Research of the Equipment Self-Calibration Methods for Different Shape Fertilizers Particles Distribution by Size Using Image Processing Measurement Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Measurements Repeatability
3.2. Cumulative Curve Correction
3.3. Neural Network Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laucka, A.; Andriukaitis, D. Research of the Defects in Anesthetic Masks. Radioengineering 2015, 24, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovič, Z.; Markovič, S. Determination of Particle Size Distributions by Laser Diffraction. Tech. New Matter 2012, 67, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Witt, W.; Heur, M.; Schaller, M. In-line particle sizing for process control in new dimensions. China Particuol. 2004, 2, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornillault, J. Particle size analyser. Appl. Opt. 1972, 11, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coghill, P.J.; Millen, M.J.; Sowerby, B.D. On-line measurement of particle size in mineral slurries. Miner. Eng. 2002, 15, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Ultrasonic Measurements in Particle Size Analysis. Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry: Applications, Theory and Instrumentation; John Wiley Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 88–127. Available online: 10.1002/9780470027318.a1518 (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Wan, Q.; Jiang, W.K. Near field acoustic holography (NAH) theory for cyclostationary sound field and its application. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 290, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, W.P.; Peck, G.R.; Morris, K.R. Determination of fluidized bed granulation end point using near-infrared spectroscopy and phenomenological analysis. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrak, D. Simultaneous measurements of particle size and particle velocity by the spatial filtering. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2002, 19, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, P.; Stefan, D.; Gunter, K. In-line particle sizing for real-time process control by fibre-optical spatial filtering technique (SFT). Adv. Powder Technol. 