Abstract
In this article we present a classical potential that respects the Pauli exclusion principle and can be used to describe nucleon-nucleon interactions at intermediate energies. The potential depends on the relative momentum of the colliding nucleons and reduces interactions at low momentum transfer mimicking the Pauli exclusion principle. We use the potential with Metropolis Monte Carlo methods and study the formation of finite nuclei and infinite systems. We find good agreement in terms of the binding energies, radii, and internal nucleon distribution of finite nuclei, and the binding energy in nuclear matter and neutron star matter, as well as the formation of nuclear pastas, and the symmetry energy of neutron star matter.
1. Introduction
1.1. Antecedents
In 1953, Bethe stated [1] that the Nucleon-Nucleon (NN) interaction was the problem most studied in the history of the world, and almost 70 years later the statement is still true. Since the discovery of the neutron by Chadwick in 1932, many experiments, labor and mental works, have been devoted to study the most fundamental problem in nuclear physics, the NN interaction. The goal of describing the atomic-nuclei properties in terms of the interactions between pairs of nucleons is the main objective of nuclear physics, unfortunately, because of the complexity of the quantum mechanical problem, no complete theory has been developed, and progress has been based on approximations.
So far it has been a trade-off; while most researchers have decided to study nuclear systems using mean field methodologies that only respect quantum mechanics approximately, a few others have overlooked some quantum aspects to use classical dynamics that preserves nucleon-nucleon correlations, statistical fluctuations, clusterization phenomena, phase changes, and critical phenomena; all features of the upmost importance in the later stages of fragmentation reactions, and that are not present in the quantum models.
Some of the mean field models are time-dependent Hartree–Fock [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11], hydrodynamics [12], relativistic and non-relativistic mean-field theories [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23], as well as quantum molecular dynamics [24,25,26]. Most of the classical models are based on applications of the molecular dynamics methods on point particles interacting through pair potentials, such as those of references [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35].
To describe nuclear collisions of intermediate-energy of nuclear collisions, classical dynamics has evolved from an initial adaptation of Nordheim’s propagation of individual nucleons in a common mean field plus some residual scattering [36], to an incorporation of nucleon-nucleon potentials [27,29,37,38]. Several pair-potentials have been used extensively to study nuclear reactions [27,28,30,37], infinite nuclear systems as found in neutron star crusts [32,33,34,35,39,40,41,42,43], the isospin dependence of nuclear matter properties [39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46], and the like.
Although this type of classical models contain the entire many-body matrix, all statistical fluctuations and clusterization phenomena, they lack important quantum effects.
1.2. Quantum Caveats
Quantum effects affect the behavior of many body systems on, at least, two fronts: Energy distribution in bound systems and wave mechanics.
From the point of view of the energy, in bound clusters the energy of individual nucleons becomes discrete and the distribution of energy levels is ruled by Fermi–Dirac statistics with the Pauli exclusion principle further regulating the occupation of such levels. Although for high excitation energies the phase space available for nuclei is ample enough to render Pauli blocking practically obsolete [44], at lower energies it is bound to have an impact on the nucleon dynamics prohibiting energy and momentum transfer in some nucleon-nucleon collisions; such a problem is expected to be relevant whenever the number of quantum states available to a nucleon at a given temperature is comparable to the number of nucleons.
A second problem of the validity of the classical approach is connected to the wave nature of the nucleons. Wave mechanics leads to classical mechanics as soon as the distance between particles is larger than their de Broglie wavelengths. This poses a problem when using classical dynamics at high densities, but not at the low sub-saturation densities [44].
Other quantum effects, such as collective excitations, superfluidity, and superconductivity, etc., occur at much lower temperatures and are unlikely to play a major role in the dynamics of medium energy nuclear collisions.
In intermediate-energy heavy-ion collisions, the nuclear systems will first be compressed and heated up to temperatures of several MeV, and then expanded and cooled down as they undergo a phase transition into a liquid-gas mixed phase. Since the first stage occurs at high energies, Pauli blocking is not expected to play a major role in the nucleon-nucleon interactions. In the second stage, however, as the system cools and expands, Pauli exclusion will regulate the final-stage interactions. Likewise, in cold stable nuclei, the occupacy exclusion in energy levels causes nuclei in their ground state to have a non-zero kinetic energy known as Fermi motion.
1.3. Pauli Blocking
To mimic Pauli blocking in classical collisions one must introduce a way to regulate the nucleon-nucleon collisions at low energies and low momentum transfer. A plausible approach to this problem is to introduce a momentum-dependent blocking or repulsion to simulate the Pauli exclusion principle. Such an approach was first taken by Wilets et al. [29], and followed up by Dorso and Randrup, who improved the approximation to the nucleon phase-space distribution. Some other models were based on similar approaches with density-dependent potentials and quasiparticles [47,48].
In the first step, Dorso and Randrup used a momentum-dependent repulsive potential to simulate the Pauli exclusion in a nuclear-like Fermi gas over the temperatures and densities attained in nuclear collisions at intermediate energies [49]. To prevent nucleons identical in spin and isospin getting too close in phase space, a repulsive, momentum-dependent two-body potential was used.
As a next step, a modified Lennard–Jones-like two-body interaction was added to mimic nuclear interactions [30], along with a standard Coulomb repulsion between protons. The resulting model yielded a system with the proper saturation energy and compressibility of nuclear matter over a broad range of temperatures and densities, as well as the proper sizes and binding energies of finite nuclei [50].
Although the potentials of [50] were very promising in simulating the Pauli exclusion principle and endowing classical models with a realistic ground-state Fermi motion, the models lack a proper nucleon-nucleon repulsion. Specifically, the model allowed the formation of dineutron structures that are not to be expected, despite the short time period during a collision.
Thus the motivation of this study: To develop a model that maintains the advantages of classical models but, at the same time, respects the Pauli exclusion principle while preventing the formation of nonphysical states. The structure of the article is as follows: Section 2 presents the new potential introducing its various components. This is followed by applications to model the finite nuclei in Section 3, and infinite systems in Section 4. The model is then used to obtain the symmetry energy of neutron star matter in Section 5. A discussion of the results in Section 6 closes the article.
2. The Model
To mimic the Pauli exclusion principle, we designed potentials following the procedure of Dorso and Randrup [49]. In a nutshell, a dimensionless distance in phase space was defined as , where, for any pair of nucleons i and j, , and , and with the parameters and determining the size of the effectively excluded volume around each particle in phase space, and adjusted such that the uncertainty relation, , is satisfied.
