Hyperbolic Scenario of Accelerating Universe in Modified Gravity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basic Equations Governing the Model
3. Solutions of Field Equations
4. Data Analysis
4.1. Data Description
4.1.1. Dataset
4.1.2. Pantheon Dataset
4.1.3. Baryon Acoustic Oscillations
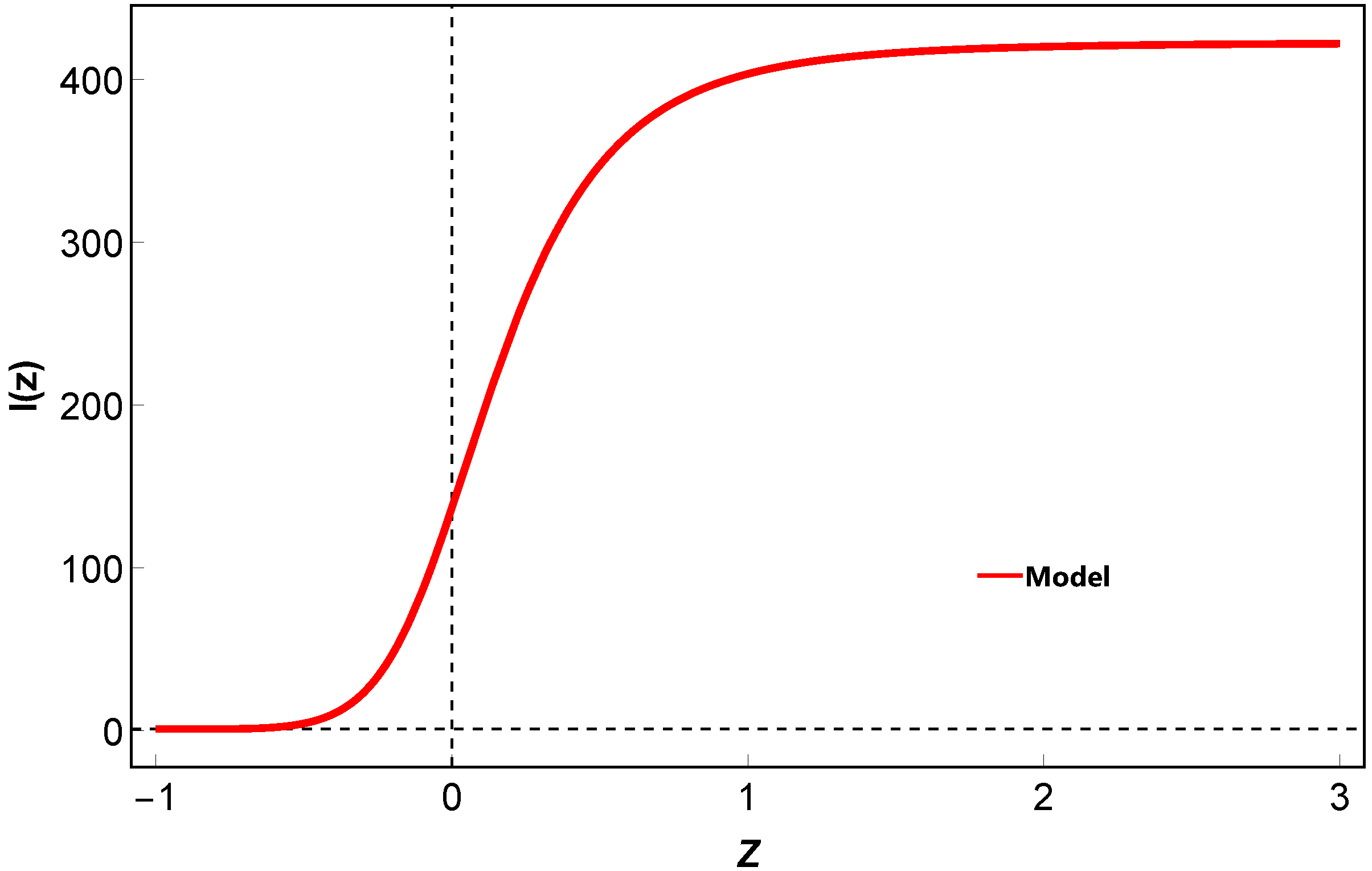
5. Cosmography
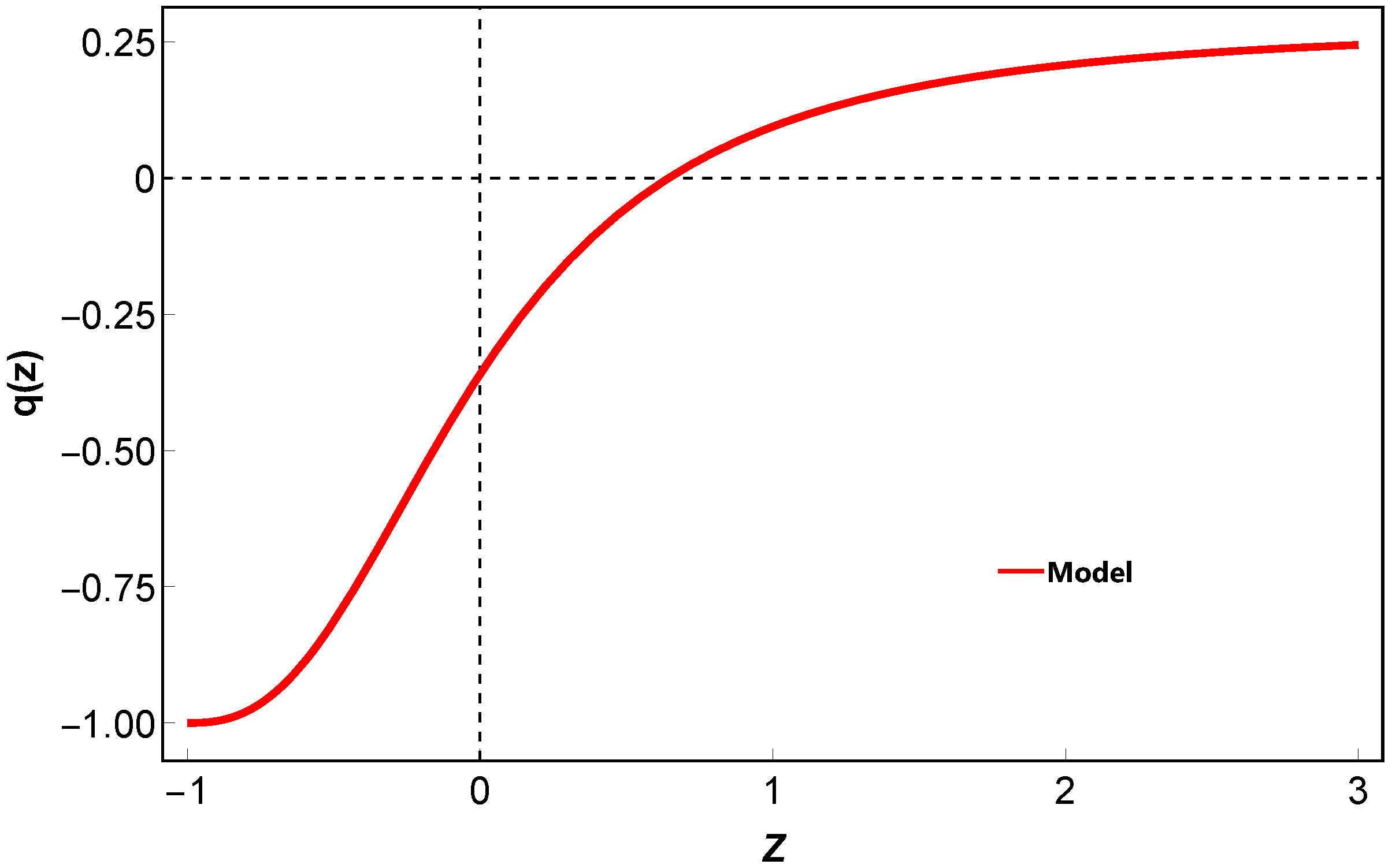
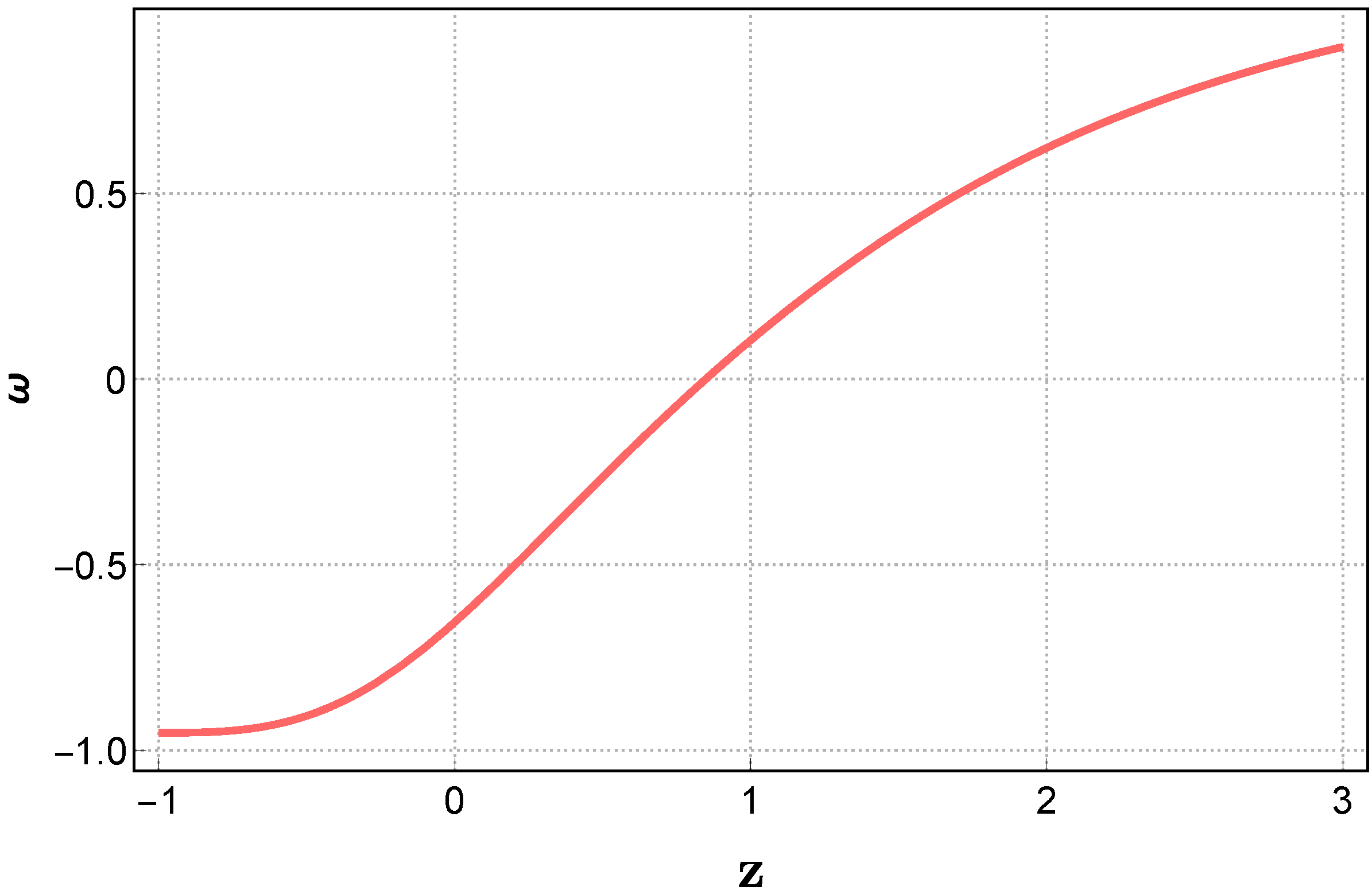
5.1. Deceleration Parameter
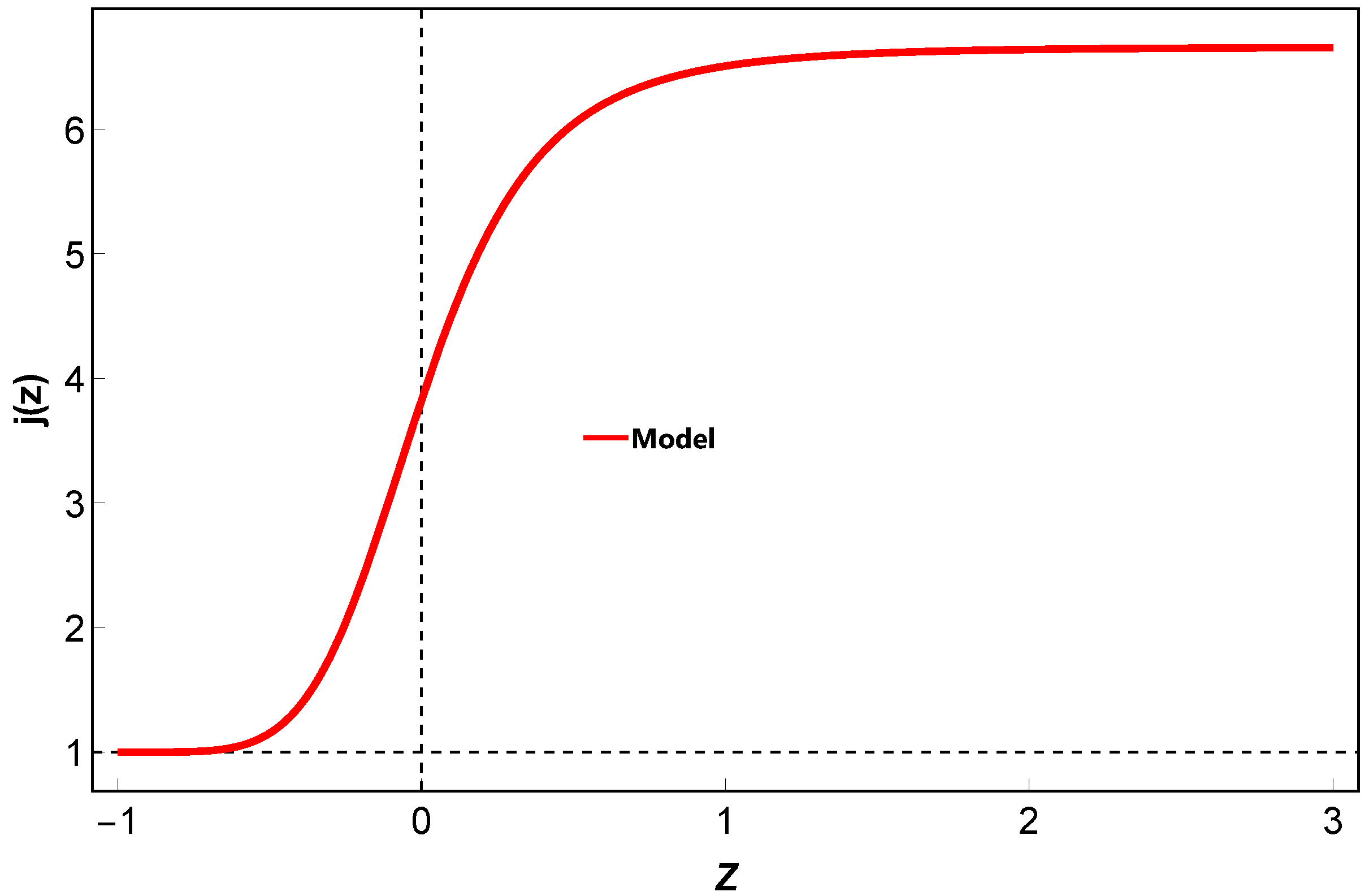
5.2. Jerk Parameter
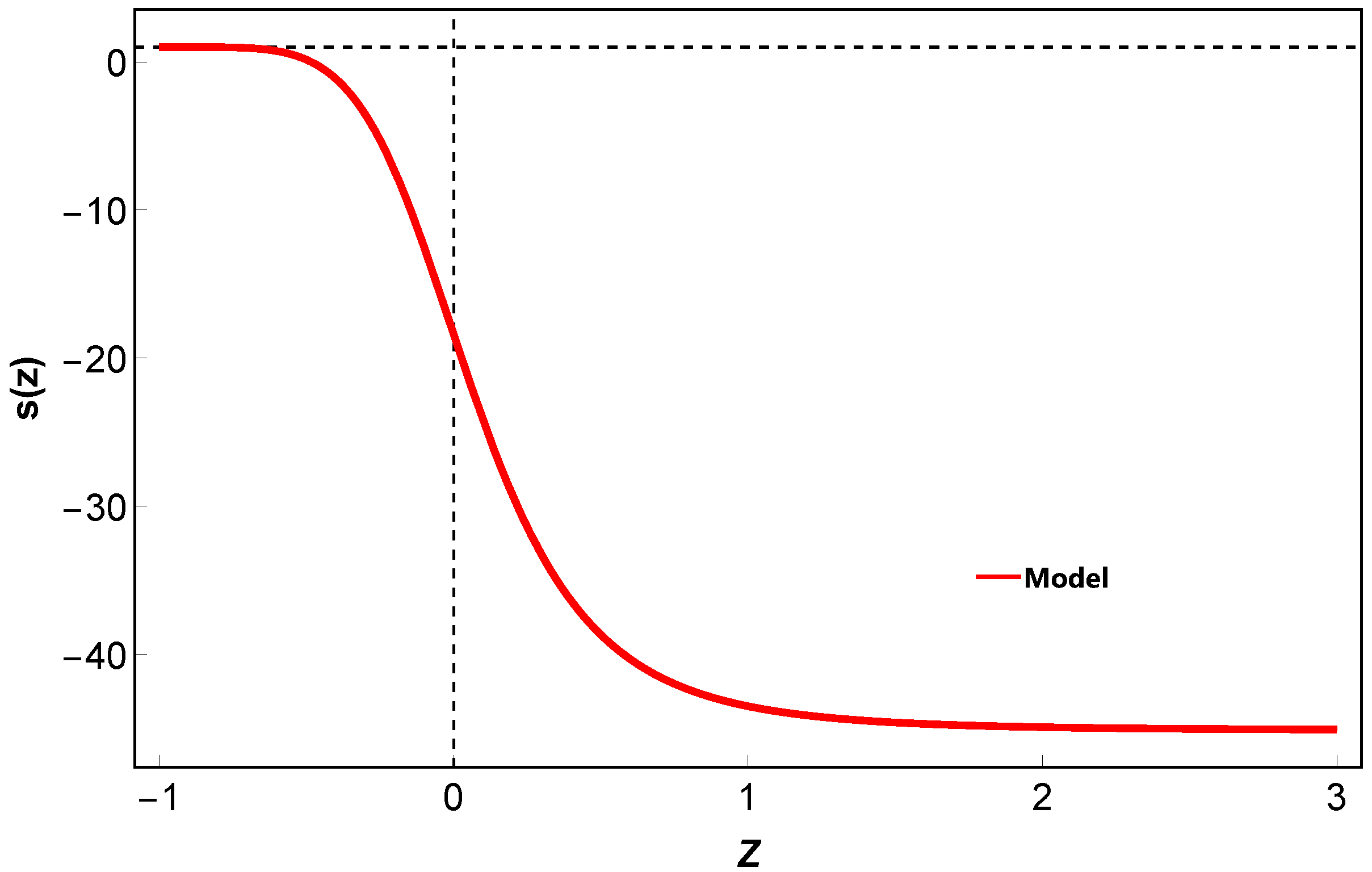
5.3. Snap Parameter
5.4. Lerk Parameter
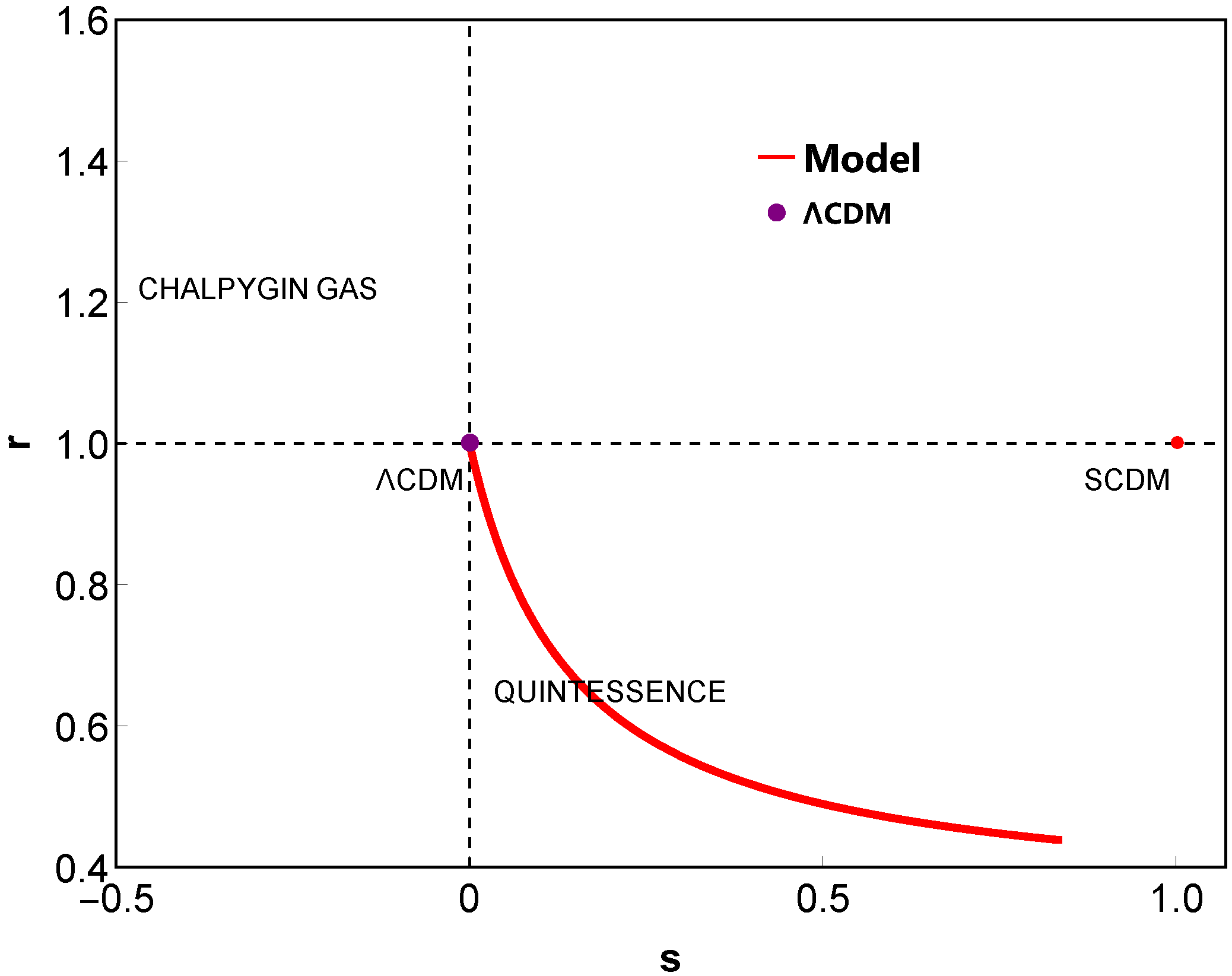
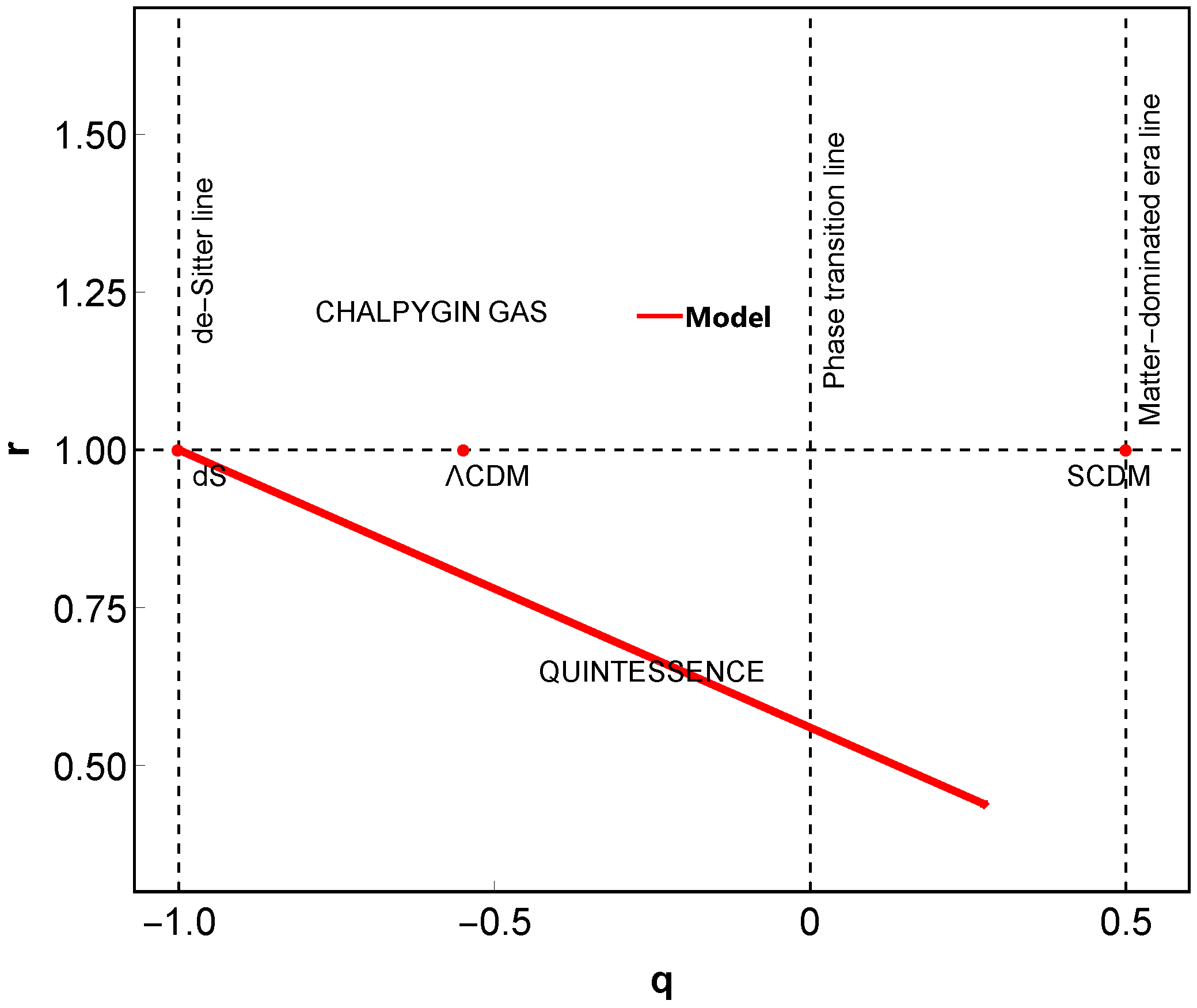
6. Statefinder Parameters
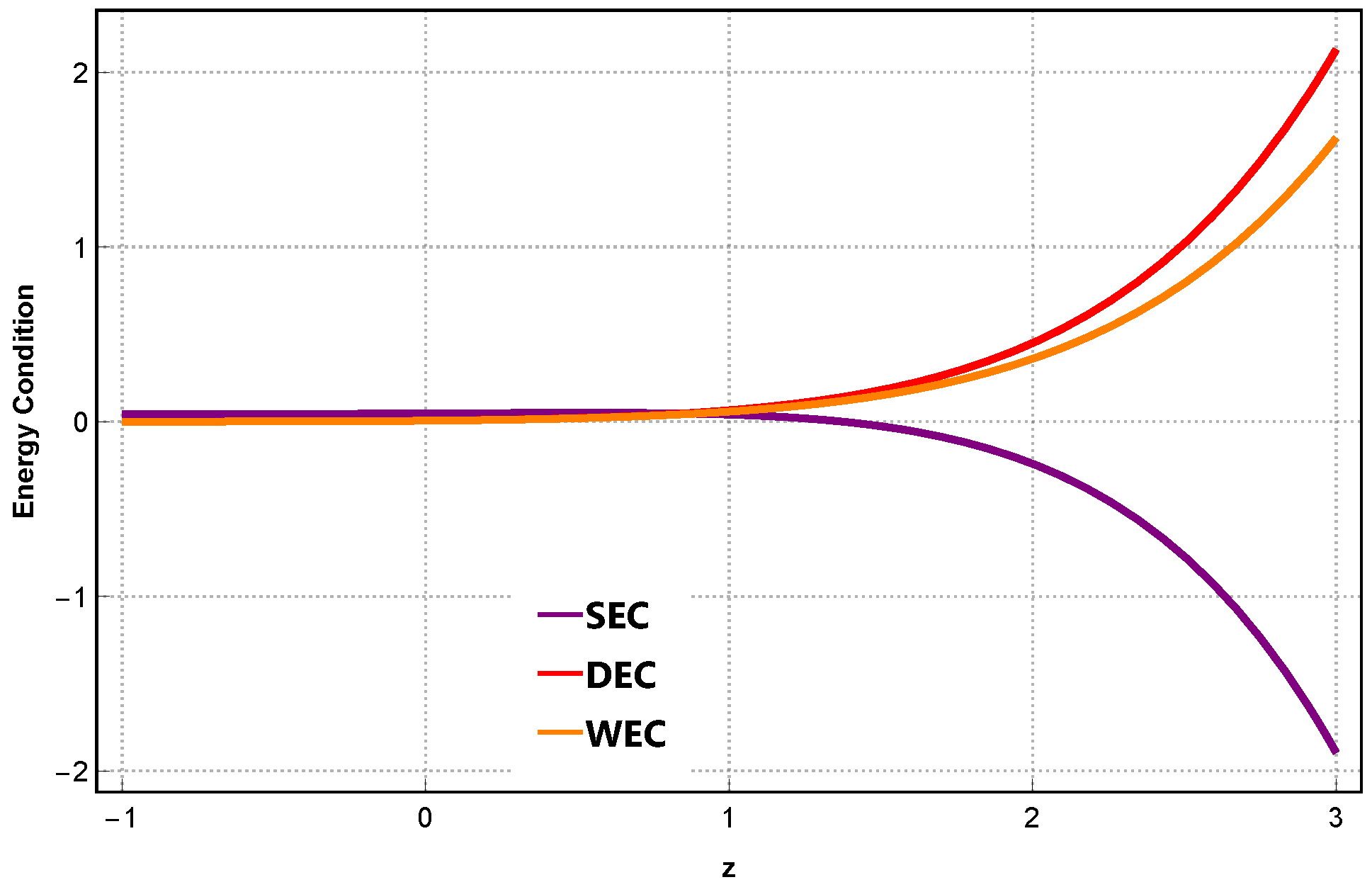
7. Energy Conditions
8. Om Diagnostic
9. Conclusions and Results
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Challis, P.; Clocchiatti, A.; Diercks, A.; Garnavich, P.M.; Gilliland, R.L.; Hogan, C.J.; Jha, S.; Tonry, J.; et al. Observational evidence from supernovae for an accelerating universe and a cosmological constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlmutter, S.; Aldering, G.; Goldhaber, G.; Knop, R.A.; Nugent, P.; Castro, P.G.; Deustua, S.; Fabbro, S.; Goobar, A.; Groom, D.E.; et al. Measurements of Ω and Λ from 42 high redshift supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1999, 517, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, B.D.; Dunkley, J.; Das, S.; Appel, J.W.; Bond, J.R.; Carvalho, C.S.; Devlin, M.J.; Dünner, R.; Essinger-Hileman, T.; Fowler, J.W.; et al. Evidence for dark energy from the cosmic microwave background alone using the Atacama Cosmology Telescope lensing measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 021302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhmadi-Lopez, M.; Errahmani, A.; Ouali, T. The cosmology of an holographic induced gravity model with curvature effects. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 083508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargach, A.; Bargach, F.; Ouali, T. Dynamical system approach of non-minimal coupling in holographic cosmology. Nucl. Phys. B 2019, 940, 10–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. The cosmological constant problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1989, 61, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, E.J.; Sami, M.; Tsujikawa, S. Dynamics of dark energy. Int. J. Mod. 1989, 11, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Unifying phantom inflation with late-time acceleration: Scalar phantom–non-phantom transition model and generalized holographic dark energy. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2006, 38, 1285–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Paul, T. Barrow entropic dark energy: A member of generalized holographic dark energy family. Phys. Lett. B 2022, 825, 136844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.; Paul, T. Unifying holographic inflation with holographic dark energy: A covariant approach. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 023540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Paul, T. Different faces of generalized holographic dark energy. Symmetry 2021, 13, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Paul, T. Early and late universe holographic cosmology from a new generalized entropy. Phys. Lett. B 2022, 831, 137189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A. Tachyon matter. J. High Energy Phys. 2002, 2002, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouabdallaoui, Z.; Errahmani, A.; Bouhmadi-Lopez, M.; Ouali, T. Constraints on tachyon inflationary models with an AdS/CFT correspondence. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 123508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T. Tracking k-essence. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 063514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.K.; Piao, Y.S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.Z. Cosmological evolution of a quintom model of dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2005, 608, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, M.; Padmanabhan, T. Viable cosmology with a scalar field coupled to the trace of the stress tensor. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 67, 083509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, R.R.; Kamionkowski, M.; Weinberg, N.N. Phantom energy: Dark energy with w < −1 causes a cosmic doomsday. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 071301. [Google Scholar]
- Bouali, A.; Albarran, I.; Bouhmadi-López, M.; Ouali, T. Cosmological constraints of phantom dark energy models. Phys. Dark Univ. 2019, 26, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouali, A.; Albarran, I.; Bouhmadi-Lopez, M.; Errahmani, A.; Ouali, T. Cosmological constraints of interacting phantom dark energy models. Phys. Dark Univ. 2021, 34, 100907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmani, S.; Bouali, A.; Bojaddaini, I.E.; Errahmani, A.; Ouali, T. Smoothing the H0 tension with a dynamical dark energy model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.04200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhamdi, D.; Bargach, F.; Dahmani, S.; Bouali, A.; Ouali, T. Comparing phantom dark energy models with various diagnostic tools. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2023, 55, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starobinsky, A.A. A new type of isotropic cosmological models without singularity. Phys. Lett. B 1980, 91, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, R. Cosmology without singularity and nonlinear gravitational Lagrangians. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 1982, 14, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Unified cosmic history in modified gravity: From F (R) theory to Lorentz non-invariant models. Phys. Rep. 2011, 505, 59–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.; Oikonomou, V. Modified gravity theories on a nutshell: Inflation, bounce and late-time evolution. Phys. Rep. 2017, 692, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengochea, G.R.; Ferraro, R. Dark torsion as the cosmic speed-up. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 124019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, E.V. Einstein’s Other Gravity and the Acceleration of the Universe. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 127301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, K.; Geng, C.Q. Thermodynamics of cosmological horizons in f (T) gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2011, 2011, 008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, K.; Odintsov, S.D.; Sebastiani, L.; Zerbini, S. Finite-time future singularities in modified Gauss–Bonnet and (R, G) gravity and singularity avoidance. Eur. Phys. J. C 2010, 67, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de S. Silva, M.V.; Rodrigues, M.E. Regular black holes in f (G) gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Harko, T.; Lobo, F.S.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. f (R, T) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 024020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brans, C.; Dicke, R.H. Mach’s principle and a relativistic theory of gravitation. Phys. Rev. 1961, 124, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, D.; Ballester, V. A simple coupling with cosmological implications. Phys. Lett. A 1986, 113, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, M.J. Kaluza-Klein theory in perspective. In Proceedings of the Symposium: The Oskar Klein Centenary; World Scientific: Singapore, 1994; pp. 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, S.D. Entropy bounds and dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2004, 594, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. A model of holographic dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2004, 603, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooft, G. Dimensional reduction in quantum gravity. arXiv 1993, arXiv:gr-qc/9310026. [Google Scholar]
- Susskind, L. The world as a hologram. J. Math. Phys. 1995, 36, 6377–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Cai, R.G. A new model of agegraphic dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 660, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Wu, F.; Chen, X.; Shen, Y.G. Holographic dark energy model from Ricci scalar curvature. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 043511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granda, L.; Oliveros, A. Infrared cut-off proposal for the holographic density. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 669, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jing, J. Dark energy model with higher derivative of Hubble parameter. Phys. Lett. B 2009, 679, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granda, L.; Oliveros, A. New infrared cut-off for the holographic scalar fields models of dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2009, 671, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsallis, C.; Cirto, L.J. Black hole thermodynamical entropy. Eur. Phys. J. C 2013, 73, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavayef, M.; Sheykhi, A.; Bamba, K.; Moradpour, H. Tsallis holographic dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 781, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, A.S.; Moosavi, S.; Moradpour, H.; Graça, J.M.; Lobo, I.; Salako, I.; Jawad, A. Generalized entropy formalism and a new holographic dark energy model. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 780, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saridakis, E.N.; Bamba, K.; Myrzakulov, R.; Anagnostopoulos, F.K. Holographic dark energy through Tsallis entropy. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2018, 2018, 012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, S.; Moradpour, H.; Lobo, I.; Graça, J.M.; Bezerra, V.B. Tsallis holographic dark energy in the Brans–Dicke cosmology. T Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykhi, A. Modified Friedmann equations from Tsallis entropy. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 785, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Golanbari, T.; Bamba, K.; Lobo, I.P. Tsallis holographic dark energy for inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 083505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.G.; Kaplan, D.B.; Nelson, A.E. Effective field theory, black holes, and the cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavon, D.; Zimdahl, W. Holographic dark energy and cosmic coincidence. Phys. Lett. B 2005, 628, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E. Hubble spheres and particle horizons. Astrophys. J. 1991, 383, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, H.M. The particle versus the future event horizon in an interacting holographic dark energy model. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2007, 2007, 026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, L. Current observational constraints to the holographic dark energy model with a new infrared cutoff via the Markov chain Monte Carlo method. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 083523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.; Kumar Singh, A.; Chouhan, D. Accelerating Bianchi type-V cosmology with perfect fluid and heat flow in Saez-Ballester theory. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2013, 52, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.K.; Zia, R.; Pradhan, A. Transit cosmological models with perfect fluid and heat flow in Sáez-Ballester theory of gravitation. J. Astrophys. Astron. 2019, 40, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhanbabu, Y.; Vijaya Santhi, M. Kantowski–Sachs Tsallis holographic dark energy model with sign-changeable interaction. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C. Tilting at cosmological singularities. Commun. Math. Phys. 1974, 39, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, P.; Ellis, G. The case for an open universe. Nature 1994, 370, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Zeyauddin, M.; Ram, S. Anisotropic Bianchi-V Cosmological Models in Saez-Ballester Theory of Gravitation. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2008, 23, 2719–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, R.; Aditya, Y.; Raju, K.D.; Vinutha, T.; Reddy, D. Kaluza-Klein FRW dark energy models in Saez-Ballester theory of gravitation. New Astron. 2021, 85, 101564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Dua, H. Bulk viscous string cosmological models in Saez-Ballester theory of gravity. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2019, 364, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katore, S.; Shaikh, A. Hypersurface-homogeneous space-time with anisotropic dark energy in scalar tensor theory of gravitation. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2015, 357, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhi, M.V.; Sobhanbabu, Y. Bianchi type-III Tsallis holographic dark energy model in Saez–Ballester theory of gravitation. Eur. Phys. J. C 2020, 80, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, M.S.; de Mello Gomide, F. Cosmological models with constant deceleration parameter. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 1988, 20, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarsu, Ö.; Dereli, T. Cosmological models with linearly varying deceleration parameter. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2012, 51, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotin, Y.L.; Cherkaskiy, V.; Lemets, O.; Yerokhin, D.; Zazunov, L. Cosmology in terms of the deceleration parameter. Part I. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.00811. [Google Scholar]
- Bouali, A.; Chaudhary, H.; Debnath, U.; Sardar, A.; Mustafa, G. Data Analysis of three parameter models of deceleration parameter in FRW Universe. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.13137. [Google Scholar]
- Bouali, A.; Chaudhary, H.; Mehrotra, A.; Pacif, S. Model-independent study for a quintessence model of dark energy: Analysis and Observational constraints. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.02652. [Google Scholar]
- Bouali, A.; Chaudhary, H.; Debnath, U.; Roy, T.; Mustafa, G. Constraints on the Parameterized Deceleration Parameter in FRW Universe. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.12107. [Google Scholar]
