Modified MHD Radiative Mixed Convective Nanofluid Flow Model with Consideration of the Impact of Freezing Temperature and Molecular Diameter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
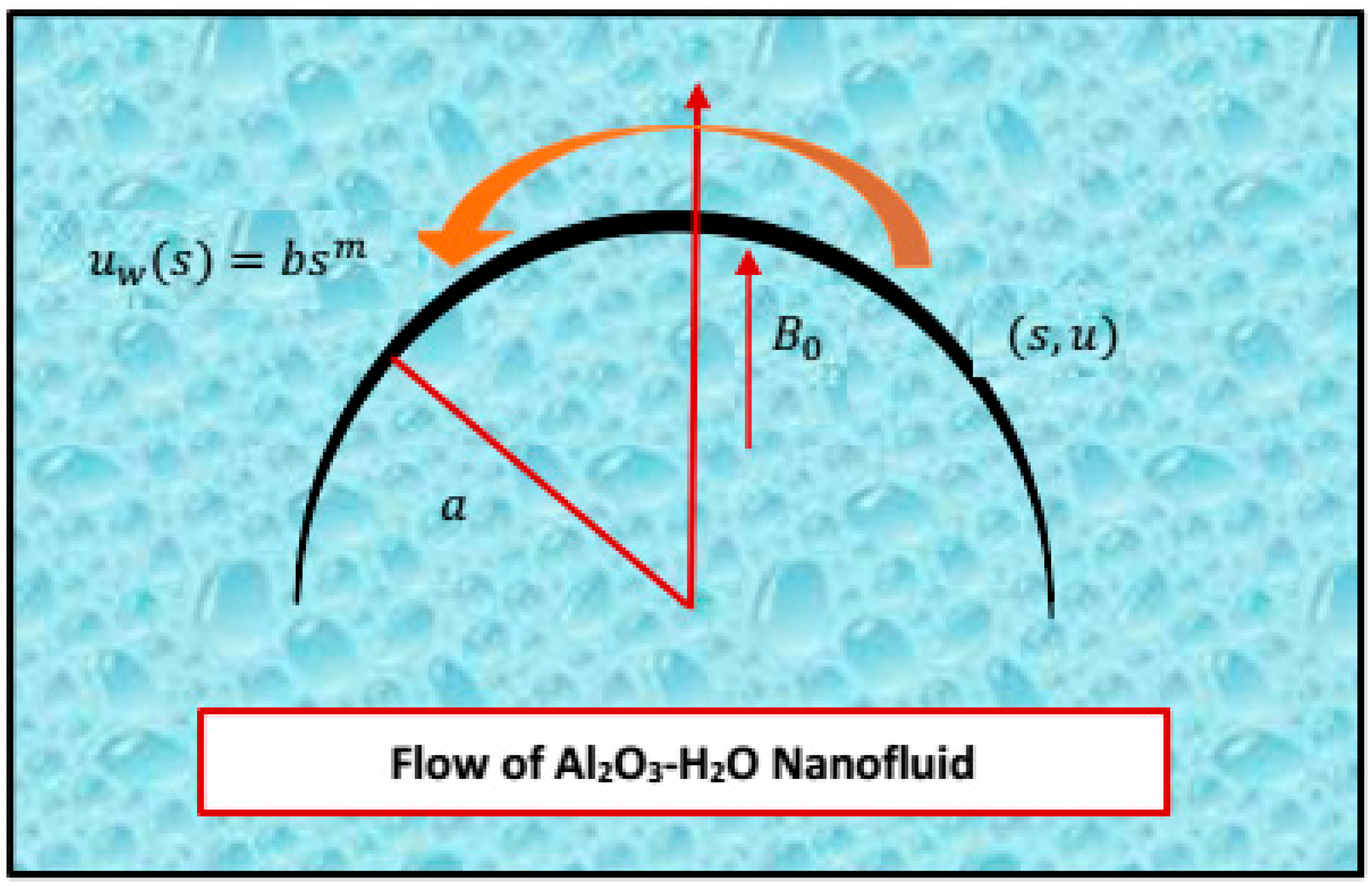
2. Model Formulation
3. Mathematical Analysis
4. Graphical Results and Discussion