2011, 22, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, T.; Muramoto, K. Z-R relation for snowfall using two small doppler radars and snow particle images. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 4122–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammermeyer, K.; Binder, J. Particle Size Determination by Sedimentation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 1941, 13, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Mori, S. Determination of Particle Size Distribution of Used Black Tea Leaves by Scanning Electron Microscope. Dhaka Univ. J. Sci. 2013, 61, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, O.; Banik, B.; Pani, C. Computational Size Measurement & Study of Nanoparticle Using Transmission Electron Microscopy Data by Image-Processing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 7th International Advance Computing Conference (IACC), Hyderabad, India, 5–7 January 2017; pp. 656–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontard, L.C.; Ozkaya, D.; Dunin-Borkowski, R.E. A Simple Algorithm for Measuring Particle Size Distributions on an Uneven Background from TEM Images. Ultramicroscopy 2011, 111, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yantong, Z.; Guoying, Z.; Yu, G. Particle Size Measurement Based on Image Multivariate Multiscale Entropy. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Trustcom/BigDataSE/ICESS, Sydney, Australia, 1–4 August 2017; pp. 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, T.; Reinholt, F.; Johnsen, O.M. Automatic Particle Analyzing System. US Patent 7154600, 2001. Available online: https://www.google.lt/patents/US7154600 (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Freiherr von Hodenberg, M. Device for Determining Parameters of a Bulk Material Particle Flow. WO Patent 2008046914, 2008. Available online: https://www.google.lt/patents/WO2008046914A1?cl=en (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Jorgensen, T.K. Online Sampling Apparatus and Method for Online Sampling. WO Patent 2012083966, 2012. Available online: https://www.google.lt/patents/WO2012083966A1?cl=en (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Maaß, S.; Rojahn, J.; Emmerich, J.; Kraume, M. On-line monitoring of fluid particle size distributions in agitated vessels using automated image analysis. