Dynamic Event-Triggered Integral Sliding Mode Adaptive Optimal Tracking Control for Uncertain Nonlinear Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Different from the combined SMC and ADP frameworks of [39,40], this paper proposes a new dynamic event-triggered (DET) mechanism. By introducing an auxiliary variable, which is non-negative. This can increase the length of the time intervals between triggering events, further reducing the communication burden compared with [39,40].
- A novel Integral Sliding Mode Control (ISMC) scheme based on DET for uncertain nonlinear systems is proposed, consisting of two control laws. A first event-triggered controller is designed to tackle the matched uncertainties and force the trajectory of the system on the sliding mode surface. A second event-triggered controller is designed to tackle the unmatched uncertainties and guarantee optimal performance.
- To solve the resulting optimal control problem, a critic-only neural network (NN) based on ADP is proposed via the experience replay technique, which helps relaxing the excitation condition typically required for ADP methods to work. Stability of the closed-loop system is proven in the sense of uniformly ultimately boundedness, while guaranteeing Zeno-free behavior of the triggering mechanism.
2. System Formulation and Preliminaries
3. DET-Based ISMC Design
- (1)
- (2)
- The modulation gain associated with is minimized, which means that the amplitude of chattering can be reduced;
- (3)
- avoids amplifying the effect of the unmatched disturbance.
4. DET-Based Optimal Controller Design
4.1. Dynamically Triggering Rule for Optimal Input
4.2. Dynamically Triggered ADP with Single Critic NN
4.3. Stability Analysis
- (1)
- Event is not triggered:
- (2)
- On the triggering instant:
