Abstract
Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution (CV-MDI-QKD) allows remote parties to share information-theoretical secure keys while defending all the side-channel attacks on measurement devices. However, the secure transmission distance and the secret key rate are quite limited due to the high untrusted equivalent excess noise in the Gaussian modulation. More particularly, extremely high-efficiency homodyne detections are required for even non-zero secure transmission distances, which directly restrict its practical realization. Here, we propose a CV-MDI-QKD protocol by encoding the key information into matched discrete phases of two groups of coherent states, which decreases the required detection efficiency for ideally asymmetric cases, and makes it possible to practically achieve secure key distribution with current low-efficiency homodyne detections. Besides, a proof-of-principle experiment with a locally generated oscillator is implemented, which, for the first time, demonstrates the realizability of CV-MDI-QKD using all fiber-based devices. The discrete-modulated phase-matching method provides an alternative direction of an applicable quantum key distribution with practical security.
1. Introduction
Continuous-variable quantum key distribution (CV-QKD) [1,2,3,4,5] allows two remote authenticated users to establish a secure key through untrusted quantum channels, and authenticated classical channels, by using coherent detection. In particular, the secret keys are always encoded by Alice on the quadrature values [2,6,7] and the quadrature choices [8] of the quantized electronmagnetic field of coherent states, while they are distilled by homodyne or heterodyne detection in Bob’s side and the cooperative postprocessing procedure. The CV-QKD protocols have inherent features of high transmission capacity, simple hardware implementation, and effective compatibility with already deployed classical optical communication systems. In addition, the ideal implementation of CV-QKD can nearly approximate the ultimate limit of the secret key capacity of repeaterless quantum communication, i.e., the PLOB bound [9]. Since the ideal assumptions in the theoretical security proof of the CV-QKD protocol may be compromised in realistic implementations [10,11,12,13,14], eavesdroppers can exploit the security vulnerabilities arising from the imperfect implementations to capture the key information [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22].
In order to thoroughly eliminate the practical security vulnerabilities at the measurement side, the Gaussian-modulated coherent-state (GMCS) continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution (CV-MDI-QKD) protocols are proposed [23,24,25,26]. In these CV-MDI-QKD schemes, two legitimate parties, Alice and Bob, are both senders, and an untrusted third party, Charlie, is employed to perform Bell-State Measurement (BSM) and broadcast the outcomes to help to create the secret correlations between Alice and Bob. Despite the possibility that Charlie’s station can be fully tampered with, the legitimate parties can still extract the secure keys under optimal coherent attacks via insecure quantum channels. Therefore, CV-MDI-QKD protocols can eliminate all side-channel attacks against detections. In recent years, some breakthroughs have been made in the theoretical security study of CV-MDI-QKD [27,28,29,30].
Unfortunately, the theoretical performance, including the secret key rate and secure transmission distance of the GMCS CV-MDI-QKD, are quite limited because of the induced high equivalent excess noise [23,25]. In particular, almost perfect detections are required even for a non-zero secure transmission distance, which restricts its practical implementations [14,23]. In order to improve the performance and develop the practical realization, many efforts are currently being dedicated, such as developing the parameter estimation [31], employing photon subtraction [32], employing non-Gaussian postselection [33], and employing discrete modulation [34]. Recently, the concept of optimized communication strategies to enhance the information transfer over a non-Gaussian noisy channel is also proposed [35]. However, the practical realization remains a challenge issue, especially since extremely high-efficiency homodyne detection is still required even against individual attacks. So far, the only experimentally confirmed CV-MDI-QKD is the one based on the free-space transmission and the advanced detection techniques with an efficiency about 98% [23,36]. Practically, the overall efficiency of fiber-based homodyne detection is around 60% at telecom wavelengths [37,38,39,40,41]. Therefore, the full implementation of CV-MDI-QKD with practical lengths of optical fibers has not been reported on in the literature yet [14]. However, there are efforts to extend the robustness of CV-MDI-QKD by resorting to postselection, such as in [42].
In this paper, we propose a realizable CV-MDI-QKD protocol by encoding the key information into some discrete specific phases. When Alice and Bob’s discrete encoding phases match each other, the correlation between them can be established after Charlie publicly announces the outcomes of the two homodyne detectors. When comparing the conventional GMCS CV-MDI-QKD schemes, the proposed discrete-modulated phase-matching (DMPM) CV-MDI-QKD protocol can theoretically achieve secure key distribution with current low-efficiency detections for the ideally asymmetric case, against a typical and powerful non-Gaussian individual attack, which could reach the quantum limit of the discrimination of the discrete encoded quantum states. Moreover, we demonstrate the realizability of the proposed scheme by performing a proof-of-principle experiment with a local oscillator (LO) and realistic homodyne detection over standard single-mode fiber (SMF) spools. The proposed protocol can be applied in an access network for cryptography communications.
For simplicity, we start by introducing the DMPM protocol. We then analyze the security of the proposed scheme under the SD attacks and show the corresponding numerical simulation performances. Finally, the experimental realizability of the proposed phase-matching scheme under realistic conditions is demonstrated.
2. DMPM CV-MDI-QKD Protocol
The proposed DMPM CV-MDI-QKD protocol, which is illustrated in Figure 1, can be described as follows.
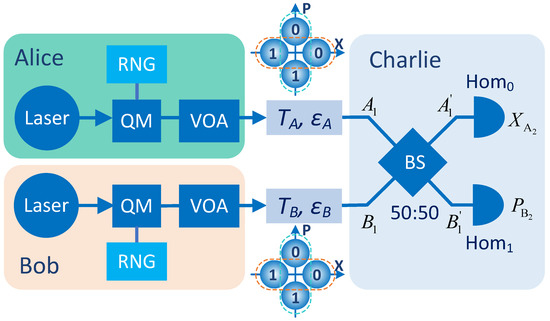
Figure 1.
(Color online). The phase-matching CV-MDI-QKD scheme. RNG is random number generator, QM is quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK) modulator, VOA is variable optical attenuator, BS is beam splitter, Hom is homodyne detection of measuring the X quadrature, Hom is homodyne detection of measuring the P quadrature, and are the transmission efficiency and excess noise of quantum channel between Alice (Bob) and Charlie, respectively.
Step 1. Alice and Bob prepare four coherent states: with , respectively. The states and with encoded binary values 0 and 1, respectively, are called X-basis states, while and with encoded binary values of 0 and 1, respectively, are called P-basis states.
Step 2. According to the binary random values, Alice and Bob choose the corresponding encoded coherent states randomly from X- or P- basis states, respectively. Then they simultaneously send them to Charlie through two different channels after adjusting for the intensities by VOAs.
Step 3. The received two modes ( and ) interfere at a 50:50 BS with two output modes and on Charlie’s side. Then, both the X quadrature of and the P quadrature of are measured by homodyne detections, and the measurement results are broadcasted by Charlie.
Step 4. Alice and Bob publicly announce their bases. And according to Charlie’s measurement results, they collect the corresponding binary RNG values with the same bases as strings and , respectively, for the X-basis case and for the P-basis case . Besides, they preserve the quadratures of the prepared inconsistent-basis states and as strings and , respectively.
Step 5. Alice keeps her binary string unchanged, and Bob generates a modified binary string by flipping the bits in when the corresponding encoding states are P-basis states. After these operations, Alice and Bob share a set of correlated binary raw keys .
Step 6. Alice and Bob perform a parameter estimation based on strings , and the corresponding broadcasted results , and then further distill a string of secret keys from with information reconciliation and privacy amplification processes through an authenticated public channel.
In the proposed protocol, Alice and Bob prepare, independently, the coherent states, and the measurements are performed by a totally untrusted third party, Charlie. Here, Alice and Bob can optimize their amplitudes and the phase-matching thresholds , to maximize the evaluated secret key rate. The phase-matching conditions in step 4 and the decoding rules in step 5 give four effective secret key generation cases, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Key generation cases for Alice and Bob in DMPM CV-MDI-QKD protocol.
3. Eavesdropping and Simulations
Here, we exemplify the security of the proposed protocol under a typical and powerful non-Gaussian individual attack, i.e., the beam-splitting (BS) and partial intercept-resend (IR) attacks, combined with the SD attacks [43], which are constructed by a SD receiver [44,45,46,47] and a heralded noiseless linear amplifier (NLA) [48,49,50,51]. Specifically, Eve can apply SD receivers to directly capture the discrete-encoded secret key with low average error probability, which has two lower bounds, i.e., the standard quantum limit (SQL) and the quantum limit (QL) [44,45,46,47], respectively. Here, SQL defines the minimum average error probability with which the nonorthogonal states can be distinguished by directly measuring the encoded physical observable coherent states, such as the intensity and phase, with conventional receivers. The QL is a lower bound which is fundamentally allowed in quantum mechanics, and it is shown in [43] that for the discrete-modulated types of CVQKD schemes, the SD attacks are powerful and can be almost close to optimal levels when combined with the NLA in some specific conditions.In practical scenarios, the phase-matching thresholds should be set according to the parameter estimation of the two quantum channels. Here, we will consider two typical cases, i.e, the symmetric case that the transmission efficiencies and excess noises of the two quantum channels are both T and , and the ideally asymmetric case has a transmission efficiency and excess noises , respectively. For the symmetric or asymmetric cases, Alice and Bob can adjust their VOAs to balance the total transmission efficiencies to optimize the performance.
