Vertical Shear Processes in River Plumes: Instabilities and Turbulent Mixing
Abstract
1. Introduction
- What is the evolution of a sheared river plume base under different flow parameters?
- Which type of vertical shear instabilities can affect the plume base and under which flow conditions?
- What are the effects of the vertical shear instabilities on vertical turbulent mixing?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Configuration
2.2. Model Experiments
2.3. Diagnostics for Stratified Sheared Flows Structure and Dynamics
2.4. Diagnostics for Instabilities
2.5. Diagnostics for Turbulent Mixing
3. Results
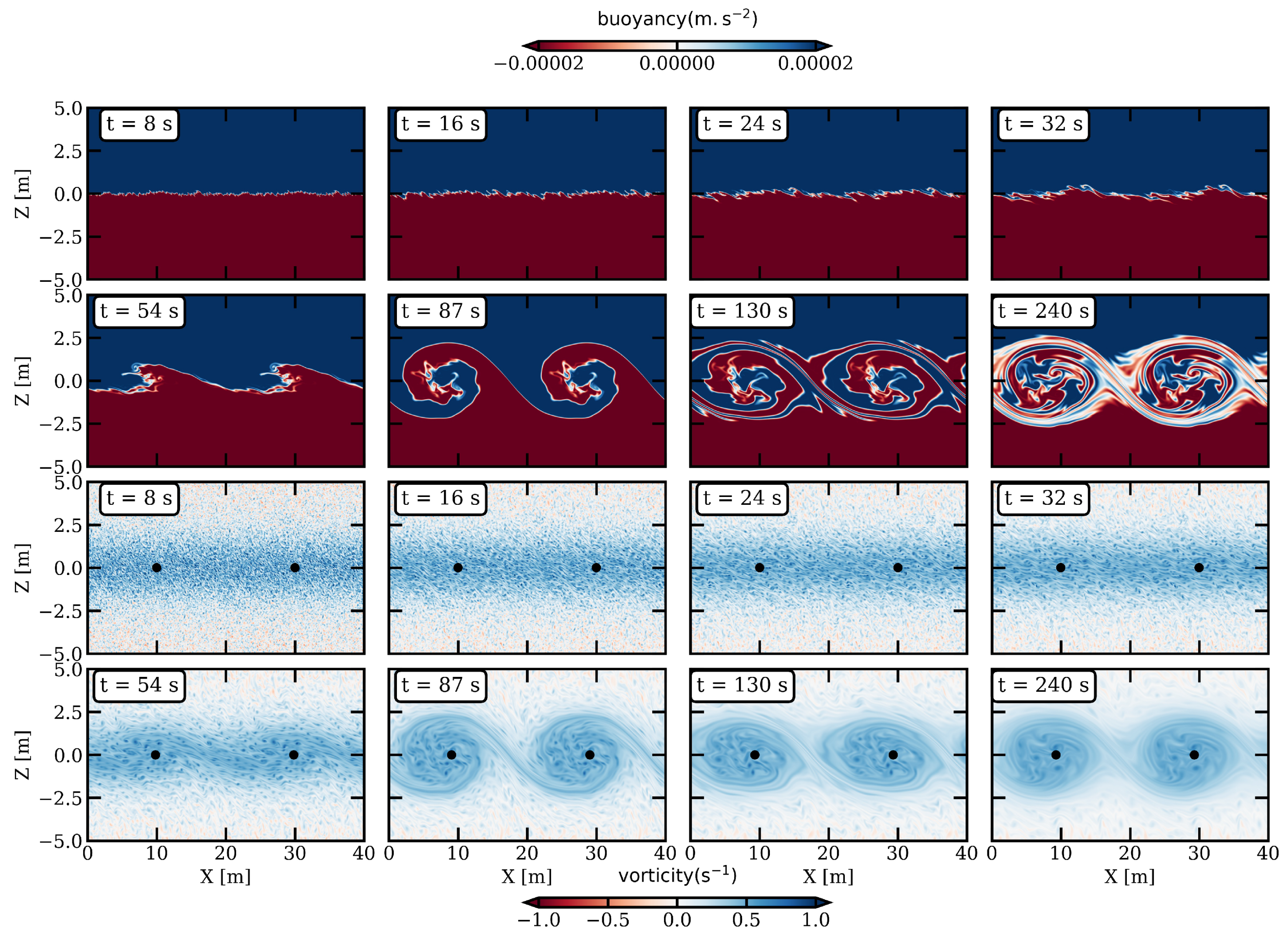
3.1. Structure and Dynamics of Stratified Sheared Flows
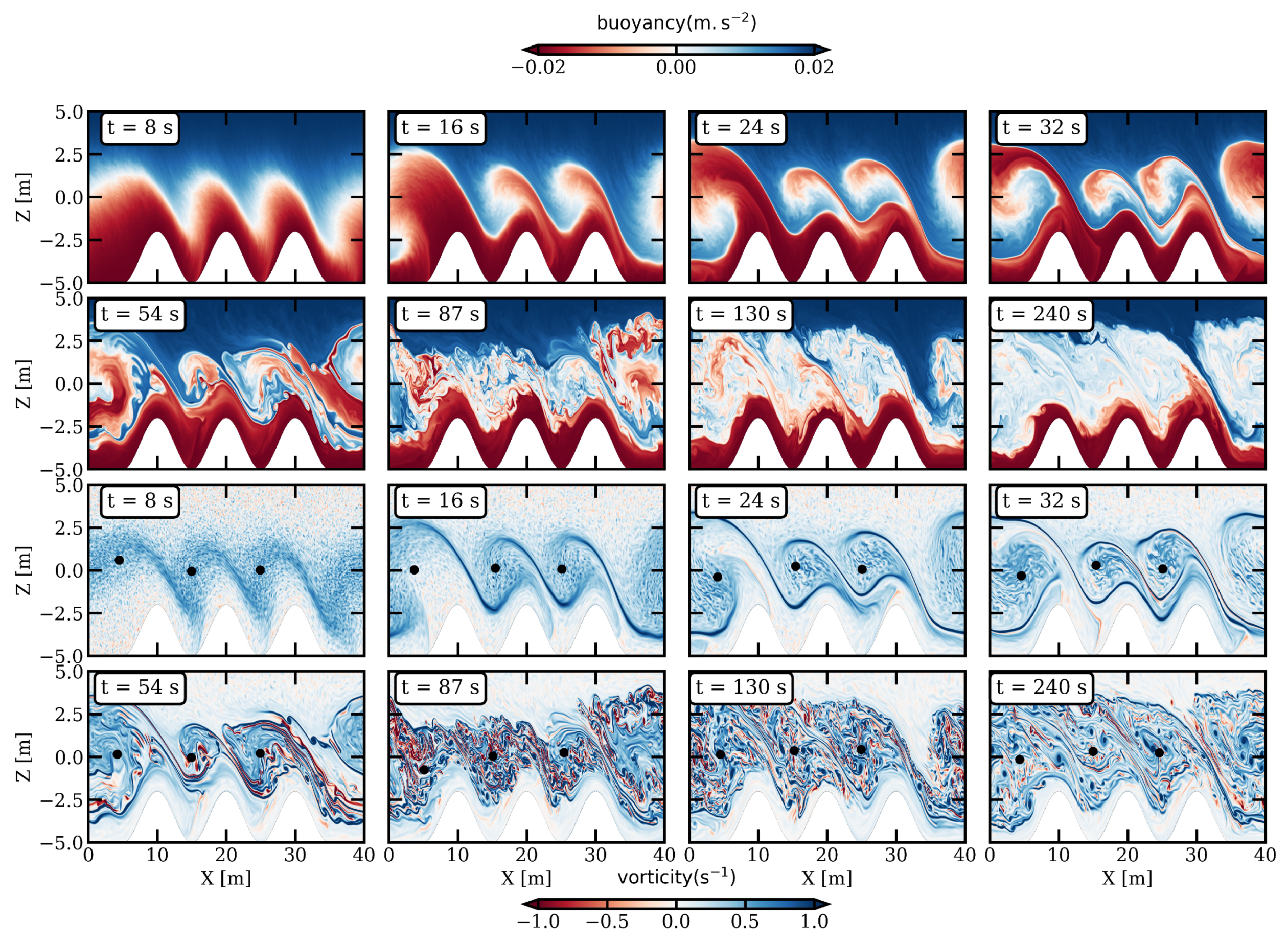
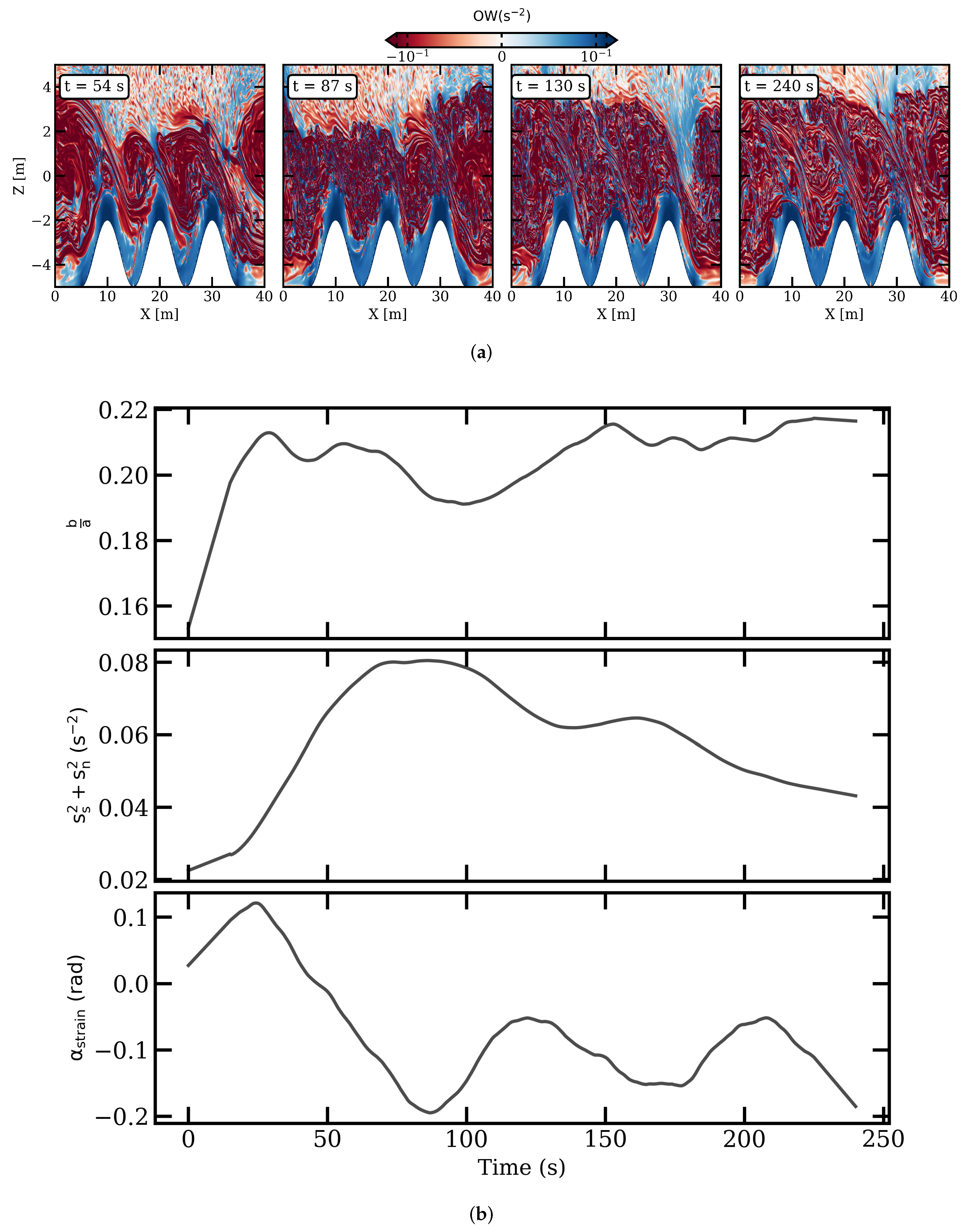
3.1.1. Reference Configuration
3.1.2. Sensitivity to the Vertical Shear (Exp2)
3.1.3. Sensitivity to the Thickness of the Interface (Exp3)
3.1.4. Sensitivity to Topographic Ridges (Exp4)
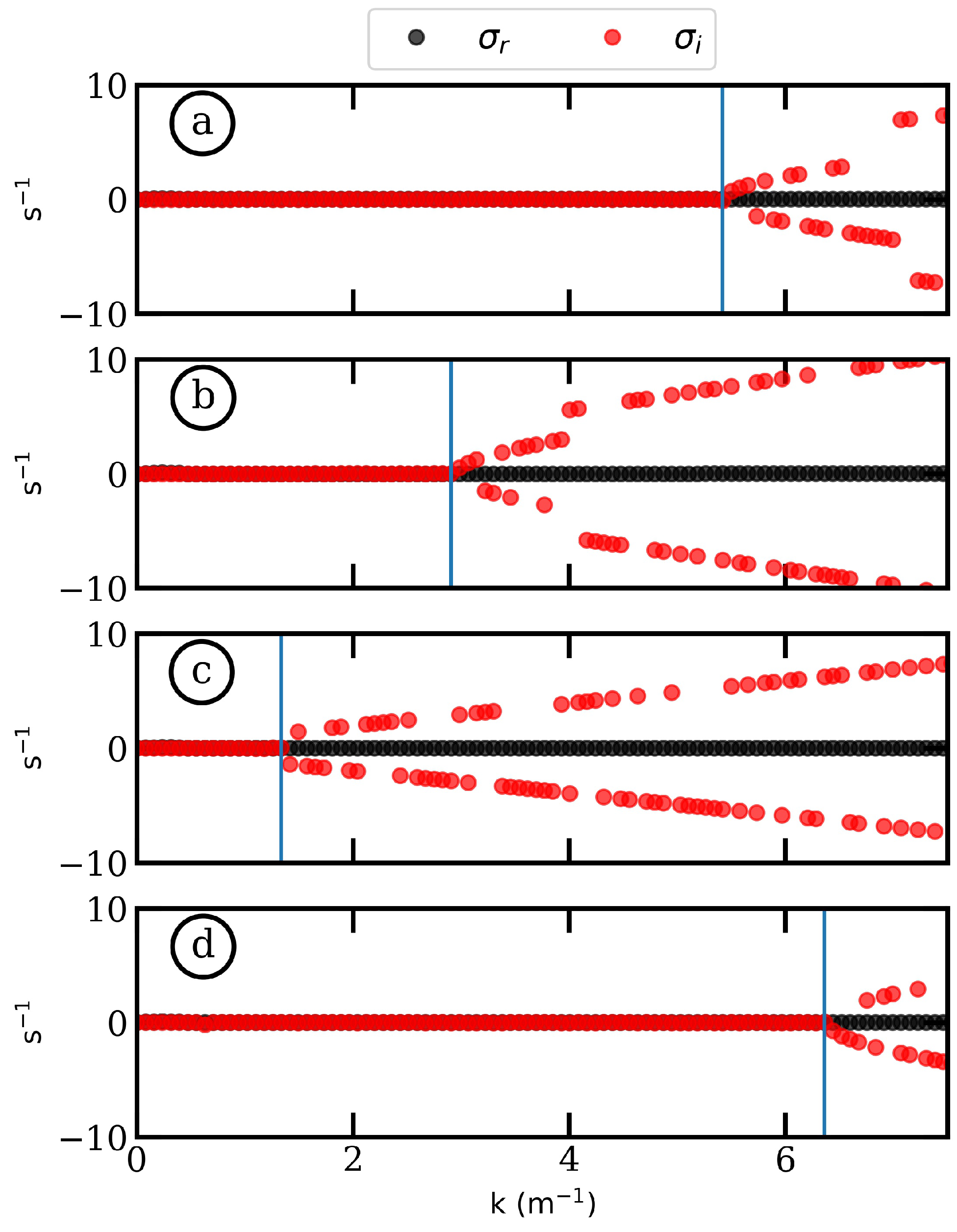
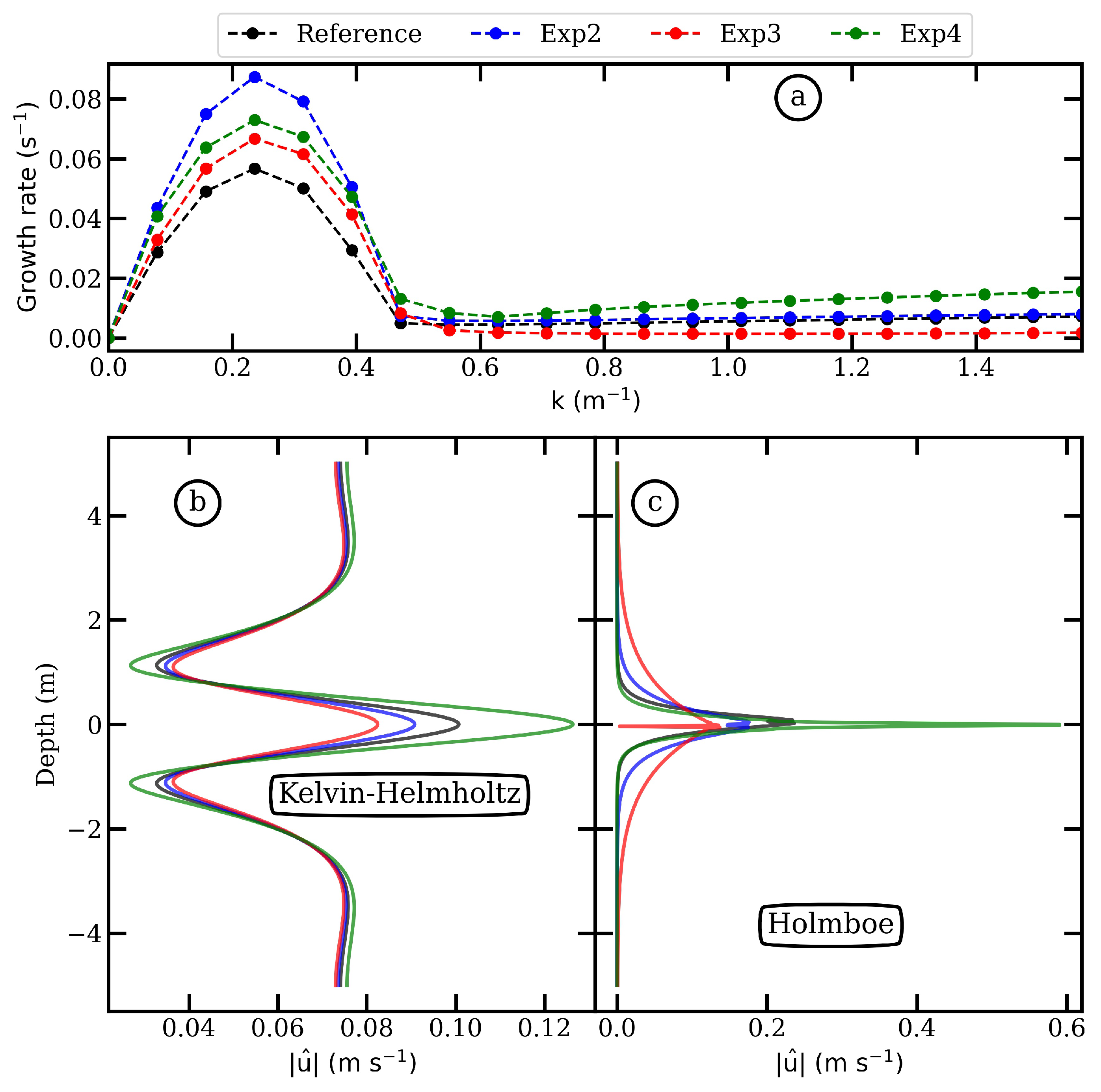
3.2. Modal Analysis and Instability Growth
3.2.1. Reference Configuration
3.2.2. Sensitivity to the Vertical Shear (Exp2)
3.2.3. Sensitivity to the Thickness of the Interface (Exp3)
3.2.4. Sensitivity to Topographic Ridges (Exp4)
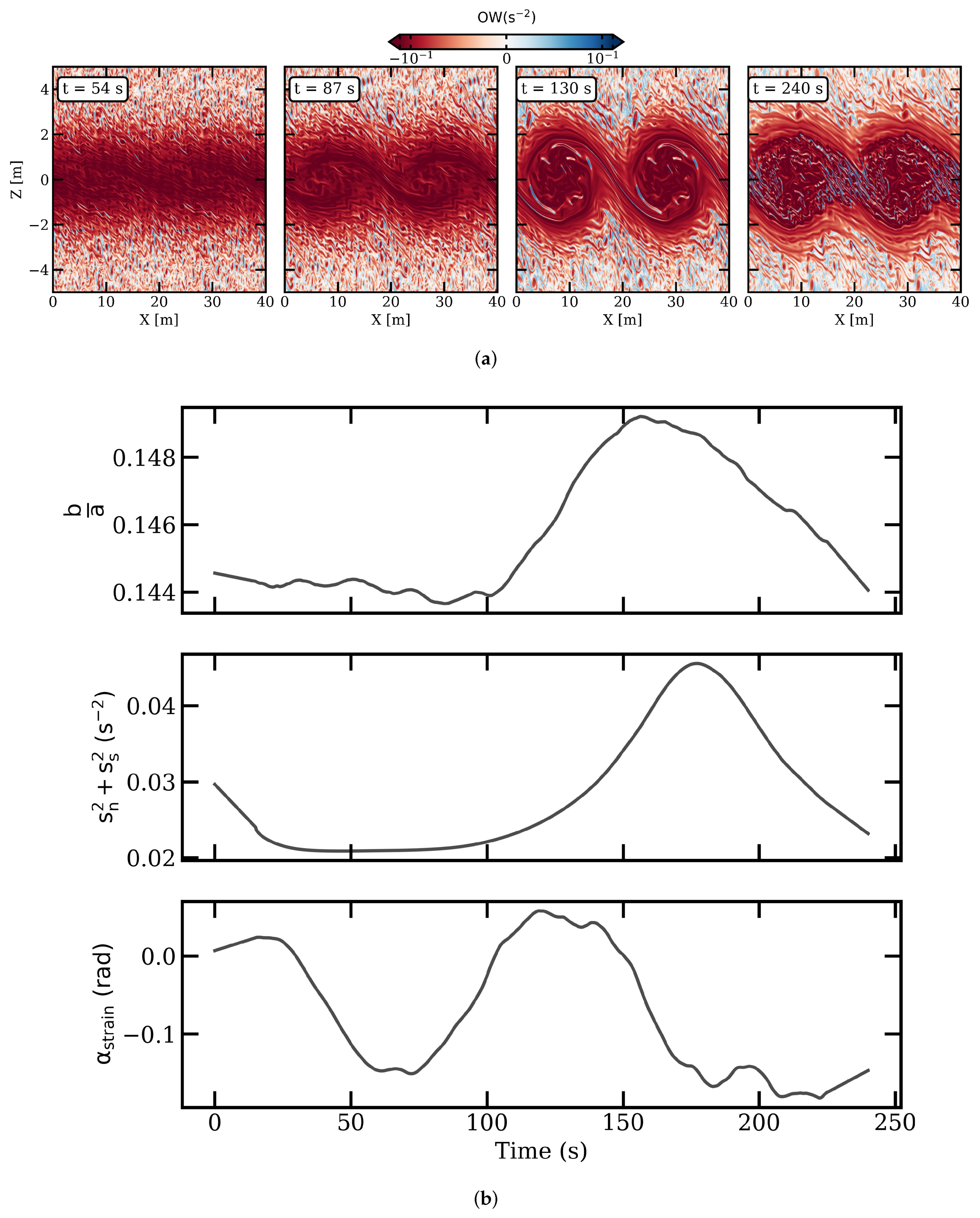
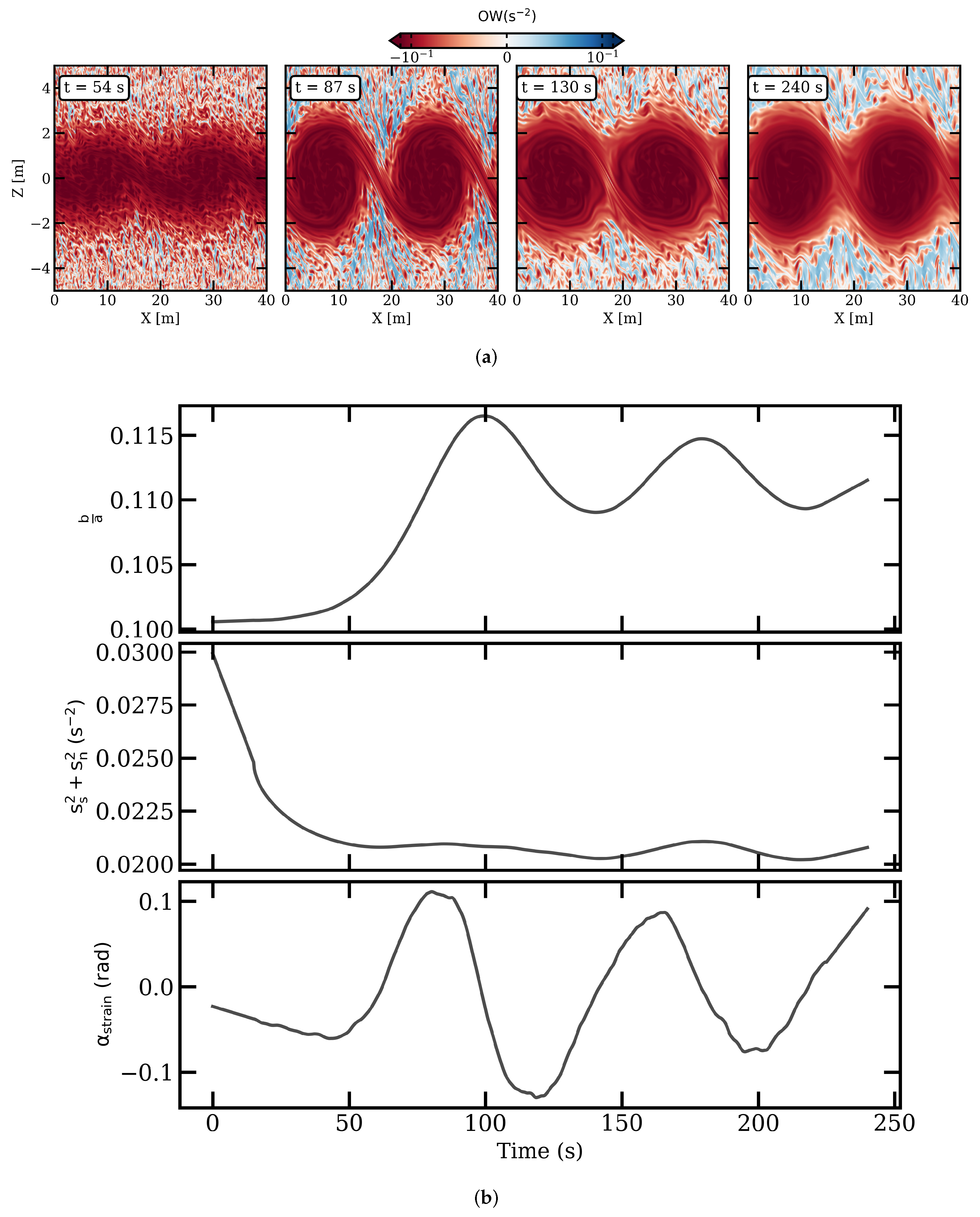
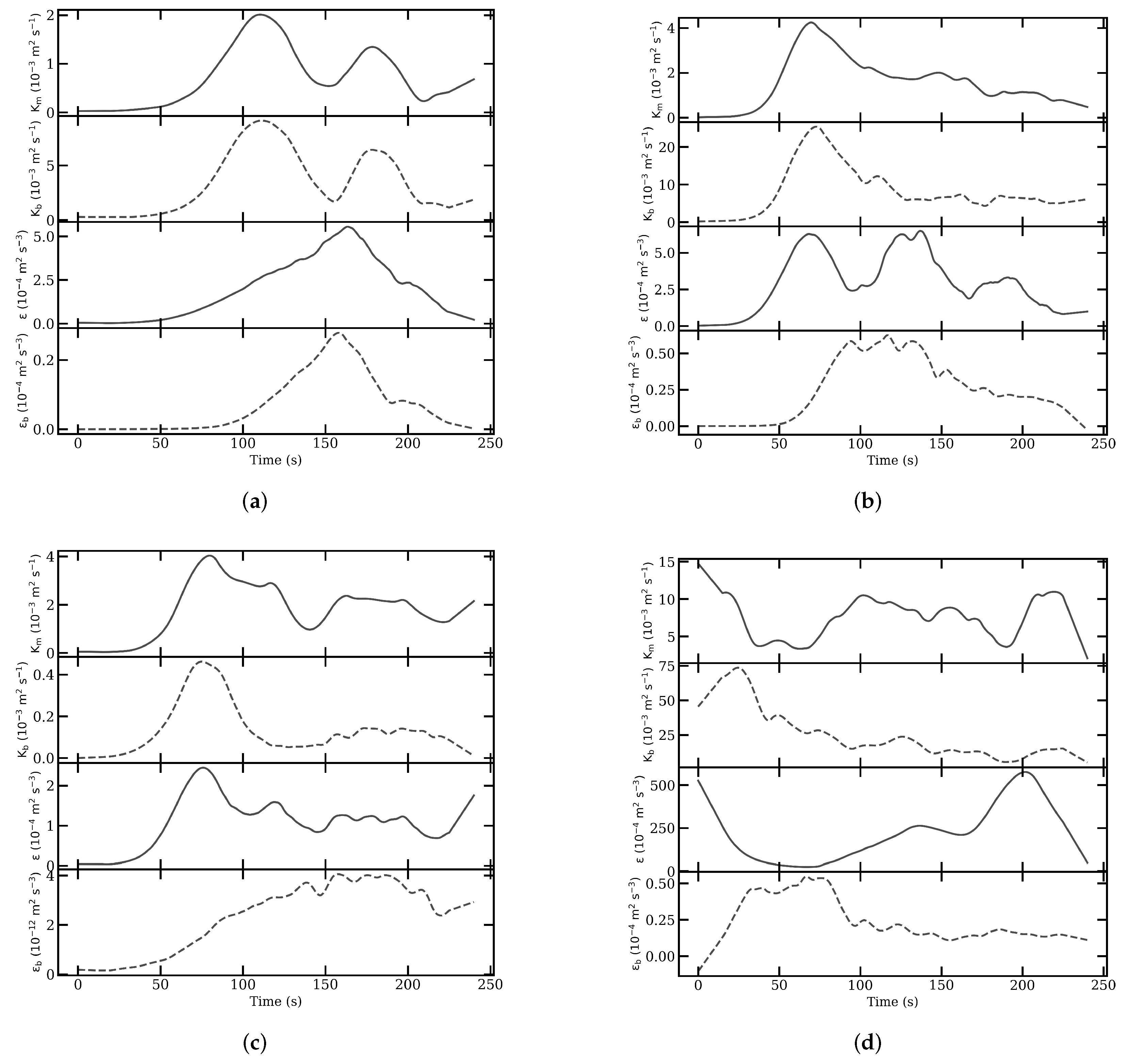
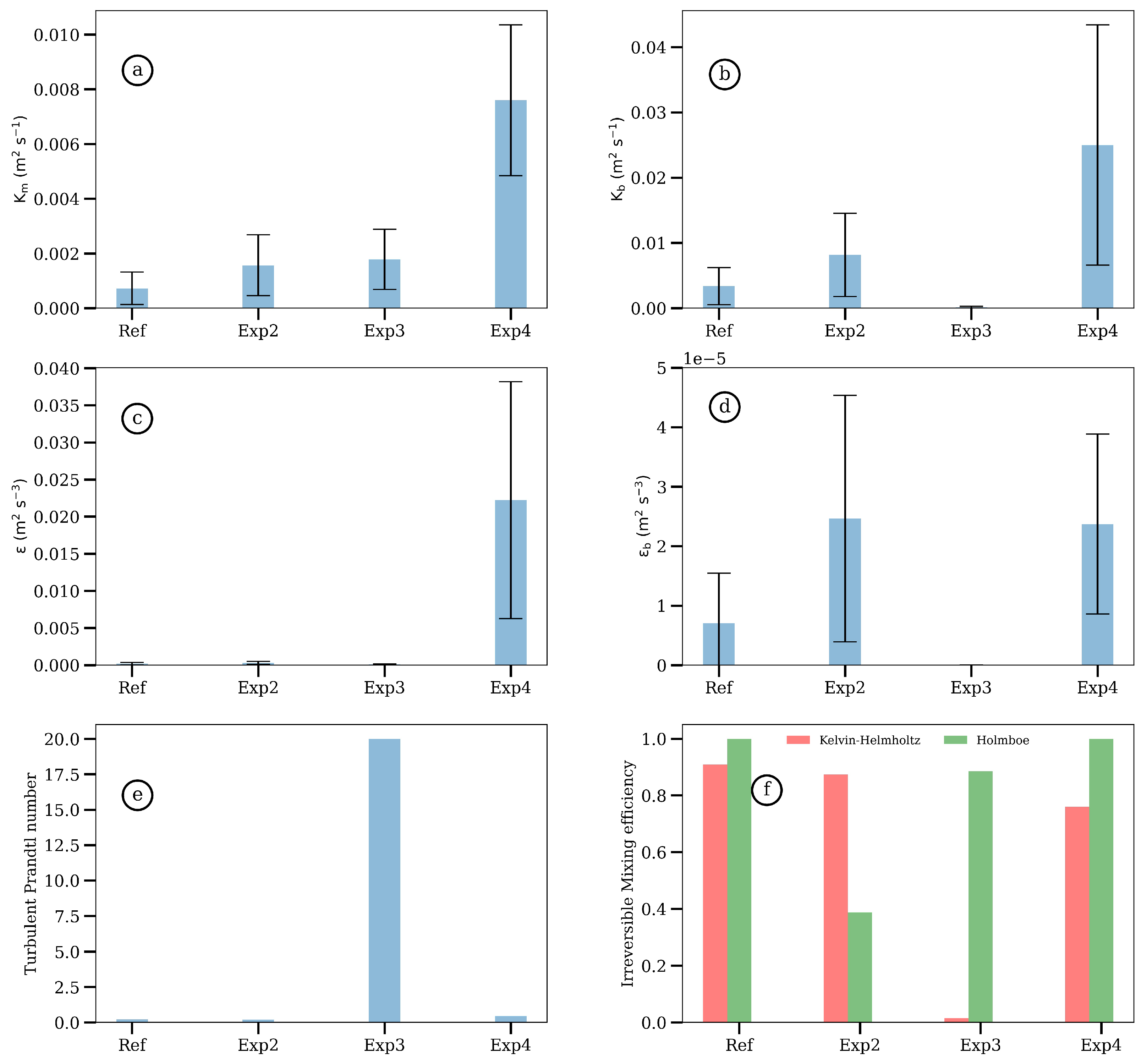
3.3. Turbulent Mixing
3.3.1. Reference Configuration
3.3.2. Sensitivity to the Vertical Shear (Exp2)
3.3.3. Sensitivity to the Thickness of the Interface (Exp3)
3.3.4. Sensitivity to Topographic Ridges (Exp4)
4. Discussion
4.1. The Structure and Dynamics of Stratified Sheared Flows
4.2. Development and Role of KH and Holmboe Instabilities
4.3. Turbulent Mixing: Intensity and Efficiency
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Linear Stability Analysis
