BlockNet: A Deep Neural Network for Block-Based Motion Estimation Using Representative Matching
Abstract
1. Introduction
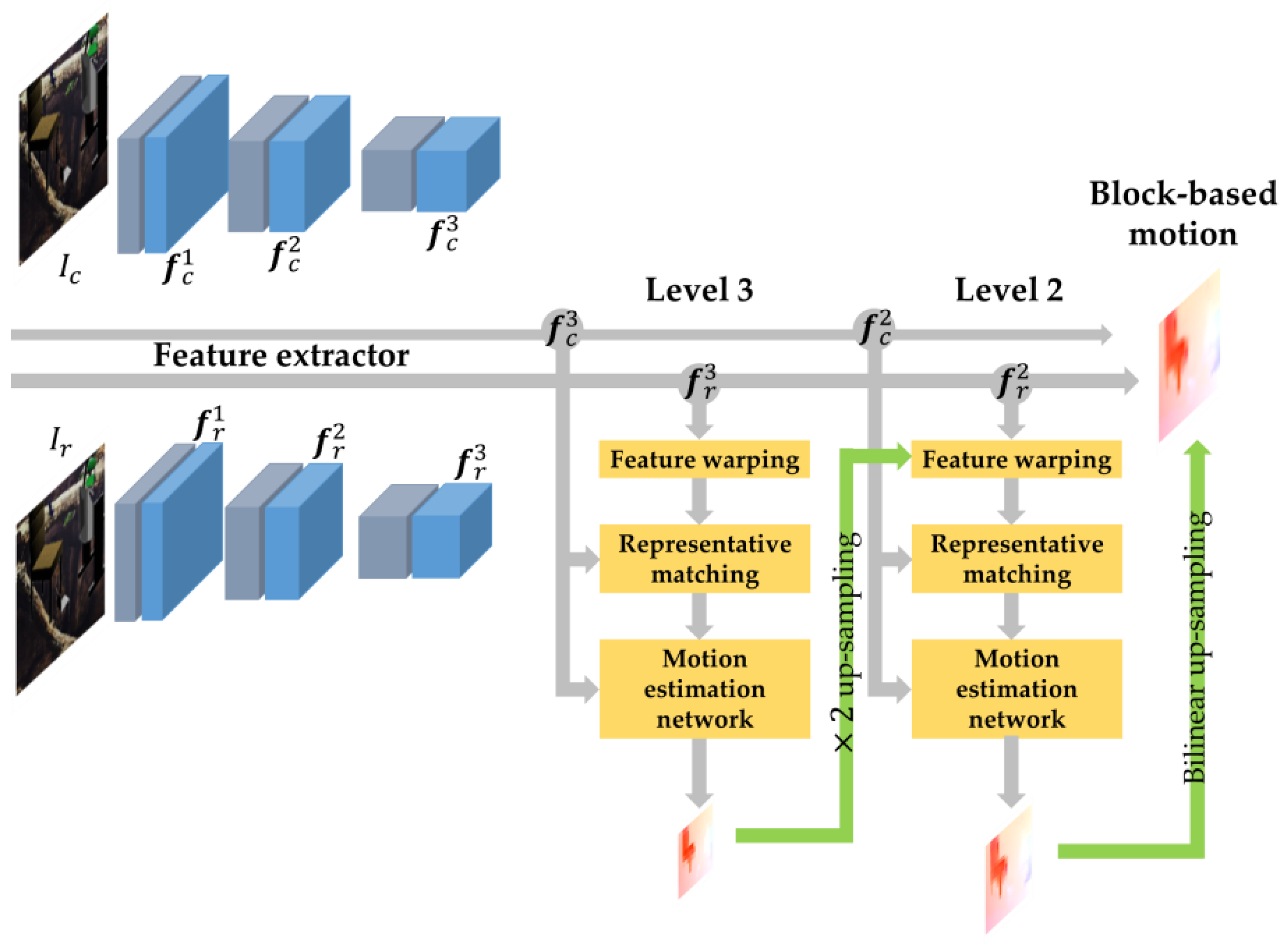
2. BlockNet
2.1. Feature Extractor
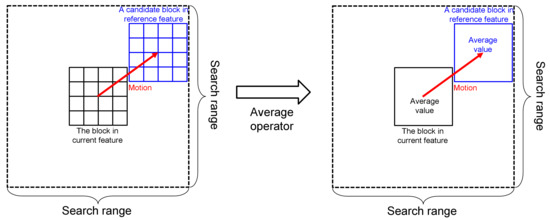
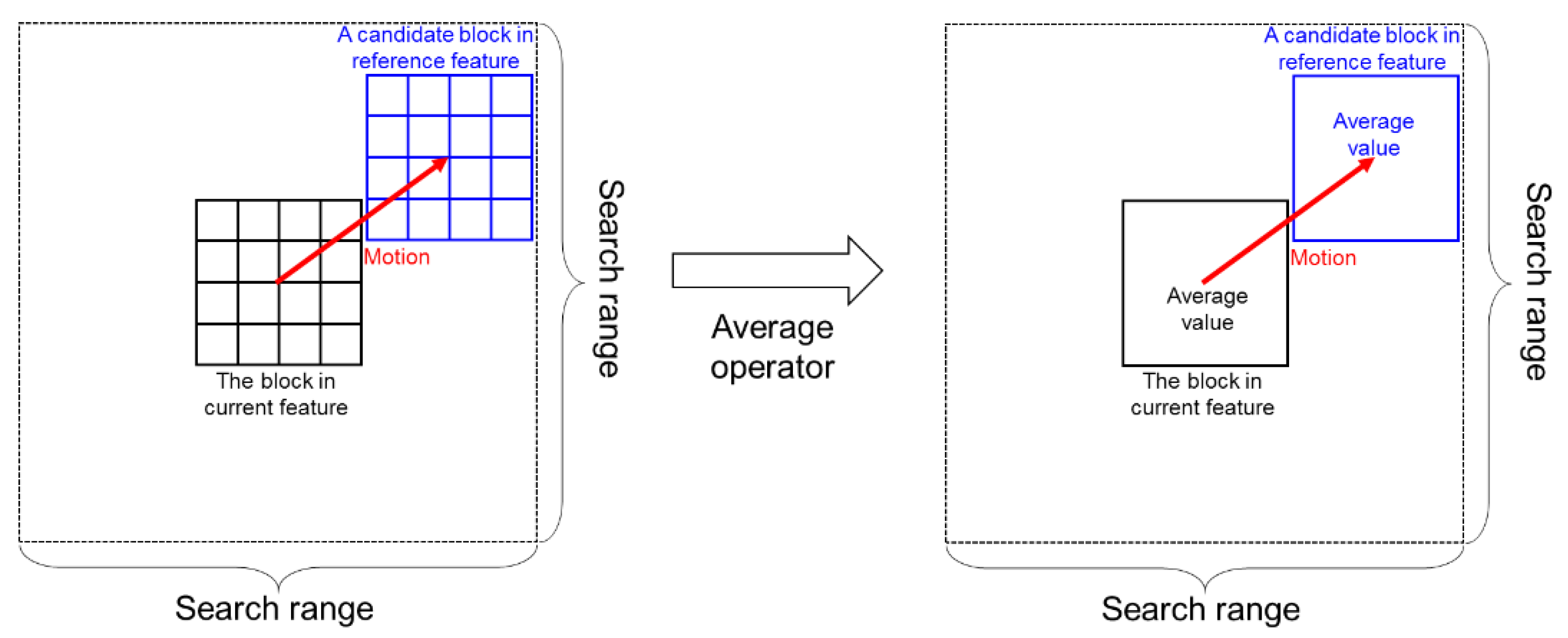
2.2. Representative Matching for Motion Estimation
2.2.1. Proposed Algorithm
2.2.2. Implementation Details
| Algorithm 1. Proposed representative matching |
| Definition |
| : The average-pooling operator |
| : Duplication of each element of the matrix |
| : Extraction of the patches repeatedly |
| Input: current feature , reference feature , block size , and search range |
| Output: |
2.3. Pyramidal Structure with Feature Warping
3. Experiments
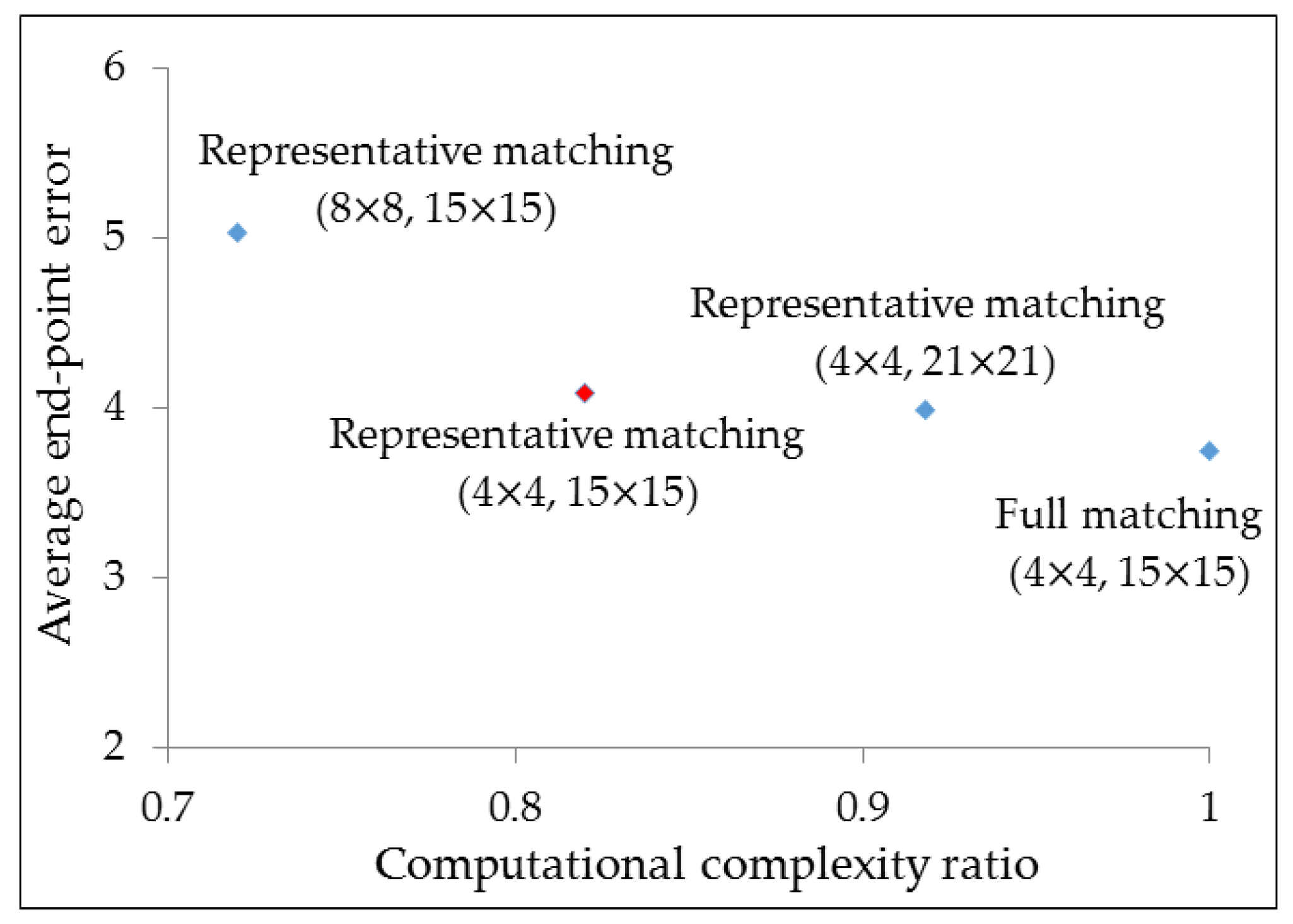
3.1. Experimental Setup
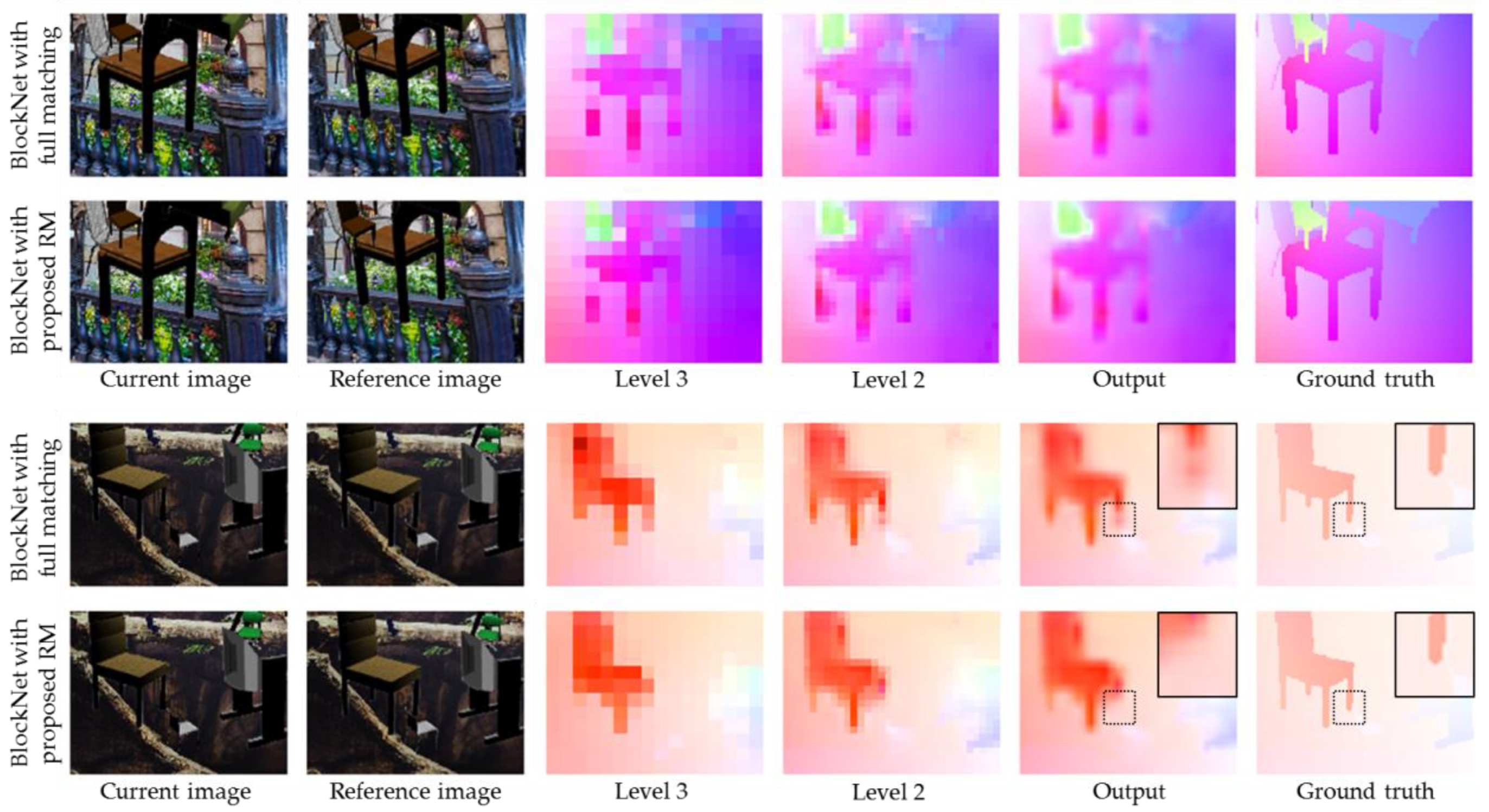
3.2. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuo, C.-M.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Jou, Y.-D.; Lin, H.-C.; Lu, P.-C. Motion estimation for video compression using Kalman filtering. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 1996, 42, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Sun, M.