For the BS-combined SD attacks, Eve first performs a standard BS attack on the transmitted signals, then she takes SD attacks on the split photons to directly capture the secret key information after the announcement of bases and Charlie’s measurement outcomes. Thus, she can decrease the discrimination error probability by just discriminating the nonorthogonal coherent states in a binary phase-shift keying (BPSK) format, other than QPSK. For the symmetric case, Eve will directly discriminate Bob’s states for eavesdropping when using reverse reconciliation. While for the ideally asymmetric case, Eve needs to judge Bob’s encoded keys according to Charlie’s measurement outcomes and the results of the SD attacks on Alice’s states. It should be mentioned that Eve will amplify the split coherent states with a heralded NLA to further lower the discriminating error probability, but with a probability of success. In this way, when the legitimate parities set the suitable intensity of coherent states and phase-matching thresholds, Eve can not obtain the secret key for both symmetric and ideally asymmetric cases. See the Appendix A and Appendix B for further details about the calculation of the secret key rate under BS-combined SD attacks.
For the IR attacks, Eve intercepts the transmitted quantum states from both Alice and Bob’s stations (for symmetric or, ideally, asymmetric cases). In particular, Eve will control the untrusted party, Charlie, and intercept the transmitted states from Alice and Bob to perform perfect heterodyne detections. However, she will not resend the reproduced quantum state here, but will directly resend the forged broadcasted measurement results. Moreover, she can capture the secret key by using the measurement results of the intercepted quantum state through the channel between Bob and Charlie. In this way, Eve can obtain the secret key for both symmetric and, ideally, asymmetric cases. See the Appendix C for further details about the calculation of the secret key rate under the complete IR attacks.However, the error discrimination will induce extra excess noise, which could be found by the legitimate parties in the parameter estimation. So, she will use the channel excess noise to cover her eavesdropping to try her best to capture the secret key.
Here, we evaluate the secret key rate under Eve’s specific attack strategy for the symmetric and, ideally, asymmetric cases. In particular, if the total channel excess noise is equal to, or larger than, the total extra excess noise induced by the complete IR attacks, Alice and Bob cannot share the secure secret key, since Eve can replace the quantum channels with noiseless ones to cover the induced extra excess noise and capture all the secret keys by performing complete IR attacks. When , Eve will perform partial IR attacks with the probability and will perform BS-combined SD attacks for other cases. Here, both the quantum channels are replaced with noiseless ones to cover Eve’s induced extra excess noise. In this state, the secret key rate can be calculated as
where is the classical mutual information between Alice and Bob, is the leaked information to Eve, and is the reconciliation efficiency. Here, all the superscripts s and a denote the symmetric and asymmetric cases, respectively. See the Appendix D for further details about the evaluation of the secret key rate of the proposed protocol under the non-Gaussian individual attack.
As shown in Figure 2, the proposed CV-MDI-QKD protocol can achieve secure key distribution with a realistic low-efficiency homodyne detector for the ideally asymmetric case. The scheme is also sensitive to channel excess noise for both symmetric and, ideally, asymmetric cases. Moreover, there exists an optimal amplitude and a threshold of for the given transmission distance and channel excess noise. Therefore, one can optimize the amplitude and thresholds to maximize the secret key rate and the secure transmission distance. It should be mentioned that the secure transmission distances for both the symmetric and, ideally, asymmetric cases are limited to the access network, since the direct IR attack utilizes the untrusted property of the measurement party, Charlie. Moreover, it restricts the required detection efficiency (RDE) (at least larger than 0.5, in theory) to guarantee a positive secret key rate for both the symmetric and, ideally, asymmetric cases. However, due to the restriction of the direct access to the encoded states from Bob’s station in the BS-combined SD attacks, the demand of extremely high-efficiency homodyne detection is removed for the ideally asymmetric case.
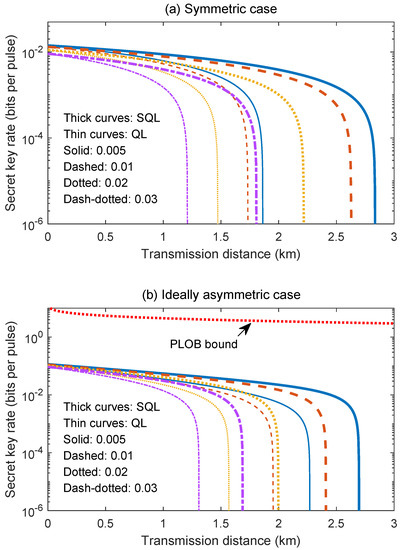
Figure 2.
(Color online). The secret key rates for different channel excess noises when the SD receivers reach QL and SQL, respectively. The results are compared to the PLOB bound [9]. The other parameters are set as (for symmetric case), (for ideally asymmetric case), .
The RDE for the different transmission distances in an ideally asymmetric case are depicted in Figure 3. The results show that the proposed protocol exhibits the capability of low RDE, which can be well implemented in realistic conditions. Compared to the conventional GMCS CV-MDI-QKD protocol [25] under the general individual attacks [52] with similar parameters (the modulation variance is set under the practical condition [25]) for the ideally asymmetric case, the RDEs of the proposed scheme are lower for most of the reachable secure transmission distances when the SD receivers reach SQL and QL. Specifically, the RDEs are 0.5344 and 0.5342 for the non-zero secure transmission distance when the SD receivers reach SQL and QL without the consideration of finite-size effects, respectively. While the RDEs are 0.6722, 0.7837, and 0.8870 for conventional GMCS CV-MDI-QKD protocols under the same type of non-Gaussian individual, as well as the general individual and collective attacks, respectively. However, for the symmetric case, the RDEs of the proposed DMPM CV-MDI-QKD are similar to the ones of conventional GMCS CV-MDI-QKD protocols, which are all approximately 0.7 for the same parameters.
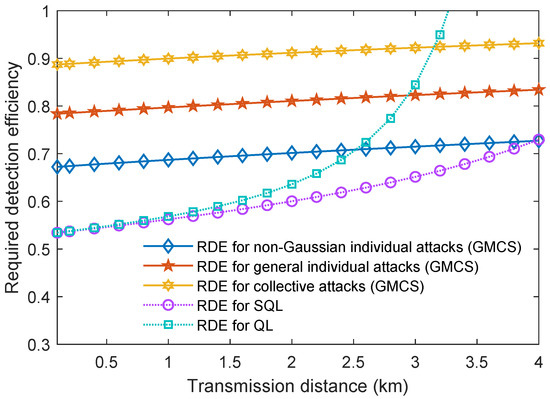
Figure 3.
(Color online). The RDEs as a function of transmission distance for ideally asymmetric case when the SD receivers reach QL and SQL. The other parameters are set as .
4. Proof-of-Principle Experiment
For the realistic implementation of the proposed DMPM CV-MDI-QKD scheme, the key issues are the interference and random phase drifts between the two remote independent lasers. By using frequency-locking and phase-reference techniques, the latest experiments [53,54] show the feasibilities of this kind of interference and phase compensation, with even weaker optical signals and a much longer transmission distance. Recently, an alternative method was proposed and demonstrated experimentally by using carrier synchronization to compensate the frequency offsets and phase drifts for the similar interference of continuous-variable quantum states with the local-LO implementation [55]. These methods pave the way for the realistic implementation of the proposed scheme.
Inspired by the method proposed in [55], a proof-of-principle experiment for the ideally asymmetric case of the DMPM CV-MDI-QKD protocol is designed here with the local-LO. It should be mentioned that the local-LO realization shows the superiority of the compatibility of the continuous-variable technique with classical optical communication, which is a promising direction for high-speed, high-integration, and low-cost applications. The schematic diagram is shown in Figure 4. is a narrow linewidth frequency-stabilized laser with a center wavelength of 1542.38 nm and a linewidth around 150 kHz, which is employed to generate both Alice and Bob’s signal states. The generated continuous-wave light (Wavelength Reference, Clarity-NLL-1542-HP) is split into two beams used as the carriers from Alice and Bob. The emission power of is controlled at −40 dbm, which meets the requirements of modulation variance in the theoretical protocol. Two VOAs are applied to control the intensities of the optical signals, where the signal includes M consecutive pilot signals and cascaded N consecutive data signals. The pilot signals are used for the cursory estimation of the frequency offset between the signals and the local-LO, and some of the data signals are used for further estimations of frequency offset and phase drifts caused by the fluctuations in the path length.
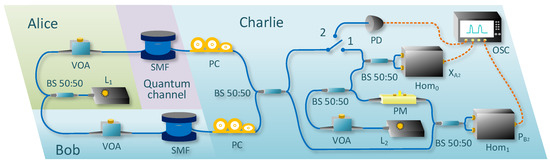
Figure 4.
