Principles of Gravitational-Wave Detection with Pulsar Timing Arrays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pulsar Timing Arrays
2.1. Millisecond Pulsars
2.2. Pulse Time of Arrivals
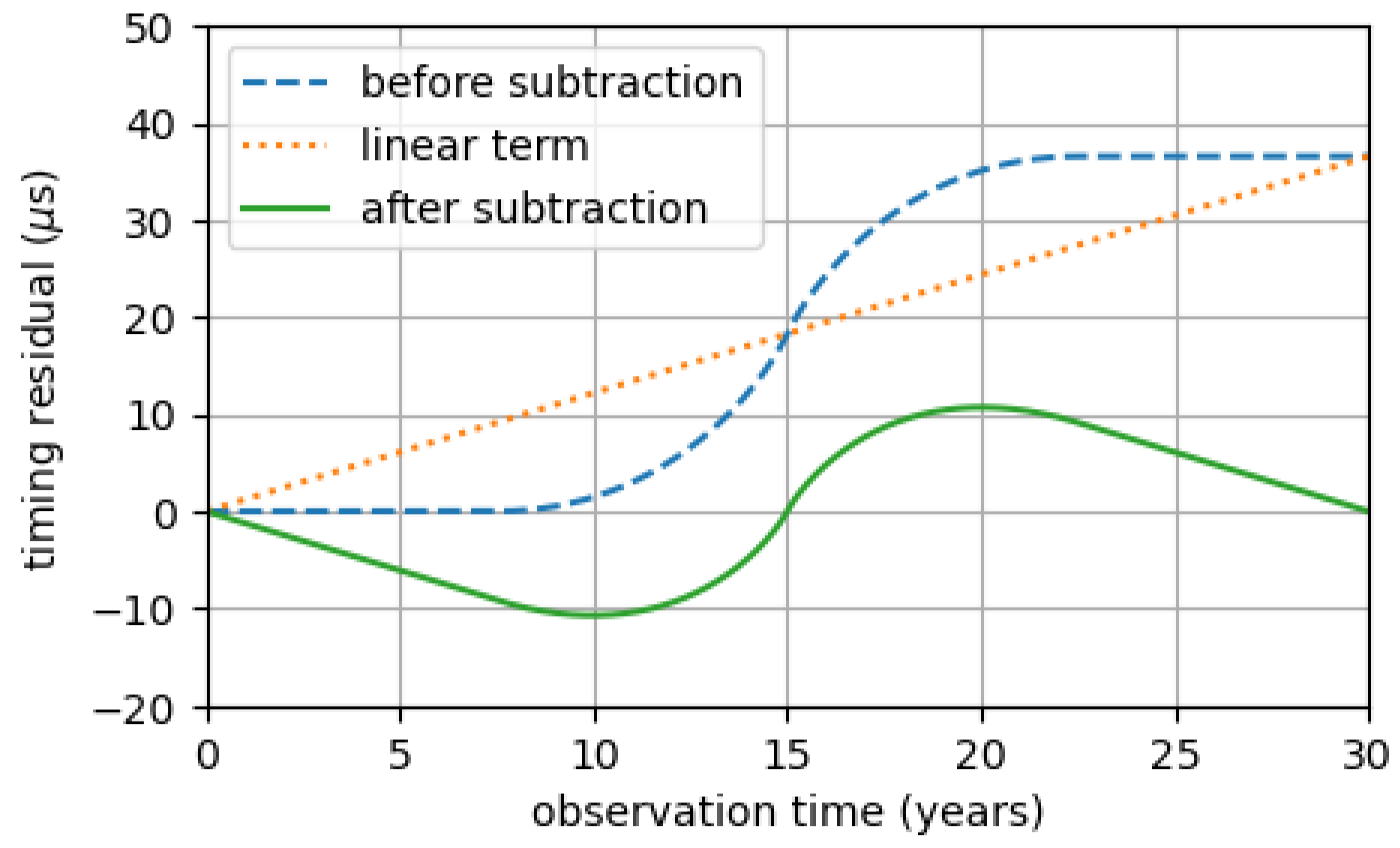
2.3. Timing Residuals
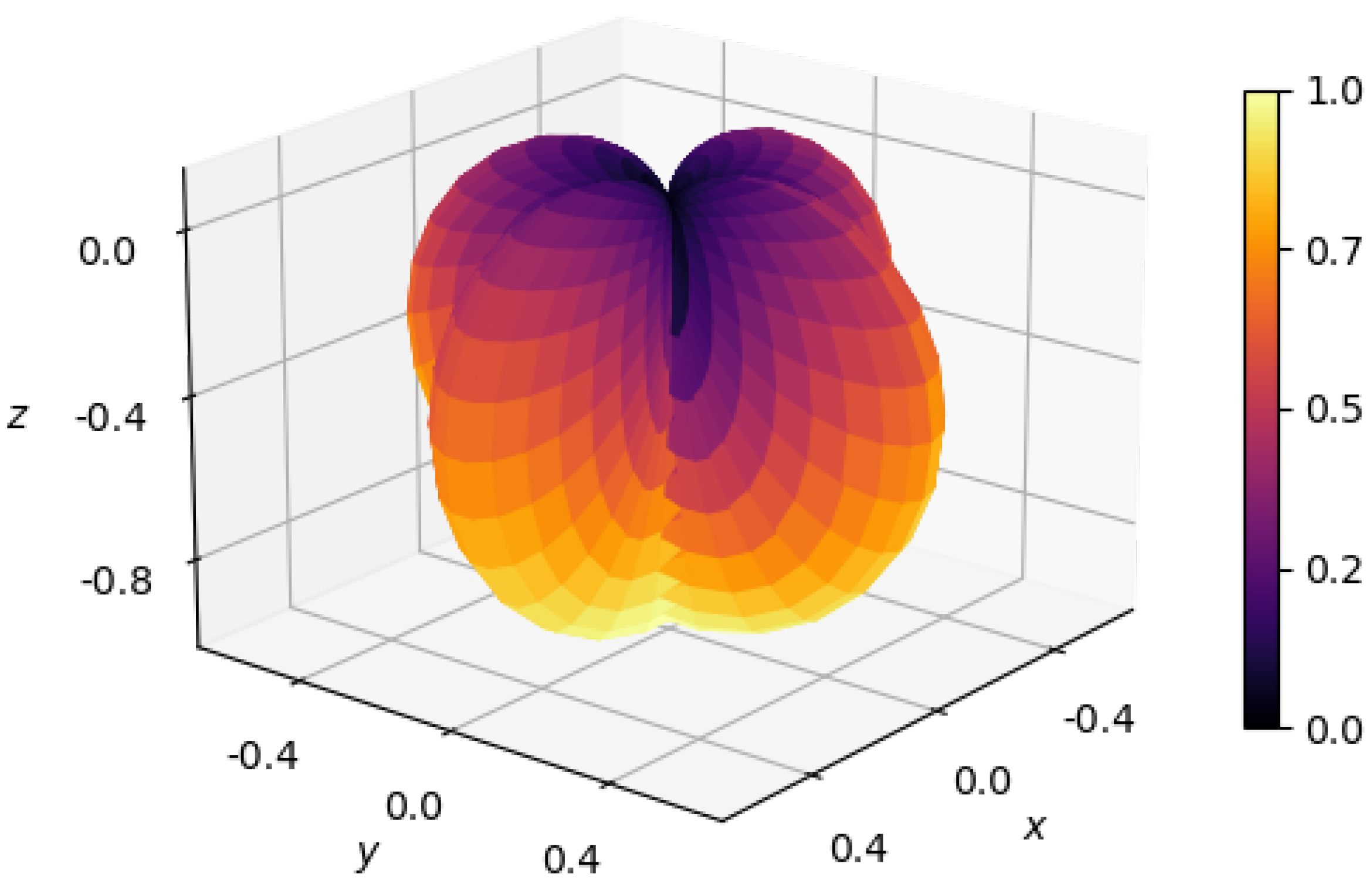
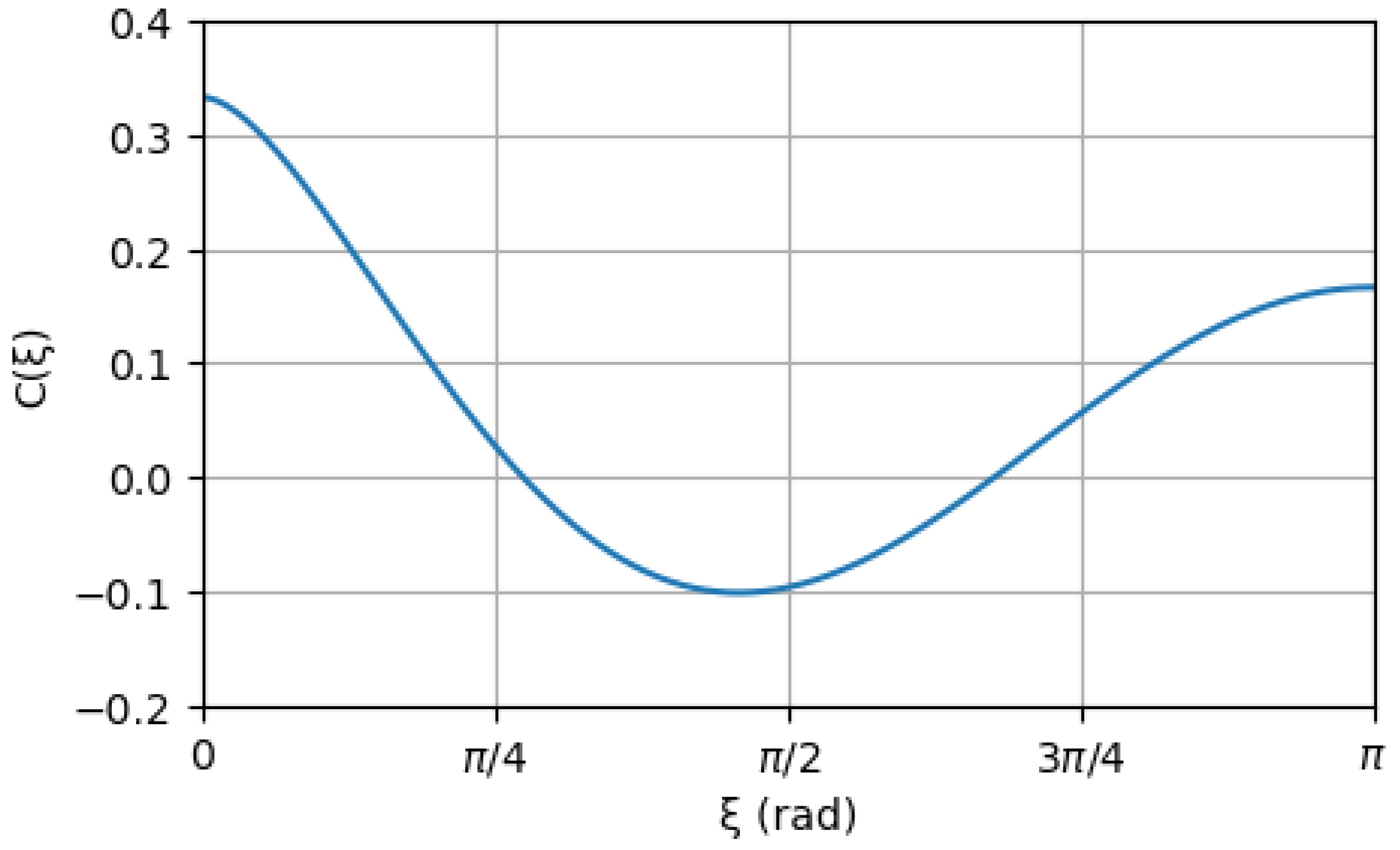
3. Gravitational-Wave Detection
4. Supermassive Black-Hole Binaries
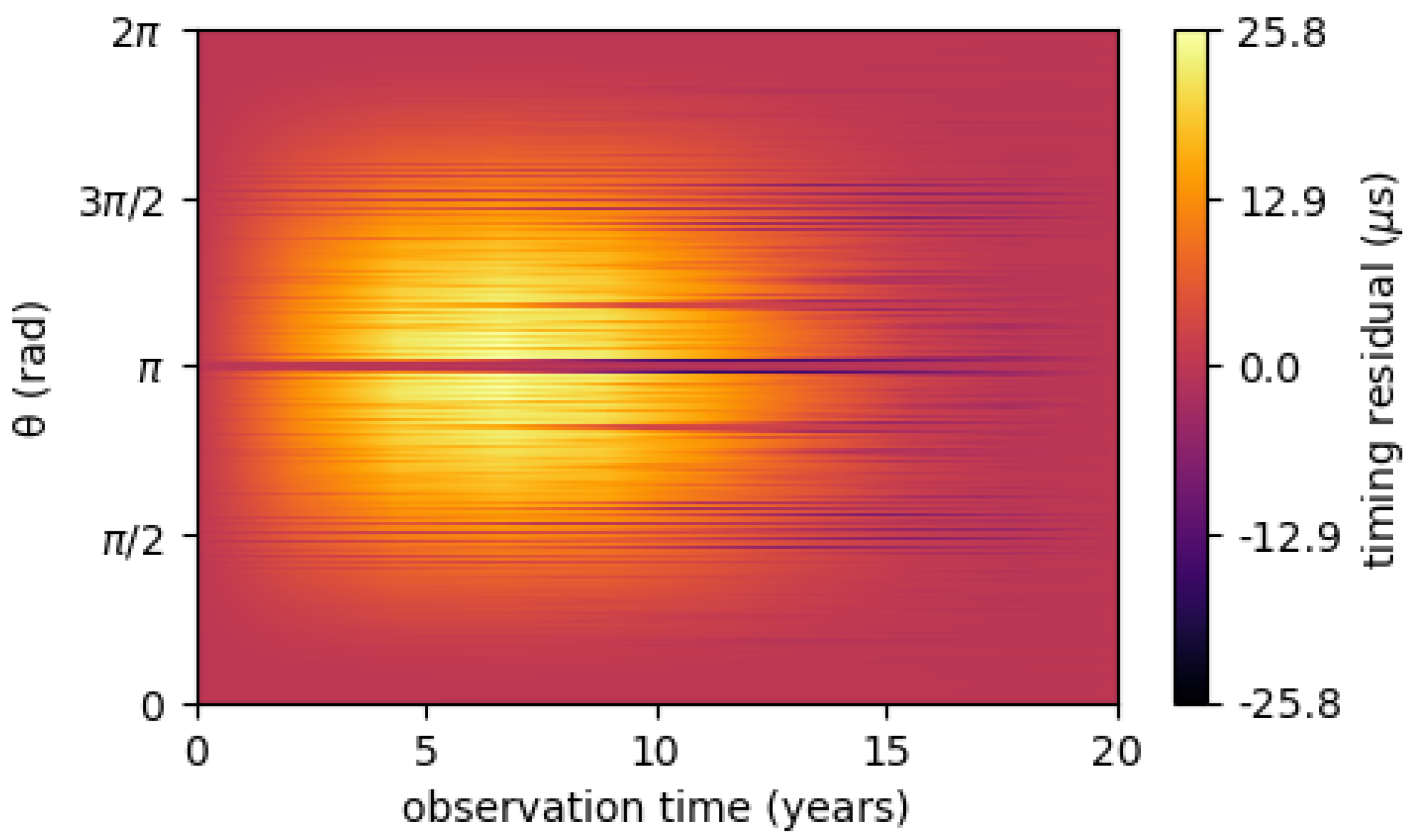
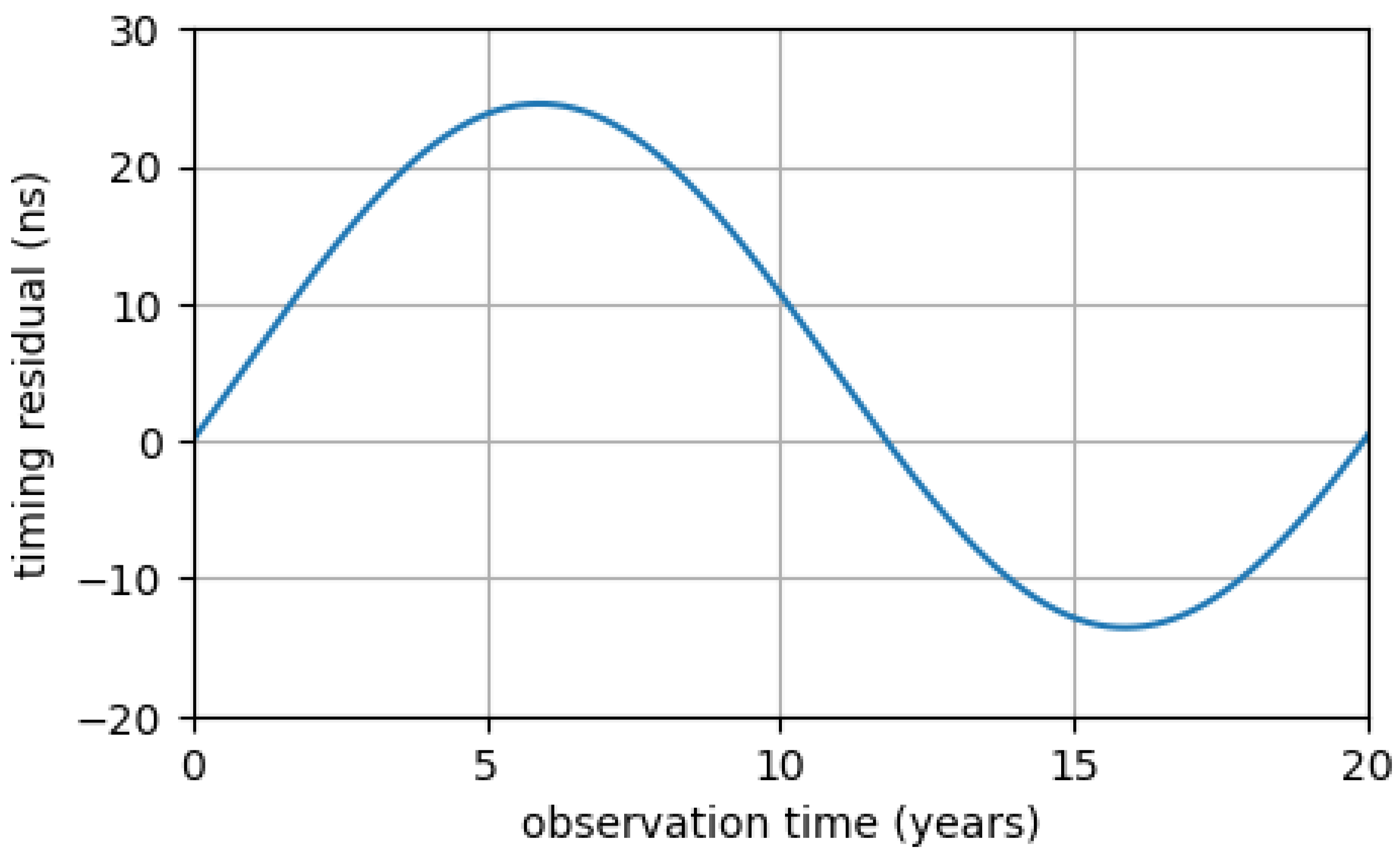
4.1. Continuous Waves
4.2. Gravitational-Wave Background
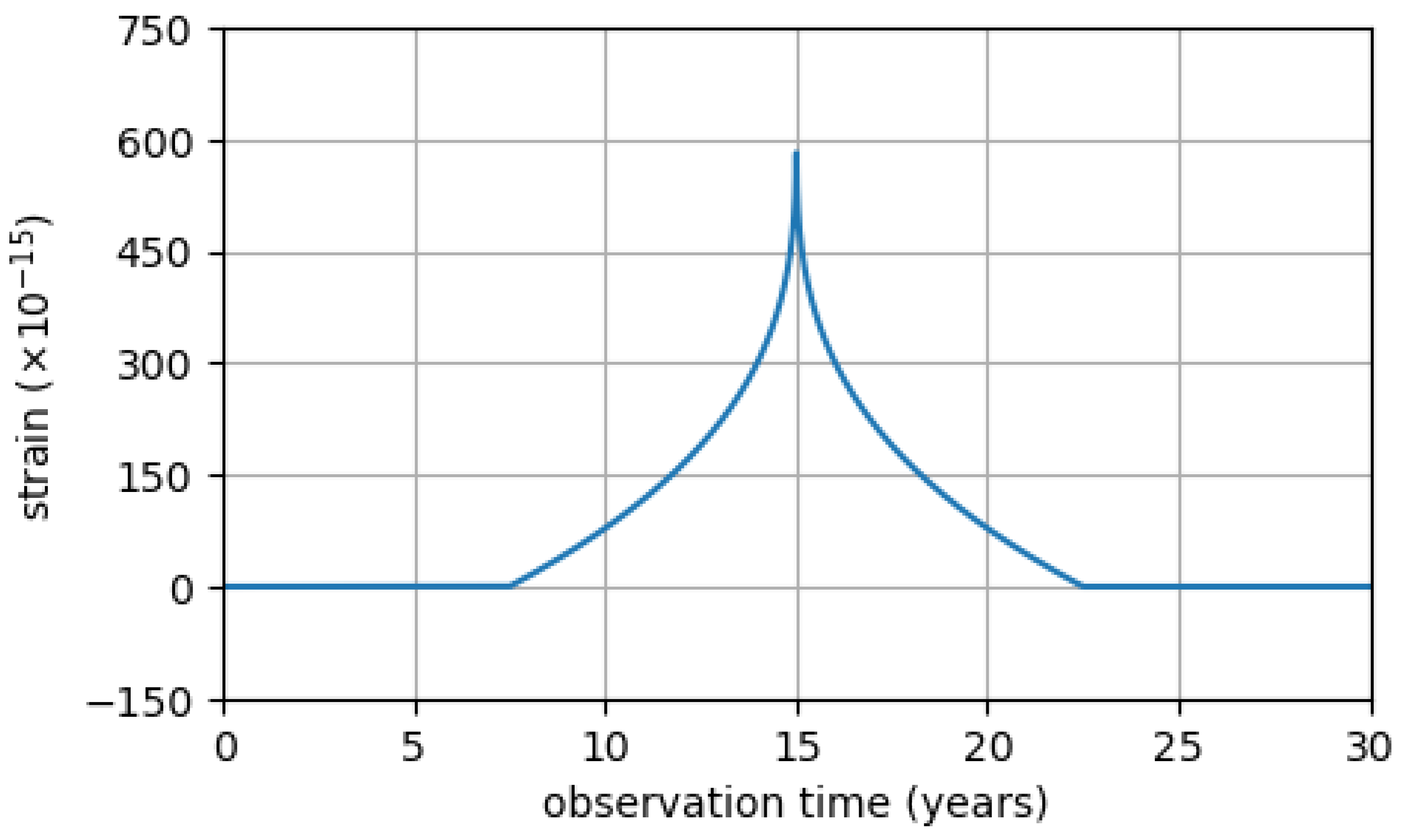
4.3. Gravitational-Wave Bursts with and without Memory
5. Cosmic Strings
5.1. Cosmological Origin of the Cosmic Strings
5.2. Cosmic Strings from U(1) Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking
5.3. Gravitational-Wave Emission from Cosmic Strings
6. Current Results
7. Conclusions and Further Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| INFN | Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare |
| INAF | Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica |
| GW | Gravitational Wave |
| GR | General Relativity |
| BH | Black Hole |
| LIGO | Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory |
| BBH | Binary Black Hole |
| BNS | Binary Neutron Star |
| ET | Einstein Telescope |
| CE | Cosmic Explorer |
| EMRI | Extreme Mass-Ratio Inspiral |
| LISA | Laser Interferometer Space Antenna |
| SMBHB | Supermassive Black-Hole Binary |
| PTA | Pulsar Timing Array |
| ToA | Time of Arrival |
| MSP | Millisecond Pulsar |
| EPTA | European Pulsar Timing Array |
| InPTA | Indian Pulsar Timing Array |
| NANOGrav | North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational Waves |
| PPTA | Parkes Pulsar Timing Array |
| IPTA | International Pulsar Timing Array |
| GC | Globular Cluster |
| SSB | Solar System Barycenter |
| ICRF | International Celestial Reference Frame |
| ICRS | International Celestial Reference System |
| IAU | International Astronomical Union |
| SMBH | Supermassive Black Hole |
| GWB | Gravitational-Wave Background |
| CMB | Cosmic Microwave Background |
| BWM | Burst With Memory |
| RMS | root mean square |
| CDM | -Cold Dark Matter |
| FAST | Five hundred meter Aperture Spherical Telescope |
| SKA | Square Kilometre Array |
| TAsP | Theoretical Astroparticle Physics |
References