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conf. on Mixing, Warsaw, Poland, 10–13 September 2012; pp. 257–262. Available online: http://mixing14.eu/p/mixing14eu_39.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Lu, Z.; Hu, X.; Lu, Y. Particle Morphology Analysis of Biomass Material Based on Improved Image Processing Method. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijazi, B.; Cool, S.; Vangeyte, J.; Mertens, K.; Cointault, F.; Paindavoine, M.; Pieters, J. High speed stereovision setup for position and motion estimation of fertilizer particles leaving a centrifugal spreader. Sensors 2014, 14, 21466–21482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Närvänen, T.; Seppälä, K.; Antikainen, O.; Yliruusi, J. A New Rapid On-Line Imaging Method to Determine Particle Size Distribution of Granules. AAPS PharmSciTec. 2008, 9, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, R.; Rana, N. Particle size and shape analysis using Imagej with customized tools for segmentation of particles. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 247–250. Available online: https://www.ijert.org/download/14339/particle-size-and-shape-analysis-using-imagej-with-customized-tools-for-segmentation-of-particles (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Watano, S.; Numa, T.; Miyanami, K. On-line Monitoring of Granule Growth in High Shear Granulation by an Image Processing System. Int. J. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoli, A.; Favoni, O. Particle size, size distribution and morphological evaluation of airbone dust particles of diverse woods by Scanning Electron Microscopy and image processing program. Int. J. Powder Technol. 2012, 225, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watano, S.; Numa, T.; Miyanami, K. A fuzzy control system of high shear granulation using image processing. Int. J. Powder Technol. 2001, 115, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Tamura, Y.; Kawaguchi, K. Measuring Particle Size Distribution. U.S. Patent 4288162, 1981. Available online: https://www.google.lt/patents/US4288162 (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Penumadu, D.; Zhao, R.; Steadman, E.F. Particle Size and Shape Distribution Analyser. U.S. Patent 6960756, 1981. Available online: https://www.google.lt/patents/US6960756 (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Lieber, K.J.; Browne, I.B.; Tuttle, J. Control Feedback System and Method for Bulk Material Industrial Processes Using Automated Object or Particle. U.S. Patent 6885904, 2005. Available online: https://www.google.lt/patents/US6885904 (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Nase, T.F.; Vourisalo, Y.R. Procedure and Apparatus for Determining Size and/or Shape Distribution. WO Patent 1990012310, 1990. Available online: https://www.google.lt/patents/WO1990012310A1?cl=en (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Ettmuller, J.; Reindel, K.; Schafer, M. Sample‘s Particle Individual, Three Dimensional form e.g. Powder Form, Automated Determining Method, Involves Observing Particles from Two Observation Directions, Where Particle Axis is Aligned along Line Transverse to Observation Direction. DE Patent 102005055825, 2007. Available online: https://www.google.lt/patents/DE102005055825A1?cl=en (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Canty, T.M.; O’Brien, P.J.; Marks, C.P. Granular Product Inspection Device. U.S. Patent 7009703, 2006. Available online: https://www.google.lt/patents/US7009703 (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Niwa, T. Particle Size Measuring Device. U.S. Patent 5379113, 1995. Available online: https://www.google.lt/patents/US5379113 (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Schumann, M. Procedure for the Determination of Particle Size Distribution in Particle Mixtures. U.S. Patent 5309215, 1994. Available online: https://www.google.lt/patents/US5309215 (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Wang, Y.; Lin, C.L.; Miller, J.D. 3D image segmentation for analysis of multisize particles in a packed particle bed. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priadarsini, S.; Ganesan, S.; Shanthi, C.; Pappa, N. Model based object recognition for particle size distribution. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Communications, Control and Computing Technologies, Ramanathapuram, India, 8–10 May 2014; pp. 