(Color online). The schematic diagram of the proof-of-principle experiment of the proposed phase-matching CV-MDI-QKD scheme. , : the lasers with stabilized frequencies, BS: beamsplitter, VOA: variable optical attenuator, SMF: single mode fiber, PC: polarization controller, PM: phase modulator, Hom: homodyne detector, PD: photoelectric detector, OSC: oscilloscope.
Since the state of polarization (SOP) in the single-mode fiber will change independently due to the birefringence effect, the SOP cannot be kept the same. After being transmitted through two 5-km SMF spools with a measured loss of 0.2 dB/km at 1542.38 nm, it is adjusted by the manual PCs to ensure that the polarization directions of the coherent states transmitted by Alice and Bob are consistent to interfere by a 50:50 BS at the receiver.Here, we consider the ideally asymmetric case, where one SMF spool is served as the quantum channel and the other is used as a the delay line to synchronize the two signals in Bob’s station, which cannot be intercepted by Eve. The quantum channel between Bob and Charlie can be seen as the one with and . Here, the actual fiber coupling efficiency and the natural loss of the fiber are all attributed to the attenuation of the quantum channel, which has been analyzed in the theoretical analysis. Another frequency stabilized laser is used as the local-LO, which is the same type as and is also divided into two beams. The optical power of is controlled by a VOA at 5 dbm to meet the shot noise detection requirement. Specifically, the power is adjusted while it is monitored in real-time by a power meter. Each of the LOs are mixed with one interference output followed by a homodyne detector with a 350-MHz bandwidth to measure the quadratures and , which contain the pilot segments , and the data segments . An oscilloscope with a 1 GS/s sampling rate is used to acquire the output results from the two homodyne detectors.
It should be mentioned that since we use a continuous-wave mode of the quantum signal, the bandwidth of the whole system mainly depends on the bandwidth of the homodyne detectors. Here, the cursory frequency offset estimation is firstly performed by using the acquired outputs from the pilot segments . In our experiment, this frequency offset mainly originates from the phase noise caused by the spontaneous emission in two lasers, which is related to the linewidth and is around 15 MHz in this experiment. In order to perform a further estimate of the frequency offset and phase drift, some data signals should be revealed. To monitor the phase drift in the quantum channel, here, the interference output power is directly detected by a PD through port 2, which reflects the phase drift of two optical fields after passing through their respective channels. The output is sampled as 2 kS/s and the result is shown in Figure 5a, and the average phase drift rate is 0.6541 rad/ms. By using these values, Alice and Bob will modify their prepared values and with frequency their offset recovery and phase drift compensation algorithms. A parameter estimation can then be performed, just like in the original protocol. See the Appendix E for further details about the method of the frequency offset recovery and phase drift compensation.
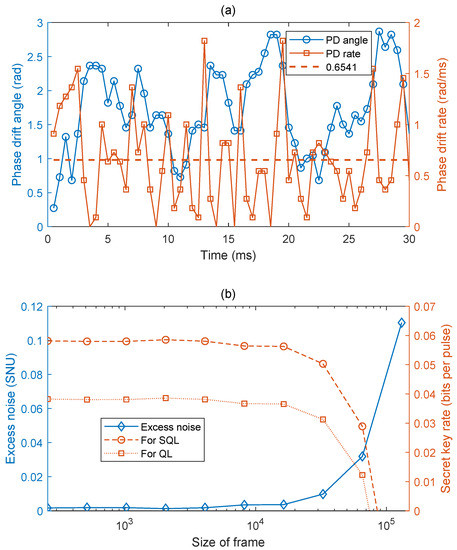
Figure 5.
(Color online). (a) Phase drift angle and phase drift rate change with time. (b) The excess noise and corresponding secret key rates for the ideally asymmetric case as a function of the size of frame. The other parameters are set as .
For simplicity, here we don’t perform modulation on the signal state and therefore random number generators are omitted, but measure the quadratures of the carrier signal, i.e., the quadratures and of pilot segments, and then perform communication simulations with constructed key data and the measured quadratures and monitored phase drifts for the same simulation model [55]. The result reflects the phase drift situation in the actual optical fiber channel and its influence on the theoretical performance. By adopting the algorithm we proposed in Ref. [55], the phase misalignment problem can be solved, and the practical realization of the proposed protocol can be guaranteed.
Especially, we evaluate the excess noise for different frame sizes, where the first symbol is used to compensate the phase of the next four symbols. It can be seen from Figure 5b that the excess noise increases with the frame sizes. The reason is that when the phase drift rate is specified, shorter frame can be used to track the phase drift more accurately, which reducing the excess noise caused by the phase deviation. More detailedly, the frame length affects the accuracy of phase compensation. Specifically, the designed phase compensation algorithm for phase drift is to make an overall compensation for each frame. If the length of a frame is longer, then the symbol phase drift in one frame is not consistent and has a significant difference, and the residual phase noise will become more prominent after the compensation. The secret key rates are also shown in Figure 5b, which are evaluated under the conditions that the length of the SMF spool served as the quantum channel is 2 km with the channel loss dB/km and . We can find that the frame size should be controlled smaller enough to guarantee secure key distribution.
5. Conclusions
We propose a realizable CV-MDI-QKD scheme by encoding the key information into some discrete and matched specific phases, where the correlation between the legitimate parities can be established after Charlie publicly announces the results of the homodyne detections. The eavesdropping analysis is provided under a typical non-Gaussian attack, which is constructed by an SD receiver and a heralded NLA, when combined with the BS and partial IR attacks. The simulation results show that the two legitimate parties can obtain a secure secret key at relatively short distances against the strongest SD attacks, even with the currently low-efficiency homodyne detections for an ideally asymmetric case. For the symmetric case, the demand of the high-efficiency homodyne detection remains.
Different from the conventional discrete-modulated CV-MDI-QKD and CVQKD protocols, the encoding of secret keys here is based on the choices of discrete-distributed matched specific phases, but not directly encoding the secret information on continuous-distributed quadrature values with further judgments. This encoding way efficiently decreases the RDE and weakens the effect of the channel’s excess noise on the secret key rate, especially for the ideally asymmetric case, which is similar to the basis of the encoding for the QKD scheme [8] where the secret keys are encoded on the quadrature choices, i.e., the discrete-distributed measurement bases of the Gaussian-modulated coherent states. However, the discrete modulation and phase-matching encoding lead to a low utilization efficiency and a low capacity of the quantum channel, thus restricting the secret key rate to a relatively low level. The proof-of-principle experiment, with a locally-generated LO, demonstrates, for the first time, that CV-MDI-QKD can be currently well implemented using fiber-based devices under realistic conditions, which also shows the potentiality to be further integrated with low-cost classical optical communications.
From the security analysis, we found that the proposed DMPM CV-MDI-QKD protocol is not able to overcome the PLOB bound. However, for the discrete-variable (DV) PM QKD protocol proposed in [56], it is shown that the secret key rate can overcome the PLOB bound. The fundamental reason may be that they have different physical principles of implementations, which leads to different security analyses frameworks. In the DV case, the PM QKD protocol executes based on single-photon interference, where the unfolding of the used Mach–Zehnder interferometer doubles the transmission distance. In the CV case, the proposed CV-MDI-QKD protocol is based on the first-order interference of the light field quadratures of the multiphoton quantum states. The optical structure is the same as the one in the known Gaussian-modulated CV-MDI-QKD protocol, but it instead uses the phase-matching method with discrete-encoding. Thus, the performances of this protocol are also fundamentally restricted by the security framework of CV-QKD, and it is not able to overcome the PLOB bound. However, the introduction of the phase-matching method with discrete-encoding relatively increases the correlation between the legitimated parties, which, to some extent, relieves the required detection efficiency.
Here, the analysed non-Gaussian individual attack against the proposed scheme are realistic and important attacks for cryptography communication, which has been thoroughly studied in theory and in experiments [57,58]. Moreover, it is shown in [43] that for the discrete-modulated four-state CV-QKD schemes, the leaked information under the SD attacks can be larger than the Holevo bound that is calculated directly with the estimated parameters from the reconstructed covariance matrix under the linear channel assumption [7], when combining with the NLA in some specific conditions. Actually, the asymptotic security of the discrete-modulated CV-QKD against the collective attacks has only recently been proven [59]. The security has also been proven, in a composable finite-size way, against the collective Gaussian attacks [60]. In particular, a lower bound of the secret key rate is given for the four-state protocol, which is also lower than the one while assuming a linear channel [59]. This proof shows that the SD attacks are powerful and close to optimal, since the proposed protocol also performs essentially discrete modulations. Nevertheless, the security should be further developed against more general attacks. Under realistic conditions, the discrete modulation can achieve a high symbol rate to G Hz, and the secret key rate with practical security can reach applicable levels for accessing networks in cryptography communications.