Modifying the Dorso and Randrup potential by trial and error we arrived at:
where the scale factors are MeV, MeV/c, and fm, and fm is a cut-off distance. In our case we find that , very close to the uncertainty relation, and in agreement with the expectation that the product be slightly smaller than due to geometric considerations [49].
Furthermore, the present potential improves over the Dorso and Randrup potential by forbidding the formation of di-neutrons. Notice that the added modulating term imposes a repulsive force between equal nucleons at short values of p and r, basically forbidding their interaction. This repulsion ceases for values of , i.e., the potential is truncated at . Also notice that for and , the potential becomes . The potential (1) generates a kinetic energy (i.e., a “Fermi energy”) that is in agreement with the results obtained by Dorso and Randrup in [49]. Figure 1 shows the potential for the case of zero momentum transfer, .
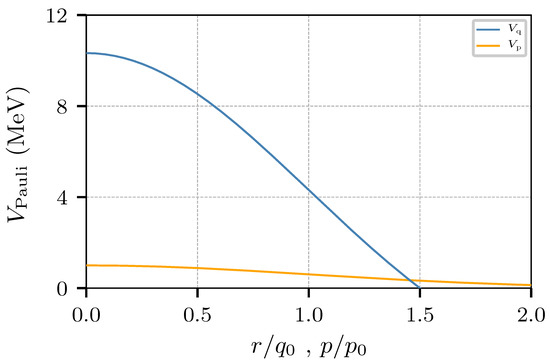
Figure 1.
The upper blue line corresponds to the spatial factor of the Pauli potential, , plotted as a function of r in units of fm; notice the truncation at fm. The lower orange curve is the exponential reduction imposed by the momentum dependent factor, , as it goes from to .
The next step is to incorporate a potential to describe the nuclear force. For the interaction potential between two nucleons, we use:
And for the Coulomb potential, we use the point-charge repulsion:
The parameters of the nuclear potential are MeV, MeV, and fm, and the rest were estimated based on the experimental value of the nuclear binding energy of the nucleus:
where a is the radius of an particle, fm, and is twice the proton radius, fm. The compressibility () yields the condition , which, for MeV, and compressibility MeV, is satisfied by and . The terms , , and are the values of their respective accompanying terms at to make the potentials smoothly go to zero and avoid the extraneous force that an abrupt cutoff at would produce. For , e is the elementary electric charge, and thus MeV fm, and fm.
3. Finite Nuclei
The model created with the potentials (1)–(3), can be used to construct finite nuclei. Since the potentials are not separable, symplectic integrators of the equations of motion cannot guarantee the conservation of certain quantities, such as the energy, and the behavior of such systems is best calculated using Metropolis-Monte Carlo methods (MMC); see Appendix A for a synoptic review of the method.
Nuclei were prepared by caging nucleons in a potential well. The systems were then cooled down employing an MMC procedure, until reaching the “ground state” (say, T = 0.01 MeV), where they were kept in thermal equilibrium through a heat bath.
Figure 2 shows the radii obtained for several nuclear-like clusters bound with the potentials (1)–(3), calculated with a Metropolis-Monte Carlo method [51], and compared to the experimental values of the radii. The radii were computed as the r.m.s value of the nucleons positions in the ground state. The curve corresponds to the best fit of the radii as a function of (see caption for details).
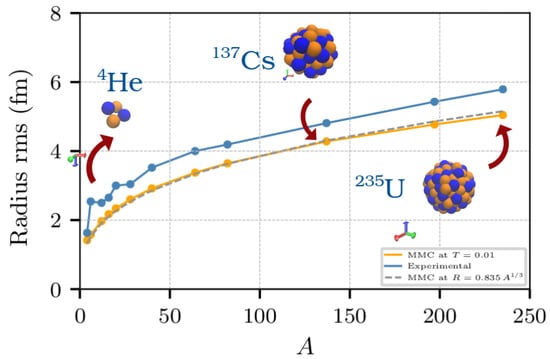
Figure 2.
Radius of nuclei at the ground state (T = 0.01 MeV). The bottom orange dots corresponds to the MMC simulation. The data points in blue correspond to commonly accepted experimental values. The dashed curve in gray is a least square fit of the MMC data of the type , where c is 0.835.
Likewise, Figure 3 shows the binding energy per nucleon obtained for the nuclei of Figure 2. Although the trend follows the same trajectory of the experimental values, the simulated nuclei are about 50% over-bound, close to the results of the Simple Semi-classical Potential of Horowitz and coworkers [33], see Figure 2 in [52] for a comparison with other models.
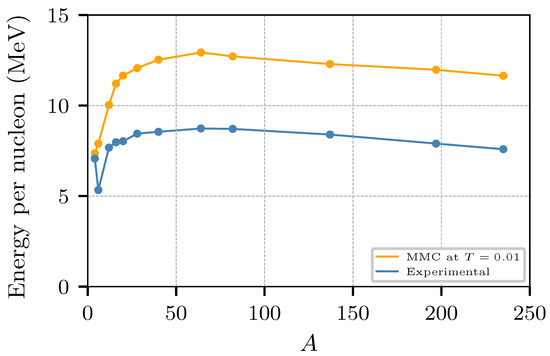
Figure 3.
Binding energy obtained for the nuclei of Figure 2.
To get an idea of the internal structure of the clusters, Figure 4 shows the average distance between nucleons for several nuclei in the ground state (at MeV). Also shown in the insets, is the un-normalized pair correlation function for , , and of and .
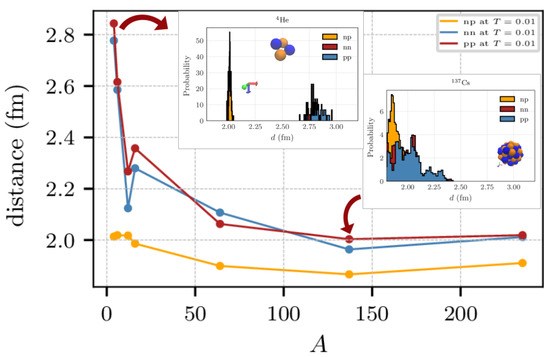
Figure 4.
Average distance between the nuclei of Figure 2. The insets show the un-normalized probability of finding a nucleon at a distance d, for the pairs , , and in the nuclei and .
