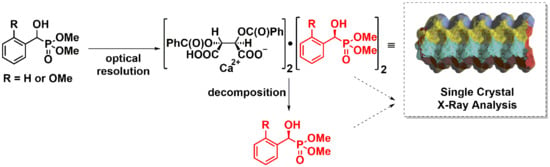
Optical Resolution of Dimethyl α-Hydroxy-Arylmethylphosphonates via Diastereomer Complex Formation Using Calcium Hydrogen O,O′-Dibenzoyl-(2R,3R)-Tartrate; X-Ray Analysis of the Complexes and Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
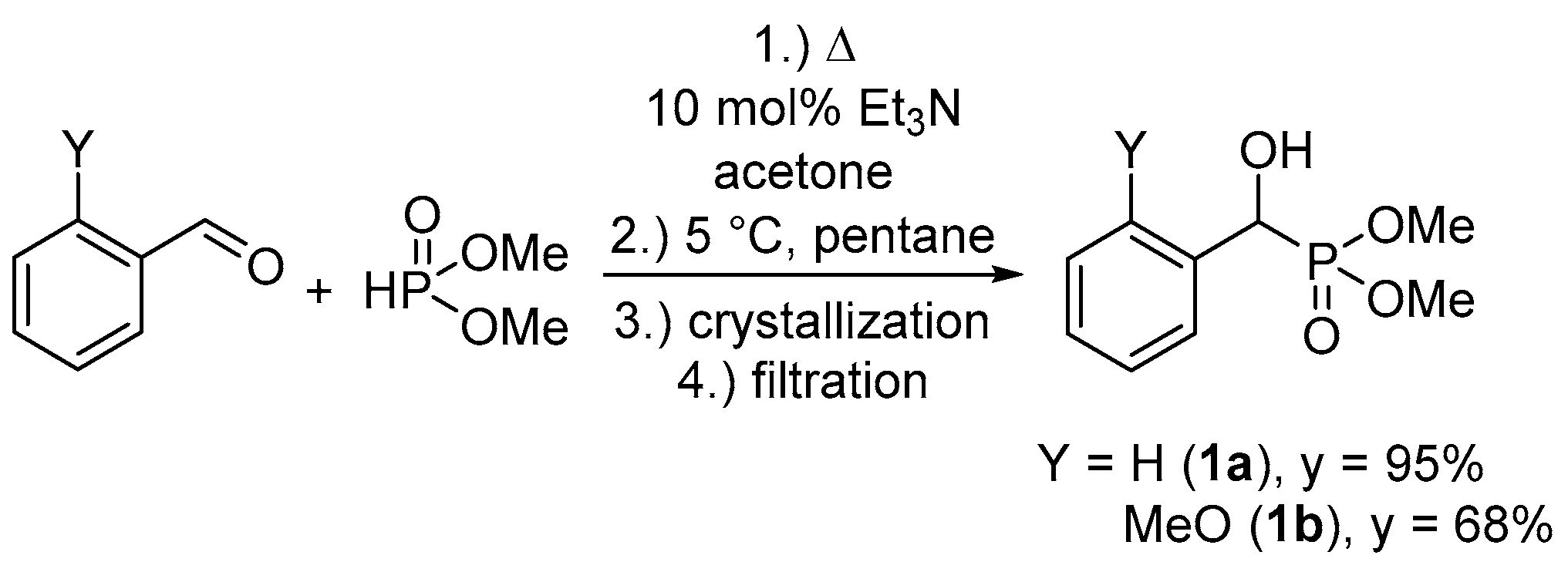
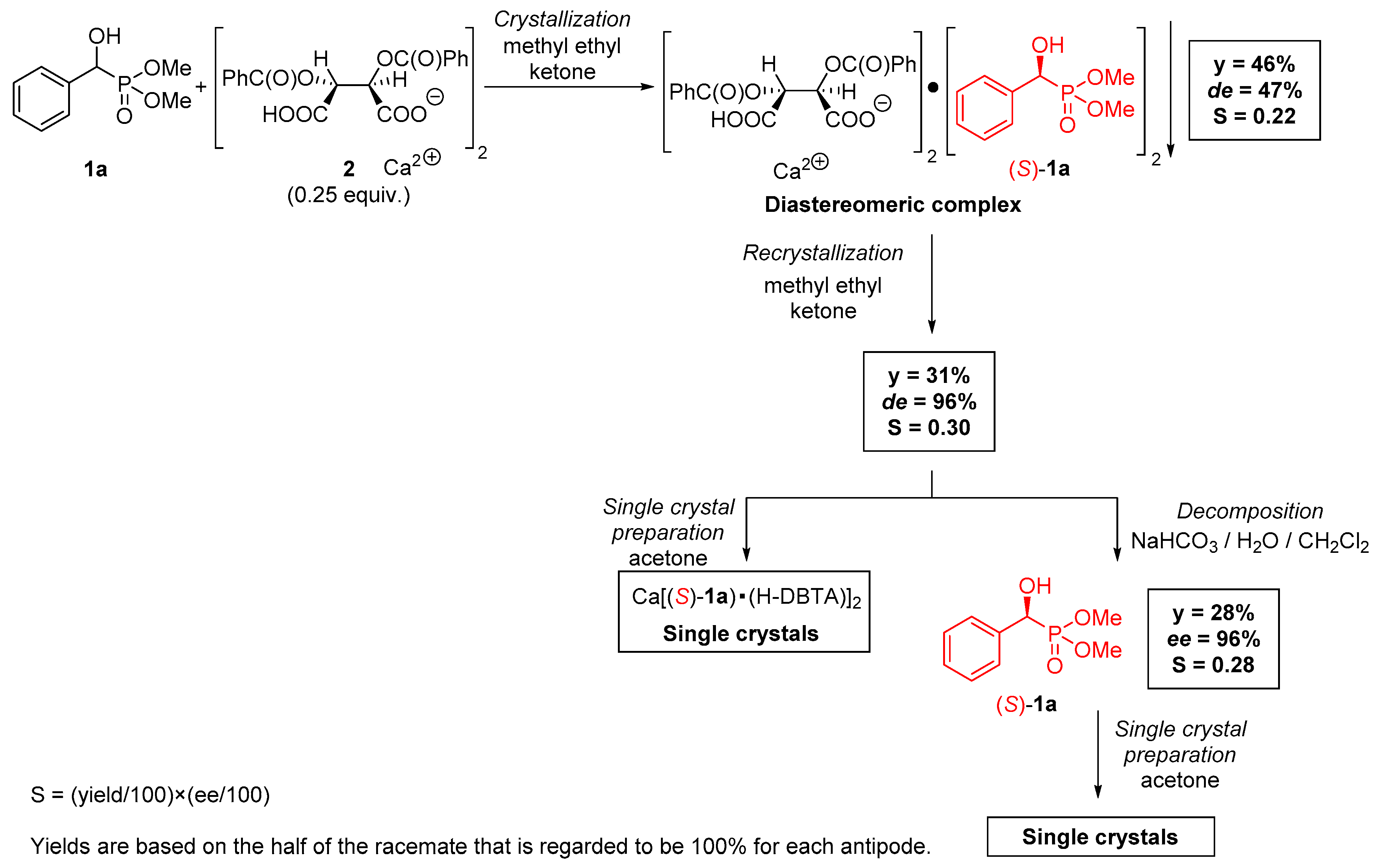
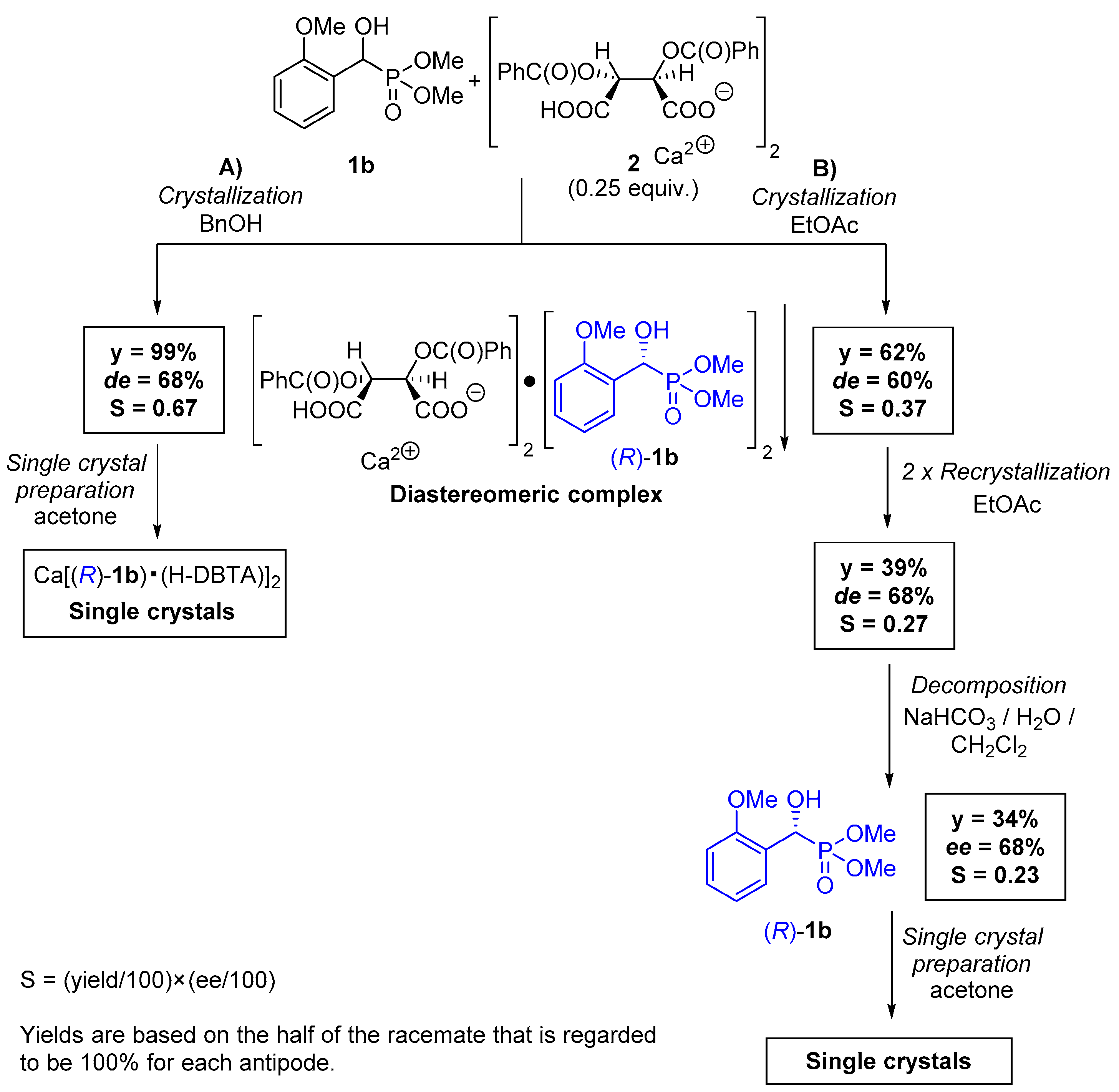
2.1. Preparation of Single Crystals from Optically Active α-Hydroxyphosphonates
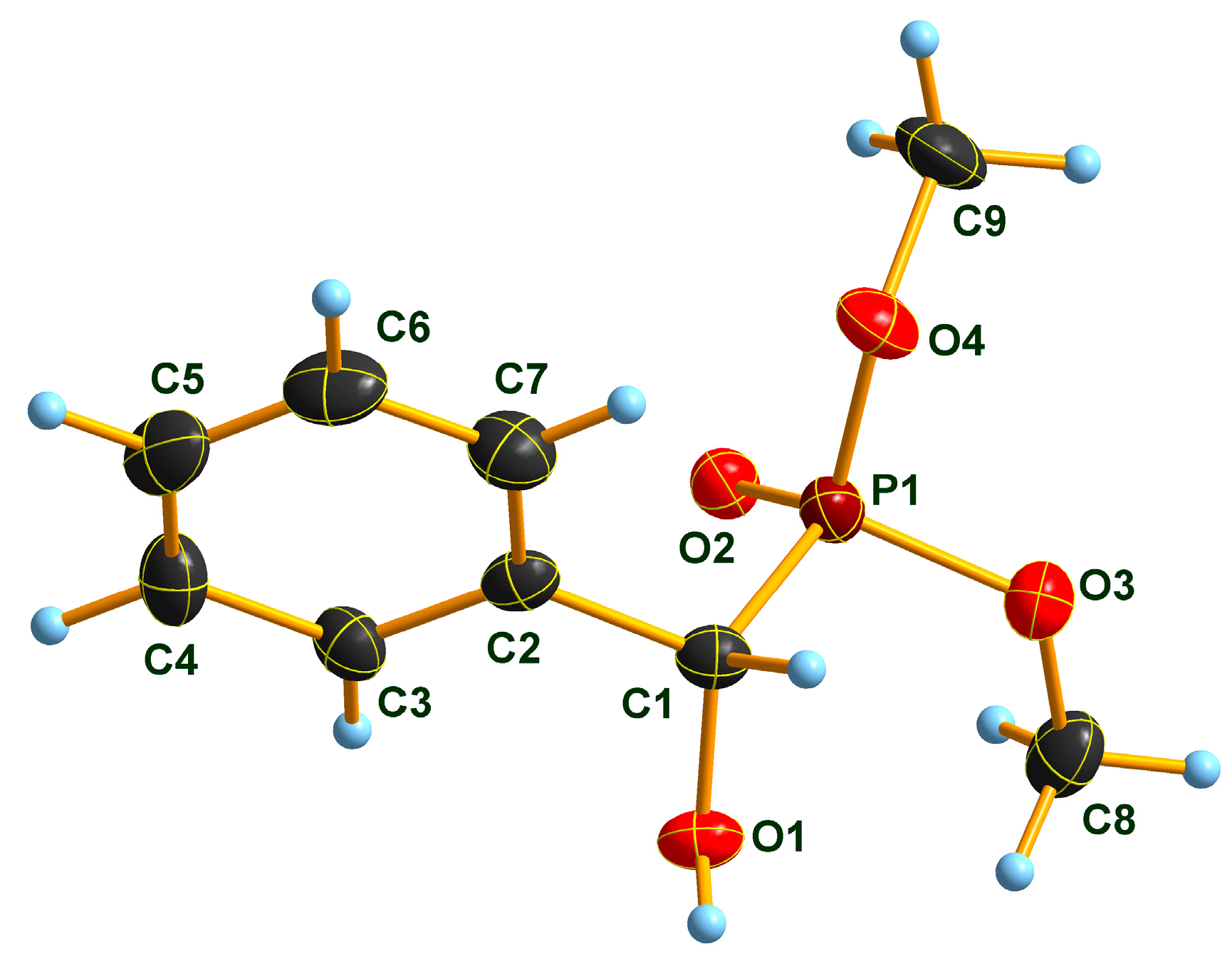
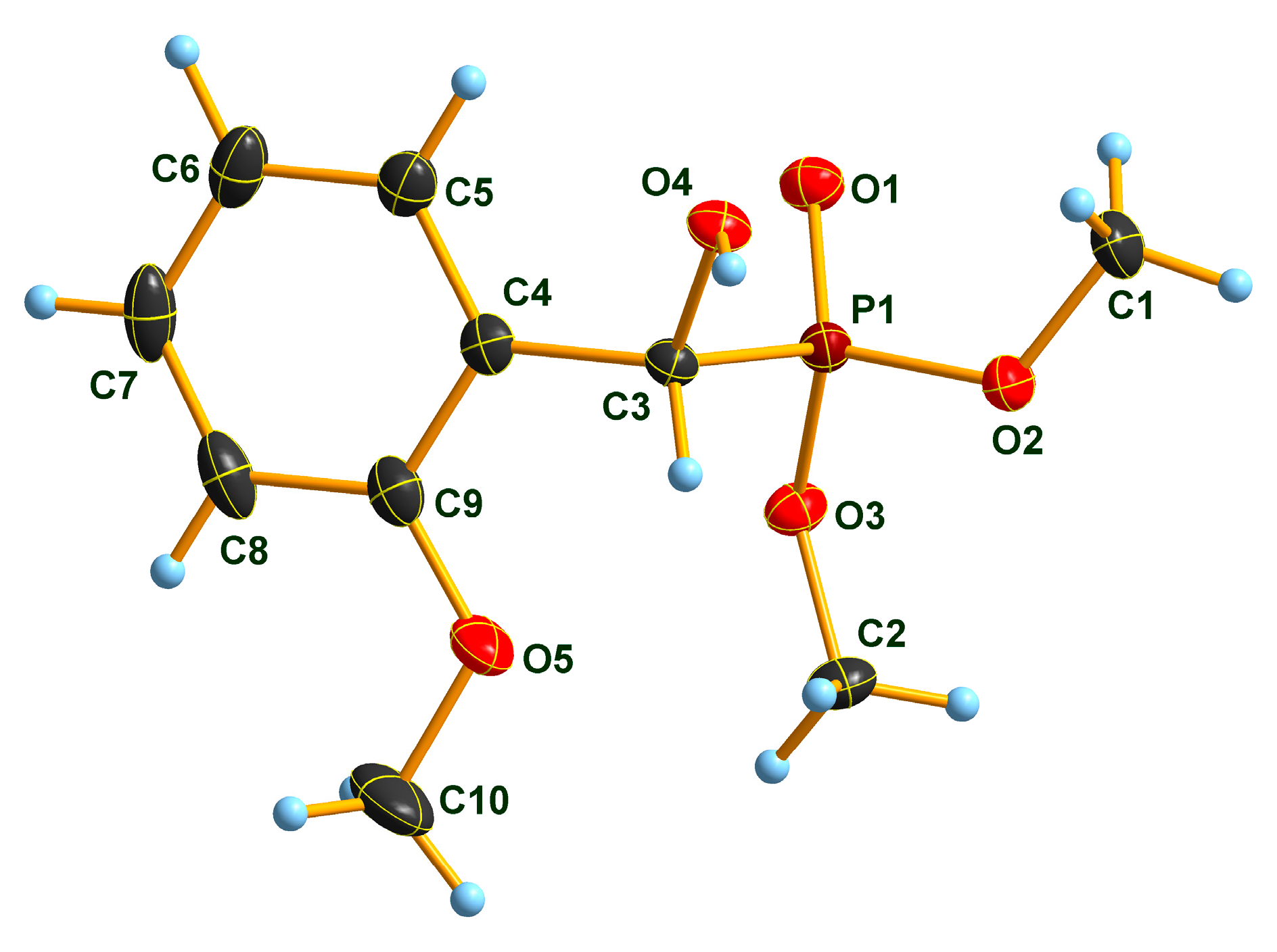
2.2. X-Ray Analysis of Optically Active (S)-1a and (R)-1b α-Hydroxyphosphonates and Ca[(S)-1a • H-DBTA]2 and Ca[(R)-1b • H-DBTA]2 Diastereomeric Complexes
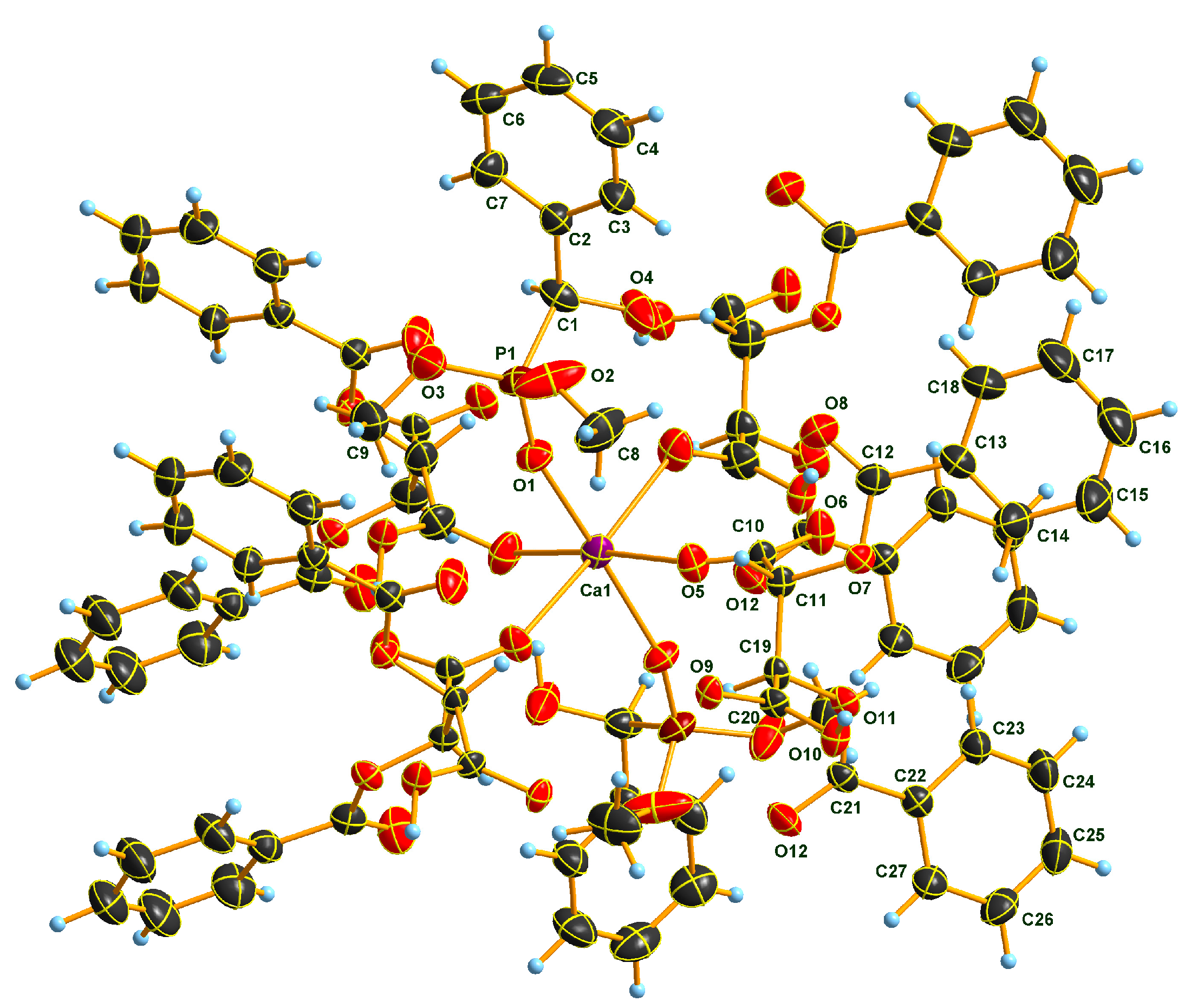
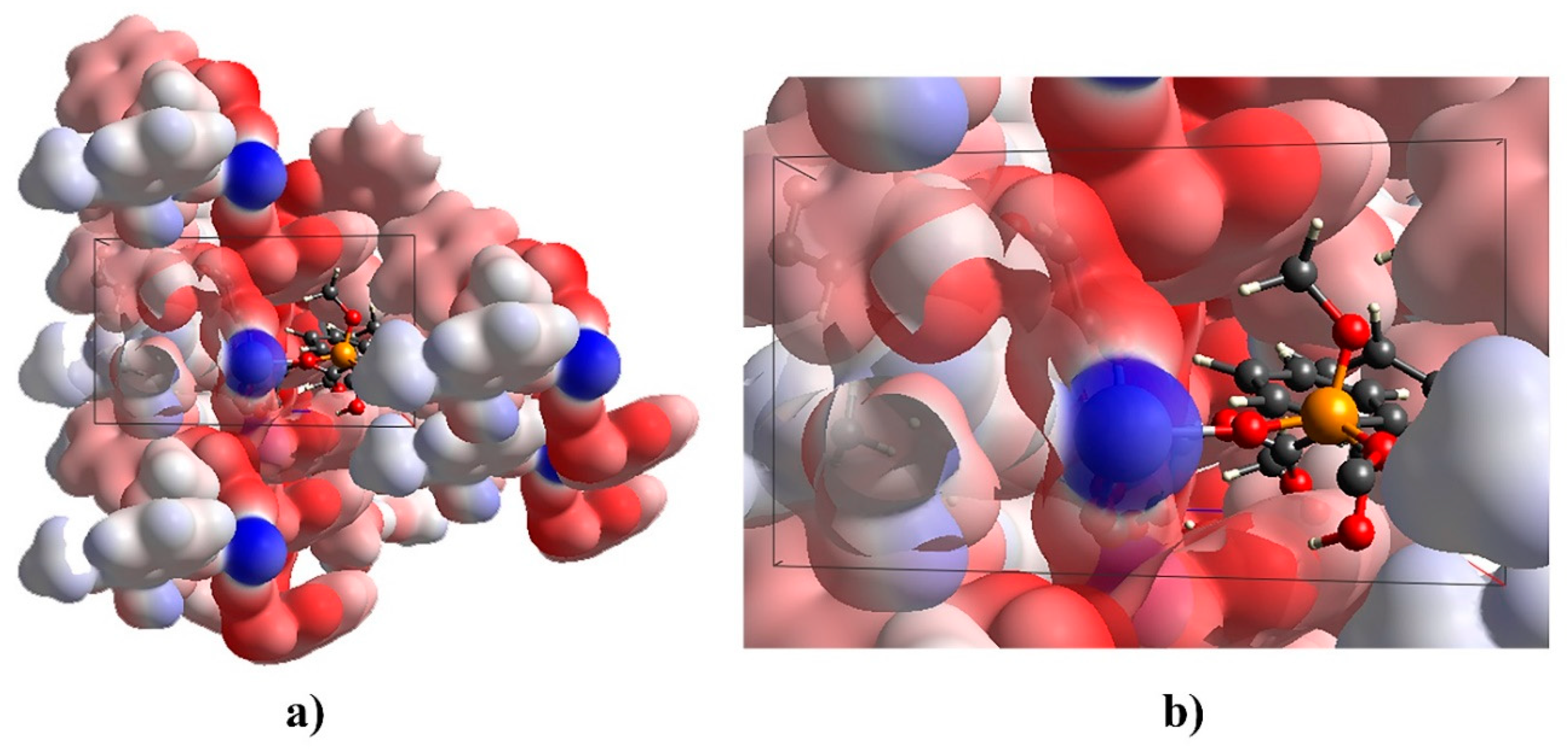
2.3. Sub-Units and Intermolecular Effects in Ca[(S)-1a • H-DBTA]2 and Ca[(R)-1b • H-DBTA]2 Diastereomeric Complexes
2.4. Coordination in Ca[(S)-1a • H-DBTA]2 and Ca[(R)-1b • H-DBTA]2 Diasteremeric Complexes
2.5. Hydrogen Bonding in Diastereomeric Complexes 3 and 4
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental
4.1. Single Crystal X-Ray Diffraction Studies of Optically Active α-Hydroxyphosphonates (S)-1a and (R)-1b as Well as of the Diastereomeric Complex Ca[(R)-1b • H-DBTA]2
4.2. Single Crystal X-Ray Diffraction Studies of Diastereomeric Complex Ca[(S)-1a • H-DBTA]2
4.3. Procedure for the Preparation of Optically Active Ca[(S)-1a • H-DBTA]2 Complex and Its Single Crystals
4.4. Procedure for the Preparation of Optically Active (S)-1a and Its Single Crystals
4.5. Procedure for the Preparation of Optically Active Ca[(R)-1b • H-DBTA]2 Complex and Its Single Crystals
4.6. Procedure for the Preparation of Optically Active (R)-1b and Its Single Crystals
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, D.V.; Rielly-Gauvin, K.; Ryono, D.E.; Free, C.A.; Rogers, W.L.; Smith, S.A.; DeForrest, J.M.; Oehl, R.S.; Petrillo, E.W. Alpha-hydroxy phosphinyl-based inhibitors of human renin. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 4557–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Mao, H.; Shi, D. Synthesis and herbicidal activity of α-hydroxy phosphonate derivatives containing pyrimidine moiety. Chin. J. Chem. 2010, 28, 2020–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokalwar, R.U. Synthesis and antibacterial activities of α-hydroxyphosphonates and α-acetyloxyphosphonates derived from 2-chloroquinoline-3-carbaldehyde. Arkivoc 2006, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kategaonkar, A.H.; Pokalwar, R.U.; Sonar, S.S.; Gawali, V.U.; Shingate, B.B.; Shingare, M.S. Synthesis, in vitro antibacterial and antifungal evaluations of new α-hydroxyphosphonate and new α-acetoxyphosphonate derivatives of tetrazolo [1, 5-a] quinoline. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, C.; Raju, C.N.; Rao, C.V. An efficient synthesis, spectral characterization, anti-microbial and anti-oxidant activities of novel ?-hydroxyphosphonates and ?-hydroxyphosphinates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2015, 191, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rádai, Z.; Windt, T.; Nagy, V.; Füredi, A.; Kiss, N.Z.; Randelovic, I.; Tóvári, J.; Keglevich, G.; Szakács, G.; Tóth, S. Synthesis and anticancer cytotoxicity with structural context of an α-hydroxyphosphonate based compound library derived from substituted benzaldehydes. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 14028–14035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalla, R.M.N.; Lee, H.R.; Cao, J.; Yoo, J.-W.; Kim, I. Phospho sulfonic acid: An efficient and recyclable solid acid catalyst for the solvent-free synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates and their anticancer properties. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 3916–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, H.-U. Chirality and its implications for the pharmaceutical industry. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2013, 24, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.A.; He, H.; Pham-Huy, C. Chiral drugs: An overview. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2006, 2, 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gröger, H.; Vogl, E.M.; Shibasaki, M. New catalytic concepts for the asymmetric aldol reaction. Chem. Eur. J. 1998, 4, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodiazhnyi, O.I. Chiral hydroxy phosphonates: Synthesis, configuration and biological properties. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2006, 75, 227–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodiazhnyi, O. Asymmetric synthesis of hydroxyphosphonates. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2005, 16, 3295–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodyazhnaya, A.O.; Kukhar, V.P.; Kolodyazhnyi, O.I. Organic catalysis of phospha-aldol condensation. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2008, 78, 2043–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirashima, S.-I.; Arai, R.; Nakashima, K.; Kawai, N.; Kondo, J.; Koseki, Y.; Miura, T. Asymmetric hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes using a cinchona-diaminomethylenemalononitrile organocatalyst. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 3863–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraguchi, D.; Ito, T.; Ooi, T. Generation of chiral phosphonium dialkyl phosphite as a highly reactive P-nucleophile: Application to asymmetric hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3836–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, J.P.; Yamamoto, H. Catalytic enantioselective pudovik reaction of aldehydes and aldimines with tethered bis (8-quinolinato) (TBOx) aluminum complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10521–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Cai, C. Bis (oxazoline)-copper catalyzed enantioselective hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 27853–27856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthupandi, P.; Sekar, G. Synthesis of an unusual dinuclear chiral iron complex and its application in asymmetric hydrophosphorylation of aldehydes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Guo, Q.-P.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.-Y.; Da, C.