A Novel Extension of the TOPSIS Method Adapted for the Use of Single-Valued Neutrosophic Sets and Hamming Distance for E-Commerce Development Strategies Selection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
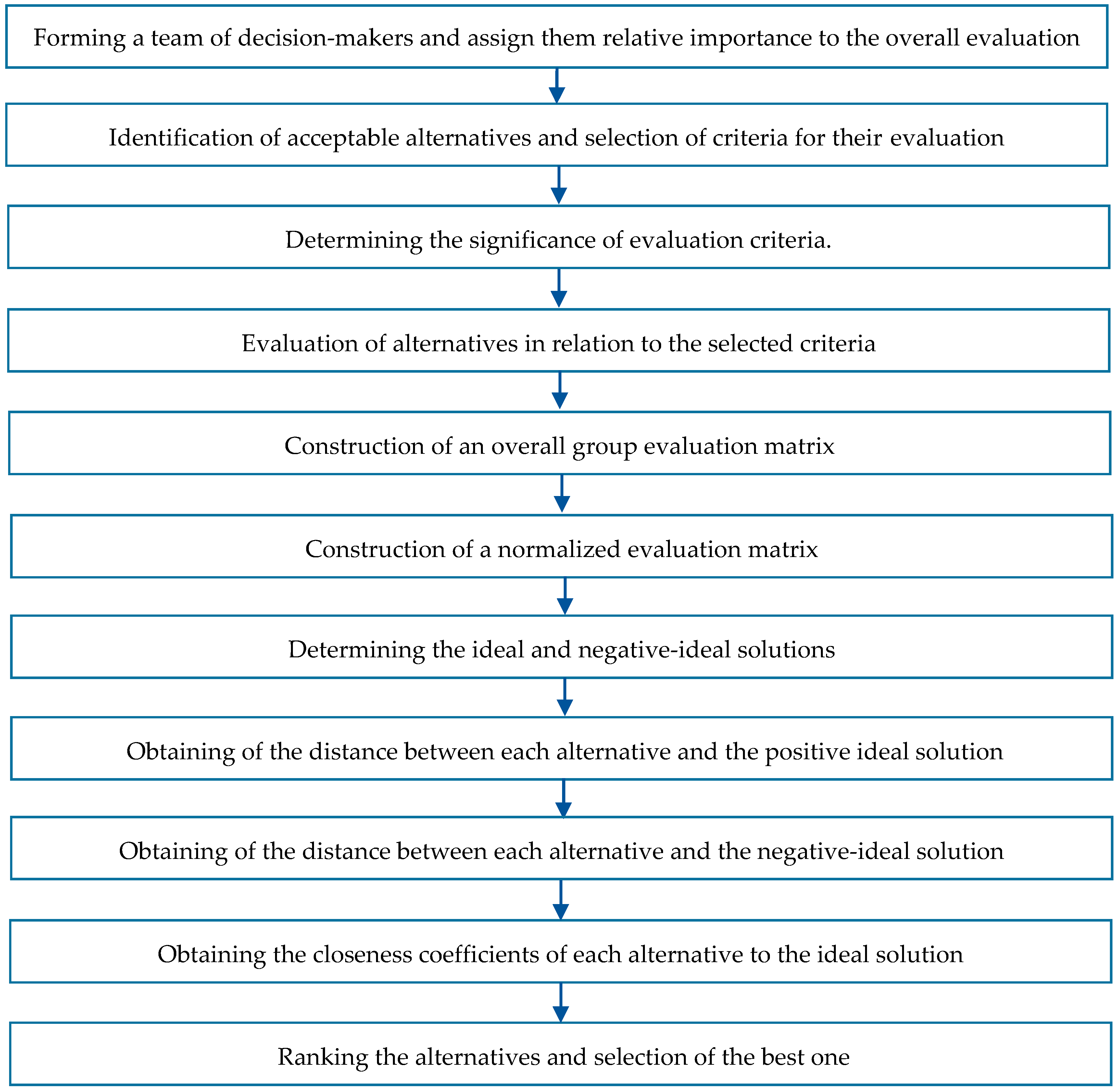
3. The TOPSIS Method Customized to the Use of SVNNs and Group Decision-Making
3.1. The TOPSIS Method
3.2. An Extension of the TOPSIS Method Adapted for the Use of SVNNs
4. A Numerical Illustration
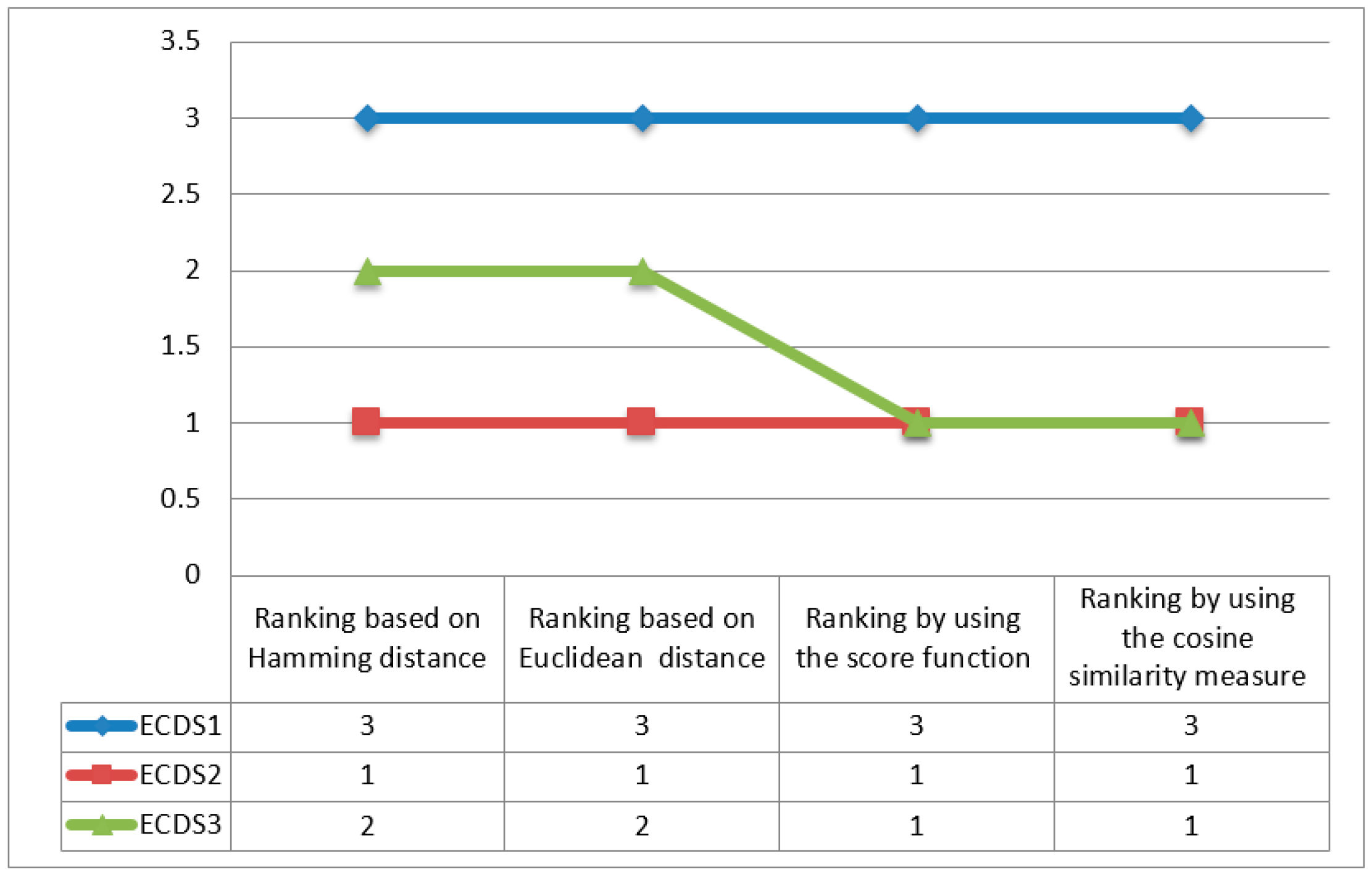
5. Discussion and Comparison Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magnusson, D.; Hermelin, B. ICT development from the perspective of connectivity and inclusion—The operation of a local digital agenda in Sweden. Nor. Geogr. Tidsskr. Nor. J. Geogr. 2019, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, K.W.; Håkansson, F. Strategical Use of ICT in Microenterprises: A Case Study. Int. J. E Entrep. Innov. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nica, E. ICT innovation, internet sustainability, and economic development. J. Self Gov. Manag. Econ. 2015, 3, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Chaffey, D.; Hemphill, T.; Edmundson-Bird, D. Digital Business and E-Commerce Management; Pearson: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, S.; Sergi, B.S.; Esposito, M. Literature review of emerging trends and future directions of e-commerce in global business landscape. World Rev. Entrep. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 15, 226–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudon, K.C.; Traver, C.G. E-Commerce: Business, Technology, Society; Pearson: Essex, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, N.; Hight, S.; Wei, W.; Ozturk, A.B.; Zhao, X.R.; Nusair, K.; DeFranco, A. The power of e-commerce. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 31, 1906–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.; Whittington, R.; Scholes, K.; Angwin, D.N.; Regnér, P. Exploring Strategy, 11th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, F.M.; Tuzovic, S.; Braun, C. Trustmarks: Strategies for exploiting their full potential in e-commerce. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 62, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćurčić, N.; Piljan, I.; Simonović, Z. Marketing concept in insurance companies. Ekonomika 2019, 65, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauković Jocić, K.; Jocić, G.; Karabašević, D.; Popović, G.; Stanujkić, D.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Thanh Nguyen, P. A Novel Integrated PIPRECIA—Interval-Valued Triangular Fuzzy ARAS Model: E-Learning Course Selection. Symmetry 2020, 12, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, M.; Pamucar, D. Evaluation of Iranian household appliance industries using MCDM models. Oper. Res. Eng. Sci. Theory Appl. 2019, 2, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabašević, D.; Maksimović, M.; Stanujkić, D.; Brzaković, P.; Brzaković, M. The evaluation of websites in the textile industry by applying ISO/IEC 91264-standard and the EDAS method. Ind. Text. 2018, 69, 4894. [Google Scholar]