It should be mentioned here that the fiber chromatic dispersion and polarization mode dispersion will not affect the current theoretical protocols and experiments. It is because the symbol rate of the discrete-modulation, currently, is not high, less than G Baud. Therefore, under a single-mode fiber, chromatic dispersion and polarization mode dispersion will not cause inter-symbol crosstalk. However, if the operation symbol rate exceeds G Baud in the future, the influence of fiber dispersion needs to be further considered. Moreover, the protocol can be also applied in the case of the free-space quantum channel [61,62,63] and the encoding may be extended to the squeezed states [64] with discrete-modulation.
Author Contributions
P.H. and G.Z. conceived the research. T.W. carried out the proof-of-principle experiment. P.H. performed the security analysis. P.H. and D.H. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the data collection, discussed the results and reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National key research and development program (Grant No. 2016YFA0302600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 61971276, 61631014), Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (Grant No. 2019SHZDZX01), and the Key R&D Program of Guangdong province (Grant No. 2020B030304002).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Secret Key Rate under BS-Combined SD Attacks
For BS-combined SD attacks, Eve first performs a beam-splitting (BS) attack on the transmitted signals, i.e., Eve replaces the quantum channel with a perfect lossless and noiseless one, connecting a beam splitter with the transmission efficiency and . Then, she performs SD attacks to directly capture the secret key information. We will first calculate the mutual information between Alice and Bob, then evaluate the mutual information between Eve and Bob, and, finally, we will show the simulations of the secret key rate under the BS-combined SD attacks.
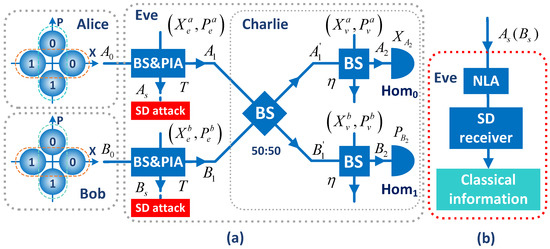
Figure A1.
(Color online). (a) The description of the SD attack strategy on the phase-matching CV-MDI-QKD scheme. BS is beam splitter, PIA is phase-insensitive amplifier, is homodyne detection of measuring the X quadrature, is homodyne detection of measuring the P quadrature, T is the transmission efficiency of quantum channel between Alice (Bob) and Charlie; (b) the construction of SD attack, NLA is noiseless linear amplifier.
Appendix A.1. The Mutual Information between Alice and Bob
We first consider the symmetric case, i.e., the transmission efficiencies and excess noises of the two quantum channels, which are are both T and . Here, Eve can directly discriminate Bob’s states for reverse reconciliation to capture the secret key, or Eve can use both the results of the SD attack, through Alice and Bob’s channels, to judge the encoded secret key. However, Eve’s BS-combined SD attacks do not change the parameters of the quantum channels between Alice and Charlie, and Bob and Charlie. Therefore, Eve’s operations will not affect the mutual information between Alice and Bob.
Here, the output intensities of Alice and Bob’s states are a set equivalent. After the beam splitting and amplification operations, the quadratures of the output modes and , in Figure A1, can be expressed as
where and are the equivalent extra input quadratures of the thermal states controlled by Eve, and they satisfy in the shot noise unit (SNU). For a noisy channel, Eve can use a beam splitter and a cascaded phase-insensitive amplifier (PIA) with total transmission efficiencies to split the photons as much as possible, thus reducing the error probability of her SD attacks. Here, is the transmission efficiency of the renewed beam splitter and is the gain of the PIA (shown in Figure A8). This restricts the largest quantity of the mean photon number captured by Eve for the SD attacks to (see Appendix B for details).
After the interference, the quadratures of the output modes and in Charlie’s side are given by
Then, we can get
where and are the quadratures of the vacuum states and the electronic noise induced from the imperfect homodyne detection, respectively, and they satisfy , and in the SNU, respectively. Moreover, we have
where , are the fixed values from the set , where is assumed to be a real and positive value, and , are the quadratures of the vacuum states induced in the encoding step.
According to Alice and Bob’s public basis announcements, they will discard one half of the measurement results with inconsistent bases. For the other half of the outcomes with consistent bases, for the X-basis case and for the P-basis case, respectively, Alice and Bob can perform correct and effective decodings after basis reconciliation. For these two cases, one can always find that
and they follow the normal distribution as
Because of the symmetry of the two bases, we assume , and the correct and effective decoding probability can then be calculated as
where is the decoding threshold, and .
While for the X-basis case and for the P-basis case, respectively, Alice and Bob will perform incorrect but effective decodings. For these two cases, one can find that
and they follow the normal distribution as
where values or have the same probability. Similarly, we assume , and the incorrect but effective decoding probability can be calculated as
Therefore, the key distribution channel between Alice and Bob can be seen as a binary symmetric channel (BSC) with utilization efficiency , and quantum bit error rate (QBER) . Thus, the mutual information between Alice and Bob under the BS-combined SD attack is given by
While, for the asymmetric case (the total channel excess noise of two channels is the same as 2), Bob will adjust the VOA in his station, where the attenuation efficiency will be equivalent to the quantum channel between Alice and Charlie, such that the decoding procedures in Equations (A5) and (A8) can be guaranteed. Therefore, the mutual information between Alice and Bob under the BS-combined SD attack for the asymmetric case can be also given by the Equation (A11).
Appendix A.2. The Mutual Information between Eve and Bob
Now, we turn to Eve’s information from the BS-combined SD attack. We first consider the symmetric case. The detailed construction of the SD attack is shown in Figure A1b. Here, Eve can use both the results of the SD attack through Alice and Bob’s channels to judge the encoded secret key. However, Eve just needs to discriminate Bob’s states for reverse reconciliation. Since the legitimate parties will discard the ineffective results according to Charlie’s measurement results, Eve will also optimize her eavesdropping to capture the secret key according to Charlie’s measurement results.
Specifically, she will reserve the split photons in the beam splitting stage and will perform the SD attack after the announcement of the bases. Thus, she can decrease the discrimination error probability by just discriminating the nonorthogonal coherent states in a BPSK format other than a QPSK one. Moreover, Eve will amplify the split coherent states with a heralded NLA to further lower the discriminating error probability with a success probability , where is the gain of the NLA and is the input amplitude of the coherent states. Moreover, according to Alice and Bob’s public basis announcements, Eve will discard one half of the split states with the inconsistent bases. For the other half of the coherent states with consistent bases, we also consider the two cases, i.e., and for the X-basis case and and for the P-basis case. Because of symmetric encoding, we just consider the X-basis case in the following equations.
We suppose that when Eve fails in the implementation of the NLA, she will randomly choose one of the two coherent states, which will induce a error probability in the decoding. Moreover, if Eve performs an incorrect discrimination of a coherent state sent from Alice or Bob’s stations after the successful implementation of the NLA, it will induce a error probability in decoding, where is the average error probability of Eve’s SD receiver, which has two lower bounds, i.e., the standard quantum limit (SQL) and the quantum limit (QL) [44,45,46,47], respectively. In particular, the SQL defines the minimum average error probability with which the nonorthogonal states can be distinguished by directly measuring the encoded physical observable coherent states, such as the intensity and phase, with conventional receivers. The QL is a lower bound which is fundamentally allowed in quantum mechanics. The SQL for the discrimination of the amplified BPSK coherent states is given by [44]
where is the amplified amplitude. The QL for the amplified signal in the BPSK format is expressed as
It should be mentioned that Eve will also discard the ineffective results according to Charlie’s measurement results. Here, we consider the first case, i.e., (), and Alice and Bob perform correct and effective decodings with the probability . There are two scenarios when referring to the SD attack results on Bob’s states. Firstly, considering the successful probability of the implementation of the NLA and when Eve performs the incorrect discrimination of the state sent from Bob’s station, the overall incorrect decoding probability will be
Secondly, when Eve correctly discriminates the state sent from Bob’s station, she will then capture the distributed secret information. Considering the successful probability of the implementation of the NLA, the overall probability of the information leakage will be
Now, we consider the second case, i.e., (), where Alice and Bob perform effective decodings with the probability , which also includes two scenarios. Firstly, considering the successful probability of the implementation of the NLA, and when Eve performs the incorrect discrimination of the state sent from Bob’s station, the overall incorrect decoding probability will be . Secondly, when Eve correctly discriminates the state sent from Bob’s station, she will capture the secret key. Considering the successful probability of the implementation of the NLA, the overall probability of information leakage will be .
Therefore, the key distribution channel between Bob and Eve, for the symmetric case, can also be seen as a BSC with a utilization efficiency of , and QBER is . Thus, the mutual information between Bob and Eve, under the BS-combined SD attack, is given by
For the ideally asymmetric case, i.e, the transmission efficiency between Bob and Charlie is , and the excess noise is . Moreover, we suppose that is the same as the total channel excess noises of both channels in the symmetric case, i.e., . In this case, Eve can not directly capture the secret key information by splitting the photons from the quantum channel between Bob and Charlie. The feasible way is that Eve performs SD attacks on the split photons from the quantum channel between Alice and Charlie to guess the secret key encoded in Bob’s states. In particular, Eve will use the same decoding criterion as the legitimate parities in the protocol to judge Bob’s encoding states. Eve will also discard one half of the split states with inconsistent bases. For the other half of coherent states with consistent bases, we also consider the two cases, i.e., and for the X-basis case and and for the P-basis case. Because of symmetric encoding, we just consider the X-basis case in the following equations.