-S. C2-symmetric homobimetallic zinc complexes as chiral catalysts for the highly enantioselective hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guin, J.; Wang, Q.; van Gemmeren, M.; List, B. The catalytic asymmetric abramov reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulioukina, N.S.; Bondarenko, G.N.; Bogdanov, A.V.; Gavrilov, K.N.; Beletskaya, I.P. Asymmetric hydrogenation of α-keto phosphonates with chiral palladium catalysts. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterov, V.; Kolodiazhnyi, O. New method for the asymmetric hydroboration of ketophosphonates and the synthesis of phospho-carnitine. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2006, 17, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterov, V.; Kolodiazhnyi, O. New method for the asymmetric reduction of ketophosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2008, 183, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skropeta, D.; Schmidt, R.R. Chiral, non-racemic α-hydroxyphosphonates and phosphonic acids via stereoselective hydroxylation of diallyl benzylphosphonates. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2003, 14, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogatchnik, D.M.; Wiemer, D.F. Enantioselective synthesis of α-hydroxy phosphonates via oxidation with (camphorsulfonyl)oxaziridines. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 3495–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafarski, P.; Lejczak, B. Application of bacteria and fungi as biocatalysts for the preparation of optically active hydroxyphosphonates. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2004, 29, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pàmies, O.; Bäckvall, J.-E. An efficient route to chiral α- and β-hydroxyalkanephosphonates. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 4815–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-F.; Hammerschmidt, F. Enzymes in organic chemistry, part 1: Enantioselective hydrolysis of α-(acyloxy)phosphonates by esterolytic enzymes. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1993, 4, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demizu, Y.; Moriyama, A.; Onomura, O. Nonenzymatic kinetic resolution of racemic α-hydroxyalkanephosphonates with chiral copper catalyst. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 5241–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboudin, B.; Alavi, S.; Kazemi, F.; Aoyama, H.; Yokomatsu, T. Resolution of racemic α-hydroxyphosphonates: bi(OTF)3-catalyzed stereoselective esterification of α-hydroxyphosphonates with (+)-dibenzoyl-l-tartaric anhydride. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15471–15478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rádai, Z.; Kiss, N.Z.; Czugler, M.; Karaghiosoff, K.; Keglevich, G. The typical crystal structures of a few representative α-aryl-α-hydroxyphosphonates. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2019, 75, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagi, P.; Ujj, V.; Czugler, M.; Fogassy, E.; Keglevich, G. Resolution of P-stereogenic P-heterocycles via the formation of diastereomeric molecular and coordination complexes (a review). Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 1823–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagi, P.; Varga, B. Preparation of enantiomerically enriched P-stereogenic dialkyl-arylphosphine oxides via coordination mediated optical resolution. Symmetry 2020, 12, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Bagi, P.; Varga, B.; Szilágyi, A.; Karaghiosoff, K.; Czugler, M.; Fogassy, E.; Keglevich, G. The resolution of acyclic P -stereogenic phosphine oxides via the formation of diastereomeric complexes: A case study on ethyl-(2-methylphenyl)-phenylphosphine oxide. Chirality 2018, 30, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravik, A.; Böcskei, Z.; Simon, K.; Elekes, F.; Izsáki, Z. Chiral recognition of alcohols in the crystal lattice of simple metal complexes of O,O′-dibenzoyltartaric Acid: Enantiocomplementarity and simultaneous resolution. Chem. Eur. J. 1998, 4, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravik, A.; Böcskei, Z.; Katona, Z.; Markovits, I.; Pokol, G.; Menyhárd, D.K.; Fogassy, E. A new optical resolution method: Coordinative resolution of mandelic acid esters. The crystal structure of calcium hydrogen (2R,3R)-O,O′-dibenzoyl tartrate–2(R)-(–)-methyl mandelate. Chem. Commun. 