Mixed Convection in a Double Lid-Driven Cavity Filled with Hybrid Nanofluid by Using Finite Volume Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Formulation
3. Numerical Method
4. Grid-Independence Test
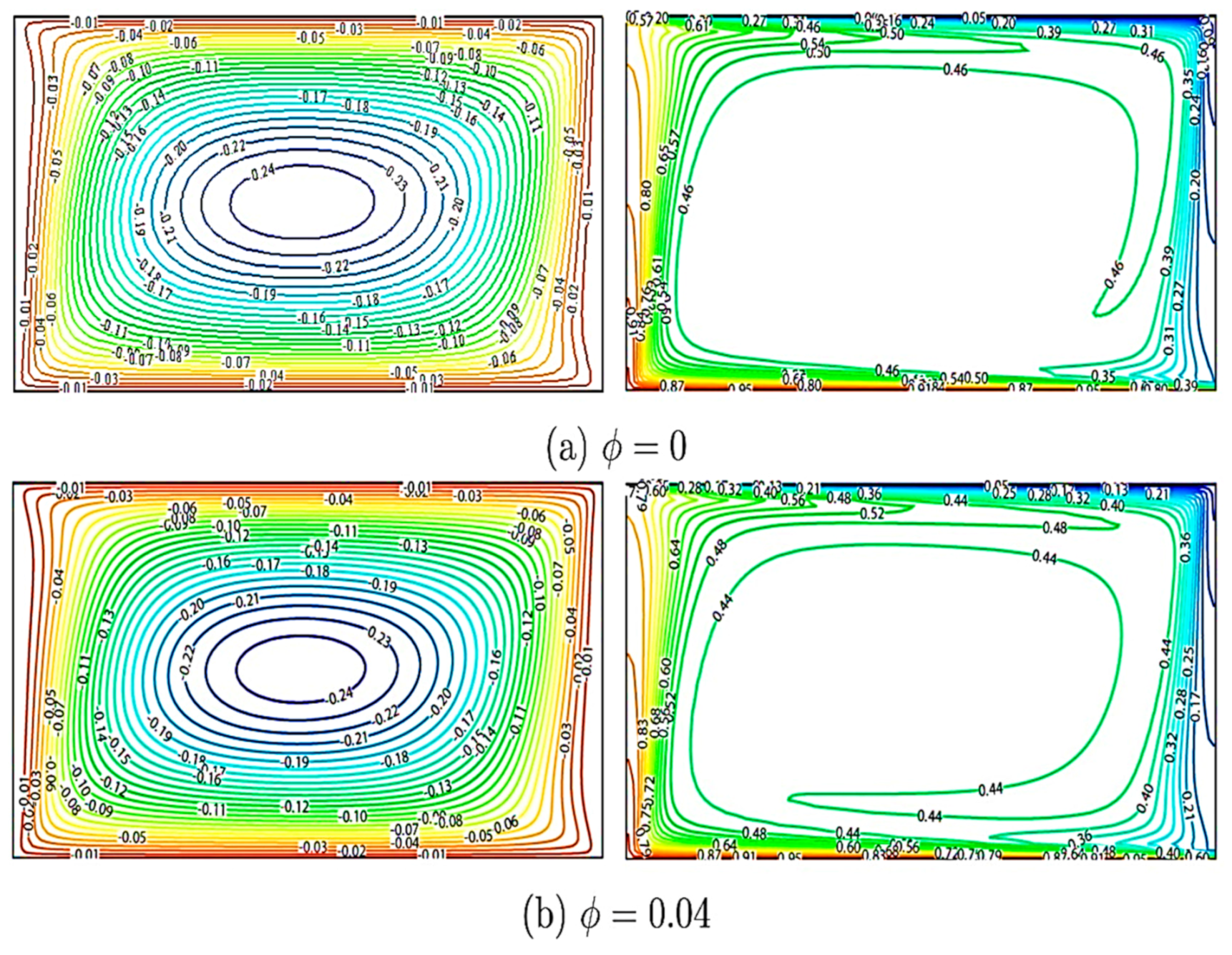
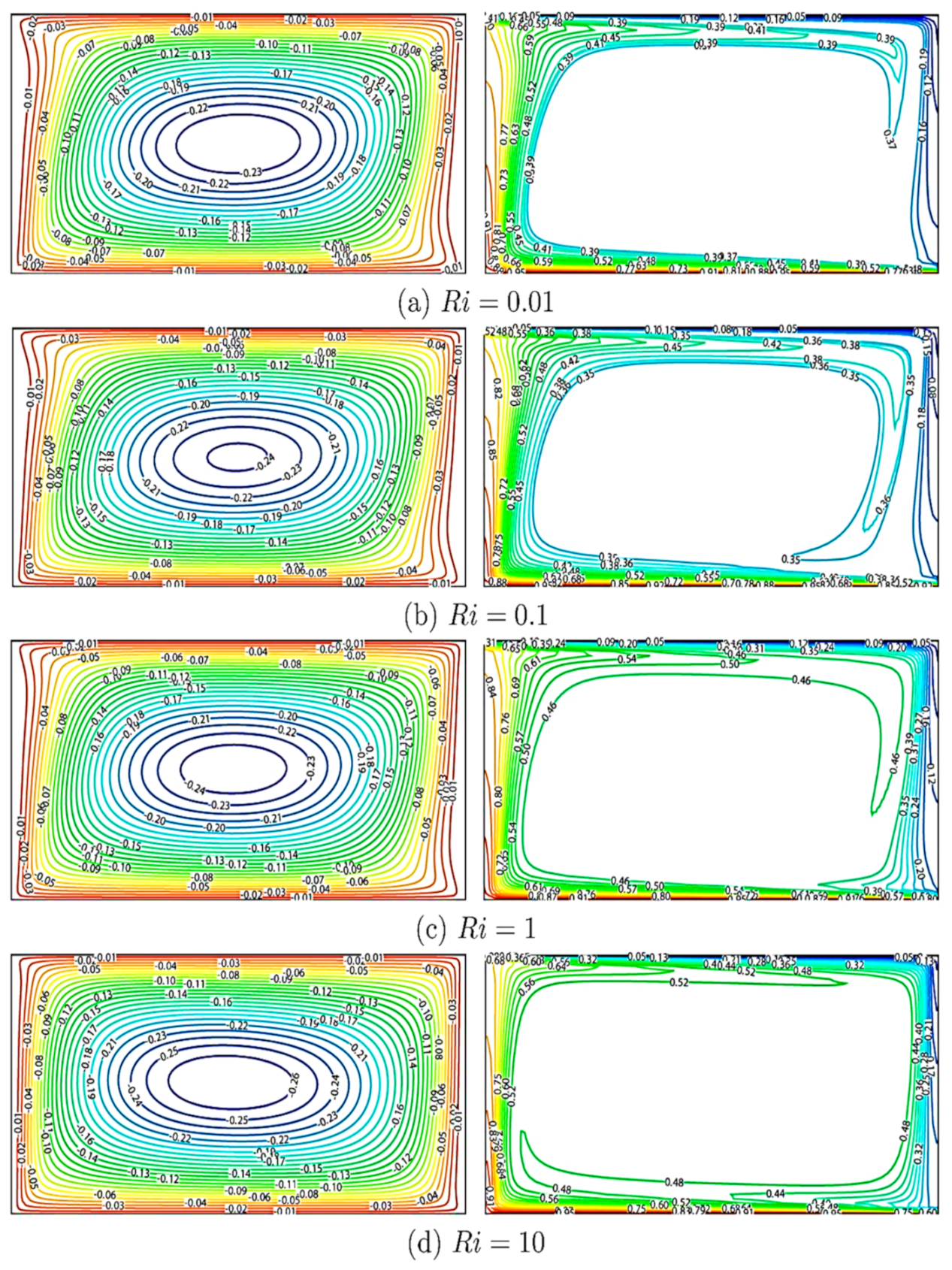
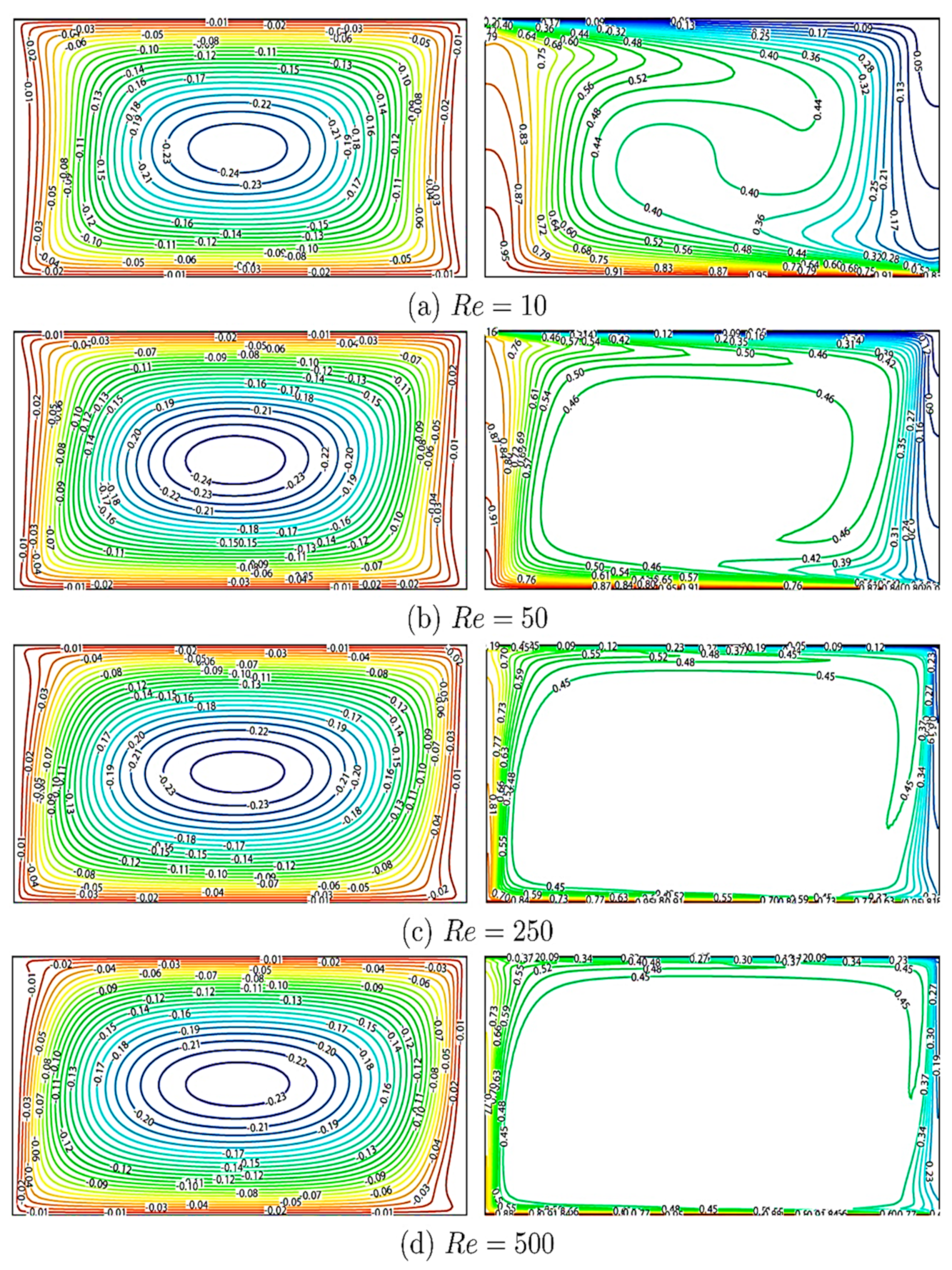
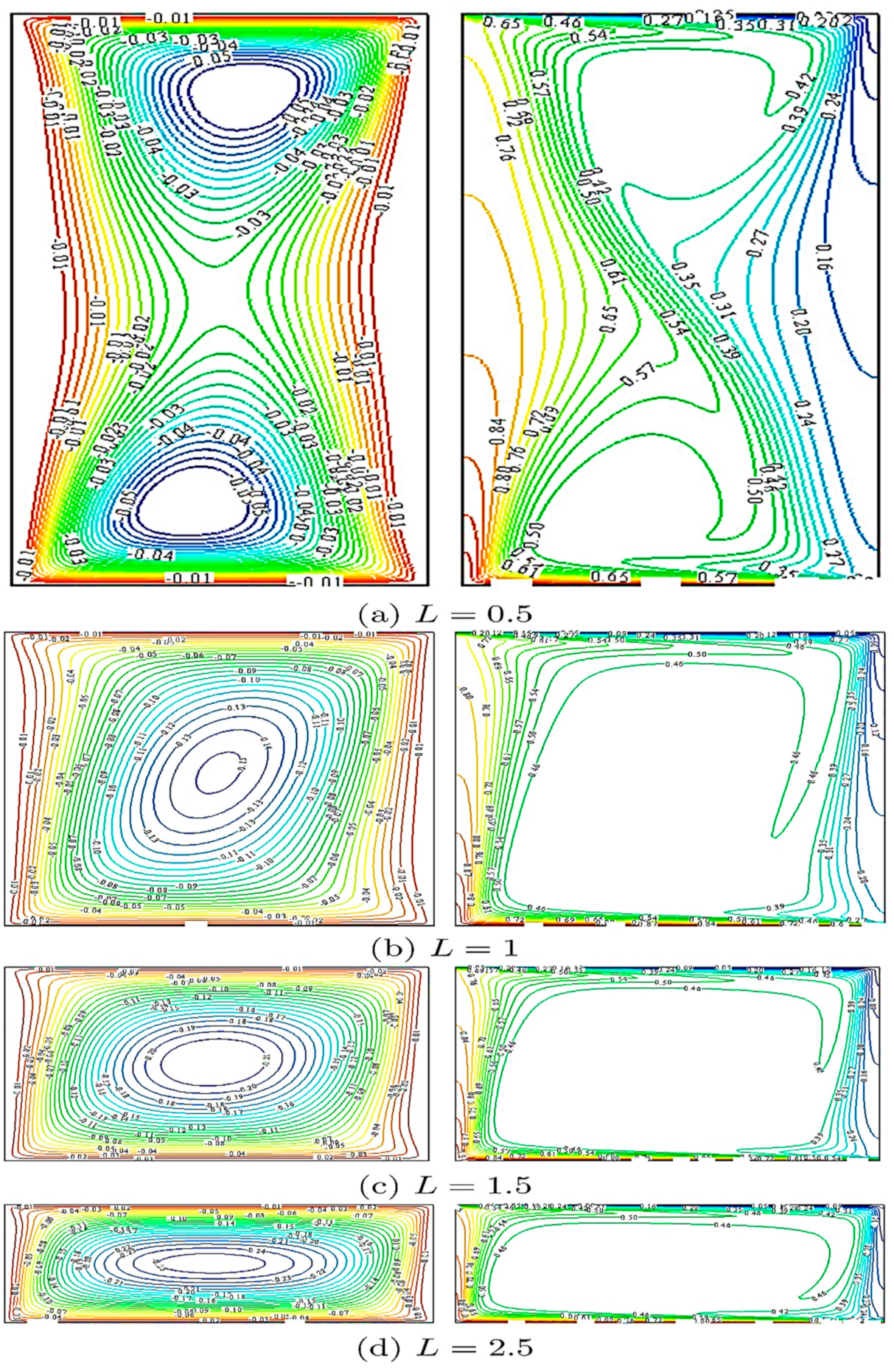
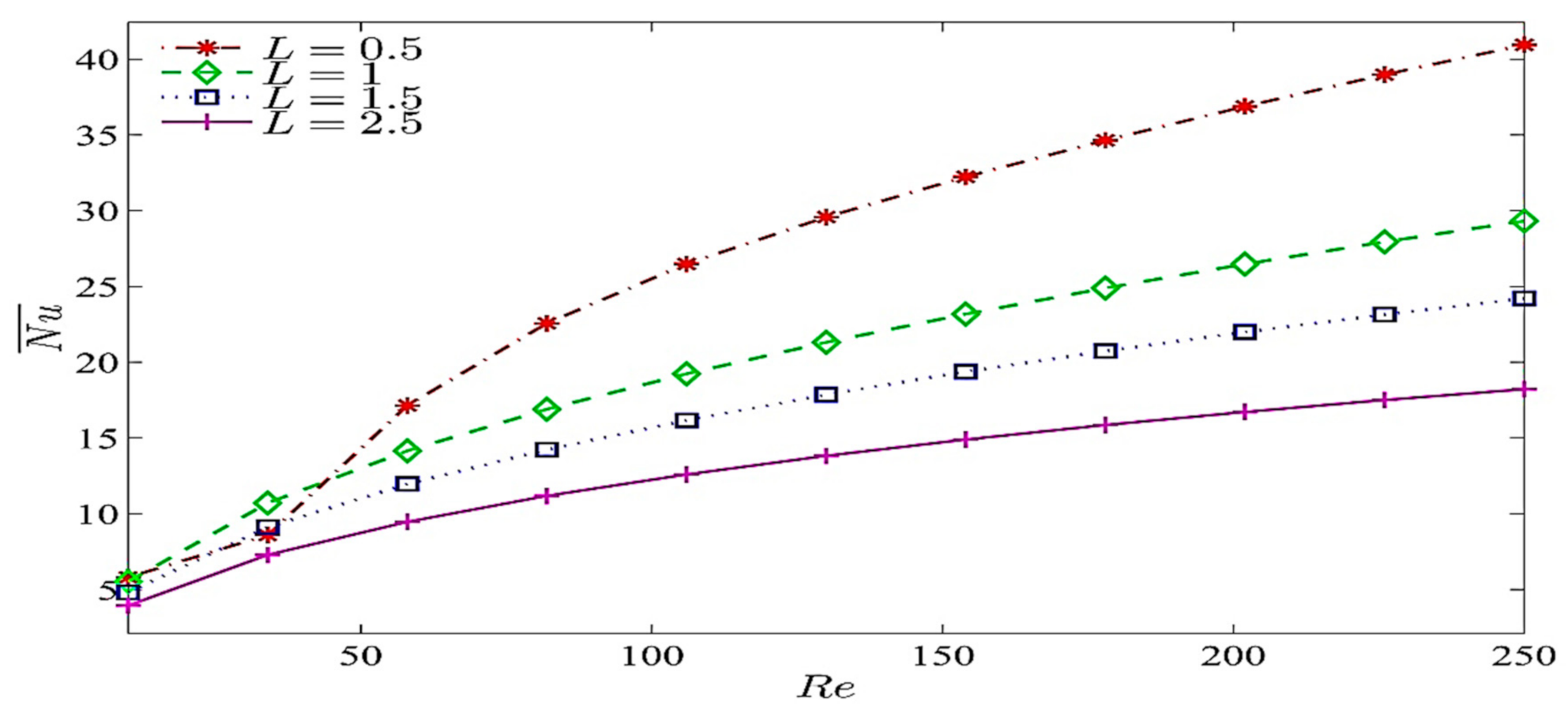
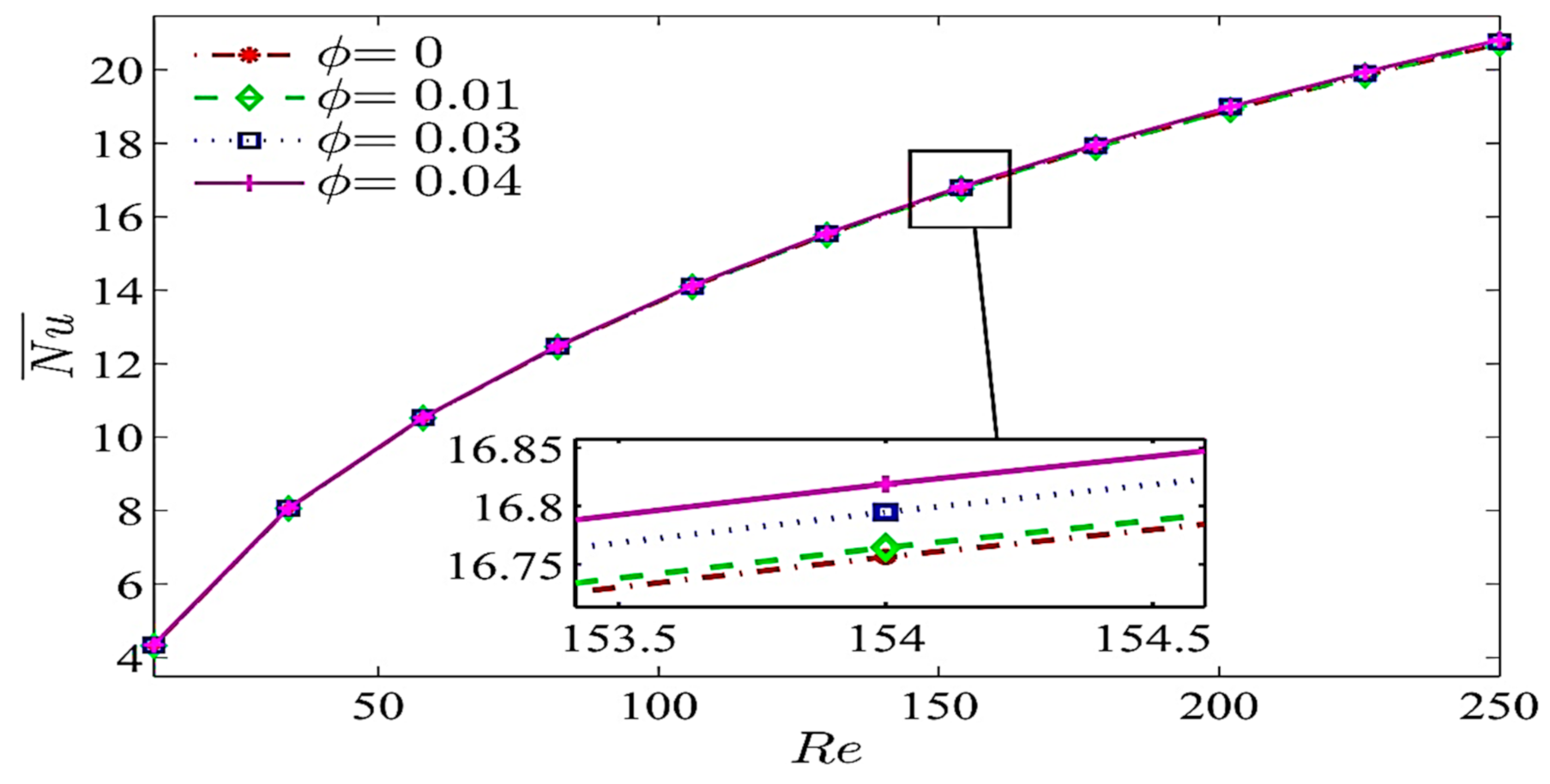
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| = specific heat capacity; |
| = diameter of the base fluid molecule; |
| = diameter of the nanoparticle; |
| = gravitational acceleration; |
| = thermal conductivity; |
| = Boltzmann’s constant ; |
| = side length of enclosure; |
| = Grashof number; |
| = pressure and dimensionless pressure, |
| = Prandtl number; |
| = Reynolds number; |
| = Brownian motion Reynolds number; |
| = Richardson number, ; |
| = temperature; |
| = reference temperature (); |
| = freezing point of the base fluid (); |
| = velocity anddimensionless velocity, |
| = Brownian velocity of the nanoparticle; and |
| = space coordinates anddimensionless space coordinates. |
| Greek symbol |
| = dimensionless temperature; |
| = thermal expansion coefficient; |
| = dynamic viscosity; |