We also suppose that when Eve fails in the implementation of the NLA, she will randomly choose one of the two coherent states, which will induce a error probability in decoding. Moreover, if Eve performs an incorrect discrimination of a coherent state sent from Alice or Bob’s stations after the successful implementation of the NLA, it will induce a error probability in decoding. It should be mentioned that Eve will also discard the ineffective results according to Charlie’s measurement outcomes.
Here, we consider the first case, i.e., (), and Alice and Bob perform the correct and effective decodings with the probability . Since Eve can not split photons from the channel between Bob and Charlie to directly capture the secret key information, she will use the result of the SD attack, through Alice’s channels and Charlie’s announced outcomes, to guess Bob’s encoded secret key. Since the legitimate parties will discard the ineffective results according to Charlie’s measurement outcomes, Eve will also optimize her eavesdropping to capture the secret key according to Charlie’s measurement results. There are two scenarios when referring to the SD attack results on Alice’s states. Firstly, considering the successful probability of the implementation of the NLA and when Eve performs the incorrect discrimination of the state sent from Alice’s station, the overall incorrect decoding probability will be . In this case, Eve will also get the incorrect encoded key on Bob’s state. Secondly, when Eve correctly discriminates the state sent from Alice’s station, she will then capture Alice’s encoded secret information and also correctly guess the encoded key in Bob’s side. Considering the successful probability of the implementation of the NLA, the overall probability of information leakage will be .
Now, we consider the second case, i.e., (). Alice and Bob perform effective decodings with the probability , which also includes two scenarios. Firstly, the successful probability of the implementation of the NLA when Eve performs the incorrect discrimination of the state sent from Alice’s station is considered.However, Eve’s incorrect decoding will lead to a correct judgment of Bob’s encoded key. Therefore, the overall correct decoding probability will be . Secondly, when Eve correctly discriminates the state sent from Alice’s station, she will capture the encoded secret key but will incorrectly guess the secret key encoded on Bob’s state. Considering the successful probability of the implementation of the NLA, the overall incorrect decoding probability will be .
Thus, the key distribution channel between Bob and Eve for the ideally asymmetric case can also be seen as a BSC with utilization efficiency , and QBER is . Therefore, the mutual information between Bob and Eve under the BS-combined SD attack is given by
When the asymmetric case is not ideal, i.e., for the cases where the transmission efficiencies and/or excess noise , Eve will choose the optimal strategy to capture the secret key information. In particular, she will compare the secret key information captured from the channel between Alice and Charlie by using the BS-combined SD attack with the one captured directly from the channel between Bob and Charlie, and will then choose the way to maximize the leaked secret key information. Therefore, the mutual information between Bob and Eve, in this case, will be changed to
Appendix A.3. Simulations of Secret Key Rate under BS-Combined SD Attacks
The secret key rate of the proposed protocol under the BS-combined SD attacks can be calculated as
where is the classical mutual information between Alice and Bob for both symmetric and asymmetric cases, is the leaked information to Eve for the symmetric or asymmetric cases, and is the reconciliation efficiency.
We first consider the symmetric case. We find that is optimal for Eve, which corresponds to the lowest estimation of the secret key rate for the BS-combined SD attacks. The secret key rates, as a function of the transmission distance against the BS-combined SD attacks for different channel excess noises are shown in Figure A2. It can be seen that the proposed CV-MDI-QKD protocol is sensitive to the channel’s excess noise. Specifically, there exists an optimal amplitude for the given transmission distance, which is shown in Figure A3. We also explore the dependence of the phase-matching threshold on the secret key rate. Figure A4 shows that the threshold does not obviously affect the secure transmission distance, but rather the quantity of the secret key rate. Therefore, one can appropriately choose a relatively large threshold to increase the secret key rate without decreasing the transmission distance.
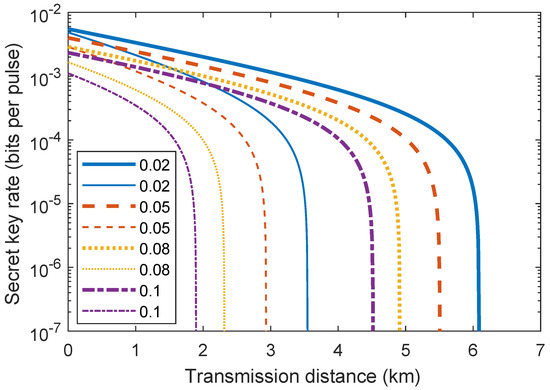
Figure A2.
(Color online). The secret key rates for different channel excess noises against the BS-combined SD attacks for the symmetric case when the SD receivers reach SQL (thick curves) and QL (thin curves), respectively. Solid, dashed, dotted, and dash-dotted curves represent the channel excess noise = 0.02, 0.05, 0.08, and 0.1, respectively. The other parameters are set as .
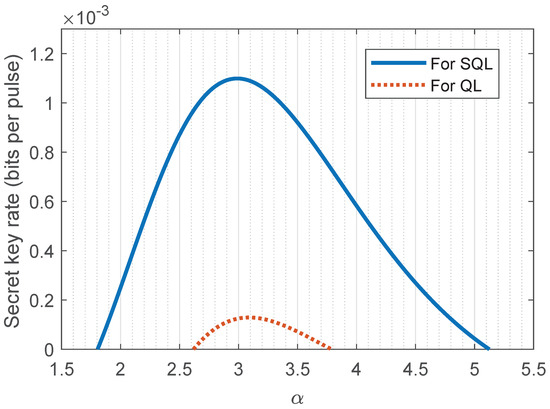
Figure A3.
(Color online). The secret key rates as a function of amplitude against the BS-combined SD attacks with transmission distance of 3 km of the standard single mode fiber for the symmetric case, when the SD receivers reach QL and SQL, respectively. The other parameters are set as .
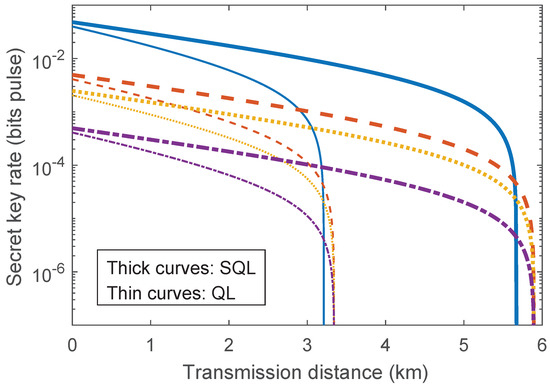
Figure A4.
(Color online). The secret key rates for different against the BS-combined SD attacks for the symmetric case when the SD receivers reach QL and SQL, respectively. The solid, dashed, dotted, and dash-dotted curves represent , , and , respectively. The other parameters are set as .
For the ideally asymmetric case, we also find that is optimal for Eve. The secret key rates, as a function of the transmission distance against the BS-combined SD attacks for different channel excess noises, in this case, are shown in Figure A5. It can be seen that the proposed CV-MDI-QKD protocol is quite insensitive to channel excess noises (the curves are overlapping with each other for different excess noises). Specifically, there exists an optimal amplitude for a given transmission distance, which is shown in Figure A6. We also explore the dependence of the phase-matching threshold on the secret key rate. Figure A7 shows that the threshold does not obviously affect the secure transmission distance, but rather the quantity of the secret key rate. Therefore, one can appropriately choose a relatively large threshold to increase the secret key rate, without decreasing the transmission distance.
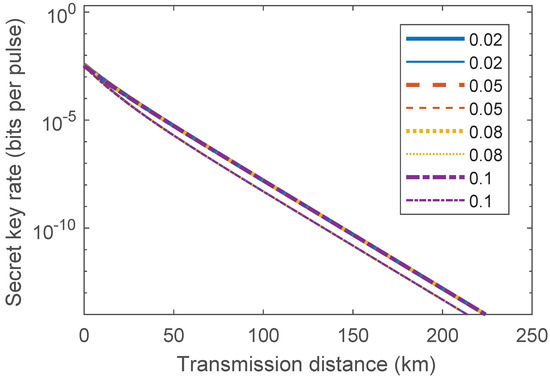
Figure A5.
(Color online). The secret key rates for different channel excess noises against the BS-combined SD attacks for the ideally asymmetric case when the SD receivers reach QL (thick curves) and SQL (thin curves), respectively. Solid, dashed, dotted, and dash-dotted curves represent the channel excess noise = 0.02, 0.05, 0.08, and 0.1, respectively. The other parameters are set as .