4. Infinite Nuclear Matter
The model presented by Equations (1) and (2), can also be used to construct infinite systems; notice that the Coulomb interaction, Equation (3), is excluded. This is achieved by placing a large number of nucleons in a cubic cell with 26 replicas surrounding the central cell. Once again, utilizing the MMC method, systems of varying density and isotopic content can be constructed at specific temperatures, and used to determine, e.g., energy-density isotherms, pasta-like structures (at low temperatures), and the corresponding symmetry energy. Infinite systems can be constructed without and with an embedding electron gas, which are known as nuclear matter and neutron star matter, respectively.
4.1. Nuclear Matter
Systems composed solely of uncharged protons (otherwise the system is thermodynamically stable) and neutrons are known as nuclear matter. Figure 5 shows the energy per nucleon obtained for nuclear matter systems constructed with 1000 nucleons with equal number of protons and neutrons (with their corresponding spin), for temperatures ranging from T = 0.01 MeV to 1.0 MeV. The minimum of the peculiar “∪” shape corresponds to the saturation density, which is observed to be close to fm−3 for σ = 1.625 fm in Equation (2). The flattening of the energy-density isotherms at sub-saturation densities indicates a departure from the liquid-like phase that exists around saturation density to a mixed liquid-gas phase; at MeV the state corresponds to a frozen medium, and to a pasta structure at low densities.
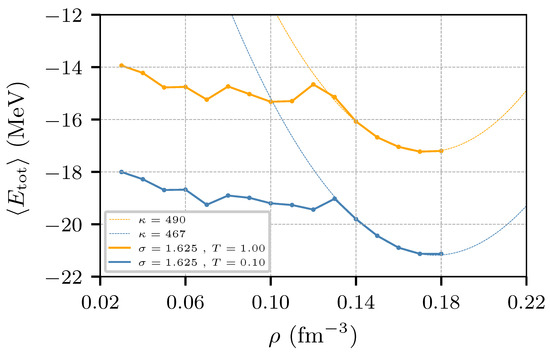
Figure 5.
Average energy per nucleon as a function of the density for nuclear matter at and MeV. The systems were constructed with 500 protons and 500 neutrons. The dashed lines correspond to quadratic fittings of the energies in the density range = 0.13–0.18 fm−3. The estimates of the compressibility can be seen in the legend.
The plot of the energy per nucleon as a function of the temperature can indicate changes of phase. Figure 6 shows how the energy per nucleon of a system at a fixed density varies with the temperature. The systems shown were constructed with 5832 nucleons with equal numbers of protons and neutrons and with densities in the range 0.04 to 0.14 fm−3. Notice that the system with ρ = 0.12 fm experiences a sharp change around T ≈ 1.5 MeV, denoting a change of phase at that density; previous studies with other potentials [31] connect these discontinuities with a liquid-to-solid change of phase.
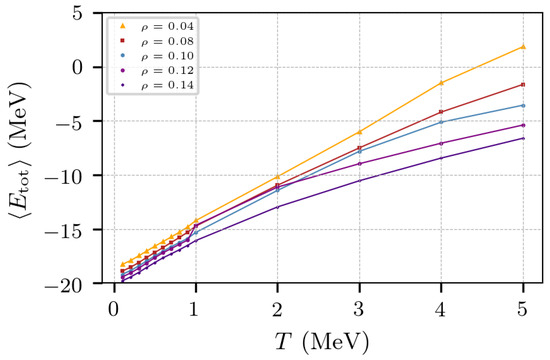
Figure 6.
Average energy per nucleon as a function of the temperature for nuclear matter.
Pastas of Nuclear Matter
Nuclear “pastas” are spatial arrangement of protons and neutrons, theorized to exist in neutron star crusts [53], in which the structures reach a free energy minima. These energy minima have been determined using static methods such as the liquid drop model [53,54], mean field theories [55], Thomas–Fermi models [56], or dynamically with quantum molecular dynamics [57,58,59] and classical potential models [31,33,39,40,60,61].
Using the present model, structures of nuclear matter with 1000 nucleons were found at sub-saturation densities and a low temperature ( MeV), see Figure 7. Structures at 0.14 and 0.12 fm−3 depict continuous liquid-like arrangements, while that at 0.08 fm−3 show pasta-like structures. Figure 8 shows the structure obtained with 5832 nucleons, equal number of protons and neutrons, at 0.04 fm−3 and T = 0.8 MeV; the structure on the left shows the simulation cell and its replicas.
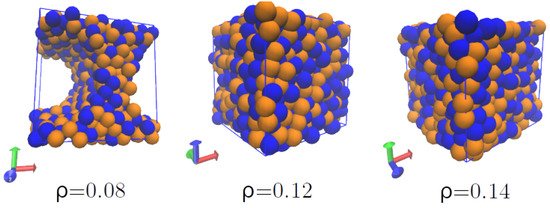
Figure 7.
Structures produced in nuclear matter at densities 0.08, 0.12, and 0.16 fm−3 and MeV. Pseudo-pastas form at sub-saturation densities.
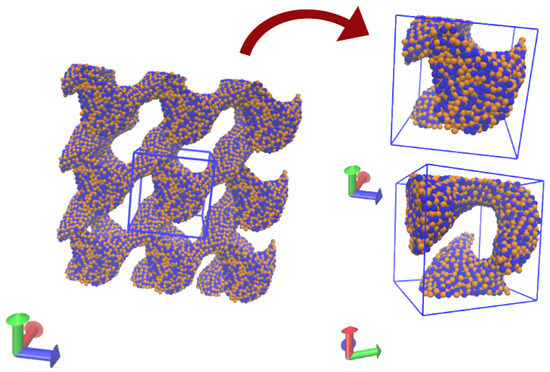
Figure 8.
Structure produced in nuclear matter at a density of 0.04 fm−3 and MeV. The snapshot on the left shows the simulation cell and its images. Detailed snapshots of the simulation cell can be seen on the right.
4.2. Neutron Star Matter
Similarly, the model can be used to study a medium generically known as “Neutron Star Matter”. It should be noted that crusts of neutron stars, i.e., the outermost layer of about 1 km of depth, are composed of neutrons, protons, and electrons with a varying ratio of protons and neutrons; here we study this type of systems with different ratios without claiming that they exist in actual neutron stars. The medium is governed by means of Equations (1) and (2), and an all embedding electron gas.