- Einstein, A. Die Grundlage der allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie. Ann. Phys. 1916, 354, 769–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Cota, J.; Galindo-Uribarri, S.; Smoot, G. A Brief History of Gravitational Waves. Universe 2016, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Gravitational Waves and Gamma-Rays from a Binary Neutron Star Merger: GW170817 and GRB170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.; Veres, P.; Burns, E.; Briggs, M.S.; Hamburg, R.; Kocevski, D.; Wilson-Hodge, C.A.; Preece, R.D.; Poolakkil, S.; Roberts, O.J.; et al. An Ordinary Short Gamma-Ray Burst with Extraordinary Implications: Fermi-GBM Detection of GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro-Seoane, P.; Audley, H.; Babak, S.; Baker, J.; Barausse, E.; Bender, P.; Berti, E.; Binetruy, P.; Born, M.; Bortoluzzi, D.; et al. Laser Interferometer Space Antenna. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.00786. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal, M.; Romani, R.W. Ultra–Low-Frequency Gravitational Radiation from Massive Black Hole Binaries. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1995, 446, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damour, T.; Vilenkin, A. Gravitational wave bursts from cusps and kinks on cosmic strings. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 064008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J.; Cole, R.H.; Berry, C.P.L. Gravitational-wave sensitivity curves. Class. Quantum Gravity 2015, 32, 015014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravitational-Wave Sensitivity Curves. Available online: https://cplberry.com/2015/01/10/1408-0740/ (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Wolszczan, A.; Frail, D.A. A planetary system around the millisecond pulsar PSR1257 + 12. Nature 1992, 355, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazhin, M.V. Opportunities for detecting ultralong gravitational waves. Astron. Zhurnal 1978, 55, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Desvignes, G.; Caballero, R.N.; Lentati, L.; Verbiest, J.P.; Champion, D.J.; Stappers, B.W.; Janssen, G.H.; Lazarus, P.; Osłowski, S.; Babak, S.; et al. High-precision timing of 42 millisecond pulsars with the European Pulsar Timing Array. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 458, 3341–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, B.C.; Arumugasamy, P.; Bagchi, M.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Basu, A.; Batra, N.D.; Bethapudi, S.; Choudhary, A.; De, K.; Dey, L.; et al. Precision pulsar timing with the ORT and the GMRT and its applications in pulsar astrophysics. J. Astrophys. Astron. 