- Fazlollahtabar, H.; Smailbašić, A.; Stević, Ž. FUCOM method in group decision-making: Selection of forklift in a warehouse. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 2019, 2, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabasević, D.; Stanujkić, D.; Maksimović, M.; Popović, G.; Momčilović, O. An Approach to Evaluating the Quality of Websites Based on the Weighted Sum Preferred Levels of Performances Method. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2019, 16, 195–215. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, B. The outranking approach and the foundation of ELECTRE methods. Theory Decis. 1991, 31, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brans, J.P.; Vincke, P. Note—A Preference Ranking Organisation Method: (The PROMETHEE Method for Multiple Criteria Decision-Making). Manag. Sci. 1985, 31, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.L.; Yoon, K. Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Kaklauskas, A.; Sarka, V. The new method of multicriteria complex proportional assessment of projects. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 1994, 1, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Opricović, S. Multicriteria Optimization of Civil Engineering Systems; Faculty of Civil Engineering: Belgrade, Serbia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Brauers, W.K.M.; Zavadskas, E.K. The MOORA method and its application to privatization in a transition economy. Control Cybern. 2006, 35, 445–469. [Google Scholar]
- Brauers, W.K.M.; Zavadskas, E.K. Project management by MULTIMOORA as an instrument for transition economies. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2010, 16, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, C.; Yeoh, W.; Lee, A.; Moayedikia, A. Deciding discipline, course and university through TOPSIS. Stud. High. Educ. 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, B.M.; Godoy, L.P.; Campos, L.M. Performance evaluation of green suppliers using entropy-TOPSIS-F. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, F.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Streimikiene, D.; Mardani, A. Assessment of concentrated solar power (CSP) technologies based on a modified intuitionistic fuzzy topsis and trigonometric entropy weights. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 140, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, P.K.; Lau, H.Y. Hotel selection using a modified TOPSIS-based decision support algorithm. Decis. Support Syst. 2019, 120, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, Y.A.; Tan, Q.; Mirjat, N.H.; Ali, S. Evaluating the strategies for sustainable energy planning in Pakistan: An integrated SWOT-AHP and Fuzzy-TOPSIS approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Barua, M.K. Supplier selection among SMEs on the basis of their green innovation ability using BWM and fuzzy TOPSIS. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 152, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efe, B. Website Evaluation Using Interval Type-2 Fuzzy-Number-Based TOPSIS Approach. In Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Models for Website Evaluation; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 166–185. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.M.; Elhag, T.M. Fuzzy TOPSIS method based on alpha level sets with an application to bridge risk assessment. Expert Syst. Appl. 2006, 31, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulsalam, K.; Ighravwe, D.; Babatunde, M. A fuzzy-TOPSIS approach for techno-economic viability of lighting energy efficiency measure in public building projects. J. Proj. Manag. 2018, 3, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, H.R.; Nekooie, M.A. An improved hierarchical fuzzy TOPSIS approach to identify endangered earthquake-induced buildings. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 76, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemenis, A.; Askounis, D. A new TOPSIS-based multi-criteria approach to personnel selection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4999–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, X.; Liu, X.; Qin, J. An analytical solution to fuzzy TOPSIS and its application in personnel selection for knowledge-intensive enterprise. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 30, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanlioglu, F.; Taskaya, Y.E.; Gulen, U.C.; Cokcan, O. A fuzzy AHP–TOPSIS-based group decision-making approach to IT personnel selection. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 20, 1576–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemenis, A.; Ergazakis, K.; Askounis, D. Support managers’ selection using an extension of fuzzy TOPSIS. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 2774–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarandache, F. Neutrosophy, Neutrosophic Probability, Set and Logic; American Res. Press: Rehoboth, DE, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Mohamed, M. A novel and powerful framework based on neutrosophic sets to aid patients with cancer. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 98, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Gamal, A.; Manogaran, G.; Long, H.V. A novel group decision making model based on neutrosophic sets for heart disease diagnosis. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Mohamed, M.; Elhoseny, M.; Chiclana, F.; Zaied AE, N.H. Cosine similarity measures of bipolar neutrosophic set for diagnosis of bipolar disorder diseases. Artif. Intell. Med. 2019, 101, 101735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulucay, V.; Kılıç, A.; Şahin, M.; Deniz, H. A new hybrid distance-based similarity measure for refined neutrosophic sets and its application in medical diagnosis. Matematika 2019, 35, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratihar, J.; Kumar, R.; Dey, A.; Broumi, S. Transportation problem in neutrosophic environment. In Neutrosophic Graph Theory and Algorithms; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 180–212. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P. Exploring public transport sustainability with neutrosophic logic. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2019, 42, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhassouny, A.; Idbrahim, S.; Smarandache, F. Machine learning in Neutrosophic Environment: A Survey. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 2019, 28, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaparthasarathy, G.; Little Flower, V.F.; Dasan, M.A. Neutrosophic Supra Topological Applications in Data Mining Process. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 2019, 27, 80–97. [Google Scholar]
- Sengur, A.; Budak, U.; Akbulut, Y.; Karabatak, M.; Tanyildizi, E. A survey on neutrosophic medical image segmentation. In Neutrosophic Set in Medical Image Analysis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 145–165. [Google Scholar]
- Tuan, T.M.; Chuan, P.M.; Ali, M.; Ngan, T.T.; Mittal, M. Fuzzy and neutrosophic modeling for link prediction in social networks. Evol. Syst. 2019, 10, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, C.; Otay, İ. Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Using Neutrosophic Sets; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Wu, L.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, H. Multi-criteria decision making method based on the single valued neutrosophic sets. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 37, 2403–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Ji, P.; Wang, J.Q.; Chen, X.H. An improved weighted correlation coefficient based on integrated weight for interval neutrosophic sets and its application in multi-criteria decision-making problems. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2015, 8, 1027–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.J.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, X.H. An outranking approach for multi-criteria decision-making problems with simplified neutrosophic sets. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 25, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarandache, F. A Unifying Field in Logics. Neutrosophy: Neutrosophic Probability, Set and Logic; American Research Press: Rehoboth, DE, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Smarandache, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sunderraman, R. Single valued neutrosophic sets. Rev. Air Force Acad. 2010, 1, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, R. Multi-criteria neutrosophic decision making method based on score and accuracy functions under neutrosophic environment. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1412.5202. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J. Multicriteria decision-making method using the correlation coefficient under single-valued neutrosophic environment. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2013, 42, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Lin, J.J.; Linc, J.H.; Chiang, M.C. Domestic open-end equity mutual fund performance evaluation using extended TOPSIS method with different distance approaches. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4642–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanian, A.; Savadogo, O. TOPSIS multiple-criteria decision support analysis for material selection of metallic bipolar plates for polymer electrolyte fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2006, 159, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.S.; Singh, S.R. An improved-based TOPSIS method in interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Life Cycle Reliab. Saf. Eng. 2018, 7, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadikhah, M. Using the Hamming distance to extend TOPSIS in a fuzzy environment. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2009, 231, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Tsao, C.Y. The interval-valued fuzzy TOPSIS method and experimental analysis. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2008, 159, 1410–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Hung, C.C. Multiple-attribute decision making methods for plant layout design problem. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2007, 23, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broumi, S.; Ye, J.; Smarandache, F. An extended TOPSIS method for multiple attribute decision making based on interval neutrosophic uncertain linguistic variables. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 2015, 8, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Elhassouny, A.; Smarandache, F. Neutrosophic-simplified-TOPSIS multi-criteria decision-making using combined simplified-TOPSIS method and neutrosophics. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 2468–2474. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, V.; Shocker, A.D. Linear programming techniques for multidimensional analysis of preferences. Psychometrika 1973, 38, 337–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersuliene, V.; Turskis, Z. Integrated fuzzy multiple criteria decision making model for architect selection. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2011, 17, 645–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamucar, D.; Stevic, Z.; Sremac, S. A new model for determining weight coefficients of criteria in MCDM models: Full consistency method (FUCOM). Symmetry 2018, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanujkić, D.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Karabašević, D.; Smarandache, F.; Turskis, Z. The use of Pivot Pair-wise Relative Criteria Importance Assessment method for determining weights of criteria. Rom. J. Econ. Forecast. 2017, 20, 116–133. [Google Scholar]
- Stanujkić, D.; Karabašević, D.; Maksimović, M.; Popović, G.; Brzaković, M. Evaluation of the e-commerce development strategies. Quaestus 2019, 1, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, A.; Mela, C.F. E-customization. J. Mark. Res. 2003, 40, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajli, M. A research framework for social commerce adoption. Inf. Manag. Comput. Secur. 2013, 21, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, R. Optimal search engine marketing strategy. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2005, 10, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Alternatives | Designation |
|---|---|
| A1—E-customization and personalization—Ansari & Mela [70] | ECDS1 |
| A2—Social E-commerce adoption model—Hajli [71] | ECDS2 |
| A3—Strong search engine optimization (SEO)—Sen [72] | ECDS3 |
| Criteria | Designation |
|---|---|
| C1—Feasibility of the strategy | FS |
| C2—Implementation speed | IS |
| C3—Compliance with the corporate strategy | CS |
| C4—Compliance of the strategy with the mission and vision of the company | MV |
| C5—General acceptance | GA |
| FS | IS | CS | MV | GA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECDS1 | <0.6, 0.1, 0.1> | <0.6, 0.1, 0.1> | <0.6, 0.1, 0.1> | <0.4, 0.1, 0.1> | <0.4, 0.1, 0.1> |
| ECDS2 | <1.0, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.8, 0.0, 0.0> | <1.0, 0.1, 0.1> | <1.0, 0.1, 0.3> | <1.0, 0.0, 0.1> |
| ECDS3 | <0.6, 0.0, 0.2> | <0.6, 0.2, 0.1> | <0.8, 0.2, 0.1> | <1.0, 0.2, 0.3> | <1.0, 0.0, 0.2> |
| FS | IS | CS | MV | GA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECDS1 | <0.5, 0.0, 0.1> | <0.7, 0.1, 0.1> | <0.5, 0.0, 0.1> | <0.4, 0.1, 0.1> | <0.4, 0.0, 0.1> |
| ECDS2 | <0.9, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.7, 0.1, 0.0> | <0.9, 0.0, 0.0> | <1.0, 0.0, 0.1> | <0.7, 0.0, 0.2> |
| ECDS3 | <0.7, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.6, 0.1, 0.1> | <0.8, 0.1, 0.2> | <0.9, 0.1, 0.3> | <0.8, 0.0, 0.2> |
| FS | IS | CS | MV | GA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECDS1 | <0.5, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.8, 0.1, 0.1> | <0.6, 0.0, 0.1> | <0.5, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.5, 0.1, 0.1> |
| ECDS2 | <0.8, 0.0, 0.1> | <0.7, 0.0, 0.0> | <1.0, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.9, 0.0, 0.1> | <0.6, 0.0, 0.1> |
| ECDS3 | <0.8, 0.1, 0.1> | <0.7, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.8, 0.0, 0.1> | <0.9, 0.1, 0.2> | <0.8, 0.0, 0.0> |
| FS | IS | CS | MV | GA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECDS1 | <0.5, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.7, 0.1, 0.1> | <0.6, 0.0, 0.1> | <0.4, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.4, 0.0, 0.1> |
| ECDS2 | <1.0, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.7, 0.0, 0.0> | <1.0, 0.0, 0.0> | <1.0, 0.0, 0.1> | <1.0, 0.0, 0.1> |