The electron cloud introduces a screening effect on the Coulomb potential of the protons, which in turn modifies the pasta structures. Such screening between the protons and the electron gas can be treated by means of a Thomas–Fermi screening potential of the form , with a screening length and . The effect of the screening on the formation of the pasta has been studied extensively [31,41,60], the value we use, fm, was found to be the minimal length at which the effects of the finite cell size are eliminated and the pasta morphology stabilizes and ceases to depend on . Likewise, the cutoff distance, , is set to the value of the screening length, fm.
Figure 9 shows the energy per nucleon as a function of the density for an isospin symmetric system with 5832 nucleons (see caption for details). The dashed lines correspond to the a quadratic fit of data between fm−3 and fm−3. The resulting compressibility for neutron star matter turns out to be MeV and MeV (not to be confused with that for nuclear matter which is about 288 MeV).
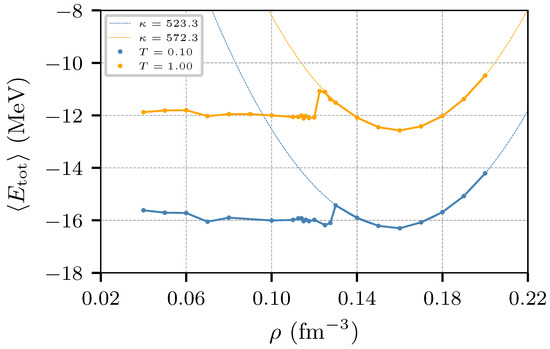
Figure 9.
Average energy per nucleon as a function of the density for neutron star matter. The dashed lines correspond to the fitting of data ( 0.13–0.19 fm−3) into a quadratic function. The estimates of the compressibility are shown in the legend.
Figure 10 shows the energy per nucleon as a function of the temperature for values of the density between 0.04–0.14 fm−3, for a system with 5832 nucleons with equal numbers of protons and neutrons (with the corresponding spins). Notice that the energy at fm−3 experiences a sharp change around T ≈ 1.5 MeV, denoting a change of phase. It should be remarked that, at a difference from molecular dynamics calculations, MMC calculations do not explore the energy landscape profusely, and arrive at configurations of minimum energy that correspond to meta-stable liquid states which, at slightly lighter densities drop in internal energy corresponding to non-uniform states; these changes appear as sudden drops in the plots at around 0.13 fm−3, and tend to diminish for 0.1 MeV, and are less noticeable in nuclear matter (cf. Figure 5).
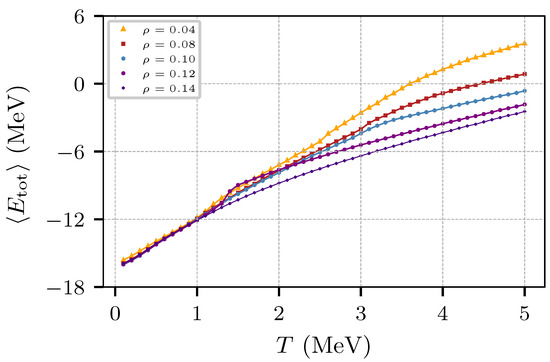
Figure 10.
Average energy per nucleon as a function of the temperature for neutron star matter.
The behavior of E can be examined in terms of the kinetic and potential energies. Figure 11 and Figure 12 show, respectively, the kinetic and potential components of the energy of Figure 10 as a function of the temperature. While the potential energy does not show a significant change at around T ≈ 1.5 MeV, the kinetic energy does show a change in the slope for low densities, especially for ρ = 0.12 fm−3. Figure 11 also shows that the potential energy changes its trend at T ≈ 3 MeV, presumably due to the Pauli potential at low and high momentum transfer.
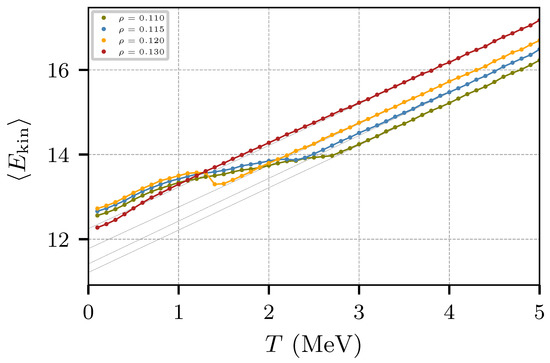
Figure 11.
Average kinetic energy per nucleon as a function of the temperature for neutron star matter.
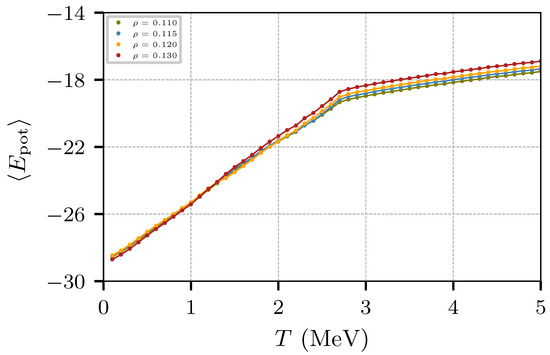
Figure 12.
Average potential energy per nucleon as a function of the temperature for neutron star matter.
To visualize changes in the internal structure we recur to the Kolmogorov statistic, which computes the discrepancy between the sampled spatial distribution of the nucleons and a uniform distribution. This statistic, plotted in Figure 13, shows changes at MeV for densities 0.11 fm−3 ≲ ρ ≲ 0.12 fm−3, denoting the changes from uniformity to pasta-like structures at low densities, but not at 0.13 fm−3.
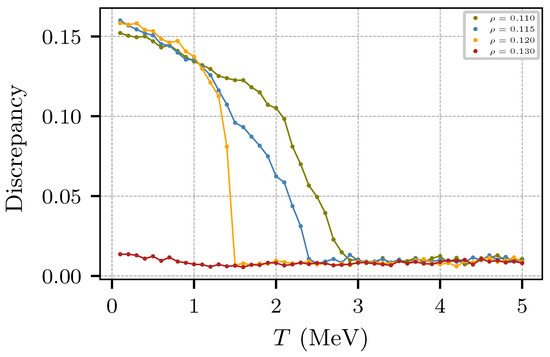
Figure 13.
Kolmogorov statistic illustrating the departures from uniformity.
Figure 14 depicts better the phenomenon by plotting the “net” kinetic energy, after subtracting the linear contribution in Figure 11 (shown in gray). The sharp slopes in Figure 14 correlate with sharp topological changes in the system, as can be noticed from successive snapshots around T ≈ 1.4 MeV (see Figure 15).