2018, 39, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzoumanian, Z.; Brazier, A.; Burke-Spolaor, S.; Chamberlin, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Christy, B.; Cordes, J.M.; Cornish, N.J.; Crawford, F.; Cromartie, H.T.; et al. The NANOGrav 11-year Data Set: High-precision Timing of 45 Millisecond Pulsars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2018, 235, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.J.; Hobbs, G.; Coles, W.; Levin, Y.; Keith, M.J.; Bailes, M.; Bhat, N.D.; Burke-Spolaor, S.; Dai, S.; Kerr, M.; et al. Timing analysis for 20 millisecond pulsars in the Parkes Pulsar Timing Array. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 455, 1751–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbiest, J.P.; Lentati, L.; Hobbs, G.; van Haasteren, R.; Demorest, P.B.; Janssen, G.H.; Wang, J.B.; Desvignes, G.; Caballero, R.N.; Keith, M.J.; et al. The International Pulsar Timing Array: First data release. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 458, 1267–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ATNF Pulsar Database. Available online: https://www.atnf.csiro.au/research/pulsar/psrcat/ (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Manchester, R.N.; Hobbs, G.B.; Teoh, A.; Hobbs, M. The Australia Telescope National Facility Pulsar Catalogue. Astron. J. 2005, 129, 1993–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorimer, D.R. Binary and Millisecond Pulsars. Living Rev. Relativ. 2008, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzoumanian, Z.; Baker, P.T.; Blumer, H.; Bécsy, B.; Brazier, A.; Brook, P.R.; Burke-Spolaor, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Chen, S.; Cordes, J.M.; et al. The NANOGrav 12.5 yr Data Set: Search for an Isotropic Stochastic Gravitational-Wave Background. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 905, L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorimer, D.R.; Kramer, M. Handbook of Pulsar Astronomy. In Cambridge Observing Handbooks for Research Astronomers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin, M. Pulsar Timing Arrays. Astron. Focus Present. IAU XXIX Gen. Assem. 2016, 29B, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, D.C.; Hellings, R.W. Pulsar timing and general relativity. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 24, 537–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallisneri, M.; Taylor, S.R.; Simon, J.; Folkner, W.M.; Park, R.S.; Cutler, C.; Ellis, J.A.; Lazio, T.J.; Vigeland, S.J.; Aggarwal, K.; et al. Modeling the Uncertainties of Solar System Ephemerides for Robust Gravitational-wave Searches with Pulsar-timing Arrays. Astrophys. J. 2020, 893, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, R.S.; Backer, D.C. Constructing a Pulsar Timing Array. Astrophys. J. 1990, 361, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.T.; Hobbs, G.B.; Manchester, R.N. TEMPO2, a new pulsar timing package - II. The timing model and precision estimates. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 372, 1549–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, G.B.; Edwards, R.T.; Manchester, R.N. TEMPO2, a new pulsar-timing package - I. An overview. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 369, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiburzi, C.; Hobbs, G.; Kerr, M.; Coles, W.A.; Dai, S.; Manchester, R.N.; Possenti, A.; Shannon, R.M.; You, X.P. A study of spatial correlations in pulsar timing array data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 455, 4339–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiore, M. Gravitational Waves: Volume 1: Theory and Experiments; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Boîtier, A.; Tiwari, S.; Philippoz, L.; Jetzer, P. Pulse redshift of pulsar timing array signals for all possible gravitational wave polarizations in modified general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 064051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyuer, D.; Zwick, L.; D’Orazio, D.J.; Saha, P. Searching for gravitational waves via Doppler tracking by future missions to Uranus and Neptune. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 503, L73–L79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detweiler, S. Pulsar timing measurements and the search for gravitational waves. Astrophys. J. 1979, 234, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunes, N.; Siemens, X. Gravitational-Wave Tests of General Relativity with Ground-Based Detectors and Pulsar-Timing Arrays. Living Rev. Relativ. 2013, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormendy, J.; Ho, L.C. Coevolution (Or Not) of Supermassive Black Holes and Host Galaxies. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 51, 511–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghez, A.M.; Salim, S.; Weinberg, N.N.; Lu, J.R.; Do, T.; Dunn, J.K.; Matthews, K.; Morris, M.R.; Yelda, S.; Becklin, E.E.; et al. Measuring Distance and Properties of the Milky Way’s Central Supermassive Black Hole with Stellar Orbits. Astrophys. J. 2008, 689, 1044–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genzel, R.; Eisenhauer, F.; Gillessen, S. The Galactic Center massive black hole and nuclear star cluster. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 3121–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madau, P.; Rees, M.J. Massive Black Holes as Population III Remnants. Astrophys. J. 2001, 551, L27–L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, B.J.; Hawking, S.W. Black holes in the early Universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1974, 168, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonoli, S.; Mayer, L.; Callegari, S. Massive black hole seeds born via direct gas collapse in galaxy mergers: Their properties, statistics and environment. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 437, 1576–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.L.; Teukolsky, S.A. Black Holes, White Dwarfs, and Neutron Stars: The Physics of Compact Objects; Wiley-Intersci. Publ.: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Maggiore, M. Gravitational Waves. Vol. 2: Astrophysics and Cosmology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellings, R.W.; Downs, G.S. Upper limits on the isotropic gravitational radiation background from pulsar timing analysis. Astrophys. J. 1983, 265, L39–L42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiore, M. Stochastic backgrounds of gravitational waves. arXiv 2000, arXiv:0008027. [Google Scholar]
- Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M.; de Paolis, F.; Ingrosso, G.; Nucita, A.A. Gravitational Waves from Hyperbolic Encounters. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2008, 23, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, C.L.; New, K.C.B. Gravitational Waves from Gravitational Collapse. Living Rev. Relativ. 2011, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, N. Search for memory and inspiral gravitational waves from supermassive binary black holes with pulsar timing arrays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 400, L38–L42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braginskii, V.B.; Thorne, K.S. Gravitational-wave bursts with memory and experimental prospects. Nature 1987, 327, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pshirkov, M.S.; Baskaran, D.; Postnov, K.A. Observing gravitational wave bursts in pulsar timing measurements. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 402, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, J.M.; Jenet, F.A. Detecting Gravitational Wave Memory with Pulsar Timing. Astrophys. J. 2012, 752, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzoumanian, Z.; Brazier, A.; Burke-Spolaor, S.; Chamberlin, S.J.; Chatterjee, S.; Christy, B.; Cordes, J.M.; Cornish, N.J.; Demorest, P.B.; Deng, X.; et al. NANOGrav Constraints on Gravitational Wave Bursts with Memory. Astrophys. J. 2015, 810, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindmarsh, M.B.; Kibble, T.W.B. Cosmic strings. Prog. Phys. 1995, 58, 477–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Pillado, J.J.; Olum, K.D. Form of cosmic string cusps. Phys. Rev. D 1999, 59, 063508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ölmez, S.; Mandic, V.; Siemens, X. Gravitational-wave stochastic background from kinks and cusps on cosmic strings. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 104028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellariadou, M. Cosmic Strings. LNP 2007, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yonemaru, N.; Kuroyanagi, S.; Hobbs, G.; Takahashi, K.; Zhu, X.J.; Coles, W.A.; Dai, S.; Howard, E.; Manchester, R.; Reardon, D.; et al. Searching for gravitational-wave bursts from cosmic string cusps with the Parkes Pulsar Timing Array. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 501, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, S.; Brdar, V.; Schmitz, K. Has NANOGrav Found First Evidence for Cosmic Strings? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 041305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentati, L.; Taylor, S.R.; Mingarelli, C.M.; Sesana, A.; Sanidas, S.A.; Vecchio, A.; Caballero, R.N.; Lee, K.J.; Van Haasteren, R.; Babak, S.; et al. European Pulsar Timing Array limits on an isotropic stochastic gravitational-wave background. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 453, 2576–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, B.; Shannon, R.M.; Reardon, D.J.; Hobbs, G.; Zic, A.; Bailes, M.; Curyło, M.; Dai, S.; Kerr, M.; Lower, M.E.; et al. On the evidence for a common-spectrum process in the search for the nanohertz gravitational-wave background with the Parkes Pulsar Timing Array. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.12112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Caballero, R.N.; Guo, Y.J.; Chalumeau, A.; Liu, K.; Shaifullah, G.; Lee, K.J.; Babak, S.; Desvignes, G.; Parthasarathy, A.; et al. Common-red-signal analysis with 24-yr high-precision timing of the European Pulsar Timing Array: Inferences in the stochastic gravitational-wave background search. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 508, 4970–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, M.C.; Bartolo, N.; Liguori, M.; Matarrese, S. Gravitational waves from inflation. Riv. Nuovo C. 2016, 39, 399–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorkavyi, N. Gravitational wave background discovered by NANOGrav as evidence of a cyclic universe. New Astron. 2022, 91, 101698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, C.; Vidotto, F. Pre-Big-Bang Black-Hole Remnants and Past Low Entropy. Universe 2018, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. Cycles of Time: An Extraordinary New View of the Universe; Bodley Head: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Q.; Trodden, M. Detecting the Stochastic Gravitational Wave Background from Massive Gravity with Pulsar Timing Arrays. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.05344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratzinger, W.; Schwaller, P. Whispers from the dark side: Confronting light new physics with NANOGrav data. SciPost Phys. 2021, 10, 047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, H.; Sesana, A.; Chen, S.; Vecchio, A.; Del Pozzo, W.; Rosado, P.A. Massive black hole binary systems and the NANOGrav 12.5 yea results. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 502, L99–L103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Lewicki, M. Cosmic String Interpretation of NANOGrav Pulsar Timing Data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 041304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration, P. Planck 2015 results. XIII. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 594, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Pillado, J.J.; Olum, K.D.; Wachter, J.M. Comparison of cosmic string and superstring models to NANOGrav 12.5-year results. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 103512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarides, G.; Maji, R.; Shafi, Q. NANOGrav and PPTA Tension: Gravity Waves, Cosmic Strings, and Inflation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.02016. [Google Scholar]
