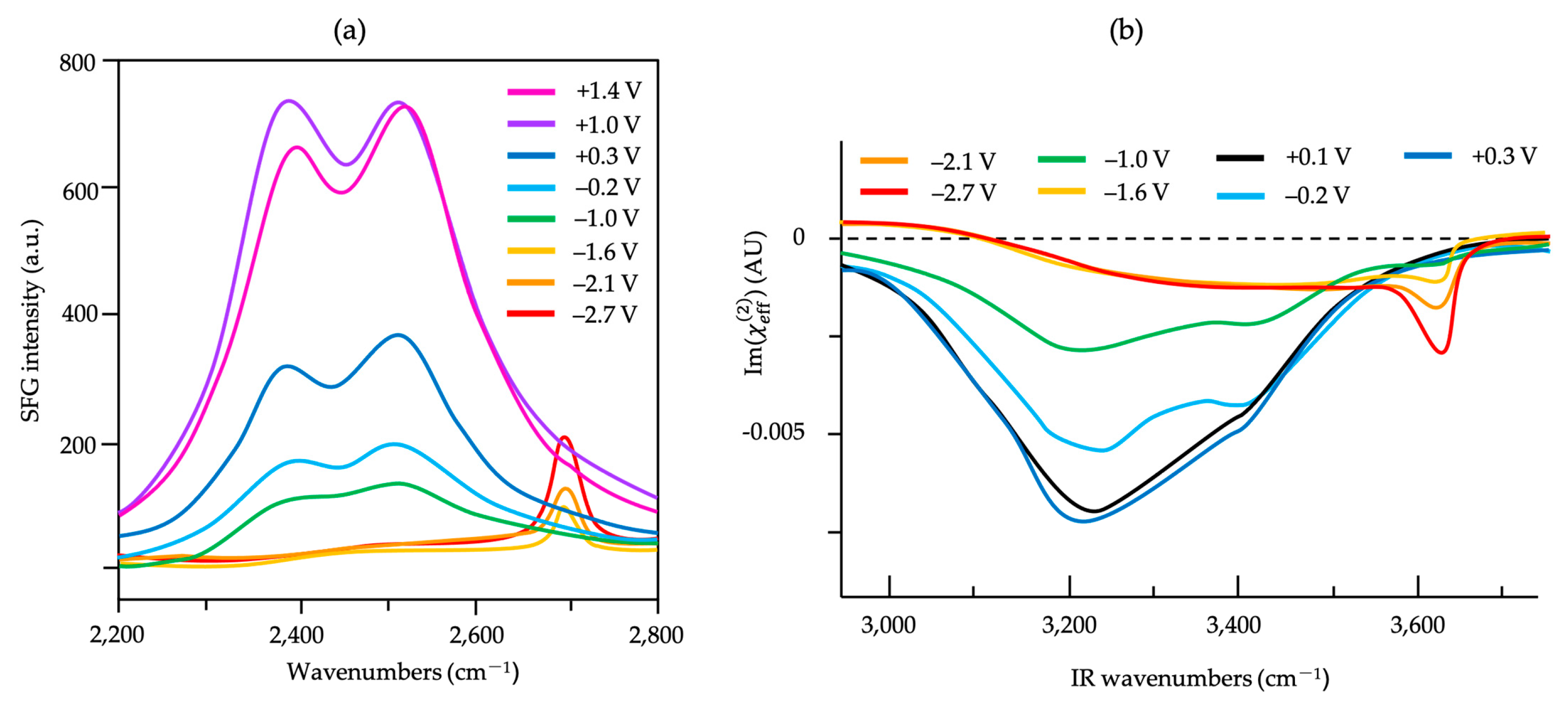
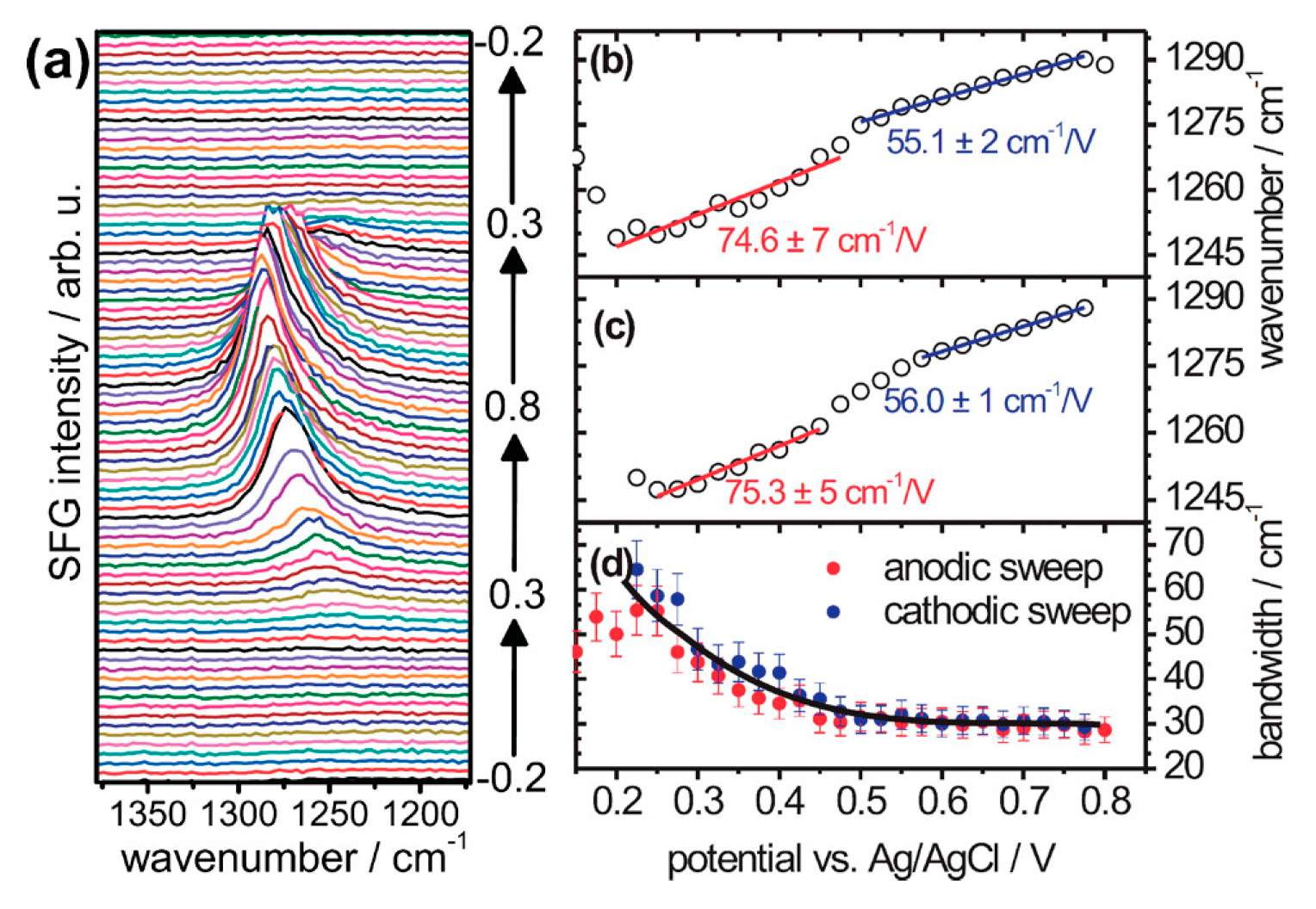
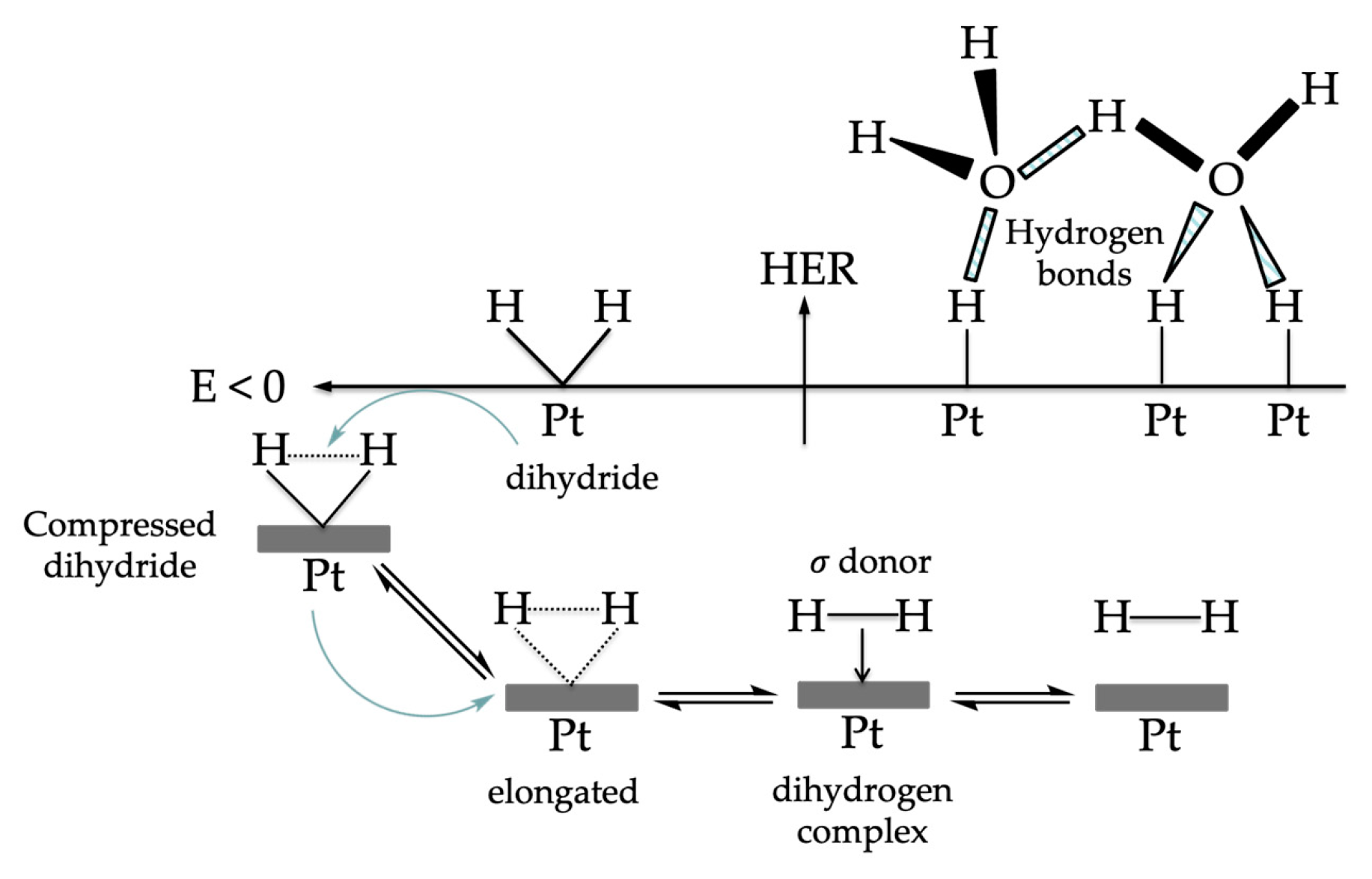

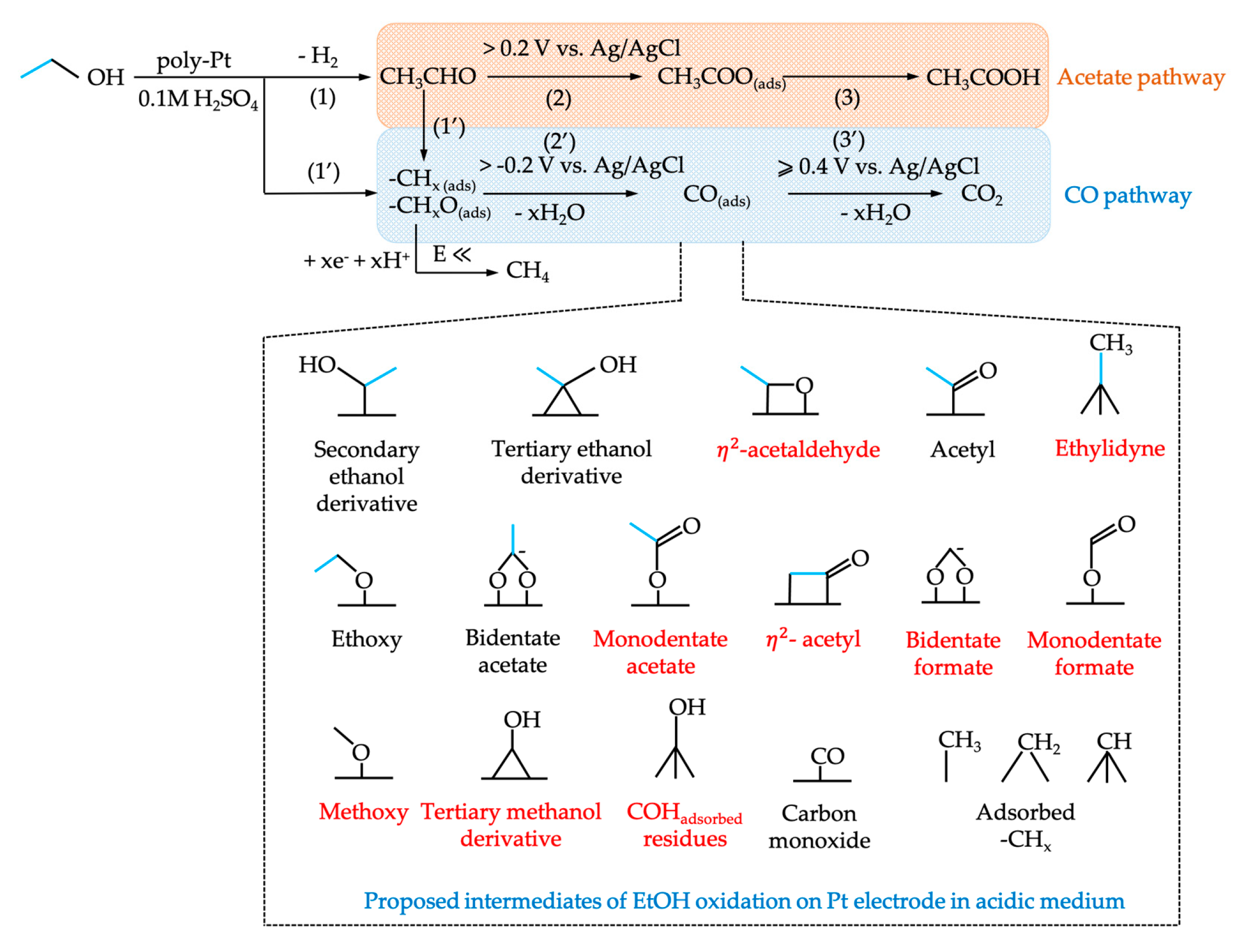

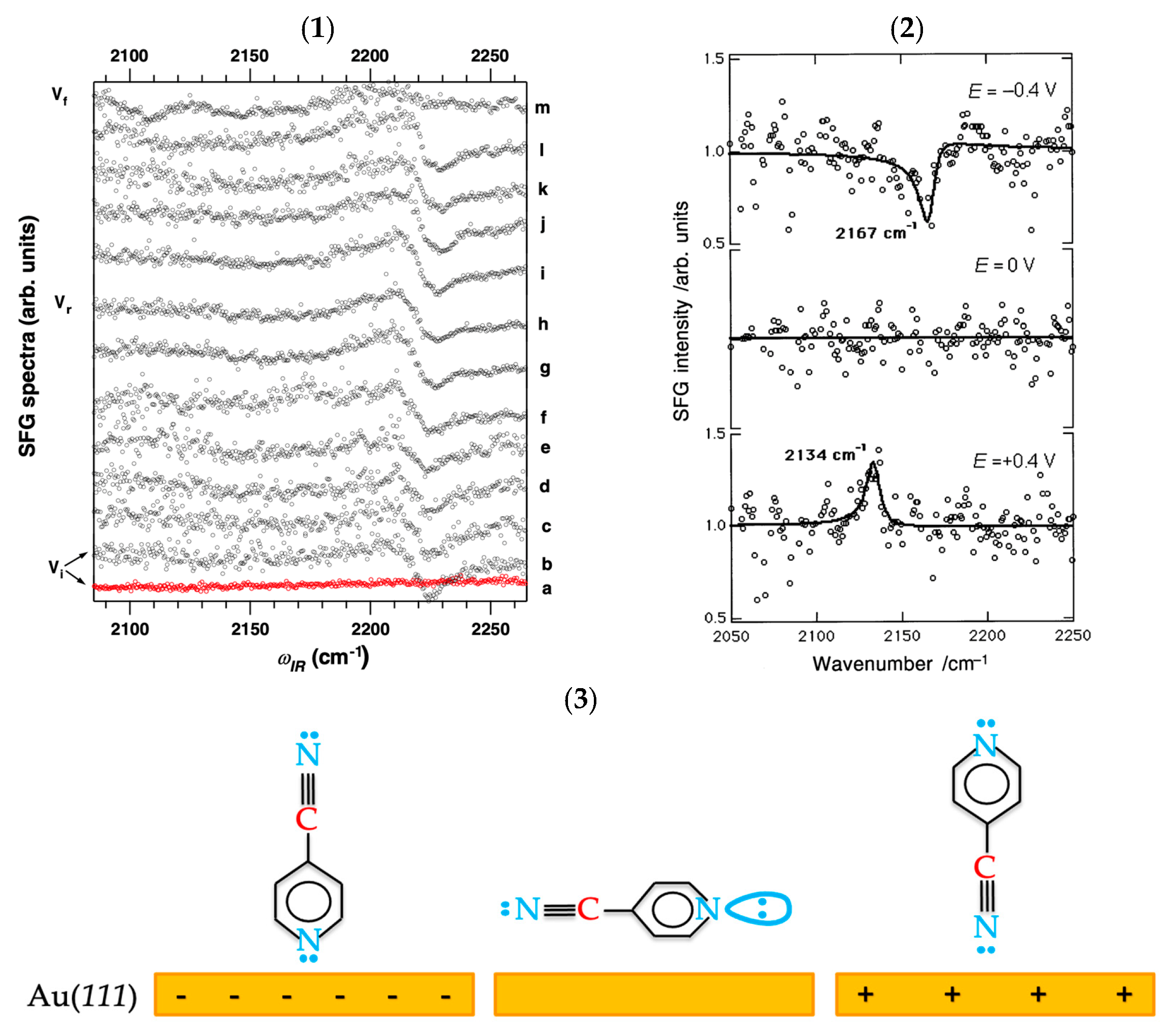
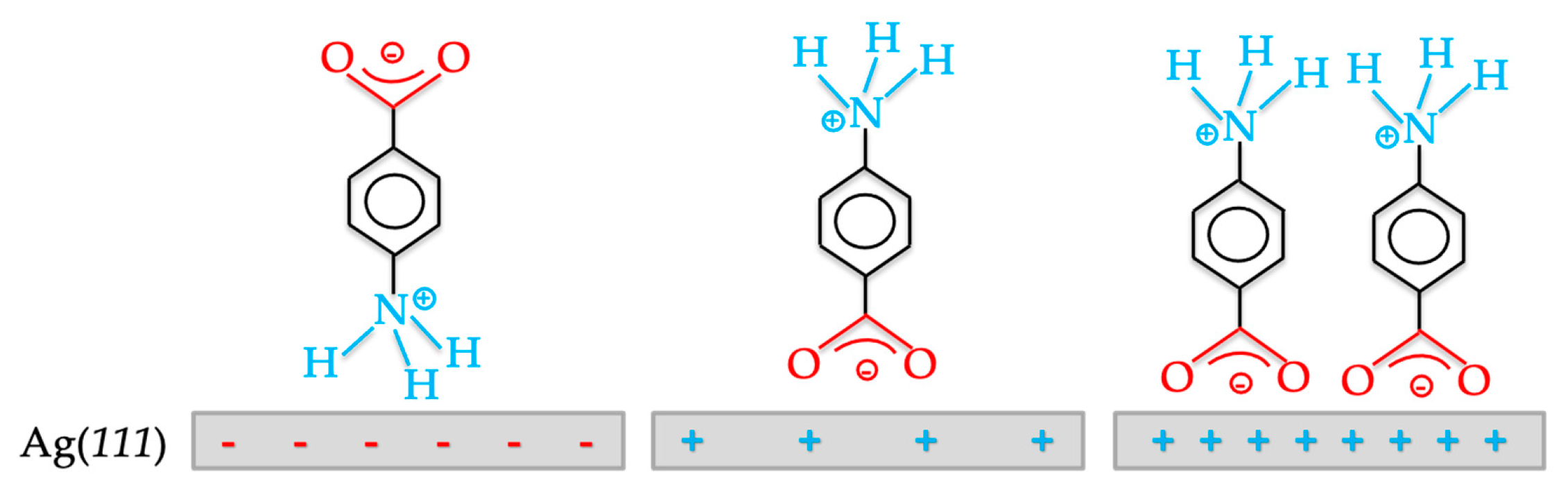
| Criteria | IR Absorption | Raman Scattering | SFG |
|---|---|---|---|
| Order of susceptibility | |||
| Selection rule | |||
| IR resonance | -resonant | -resonant | -resonant |
| VIS resonance | -resonant | -resonant 1 | -resonant 2 |