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atasoy, H.; Yildirim, E.; Yildirim, S.; Kutlu, Y. A Real-Time Parallel Image Processing Approach on Regular PCs with Multi-Core CPUs. Elektronika ir Elektrotechnika 2017, 23, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lech, P.; Okarma, K. Prediction of the Optical Character Recognition Accuracy based on the Combined Assessment of Image Binarization Results. Elektronika ir Elektrotechnika 2015, 21, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumara, J.J.; Hayano, K.; Ogiwara, K. Fundamental Study on Particle Size Distribution of Coarse Materials by Image Analysis. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301692754_Fundamental_study_on_particle_size_distribution_of_coarse_materials_by_image_analysis (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Tadeusiewicz, R.; Ogiela, L.; Ogiela, M.R. Cognitive Analysis Techniques in Business Planning and Decision Support Systems. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing, Zakopane, Poland, 12–16 June 2006; pp. 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbancic, G.; Podgorelec, V. Automatic Classification of Motor Impairment Neural Disorders from EEG Signals Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Elektronika ir Elektrotechnika 2018, 24, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Piuri, V.; Scotti, F. Image processing for granulometry analysis via neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Measurement Systems and Applications, Instanbul, Turkey, 14–16 July 2008; pp. 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. An estimation of coal density distributions by weight based on image analysis and MIV-SVM. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 19–20 December 2015; pp. 1110–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H. Artificial Neural Networks: Approximation and Learning Theory; Blackwell Publishers, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ogiela, L.; Tadeusiewicz, R.; Ogiela, M.R. Cognitive Analysis in Diagnostic DSS-type IT Systems. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing, Zakopane, Poland, 12–16 June 2006; pp. 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
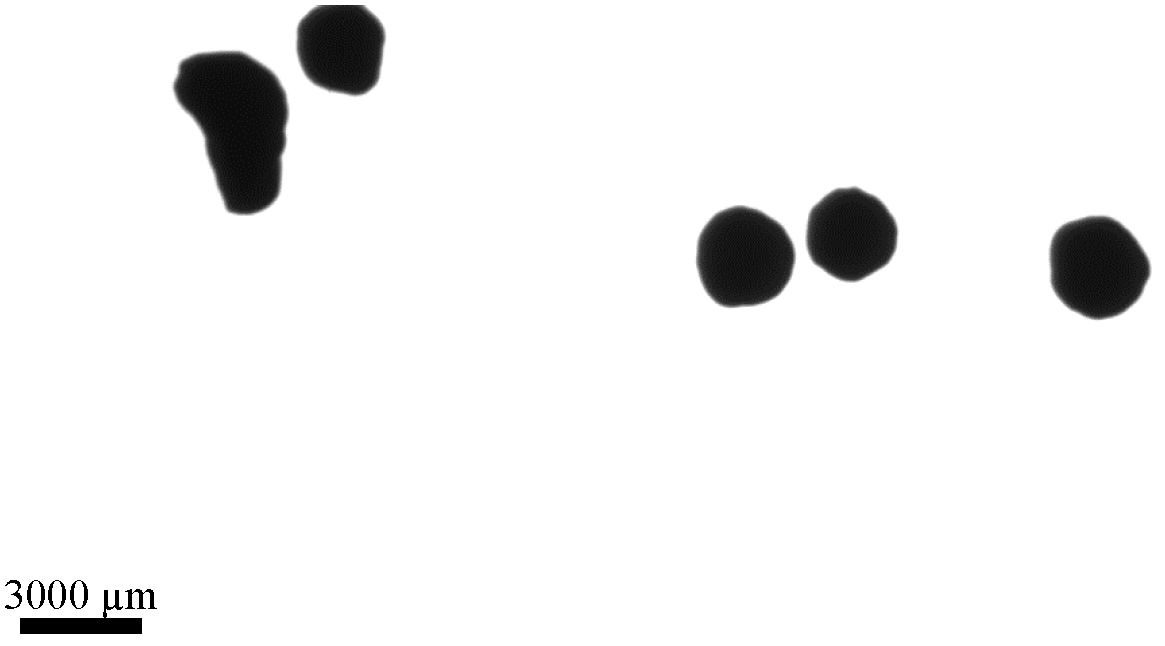

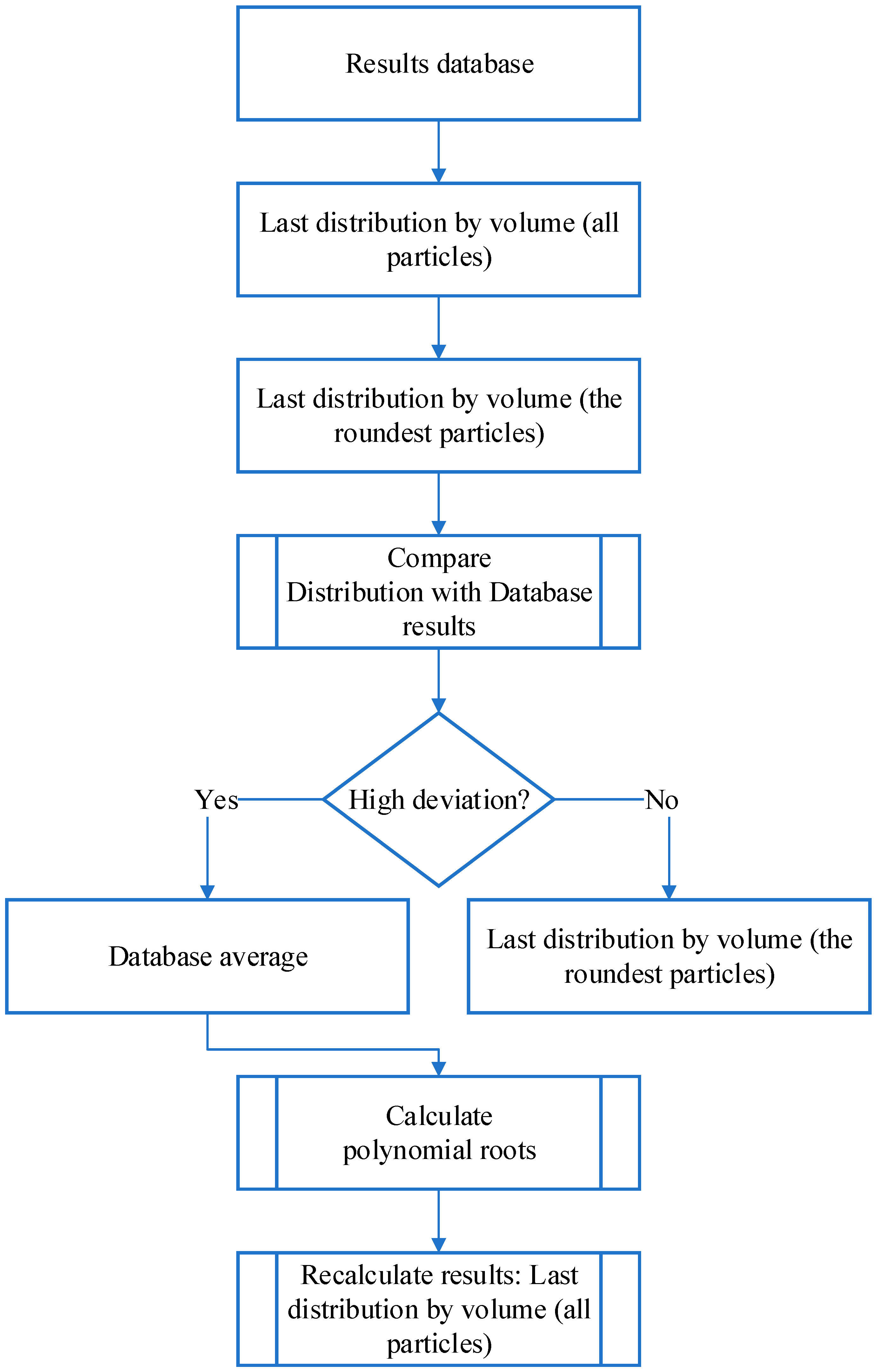
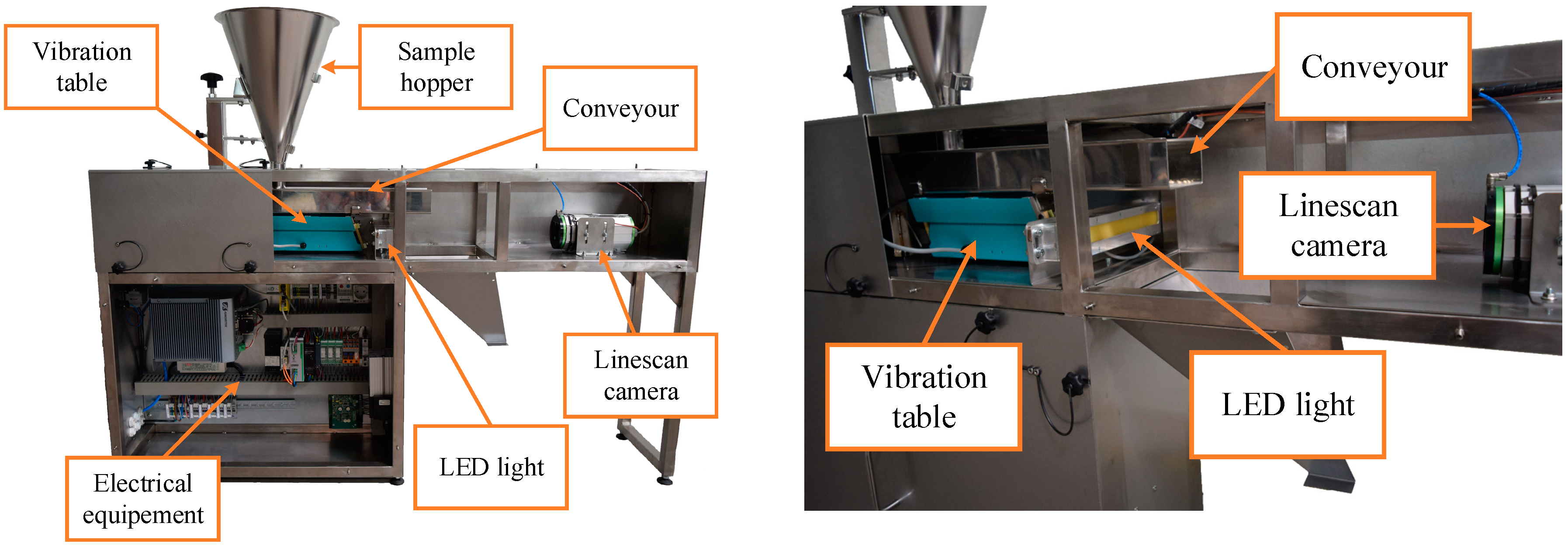
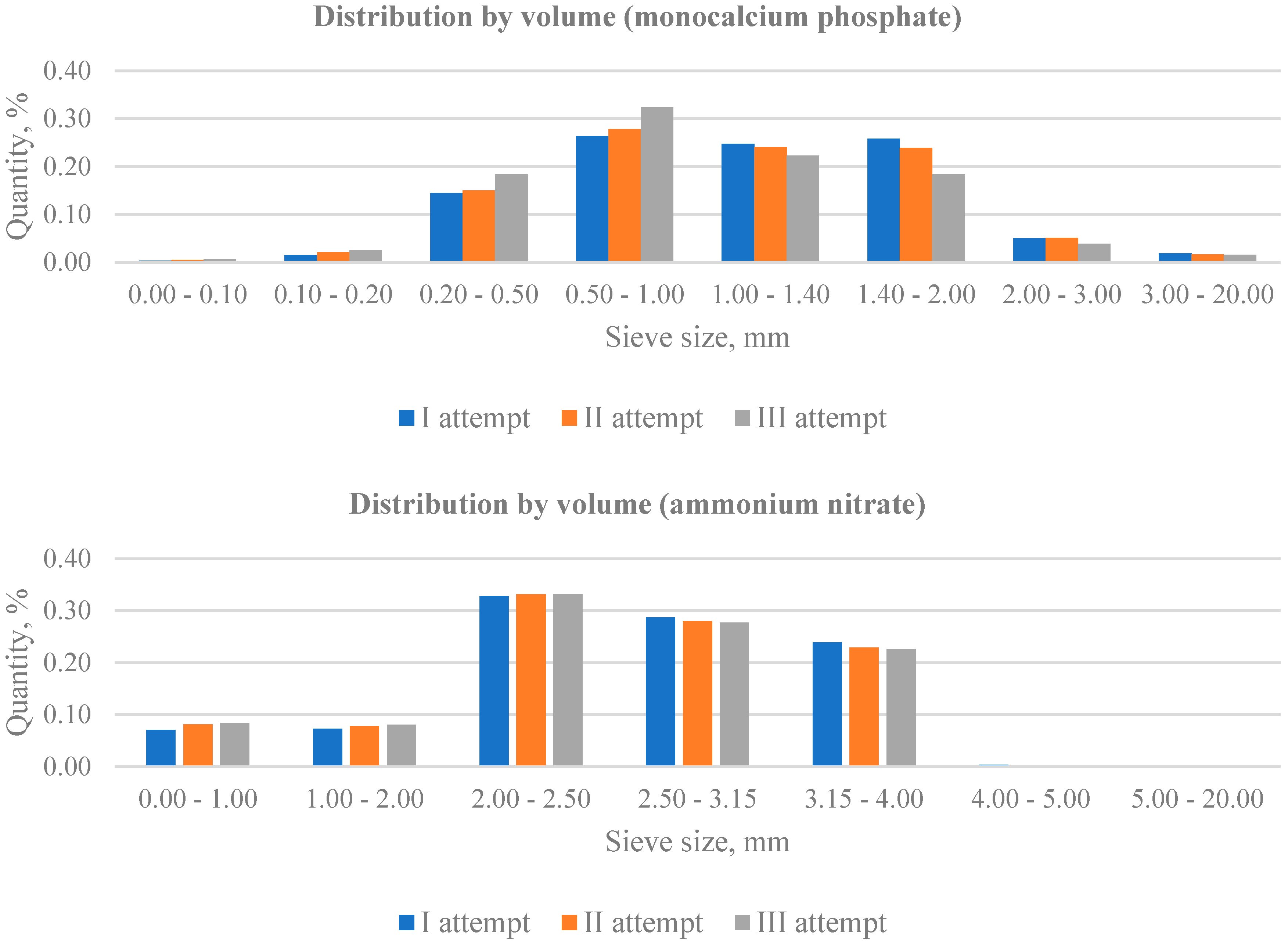
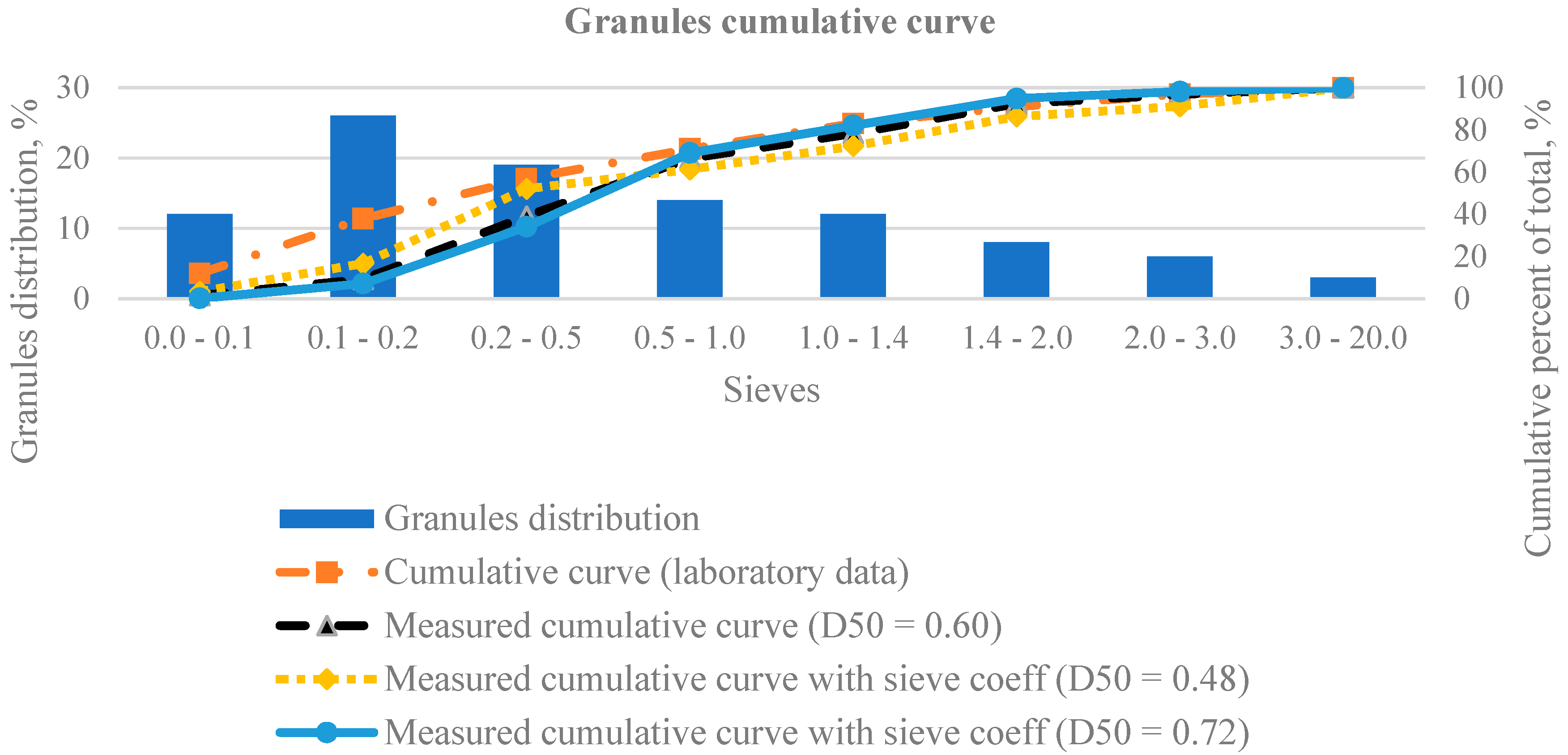
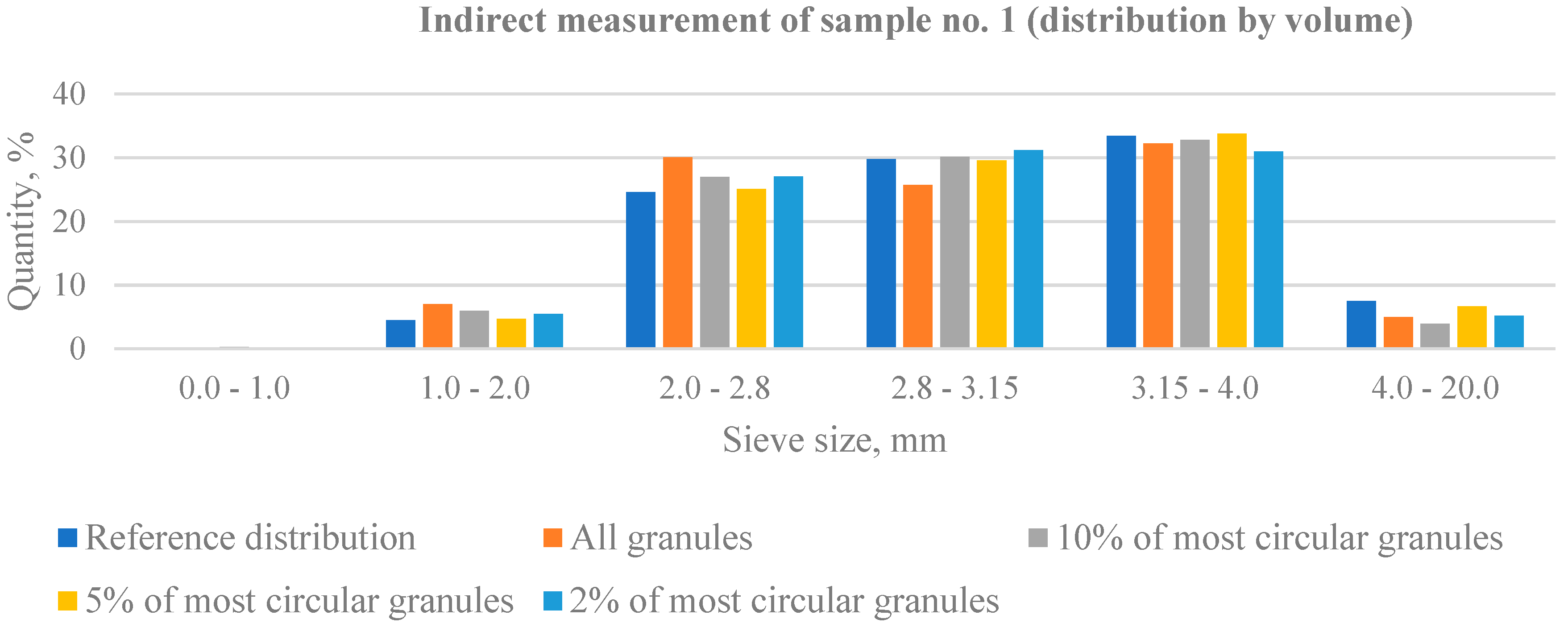

| Sample No. 1 | Sieve Size | |||||
| 0.0–1.0 | 1.0–2.0 | 2.0–2.8 | 2.8–3.15 | 3.15–4.0 | 4.0–20.0 | |