-T.; Hsu, V. Global motion estimation from coarsely sampled motion vector field and the applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2005, 15, 232–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, K.; Shin, S.; Lee, J.; Song, W.-J. How to estimate global motion non-Iteratively from a coarsely sampled motion vector field. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 29, 3729–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-J.; Yoo, S.; Kim, Y.H. Dual motion estimation for frame rate up-conversion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2010, 20, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.-G.; Kang, S.-J.; Kim, Y.H. Direction-select motion estimation for motion-compensated frame rate up-conversion. J. Disp. Technol. 2013, 9, 840–850. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, K.; Lee, J.; Song, W.-J.; Kang, M.; Kwon, K.J.; Kim, S.G. Multitask bilateral learning for real-time image enhancement. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2019, 27, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpathy, A.; Toderici, G.; Shetty, S.; Leung, T.; Sukthankar, R.; Fei-Fei, L. Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 1725–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, K.; Lee, J.; Kwak, Y.; Kang, M.; Kim, S.G.; Song, W.-J. Recycling: Semi-supervised learning with noisy labels in deep neural networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 66998–67005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmans, T.; Javed, S.; Sultana, M.; Jung, S.K. Deep neural network concepts for background subtraction: A systematic review and comparative evaluation. Neural Netw. 2019, 117, 8–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Ciaparrone, G.; Sánchez, F.L.; Tabik, S.; Troiano, L.; Tagliaferri, R.; Herrera, F. Deep learning in video multi-object tracking: A survey. Neurocomputing 2020, 381, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Fischer, P.; Ilg, E.; Hausser, P.; Hazirbas, C.; Golkov, V.; Van Der Smagt, P.; Cremers, D.; Brox, T. Flownet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2758–2766. [Google Scholar]
- Ilg, E.; Mayer, N.; Saikia, T.; Keuper, M.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Brox, T. Flownet 2.0: Evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2462–2470. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Yang, X.; Liu, M.Y.; Kautz, J. Pwc-net: Cnns for optical flow using pyramid, warping, and cost volume. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8934–8943. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, T.W.; Tang, X.; Change Loy, C. Liteflownet: A lightweight convolutional neural network for optical flow estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8981–8989. [Google Scholar]
- Metkar, S.; Talbar, S. Motion Estimation Techniques for Digital Video Coding; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Jin, G.; Huang, M.; Xu, G. A novel partial block-matching motion estimation algorithm. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Multispectral Image Processing and Pattern Recognition, Beijing, China, 20–22 October 2003; pp. 839–842. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zaccarin, A. New fast algorithms for the estimation of block motion vectors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 1993, 3, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.-L.; Siu, W.-C. New adaptive pixel decimation for block motion vector estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 1996, 6, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.J.; Wulff, J.; Stanley, G.B.; Black, M.J. A naturalistic open source movie for optical flow evaluation. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 611–625. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]

| BME with Full Matching | BME with Proposed RM | BlockNet with Full Matching | BlockNet with Proposed RM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average EPE | 10.33 | 16.86 | 3.74 | 4.09 |
| Std. of EPE | 7.64 | 7.09 | 3.53 | 3.57 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Kong, K.; Bae, G.; Song, W.-J. BlockNet: A Deep Neural Network for Block-Based Motion Estimation Using Representative Matching. Symmetry 2020, 12, 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050840
Lee J, Kong K, Bae G, Song W-J. BlockNet: A Deep Neural Network for Block-Based Motion Estimation Using Representative Matching. Symmetry. 2020; 12(5):840. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050840
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Junggi, Kyeongbo Kong, Gyujin Bae, and Woo-Jin Song. 2020. "BlockNet: A Deep Neural Network for Block-Based Motion Estimation Using Representative Matching" Symmetry 12, no. 5: 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050840
APA StyleLee, J., Kong, K., Bae, G., & Song, W.-J. (2020). BlockNet: A Deep Neural Network for Block-Based Motion Estimation Using Representative Matching. Symmetry, 12(5), 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050840