| Coherence | coherent | incoherent | coherent |
| Optical configuration | directional | diffused | directional |
| Surface selectivity | non surface-specific | non surface-specific | intrinsically high |
| Detection sensitivity | High but not intrinsic | Low 3 | High |
| Reference spectra substraction | Yes | Yes | No |
| No. | Half-Electrochemical Thermodynamic Reactions | E° (V), pH = 0 | E°′ (V), pH = 7 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | CO2(g) + e− CO2∙− | −1.500 | −1.900 |
| (2) | CO2(g) + 2H+(aq) + 2e− HCOOH(aq) | −0.198 | −0.613 |
| (3) | CO2(g) + 2H+(aq) + 2e− CO(g) + H2O(l) | −0.110 | −0.520 |
| (4) | CO2(g) + 4H+(aq) + 4e− HCHO(aq) + H2O(l) | −0.070 | −0.485 |
| (5) | 2H+(aq) + 2e− H2(g) | 0.000 | −0.414 |
| (6) | CO2(g) + 6H+(aq) + 6e− MeOH(aq) + H2O(l) | 0.030 | −0.384 |
| (7) | 2CO2(g) + 12H+(aq) + 12e− H2C=CH2(g) + 4H2O(l) | 0.064 | −0.350 |
| (8) | 2CO2(g) + 12H+(aq) + 12e− EtOH(aq) + 3H2O(l) | 0.084 | −0.330 |
