Variation and Correlations in Departures from Symmetry of Brain Torque, Humeral Morphology and Handedness in an Archaeological Sample of Homo sapiens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
3. Methods
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trinkaus, E.; Churchill, S.E.; Ruff, C.B. Post-cranial robusticity in Homo II: Humeral bilateral asymmetry and bone plasticity. Am. J. Phys. Anthrop. 1994, 93, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzeau, A.; Gilissen, E.; Grimaud-Hervé, D. Shared pattern of quantified endocranial shape asymmetries among anatomically modern humans, great apes and fossil hominins. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, C.N.; Stock, J.T. Extreme mobility in the Late Pleistocene? Comparing limb biomechanics among fossil Homo, varsity athletes and Holocene foragers. J. Hum. Evol. 2013, 64, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, T.G.; Stock, J.T. Human variation in the periosteal geometry of the lower limb: Signatures of behaviour among human Holocene populations. In Reconstructing Mobility: Environmental, Behavioral, and Morphological Determinants; Carlson, K.J., Marchi, D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 67–90. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, E.; Roediger, D.; Kucukboyaci, N.E.; Carlson, C.; Devinsky, O.; Kuzniecky, R.; Cash, S.; Thesen, T. Hemispheric asymmetries of cortical volume in the human brain. Cortex 2013, 49, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, P.V. The brain of Homo habilis: A new level of organization in cerebral evolution. J. Hum. Evol. 1987, 16, 741–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaud-Hervé, D. L’évolution de l’encéphale chez Homo Erectus et Homo Sapiens: Exemples de l’Asie et de l’Europe; Cahiers de Paléoanthropologie, CNRS: Paris, France, 1997; 406p. [Google Scholar]
- Holloway, R.L.; Broadfield, D.C.; Yuan, M.S. The Human Fossil Record: Brain Endocasts, Paleoneurological Evidence; Wiley-Liss: New York, NY, USA, 2004; 315p. [Google Scholar]
- Balzeau, A.; Grimaud-Hervé, D.; Holloway, R.L.; Détroit, F.; Combès, B.; Prima, S. First description of the Cro-Magnon 1 endocast and study of brain variation an evolution in anatomically modern Homo Sapiens. BMSAP 2013, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzeau, A.; Gilissen, E.; Holloway, R.L.; Prima, S.; Grimaud-Hervé, D. Variations in size, shape and asymmetries of the third frontal convolution in hominids: Paleoneurological implications for hominin evolution and the origin of language. J. Hum. Evol. 2014, 76, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, M.E.; Güntürkün, O.; Hopkins, W.D.; Rogers, L.J. Lateralization of the vertebrate brain: Taking the side of model systems. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10351–10357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecaen, H.; Albert, M.L. Human Neuropsychology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1978; 509p. [Google Scholar]
