Detection of Username Enumeration Attack on SSH Protocol: Machine Learning Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Setup
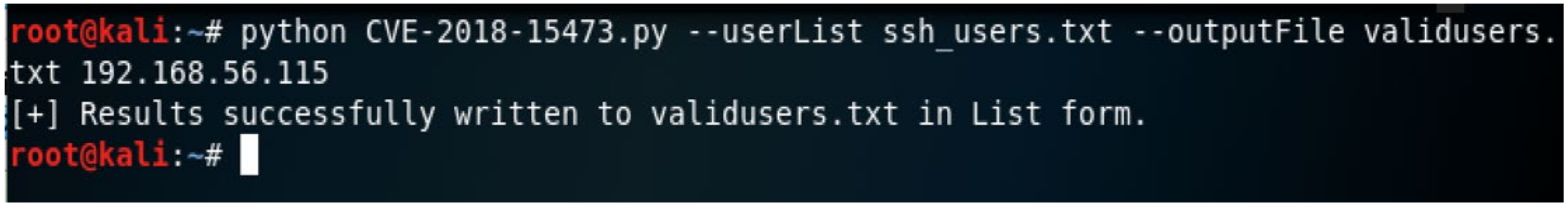
3.2. Attack Scenario
3.3. Data Collection and Labelling
3.4. Data Preprocessing
3.5. Applying Machine-Learning Classifiers to Dataset
4. Results and Discussion
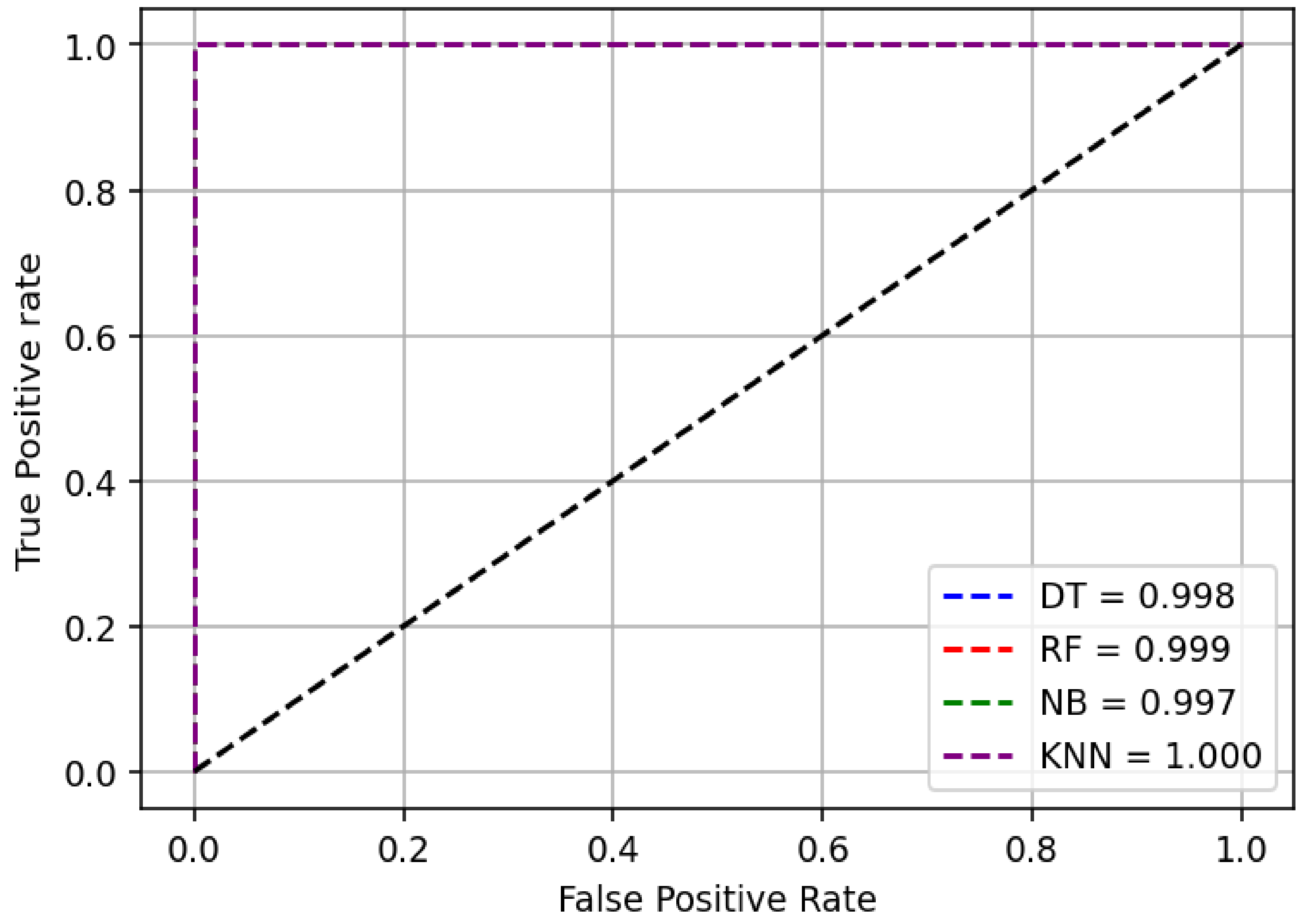
Effectiveness Comparison When Including and Excluding Ports Information
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alshehri, H.; Meziane, F. Current state on internet growth and usage in Saudi Arabia and its ability to support e-commerce development. J. Adv. Manag. Sci. 2017, 5, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Infante-Moro, A.; Infante-Moro, J.-C.; Martínez-López, F.-J.; García-Ordaz, M. The importance of internet and online social networks in the Spanish hotel sector. Appl. Comput. Sci. 2016, 12, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- World Internet Users Statistics and 2021 World Population Stats. 2021. Available online: https://www.internetworldstats.com/stats.htm (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Hoque, N.; Bhuyan, M.H.; Baishya, R.C.; Bhattacharyya, D.K.; Kalita, J.K. Network attacks: Taxonomy, tools and systems. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2014, 40, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaw, E.; Wang, X. Feature Selection and Ensemble-Based Intrusion Detection System: An Efficient and Comprehensive Approach. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafabadi, M.M.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M.; Kemp, C.; Seliya, N.; Zuech, R. Machine learning for detecting brute force attacks at the network level. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering, Boca Raton, FL, USA, 10–12 November 2014; pp. 379–385. [Google Scholar]
- Jang-Jaccard, J.; Nepal, S. A survey of emerging threats in cybersecurity. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 2014, 80, 973–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meryem, A.; Ouahidi, B.E.L. Hybrid intrusion detection system using machine learning. Netw. Secur. 2020, 2020, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, M.V.; Anuradha, J. Network security and types of attacks in network. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 48, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.F. CompTIA Security+ Certification Study Guide; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Morgan, Y. Security against passive attacks on network coding system—A survey. Comput. Netw. 2018, 138, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M. An Introduction to Network Security Attacks. In Inventive Systems and Control; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2021; pp. 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamalai, D.; Renault, E.; Dhanuskodi, M. Trends in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology: Proceedings of the First International Conference (CCSEIT) Tirunelveli, Tamil Nadu, India, 23–25 September 2011; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 204. [Google Scholar]
- Alata, E.; Nicomette, V.; Kaâniche, M.; Dacier, M.; Herrb, M. Lessons learned from the deployment of a high-interaction honeypot. In Proceedings of the Sixth European Dependable Computing Conference, Coimbra, Portugal, 18–20 October 2006; pp. 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett-Packard Development Company. Top Cyber Security Risks Threat Report for (2010). Available online: http://dvlabs.tippingpoint.com/toprisks2010 (accessed on 4 June 2021).