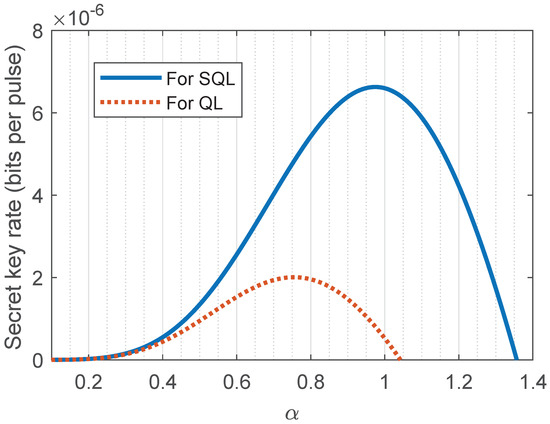
Figure A6.
(Color online). The secret key rates as a function of amplitude against the BS-combined SD attacks with transmission distance of 50 km of standard single mode fiber for the ideally asymmetric case. The black dashed and red solid curves denote the secret key rates when the SD receivers reach QL and SQL, respectively. The other parameters are set as .
We find that the legitimate parties can obtain the secure secret key for both symmetric and, ideally, asymmetric cases, if they only consider Eve performing the BS-combined SD attacks. Moreover, it shows that the BS-combined SD attacks are stronger for the symmetric case than the ideally asymmetric case.
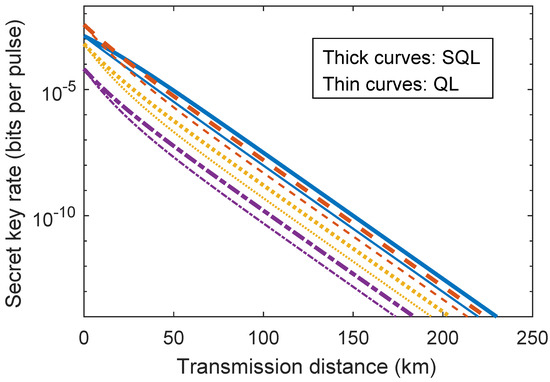
Figure A7.
(Color online). The secret key rates for different against the BS-combined SD attacks for the ideally asymmetric case when the SD receivers reach QL and SQL, respectively. The solid, dashed, dotted, and dash-dotted curves represent , , and , respectively. The other parameters are set as .
Appendix B. Eve’s BS-Combined SD Attack Strategy
The equivalent beam-splitting operation with the transmission efficiency T for Eve’s SD attack in Figure A1 are realized by a beam splitter with transmission efficiencies and a cascaded PIA with the gain of amplification . We will show below that this operation can be equivalently realized by a virtual beam splitter with the transmission efficiency to fully consider the ability of Eve’s SD attacks.
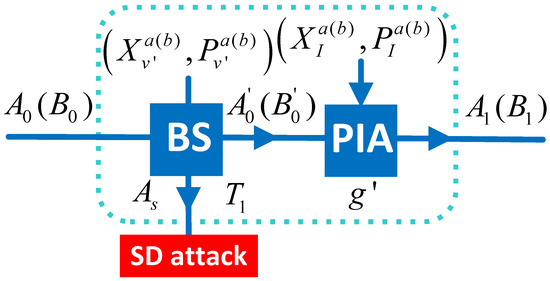
Figure A8.
(Color online). Equivalent realization of beam splitting and amplification operation for Eve’s optimized SD attack.
The quadratures of the output modes and in Figure A8 can be expressed as
where and are the quadratures of the induced vacuum states. The split quantum state for the output mode () will be a coherent state with the mean photon number . Thus, Eve can directly discriminate between the nonorthogonal coherent states and can capture the secret information with an extremely low error rate, which can be below the SQL and can reach the Helstrom bound (QL). The value of is directly related to the performance of Eve’s SD attacks.
After transmission through the amplifier, the quadratures of the output modes and are given by
where , and
are the equivalent extra input quadratures of the thermal states controlled by Eve in Figure A1a, and satisfy in the SNU. Moreover, are the quadratures of the idler mode for Eve’s PIA. When the idler mode is ideally in a vacuum state, one can get
Thus, we can get a lower bound of as . It should be mentioned that the channel excess noise is attributed to the induced excess noises by the beams splitting and amplification operations.
Appendix C. Secret Key Rate under Complete IR Attacks
For CV-MDI-QKD, the measurement procedure is performed by a third untrusted party. Thus, Eve can directly intercept the quantum signals without resending the real quantum states, but can just broadcast the measurement outcomes without introducing extra excess noises in state reproduction procedure.
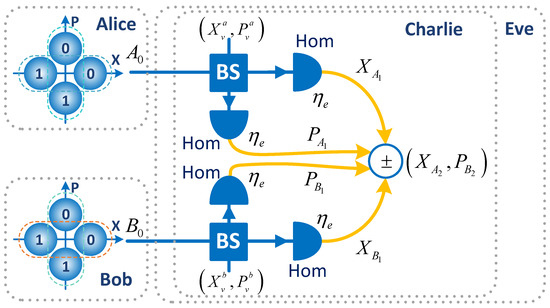
Figure A9.
(Color online). The description of the IR attack on the symmetric case of DMPM CV-MDI-QKD scheme. BS is the 50:50 beam splitter, is homodyne detection of measuring the X or P quadrature with quantum efficiency . These components are all controlled by Eve without reproduction of quantum states. Eve will guess Bob’s encoding state to capture the secret key.
For the symmetric or, ideally, asymmetric cases, the complete IR attacks are some of the optimal attacks on the proposed protocol, which can be depicted in Figure A9. While Charlie is untrusted, Eve can control Charlie’s station. After Alice and Bob send the quantum states, Eve will simultaneously perform two standard IR attacks on the two quantum channels between Alice and Charlie, and Bob and Charlie. In particular, Eve will replace the quantum channels between Alice and Charlie, and Bob and Charlie, and the two heterodyne detections, with two perfect channels and two 50:50 beam splitters connecting two perfect heterodyne detections, i.e., , respectively. The outputs of Charlie’s two heterodyne detections can be expressed as
Charlie will use the above outcomes to forge the broadcasted results as
Alice and Bob cannot judge whether these values are forged or are practical measurement results. Here, Eve can capture the secret key encoded in Bob’s quantum state by using the measurement results after Alice and Bob’s announcements of the bases, when is for the X-basis and is for the P-basis case, respectively, Alice and Bob can perform correct and effective decodings after basis reconciliation. For these two cases, one can get
and they follow the normal distribution as
Because of the symmetry of the two bases, we assume , and the correct and effective decoding probability can then be calculated as
where is the decoding threshold.
While is for the X-basis case and is for the P-basis case, respectively, Alice and Bob will perform incorrect but effective decodings. For these two cases, one can find that
and they follow the normal distribution as
where values or with the same probability. Similarly, we assume , and the incorrect but effective decoding probability can be calculated as
We will first calculate the mutual information between Alice and Bob, and the mutual information between Eve and Bob. Then, we will evaluate the induced extra excess noise under Eve’s IR attacks, which will be used for the further consideration of Eve’s optimal attack strategy. Finally, we will show the simulations of the secret key rate under the complete IR attacks.
Appendix C.1. The Mutual Information between Alice and Bob
It should be noted that whenever Eve’s judgments on Bob’s encoded states in the IR attacks are correct or incorrect, Alice and Bob will discard one half of the measurement results with inconsistent bases according to their public basis announcements. For the other half of the outcomes with consistent bases, we consider two cases, and for the X-basis case and and for the P-basis case. We also need to consider the X-basis case here, because of the symmetric encoding. After Eve’s IR attacks, the measurement outcomes in Charlie’s side can also be expressed as Equation (A25).
We consider the first case, i.e., (). The effective detections for this case will be regarded as correct decodings after Alice and Bob’s announcements of bases with the probability . For (), the effective detections for inconsistent bases will be regarded as incorrect decodings with the probability . Thus, the key distribution channel between Alice and Bob under Eve’s IR attacks can be seen as a BSC with utilization efficiency , and QBER . Therefore, the mutual information between Alice and Bob under the BS-combined SD attack for the symmetric case is given by
Appendix C.2. The Mutual Information between Eve and Bob
Now, we turn to Eve’s information from the IR attack. According to Alice and Bob’s public basis announcements, Eve will discard one half of the intercepted states with the inconsistent bases. Here, the total probability of the efficient decoding will be . Since Eve will not reproduce the quantum states intercepted from Alice and Bob, she will instead perform the discrimination operation with the measurement result from Bob to capture the encoded secret key. In this case, whether Alice and Bob send the matched states, i.e., and or not, i.e, and , the QBER can be bound by the SQL for the discrimination of the BPSK coherent states with the amplitude .
Therefore, the key distribution channel between Bob and Eve can be seen as a BSC with a utilization efficiency of , and QBER is with . Here, corresponds to the unamplified BPSK signal, which is optimal when considering the successful probability of the implementation of the NLA. Thus, the mutual information between Alice and Bob, under the SD attack, is given by
Appendix C.3. The Evaluation of Extra Excess Noise
As shown in the protocol procedure, the excess noise will be evaluated with the broadcasted measurement results and the quadratures of the prepared inconsistent-basis states and . In particular, Alice and Bob will first get the prepared values as
We suppose that the quadrature of the prepared states and the measurement results are linked through the following relation
which is a normal linear model. Moreover, is the total transmission efficiency, z follows a centered normal distribution with an unknown variance for the phase-matched outcomes, and is the average channel excess noise for the two quantum channels between Alice and Charlie, and Bob and Charlie. For the ineffective decoding cases, the centers will shift. When the measurement outcomes meet the phase-matching condition, there may be error decodings. Because of the symmetric encoding, we need to consider the X-basis case here.