- Bryden, M.P. Cerebral specialization: Clinical and experimental assessment. In Handbook of Neuropsychology; Boller, F., Grafman, J., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 1, pp. 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- Gazzaniga, M.S. On neural circuits and cognition. Neural Comput. 1994, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaniga, M.S. Principles of human brain organization derived from split-brain studies. Neuron 1995, 14, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, A. Unfinished business: Models of laterality in the nineteenth century. In Brain Asymmetry; Davidson, R.J., Hugdahl, K., Eds.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, Y.I.; Fernández, A.P.; Morris, D.M.; Canales-Rodríguez, E.J.; Haroon, H.; Garcia-Penton, L.; Augath, M.; García, L.G.; Logothetis, N.; Parker, G.; et al. Brain hemispheric structural efficiency and interconnectivity rightward asymmetry in human and nonhuman primates. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeMay, M. Morphological cerebral asymmetries of modern man, fossil man and nonhuman primate. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1976, 280, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeMay, M. Asymmetries of the skull and handedness. J. Neurol. Sci. 1977, 32, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, R.L.; De La Coste-Lareymondie, M.C. Brain endocast asymmetry in pongids and hominids: Some preliminary findings on the paleontology of cerebral dominance. Am. J. Phys. Anthrop. 1982, 58, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.D.; Marino, L. Asymmetries in cerebral width in nonhuman primate brains as revealed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Neuropsychologia 2000, 38, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilcher, D.L.; Hammock, E.A.D.; Hopkins, W.D. Cerebral volumetric asymmetries in non-human primates: A magnetic resonance imaging study. Laterality 2001, 6, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, C.D.; Johnsrude, I.; Ashburner, J.; Henson, R.N.; Friston, K.J.; Frackowiak, R. Cerebral asymmetry and the effects of sex and handedness on brain structure: A voxel-based morphometric analysis of 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage 2001, 14, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, K.E.; Paus, T.; Lerch, J.; Zijdenbos, A.; Collins, D.L.; Neelin, P.; Taylor, J.; Worsley, K.; Evans, A. Structural asymmetries in the human brain: A voxel-based statistical analysis of 142 MRI scans. Cereb. Cortex 2001, 11, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.D.; Taglialatela, J.P.; Meguerditchian, A.; Nir, T.; Schenker-Ahmed, N.M.; Sherwood, C.C. Gray matter asymmetries in chimpanzees as revealed by voxel-based morphometry. Neuroimage 2008, 42, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, R.L. Volumetric and asymmetry determinations on recent hominid endocasts: Spy I and II, Djebel Ihroud I, and the Salé Homo erectus specimens. Am. J. Phys. Anthrop. 