4.4. Algorithm Design of the Event-Triggered ISM Optimal Tracking Control
| Algorithm 1 Event-Triggered ISM Optimal Tracking Control. |
| Input: initial states of the sliding mode dynamics (11) |
| 1: Select an initial admissible policy and a proper small scalar |
| 2: To tackle the uncertainty affecting the nonlinear system (5), an integral type sliding surface is designed as
|
| 3: To extend the continuous-time control in the event-triggered paradigm, we define a virtual control input satisfying , where
|
| 4: Hence, the event-triggered ISMC becomes
|
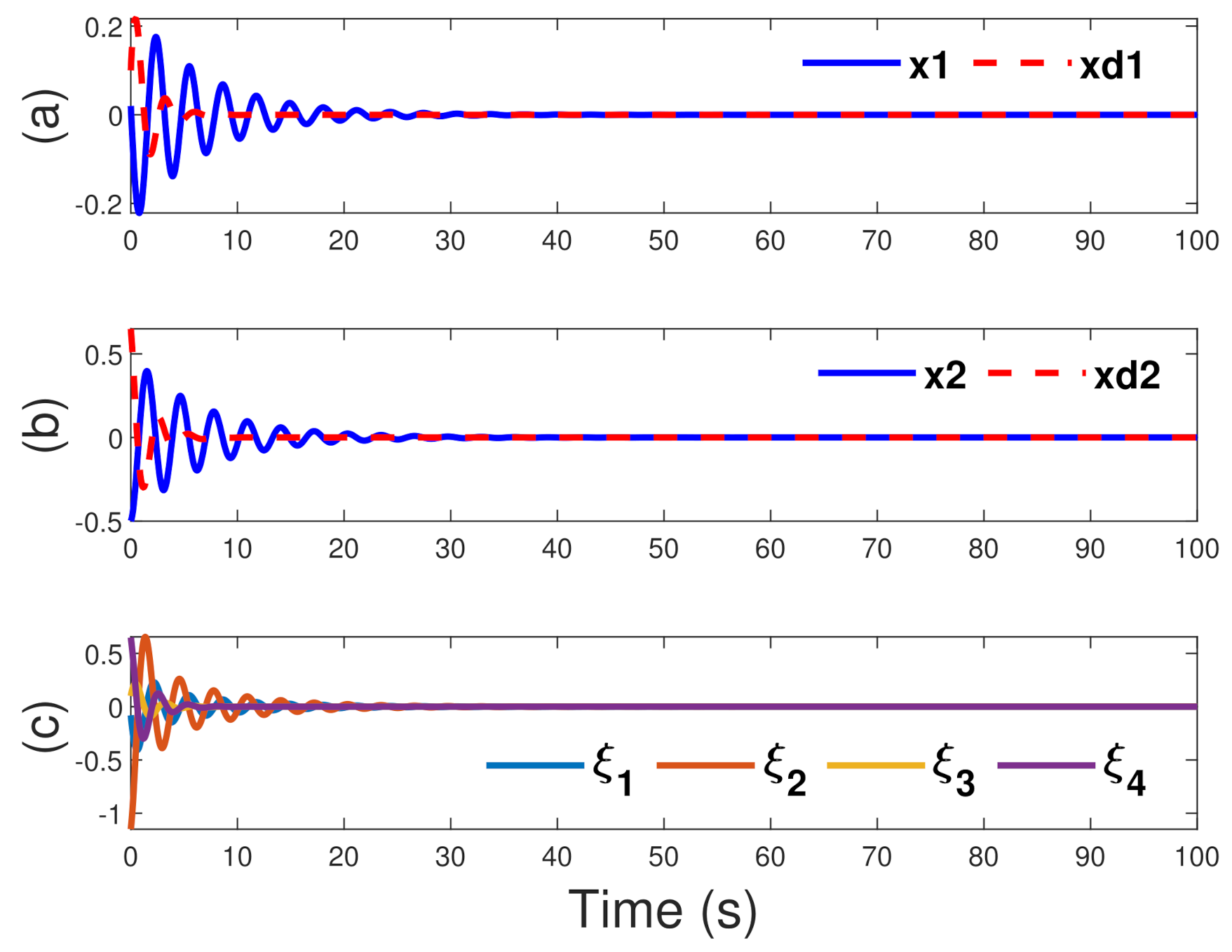
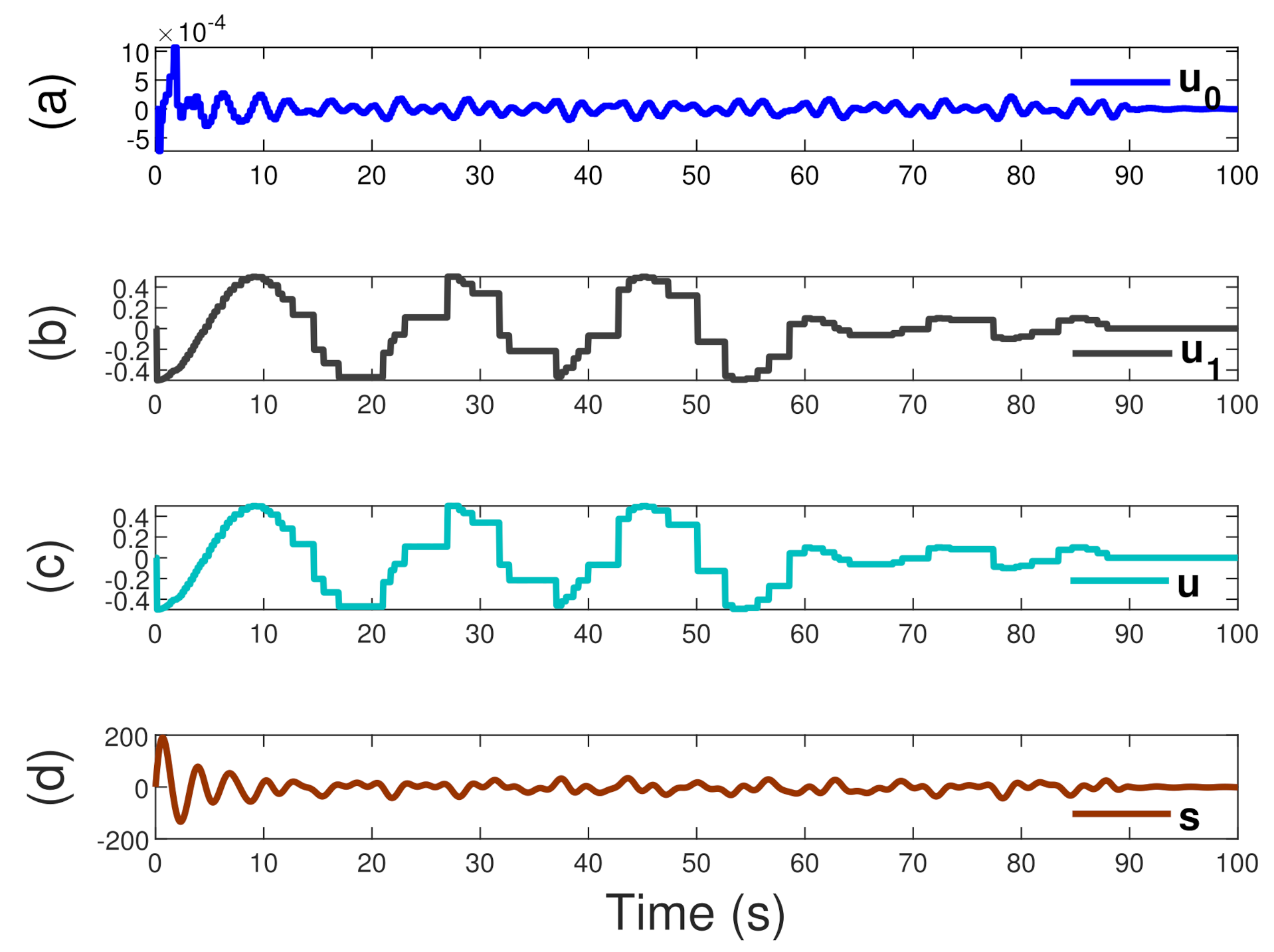
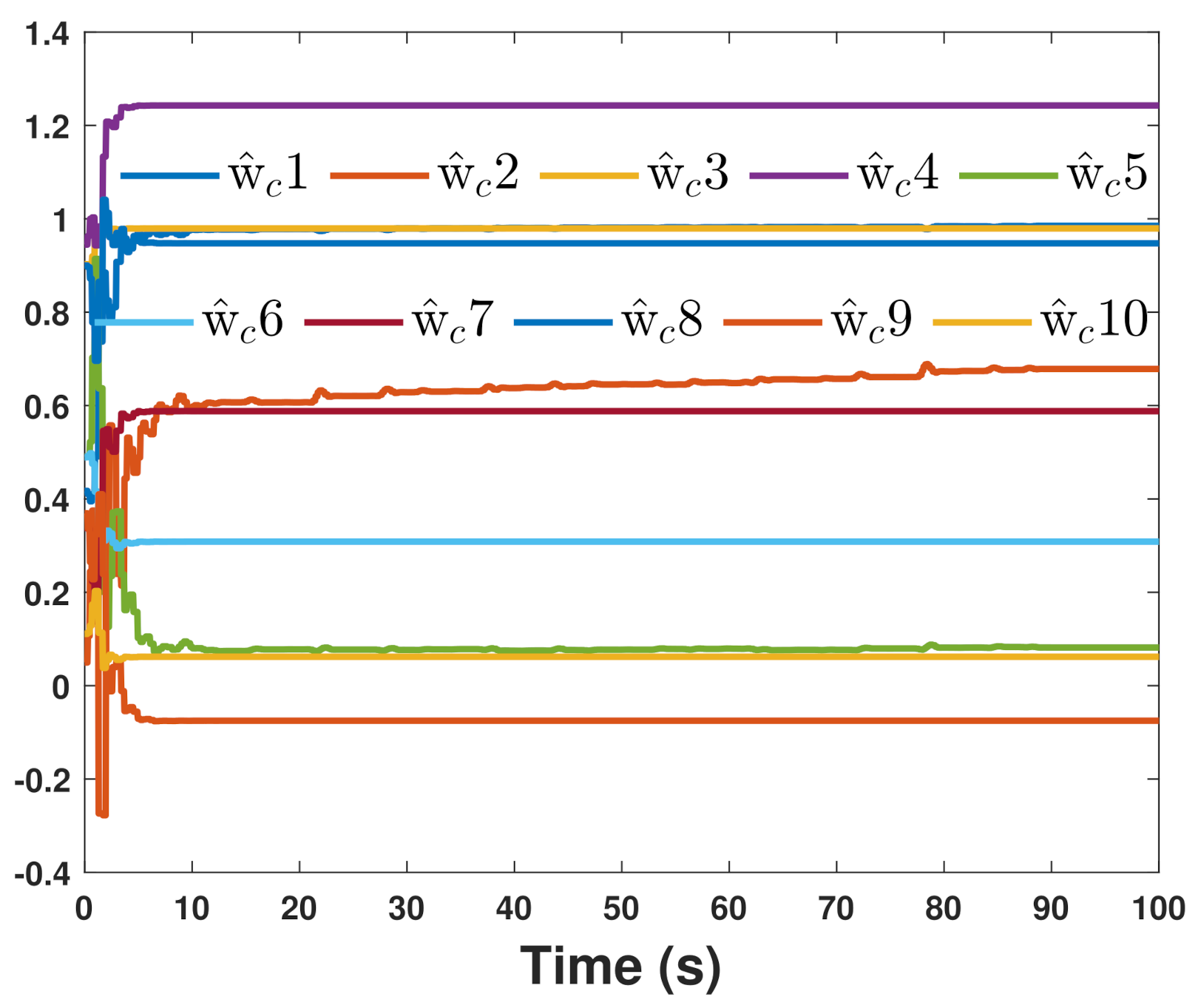
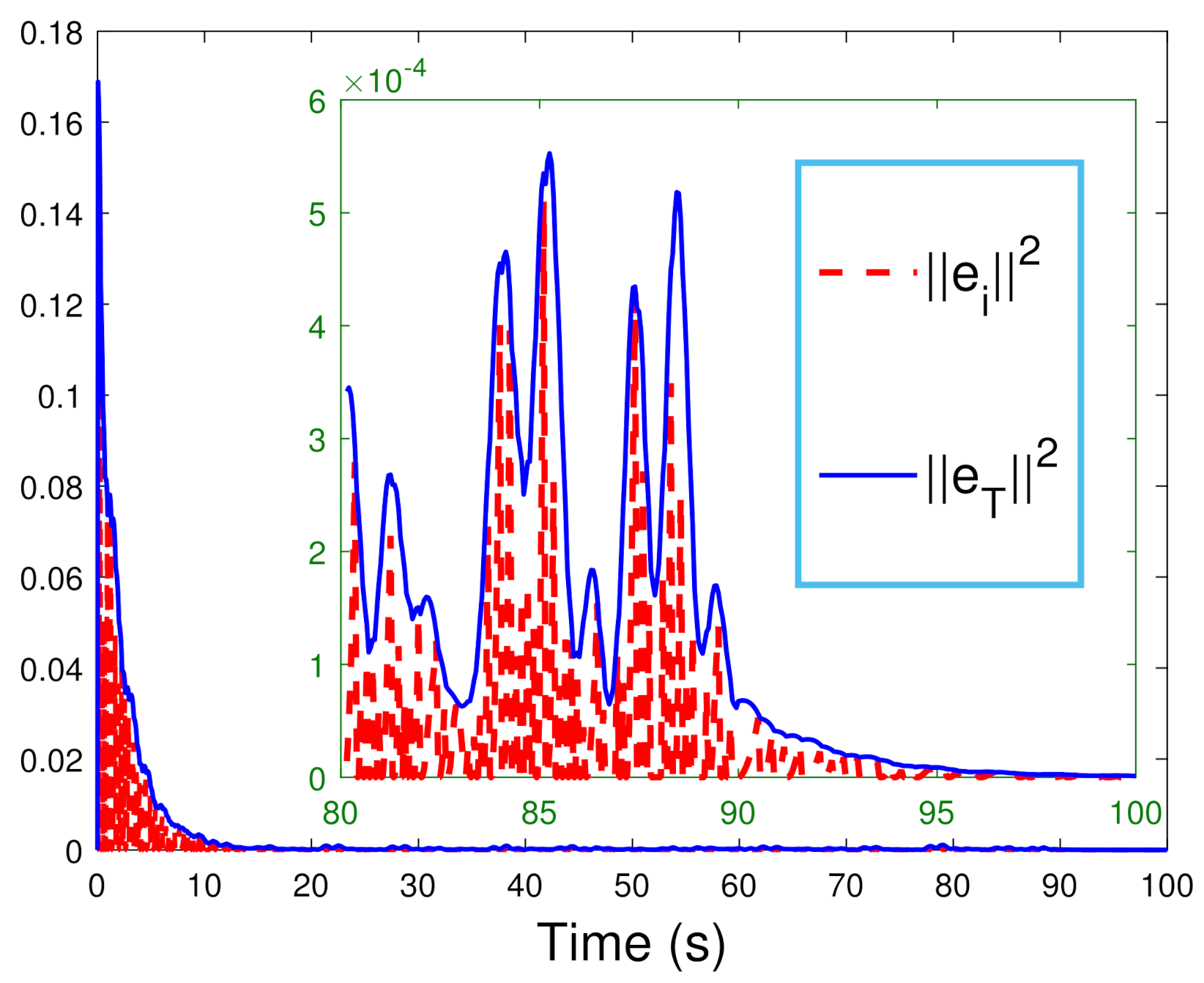
5. Simulation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Isermann, R. Digital Control Systems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Astrom, K.J.; Bernhardsson, B.M. Comparison of Riemann and Lebesque sampling for first order stochastic systems. In Proceedings of the 41st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–13 December 2002; pp. 2011–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tabuada, P. Event-triggered real-time scheduling of stabilizing control tasks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2007, 52, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girard, A. Dynamic Triggering Mechanisms for Event-Triggered Control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 60, 1992–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, L.; Han, Q.L.; Ge, X.; Zhang, X.M. An overview of recent advances in event-triggered consensus of multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.; Li, F. A survey on recent advances in event-triggered communication and control. Inf. Sci. 