| = kinematic viscosity; |
| = density; |
| = solid volume fraction; |
| = thermal diffusivity; |
| = Thermal expansion coefficient |
| Subscript |
| = cold; |
| = base fluid; |
| = hot; |
| = hybrid nanofluid; |
| = solid nanoparticles; |
| = lid-driven direction |
| b = bottom wall |
| t = top wall |
References
- Alsabery, A.I.; Ismael, M.A.; Chamkha, A.J.; Hashim, I. Mixed convection of Al2O3-water nanofluid in a double lid-driven square cavity with a solid inner insert using Buongiorno’s two-phase model. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 119, 939–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulepova, E.V.; Sheremet, M.A.; Oztop, H.F.; Abu-hamdeh, N. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences Mixed convection of Al2O3–H2O nanoliquid in a square chamber with complicated fin. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 165, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizul, F.M.; Alsabery, A.I.; Hashim, I. Heatlines visualisation of mixed convection flow in a wavy heated cavity filled with nanofluids and having an inner solid block. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 175, 105529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louaraychi, A.; Lamsaadi, M.; Naïmi, M.; El Harfi, H.; Kaddiri, M.; Raji, A.; Hasnaoui, M. Mixed convection heat transfer correlations in shallow rectangular cavities with single and double-lid driven boundaries. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 132, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, M.; Safaei, M.R.; Vafai, K.; Ahmadi, G.; Dahari, M.; Kazi, S.; Jomhari, N. Investigation of nanofluid mixed convection in a shallow cavity using a two-phase mixture model. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2014, 75, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimipour, A.; Esfe, M.H.; Safaei, M.R.; Semiromi, D.T.; Jafari, S.; Kazi, S.N. Mixed convection of copper-water nanofluid in a shallow inclined lid driven cavity using the Lattice Boltzmann method. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 402, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, M. Mixed convection inside nanofluid filled rectangular enclosures with moving bottom wall. Therm. Sci. 2011, 15, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimipour, A.; Nezhad, A.H.; Behzadmehr, A.; Alikhani, S.; Abedini, E. Periodic mixed convection of a nanofluid in a cavity with top lid sinusoidal motion. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C 2011, 225, 2149–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaseen, D.T.; Ismael, M.A. Analysis of power law fluid-structure interaction in an open trapezoidal cavity. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 174, 105481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purusothaman, A.; Malekshah, E.H. Lattice Boltzmann modeling of MHD free convection of nanofluid in a V-shaped microelectronic module. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2019, 10, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M. Solidification of NEPCM under the effect of magnetic field in a porous thermal energy storage enclosure using CuO nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purusothaman, A. Investigation of natural convection heat transfer performance of the QFN-PCB electronic module by using nanofluid for power electronics cooling applications. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahiraei, M. A Comprehensive Review on Different Numerical Approaches for Simulation in Nanofluids: Traditional and Novel Techniques. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2014, 35, 984–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidik, N.A.C.; Razali, S.A. Lattice Boltzmann method for convective heat transfer of nanofluids—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Venkitaraj, K.P.; Selvakumar, P.; Chandrasekar, M. Synthesis of Al2O3-Cu/water hybrid nanofluids using two step method and its thermo physical properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 388, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, J.; Ghosh, P.; Adil, A. A review on hybrid nanofluids: Recent research, development and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, J.A.R.; Kumar, K.K.; Rao, S.S. State-of-art review on hybrid nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabi, B.; Salehi, S. Augmentation of the heat transfer performance of a sinusoidal corrugated enclosure by employing hybrid nanofluid. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkha, A.J.; Miroshnichenko, I.V.; Sheremet, M.A. Numerical analysis of unsteady conjugate natural convection of hybrid water-based nanofluid in a semicircular cavity. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2017, 9, 041004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nine, M.J.; Munkhbayar, B.; Rahman, M.S.; Chung, H.; Jeong, H. Highly productive synthesis process of well dispersed Cu2O and Cu/Cu2O nanoparticles and its thermal characterization. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 141, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, P.K.; Brocchi, E.A.; Motta, M.S. In-situ formation of Cu-Al2O3 nano-scale composites by chemical routes and studies on their microstructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 313, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, T.T.; Sundara, R. Synthesis and transport properties of metal oxide decorated graphene dispersed nanofluids. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 8527–8533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadkhast, M.; Toghraie, D.; Karimipour, A. Developing a new correlation to estimate the thermal conductivity of MWCNT-CuO/water hybrid nanofluid via an experimental investigation. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 129, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfe, M.H.; Arani, A.A.A.; Rezaie, M.; Yan, W.M.; Karimipour, A. Experimental determination of thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of Ag-MgO/water hybrid nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 66, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsabery, A.I.; Hashim, I.; Hajjar, A.; Ghalambaz, M.; Nadeem, S.; Pour, M.S. Entropy Generation and Natural Convection Flow of Hybrid Nanofluids in a Partially Divided Wavy Cavity Including Solid Blocks. Energies 2020, 13, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcione, M. Empirical correlating equations for predicting the effective thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of nanofluids. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, S.V. Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow; Hemisphere: Washington, DC, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Ismael, M.A.; Pop, I.; Chamkha, A.J. Mixed convection in a lid-driven square cavity with partial slip. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2014, 82, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M.; Chamkha, A.J.; Ismael, M.A.; Salah, T. Magnetohydrodynamics Natural Convection in a Triangular Cavity Filled with a Cu-Al2O3/Water Hybrid Nanofluid with Localized Heating from below and Internal Heat Generation. J. Heat Transf. 2018, 140, 072502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

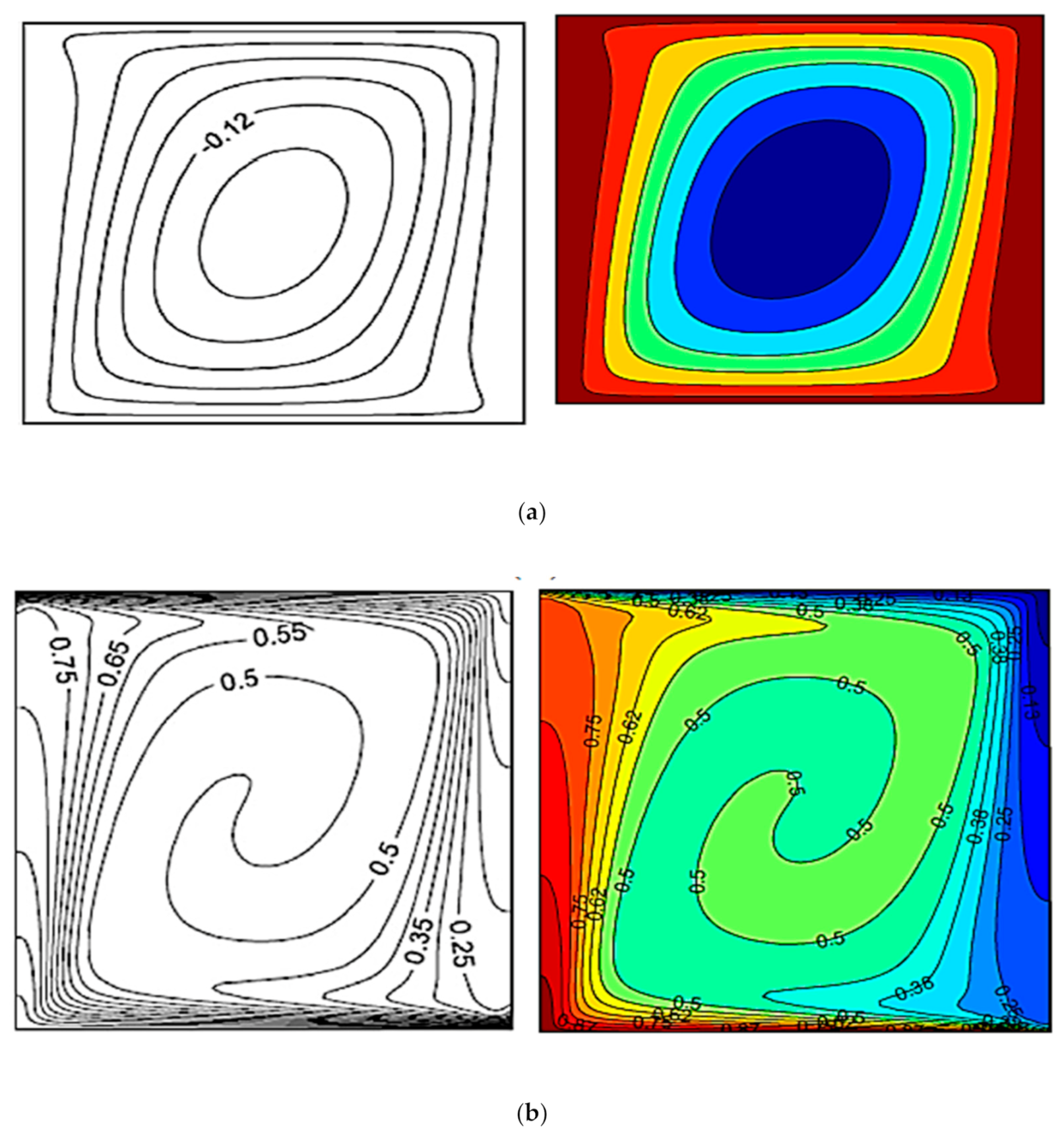



| Size | Average Nusselt Number |
|---|---|
| 60 × 30 | 12.237437 |
| 80 × 40 | 13.041916 |
| 100 × 50 | 13.457630 |
| 120 × 60 | 13.714399 |
| 140 × 70 | 13.892601 |
