Abstract
Neutrosophic sets have been recognized as an effective approach in solving complex decision-making (DM) problems, mainly when such problems are related to uncertainties, as published in numerous articles thus far. The use of the three membership functions that can be used to express accuracy, inaccuracy, and indeterminacy during the evaluation of alternatives in multiple-criteria DM can be said to be a significant advantage of these sets. By utilizing these membership functions, neutrosophic sets provide an efficient and flexible approach to the evaluation of alternatives, even if DM problems are related to uncertainty and predictions. On the other hand, the TOPSIS method is a prominent multiple-criteria decision-making method used so far to solve numerous decision-making problems, and many extensions of the TOPSIS method are proposed to enable the use of different types of fuzzy as well as neutrosophic sets. Therefore, a novel extension of the TOPSIS method adapted for the use of single-valued neutrosophic sets was considered in this paper.
1. Introduction
As one of the essential elements of the modern world economy and the increasing use of advanced information and communication technology (ICT), technological changes have driven fundamental changes in the economic and social environments, thereby transforming society from the industrial into the information age [1]. The increasing use of ICT has significantly changed the way we live, learn, and work, transforming the direction of the interaction of people, business systems, and public institutions. The development of information technologies, and in particular, the advancement of Internet technologies, enables existing businesses to progress and the opening of new businesses, leading to the growth of e-business and the digital economy [2,3].
The Internet has contributed to the extremely dynamic development of e-commerce within e-business. In its simplest sense, e-commerce implies the purchase and sale of goods or services online as well as advertising revenue. Without the Internet, e-commerce would be virtually non-existent. Therefore, e-commerce includes all activities of buying and selling products and services that are performed via the Internet or other electronic communication channels [4]. First of all, e-commerce consists of distributing, buying, selling, marketing, and servicing products and services through the Internet. It also incorporates electronic money transfer, supply chain management, e-marketing, electronic data exchange, and automated data collection systems [5]. Over time, e-commerce has transformed from a mechanism for online retail sales into something much broader [6]. This is why it is of great importance which e-commerce strategy the company will choose to implement [7]. The selection of an optimal strategy is vital because the strategy defines the future direction and actions of the organization or part of the organization [8]. Developing an e-commerce strategy requires combining existing approaches to business and developing an information systems strategy. In order to achieve a competitive advantage, it is crucial to join innovative techniques in traditional strategic approaches [9]. The implementation of an adequate strategy may help the company to achieve and maintain its competitive advantage in the long run [10].
Many of the real problems are often characterized by a number of mostly antagonistic criteria. Multiple-criteria decision-making (MCDM) is a notable part of operational research. It considers the issues in which we are faced with a greater number of, most often conflicting, criteria when making a decision [11,12,13]. The extraordinarily rapid and dynamic development of MCDM worldwide has contributed to a number of MCDM methods and techniques proposed by scholars to solve a wide variety of problems [14,15]. Some of the prominent methods that are most applied are the AHP method (Analytic hierarchy process) [16], the ELECTRE method (Elimination et choix traduisant la realité) [17], the PROMETHEE method (Preference ranking organization method for enrichment evaluations) [18], the TOPSIS method (Technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution) [19], the COPRAS method (Complex proportional assessment of alternatives) [20], the VIKOR method (Visekriterijumska optimizacija i kompromisno resenje) [21], the MOORA method (Multi-objective optimization on basis of ratio analysis) [22], the MULTIMOORA method (Multi-objective optimization by ratio analysis plus the full multiplicative form) [23], and so on.
Hwang and Yoon [19] develop the TOPSIS method (Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution). To solve a broader range of problems when problems are related to uncertainties, ambiguities, and vagueness, the TOPSIS method has a proper extension based on the application of fuzzy, intuitionistic, grey, and neutrosophic numbers to be able to cope with these problems. To date, the TOPSIS method has been applied to solving many cases, often in combination with other techniques, some of which are as follows: the application of TOPSIS when deciding on a discipline, course, and university [24]; the application of entropy TOPSIS-F for the performance assessment of green suppliers [25]; the evaluation of solar power technologies based on the application of the intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS [26]; hotel evaluation and selection based on the modified TOPSIS decision support algorithm [27]; the evaluation of the sustainable energy planning strategies based on the SWOT-AHP method and Fuzzy TOPSIS method [28]; supplier evaluation and selection based on the green innovation ability based on the BWM and fuzzy TOPSIS [29]; website assessment by employing the interval type-2 fuzzy number TOPSIS approach [30]; assessment in civil engineering [31,32,33]; evaluation and selection of personnel [34,35,36,37]; and so on.