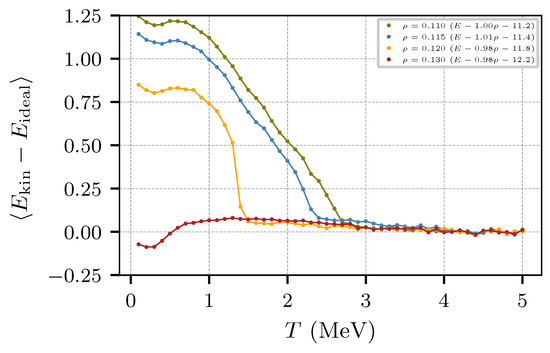
Figure 14.
Kinetic energy in excess, as expressed in the legend.
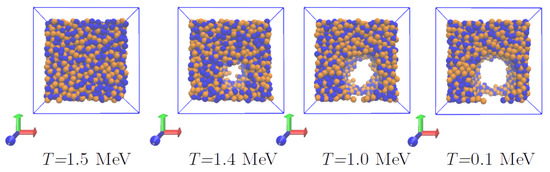
Figure 15.
Snapshots of the simulation cell for 0 ≤ z < 20 fm. The density is ρ = 0.12 fm−3.
The divergence from uniformity can also be seen in Figure 15, which shows the structures formed in systems with ρ = 0.12 fm−3, with a “bubble” appearing in the simulation cell appearing at MeV.
Pastas of Neutron Star Matter
The structures of neutron star matter at low temperatures are shown in Figure 16. Again, the structures appear homogeneous at 0.16 fm−3, while the first bubble can be seen at 0.12 fm−3. At 0.08 fm−3 a “pasta-like” structure is formed. Examining the low density region more closely, Figure 17 shows the pseudo-pasta structures obtained at 0.04, 0.08, and 0.10 fm−3 for a system with 2916 protons and 2916 neutrons.
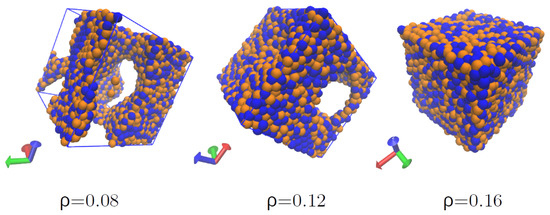
Figure 16.
Structures formed in neutron star matter at densities 0.08, 0.12, and 0.16 fm−3 and MeV. The system has equal number of protons and neutrons (5832 total nucleons). Notice the formation of pasta-like structures at sub-saturation densities.
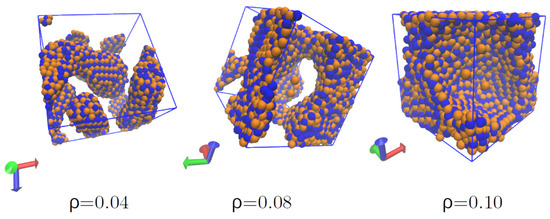
Figure 17.
Pasta structures formed in neutron star matter at densities 0.04, 0.08, and 0.10 fm−3 and MeV for a 5832-nucleon system with a similar number of neutrons and protons.
Figure 18 shows two structures of neutron star matter obtained with 1944 protons and 3888 neutrons (), at a temperature of 0.1 MeV and 0.04 and 0.08 fm−3; to clarify the structures, the position of the protons is also presented.
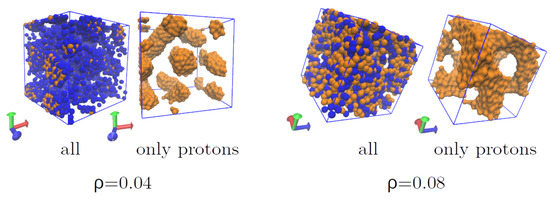
Figure 18.
Pasta structures formed in isospin asymmetric neutron star matter at densities and 0.08 fm−3 and MeV for a 5832-nucleon system with 30% of protons and the remainder as neutrons.
5. Symmetry Energy
The nuclear symmetry energy became a topic of intense investigations when radioactive beam facilities began to study nuclei away from the stability valley; understanding isospin asymmetric nuclear matter is needed in areas of nuclear physics and astrophysics [22].
In 1935, Weizsäcker introduced an asymmetry term in a parametrization of the nuclear binding energy to provide favorable binding to those nuclei with a similar number of protons than neutrons [62]. Such a term was later modified to include the role of isospin in a generalized density-dependent asymmetry term [63]. For the case of microscopic models, the symmetry energy can be evaluated numerically following the procedure outlined in Appendix A, and introduced in [44,64], see also [31].
To calculate the symmetry energy it is necessary to know the energy per nucleon at various densities and temperatures, and for various values of the isospin asymmetry, x. Figure 19 shows the behavior of the energy per nucleon as a function of x for temperatures 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 MeV, and densities 0.04, 0.06, 0.08, and 0.10 fm−3.
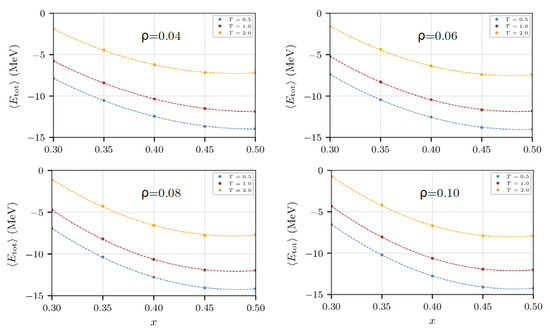
Figure 19.
Energy per nucleon as a function of x for 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 MeV, and 0.04, 0.06, 0.08, and 0.10 fm−3.
Following the procedure of [31,44,64] (cf. Appendix B), one can compute the symmetry energy both of nuclear matter and of neutron star matter. Figure 20 shows the variation of with the temperature for four sub-saturation densities.
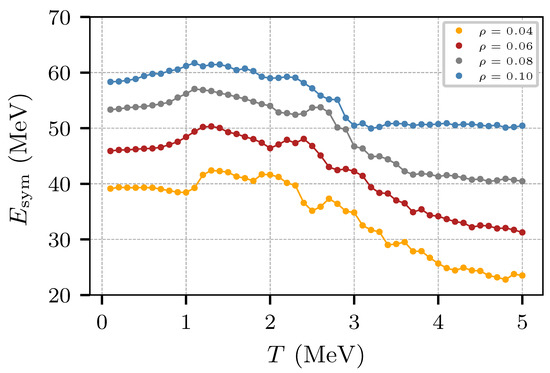
Figure 20.