Appendix B. Identification of the Holmboe Mode: The Bifurcation Theory
References
- Helmholtz, P. XLIII. On discontinuous movements of fluids. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1868, 36, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, W. Hydrokinetic solutions and observations. Philos. Mag. 1871, 42, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Effect of Variation in Density on the Stability of Superposed Streams of Fluid. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Character 1931, 132, 499–523. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, S.; Taylor, G.I. On the stability of superposed streams of Fluids of different densities. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Character 1931, 132, 524–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamere, P.A.; Bagenal, F. Solar wind interaction with Jupiter’s magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, A10201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamere, P.A.; Bagenal, F. Magnetotail structure of the giant magnetospheres: Implications of the viscous interaction with the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 7045–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Delamere, P.A.; Ma, X.; Burkholder, B.; Wiltberger, M.; Lyon, J.G.; Merkin, V.G.; Sorathia, K.A. Asymmetric Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability at Jupiter’s Magnetopause Boundary: Implications for Corotation-Dominated Systems. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foullon, C.; Verwichte, E.; Nakariakov, V.; Nykyri, K.; Farrugia, C. Magnetic Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability at the Sun. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 729, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, K.A. Structure of the atmosphere in the vicinity of large-amplitude Kelvin-Helmholtz billows. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1971, 97, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Mahajan, K.K.; Choudhary, R.K.; Nagpal, O.P. Detection of Kelvin-Helmholtz instability with the Indian mesosphere-stratosphere-troposphere radar: A case study. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 3937–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, J.T. Experiments on Kelvin-Helmholtz billows influenced by boundaries. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 1998, 89, 205–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yamazaki, H. Observations of a Kelvin-Helmholtz Billow in the Ocean. J. Oceanogr. 2001, 57, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, V.M.; Zhu, D.Z.; Loewen, M.R. Supercritical Exchange Flow Down a Sill. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 130, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, L.K.; Nomura, K.K. The physics of vortex merger and the effects of ambient stable stratification. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 592, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dixit, H.N.; Govindarajan, R. Effect of density stratification on vortex merger. Phys. Fluids 2013, 25, 016601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.L.; Fritts, D.C.; Andreassen, Ø.; Lie, I. Three-dimensional evolution of Kelvin-Helmholtz billows in stratified compressible flow. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 2287–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, S.; Chomaz, J.M.; Loiseleux, T. Spatial Holmboe instability. Phys. Fluids 2002, 14, 2585–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, A. On Holmboe’s instability for smooth shear and density profiles. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 084103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagvozkin, T.; Vorobev, A.; Lyubimova, T. Kelvin-Helmholtz and Holmboe instabilities of a diffusive interface between miscible phases. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 023103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, S.A. On the Kelvin–Helmholtz route to turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 708, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedford, E.W.; Carpenter, J.R.; Pawlowicz, R.; Pieters, R.; Lawrence, G.A. Observation and analysis of shear instability in the Fraser River estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2009, 114, C11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Tong, C.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, C.; Gao, X. Kelvin-Helmholtz Billows Induced by Shear Instability along the North Passage of the Yangtze River Estuary, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaka, Y.; Isobe, A. Tidally Induced Instability Processes Suppressing River Plume Spread in a Nonrotating and Nonhydrostatic Regime. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 3545–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, W.; Moum, J. Ocean Mixing by Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability. Oceanography 2012, 25, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Haren, H.; Gostiaux, L. A deep-ocean Kelvin-Helmholtz billow train. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L03605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner-Devine, A.R.; Hetland, R.D.; MacDonald, D.G. Mixing and Transport in Coastal River Plumes. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2015, 47, 569–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granskog, M.; Ehn, J.; Niemelä, M. Characteristics and potential impacts of under-ice river plumes in the seasonally ice-covered Bothnian Bay (Baltic Sea). J. Mar. Syst. 2005, 53, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetland, R.D. Relating River Plume Structure to Vertical Mixing. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 35, 1667–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayouche, A.; Carton, X.; Charria, G.; Theettens, S.; Ayoub, N. Instabilities and vertical mixing in river plumes: Application to the Bay of Biscay. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 2020, 114, 650–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dritschel, D. On the persistence of non-axisymmetric vortices in inviscid two-dimensional flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1998, 371, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Dizès, S.; Verga, A. Viscous interactions of two co-rotating vortices before merging. J. Fluid Mech. 2002, 467, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, A. Horizontal dispersion of floatable particles in the vicinity of velocity singularities such as convergences. Deep Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1970, 17, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J. The dynamics of enstrophy transfer in two-dimensional hydrodynamics. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1991, 48, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Yoshida, J. A note on estimating eddy diffusivity for oceanic double-diffusive convection. J. Oceanogr. 2019, 75, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Nikurashin, M.; Sasaki, H.; Sun, H.; Tian, J. Dissipation of mesoscale eddies and its contribution to mixing in the northern South China Sea. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, A.K.; Smyth, W.D. Stratified shear instability in a field of pre-existing turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 862, 639–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, T.R. Estimates of the Local Rate of Vertical Diffusion from Dissipation Measurements. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1980, 10, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Vu, B.; Stegner, A.; Arsouze, T. Angular Momentum Eddy Detection and Tracking Algorithm (AMEDA) and Its Application to Coastal Eddy Formation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2018, 35, 739–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, A.; Stegner, A.; Tuel, A.; LeVu, B.; Dumas, F.; Speich, S. Cyclostrophic Corrections of AVISO/DUACS Surface Velocities and Its Application to Mesoscale Eddies in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124, 8913–8932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Marez, C.; Carton, X.; L’Hégaret, P.; Meunier, T.; Stegner, A.; Le Vu, B.; Morvan, M. Oceanic vortex mergers are not isolated but influenced by the β- effect and surrounding eddies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayouche, A.; De Marez, C.; Morvan, M.; L’Hegaret, P.; Carton, X.; Le Vu, B.; Stegner, A. Structure and Dynamics of the Ras al Hadd Oceanic Dipole in the Arabian Sea. Oceans 2021, 2, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.B.; Rossi, L.F. The evolution of Kirchhoff elliptic vortices. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20, 054103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Rahmani, M.; Lawrence, G.A. Evolution of a barotropic shear layer into elliptical vortices. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 87, 013020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontane, J.; Joly, L. The stability of the variable-density Kelvin–Helmholtz billow. J. Fluid Mech. 2008, 612, 237–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayouche, A.; Charria, G.; Carton, X.; Ayoub, N.; Theetten, S. Non-Linear Processes in the Gironde River Plume (North-East Atlantic): Instabilities and Mixing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, W.D.; Peltier, W.R. Instability