2018, 457, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Han, Q.L.; Zhang, B.L. An overview and deep investigation on sampled-data-based event-triggered control and filtering for networked systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 13, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yang, G.H. Event-triggered fault detection filter design for nonlinear networked systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2008, 48, 1851–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Song, Y. Event-Triggered Prescribed Performance Control for a Class of Unknown Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 6576–6586. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.; Han, Q.; Zhang, X.M.; Ding, D. Dynamic event-triggered control and estimation: A survey. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2021, 18, 857–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Han, Q.L.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, X.M. Dynamic event-triggered distributed coordination control and its applications: A survey of trends and techniques. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 50, 3112–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Ho, D.W.C.; Lam, J. Robust integral sliding mode control for uncertain stochastic systems with time-varying delay. Automatica 2005, 41, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Baldi, S.; Fridman, L.M. Adaptive sliding mode control without a priori bounded uncertainty. Automatica 2020, 111, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Roy, S.B.; Lee, J.; Baldi, S. Overcoming the Underestimation and Overestimation Problems in Adaptive Sliding Mode Control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Wang, H.; Cheng, F.; Yu, X.; Wen, G. Second-Order Consensus in Multiagent Systems via Distributed Sliding Mode Control. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 47, 1872–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradini, M.L.; Cristofaro, A. Nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control of nonlinear planar systems with global fixed-time stability guarantees. Automatica 2018, 95, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, P.; Yao, D. Adaptive sliding-mode control of Markov jump nonlinear systems with actuator faults. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2017, 64, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castan˜os, F.; Fridman, L. Analysis and Design of Integral Sliding Manifolds for Systems With Unmatched Perturbations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2006, 51, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Truc, L.N.; Vu, L.A.; Thoan, T.V.; Thanh, B.T.; Nguyen, T.L. Adaptive Sliding Mode Control Anticipating Proportional Degradation of Actuator Torque in Uncertain Serial Industrial Robots. Symmetry 2022, 14, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xiong, W.; Zhou, M.; Chen, L. A Continuous Terminal Sliding-Mode Observer-Based Anomaly Detection Approach for Industrial Communication Networks. Symmetry 2022, 14, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, F. Event-Triggered Sliding Mode Control of Switched Neural Networks With Mode-Dependent Average Dwell Time. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.C.; Yu, X.; Xue, Y. Quantized feedback sliding-mode control: An event-triggered approach. Automatica 2018, 91, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.R.; Behera, L.; Kumar, S. Event-triggered finite-time integral sliding mode controller for consensus-based formation of multi-robot systems with disturbances. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2019, 27, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Doyle, J.C.; Glover, K. Robust and Optimal Control; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, T.L. Nonlinear and Optimal Control Systems; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, F.L.; Vrabie, D.; Syrmos, V.L. Optimal Control; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Basar, T.; Bernard, P. H∞-Optimal Control and Related Minimax Design Problems; Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Vrabie, D.; Lewis, F. Neural network approach to continuous-time direct adaptive optimal control for partially unknown nonlinear systems. Neural Netw. 2009, 22, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellman, R.E. Dynamic Programming; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D. Adaptive dynamic programming: An introduction. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2009, 4, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, I.; Baldi, S.; Kosmatopoulos, E.B.; Ioannou, P.A. Adaptive Optimal Control for Large-Scale Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2017, 62, 5567–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Xue, S.; Zhao, B.; Luo, B.; Wei, Q. Adaptive Dynamic Programming for Control: A Survey and Recent Advances. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.Y.; Yang, G.H. Adaptive actor-critic design-based integral sliding-mode control for partially unknown nonlinear systems with input disturbances. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 27, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yu, R.; Liu, Y. Neural network-based H∞ sliding mode control for nonlinear systems with actuator faults and unmatched disturbances. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 2009–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qu, Q.; Xia, G.; Cui, Y. Optimal guaranteed cost sliding mode control for constrained-input nonlinear systems with matched and unmatched disturbances. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 2112–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamvoudakis, K.G. Event-triggered optimal adaptive control algorithm for continuous-time nonlinear systems. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2014, 1, 282–293. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, D.; Zhu, Y. Event-triggered H∞ control for continuous-time nonlinear system via concurrent learning. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2017, 47, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Luo, B.; Liu, D. Event-Triggered Adaptive Dynamic Programming for Unmatched Uncertain Nonlinear Continuous-Time Systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 99, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.S.; Li, T.; Xie, X.P.; Zhang, H.G.; Liu, D.R.; Li, Y.H. Event-Triggered Integral Sliding-Mode Control for Nonlinear Constrained-Input Systems With Disturbances via Adaptive Dynamic Programming. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 50, 2168–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.G.; Liang, Y.; Su, H.; Liu, C. Event-Driven Guaranteed Cost Control Design for Nonlinear Systems with Actuator Faults via Reinforcement Learning Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 50, 4135–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, M.; Do, X.P. Optimal adaptive neural PI full-order sliding mode control for robust fault tolerant control of uncertain nonlinear system. Eur. J. Control. 2020, 54, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


