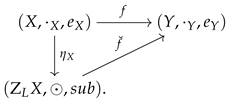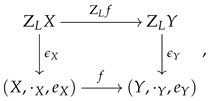1. Introduction
Complete residuated lattices are important symmetric algebraic structures for fuzzy logic, probabilistic logic and linear logic. As the table of truth values, it has been extensively applied to fuzzy order (or
L-order,
-order) theory originated by Zadeh [
1]. A fuzzy order is a kind of fuzzy relation with reflexivity, transitivity and asymmetry. Now, fuzzy order theory has been widely used in various branches of mathematics and computer sciences. For crisp order structures as models in theoretical computer science, some form of completeness should be required, such as the DM-completion, the ideal completion, the join-completion, the
-completion, and so on (see [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]).
The fruitful results about completions of crisp order structures have inspired some scholars to study the completions in the fuzzy setting. Wagner [
14], Bĕlohlávek [
15,
16] and Xie [
17] generalized the DM-completion to the multi-valued framework from different perspectives. The interesting thing is that the DM-completions above are exactly the same when
is a frame. Subsequently, Wang and Zhao [
18] obtained a category characterization of the DM-completion of fuzzy posets by constructing the join-completion of fuzzy posets. Moreover, they also solved the problem of whether the join-completions of fuzzy posets are entirely determined by the consistent fuzzy closure operators. Based on the work of [
18], Su and Li [
19] constructed the
-completion and discussed how it relates to formal
L-contexts over fuzzy posets. In general, the completion of fuzzy posets can be composed of some special fuzzy subset selection. Ma [
20], Rao [
21] and Zhao [
22] systematically studied the fuzzy subset system and used it to construct the
-continuity and
-algebra of fuzzy posets. Following this line, Su et al. [
23] established the
-completions of fuzzy posets and then constructed a minimum
-completion.
In order to enhance the applicability of ordered semigroups as mathematical tools, the combination of a fuzzy order and an algebraic system has appeared in recent years. Šešlja [
24], Hao [
25], Wang [
26] and Borzooei [
27] fused fuzzy order and algebraic structure in different ways and put forward new concepts such as fuzzy ordered group, fuzzy ordered semigroup and fuzzy lattice ordered group. Most of the above studies focus on the discussion of fuzzy order structure, in which algebraic structure only plays a secondary role. Then, Huang et al. [
28] established various fuzzy ideals on fuzzy ordered semigroups from the perspective of algebraic structure as the main and fuzzy order structure as the auxiliary. In addition, they also established the category characterization of fuzzy ordered semigroups, which further improved fuzzy set theory of ordered algebra. Following this viewpoint, Su et al. [
29] constructed an organic combination of fuzzy poset and semihypergroup, which is called an
L-ordered
L-semihypergroup. Then, they established three types of
L-hyperideals and intra-regularity on it.
Motivated by studies for fuzzy ordered semigroups and completions of fuzzy posets, Zhao et al. [
30] proposed the concept of
L-quantale as a generalization of a crisp quantale. For each fuzzy ordered semigroup, they defined the
L-quantale completion to be an
L-quantale together with a special embedding. In particular, they discussed the relationship between fuzzy ordered semigroups and
L-quantales from the categorical perspective. Following this line, Xia and Zhao [
31] further studied the
L-quantale completion and obtained the minimum
L-quantale completion of every fuzzy ordered semigroup.
In the crisp setting, Erné and Reichman [
32] introduced
-semigroups with ordered semigroups as a special case, and established a standard completion
for a
-semigroup. This completion provided the common pattern for various completions of ordered semigroups. It is then natural to ask whether one can extend the theory of standard completions to the setting of
L-ordered semigroups. In this paper, we answer this question by defining a new completion for fuzzy ordered semigroups, called
-completion. It turns out that many kinds of completions, such as the DM-completion and
L-quantale completion, are a special case of the
-completion.
This paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 lists some notions and results in [
16,
25,
26,
30,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38]. In
Section 3, based on an
L-subset selection, a standard
L-completion
of an
L-ordered semigroup and (weakly)
-continuous mapping preserving structures are introduced. In particular, some examples of compositive standard completions are presented. In
Section 4, a
-semigroup and its
-completion with the university property are built. Moreover, it is shown that for every
-semigroup, the standard
L-completion
with a join-dense
L-ordered semigroup embedding is a
-completion. In
Section 5, for different cases of
, the corresponding categorical characterization of a
-completion is established. Finally, we present conclusions in
Section 6.
2. Preliminaries
This section reviews some basic concepts and results on fuzzy posets (see [
16,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38]). Throughout this paper,
L denotes a complete residuated lattice
[
39], where
L is a complete lattice with the bottom 0 and the top 1, and
is a commutative, associative binary operator such that (1) ∗ is monotone on each argument; (2) ∗ has a right adjoint →, that is,
for all
; (3)
for all
. Such a symmetry algebraic structure is significant in the narrow sense of fuzzy logic (see [
15,
39]).
An L-subset of X is a mapping from X to L; write for the set . For , define as . We never distinguish between an element and the constant function satisfying , such as and .
Definition 1 ([
16,
34]).
A fuzzy order (or an L-order) e on a set X is an L-relation such that- (1)
, (reflexivity);
- (2)
, (transitivity);
- (3)
, (asymmetry).
The pair is called a fuzzy poset (or an L-ordered set).
For an L-ordered set , define a crisp order on X as follows: iff , and so is a poset.
For a nonempty set
X,
is an
L-ordered set, where the inclusion
L-order
[
15] defined by
.
Proposition 1 ([
16,
33]).
is an L-closure system (or a fuzzy closure system) on X iff- (1)
;
- (2)
.
For an L-closure operator C on X and an L-closure system on X, is an L-closure system on X and is an L-closure operator on X given by . Moreover, and . In particular, .
Definition 2 ([
36,
38]).
Let be an L-ordered set. is called a join of A denoted by , iff- (1)
;
- (2)
.
An L-ordered set is a complete L-lattice iff exists. is called a lower L-subset if and is defined by . As usually, the set of all lower L-subsets of X is denoted by and iff . Obviously, is an L-closure system and so is a complete L-lattice. is called a directed L-subset if and . Let denote the set of all directed L-subsets of X. For , a mapping defined by is called a principal L-ideal of X. Then . Similarly, for , we can obtain a mapping defined by .
For each mapping
, we can define
and
(see [
15,
35]) as
Definition 3 ([
37,
38]).
A mapping is called- (1)
L-order preserving if ;
- (2)
L-order embedding if ;
- (3)
join-preserving if with existing;
- (4)
join-dense if .
For an L-ordered set , is said to be join-dense in X iff for every , there is such that iff . Therefore, a mapping is join-dense iff is join-dense in Y.
Definition 4 ([
35,
37]).
If two L-order preserving mappings satisfy , then is called an L-adjunction between X and Y, where f is called the left L-adjoint of g and dually g the right L-adjoint of f. In this case, a left L-adjoint is also called a residuated mapping and its right L-adjoint a residual mapping. Obviously, for each mapping , the pair is an L-adjunction between and .
Theorem 1 ([
35,
37]).
Let be two mappings.- (1)
If is complete, then f has a right L-adjoint iff ;
- (2)
If is complete, then g has a left L-adjoint iff .
Clearly, a mapping between complete L-lattices is join-preserving iff it is residuated.
For an
L-ordered set
and
,
are defined as follows:
The cut operator is defined by . A is called a cut if . Obviously, every cut is always a lower L-subset and the cut operator is an L-closure operator on X. Moreover, is the Dedekind–MacNeille completion.
Definition 5 ([
25,
26,
30]).
A triple is called an L-ordered semigroup (L-OS for short) provided that- (1)
is an L-ordered set;
- (2)
is a semigroup;
- (3)
and .
Remark 1. - (1)
The condition (3) is equivalent to all left translations and all right translations are L-order preserving.