- Bouali, A.; Chaudhary, H.; Hama, R.; Harko, T.; Sabau, S.V.; Martín, M.S. Cosmological tests of the osculating Barthel–Kropina dark energy model. Eur. Phys. J. C 2023, 83, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Beesham, A.; Shukla, B.K. Scenario of two-fluid dark energy models in Bianchi type-III Universe. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2018, 15, 1850189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Beesham, A.; Shukla, B. Cosmological models with viscous fluid and variable deceleration parameter. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2017, 132, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Beesham, A.; Shukla, B. Behaviour of the cosmological model with variable deceleration parameter. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2016, 131, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Beesham, A.; Shukla, B.K. FLRW Cosmological Models with Dynamic Cosmological Term in Modified Gravity. Universe 2021, 7, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, W.; Hobson, M.; Lasenby, A. PolyChord: Nested sampling for cosmology. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2015, 450, L61–L65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A. GetDist: A Python package for analysing Monte Carlo samples. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.13970. [Google Scholar]
- Foreman-Mackey, D.; Hogg, D.W.; Lang, D.; Goodman, J. emcee: The MCMC hammer. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2013, 125, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaztanaga, E.; Bonvin, C.; Hui, L. Measurement of the dipole in the cross-correlation function of galaxies. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 2017, 032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, M.; Rubin, D.; Aldering, G.; Agostinho, R.; Amadon, A.; Amanullah, R.; Balland, C.; Barbary, K.; Blanc, G.; Challis, P.; et al. Improved cosmological constraints from new, old, and combined supernova data sets. Astrophys. J. 2008, 686, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanullah, R.; Lidman, C.; Rubin, D.; Aldering, G.; Astier, P.; Barbary, K.; Burns, M.; Conley, A.; Dawson, K.; Deustua, S.; et al. Spectra and Hubble Space Telescope light curves of six type Ia supernovae at 0.511 < z < 1.12 and the Union2 compilation. Astrophys. J. 2010, 716, 712. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, N.; Rubin, D.; Lidman, C.; Aldering, G.; Amanullah, R.; Barbary, K.; Barrientos, L.; Botyanszki, J.; Brodwin, M.; Connolly, N.; et al. The Hubble Space Telescope cluster supernova survey. V. Improving the dark-energy constraints above z > 1 and building an early-type-hosted supernova sample. Astrophys. J. 2012, 746, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betoule, M.; Kessler, R.; Guy, J.; Mosher, J.; Hardin, D.; Biswas, R.; Astier, P.; El-Hage, P.; Konig, M.; Kuhlmann, S.; et al. Improved cosmological constraints from a joint analysis of the SDSS-II and SNLS supernova samples. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 568, A22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolnic, D.M.; Jones, D.; Rest, A.; Pan, Y.; Chornock, R.; Foley, R.; Huber, M.; Kessler, R.; Narayan, G.; Riess, A.; et al. The complete light-curve sample of spectroscopically confirmed SNe Ia from Pan-STARRS1 and cosmological constraints from the combined pantheon sample. Astrophys. J. 2018, 859, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolnic, D.; Brout, D.; Carr, A.; Riess, A.G.; Davis, T.M.; Dwomoh, A.; Jones, D.O.; Ali, N.; Charvu, P.; Chen, R.; et al. The Pantheon+ Type Ia Supernova sample: The full dataset and light-curve release. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.03863. [Google Scholar]