1981, 5, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, R.L. The Indonesian Homo erectus brain endocasts revisited. Am. J. Phys. Anthrop. 1981, 55, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeMay, M.; Kido, D.K. Asymmetries of the cerebral hemispheres on computed tomograms. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1978, 2, 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- LeMay, M.; Billig, M.S.; Geschwind, N. Asymmetries of the brains and skulls of nonhuman primates. In Primate Brain Evolution, Methods and Concepts; Falk, D., Armstrong, E., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 263–277. [Google Scholar]
- Galaburda, A.M.; LeMay, M.; Kemper, T.L.; Geschwind, N. Right-left asymmetries in the brain. Science 1978, 199, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kertesz, A.; Black, S.E.; Polk, M.; Howell, J. Cerebral asymmetries on magnetic resonance imaging. Cortex 1986, 22, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, D.; Hildebolt, C.; Cheverud, J.; Vannier, M.W.; Helmkamp, R.C.; Konigsberg, L. Cortical asymmetries in frontal lobes of rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Brain Res. 1990, 512, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzeau, A.; Gilissen, E. Endocranial shape asymmetries in Pan paniscus, Pan troglodytes and Gorilla gorilla assessed via skull based landmark analysis. J. Hum. Evol. 2010, 59, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeMay, M. Asymmetries of the brains and skulls of nonhuman primates. In Cerebral Lateralization in Nonhuman Species; Glick, S.D., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 233–245. [Google Scholar]
- Cain, D.P.; Wada, J.A. An anatomical asymmetry in the baboon brain. Brain Behav. Evol. 1979, 16, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheverud, J.M.; Falk, D.; Hildebolt, C.; Moore, A.J.; Helmkamp, R.C.; Vannier, M.W. Heritability and association of cortical petalias in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Brain Behav. Evol. 1990, 35, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.D.; Phillips, K.; Bania, A.; Calcutt, S.E.; Gardner, M.; Russell, J.; Schaeffer, J.; Lonsdorf, E.V.; Ross, S.R.; Schapiro, S.J. Hand preferences for coordinated bimanual actions in 777 great apes: Implications for the evolution of handedness in hominins. J. Hum. Evol. 2011, 60, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogart, S.L.; Mangin, J.