Abstract
Chaotic maps have simple structures but can display complex behavior. In this paper, we apply discrete memristance and a nonlinear term in order to design new memristive maps. A general model for constructing memristive maps has been presented, in which a memristor is connected in serial with a nonlinear term. By using this general model, different memristive maps have been built. Such memristive maps process special fixed points (infinite and without fixed point). A typical memristive map has been studied as an example via fixed points, bifurcation diagram, symmetry, and coexisting iterative plots.
1. Introduction
Discrete maps, memristor, and hidden attractor have attracted significant attention in recent years [1,2,3,4]. Discrete maps are noticeable examples of simple structures, which can exhibit complex dynamics [5,6]. Both chaos and hyperchaos were observed in discrete maps [7,8,9]. In the literature, numerous chaotic maps were reported range from common discrete maps to recent fractional maps. Discrete maps are suitable for developing various applications such as audio encryption, robot motion, secure systems, and so on [10,11,12,13,14,15]. Interestingly, Lu et al. develop a symmetric algorithm using trigonometric map for image encryption [16]. Application of hyperchaotic maps in generative adversarial nets is reported in [17].
Memristor is a basic circuit element presenting the relationship between charge and magnetic flux. With the development of memristor models and memristive devices, various structures of memristive systems have been established, and their dynamics have been explored [18,19,20]. Memristive neural networks propose novel research directions about artificial neural networks [21]. Xu et al. introduced a jerk system using a generalized memristor [22]. In the work [23], the authors investigated a memristor circuit. Asymmetric bifurcations were discovered in an asymmetric memristive jerk circuit [24]. Asymmetric coexisting bifurcations, multistability, and similar features in asymmetric circuits are the attractive features. Recently, memristors have been used to develop memristive maps [25,26].
Studies on chaotic attractors in nonlinear systems have been published in several papers [27,28,29,30,31,32]. It is noted that chaotic attractors found in a conventional system belong to a common type of self-excited attractor [33]. In order to obtain chaos, the initial states are located closely to the unstable equilibrium points. However, there are hidden attractors characterized by the existence of stable equilibrium or the absence of equilibrium [34,35,36,37]. It is challenge to find and analyze this kind of attractor [38,39,40].
The combination of three research topics (discrete map, memristor, and hidden attractor), as illustrated in Figure 1, opens up new research directions. For example, memristor-based systems with hidden attractors have been discovered when combining two research topics (memristor and hidden attractor). This work focuses on the overlap of three such research topics by introducing an approach to design discrete maps with a memristor. It is worth noting that the designed discrete maps belong to systems with a hidden attractor. We believe that memristor-based discrete maps have special features such as chaos, multistability, an infinite number of fixed points, etc. There are a few published works on memristor-based maps [25,26].
Figure 1.
Relationships of three research topics. The overlapped area of three circles shows the memristive maps with hidden attractor.
The remainder of the work is organized as follows. A general model for designing memristive maps is proposed and analyzed in Section 2. In Section 3, a typically designed map (the MM map) is investigated via fixed points, bifurcation diagram, symmetry, iterative plots, and implementation. Finally, the conclusions are presented in Section 4.
2. General Model
Motivated by the flexibility, practicability, and attention of discrete maps, memristors, and hidden attractors, we would like to introduce an approach to building new memristive maps. The general map is designed as illustrated in Figure 2. The two main components needed to construct the map are a memristor and a nonlinear term , which are connected serially. The amplifiers b and a indicate the effect of the memristor and the nonlinear term on the structure, respectively. In addition, there is the presence of a controller c used to control the fixed points.
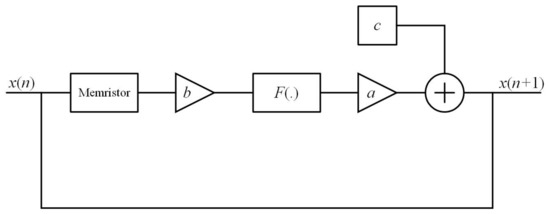
Figure 2.
Design of map with memristor and nonlinear function .
By denoting the discrete memristance as , the general model is characterized by
with parameters a, b, c. The nonlinear term satisfying . Equation (1) presents the general model of memristor-based discrete maps. It is used to design discrete maps with a memristor.
If is the fixed point of model (1), we have
Therefore, we get
The number of fixed points in the model (1) depends on c. There are two attractive cases. In the first case, there is no fixed point for . In the second case, there are infinite fixed points given by .
Based on the proposed general model, different maps can be constructed with appropriated discrete memristance and nonlinear terms. For instance, when applying the following discrete memristance , and nonlinear term
we obtain the MM memristive map
Chaotic dynamics of the MM map are illustrated in Figure 3a for , , , and .