Symmetry energy as a function of T, and for 0.04, 0.06, 0.08, and 0.10 fm−3.
The behavior of for neutron star matter is reminiscent to that obtained with molecular dynamics with the “new medium” potential for nuclear matter. Relatively constant values of are observed at temperatures below 2.0 MeV, corresponding to the pasta regime, and with smaller values at higher temperatures corresponding to more uniform systems. See [31,38] for a related analysis.
The observed values of , namely, ranging between 20 MeV and 50 MeV, are reminiscent of previous results obtained with microscopic field theories, see e.g., [23]. Similarly, the trend of , decreasing for larger temperatures, is similar to the behavior found using an equation of state obtained through a virial expansion at , 4, and 8 MeV [65], and through a self-consistent model using various effective interactions [66]. Comparing these results with previous computations of the symmetry energy obtained with classical potentials, e.g., those of Figure 68b of [31], we can see a major change in the behavior of at low temperatures; surely due to the effect of the repulsion introduced at low momentum transfer.
6. Discussion
In this article we presented a nucleon-nucleon potential whose strength depends on the relative momenta of the colliding nucleons and, thus, has the ability to reduce interactions at low momentum transfer mimicking the Pauli exclusion principle.
Comparing to previous attempts at introducing Pauli blocking to a classical potential, we improved on the best attempt (i.e., that of Dorso and Randrup from 1987 [49]) by constructing a potential that respects an excluded volume in phase space, respects the uncertainty relation, and inhibits the production of di-neutrons.
As a first test, the potential was used with Metropolis Monte Carlo simulations to study the formation of finite nuclei, their binding energies, radii, and internal nucleon distribution. It was also used to study the binding energy in infinite systems such as nuclear matter and neutron star matter, as well as the structures formed at sub-saturation densities and cold temperatures, known as nuclear pastas. Finally, the symmetry energy was also obtained for the case of neutron star matter.
In general terms, the potential functioned as expected in most areas reproducing binding energy and radii trends of finite nuclei. The saturation density and compressibility of infinite systems were observed near the expected values. Pasta structures were observed to appear at low temperatures and sub-saturation densities. Finally, the magnitude and trends of the symmetry energy were in the ball park predicted by mean field theories.
An observed weakness of the potential is the over-binding found in the synthetic nuclei (cf. Figure 3). By inspecting the radii of the nuclei in Figure 2, and the distance between nucleons in Figure 4, it is easy to see that the model produces nuclei that are too tight, with nucleons closer to one another more than expected, which leads to over-binding. Since the over-binding and smaller radii are a problem of finite nuclei, we do not expect that they will affect the results of infinite systems, vis-à-vis the pasta structures and symmetry energy as they are obtained from systems with fixed densities.
Ongoing investigations are addressing these problems, especially as future studies will concentrate on using finite nuclei in collisions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.O.D. and G.F.; methodology, C.O.D. and G.F.; software, C.O.D. and G.F.; validation, C.O.D., G.F. and J.A.L.; formal analysis, C.O.D., G.F. and J.A.L.; investigation, C.O.D., G.F. and J.A.L.; resources, C.O.D. and G.F.; data curation, G.F.; writing—original draft preparation, J.A.L.; writing—review and editing, C.O.D., G.F. and J.A.L.; visualization, G.F.; supervision, C.O.D.; project administration, C.O.D.; funding acquisition, C.O.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
C.O.D. received support from the Carrera de Investigador CONICET, by CONICET grants PIP0871, PIP 2015-2017 GI, founding D4247(22 December 2016), and Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), Grant Number PICT 1692.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Metropolis Monte Carlo
The simulations were performed by means of the Metropolis Monte Carlo procedure. It consists essentially on building an appropriate Markov chain by sampling the configurational space. The system was assumed to be in thermal equilibrium with an external heat bath, and thus, the sampled energy states were those of the canonical ensemble.
The nucleons were first placed at the vertices of a cubic lattice, in order to avoid overlapping. The momenta were further set to random with a vanishing mean value. Then, the system was driven to the thermal equilibrium following the same procedure as in the simulation stage (see below), but fixing the thermal bath at T = 5 MeV. The thermalization required 1000 steps, that is, 1000 times the degrees of freedom of the system to arrive to equilibrium.
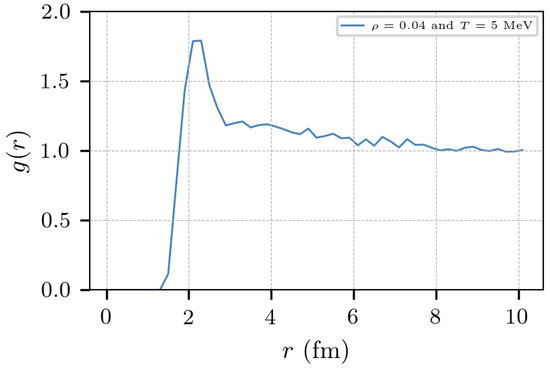
Figure A1.
Radial pair distribution for nuclear matter at fm−3 and 5 MeV.
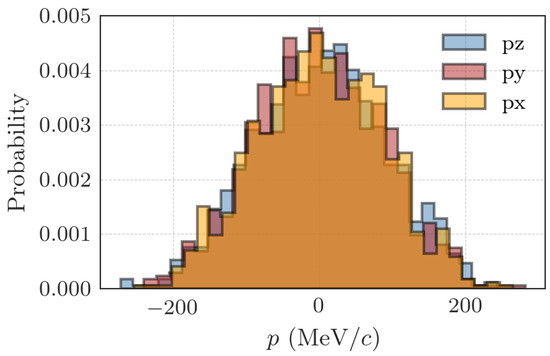
Figure A2.
Momentum distribution for nuclear matter at fm−3 and 5 MeV.
The equilibrium temperature, MeV, was warm enough to mimic a liquid state. This can be verified through the radial pair distribution and the distribution of the components of the momentum; Figure A1 and Figure A2 show the radial distribution function and the momentum distribution, respectively, for the case of ρ = 0.04 fm−3 with 1000 nucleons. All the simulations ran over 1000 nucleons for nuclear matter and 6000 for neutron star matter.