-F.; Schapiro, S.J.; Reamer, L.; Bennett, A.J.; Pierre, P.J.; Hopkins, W.D. Cortical sulci asymmetries in chimpanzees and macaques: A new look at an old idea. Neuroimage 2012, 61, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corballis, M.C.; Badzakova-Trajkov, G.; Häberling, I.S. Right hand, left brain: Genetic and evolutionary bases of cerebral asymmetries for language and manual action. WIREs Cogn. Sci. 2012, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubelaker, D.H.; Zarenko, K.M. Can Handedness be Determined from Skeletal Remains? A Chronological Review of the Literature. J. Forensic Sci. 2012, 57, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shaw, C.N. Is ‘hand preference’ coded in the hominin skeleton? An in-vivo study of bilateral morphological variation. J. Hum. Evol. 2011, 61, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubicka, A.M.; Nowaczewska, W.; Balzeau, A.; Piontek, J. Bilateral asymmetry of the humerus in Neandertals, Australian aborigines and medieval humans. Am. J. Phys. Anthrop. 2018, 167, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, C.N.; Ryan, T.M. Does skeletal anatomy reflect adaptation to locomotor Patterns? Cortical and trabecular architecture in human and nonhuman Anthropoids. Am. J. Phys. Anthrop. 2012, 147, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćwirko-Godycki, M. Early Medieval Burial Ground on the Lednicki Promontory. Materiały i Prace Antropologiczne 1956, 11, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Buikstra, J.E.; Ubelaker, D.H. Standards for Data Collection from Human Skeletal Remains; Arkansas Archeological Survey Research: Fayetteville, NC, USA, 1994; 44, 272pp. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.D.; Folkens, P.A. The Human Bone Manual; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wrzesińska, A.; Wrzesiński, J. Wczesnośredniowieczne cmentarzysko w Dziekanowicach, stanowisko 22. Studia Lednickie 1998, 5, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Makohonienko, M. Analiza palinologiczna zawartości ziemi z misy brązowej z wczesnośredniowiecznego cmentarzyska w Dziekanowicach, stanowisko 22. Studia Lednickie 2000, 6, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Makowiecki, D.; Tomek, T.; Bochenski, Z.M. Birds in Early Medieval Greater Poland: Consumption and Hawking. Int. J. Osteoarchaeol. 2014, 24, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profico, A.; Schlager, S.; Valoriani, V.; Buzi, C.; Melchionna, M.; Veneziano, A.; Raia, P.; Moggi-Cecchi, J.; Manzi, G. Reproducing the internal and external anatomy of fossil bones: Two new automatic digital tools. Am. J. Phys. Anthrop. 2018, 166, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profico, A.; Buzi, C.; Melchionna, M.; Veneziano, A.; Raia, P. Technical note: Endomaker, a new algorithm for fully automatic extraction of cranial endocasts and the calculation of their volumes. Am. J. Phys. Anthrop. 2020, accepted, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruff, C.B. Body size, body shape, and long bone strength in modern humans. J. Hum. Evol. 2000, 38, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruff, C.B. Moment Macro for NIH Image and Image J. Available online: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/fae/mmacro.html (accessed on 6 February 2020).