For this normal linear model, the known maximum-likelihood estimator can be expressed as
Therefore, in the parameter estimation, if no IR attacks exist, z will follow a centered normal distribution with the variance . If Eve performs complete IR attacks, according to the output in Equation (A25), the induced total excess noise in the two quantum channels will change to .
Since the evaluated excess noise reflects the total one from both quantum channels, Eve will try her best to lower the total induced extra excess noise. One simple way is to replace the channels with the noiseless ones. Therefore, in a practical security analysis, considering Eve’s strongest attacks, the legitimate parties will attribute the evaluated total excess noise to Eve’s eavesdropping from the attacked quantum channels.
Appendix C.4. Simulations of Secret Key Rate under Complete IR Attacks
The secret key rate of the proposed protocol under the IR attacks can be calculated as
where is the classical mutual information between Alice and Bob, is the leaked information to Eve, and is the reconciliation efficiency.
We find that is optimal for Eve, which corresponds to the lowest estimation of the secret key rate. The secret key rate, as a function of the transmission distance and state amplitude against the IR attacks, are shown in Figure A10. It can be seen that Eve can always capture the secret key by using the complete IR attacks, whatever the transmission distance and state amplitude are for the specified threshold and homodyne detections, if ignoring the disturbance of the channel excess noise. We can see that Eve will optimize her eavesdropping strategy by first considering the use of the IR attacks. However, Eve’s IR attacks will inevitably introduce extra excess noise. Thus, she will try to find an optimal eavesdropping strategy to cover her IR attacks.
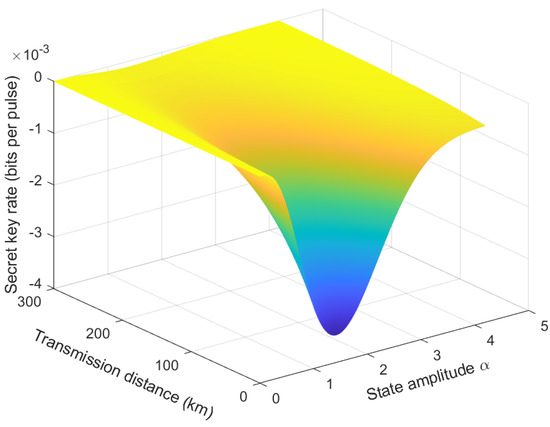
Figure A10.
(Color online). The secret key rates under the complete IR attacks. The other parameters are set as .
Appendix D. Secret Key Rate of the Phase-Matching Protocol
The secret key rate of the proposed protocol under the non-Gaussian individual attacks, i.e., the one based on the SD attacks, combined with BS and partial IR attacks, can be evaluated as
where is the classical mutual information between Alice and Bob for the symmetric or, ideally, asymmetric case, is the leaked information to Eve for the symmetric or, ideally, asymmetric case, and is the reconciliation efficiency.
We first consider eavesdropping in the symmetric case, and we suppose the transmission efficiencies and excess noises of the quantum channels between Alice and Charlie, and Bob and Charlie, are both T and , respectively. Eve will preferentially perform IR attacks on two quantum channels and the whole measurement station due to its effectiveness. However, she should use the channel excess noise to cover her eavesdropping. In particular, if the total channel excess noise is equal to, or larger than, the total evaluated excess noise induced by the complete IR attacks, Eve can replace the quantum channels with noiseless ones to cover the induced extra excess noise and capture all the secret keys by performing complete IR attacks. When , she will perform IR attacks on a fraction of the states, and will performs BS-combined SD attacks on the remaining fraction of the states. Here, both the quantum channels are replaced with noiseless ones to cover Eve’s induced extra excess noise.
Thus, the mutual information between Alice and Bob for the proposed protocol can be calculated as
where , . The mutual information between Bob and Eve will be
where , . We find is optimal for Eve.
For the ideally asymmetric case, Eve can access the channel between Alice and Charlie. She will preferentially perform IR attacks due to their effectiveness, and to capture the secret key. Moreover, she will use the channel excess noise to cover her eavesdropping. If the total channel excess noise is equal to, or larger than, the total extra excess noise induced by the complete IR attacks, Eve can capture all the secret keys by performing complete IR attacks. While , she will perform IR attacks on a fraction of the states, and will perform BS-combined SD attacks on the remaining fraction of the states. We can, similarly, obtain the mutual information between Alice and Bob as
Moreover, the leaked information to Eve will be
where . We find is also optimal for Eve.
Appendix E. Frequency Offset Recovery and Phase Drift Compensation
Before the frequency offset recovery, we should firstly perform the frequency offset estimation. The purpose is to accurately evaluate the frequency offset between Alice’s (Bob’s) laser and the local-LO laser (here, the frequency offsets for Alice and Bob are all in the proof-of-principle experiment). The annihilation operator of Alice and Bob’s pilots after transmitting through the quantum channel, which consist of some classical unmodulated signals, can be expressed as
where is the constant complex amplitude of the pilot, is the center frequency of Alice’s (Bob’s) laser, and is the phase drift of the pilot. Moreover, since LO is a classical signal, its annihilation operator can be also expressed as
where , are the center frequencies and the initial phases of LO, respectively. The pilot signals are then sent by Alice and Bob simultaneously to Charlie for interference through the BS, and are detected by homodyne detectors the same as the quantum signals. Here, and are set to get the quadratures and , respectively. The photocurrent signals of the pilots obtained from the homodyne detectors can be expressed as
where q is the electron charge, is the signal duration, and and , and represent the shot noise in detections. Since the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the pilots is relatively high in comparison to the quantum signal, classic frequency offset estimation algorithms [65] can be adopted here. We can see the output signals are good indicators for the estimation of the frequency offset. The peak points in the spectrum of the signals will show the frequency offsets and , which can be directly realized via fast Fourier transform (FFT) on the received quadrature signals and . The peaks can still appear clearly at a low SNR, which is demonstrated in [55].
In practical scenarios, the intensity of the pilot should be reasonably designed based on the channel loss, such that Charlie can distinguish them. It should be mentioned that although we estimate the absolute value , the sign is not confirmed. A method is proposed in [65] that one can try out the positive and negative values to verify the correctness. However, in the proposed CV-MDI-QKD protocol, since only one quadrature is detected for the output modes and , phase compensation cannot be performed at the receiver’s site. Therefore, the frequency offset can only be compensated at the senders’ sites. Here, the correlation coefficient can be used to determine the sign of the frequency offset.
Specifically, Alice and Bob first disclose a part of the modulated data and , which are used for parameter estimations. Then, they perform frequency offset recovery on them. Since the sign of the offset is not known, one will try four cases. Supposing that the phase drifts through the transmission are and , one can get
It should be noted that the added shot noise in the state preparation and transmission and the electronic noise of detection will not affect the evaluation of the correlation coefficient, and the channel loss and detection inefficiency will just affect the whole correlation coefficient value. Therefore, we will simplify the following processing without considering the transmission and detection inefficiency and the induced shot noise and electronic noise. Thus, the quadrature components and can be evaluated by the homodyne detection results as
One can then calculate the cross-correlation coefficient between and the real measurement results for different signs of frequency offsets. In each case, the phase angles are traversed from 0 to to calculate the corresponding value of correlation coefficient. We will find that only one frequency offset sign has the highest peak value of the correlation coefficient with specified phase angles and . Therefore, the signs of frequency offsets can be determined, and the phase angles and are just the estimated drifted phases in Alice and Bob’s data segments, respectively.
Finally, the frequency offset recovery and phase drift compensation can be implemented on Alice and Bob’s preparation values, according to the estimated frequency offset and phase drift, as
where and represent the recovered data in Alice and Bob’s sites. Based on these, Alice and Bob can perform parameter estimations and data reconciliations, just like the original protocol. We should note that the phase drifts in one frame are assumed constant. In practical scenarios, the size of one frame should be determined according to the realistic rate of phase drifts, such that the phase drift estimation algorithm can track the fluctuation of phase drifts in real time.