The simulation stage was as follows: At each step, any nucleon was selected randomly, and either moved to a new position, or changed its momentum. This yields an energy jump . Such an energy jump corresponds to the following transition probability in the canonical ensemble.
where (K meaning Boltzmann constant and T is the associated bath temperature). Thus, accepting the transition with probability p attains the right samples for the canonical space.
The above “trials” alternate between the positions and momenta of randomly selected particles. The fraction of accepted trials commonly lies in the interval 0.35–0.75. A control mechanism was implemented to keep this fraction between these limits. The controlling magnitudes were the degree of the perturbation of the positions and momenta. The final Markov chain was afterward sub-sampled, in order to get non-correlated observables.
Appendix B. Symmetry Energy
The excess of neutrons to protons in nuclear systems affects the nuclear equation of state through the symmetry energy, ; its importance in topics ranging from nuclear structure to astrophysical processes is the subject of intense investigations [22].
The symmetry energy is defined as:
with . The symmetry energy can be evaluated with data obtained from the MMC calculations using a procedure introduced before [44,64].
Using the MMC results of the internal energy , it is possible to construct a continuous function by fitting for each T and with an expression of the type:
The dependence of the coefficients , , , can be easily extracted from the MMC data assuming an dependence of the type:
for , 1, 2, and 3; odd terms in are not included to respect the isospin symmetry of the strong force (without the Coulomb potential). With this, the symmetry energy is then given by:
with the coefficients given by the fitting procedure.
It is important to mention that the mechanism to extract from MMC data is sensitive to the type of data used. For instance, for neutron star matter the odd terms in are maintained, and depending on the density region, some of the fits may require higher order terms in ; see [31] for more general details.
References
- Bethe, H.A. What holds the nucleus together? Sci. Am. 1953, 189, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, S.E. Time-dependent Hartree-Fock calculations for/sup 16/O+/sup 16/O reactions. Phys. Lett. B 1976, 61, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrych, S.; Mauther, H. Relativistic structure of the nucleon self-energy in asymmetric nuclei. Phys. Rev. C 1997, 56, 1788–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dalen, E.N.E.; Fuchs, C.; Faessler, A. The relativistic Dirac–Brueckner approach to asymmetric nuclear matter. Nucl. Phys. A 2004, 741, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Y.; Rong, J.; Chen, B.Q.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Song, H.Q. Isospin dependence of nucleon effective mass in Dirac Brueckner–Hartree–Fock approach. Phys. Lett. B 2004, 604, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sammarruca, F.; Barredo, W.; Krastev, P. Predicting the single-proton and single-neutron potentials in asymmetric nuclear matter. Phys. Rev. C 2005, 71, 064306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dalen, E.N.E.; Fuchs, C.; Faessler, A. Effective nucleon masses in symmetric and asymmetric nuclear matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 022302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dalen, E.N.E.; Fuchs, C.; Faessler, A. Momentum, density, and isospin dependence of symmetric and asymmetric nuclear matter properties. Phys. Rev. C 2005, 72, 065803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.; Ma, Z.Y.; Giai, N.V. Isospin-dependent optical potentials in Dirac-Brueckner-Hartree-Fock approach. Phys. Rev. C 2006, 73, 014614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombaci, I.; Lombardo, U. Asymmetric nuclear matter equation of state. Phys. Rev. C 1991, 44, 1892–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, W.; Cao, L.G.; Li, B.A.; Lombardo, U.; Shen, C.W. Isospin splitting of the nucleon mean field. Phys. Rev. C 2005, 72, 014005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.T.R.; Sierk, A.J.; Nix, J.R. Effect of viscosity on the dynamics of fission. Phys. Rev. C 1976, 13, 2385–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, V.; Colonna, M.; Greco, V.; Toro, M.D. Reaction dynamics with exotic nuclei. Phys. Rep. 2005, 410, 335–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, C.B.; Gupta, S.D.; Gale, C.; Li, B.A. Momentum dependence of symmetry potential in asymmetric nuclear matter for transport model calculations. Phys. Rev. C 2003, 67, 034611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.A.; Das, C.B.; Gupta, S.D.; Gale, C. Momentum dependence of the symmetry potential and nuclear reactions induced by neutron-rich nuclei at RIA. Phys. Rev. C 2004, 69, 011603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.A.; Das, C.B.; Gupta, S.D.; Gale, C. Effects of momentum-dependent symmetry potential on heavy-ion collisions induced by neutron-rich nuclei. Nucl. Phys. A 2004, 735, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.A. Constraining the neutron-proton effective mass splitting in neutron-rich matter. Phys. Rev. C 2004, 69, 064602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.W.; Ko, C.M.; Li, B.A. Effects of momentum-dependent nuclear potential on two-nucleon correlation functions and light cluster production in intermediate energy heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. C 2004, 69, 054606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, J.; Colonna, M.; Toro, M.D.; Greco, V. Transport properties of isospin effective mass splitting. Nucl. Phys. A 2004, 732, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.; Routray, T.R.; Pradhan, A.; Patra, S.K.; Sahu, P.K. Momentum and density dependence of the isospin part of nuclear mean field and equation of state of asymmetric nuclear matter. Nucl. Phys. A 2005, 753, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, J.; Colonna, M.; Toro, M.D. Fast nucleon emission as a probe of the momentum dependence of the symmetry potential. Phys. Rev. C 2005, 72, 064609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.A.; Chen, L.W.; Ko, C.M. Recent progress and new challenges in isospin physics with heavy-ion reactions. Phys. Rep. 2008, 464, 113–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.W.; Ko, C.M.; Li, B.A. Isospin-dependent properties of asymmetric nuclear matter in relativistic mean field models. Phys. Rev. C 2007, 76, 054316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichelin, J. “Quantum” molecular dynamics—A dynamical microscopic n-body approach to investigate fragment formation and the nuclear equation of state in heavy ion collisions. Phys. Rept. 1991, 202, 233–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A. Antisymmetrized molecular dynamics with quantum branching processes for collisions of heavy nuclei. Phys. Rev. C 1999, 59, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.; Horiuchi, H. Antisymmetrized molecular dynamics for heavy ion collisions. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. A 2004, 53, 501–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.A.; Lübeck, G. Nuclear spinodal decomposition. Phys. Lett. B 1989, 219, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilets, L.; Henley, E.M.; Kraft, M.; Mackellar, A.D. Classical many-body model for heavy-ion collisions incorporating the Pauli principle. Nucl. Phys. A 1977, 282, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilets, L.; Yariv, Y.; Chestnut, R. Classical many-body model for heavy-ion collisions (II). Nucl. Phys. A 1978, 301, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorso, C.; Randrup, J. Classical simulation of nuclear systems. Phys. Lett. B 1988, 215, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- López, J.; Dorso, C.O.; Frank, G. Properties of nuclear pastas. Front. Phys. 2021, 16, 24301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, C.J.; Pérez-García, M.A.; Piekarewicz, J. Neutrino-“pasta” scattering: The opacity of nonuniform neutron-rich matter. Phys. Rev. C 2004, 69, 045804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, C.J.; Pérez-García, M.A.; Carriere, J.; Berry, D.K.; Piekarewicz, J. Nonuniform neutron-rich matter and coherent neutrino scattering. Phys. Rev. C 2004, 70, 065806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, C.J.; Pérez-García, M.A.; Berry, D.K.; Piekarewicz, J. Dynamical response of the nuclear “pasta” in neutron star crusts. Phys. Rev. C 2005, 72, 035801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekarewicz, J.; Sánchez, G.T. Proton fraction in the inner neutron-star crust. Phys. Rev. C 2012, 85, 015807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordheim, L.W. Transport phenomena in Einstein-Bose and fermi-dirac gases. Proc. R. Soc. 1928, 119, 689. [Google Scholar]
- Lenk, R.J.; Schlagel, T.J.; Pandharipande, V.R. Accuracy of the Vlasov-Nordheim approximation in the classical limit. Phys. Rev. C 1990, 42, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorso, C.O.; Frank, G.; López, J.A. Phase transitions and symmetry energy in nuclear pasta. Nucl. Phys. A 2018, 978, 35–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorso, C.O.; Molinelli, P.A.G.; López, J.A. From nuclei to nuclear pasta. In Neutron Star Crust; Bertulani, C.A., Piekarewicz, J., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 151–169. [Google Scholar]
- Dorso, C.O.; Molinelli, P.A.G.; López, J.A. Topological characterization of neutron star crusts. Phys. Rev. C 2012, 86, 055805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.A.; Ramírez-Homs, E. Effect of an electron gas on a neutron-rich nuclear pasta. Nuc. Sci. Tech. 2015, 26, S20502. [Google Scholar]
- Dorso, C.O.; Frank, G.; López, J.A. Symmetry energy in neutron star matter. Nucl. Phys. A 2019, 984, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinelli, P.A.G.; Nichols, J.I.; López, J.A.; Dorso, C.O. Simulations of cold nuclear matter at sub-saturation densities. Nucl. Phys. A 2014, 923, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.A.; Ramírez-Homs, E.; González, R.; Ravelo, R. Isospin-asymmetric nuclear matter. Phys. Rev. C 2014, 89, 024611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorso, C.O.; Molinelli, P.A.; López, J.A. Isoscaling and the nuclear EoS. J. Phys. G Nucl. Part. Phys. 2011, 38, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.A.; Terrazas, A.G.; Porras, S.T. Isospin-dependent phase diagram of nuclear matter. Nucl. Phys. A 2020, 994, 121664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boal, D.H.; Glosli, J.N. From binary breakup to multifragmentation: Computer simulation. Phys. Rev. C 1988, 37, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boal, D.H.; Glosli, J.N. Quasiparticle model for nuclear dynamics studies: Ground-state properties. Phys. Rev. C 1988, 38, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorso, C.O.; Duarte, S.; Randrup, J. Classical simulation of the Fermi gas. Phys. Lett. B 1987, 188, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dorso, C.O.; Randrup, J. Early recognition of clusters in molecular dynamics. Phys. Lett. B 1993, 301, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metropolis, N.; Rosenbluth, A.W.; Rosenbluth, M.N.; Teller, A.H.; Teller, E. Equation of state calculations by fast computing machines. J. Chem. Phys. 1953, 21, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcain, P.N.; Dorso, C.O. Dynamics of fragment formation in neutron-rich matter. Phys. Rev. C 2018, 97, 015803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravenhall, D.G.; Pethick, C.J.; Wilson, J.R. Structure of matter below nuclear saturation density. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 50, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Seki, H.; Yamada, M. Shape of nuclei in the crust of neutron star. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1984, 71, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, D.; Lattimer, J.M.; Prakash, M.; Steiner, A.W. Minimal cooling of neutron stars: A new paradigm. Strophys. J. Supp. 2004, 155, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.D.; Koonin, S.E. Sub-saturation phases of nuclear matter. Nucl. Phys. A 1985, 435, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Niita, K.; Oyamatsu, K.; Maruyama, T.; Chiba, S.; Iwamoto, A. Quantum molecular dynamics approach to the nuclear matter below the saturation density. Phys. Rev. C 1998, 57, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, T.; Maruyama, T.; Niita, K.; Chiba, S. MD simulation study for nuclear matter. Nucl. Phys. A 2000, 663–664, 877c–880c. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, G.; Sato, K.; Yasuoka, K.; Ebisuzaki, T. Microscopic study of slablike and rodlike nuclei: Quantum molecular dynamics approach. Phys. Rev. C 2002, 66, 012801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcain, P.N.; Molinelli, P.A.G.; Dorso, C.O. Beyond nuclear “pasta”: Phase transitions and neutrino opacity of new “pasta” phases. Phys. Rev. C 2014, 90, 065803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcain, P.N.; Molinelli, P.A.G.; Nichols, J.I.; Dorso, C.O. Effect of Coulomb screening length on nuclear “pasta” simulations. Phys. Rev. C 2014, 89, 055801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Weizsäcker, C.F. Zur theorie der kernmassen. Z. Physik 1935, 96, 431–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, M.B.; Zhang, Y.; Danielewicz, P.; Famiano, M.; Li, Z.; Lynch, W.G.; Steiner, A.W. Constraints on the density dependence of the symmetry energy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 122701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, J.A.; Porras, S.T. Symmetry energy in the liquid–gas mixture. Nucl. Phys. A 2017, 957, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, C.J.; Schwenk, A. Cluster formation and the virial equation of state of low-density nuclear matter. Nucl. Phys. A 2006, 776, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, L.W.; Li, B.A.; Ma, H.R. Temperature effects on the nuclear symmetry energy and symmetry free energy with an isospin and momentum dependent interaction. Phys. Rev. C 2007, 75, 014607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).