| Actual weight (g) | 0.4 | 9.0 | 49.2 | 59.6 | 66.8 | 15 |
| Reference distribution (%) | 0.2 | 4.5 | 24.6 | 29.8 | 33.4 | 7.5 |
| Cumulative curve | 0.2 | 4.7 | 29.3 | 59.1 | 92.5 | 100 |
| Particles diagonal ratio (min/max) | Indirect measurement (distribution by volume) | |||||
| 0–100% | 0.03 | 7.01 | 30.03 | 25.72 | 32.24 | 4.97 |
| 90–100% | 0.29 | 5.92 | 26.94 | 30.15 | 32.78 | 3.92 |
| 95–100% | 0.14 | 4.72 | 25.10 | 29.60 | 33.80 | 6.64 |
| 98–100% | 0.23 | 5.43 | 27.03 | 31.20 | 30.94 | 5.17 |
| Circularity distribution | ||||||
| Intervals (%) | 0–92 | 92–94 | 94–96 | 96–98 | 98–100 | |
| Quantity (%) | 38.25 | 23.16 | 15.38 | 10.79 | 12.42 | |
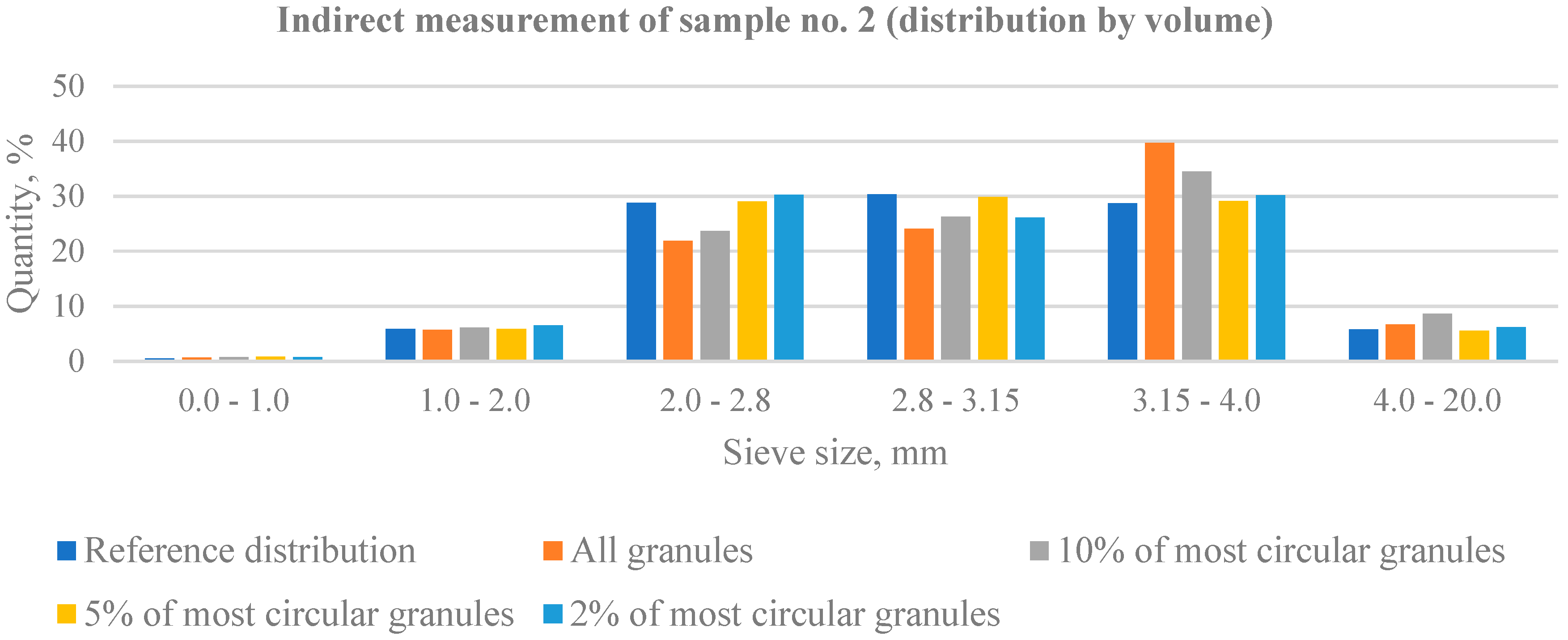
| Sample No. 2 | Sieve Size | |||||
| 0.0–1.0 | 1.0–2.0 | 2.0–2.8 | 2.8–3.15 | 3.15–4.0 | 4.0–20.0 | |
| Actual weight (g) | 1.0 | 11.8 | 57.6 | 60.6 | 57.4 | 11.6 |
| Reference distribution (%) | 0.5 | 5.9 | 28.8 | 30.3 | 28.7 | 5.8 |
| Cumulative curve | 0.5 | 6.4 | 35.2 | 65.5 | 94.2 | 100 |
| Particles diagonal ratio (min/max) | Indirect measurement (distribution by volume) | |||||
| 0–100% | 0.68 | 5.72 | 23.17 | 24.06 | 39.70 | 6.67 |
| 90–100% | 0.74 | 6.14 | 23.64 | 26.30 | 34.50 | 8.68 |
| 95–100% | 0.86 | 5.90 | 29.06 | 29.57 | 29.09 | 5.52 |
| 98–100% | 0.79 | 6.52 | 30.21 | 26.14 | 30.16 | 6.18 |
| Circularity distribution | ||||||
| Intervals (%) | 0–92 | 92–94 | 94–96 | 96–98 | 98–100 | |
| Quantity (%) | 35.59 | 21.62 | 10.84 | 17.22 | 14.73 | |
| Sieves | Measurements | Cumulative Curve Recalculation | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Weight | Indirect Measurements | Polynomial (5th) | Exponential (Half-Life) | Power Curve | Michaelis-Menten (Rectangular Hyperbola) | |||||||
| No. 1 | No. 2 | No. 1 | No. 2 | No. 1 | No. 2 | No. 1 | No. 2 | No. 1 | No. 2 | No. 1 | No. 2 | |
| 0.0–1.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.33 | −0.14 | −0.12 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.16 |
| 1.0–2.0 | 4.7 | 6.3 | 5.01 | 7.03 | 4.72 | 6.35 | 4.30 | 6.14 | 3.82 | 5.69 | 4.43 | 6.34 |
| 2.0–2.8 | 29.3 | 34.2 | 34.28 | 38.85 | 29.38 | 34.29 | 31.49 | 36.28 | 31.10 | 35.99 | 31.45 | 36.23 |
| 2.8–3.15 | 59.1 | 64.4 | 60.07 | 64.57 | 59.22 | 64.35 | 57.04 | 62.03 | 57.33 | 62.24 | 56.97 | 61.93 |