Neutrosophic sets were established by Smarandache [38] to deal with complex DM problems related to uncertainties, which are followed by inconsistent and indeterminate information. The use of the three membership functions in order to express accuracy, indeterminacy, and inaccuracy during the evaluation of alternatives in MCDM can be said to be a very important and significant advantage of neutrosophic sets. So far, neutrosophic sets have been utilized in different fields such as medical analysis [39,40,41,42], transport [43,44], information and communication technology [45,46,47], MCDM [48,49,50,51,52], and so forth.
Therefore, a novel extension of the TOPSIS method adapted for the application of single-valued neutrosophic sets is the subject matter of consideration in this manuscript. The applicability and usability of the developed single-valued neutrosophic TOPSIS extension are demonstrated on a numerical illustration of the evaluation and selection of e-commerce development strategies. For all of the preceding reasons, the remainder of the manuscript is based on the following global organization of sections. The preliminaries are presented in Section 2; in Section 3, the TOPSIS method customized to the use of single-valued neutrosophic numbers (SVNNs) and group decision-making is presented; Section 4 contains a presentation of the numerical clarification, whereas Section 5 presents a discussion and a comparison analysis. Finally, concluding remarks are specified at the end of the manuscript.
2. Preliminaries
In this part of the manuscript, some fundamental definitions and notations of neutrosophic sets (NS), single-valued neutrosophic set (SVNS), and single-valued neutrosophic numbers (SVNN) are given.
Definition 1.
[53] Let X denote the universe of discourse. The NS A in X has the following form
wheredenotes the truth–membership function;;denotes the falsity-membership function;; anddenotes the falsity–membership function,.
These membership functions must satisfy the following constraint.
Definition 2.
[54] Let X be a nonempty set. The SVNS A in X has the following form
wheremembership functions TA, IA, and FAand satisfy the following constraint.
Definition 3.
[54]
A SVNNis a special case of a SVNS on the set of real numbers ℜ, whereand.
Definition 4.
[53] Letbe a SVNN and λ > 0. The multiplication SVNNs and λ are as follows:
Definition 5.
Let X = (x1, x2, ..., xn) and Y = (y1, y2, ..., yn) be two n-dimensional vectors,and. The Hamming distance between X and Y is defined as
Definition 6.
Let X = (x1, x2, ..., xn ) and Y = (y1, y2, ..., yn) be two n-dimensional vectors,and. The Euclidean distance between X and Y is defined as
Definition 7.
[55] Letbe a SVNN. The score function s of x is defined as
where .
Definition 8.
[56] Letbe a SVNN. The cosine similarity measure of x is the expression
Definition 9.
[55] Letbe a collection of SVNSs andbe an associated weighting vector. The Single-Valued Neutrosophic Weighted Average (SVNWA) operator of aj is
where wj is the element j of the weighting vector,and.
3. The TOPSIS Method Customized to the Use of SVNNs and Group Decision-Making
3.1. The TOPSIS Method
The TOPSIS method, originated by Hwang and Yoon [19], is a very prominent and frequently used MCDM method. Compared to other MCDM methods, this method has a characteristic approach to determine the most acceptable alternative and is based upon the concept that an alternative is defined on the basis of the shortest distance to the ideal solution and the longest distance to the anti-ideal solution. The relative distance Ci of the ith alternative to the ideal and anti-ideal solutions is calculated as
where and denote the distance of the alternative i from the ideal and anti-ideal solutions, respectively, and .