1996, 1983–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravik, A.; Bocskei, Z.; Katona, Z.; Markovits, I.; Fogassy, E. Coordination-mediated optical resolution of carboxylic acids with O, O′-dibenzoyltartaric acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 1534–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xie, H.; Ran, K.; Gan, Y. Efficient synthesis and resolution of tenofovir alafenamide. Lett. Org. Chem. 2017, 15, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keglevich, G.; Rádai, Z.; Kiss, N.Z. To date the greenest method for the preparation of α-hydroxyphosphonates from substituted benzaldehydes and dialkyl phosphites. Green Process. Synth. 2017, 6, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujj, V.; Schindler, J.; Novák, T.; Czugler, M.; Fogassy, E.; Keglevich, G. Coordinative resolution of 1-phenyl- and 1-naphthyl-3-methyl-3-phospholene 1-oxides with calcium hydrogen O,O′-dibenzoyl-(2R,3R)-tartrate or calcium hydrogen O,O′-di-p-toluyl-(2R,3R)-tartrate. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2008, 19, 1973–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putz, H.; Brandenburg, K. Diamond—Crystal and Molecular Structure Visualization. Cryst. Impact-GbR Kreuzherrenstr. 2006, 102, 53227. [Google Scholar]
- McKinnon, J.; Spackman, M.A.; Mitchell, A.S. Novel tools for visualizing and exploring intermolecular interactions in molecular crystals. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. 2004, 60, 627–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, M.A.; Jayatilaka, D. Hirshfeld surface analysis. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2009, 11, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.; Gibbs, G.V.; Ribbe, P.H. Quadratic elongation: A quantitative measure of distortion in coordination polyhedra. Science 1971, 172, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, I.D. On measuring the size of distortions in coordination polyhedra. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. 