- Lieberman, D.E.; Polk, J.D.; Demes, B. Predicting long bone loading from cross-sectional geometry. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2004, 123, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, J.T.; Shaw, C.N. Which measures of diaphyseal robusticity are robust? A comparison of external methods of quantifying the strength of long bone diaphyses to cross-sectional geometric properties. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2007, 134, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, K.J.; Grine, F.E.; Pearson, O.M. Robusticity and Sexual Dimorphism in the Postcranium of Modern Hunter-Gatherers from Australia. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2007, 134, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, T.G.; Stock, J.T. The influence of relative body breadth on the diaphyseal morphology of the human lower limb. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2014, 26, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.R.; Strobeck, C. Fluctuating asymmetry analyses revisited. In Developmental Instability: Causes and Consequences; Polak, M., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 279–319. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, A.R. From symmetry to asymmetry: Phylogenetic patterns of asymmetry variation in animals and their evolutionary significance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14279–14286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubbs, F.E. procedures for detecting outlying observations in samples. Technometrics 1969, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.R. Fluctuating asymmetry analyses: A primer. In Developmental Instability: Its Origins and Evolutionary Implications; Markow, T.A., Ed.; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 335–364. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, J.H.; Emlen, J.M.; Freeman, D.C.; Leamy, L.J.; Kieser, J.A. Directional asymmetry and the measurement of developmental instability. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1998, 64, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Valen, L. A study of fluctuating asymmetry. Evolution 1962, 16, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry; Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, W.R. Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 1989, 43, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, O.