- Benisty, D.; Staicova, D. Testing late-time cosmic acceleration with uncorrelated baryon acoustic oscillation dataset. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 647, A38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, N.B.; Martinelli, M.; Nesseris, S. Constraints on the distance duality relation with standard sirens. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2020, 2020, 019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, M.; Martins, C.J.A.P.; Nesseris, S.; Sapone, D.; Tutusaus, I.; Avgoustidis, A.; Camera, S.; Carbone, C.; Casas, S.; Ilić, S.; et al. Euclid: Forecast constraints on the cosmic distance duality relation with complementary external probes. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 644, A80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otalora, G.; Saridakis, E.N. Effective dark energy through spin-gravity coupling. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.06598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, V.; Saini, T.D.; Starobinsky, A.A.; Alam, U. Statefinder—A new geometrical diagnostic of dark energy. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. Lett. 2003, 77, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. The role of energy conditions in f (R) cosmology. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 781, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, P.; Sahoo, P. The simplest non-minimal matter–geometry coupling in the f (R, T) cosmology. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Sahoo, P.; Bishi, B.K. Anisotropic cosmological models in f (R, T) gravity with variable deceleration parameter. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2017, 14, 1750097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.; Fatima, H.I. Energy conditions for Bianchi type I universe in f (G) gravity. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2014, 353, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Lobo, F.S.; Mimoso, J.P. Generalized energy conditions in extended theories of gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 124019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.S.; Santos, J.; Capozziello, S.; Alcaniz, J.S. Strong energy condition and the repulsive character of f (R) gravity. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2017, 49, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M. General relativistic energy conditions: The Hubble expansion in the epoch of galaxy formation. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 56, 7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Alcaniz, J.; Rebouças, M. Energy conditions and supernovae observations. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 067301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergliaffa, S.P. Constraining f (R) theories with the energy conditions. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 642, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Alcaniz, J.; Reboucas, M.; Carvalho, F. Energy conditions in f (R) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 083513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Alcaniz, J.; Reboucas, M.; Pires, N. Lookback time bounds from energy conditions. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 043519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SANTOS, J.; REBOUÇAS, M.J.; ALCANIZ, J.S. Energy conditions constraints on a class of f (R)-gravity. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2010, 19, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wang, A. Energy conditions and current acceleration of the universe. Phys. Lett. B 2007, 652, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, R.; Yau, S.T. Proof of the positive mass theorem. II. Commun. Math. Phys. 1981, 79, 231–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawking, S.W.; Ellis, G.F. The Large Scale Structure of Space-Time; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell, R.R. A phantom menace? Cosmological consequences of a dark energy component with super-negative equation of state. Phys. Lett. B 2002, 545, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, V.; Shafieloo, A.; Starobinsky, A.A. Two new diagnostics of dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.; Moraes, P.; Sahoo, P.; Ribeiro, G. Phantom fluid supporting traversable wormholes in alternative gravity with extra material terms. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2018, 27, 1950004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Model | Parameters | Best-Fit Value |
|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, R.A.A.; Tiwari, R.K.; Bharali, J.; Bouali, A.; Yildiz, G.D.A.; Güdekli, E. Hyperbolic Scenario of Accelerating Universe in Modified Gravity. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15061238
Khan RAA, Tiwari RK, Bharali J, Bouali A, Yildiz GDA, Güdekli E. Hyperbolic Scenario of Accelerating Universe in Modified Gravity. Symmetry. 2023; 15(6):1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15061238
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Raja Azhar Ashraaf, Rishi Kumar Tiwari, Jumi Bharali, Amine Bouali, G. Dilara Açan Yildiz, and Ertan Güdekli. 2023. "Hyperbolic Scenario of Accelerating Universe in Modified Gravity" Symmetry 15, no. 6: 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15061238
APA StyleKhan, R. A. A., Tiwari, R. K., Bharali, J., Bouali, A., Yildiz, G. D. A., & Güdekli, E. (2023). Hyperbolic Scenario of Accelerating Universe in Modified Gravity. Symmetry, 15(6), 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15061238