The distance of each alternative from the ideal and anti-ideal solutions are computed as follows:
and
In Equations (10) and (11), denotes the weight of the criterion j; and denote the coordinate j of the ideal and anti-ideal solutions, respectively; and is the normalized rating of the alternative i to the criterion j.
The ordinary TOPSIS method utilizes the Euclidean distance to determine the separation measures. However, some authors such as Chang et al. [57], Shanian and Savadogo [58], and Hwang and Yoon [19], have also considered the application of the Hamming distance for that purpose:
In the numerous extensions of the TOPSIS method that were later proposed, the application of the Hamming distance has become more common such as in the research of Gautam and Singh [59], Izadikhah [60], and Chen and Tsao [61].
The ordinary TOPSIS method uses the vector normalization procedure for the calculation of normalized ratings, as
where is the normalized rating of the alternative i to the criterion j, and is the rating of the alternative i to the criterion j.
In some extensions of the TOPSIS method, however, this normalization procedure is followed with a simpler normalization procedure [31,62], as follows:
In Equation (15), it is assumed that denotes the largest rating of the criterion j.
The ideal and the anti-ideal solutions are defined by
where denotes the coordinate j of the ideal solution; denotes the coordinate j of the anti-ideal solution; and and denote the sets of beneficial and non-beneficial criteria, respectively.
3.2. An Extension of the TOPSIS Method Adapted for the Use of SVNNs
The typical MCDM problem that includes m alternatives and n criteria can concisely be presented in the following matrix form:
The entry xij in the evaluation matrix D means the rating of the alternative i with respect to the criterion j and entries wj in W of the weight vector denote the weights of the criterion j, for each i = 1, … m and j = 1, ..., n.
However, many practical DM problems require the participation of more decision-makers or experts in the evaluation process. Therefore, in multiple-criteria group decision-making (MCGDM), there is more than one decision-making matrix
where denotes an evaluation matrix formed by the decision-maker and/or expert k; is the rating of the alternative i with respect to the criterion j obtained from the decision-maker and/or expert k; and K denotes the number of decision-makers and/or experts.
In the MCGDM process, decision-makers and/or experts often have different experiences and/or specific knowledge of the problem that has to be solved, which is why another weighting vector can be used to express the impact of the decision-makers and/or experts on the final evaluation, namely as follows:
The value is the significance or impact of the decision-maker and/or expert k on the overall evaluation.
Using the weighting vector that expresses the impact of decision-makers on the overall evaluation, the individual evaluation matrix obtained from the decision-makers and/or experts, and a sort of aggregation operator, an overall group decision-making matrix can be constructed.
Taking into consideration the foregoing facts pertaining to the MCGDM, the specifics of SVNNs and operations over them as well as the previously proposed extension of the TOPSIS method [54,63,64], a thorough step-by-step procedure of the adapted TOPSIS method, as shown in Figure 1, can be accurately presented through the following basic steps:
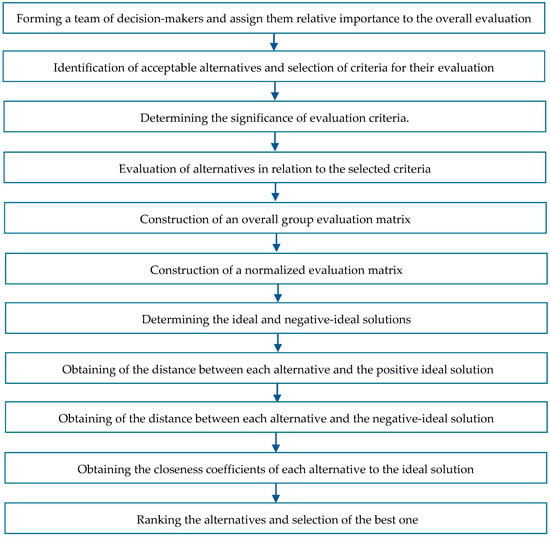
Figure 1.
Computational procedure of the adapted TOPSIS method.
Step 1. Forming a team of decision-makers and assigning them relative importance to the overall evaluation. In the first step, a team of decision-makers and/or experts is formed and relative importance is assigned to each of them, if necessary. In many cases, all decision-makers and/or experts have equal importance to the final evaluation.