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Palaeontological Statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Amrhein, V.; Greenland, S.; McShane, B. Scientists rise up against statistical significance. Nature 2019, 567, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontulainen, S.; Sievänen, H.; Kannus, P.; Pasanen, M.; Vuori, I. Effect of long-term impact-loading on mass, size, and estimated strength of humerus and radius of female racquet-sports players: A peripheral quantitative computed tomography study between young and old starters and controls. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2003, 18, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaburda, A.M. Anatomic basis of cerebral dominance. In Brain Asymmetry; Davidson, R.J., Hugdahl, K., Eds.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 51–73. [Google Scholar]
- Sládek, V.; Ruff, C.B.; Berner, M.; Holt, B.; Niskanen, M.; Schuplerová, E.; Hora, M. The impact of subsistence changes on humeral bilateral asymmetry in Terminal Pleistocene and Holocene Europe. J. Hum. Evol. 2016, 92, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinkaus, E.; Ruff, C.B. Diaphyseal Cross-sectional Geometry of Near Eastern Middle Palaeolithic Humans: The Humerus. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1999, 26, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, O. Activity, climate, and postcranial robusticity. Curr. Anthropol. 2000, 41, 569–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicka, A.M.; Lubiatowski, P.; Dlugosz, J.D.; Romanowski, L.; Piontek, J. Directional Asymmetry of Upper Limbs in a Medieval Population from Poland: A Combination of Linear and Geometric Morphometrics. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2016, 28, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, O.M. Postcranial remains and the origin of modern humans. Evol. Anthropol. 2000, 9, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
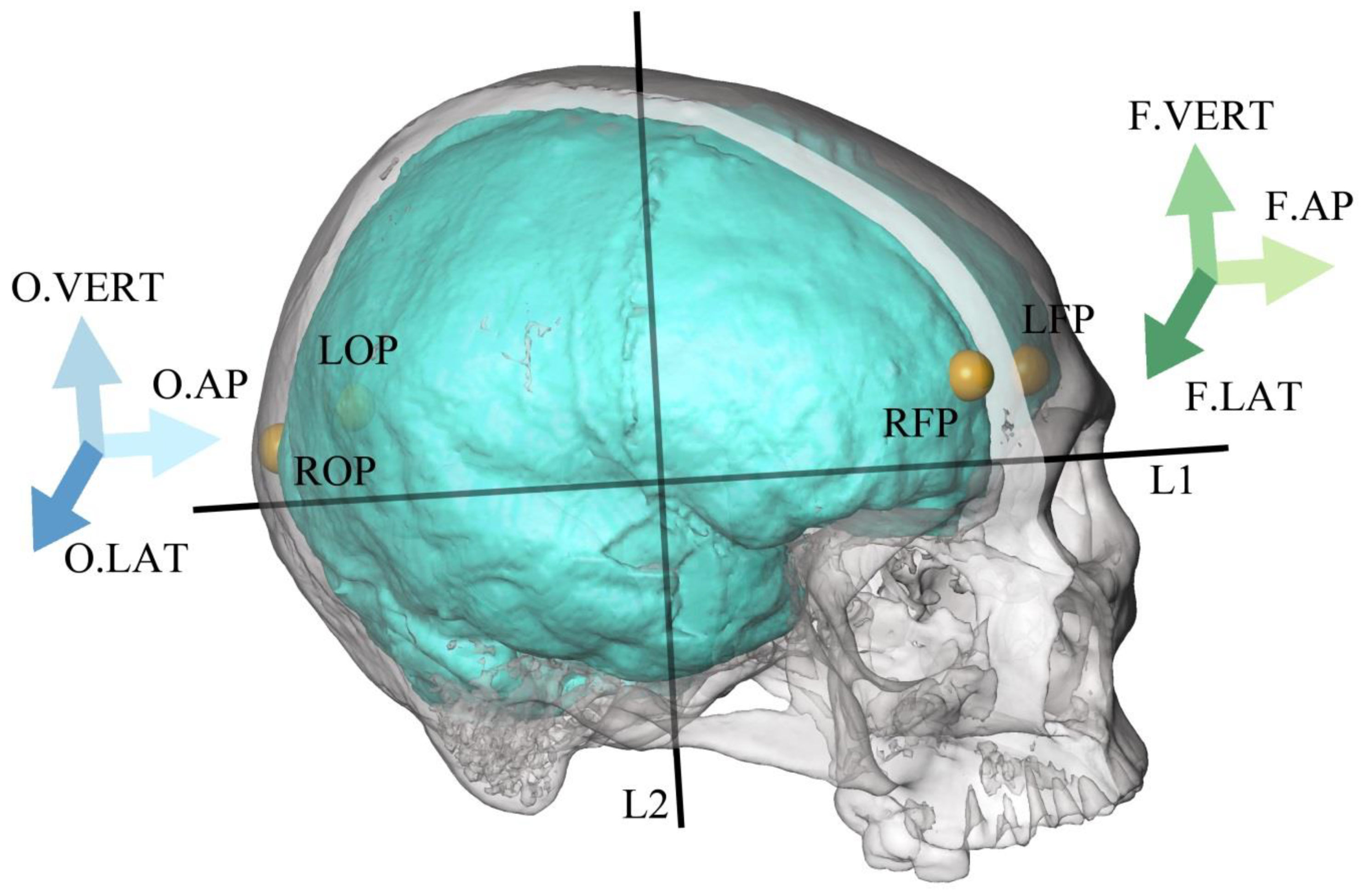
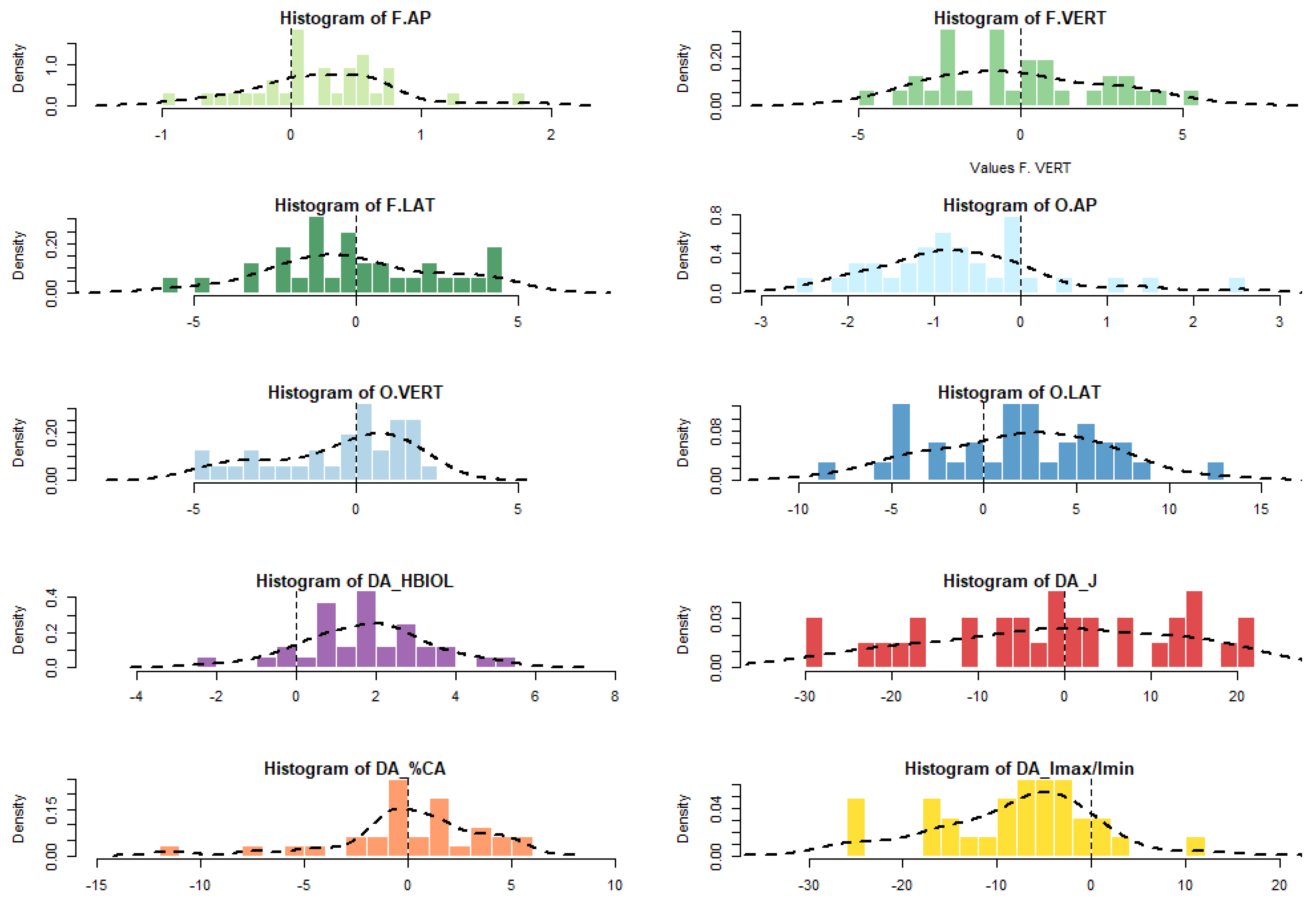
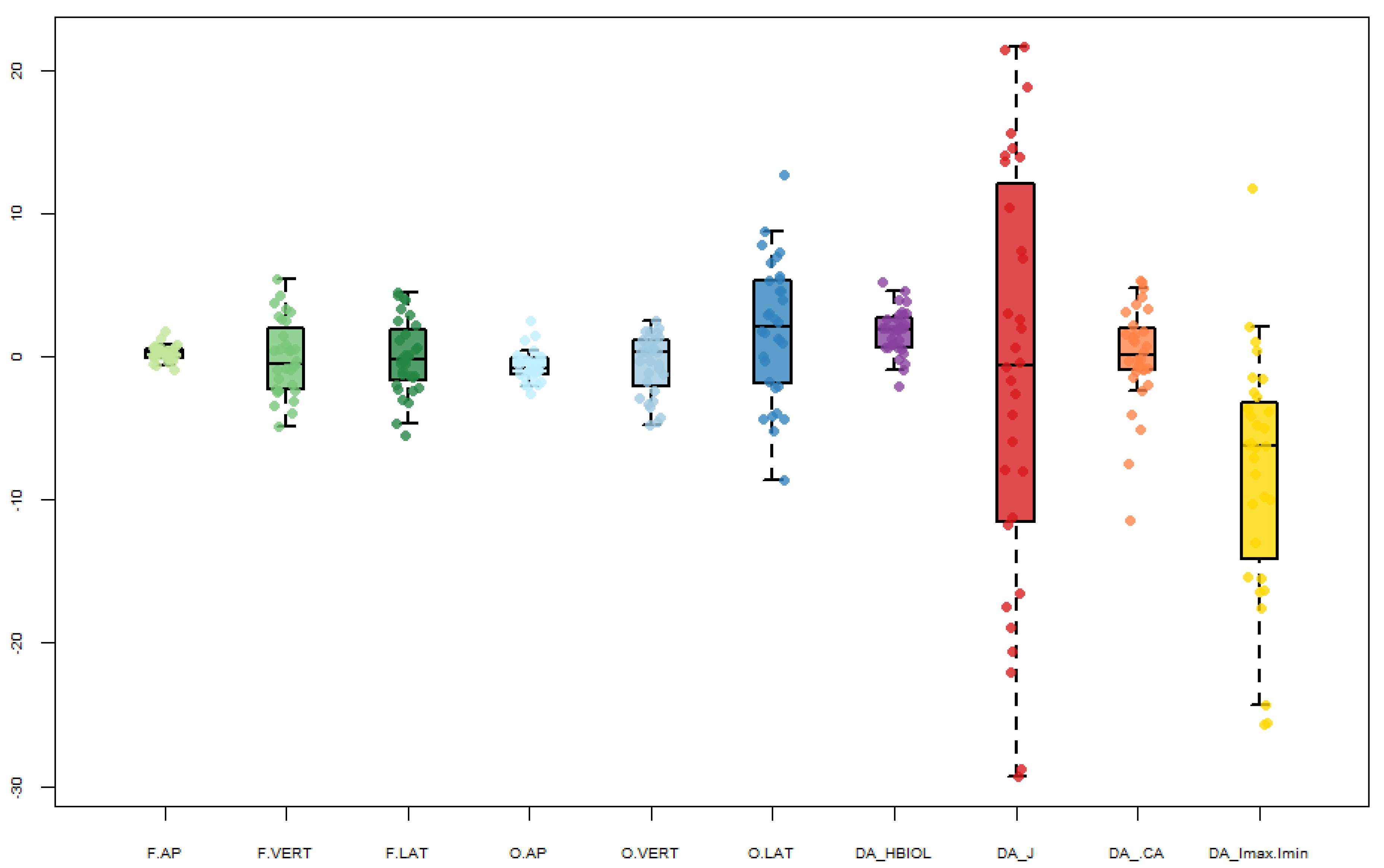
| Abbreviation | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| HBIOL | the biomechanical length of the humerus | measured from the most proximal point on the head to the most distal point on the lateral lip of the trochlea |
| J | the polar moment of area | indicates resistance to bending and torsional rigidity |
| %CA | percentage of cortical area | calculated as %CA = (CA/TA) × 100, it shows the distribution of cortical area versus total subperiosteal area |
| Imax/Imin | ratio of maximum to minimum second moments of area | calculated as Imax/Imin, ratio close to 1 indicates circular shape of the cross-section |
| F.AP | F.VERT | F.LAT | O.AP | O.VERT | O.LAT | HBIOL | J | %CA | Imax/Imin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 31 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 31 | 32 |
| Min | −0.9 | −4.9 | −5.6 | −2.6 | −4.8 | −8.6 | −2.1 | −29.3 | −7.4 | −25.7 |