| (1) Interfacial pH buffering (water as the primary proton donor) | ||
| 2H2O(l) + 2e− H2(g) + 2OH−(aq) | (39) | |
| CO2(aq) + OH−(aq) HCO3−(aq) | (40) | |
| HCO3−(aq) + OH−(aq) H2O(l) + CO32−(aq) | (41) | |
| (2) Direct H2CO3/HCO3− reduction (H2CO3/HCO3− as the primary proton donor) | ||
| 2CO2(aq) + 2H2O(l) + 2e− H2(g) + 2HCO3−(aq) | (42) | |
| 2HCO3−(aq) + 2e− H2(g) + 2CO32−(aq) | (43) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pham, B.L.; Ranjbari, A.; Tadjeddine, A.; Dalstein, L.; Humbert, C. Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy at Aqueous Electrochemical Interfaces. Symmetry 2024, 16, 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16121699
Pham BL, Ranjbari A, Tadjeddine A, Dalstein L, Humbert C. Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy at Aqueous Electrochemical Interfaces. Symmetry. 2024; 16(12):1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16121699
Chicago/Turabian StylePham, Ba Lich, Alireza Ranjbari, Abderrahmane Tadjeddine, Laetitia Dalstein, and Christophe Humbert. 2024. "Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy at Aqueous Electrochemical Interfaces" Symmetry 16, no. 12: 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16121699
APA StylePham, B. L., Ranjbari, A., Tadjeddine, A., Dalstein, L., & Humbert, C. (2024). Sum-Frequency Generation Spectroscopy at Aqueous Electrochemical Interfaces. Symmetry, 16(12), 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16121699