Step 2. Identification of acceptable alternatives and selection of criteria for their evaluation. In the second step, the team of decision-makers identified the feasible alternatives and determined a set of evaluation criteria.
Step 3. Determining the significance of evaluation criteria. In this step, the team of decision-makers and/or experts determined the weights of the evaluation criteria. A number of methods that can be used to determine criteria weights have been considered in many papers published in scientific and professional journals [16,65,66,67,68].
Step 4. Evaluation of alternatives in relation to the selected criteria. In the fourth step, each decision-maker performs an evaluation and forms their own evaluation matrix, in which the ratings are expressed by using SVNNs. As a result of performing this step, a K evaluation matrix is formed as follows:
where denotes the rating of the alternative i with respect to the criterion j, obtained from the decision-maker expert k.
Step 5. Construction of an overall group evaluation matrix. In this step, the individual attitudes of the decision-makers involved in the evaluation are transformed into one overall group evaluation matrix by using a SVNWA operator (i.e., by applying Equation (8)). As a result of performing this step, a matrix of the following form is formed:
where denotes the rating of the alternative i in relation to the criterion j.
Step 6. Construction of a normalized evaluation matrix. The normalization of the overall group evaluation matrix can be performed by applying Equation (3) and the following λ:
This step is not necessary if all ratings belong to the interval [0, 1].
Step 7. Determining the ideal and negative-ideal solutions. In the case when all evaluation criteria are beneficial, the ideal and negative ideal solutions are calculated as follows:
Step 8. Obtaining the distance between each alternative and the positive ideal solution. The distances between the alternatives and the positive ideal solution can be determined by applying Equations (4) or (5).
Step 9. Obtaining the distance between each alternative and the negative-ideal solution. The distances between the alternatives and the negative ideal solution can be determined in a similar manner as the distances to the ideal solution.
Step 10. Obtaining the closeness coefficients of each alternative to the ideal solution. Applying Equations (4) and (5), SVNNs are transformed into the resulting crisp values, thus allowing the application of Equation (9) to determine the closeness coefficients to the ideal solution, as in the ordinary TOPSIS method.
Step 11. Ranking the alternatives and selection of the best one. The final ranking of the considered alternatives remains the same as in the ordinary TOPSIS method, which means that an alternative with a higher value of the closeness coefficient is more preferable.
4. A Numerical Illustration
To demonstrate the efficiency and the applicability of the proposed extension, an example of the evaluation of e-commerce strategies adopted from Stanujkić et al. [69] is the subject matter of consideration in this section of the paper. Suppose a team of three decision-makers should evaluate three e-commerce development strategies based on five criteria. The e-commerce development strategies (ECDS) and the evaluation criteria are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 1.
E-commerce development strategies.

Table 2.
E-commerce development strategy evaluation criteria.
The ratings obtained from the three decision-makers for the proposed strategies are shown in Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5.

Table 3.
The ratings received from the first decision-maker.

Table 4.
The ratings received from the second decision-maker.

Table 5.
The ratings received from the third decision-maker.
After that, a group evaluation matrix was determined by using Equation (6), whereby all the decision-makers had the same importance . The group evaluation matrix is presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
The group evaluation matrix.
In the following step, the ideal and negative ideal solutions shown in Table 7 are determined by applying Equations (23) and (24).

Table 7.
The ideal and negative ideal solutions.
The calculation details obtained by applying the TOPSIS method and the two distance measures are presented in Table 8 and Table 9.

Table 8.
The computational details obtained by using the Hamming distance.

Table 9.
The computational details obtained by using the Euclidean distance.
The calculation details obtained by utilizing the TOPSIS method and the Hamming distance are presented in Table 8. In this case, all the criteria had the same importance of wj = 0.20.
As can be observed from Table 8, the most acceptable alternative (i.e., e-commerce development strategy) is designated as ECDS2, which means that the most appropriate e-commerce development strategy is the “social e-commerce adoption” alternative.