| 3.15–4.0 | 92.5 | 93.9 | 93.43 | 95.36 | 92.52 | 94.51 | 92.64 | 94.70 | 92.79 | 94.77 | 92.64 | 94.70 |
| 4.0–5.0 | 98.8 | 99.1 | 99.32 | 99.62 | 99.01 | 99.37 | 99.26 | 99.39 | 99.18 | 99.35 | 99.28 | 99.42 |
| 5.0–20.0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Goodness measure | ||||||||||||
| SSE | 26.99 | 24.60 | 0.063 | 0.147 | 9.547 | 10.87 | 7.416 | 9.151 | 9.508 | 10.99 | ||
| RMSE | 5.196 | 4.959 | 0.251 | 0.383 | 3.089 | 3.297 | 2.723 | 3.025 | 3.083 | 3.315 | ||
| Sample No. 2 | Sieve Size | |||||
| 0.0–1.0 | 1.0–2.0 | 2.0–2.8 | 2.8–3.15 | 3.15–4.0 | 4.0–20.0 | |
| Actual weight (g) | 1.0 | 11.8 | 57.6 | 60.6 | 57.4 | 11.6 |
| Reference distribution (%) | 0.5 | 5.9 | 28.8 | 30.3 | 28.7 | 5.8 |
| Cumulative curve | 0.5 | 6.4 | 35.2 | 65.5 | 94.2 | 100 |
| Particles diagonal ratio (min/max) | Indirect measurement (distribution by volume) cumulative curve | |||||
| 95–100% | 0.86 | 6.76 | 35.82 | 65.39 | 94.48 | 100 |
| Conversion of results with 3rd degree polynomial | ||||||
| Recalculated cumulative curve | 0.28 | 7.39 | 36.50 | 64.70 | 96.70 | 100 |
| SSE 1 | 6.6351 | |||||
| Conversion of results with 4th degree polynomial | ||||||
| Recalculated cumulative curve | 1.08 | 6.41 | 36.10 | 65.20 | 94.60 | 100 |
| SSE 1 | 0.2919 | |||||
| Conversion of results with 5th degree polynomial | ||||||
| Recalculated cumulative curve | 0.86 | 6.75 | 35.80 | 65.30 | 94.30 | 100 |
| SSE 1 | 1.739 × 10−27 | |||||
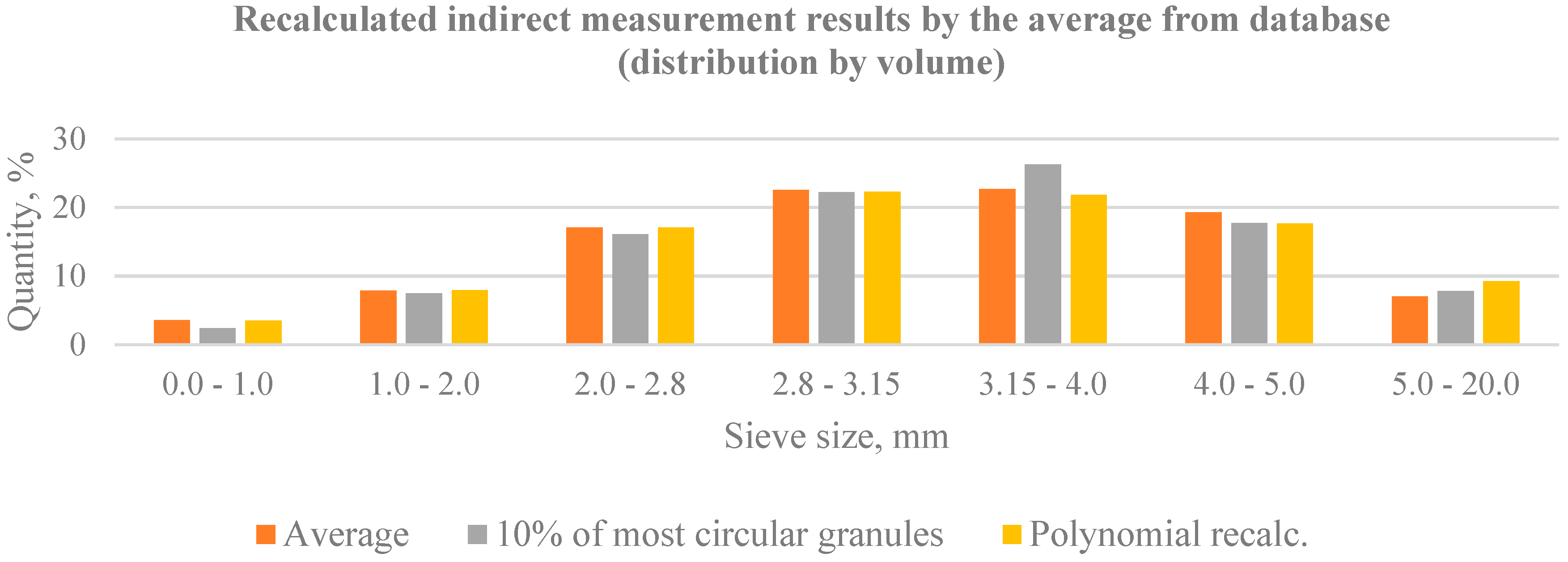
| Sieves (mm) | Sample Measurements Result | Indirect Measurement | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (g) | Distribution (%) | Cumulative Curve | Last 3 Results from DB Cumulative Curve | Last Meas. Cumulative Curve | 10% of most Circular Granules | Polynomial Recalc. | ||||
| No. 1 | No. 2 | No. 3 | AVG | |||||||
| 0.0–1.0 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 3.19 | 3.47 | 4.06 | 3.57 | 1.48 | 2.41 | 3.52 |
| 1.0–2.0 | 14 | 7 | 11 | 10.52 | 12.27 | 11.45 | 11.41 | 2.53 | 9.88 | 11.47 |
| 2.0–2.8 | 32 | 16 | 27 | 29.74 | 27.82 | 27.94 | 28.50 | 18.44 | 25.95 | 28.54 |
| 2.8–3.15 | 44 | 22 | 49 | 51.20 | 50.77 | 51.08 | 51.02 | 47.29 | 48.18 | 50.85 |
| 3.15–4.0 | 52 | 26 | 73 | 73.63 | 73.19 | 74.26 | 73.69 | 70.97 | 74.46 | 72.69 |
| 4.0–5.0 | 32 | 16 | 91 | 93.32 | 93.15 | 92.45 | 92.97 | 92.68 | 92.17 | 90.36 |