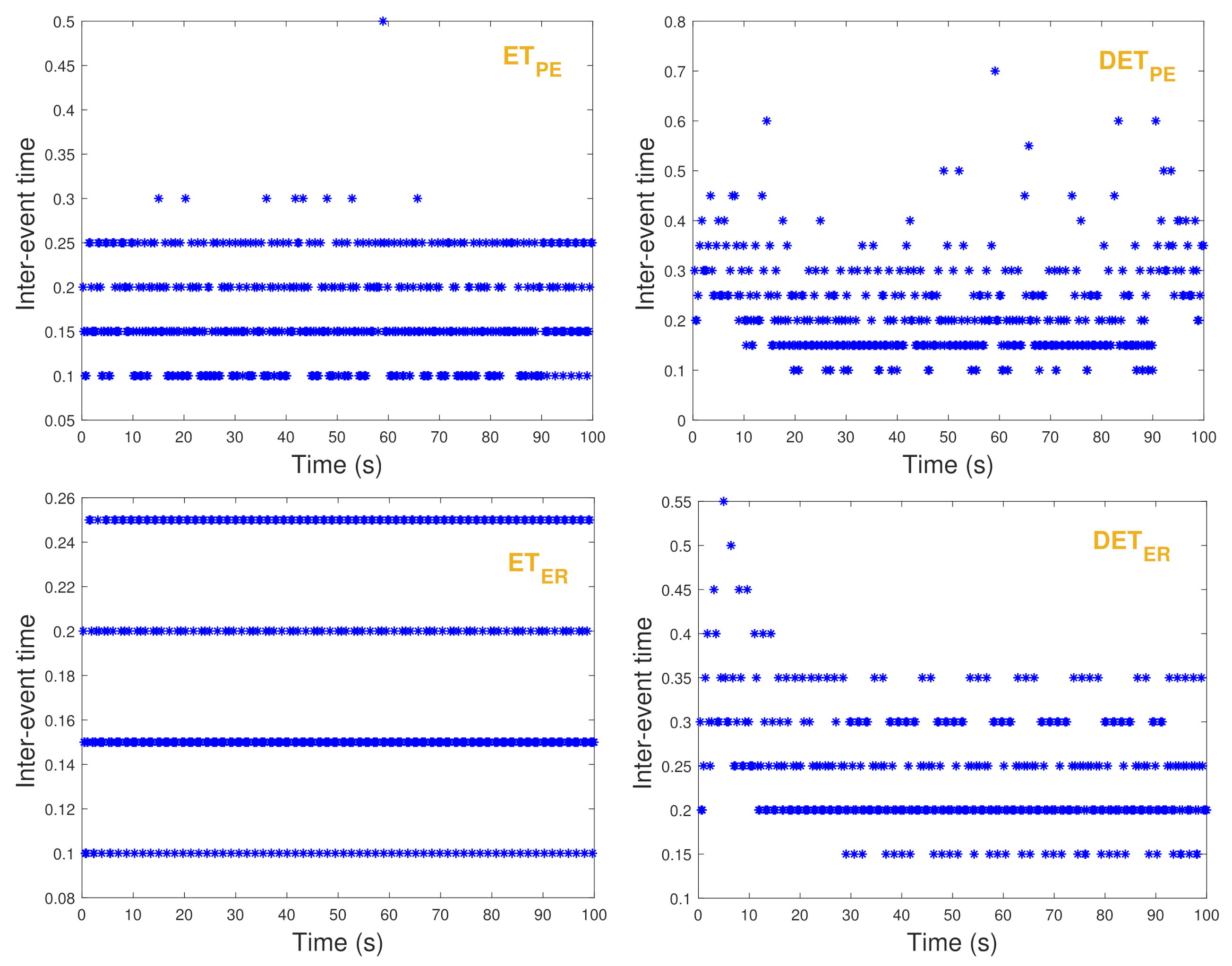
| Strategies | Samples | Average Interval | Minimal Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| 632 | 0.1582 | 0.1 | |
| 476 | 0.2101 | 0.1 | |
| 577 | 0.1733 | 0.1 | |
| 418 | 0.2392 | 0.15 |
| Triggering Rate (%) | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22.35 | 23.75 | 27.45 | 29.00 | ||
| 3 | 17.95 | 22.4 | 28.55 | 30.15 | ||
| 5 | 15.55 | 22.25 | 29.20 | 30.65 | ||
| 10 | 12.55 | 22.85 | 30.05 | 31.10 | ||
| Triggering Rate (%) | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 24.90 | 25.10 | 25.45 | 25.65 | ||
| 0.5 | 22.10 | 22.90 | 25 | 25.80 | ||
| 1 | 17.10 | 20.80 | 25.25 | 26.60 | ||
| 3 | 1.75 | 3.6 | 26.30 | 27.50 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, W.; Yu, W.; Wang, H. Dynamic Event-Triggered Integral Sliding Mode Adaptive Optimal Tracking Control for Uncertain Nonlinear Systems. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14061264
Tan W, Yu W, Wang H. Dynamic Event-Triggered Integral Sliding Mode Adaptive Optimal Tracking Control for Uncertain Nonlinear Systems. Symmetry. 2022; 14(6):1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14061264
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Wei, Wenwu Yu, and He Wang. 2022. "Dynamic Event-Triggered Integral Sliding Mode Adaptive Optimal Tracking Control for Uncertain Nonlinear Systems" Symmetry 14, no. 6: 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14061264
APA StyleTan, W., Yu, W., & Wang, H. (2022). Dynamic Event-Triggered Integral Sliding Mode Adaptive Optimal Tracking Control for Uncertain Nonlinear Systems. Symmetry, 14(6), 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14061264