| 25 prcntil | −0.1 | −2.4 | −1.8 | −1.3 | −2.4 | −2.0 | 0.6 | −11.6 | −0.9 | −14.7 |
| Mean (R-L) | 0.2 | −0.1 | −0.1 | −0.7 | −0.6 | 1.9 | 1.7 | −1.3 | 0.4 | −7.6 |
| Median | 0.3 | −0.5 | −0.3 | −0.8 | 0.3 | 2.1 | 1.9 | −0.6 | 0.3 | −6.2 |
| 75 prcntil | 0.6 | 2.2 | 2.0 | −0.1 | 1.2 | 5.3 | 2.8 | 12.8 | 2.2 | −2.6 |
| Max | 1.8 | 5.4 | 4.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 12.7 | 5.2 | 21.6 | 5.3 | 12.3 |
| Sum | 7.9 | −2.9 | −1.6 | −21.1 | −17.3 | 59.9 | 55.3 | −41.7 | 13.2 | −241.8 |
| FA4a | 0.4 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 0.8 | 1.7 | 3.7 | 1.3 | 11.2 | 2.9 | 6.3 |
| Std. error | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 2.6 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| Variance | 0.3 | 6.7 | 6.6 | 1.1 | 4.5 | 22.6 | 2.5 | 208.6 | 8.5 | 82.0 |
| Stand. dev | 0.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 1.1 | 2.1 | 4.8 | 1.6 | 14.4 | 2.9 | 9.1 |
| ((R-L)/0) t | 2.5 | −0.2 | −0.1 | −3.5 | −1.4 | 2.2 | 6.2 | −0.5 | 0.1 | −5.4 |
| p | 3.4 × 10−2 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 4 × 10−3 | 0.15 | 3.3 × 10−2 | 3.9 × 10−6 | 0.61 | 0.93 | 2.9 × 10−5 |
| Skewness | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 1.0 | −0.6 | −0.1 | −0.1 | −0.2 | −0.5 | −0.1 |
| Ts | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 2.3 | −1.5 | −0.2 | −0.3 | −0.6 | −1.2 | −0.2 |
| P | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | < 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 |
| Kurtosis | 1.2 | −0.7 | −0.4 | 1.7 | −0.8 | −0.2 | 0.3 | −0.8 | 0.7 | 0.4 |
| P | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | < 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balzeau, A.; Ball-Albessard, L.; Kubicka, A.M. Variation and Correlations in Departures from Symmetry of Brain Torque, Humeral Morphology and Handedness in an Archaeological Sample of Homo sapiens. Symmetry 2020, 12, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12030432
Balzeau A, Ball-Albessard L, Kubicka AM. Variation and Correlations in Departures from Symmetry of Brain Torque, Humeral Morphology and Handedness in an Archaeological Sample of Homo sapiens. Symmetry. 2020; 12(3):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12030432
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalzeau, Antoine, Lou Ball-Albessard, and Anna Maria Kubicka. 2020. "Variation and Correlations in Departures from Symmetry of Brain Torque, Humeral Morphology and Handedness in an Archaeological Sample of Homo sapiens" Symmetry 12, no. 3: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12030432
APA StyleBalzeau, A., Ball-Albessard, L., & Kubicka, A. M. (2020). Variation and Correlations in Departures from Symmetry of Brain Torque, Humeral Morphology and Handedness in an Archaeological Sample of Homo sapiens. Symmetry, 12(3), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12030432