| 5.0–20.0 | 18 | 9 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.63 |
| Sieves | Measurements | Cumulative Curve Recalculation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Indirect Measurement | Polynomial (6th) | Neural Network | |||||
| No. 1 (avg) | No. 2 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 3 | ||
| 0.0–1.0 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| 1.0–2.0 | 4.7 | 5.01 | 6.17 | 7.12 | 6.12 | 7.32 | 4.70 | 4.82 |
| 2.0–2.8 | 29.3 | 38.37 | 38.21 | 39.56 | 29.08 | 29.69 | 29.17 | 29.26 |
| 2.8–3.15 | 59.1 | 64.16 | 63.97 | 65.61 | 57.85 | 60.58 | 59.22 | 59.83 |
| 3.15–4.0 | 92.5 | 93.43 | 95.08 | 95.29 | 89.31 | 89.45 | 95.74 | 96.12 |
| 4.0–5.0 | 98.8 | 99.32 | 99.54 | 99.68 | 93.83 | 94.05 | 98.03 | 98.07 |
| 5.0–20.0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 94.56 | 94.55 | 99.94 | 99.97 |
| Goodness measure | ||||||||
| SSE | 109.1 | 112.5 | 162.1 | 68.1 | 70.8 | 11.13 | 14.19 | |
| RMSE | 10.45 | 10.61 | 12.73 | 8.25 | 8.41 | 3.34 | 3.77 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laucka, A.; Adaskeviciute, V.; Andriukaitis, D. Research of the Equipment Self-Calibration Methods for Different Shape Fertilizers Particles Distribution by Size Using Image Processing Measurement Method. Symmetry 2019, 11, 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11070838
Laucka A, Adaskeviciute V, Andriukaitis D. Research of the Equipment Self-Calibration Methods for Different Shape Fertilizers Particles Distribution by Size Using Image Processing Measurement Method. Symmetry. 2019; 11(7):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11070838
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaucka, Andrius, Vaida Adaskeviciute, and Darius Andriukaitis. 2019. "Research of the Equipment Self-Calibration Methods for Different Shape Fertilizers Particles Distribution by Size Using Image Processing Measurement Method" Symmetry 11, no. 7: 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11070838
APA StyleLaucka, A., Adaskeviciute, V., & Andriukaitis, D. (2019). Research of the Equipment Self-Calibration Methods for Different Shape Fertilizers Particles Distribution by Size Using Image Processing Measurement Method. Symmetry, 11(7), 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11070838