2006, 62, 692–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, I.D. Recent developments in the methods and applications of the bond valence model. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6858–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ascenzo, L.; Auffinger, P. A comprehensive classification and nomenclature of carboxyl-carboxyl(ate) supramolecular motifs and related catemers: Implications for biomolecular systems. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 2015, 71, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudake, Y.; Kamble, S.; Patil, S.; Khirade, P.; Mehrotra, S. Study of dynamics of allyl chloride-2-butanone binary system using time domain reflectometry. J. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 56, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Common Solvents Used in Organic Chemistry: Table of Properties. 2016. Available online: https://www.organicdivision.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/organic_solvents.html (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Program Package CrysAlisPro 1.171.39.46e (Rigaku OD). 2018. Available online: http://www.rsc.org/suppdata/c8/tc/c8tc04867c/c8tc04867c1.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXS-97: Program for Crystal Structure Solution; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXL-97: Program for the Refinement of Crystal Structures; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Spek, A.L. PLATON: A Multipurpose Crystallographic Tool; Utrecht University: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bruker Instrument Service v3.0.21. Available online: https://www.bruker.com/products/x-ray-diffraction-and-elemental-analysis/single-crystal-x-ray-diffraction/sc-xrd-software/apex3.html (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- SAINT V8.18C (Bruker AXS Inc.). 2011. Available online: https://www.bruker.com/products/x-ray-diffraction-and-elemental-analysis/single-crystal-x-ray-diffraction/sc-xrd-software/apex3.html (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- SADABS-2016/2. Available online: https://www.bruker.com/products/x-ray-diffraction-and-elemental-analysis/single-crystal-x-ray-diffraction/sc-xrd-software/apex3.html (accessed on 1 April 2020).