- (2)
An L-OS is called residuated if all left and right translations are residuated.
A mapping is called a semigroup homomorphism if . Moreover, a semigroup homomorphism is called (1) an L-OS homomorphism if it is L-ordered preserving; (2) an L-OS embedding if it is an L-ordered embedding. Then L-OSs with L-OS homomorphisms as morphisms form a category, denoted by L-OSG.
A complete L-OS means exists for all . Let be an L-OS and , define a binary operator , as follows: . Then we can check that is a complete L-OS and .
3. Standard -Completions for -Ordered Semigroups
In the crisp setting, a systematic analysis of standard completions for ordered semigroups has been developed in [
32]. In this section, let us discuss such completions under a fuzzy framework.
An L-subset selection (or a fuzzy subset selection) denotes a function which assigns to every L-OS a set of L-subsets of X, and is called (1) a standard L-completion if and is an L-closure system; (2) an L-subset system if for each L-ordered preserving mapping and each , . Clearly, there is no implication relationship between the two L-subset selections.
is called -complete if exists for all . It is noteworthy that for any standard L-completion , is -complete iff is complete. Moreover, for every , we may form the system and call -union complete if for all . Of course, for any , -union completeness entails -completeness, but not conversely. is called a -complete subsemigroup if is a subsemigroup of and for all . To simplify the description, and are referred to as a standard L-completion without distinction.
Example 1. Each of the following listed L-subset selection is a standard L-completion:
- (1)
the Alexandroff completion ;
- (2)
the Dedekind–MacNeille completion ;
- (3)
the L-Frink ideal completion defined by where finite L-subset F means that is finite;
- (4)
the ⊔-ideal completion given by - (5)
the Scott completion defined by - (6)
the Scott join-completion given by In fact, it obtained from (4) by admitting directed L-subsets D only;
- (7)
the -completion defined by (See [31]); - (8)
Any L-subset selection gives rise to the following standard L-completions: Obviously, and for every -complete L-ordered semigroup , .
Through simple calculation we get the following conclusion:
Proposition 2. For an L-OS , is the greatest standard L-completion and is the least one.
Proof. It is obviously true that is the greatest standard L-completion. So we only need to show that is the least standard L-completion. In fact, for any and any standard L-completion with , then and and so . This means that . □
Obviously, for an arbitrary standard
L-completion
,
is a complete
L-OS by [
30], where
is defined by
.
Example 2. For an L-OS , , , and are L-subset selections and so , , , , , are standard L-completions.
Given an arbitrary standard L-completion , we call a mapping weakly -continuous if for all , and we call f-continuous if for all . Then we can check that for a standard L-completion , f is -continuous iff .
Proposition 3. Let be an L-subset selection and consider the following conditions on a mapping :
- (1a)
f is -continuous;
- (1b)
f is weakly -continuous;
- (1c)
f is L-order preserving and ;
- (2a)
f is -continuous;
- (2b)
f is weakly -continuous;
- (2c)
f is L-order preserving and for all with existing.
If is an L-subset system then . If, in addition, is -complete then all six conditions are equivalent.
Proof. (1a)⇒(1b): It is obvious by .
(1b)⇒(1c): Obviously,
f is
L-order preserving. Now we need to show that
. In fact, for any
and any
,
(1c)⇒(1b): Suppose that
f is
L-order preserving and
-join preserving, then for any
,
is a lower
L-subset. Moreover, for any
,
Therefore .
If
is an
L-subset system, then we have (1c)⇒(1a). In fact, for any
and any
,
is a lower
L-subset and
; moreover,
Therefore .
(1b)⇒(2b): It holds by .
(2a)⇒(2b): It is obvious by .
(2b)⇒(2c): Similar to (1b)⇒(1c), we only need to show that
for all
with
existing. In fact, for any
and any
with
existing, we have
Moreover, for any
and any
, we have
, and so
. Therefore,
.
(2c)⇒(2b): For any and any with existing, is a lower L-subset and . Therefore and thus f is weakly -continuous.