- De Paolis, F.; Ingrosso, G.; Nucita, A.A. A super massive black hole binary in 3C 66B: Future observational perspectives. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 426, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzoumanian, Z.; Baker, P.T.; Brazier, A.; Brook, P.R.; Burke-Spolaor, S.; Bécsy, B.; Charisi, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Cordes, J.M.; Cornish, N.J.; et al. Multimessenger Gravitational-wave Searches with Pulsar Timing Arrays: Application to 3C 66B Using the NANOGrav 11-year Data Set. Astrophys. J. 2020, 900, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, R.; Li, D.; Jin, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, H.; Yue, Y.; Qian, L. The Five-Hundred Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST) Project. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2011, 20, 989–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailes, M.; Jameson, A.; Abbate, F.; Barr, E.D.; Bhat, N.D.; Bondonneau, L.; Burgay, M.; Buchner, S.J.; Camilo, F.; Champion, D.J.; et al. The MeerKAT telescope as a pulsar facility: System verification and early science results from MeerTime. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2020, 37, e028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltman, A.; Bull, P.; Camera, S.; Kelley, K.; Padmanabhan, H.; Pritchard, J.; Raccanelli, A.; Riemer-Sørensen, S.; Shao, L.; Andrianomena, S.; et al. Fundamental physics with the Square Kilometre Array. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2020, 37, e002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorano, M.; De Paolis, F.; Nucita, A.A. Including Millisecond Pulsars inside the Core of Globular Clusters in Pulsar Timing Arrays. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maiorano, M.; De Paolis, F.; Nucita, A.A. Principles of Gravitational-Wave Detection with Pulsar Timing Arrays. Symmetry 2021, 13, 2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13122418
Maiorano M, De Paolis F, Nucita AA. Principles of Gravitational-Wave Detection with Pulsar Timing Arrays. Symmetry. 2021; 13(12):2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13122418
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaiorano, Michele, Francesco De Paolis, and Achille A. Nucita. 2021. "Principles of Gravitational-Wave Detection with Pulsar Timing Arrays" Symmetry 13, no. 12: 2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13122418
APA StyleMaiorano, M., De Paolis, F., & Nucita, A. A. (2021). Principles of Gravitational-Wave Detection with Pulsar Timing Arrays. Symmetry, 13(12), 2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13122418