5. Discussion and Comparison Analysis
In order to confirm the obtained results, similar calculations were performed by applying the TOPSIS method with the Euclidean distance, and the two commonly used approaches in the case of applying neutrosophic sets (i.e., the score function and the cosine similarity measure).
The calculation details obtained by using the TOPSIS method and the Euclidean distance are presented in Table 9. As can be observed from Table 9, the application of the TOPSIS method with the Euclidean distance produced the same ranking results.
To check the stability of the obtained ranking order of the alternatives, the calculation was repeated five times with the weighting vectors shown in Table 10.

Table 10.
The weighting vectors used for the recalculation.
The ranking results obtained by using the five different weighting vectors and the two distances are given in Table 11 and Table 12.

Table 11.
The ranking results obtained by using the Hamming distance and different Wi.

Table 12.
The ranking results obtained by using the Euclidean distance and different Wi.
The use of different weighting vectors caused changes in the ranking order in two cases, namely: W2 and W5. In the first case (W2), both distances gave the same ranking order, whereas in the second case (W5), there was a difference in the second- and third-ranked alternatives.
Based on the foregoing, it can be concluded that the developed extension of the TOPSIS method can be employed with any of the two previously considered distances (i.e., with the one easier to calculate such as the Hamming distance, or the one slightly more complex to calculate in the case of using SVNNs like Euclidean distance).
To finally verify the ranking results obtained by the developed adaptation of the TOPSIS method, an additional ranking of the strategies was performed by using two commonly used approaches (i.e., the score function and the cosine similarity measure). The values of the score function and the cosine similarity measure for the considered alternatives were determined by applying Equations (6) and (7), respectively, to the overall ratings calculated by applying Equation (8). In this calculation, all the criteria again had the same importance of wj = 0.20. The achieved ranking results are shown in Table 13.

Table 13.
The ranking by using the score function and the cosine similarity measure.
Table 13 allows us to note that the obtained results were partly different from the results shown in Table 8 and Table 9. The difference occurs with the alternative ECDS3, which now shared first place with the alternative ECDS2, whereas the alternative ECDS1 ranked second when using the TOPSIS method.
Generally speaking, the alternative ECDS2 was the best-ranked when using all the approaches (as seen in Figure 2), although some deviations in the ranking orders obtained by using different approaches were expected. Possible deviations in the ranking orders obtained by using different approaches are caused by the differences and specificities of the calculation procedures applied in different approaches, whereas deviations usually reflect in the case of worse-ranked alternatives.
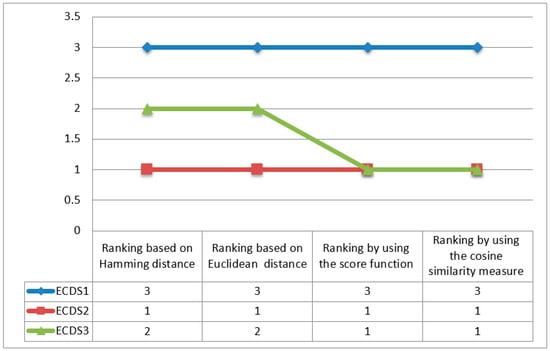
Figure 2.
Ranking results achieved by utilizing different procedures.
6. Conclusions
As a generalization of fuzzy sets and their various extensions, neutrosophic sets introduce three membership functions, thus enabling an easier and more efficient evaluation of alternatives in the cases of solving problems associated with ambiguities and uncertainties. Therefore, several approaches have been proposed for ranking neutrosophic numbers, and numerous MCDM methods have been adapted for the purpose of their use.
The TOPSIS method is a prominent MCDM method that has been used so far to solve numerous decision-making problems, and many extensions of the TOPSIS method have been proposed to enable using different types of fuzzy as well as neutrosophic numbers. Based on a previously proposed extension, a new adaptation to use single-valued neutrosophic numbers is being considered. The additional goal of this study was to confirm the applicability of the Hamming distance alternatively to the Euclidean distance. The results of the considered numerical illustration and the conducted comparative analysis indicate the justified application of the Hamming distance with a less complex calculation procedure instead of the Euclidean distance with a much more complex calculation procedure, especially in the case of neutrosophic set application. Furthermore, the proposed approach has enabled the use of the Hamming distance and/or Euclidean distance.