Suppose that
is an
L-subset system, then (1c)⇒(1a). In fact, for any
and any
,
is a lower
L-subset and
; moreover,
Therefore,
. Suppose that
is
-complete, then
. In fact, for any
,
and
exist. Moreover,
and
□
Clearly, all identity mappings are -continuous and the compositions of -continuous mappings are again -continuous. Thus all L-OSs with -continuous L-OS homomorphisms form a category denoted by L-OSG, and it is a subcategory of L-OSG. We call a standard L-completion compositive if the class of all weakly -continuous mappings is closed under composition.
Lemma 1. - (1)
The embedding is weakly -continuous, and so are all corestrictions with ; is -continuous iff for all .
- (2)
An arbitrary mapping is -continuous iff the composite mapping is weakly -continuous.
Proof. (1) For any and any , , which implies that is weakly -continuous. Similarly, we can check that is also weakly -continuous. Note the following fact: , . Therefore, is -continuous iff for all .
(2) Suppose that is -continuous. By (1), we have that for any , and so . Therefore, is weakly -continuous. Conversely, suppose that is weakly -continuous, then for any and any , and . Thus f is -continuous. □
According to Lemma 1 we immediately get the following characterization of -union completeness and compositeness.
Proposition 4. - (1)
A standard L-completion is compositive iff every weakly -continuous mapping is already -continuous.
- (2)
A standard L-completion is -union complete iff for each L-OS the embedding is -continuous.
- (3)
Every compositive standard L-completion is -union complete.
- (4)
For every compositive standard L-completion , every residuated mapping is -continuous.
Corollary 1. For an L-subset system , the standard L-completions and are compositive.
From Proposition 4, it is easy to check the following relationships among mappings:
where “compositive" means the standard L-completion is compositive.
4. -Completions for -Semigroups
In this section, we shall consider completions for
-semigroups. In one special case, it is the
-quantale completion of the
-ordered semigroup constructed and characterized in [
30,
31].
Definition 6. Let be a standard L-completion, we call an L-OS a -semigroup if all left and right translations are -continuous.
Obviously, when
, a
-semigroup is just the
-semigroup defined in [
32].
Example 3. - (1)
An L-OS is an -semigroup since , and are still lower L-subsets.
- (2)
A -semigroup is characterized by the identities for all L-subsets with existing. Moreover, we can check that the equation (*) is equivalent to for any with existing.
- (3)
The example (2) can be generalized in an obvious way. Given an arbitrary L-subset system , it is easy to check that the -semigroups are those in which the identities (*) are valid for any L-subset with existing.
- (4)
Let be a meet L-semilattice (i.e., each finite L-subset has a meet), then is a meet-semilattice and so is an L-OS, where ∧ is the meet operation on . In this case, is a -semigroup characterized by for all and all L-ideals D possessing a join. This means that is -semigroup iff is meet-continuous (See [40]). - (5)
Every residuated L-OS is a -semigroup for compositive .
- (6)
is a -subsemigroup of iff it is an L-ordered subsemigroup of and a -semigroup with respect to the induced L-order.
Proposition 5. Let be a -semigroup and . Then
- (1)
and ;
- (2)
; in particular, ;
- (3)
is a complete residuated L-OS;
- (4)
The natural embedding is a join-dense and weakly -continuous semigroup homomorphism.
Proof. (1) Let
and
,
by the
-continuity of translations. Then for any
,
which implies
. Similarly, we have
.
(2) By (1), it is easy to check.
(3) It only needs to show that
is residuated. For
and any
,
and so
by Proposition 1. Now, we can define two mappings
and
as follows:
and
, respectively. Then we have
This implies that is a residuated mapping. Similarly, is residuated. Therefore, is residuated.
(4) Obviously,
is weakly
-continuous by Lemma 1 (1). Moreover, for all
and all
,
which implies that
. Therefore,
is join-dense. Next, we show that
is a semigroup homomorphism. In fact, for any
,
and
Hence . □
Remark 2. - (1)
If is an L-ordered monoid then so is . In fact, let be a unit element and then and . Thus it follows that and similarly.