References
- Ralph, T.C. Continuous variable quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. A 1999, 61, 010303(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosshans, F.; Grangier, P. Continuous variable quantum cryptography using coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 057902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosshans, F.; Grangier, P. Quantum key distribution using gaussian-modulated coherent states. Nature 2003, 421, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weedbrook, C.; Pirandola, S.; García-Patrón, R.; Cerf, N.J.; Ralph, T.C.; Shapiro, J.H.; Lloyd, S. Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2012, 84, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S.; Andersen, U.L.; Banchi, L.; Berta, M.; Bunandar, D.; Colbeck, R.; Englund, D.; Gehring, T.; Lupo, C.; Ottaviani, C.; et al. Advances in quantum cryptography. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2020, 12, 1012–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S.; Mancini, S.; Lloyd, S.; Braunstein, S.L. Continuous-variable quantum cryptography using two-way quantum communication. Nat. Phys. 2008, 4, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverrier, A.; Grangier, P. Unconditional Security Proof of Long-Distance Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution with Discrete Modulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 180504, Erratum in Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 259902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, G. Quantum key distribution using basis encoding of Gaussian-modulated coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 042311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S.; Laurenza, R.; Ottaviani, C.; Banchi, L. Fundamental limits of repeaterless quantum communications. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, G.; Lütkenhaus, N.; Mor, T.; Sanders, B.C. Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, R. Continuous-variable quantum key distribution with noisy coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 77, 022310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouguet, P.; Kunz-Jacques, S.; Diamanti, E.; Leverrier, A. Analysis of imperfections in practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 032309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti, E.; Lo, H.-K.; Qi, B.; Yuan, Z. Practical challenges in quantum key distribution. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2016, 2, 16025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lo, H.; Pan, J. Secure quantum key distribution with realistic devices. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2020, 92, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.-C.; Sun, S.-H.; Jiang, M.-S.; Liang, L.-M. Local oscillator fluctuation opens a loophole for Eve in practical continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 88, 022339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouguet, P.; Kunz-Jacques, S.; Diamanti, E. Preventing calibration attacks on the local oscillator in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 062313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.-C.; Sun, S.-H.; Jiang, M.-S.; Liang, L.M. Wavelength attack on practical continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system with a heterodyne protocol. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 052309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-Z.; Weedbrook, C.; Yin, Z.-Q.; Wang, S.; Li, H.-W.; Chen, W.; Guo, G.-C.; Han, Z.-F. Quantum hacking of a continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system using a wavelength attack. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 062329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Kumar, R.; Alléaume, R. Quantum hacking: Saturation attack on practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 012325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, P.; Huang, D.; Lin, D.; Zeng, G. Practical security of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with finite sampling bandwidth effects. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 022315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Huang, P.; Huang, A.; Peng, J.; Zeng, G. Practical security of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with reduced optical attenuation. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 012313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Huang, P.; Huang, A.; Peng, J.; Zeng, G. Security analysis of practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution systems under laser seeding attack. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 27369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirandola, S.; Ottaviani, C.; Spedalieri, G.; Weedbrook, C.; Braunstein, S.L.; Lloyd, S.; Gehring, T.; Jacobsen, C.S.; Andersen, U.L. High-rate measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.-C.; Sun, S.-H.; Jiang, M.-S.; Gui, M.; Liang, L.-M. Gaussian-modulated coherent-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 042335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Xu, F.; Peng, X.; Guo, H. Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 052301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, C.; Spedalieri, G.; Braunstein, S.L.; Pirandola, S. Continuous-variable quantum cryptography with an untrusted relay: Detailed security analysis of the symmetric configuration. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 91, 022320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasiou, P.; Ottaviani, C.; Pirandola, S. Finite-size analysis of measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography with continuous variables. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 042332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Guo, H. Finite-size analysis of continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 042334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, C.; Ottaviani, C.; Papanastasiou, P.; Pirandola, S. Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution: Composable security against coherent attacks. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 052327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Guo, H. Composable security analysis of continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with squeezed states for coherent attacks. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 012314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, C.; Ottaviani, C.; Papanastasiou, P.; Pirandola, S. Parameter Estimation with Almost No Public Communication for Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 220505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.-X.; Huang, P.; Bai, D.-Y.; Wang, S.-Y.; Bao, W.-S.; Zeng, G.-H. Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with photon subtraction. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 042329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Yu, S.; Guo, H. Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with virtual photon subtraction. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 042328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.-X.; Huang, P.; Bai, D.-Y.; Wang, S.-Y.; Bao, W.-S.; Zeng, G.-H. Long-distance continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with discrete modulation. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 99, 022322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMario, M.T.; Kunz, L.; Banaszek, K.; Becerra, F.E. Optimized communication strategies with binary coherent states over phase noise channels. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2019, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S.; Ottaviani, C.; Spedalieri, G.; Weedbrook, C.; Braunstein, S.L.; Lloyd, S.; Gehring, T.; Jacobsen, C.S.; Andersen, U.L. Reply to ‘Discrete and continuous variables for measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography’. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouguet, P.; Kunz-Jacques, S.; Leverrier, A.; Grangier, P.; Diamanti, E. Experimental demonstration of long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Curty, M.; Qi, B.; Qian, L.; Lo, H.-K. Discrete and continuous variables for measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Huang, P.; Lin, D.; Zeng, G. Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution by controlling excess noise. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Weedbrook, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Continuous-variable QKD over 50 km commercial fiber. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 035006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Pirandola, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C.; Chu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, B.; Yu, S.; Guo, H. Long-Distance Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution over 202.81 km of Fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 010502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, K.N.; Papanastasiou, P.; Ottaviani, C.; Gehring, T.; Pirandola, S. Long-distance continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with postselection. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 033424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Fang, J.; Zeng, G. State-discrimination attack on discretely modulated continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 042330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujino, K.; Fukuda, D.; Fujii, G.; Inoue, S.; Fujiwara, M.; Takeoka, M.; Sasaki, M. Quantum Receiver beyond the Standard Quantum Limit of Coherent Optical Communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 250503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becerra, F.E.; Fan, J.; Baumgartner, G.; Polyakov, S.V.; Goldhar, J.; Kosloski, J.T.; Migdall, A. M-ary-state phase-shift-keying discrimination below the homodyne limit. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 84, 062324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, F.E.; Fan, J.; Baumgartner, G.; Goldhar, J.; Kosloski, J.T.; Migdall, A. Experimental demonstration of a receiver beating the standard quantum limit for multiple nonorthogonal state discrimination. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.R.; Usuga, M.A.; Wittmann, C.; Takeoka, M.; Marquardt, C.; Andersen, U.L.; Leuchs, G. Quadrature phase shift keying coherent state discrimination via a hybrid receiver. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 083009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ferreyrol, F.; Barbieri, M.; Blandino, R.; Fossier, S.; Tualle-Brouri, R.; Grangier, P. Implementation of a Nondeterministic Optical Noiseless Amplifier. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 123603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavatta, A.; Fiurasek, J.; Bellini, M. A high-fidelity noiseless amplifier for quantum light states. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, G.Y.; Ralph, T.C.; Lund, A.P.; Walk, N.; Pryde, G.J. Heralded noiseless linear amplification and distillation of entanglement. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuga, M.A.; Muller, C.R.; Wittmann, C.; Marek, P.; Filip, R.; Marquardt, C.; Leuchs, G.; Andersen, U.L. Noise-powered probabilistic concentration of phase information. Nat. Phys. 2010, 6, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewyck, J.; Grangier, P. Tight bound on the coherent-state quantum key distribution with heterodyne detection. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 76, 022332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X.-L.; Guan, J.-Y.; Yu, Z.-W.; Xu, H.; Lin, J.; et al. Sending-or-Not-Sending with Independent Lasers: Secure Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution over 509 km. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 070501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.-T.; Zeng, P.; Liu, H.; Zou, M.; Wu, W.; Tang, Y.-L.; Sheng, Y.-J.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; et al. Implementation of quantum key distribution surpassing the linear rate-transmittance bound. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, P.; Ma, H.; Wang, S.; Zeng, G. Carrier synchronization for continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with a real local oscillator. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 104, 022606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zeng, P.; Zhou, H. Phase-matching quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 031043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosshans, F.; Grangier, P. Continuous-variable quantum cryptography is secure against non-Gaussian attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 047905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewyck, J.; Debuisschert, T.; García-Patrón, R.; Tualle-Brouri, R.; Cerf, N.J.; Grangier, P. Experimental Implementation of Non-Gaussian Attacks on a Continuous-Variable Quantum-Key-Distribution System. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 030503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, S.; Grangier, P.; Diamanti, E.; Leverrier, A. Asymptotic security of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a discrete modulation. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 021059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasiou, P.; Pirandola, S. Continuous-variable quantum cryptography with discrete alphabets: Composable security under collective Gaussian attacks. Phys. Rev. Res. 2021, 3, 013047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabuncu, M.; Filip, R.; Leuchs, G.; Andersen, U.L. Environment-assisted quantum-information correction for continuous variables. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 012325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabuncu, M.; Mišta, L., Jr.; Fiurášek, J.; Filip, R.; Leuchs, G.; Andersen, U.L. Nonunity gain minimal-disturbance measurement. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 76, 032309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, P.; Wang, T.; Zeng, G. Environment-assisted quantum-information correction for continuous variables. New J. Phys. 2018, 20, 083037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, M.; Madsen, L.S.; Sabuncu, M.; Filip, R.; Andersen, U.L. Experimental demonstration of squeezed-state quantum averaging. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 82, 021801(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yu, S.; Shen, J.; Gu, W.; Ji, Y. Frequency Estimation for Optical Coherent MPSK System without Removing Modulated Data Phase. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2010, 22, 691–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).