- Hossain, M.D.; Ochiai, H.; Doudou, F.; Kadobayashi, Y. SSH and FTP brute-force Attacks Detection in Computer Networks: LSTM and Machine Learning Approaches. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), Shanghai, China, 22–24 February 2020; pp. 491–497. [Google Scholar]
- Anandita, S.; Rosmansyah, Y.; Dabarsyah, B.; Choi, J.U. Implementation of dendritic cell algorithm as an anomaly detection method for port scanning attack. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information Technology Systems and Innovation (ICITSI), Bandung, Indonesia, 16–19 November 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Vykopal, J. A flow-level taxonomy and prevalence of brute force attacks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computing and Communications (ACC), Kochi, India, 22–24 July 2011; pp. 666–675. [Google Scholar]
- Dave, K.T. Brute-force Attack ‘Seeking but Distressing’. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Technol. Brute Force 2013, 2, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Qiu, X. NodeRank: An algorithm to assess state enumeration attack graphs. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Shanghai, China, 21–23 September 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Virtue Security. Username Enumeration. 2021. Available online: https://www.virtuesecurity.com/kb/username-enumeration/ (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Portswigger—Web Security Academy. 2018. Vulnerabilities in Password-Based Login. Available online: https://portswigger.net/web-security/authentication/password-based (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Kannisto, J.; Harju, J. The time will tell on you: Exploring information leaks in ssh public key authentication. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Network and System Security, Helsinki, Finland, 21–23 August 2017; pp. 301–314. [Google Scholar]
- Elmrabit, N.; Zhou, F.; Li, F.; Zhou, H. Evaluation of machine learning algorithms for anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Protection of Digital Services (Cyber Security), Dublin, Ireland, 15–17 June 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Eltanbouly, S.; Bashendy, M.; AlNaimi, N.; Chkirbene, Z.; Erbad, A. Machine learning techniques for network anomaly detection: A survey. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Informatics, IoT, and Enabling Technologies (ICIoT), Doha, Qatar, 2–5 February 2020; pp. 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Nawir, M.; Amir, A.; Yaakob, N.; Lynn, O.B. Effective and efficient network anomaly detection system using machine learning algorithm. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2019, 8, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahesh, B. Machine Learning Algorithms—Review Self Flowing Generator View Project Machine Learning Algorithms. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2020, 9, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apruzzese, G.; Colajanni, M.; Ferretti, L.; Guido, A.; Marchetti, M. On the effectiveness of machine and deep learning for cyber security. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Cyber Conflict (CyCon), Tallinn, Estonia, 29 May–1 June 2018; pp. 371–390. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczak, A.L.; Guven, E. A Survey of Data Mining and Machine Learning Methods for Cyber Security Intrusion Detection. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 1153–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.; Gomes, R.; Chowdhury, M.; Nygard, K.E. Enhancing Machine Learning Prediction in Cybersecurity Using Dynamic Feature Selector. J. Cybersecur. Priv. 2021, 1, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndibwile, J.D.; Govardhan, A.; Okada, K.; Kadobayashi, Y. Web server protection against application layer DDoS attacks using machine learning and traffic authentication. In Proceedings of the IEEE 39th Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference, Taichung, Taiwan, 1–5 July 2015; Volume 3, pp. 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, A.J.; Scobell, A. 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report. Verizon. 2020. Available online: https://enterprise.verizon.com/resources/reports/2020-data-breach-investigations-report.pdf%0Ahttp://bfy.tw/HJvH (accessed on 12 July 2021).
- Vykopal, J.; Plesnik, T.; Minarik, P. Network-based dictionary attack detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Future Networks, Bangkok, Thailand, 7–9 March 2009; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Ikenaga, T. SSH dictionary attack detection based on flow analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/IPSJ 12th International Symposium on Applications and the Internet, Izmir, Turkey, 16–20 July 2012; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, M.; Paxson, V. Detecting stealthy, distributed SSH brute-forcing. In Proceedings of the 2013 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer & Communications Security, Berlin, Germany, 4–8 November 2013; pp. 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Thu, H.L.T.; Kim, H. Long short term memory recurrent neural network classifier for intrusion detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Platform Technology and Service (PlatCon), Jeju, Korea, 15–17 February 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstede, R.; Jonker, M.; Sperotto, A.; Pras, A. Flow-based web application brute-force attack and compromise detection. J. Netw. Syst. Manag. 2017, 25, 735–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hynek, K.; Beneš, T.; Čejka, T.; Kubátová, H. Refined Detection of SSH Brute-Force Attackers Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 35th IFIP International Conference on ICT Systems Security and Privacy Protection, Maribor, Slovenia, 21–23 September 2020; pp. 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Stiawan, D.; Idris, M.; Malik, R.F.; Nurmaini, S.; Alsharif, N.; Budiarto, R. Investigating Brute Force Attack Patterns in IoT Network. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4568368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenSSH. 2021. Available online: https://www.openssh.com/ (accessed on 18 August 2021).
- Exploit Database. OpenSSH 2.3 < 7.7—Username Enumeration. 2018. Available online: https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/45233 (accessed on 21 August 2021).
- Stratosphere Lab. Malware Capture Facility Project: Normal Captures—Stratosphere IPS. 2019. Available online: https://www.stratosphereips.org/datasets-normal (accessed on 21 August 2021).
- Li, Y.; Miao, R.; Alizadeh, M.; Yu, M. {DETER}: Deterministic {TCP} Replay for Performance Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 16th {USENIX} Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation ({NSDI} 19), Boston, MA, USA, 26–28 February 2019; pp. 437–452. [Google Scholar]
- TCPDUMP/LIBPCAP Public Repository. 2021. Available online: https://www.tcpdump.org/ (accessed on 5 September 2021).
- Wireshark. 2021. Available online: https://www.wireshark.org/ (accessed on 5 September 2021).