- (2)
of commutative -semigroup is again commutative. From for any , we have .
- (3)
For every standard L-completion , is join-dense in .
- (4)
Every residuated L-OS is a -semigroup.
Definition 7. Let be a -semigroup. A complete residuated L-OS together with a join-dense L-OS embedding is called a -completion of if has the following universal property: For any weakly -continuous semigroup homomorphism mapping into a complete residuated L-OS , there exists a unique join-preserving L-OS homomorphism such that .
Clearly, a complete residuated L-OS is a -completion of itself.
Lemma 2. Let be join-preserving mappings between two -semigroups and and join-dense in X.
- (1)
If for all , then ;
- (2)
In the case that and are -semigroups, f is a semigroup homomorphism if .
Proof. (1) Let
, then for any
,
which implies that
for all
.
(2) For
, let
and
. Then
,
, and
Hence . □
Theorem 2. For each -semigroup , is a -completion of .
Proof. By Proposition 5 (3) and (4), we only need to show that has the universal property. Let be a weakly -continuous semigroup homomorphism from to a complete residuated L-OS , then for any and , exists and . Define as . Then . This implies that the mapping is a right adjoint of and so is residuated. Moreover, for any , and ; thus . The uniqueness of can be obtained by Lemma 2 and Remark 2 (3). □
Remark 3. - (1)
In the case of , the -completion of a -semigroup is the Dedekind–MacNeille completion.
- (2)
In the case of , the -completion of a -semigroup is the Q-quantale completion defined in [31]. Therefore, the Q-quantale completion has the universal property and the -completion can be as a generalization of the Q-quantale completion.
From the proof of Theorem 2, we can directly reach the following conclusion:
Proposition 6. We call a weakly -continuous mapping between two L-OSs and a -arrow if for every , exists. Then a mapping between L-OSs and is a -arrow iff there exists a unique residuated mapping with , viz. , i.e., the following commutative diagram:
5. A Category Characterization of the -Completion
The
-semigroups together with
-continuous semigroup homomorphisms form a category
. For example,
is the category of
L-OSs and
L-OS homomorphisms. Moreover, denote by
the category of complete residuated
L-ordered semigroups together with join-preserving
L-OS homomorphisms. Obviously,
-
Quant, defined in [
31]. In this section, we describe the
-completion of a
-semigroup from the perspective of category. Next, we first discuss whether an arbitrary
-continuous semigroup homomorphism
may be lifted to a join-preserving semigroup homomorphism between the
-completions
and
.
Lemma 3. For every -continuous semigroup homomorphism , the mapping is a join-preserving semigroup homomorphism.
Proof. Since
is
-continuous,
for any
. So we obtain a mapping
. Then for any
and any
,
Hence
is residuated and thus is join-preserving by Theorem 1. Moreover, for any
,
and so
. On the other hand, for all
,
Hence . This means is a semigroup homomorphism. To sum up, we have that is a join-preserving semigroup homomorphism. □
From this lemma, the following conclusion can be drawn directly:
Corollary 2. Every standard L-completion gives rise to a functor between and .
However, it should be pointed out that for a -continuous mapping f the lifted mapping need not be -continuous. See the following example:
Example 4. Define a standard L-completion by Let , and , define , , and as follows, respectively: Then , where . It is easy to check that and . By simple calculations, and are -semigroups. Moreover, is a four element Boolean lattice and is a three element Boolean lattice and so and . Now, a mapping is defined by , then f is obviously -continuous and is residuated. Note that , while
Example 4 implies that the functor does not necessarily induce an endofunctor of .
Lemma 4 ([
41]).
Let the category be the full subcategory of the category and the reflective subcategory of , then the inclusion functor is monadic. Proposition 7. - (1)
Every CS-morphism satisfies the following commutative diagram:
where is defined by for all .
- (2)
is the full subcategory of the category L-OSG of L-OSs and residuated semigroup homomorphisms.
- (3)
is the reflective subcategory of L-OSG; moreover, the inclusion functor I from to L-OSG is monadic.