| Physical Properties | Fluid (Water) | Copper | Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.628 | 400 | 40 | |
| 695 | - | - | |
| 993 | 8933 | 3970 | |
| 4178 | 385 | 765 | |
| 36.2 | 1.67 | 0.85 | |
| 0.385 | 29 | 33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, I.R.; Alsabery, A.I.; Bakar, N.A.; Roslan, R. Mixed Convection in a Double Lid-Driven Cavity Filled with Hybrid Nanofluid by Using Finite Volume Method. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12121977
Ali IR, Alsabery AI, Bakar NA, Roslan R. Mixed Convection in a Double Lid-Driven Cavity Filled with Hybrid Nanofluid by Using Finite Volume Method. Symmetry. 2020; 12(12):1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12121977
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, I.R., Ammar I. Alsabery, N.A. Bakar, and Rozaini Roslan. 2020. "Mixed Convection in a Double Lid-Driven Cavity Filled with Hybrid Nanofluid by Using Finite Volume Method" Symmetry 12, no. 12: 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12121977
APA StyleAli, I. R., Alsabery, A. I., Bakar, N. A., & Roslan, R. (2020). Mixed Convection in a Double Lid-Driven Cavity Filled with Hybrid Nanofluid by Using Finite Volume Method. Symmetry, 12(12), 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12121977