Based on the conducted numerical illustration, the most acceptable alternative is ECDS2, the Social E-commerce adoption model. Furthermore, the reliability of the TOPSIS extension based on SVNNs was additionally verified by utilizing the score function and cosine similarity measure. It is noticeable that alternatives ECDS2 and ECDS3 had the same ranking result. Additionally, alternative ECDS2, the Social E-commerce adoption model, was the best-ranked when using different ranking approaches (ranking based on Hamming distance and Euclidean distance, and ranking based on score function and cosine similarity measure).
The proposed TOPSIS extension based on SVNNs proved to be efficient and easy to use when solving decision-making problems that are complex, multifaceted, and often associated with ambiguities and uncertainties. In addition, TOPSIS SVNNs is a good choice when it comes to the evaluation and selection of e-commerce development strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.K., P.S., and G.P.; Methodology, D.K., D.S., and E.K.Z.; Validation, B.P. and A.U.; Investigation, B.P.; Data curation, G.P.; Writing—original draft preparation, D.S. and E.K.Z.; Writing—review and editing, P.S. and A.U.; Supervision, D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Magnusson, D.; Hermelin, B. ICT development from the perspective of connectivity and inclusion—The operation of a local digital agenda in Sweden. Nor. Geogr. Tidsskr. Nor. J. Geogr. 2019, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, K.W.; Håkansson, F. Strategical Use of ICT in Microenterprises: A Case Study. Int. J. E Entrep. Innov. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nica, E. ICT innovation, internet sustainability, and economic development. J. Self Gov. Manag. Econ. 2015, 3, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Chaffey, D.; Hemphill, T.; Edmundson-Bird, D. Digital Business and E-Commerce Management; Pearson: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, S.; Sergi, B.S.; Esposito, M. Literature review of emerging trends and future directions of e-commerce in global business landscape. World Rev. Entrep. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 15, 226–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudon, K.C.; Traver, C.G. E-Commerce: Business, Technology, Society; Pearson: Essex, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, N.; Hight, S.; Wei, W.; Ozturk, A.B.; Zhao, X.R.; Nusair, K.; DeFranco, A. The power of e-commerce. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 31, 1906–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.; Whittington, R.; Scholes, K.; Angwin, D.N.; Regnér, P. Exploring Strategy, 11th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, F.M.; Tuzovic, S.; Braun, C. Trustmarks: Strategies for exploiting their full potential in e-commerce. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 62, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćurčić, N.; Piljan, I.; Simonović, Z. Marketing concept in insurance companies. Ekonomika 2019, 65, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauković Jocić, K.; Jocić, G.; Karabašević, D.; Popović, G.; Stanujkić, D.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Thanh Nguyen, P. A Novel Integrated PIPRECIA—Interval-Valued Triangular Fuzzy ARAS Model: E-Learning Course Selection. Symmetry 2020, 12, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, M.; Pamucar, D. Evaluation of Iranian household appliance industries using MCDM models. Oper. Res. Eng. Sci. Theory Appl. 2019, 2, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabašević, D.; Maksimović, M.; Stanujkić, D.; Brzaković, P.; Brzaković, M. The evaluation of websites in the textile industry by applying ISO/IEC 91264-standard and the EDAS method. Ind. Text. 2018, 69, 4894. [Google Scholar]
- Fazlollahtabar, H.; Smailbašić, A.; Stević, Ž. FUCOM method in group decision-making: Selection of forklift in a warehouse. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 2019, 2, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabasević, D.; Stanujkić, D.; Maksimović, M.; Popović, G.; Momčilović, O. An Approach to Evaluating the Quality of Websites Based on the Weighted Sum Preferred Levels of Performances Method. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2019, 16, 195–215. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, B. The outranking approach and the foundation of ELECTRE methods. Theory Decis. 1991, 31, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brans, J.P.; Vincke, P. Note—A Preference Ranking Organisation Method: (The PROMETHEE Method for Multiple Criteria Decision-Making). Manag. Sci. 1985, 31, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.L.; Yoon, K. Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Kaklauskas, A.; Sarka, V. The new method of multicriteria complex proportional assessment of projects. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 1994, 1, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Opricović, S. Multicriteria Optimization of Civil Engineering Systems; Faculty of Civil Engineering: Belgrade, Serbia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Brauers, W.K.M.; Zavadskas, E.K. The MOORA method and its application to privatization in a transition economy. Control Cybern. 2006, 35, 445–469. [Google Scholar]