and transition in finite-amplitude Kelvin–Helmholtz and Holmboe waves. J. Fluid Mech. 1991, 228, 387–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.P.; Caulfield, C.P.; Kerswell, R.R. The viscous Holmboe instability for smooth shear and density profiles. J. Fluid Mech. 2020, 896, A14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, J.R.; Balmforth, N.J.; Lawrence, G.A. Identifying unstable modes in stratified shear layers. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 054104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.G. Mixing Processes and Hydraulic Control in a Highly Stratified Estuary; Technical Report; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, D.G.; Geyer, W.R. Turbulent energy production and entrainment at a highly stratified estuarine front. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2004, 109, C05004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilcher, L.F.; Nash, J.D.; Moum, J.N. The role of turbulence stress divergence in decelerating a river plume. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117, C05032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, W.D.; Carpenter, J.R.; Lawrence, G.A. Mixing in Symmetric Holmboe Waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2007, 37, 1566–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, W.D.; Winters, K.B. Turbulence and Mixing in Holmboe Waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2003, 33, 694–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehipour, H.; Caulfield, C.P.; Peltier, W.R. Turbulent mixing due to the Holmboe wave instability at high Reynolds number. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 803, 591–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, W.D.; Nash, J.D.; Moum, J.N. Differential Diffusion in Breaking Kelvin–Helmholtz Billows. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 35, 1004–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochar, G.T.; Jain, R.K. Note on Howard’s semicircle theorem. J. Fluid Mech. 1979, 91, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavasi, E.; Firoozabadi, B.; Afshin, H. Linear analysis of the stability of particle-laden stratified shear layers. Can. J. Phys. 2014, 92, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Experiments | Initial Shear (s) | Initial Stratification (s) | Minimum Richardson Number | Interface | Bottom | Boundaries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.04 | plane () | flat | Periodic in x + Rigid in z |
| Exp 2 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.02 | plane () | flat | Periodic in x + Rigid in z |
| Exp 3 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.04 | plane () | flat | Periodic in x + Rigid in z |
| Exp 4 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.04 | plane () | sloping | Periodic in x + Rigid in z |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayouche, A.; Carton, X.; Charria, G. Vertical Shear Processes in River Plumes: Instabilities and Turbulent Mixing. Symmetry 2022, 14, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020217
Ayouche A, Carton X, Charria G. Vertical Shear Processes in River Plumes: Instabilities and Turbulent Mixing. Symmetry. 2022; 14(2):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020217
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyouche, Adam, Xavier Carton, and Guillaume Charria. 2022. "Vertical Shear Processes in River Plumes: Instabilities and Turbulent Mixing" Symmetry 14, no. 2: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020217
APA StyleAyouche, A., Carton, X., & Charria, G. (2022). Vertical Shear Processes in River Plumes: Instabilities and Turbulent Mixing. Symmetry, 14(2), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020217