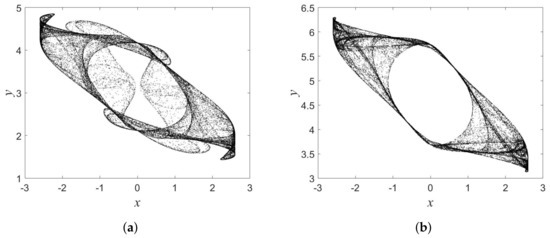
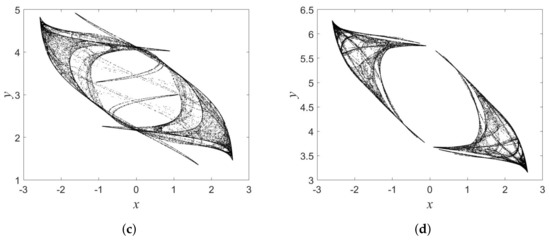
Figure 3.
Iterative plots obtained from: (a) MM map, (b) MM map, (c) MM map, and (d) MM map.
Three other new memristive maps are found and listed in Table 1. It is noted that Equation (1) is classified and presented in Table 1 based on the selected discrete memristance and nonlinear term. These memristive maps displayed chaos, as shown in Figure 3.

Table 1.
Constructed maps using memristor and nonlinear term.
3. MM Map
We focus on the MM map described by Equation (5) to illustrate noticeable features of such newly constructed maps. The fixed point of the MM map must satisfy the condition
In the first case, there is no fixed point for . In the second case, there are infinite fixed points given by . The Jacobian matrix of the map is
Therefore, at , we obtain
As a result, we get its characteristic equation
From the characteristic equation, the fixed point is stable for
otherwise is unstable.
3.1. Case 1 When
For , there is no fixed point in the map. We study the map with , and varying a. Both the bifurcation plot in Figure 4a and Lyapunov exponents in Figure 4b exhibit dynamical behavior in the range . Positive Lyapunov exponents appear when increasing a and indicate chaos in the map.
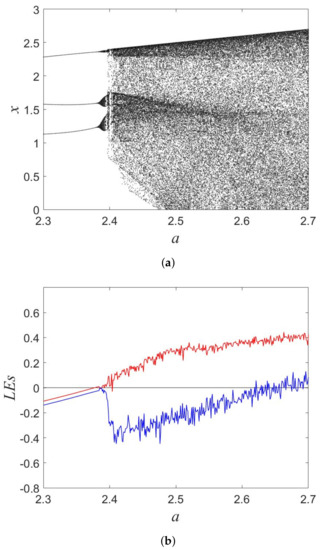
Figure 4.
(a) Bifurcation diagram, (b) Lyapunov exponents of MM map when changing a from 2.3 to 2.7. The red and blue colors present the first and second Lyapunov exponents, respectively.
It is noted that the map is symmetrical via the transformation
Figure 5 show seven iterative plots, which coexist with , , for different values of .
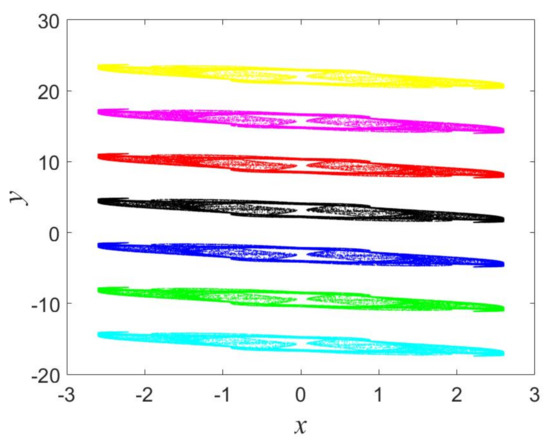
Figure 5.
Coexisting iterative plots are observed when changing : (yellow), (magenta), (red), (black), (blue), (green), (cyan).
3.2. Case 2 When
When , the map is given by
The symmetry of the MM map is confirmed by
The coexistence of two iterative plots is shown in Figure 6 for , with two values (black color) and (red color).
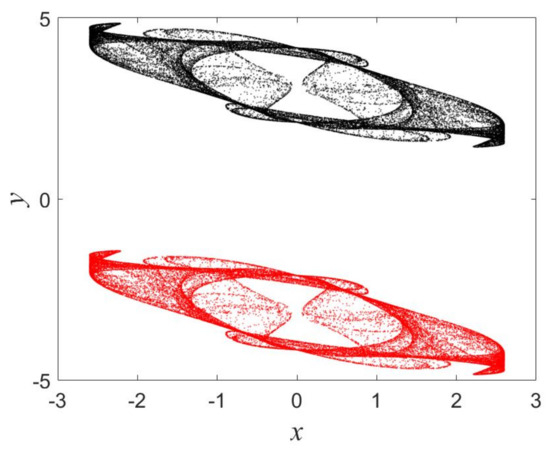
Figure 6.