| Atoms 3 | 3 d(I,J) | 4 d(I,J) | Atoms 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(1) | 2.2932(12) | 2.284(3) | O(1) |
| O(1)c | 2.2932(12) | 2.284(3) | O(1)d |
| O(6) | 2.3181(15) | 2.324(4) | O(5) |
| O(6)c | 2.3181(15) | 2.324(4) | O(5)d |
| O(10) | 2.2961(15) | 2.331(4) | O(9)a |
| O(10)c | 2.2961(15) | 2.331(4) | O(9)b |
| Donor—H | Acceptor | D-H (Å) | H…A (Å) | D…A (Å) | D-H…A (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O(4)—H(4) | O(13) [i] | 0.77(3) | 2.04(3) | 2.795(2) | 166(3) |
| O(7)—H(70) | O(11) | 1.07(4) | 1.39(5) | 2.445(2) | 169(4) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rádai, Z.; Bagi, P.; Czugler, M.; Karaghiosoff, K.; Keglevich, G. Optical Resolution of Dimethyl α-Hydroxy-Arylmethylphosphonates via Diastereomer Complex Formation Using Calcium Hydrogen O,O′-Dibenzoyl-(2R,3R)-Tartrate; X-Ray Analysis of the Complexes and Products. Symmetry 2020, 12, 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050758
Rádai Z, Bagi P, Czugler M, Karaghiosoff K, Keglevich G. Optical Resolution of Dimethyl α-Hydroxy-Arylmethylphosphonates via Diastereomer Complex Formation Using Calcium Hydrogen O,O′-Dibenzoyl-(2R,3R)-Tartrate; X-Ray Analysis of the Complexes and Products. Symmetry. 2020; 12(5):758. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050758
Chicago/Turabian StyleRádai, Zita, Péter Bagi, Mátyás Czugler, Konstantin Karaghiosoff, and György Keglevich. 2020. "Optical Resolution of Dimethyl α-Hydroxy-Arylmethylphosphonates via Diastereomer Complex Formation Using Calcium Hydrogen O,O′-Dibenzoyl-(2R,3R)-Tartrate; X-Ray Analysis of the Complexes and Products" Symmetry 12, no. 5: 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050758
APA StyleRádai, Z., Bagi, P., Czugler, M., Karaghiosoff, K., & Keglevich, G. (2020). Optical Resolution of Dimethyl α-Hydroxy-Arylmethylphosphonates via Diastereomer Complex Formation Using Calcium Hydrogen O,O′-Dibenzoyl-(2R,3R)-Tartrate; X-Ray Analysis of the Complexes and Products. Symmetry, 12(5), 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050758