- Brauers, W.K.M.; Zavadskas, E.K. Project management by MULTIMOORA as an instrument for transition economies. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2010, 16, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, C.; Yeoh, W.; Lee, A.; Moayedikia, A. Deciding discipline, course and university through TOPSIS. Stud. High. Educ. 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, B.M.; Godoy, L.P.; Campos, L.M. Performance evaluation of green suppliers using entropy-TOPSIS-F. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, F.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Streimikiene, D.; Mardani, A. Assessment of concentrated solar power (CSP) technologies based on a modified intuitionistic fuzzy topsis and trigonometric entropy weights. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 140, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, P.K.; Lau, H.Y. Hotel selection using a modified TOPSIS-based decision support algorithm. Decis. Support Syst. 2019, 120, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, Y.A.; Tan, Q.; Mirjat, N.H.; Ali, S. Evaluating the strategies for sustainable energy planning in Pakistan: An integrated SWOT-AHP and Fuzzy-TOPSIS approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Barua, M.K. Supplier selection among SMEs on the basis of their green innovation ability using BWM and fuzzy TOPSIS. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 152, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efe, B. Website Evaluation Using Interval Type-2 Fuzzy-Number-Based TOPSIS Approach. In Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Models for Website Evaluation; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 166–185. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.M.; Elhag, T.M. Fuzzy TOPSIS method based on alpha level sets with an application to bridge risk assessment. Expert Syst. Appl. 2006, 31, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulsalam, K.; Ighravwe, D.; Babatunde, M. A fuzzy-TOPSIS approach for techno-economic viability of lighting energy efficiency measure in public building projects. J. Proj. Manag. 2018, 3, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, H.R.; Nekooie, M.A. An improved hierarchical fuzzy TOPSIS approach to identify endangered earthquake-induced buildings. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 76, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemenis, A.; Askounis, D. A new TOPSIS-based multi-criteria approach to personnel selection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4999–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, X.; Liu, X.; Qin, J. An analytical solution to fuzzy TOPSIS and its application in personnel selection for knowledge-intensive enterprise. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 30, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanlioglu, F.; Taskaya, Y.E.; Gulen, U.C.; Cokcan, O. A fuzzy AHP–TOPSIS-based group decision-making approach to IT personnel selection. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 20, 1576–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemenis, A.; Ergazakis, K.; Askounis, D. Support managers’ selection using an extension of fuzzy TOPSIS. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 2774–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarandache, F. Neutrosophy, Neutrosophic Probability, Set and Logic; American Res. Press: Rehoboth, DE, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Mohamed, M. A novel and powerful framework based on neutrosophic sets to aid patients with cancer. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 98, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Gamal, A.; Manogaran, G.; Long, H.V. A novel group decision making model based on neutrosophic sets for heart disease diagnosis. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Mohamed, M.; Elhoseny, M.; Chiclana, F.; Zaied AE, N.H. Cosine similarity measures of bipolar neutrosophic set for diagnosis of bipolar disorder diseases. Artif. Intell. Med. 2019, 101, 101735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulucay, V.; Kılıç, A.; Şahin, M.; Deniz, H. A new hybrid distance-based similarity measure for refined neutrosophic sets and its application in medical diagnosis. Matematika 2019, 35, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratihar, J.; Kumar, R.; Dey, A.; Broumi, S. Transportation problem in neutrosophic environment. In Neutrosophic Graph Theory and Algorithms; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 180–212. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P. Exploring public transport sustainability with neutrosophic logic. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2019, 42, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhassouny, A.; Idbrahim, S.; Smarandache, F. Machine learning in Neutrosophic Environment: A Survey. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 2019, 28, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaparthasarathy, G.; Little Flower, V.F.; Dasan, M.A. Neutrosophic Supra Topological Applications in Data Mining Process. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 2019, 27, 80–97. [Google Scholar]
- Sengur, A.; Budak, U.; Akbulut, Y.; Karabatak, M.; Tanyildizi, E. A survey on neutrosophic medical image segmentation. In Neutrosophic Set in Medical Image Analysis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 145–165. [Google Scholar]