Proof. (1) Let
be a
-morphism and
, then
and so
(2) Clearly, Obj()⊆Obj(L-OSG). Moreover, for any Obj(), Hom(L-OSG) iff Hom() by Theorem 1. Therefore, is the full subcategory of L-OSG.
(3) By Definition 4.16 of reflective subcategory in [
42] and Theorem 2,
is the reflective subcategory of
L-
OSG and so the inclusion functor
I from
to
L-
OSG is monadic by Lemma 4. □
Remark 4. Obviously, L-OSG is a subcategory of L-OSG as Obj(L-OSG )=Obj(L-OSG) and Hom(L-OSG )⊆ Hom(L-OSG). Then we have that is also a reflective subcategory of L-OSG. This is just Proposition 6.19 in [31]. Theorem 3. For any standard L-completion , if every -arrow into a complete L-OS is -continuous, then is a reflective subcategory of with reflection mappings . In this case, the inclusion functor is the right adjoint of the functor defined by for any Obj and for any Hom.
Proof. Hypothesis and Corollary 2 ensure that is a reflective subcategory of with reflection mappings . □
By Proposition 4 and Theorem 3, for every compositive standard L-completion , is a reflective subcategory of , but not vice versa. See the following:
Proposition 8. Let be an arbitrary standard L-completion such that for every complete L-OS . Then is a reflective subcategory of . However, if for at least one -semigroup possessing a least element 0 (i.e., ) then is not compositive.
Proof. Notice that for a complete
L-OS
,
is
-continuous, i.e.,
for any
. In fact,
,
Then for every -arrow f into a complete L-OS , is weakly -continuous and so f is -continuous by Lemma 1 (2). Therefore, is a reflective subcategory of . However, if has a least element 0 and then the inclusion mapping is weakly -continuous but not -continuous since . □
Lemma 5. Let be a weakly -continuous L-OS embedding between an L-OS and a complete residuated L-OS . Then the following three conditions are equivalent:
- (1)
f is join-dense;
- (2)
is surjective;
- (3)
There is a (unique) surjective -morphism with .
Proof. (1)⇒(2): For any , we have and so . Hence is surjective.
(2)⇒(3): Obviously.
(3)⇒(1): For any , there is with . Let , then and . Hence . This means that f is join-dense. □
The category of weakly -continuous L-OS embeddings of -semigroups is defined as follows: The objects of are weakly -continuous L-OS embeddings of -semigroups into complete residuated L-OSs and the morphisms of are join-preserving semigroup homomorphisms between two weakly -continuous L-OS embeddings, that is, a morphism between two weakly -continuous L-OS embeddings and is a join-preserving semigroup homomorphism such that there is a -continuous mapping satisfying . The objects of a full subcategory of are the weakly -continuous and join-dense L-OS embeddings. Then for an arbitrary standard L-completion , we can define a functor with domain of f for a -object f and for a -morphism h.
Theorem 4. Let be an arbitrary standard L-completion.
- (1)
has a left adjoint with for a -object X and for a -morphism f.
- (2)
restricts to a forgetful (i.e., faithful) functor from to which is a right adjoint to the corestriction of the functor to .
- (3)
In each of these adjunctions, the counit ϵ is given by for all weakly -continuous L-OS embeddings .
Proof. Let be a -morphism and a weakly -continuous L-OS embedding. Then is weakly -continuous, and the mapping is the unique -morphism with by Proposition 6. This means that the functor has a left adjoint . Therefore, (1) holds and thus (2) and (3) hold. □
6. Conclusions
In order to provide a common completion pattern for L-OSs, we introduced the notion of standard L-completion as a generalization of various completions, such as the Dedekind–MacNeille completion, the Alexandroff completion, ect. For L-OSs, the basic notions about (weakly) -continuous mappings arose naturally. In addition, we built -semigroups and their -completion with the universal property. We also present the categorical characterization of -completion under different cases of . The work is an extension of the crisp case and an attempt to further study asymmetric fuzzy algebraic structures.