The presence of two iterative plots for (black) and (red).
Similar to Case 1, the MM map can generate various iterative plots when keeping , and changing (see Figure 7).
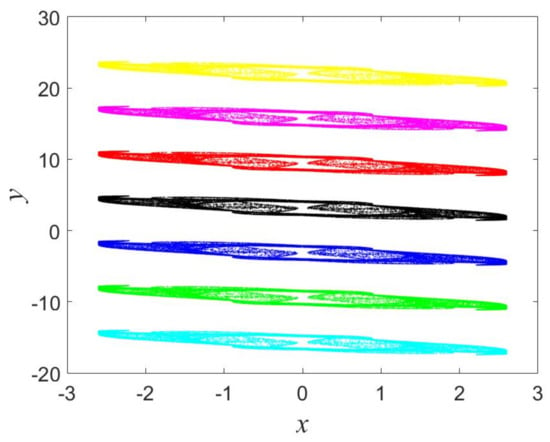
Figure 7.
Coexistence of seven iterative plots for different values : (yellow), (magenta), (red), (black), (blue), (green), (cyan).
3.3. Discussion
The purposed memristive maps display attractive behavior. In addition, such maps can be implemented using a hardware platform, for example, microcontroller or FPGA. We have used a microcontroller to realize the MM map by applying the general approach [13]. The microcontroller-based approach is a simple one and can be implemented conveniently [41]. A display is connected to the microcontroller directly to show the iterative plot, which is reported in Figure 8. The feasibility and chaos of the map are suitable for practical applications.
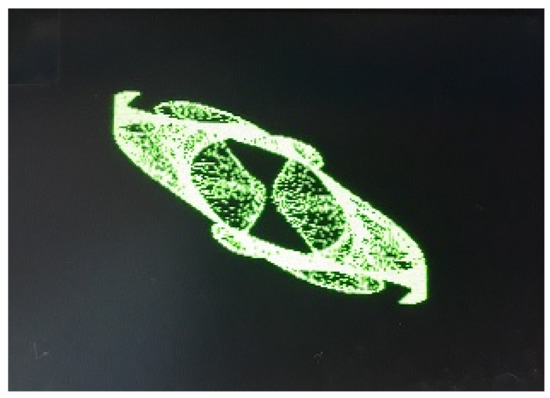
Figure 8.
Experimental result of the MM map, which is captured from the microcontroller.
4. Conclusions
The ability to connect the memristor and nonlinear term to propose chaotic maps was examined in this work. Our finding reveals that constructed maps depend on the selected discrete memristance and nonlinearity. We study a typical map as an example and observe its dynamical behaviors. Numerical simulations demonstrate the chaos, symmetry, and coexistence of iterative plots in the map. The implementation of the MM map with microcontroller confirms its feasibility. We believe that memristive maps can provide advantages in practical applications such as random signal generators.
Author Contributions
Funding acquisition, J.R.; Investigation, O.A.A.; Methodology, J.R. and V.P.T.; Software, O.A.A. and V.-T.P.; Supervision, Shaher Momani; Visualization, V.-T.P.; Writing—original draft, V.P.T.; Writing—review and editing, S.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is partially funded by the Centre for Nonlinear Systems, Chennai Institute of Technology, India, vide funding number CIT/CNS/2021/RD/064.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yan, X.; Wang, X.; Xian, Y. Synchronously scrambled diffuse image encryption method based on a new cosine chaotic map. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 080504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.C.; Bao, H.; Wang, N.; Chen, M.; Xu, Q. Hidden extreme multistability in memristive hyperchaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2017, 94, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Cang, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z. Simplified hyper–chaotic systems generating multi–wing non–equilibrium attractors. Neurocomputing 2016, 127, 2424–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, K.; Karthikeyan, A.; Srinivasan, A.K. FPGA implementation of novel fractional–order chaotic systems with two equilibriums and no equilibrium and its adaptive sliding mode synchronization. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 87, 2281–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, C.; Jean-Pierre, E. Iterated Map on the Interval as Dynamical Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Elaydi, S.N. Discrete Chaos: With Applications in Science and Engineering, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hénon, M.A. A two-dimensional mapping with a strange attractor. Commun. Math. Phys. 1976, 50, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, W.T.; Wilson, W.C. Individual-based chaos: Extensions of the discrete logistic model. J. Theory Biol. 2013, 339, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Li, G.; Xu, X. Design of a new dimension-changeable hyperchaotic model based on discrete memristor. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Xu, X.; Song, X.; Li, G. Audio encryption algorithm based on Chen memristor chaotic system. Symmetry 2022, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambic, D. A novel method of S-box design based on chaotic map and composition method. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2014, 58, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtierra, J.L.; Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; Rodriguez-Vazquez, A. A switched-capacitor skew-tent map implementation for random number generation. Int. J. Circ. Theory Appl. 2017, 45, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acho, L. A discrete-time chaotic oscillator based on the logistic map: A secure communication scheme and a simple experiment using Arduino. J. Frankl. Inst. 2015, 352, 3113–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fraga, L.G.; Torres-Perez, E.; Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; Mancillas-Lopez, C. Hardware implementation of pseudo-random number generators based on chaotic maps. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 90, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borujeni, S.; Ehsani, M. Modified logistic maps for cryptographic application. Appl. Math. 2015, 6, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhu, C. Symmetric image encryption algorithm based on a new product trigonometric chaotic map. Symmetry 2022, 14, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Hua, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, M.; Bao, B. Memristor-based hyperchaotic maps and application in auxiliary classifier generative adversarial nets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 5297–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscarino, A.; Fortuna, L.; Frasca, M.; Gambuzza, L.V. A chaotic circuit based on Hewlett–Packard memristor. Chaos 2012, 22, 023136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hu, S.; Tang, S.; Zeng, G. Hyperchaos and horseshoe in a 4D memristive system with a line of equilibria and its implementation. Int. J. Cir. Theory Appl. 2014, 42, 1172–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Wang, N.; Bao, B.; Chen, M.; Jin, P.; Wang, G. Initial condition-dependent dynamics and transient period in memristor–based hypogenetic jerk system with four line equilibria. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2018, 57, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ding, S.; Bao, H.; Chen, M.; Bao, B. Piecewise-linear simplification for adaptive synaptic neuron model. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 1832–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; He, S.; Tan, W.; Wang, H. From memristor-modeled jerk system to the nonlinear systems with memristor. Symmetry 2022, 14, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, Z.; Tian, H.; Liu, J. Symplectic Dynamics and Simultaneous Resonance Analysis of Memristor Circuit Based on Its van der Pol Oscillator. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Cheng, S.; Ju, Z.; Chen, M.; Wu, H. Asymmetric coexisting bifurcations and multi-stability in an asymmetric memristive diode-bridge-based jerk circuit. Chin. J. Phys. 2021, 70, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Li, H.; Hua, Z.; Xu, Q.; Bao, B. Sine-transform-based memristive hyperchaotic model with hardware implementation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Bao, B. Parallel bi-memristor hyperchaotic map with extreme multistability. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 160, 112273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprott, J.C. Elegant Chaos Algebraically Simple Chaotic Flows; World Scientific: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bouali, S.; Buscarino, A.; Fortuna, L.; Frasca, M.; Gambuzza, L.V. Emulating complex business cycles by using an electronic analogue. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2012, 13, 2459–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Tong, Y. Analysis of a novel three–dimensional chaotic system. Optik 2013, 124, 1516–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Yang, L. Chaos, bifurcation, coexisting attractors and circuit design of a three–dimensional continuous autonomous system. Optik 2016, 127, 5400–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, P.; Bo, K.; Yin, B. Research progess of multi–scroll chaotic oscillators based on current–mode devices. Optik 2016, 127, 5486–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgul, A.; Moroz, I.; Pehlivan, I.; Vaidyanathan, S. A new four–scroll chaotic attractor and its engineering applications. Optik 2016, 127, 5491–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudkowski, D.; Jafari, S.; Kapitaniak, T.; Kuznetsov, N.; Leonov, G.; Prasad, A. Hidden attractors in dynamical systems. Phys. Rep. 2016, 637, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadras, S.; Momeni, H.R.; Qi, G.; Wang, Z. Four–wing hyperchaotic attractor generated from a new 4D system with one equilibrium and its fractional–order form. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 67, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cang, S.; Ochala, E.; Sun, Y. A hyperchaotic system without equilibrium. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 69, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Sprott, J.C.; Golpayegani, S.M.R.H. Elementary quadratic chaotic flows with no equilibria. Phys. Lett. A 2013, 377, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.T.; Rahma, F.; Frasca, M.; Fortuna, L. Dynamics and synchronization of a novel hyperchaotic system without equilibrium. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2014, 24, 1450087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitaniak, T.; Leonov, G.A. Multistability: Uncovering hidden attractors. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2015, 224, 1405–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhusubaliyev, Z.T.; Mosekilde, E. Multistability and hidden attractors in a multilevel DC/DC converter. Math. Comput. Simul. 2015, 109, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Pham, V.T.; Moghtadaei, M.; Kingni, S.T. The relationship between chaotic maps and some chaotic systems with hidden attractors. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2016, 26, 1650211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, C.E.; Lopez-Mancilla, D.; Chiu, R.; Villafana-Rauda, E.; Orozco-Lopez, O.; Casillas-Rodriguez, F.; Sevilla-Escoboza, R. Discrete-time neural synchronization between an Arduino microcontroller and a Compact Development System using multiscroll chaotic signals. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2019, 119, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).