- Tuan, T.M.; Chuan, P.M.; Ali, M.; Ngan, T.T.; Mittal, M. Fuzzy and neutrosophic modeling for link prediction in social networks. Evol. Syst. 2019, 10, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, C.; Otay, İ. Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Using Neutrosophic Sets; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Wu, L.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, H. Multi-criteria decision making method based on the single valued neutrosophic sets. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 37, 2403–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Ji, P.; Wang, J.Q.; Chen, X.H. An improved weighted correlation coefficient based on integrated weight for interval neutrosophic sets and its application in multi-criteria decision-making problems. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2015, 8, 1027–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.J.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, X.H. An outranking approach for multi-criteria decision-making problems with simplified neutrosophic sets. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 25, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarandache, F. A Unifying Field in Logics. Neutrosophy: Neutrosophic Probability, Set and Logic; American Research Press: Rehoboth, DE, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Smarandache, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sunderraman, R. Single valued neutrosophic sets. Rev. Air Force Acad. 2010, 1, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, R. Multi-criteria neutrosophic decision making method based on score and accuracy functions under neutrosophic environment. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1412.5202. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J. Multicriteria decision-making method using the correlation coefficient under single-valued neutrosophic environment. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2013, 42, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Lin, J.J.; Linc, J.H.; Chiang, M.C. Domestic open-end equity mutual fund performance evaluation using extended TOPSIS method with different distance approaches. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4642–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanian, A.; Savadogo, O. TOPSIS multiple-criteria decision support analysis for material selection of metallic bipolar plates for polymer electrolyte fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2006, 159, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.S.; Singh, S.R. An improved-based TOPSIS method in interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Life Cycle Reliab. Saf. Eng. 2018, 7, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadikhah, M. Using the Hamming distance to extend TOPSIS in a fuzzy environment. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2009, 231, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Tsao, C.Y. The interval-valued fuzzy TOPSIS method and experimental analysis. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2008, 159, 1410–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Hung, C.C. Multiple-attribute decision making methods for plant layout design problem. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2007, 23, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broumi, S.; Ye, J.; Smarandache, F. An extended TOPSIS method for multiple attribute decision making based on interval neutrosophic uncertain linguistic variables. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 2015, 8, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Elhassouny, A.; Smarandache, F. Neutrosophic-simplified-TOPSIS multi-criteria decision-making using combined simplified-TOPSIS method and neutrosophics. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 2468–2474. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, V.; Shocker, A.D. Linear programming techniques for multidimensional analysis of preferences. Psychometrika 1973, 38, 337–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersuliene, V.; Turskis, Z. Integrated fuzzy multiple criteria decision making model for architect selection. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2011, 17, 645–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamucar, D.; Stevic, Z.; Sremac, S. A new model for determining weight coefficients of criteria in MCDM models: Full consistency method (FUCOM). Symmetry 2018, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanujkić, D.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Karabašević, D.; Smarandache, F.; Turskis, Z. The use of Pivot Pair-wise Relative Criteria Importance Assessment method for determining weights of criteria. Rom. J. Econ. Forecast. 2017, 20, 116–133. [Google Scholar]
- Stanujkić, D.; Karabašević, D.; Maksimović, M.; Popović, G.; Brzaković, M. Evaluation of the e-commerce development strategies. Quaestus 2019, 1, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, A.; Mela, C.F. E-customization. J. Mark. Res. 2003, 40, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajli, M. A research framework for social commerce adoption. Inf. Manag. Comput. Secur. 2013, 21, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, R. Optimal search engine marketing strategy. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2005, 10, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).