- Agghey, A. SSH Username Enumeration Attack Detection Dataset. Zenodo 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunford, R.; Su, Q.; Tamang, E. The pareto principle. Plymouth Stud. Sci. 2014, 7, 140–148. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Li, Y.F.; Xie, M. An empirical analysis of data preprocessing for machine learning-based software cost estimation. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2015, 67, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherfi, A.; Nouira, K.; Ferchichi, A. Very fast C4. 5 decision tree algorithm. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 32, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.J. An extended idea about decision trees. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI), Las Vegas, NA, USA, 5–7 December 2019; pp. 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L. Building auto-encoder intrusion detection system based on random forest feature selection. Comput. Secur. 2020, 95, 101851. [Google Scholar]
- Bhavani, T.T.; Rao, M.K.; Reddy, A.M. Network intrusion detection system using random forest and decision tree machine learning techniques. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Sustainable Technologies for Computational Intelligence, Jaipur, India, 29–30 March 2019; pp. 637–643. [Google Scholar]
- Alqahtani, H.; Sarker, I.H.; Kalim, A.; Hossain, S.M.M.; Ikhlaq, S.; Hossain, S. Cyber intrusion detection using machine learning classification techniques. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing Science, Communication and Security, Gujarat, India, 26–27 March 2020; pp. 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- John, G.H.; Langley, P. Estimating Continuous Distributions in Bayesian Classifiers. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1302.4964. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1302.4964v1 (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Han, J.; Pei, J.; Kamber, M. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers: Waltham, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, S.; Bali, V.; Paliwal, K.K. Genetic programming and K-nearest neighbour classifier based intrusion detection model. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering-Confluence, Noida, India, 12–13 January 2017; pp. 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, N. Survey of Nearest Neighbor Techniques. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1007.0085. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1007.0085v1 (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- Soofi, A.A.; Awan, A. Classification techniques in machine learning: Applications and issues. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2017, 13, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Class | Instances in Each Class |
|---|---|
| SSH username enumeration attack | 18,844 |
| Non-username enumeration | 17,429 |
| Total instances | 36,273 |
| Class | Instances | Training Set | Testing Set |
|---|---|---|---|
| Username enumeration | 18,844 | 15,075 | 3769 |
| Non-username enumeration | 17,429 | 13,943 | 3486 |
| Feature Name | Feature Description |
|---|---|
| Time | Packet duration time in seconds |
| Packet Length | The length of the packet in bytes |
| Delta | Time interval between packets in seconds |
| Flags | Flags seen in the packet |
| Total Length | The total length of the packet in bytes |
| Source Port | The source port of the packet |
| Destination Port | The destination port of the packet |
| Classifier | Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Random Forest (RF) | Bootstrap | True |
| Maximum depth | 90 | |
| Maximum features | Auto | |
| Minimum sample leaf | 1 | |
| Minimum sample split | 5 | |
| N estimators | 1600 | |
| Decision Tree (DT) | Criterion | Gini |
| Maximum depth | 50 | |
| Maximum features | Auto | |
| Maximum leaf nodes | 950 | |
| Splitter | Best | |
| Naïve Bayes (NB) | Var._Smoothing | 2.848035868435799 × 10−5 |
| K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) | N | 4 |
| Leaf size | 7 | |
| P | 1 |
| Classifier | Precision | Accuracy | ROC |
|---|---|---|---|
| DT | 99.84 | 99.88 | 0.997 |
| RF | 99.87 | 99.92 | 0.998 |
| NB | 94.85 | 95.70 | 0.994 |
| KNN | 99.95 | 99.93 | 0.999 |
| Classifier | Precision | Accuracy | ROC |
|---|---|---|---|
| DT | 99.97 | 99.93 | 0.998 |
| RF | 99.89 | 99.94 | 0.999 |
| NB | 99.72 | 99.85 | 0.997 |
| KNN | 100 | 99.95 | 1.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agghey, A.Z.; Mwinuka, L.J.; Pandhare, S.M.; Dida, M.A.; Ndibwile, J.D. Detection of Username Enumeration Attack on SSH Protocol: Machine Learning Approach. Symmetry 2021, 13, 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13112192
Agghey AZ, Mwinuka LJ, Pandhare SM, Dida MA, Ndibwile JD. Detection of Username Enumeration Attack on SSH Protocol: Machine Learning Approach. Symmetry. 2021; 13(11):2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13112192
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgghey, Abel Z., Lunodzo J. Mwinuka, Sanket M. Pandhare, Mussa A. Dida, and Jema D. Ndibwile. 2021. "Detection of Username Enumeration Attack on SSH Protocol: Machine Learning Approach" Symmetry 13, no. 11: 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13112192
APA StyleAgghey, A. Z., Mwinuka, L. J., Pandhare, S. M., Dida, M. A., & Ndibwile, J. D. (2021). Detection of Username Enumeration Attack on SSH Protocol: Machine Learning Approach. Symmetry, 13(11), 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13112192