| ECDS3 | <0.7, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.6, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.8, 0.0, 0.1> | <1.0, 0.1, 0.3> | <1.0, 0.0, 0.0> |
| FS | IS | CS | MV | GA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECDS+ | <1.0, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.7, 0.0, 0.0> | <1.0, 0.0, 0.0> | <1.0, 0.0, 0.0> | <1.0, 0.0, 0.0> |
| ECDS− | <0.5, 0.0, 0.0> | <0.6, 0.1, 0.1> | <0.6, 0.0, 0.1> | <0.4, 0.1, 0.3> | <0.4, 0.0, 0.1> |
| Rank | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECDS1 | 0.87 | 0.69 | 0.44 | 3 |
| ECDS2 | 0.38 | 1.08 | 0.74 | 1 |
| ECDS3 | 0.63 | 0.66 | 0.51 | 2 |
| Rank | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECDS1 | 3.38 | 3.24 | 0.490 | 3 |
| ECDS2 | 1.70 | 4.25 | 0.714 | 1 |
| ECDS3 | 2.60 | 2.54 | 0.495 | 2 |
| w1 | w2 | w3 | w4 | w5 | Σwj | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 1.00 |
| W2 | 0.15 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 1.00 |
| W3 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 1.00 |
| W4 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 1.00 |
| W5 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.40 | 1.00 |
| W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Rank | Rank | Rank | Rank | ||||||
| ECDS1 | 0.45 | 3 | 0.51 | 2 | 0.44 | 3 | 0.39 | 3 | 0.43 | 3 |
| ECDS2 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.70 | 1 | 0.72 | 1 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.78 | 1 |
| ECDS3 | 0.50 | 2 | 0.43 | 3 | 0.54 | 2 | 0.59 | 2 | 0.49 | 2 |
| W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Rank | Rank | Rank | Rank | ||||||
| ECDS1 | 0.49 | 3 | 0.56 | 2 | 0.48 | 3 | 0.44 | 3 | 0.48 | 2 |
| ECDS2 | 0.72 | 1 | 0.67 | 1 | 0.70 | 1 | 0.73 | 1 | 0.76 | 1 |
| ECDS3 | 0.50 | 2 | 0.41 | 3 | 0.54 | 2 | 0.57 | 2 | 0.46 | 3 |
| Overall Ratings | Score | Rank | Cosine | Rank | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECDS1 | <0.55, 0.00, 0.00> | 0.78 | 3 | 0.55 | 3 |
| ECDS2 | <1.00, 0.00, 0.00> | 1.00 | 1 | 1.00 | 1 |
| ECDS3 | <1.00, 0.00, 0.00> | 1.00 | 1 | 1.00 | 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karabašević, D.; Stanujkić, D.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Stanimirović, P.; Popović, G.; Predić, B.; Ulutaş, A. A Novel Extension of the TOPSIS Method Adapted for the Use of Single-Valued Neutrosophic Sets and Hamming Distance for E-Commerce Development Strategies Selection. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12081263
Karabašević D, Stanujkić D, Zavadskas EK, Stanimirović P, Popović G, Predić B, Ulutaş A. A Novel Extension of the TOPSIS Method Adapted for the Use of Single-Valued Neutrosophic Sets and Hamming Distance for E-Commerce Development Strategies Selection. Symmetry. 2020; 12(8):1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12081263
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarabašević, Darjan, Dragiša Stanujkić, Edmundas Kazimieras Zavadskas, Predrag Stanimirović, Gabrijela Popović, Bratislav Predić, and Alptekin Ulutaş. 2020. "A Novel Extension of the TOPSIS Method Adapted for the Use of Single-Valued Neutrosophic Sets and Hamming Distance for E-Commerce Development Strategies Selection" Symmetry 12, no. 8: 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12081263
APA StyleKarabašević, D., Stanujkić, D., Zavadskas, E. K., Stanimirović, P., Popović, G., Predić, B., & Ulutaş, A. (2020). A Novel Extension of the TOPSIS Method Adapted for the Use of Single-Valued Neutrosophic Sets and Hamming Distance for E-Commerce Development Strategies Selection. Symmetry, 12(8), 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12081263