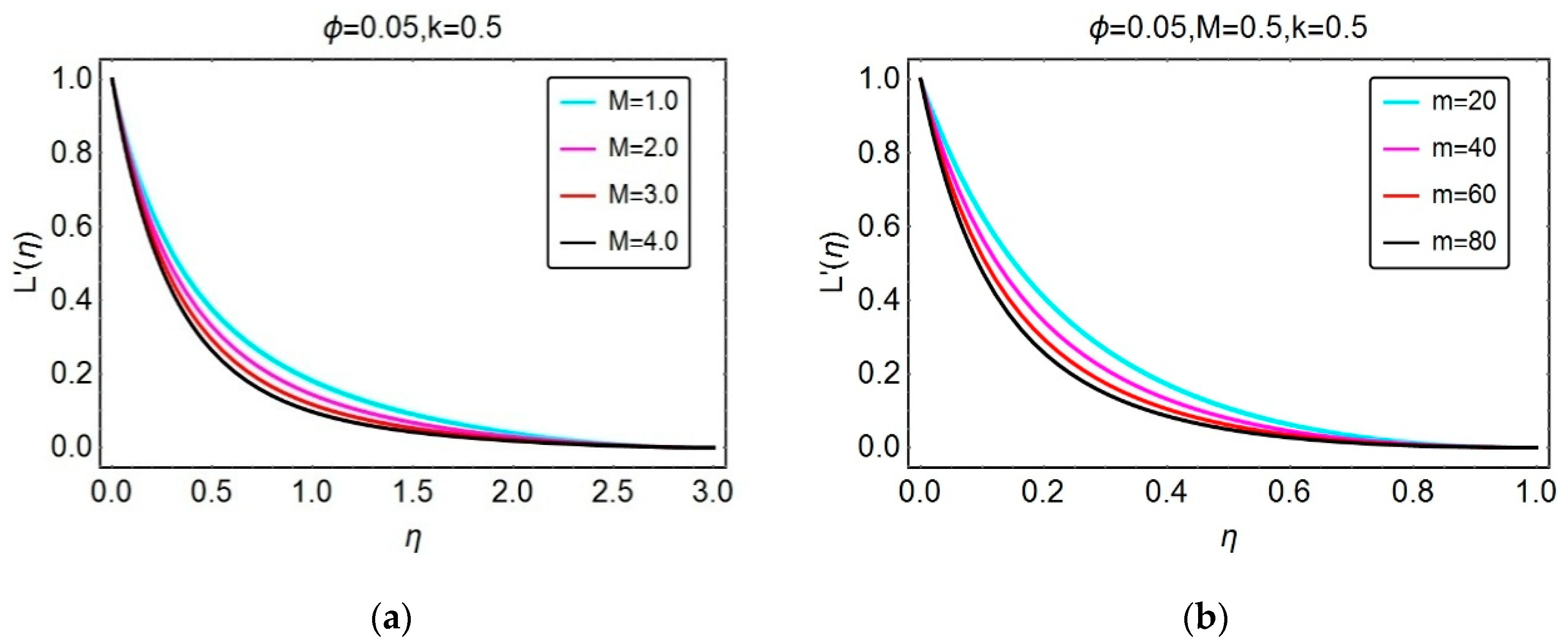
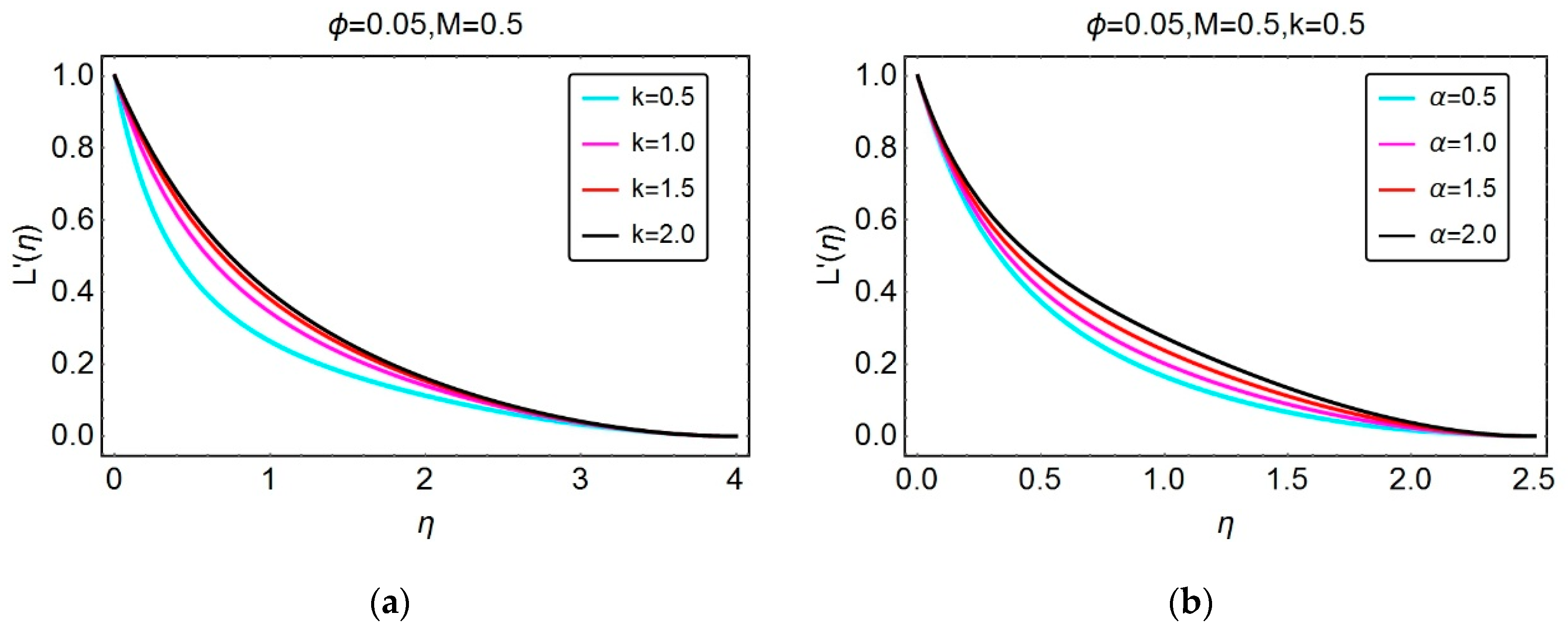
4.1. Velocity and Temperature Distribution
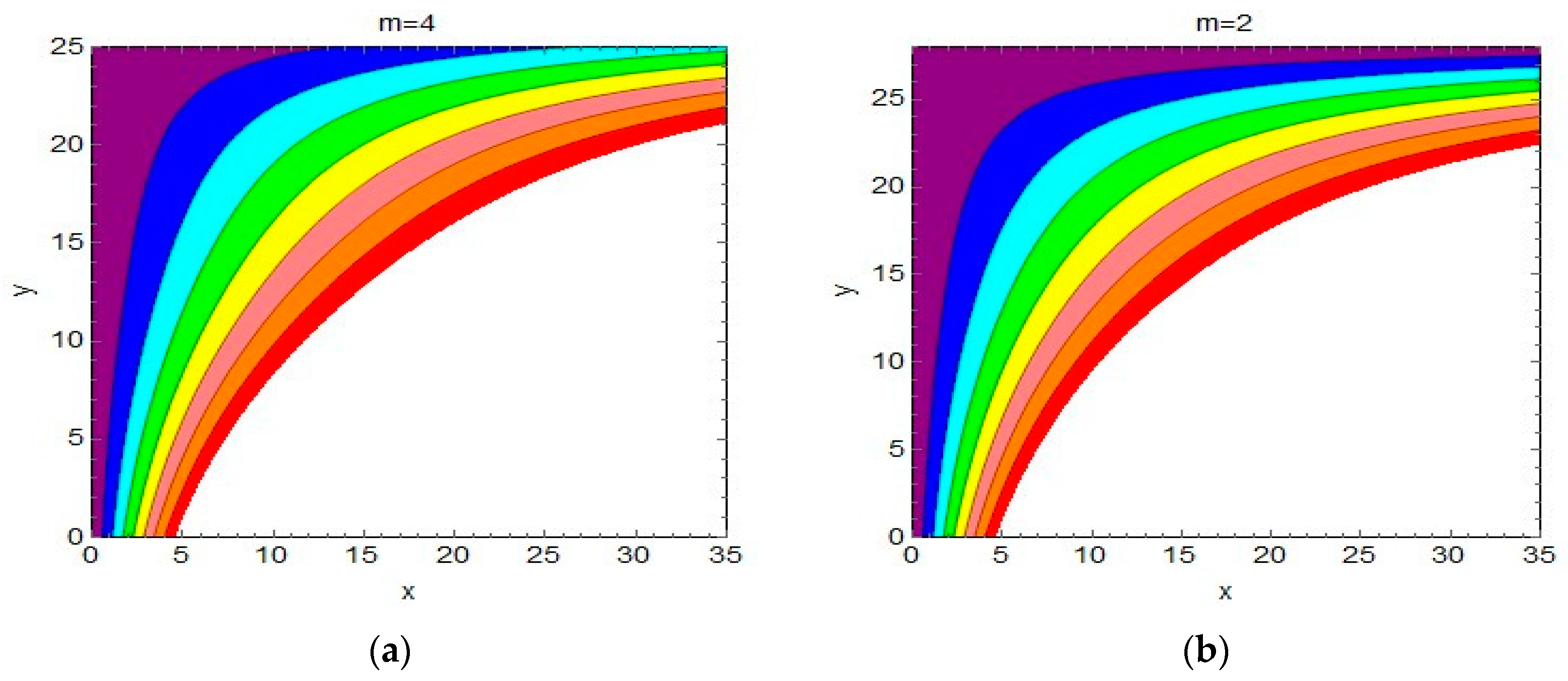
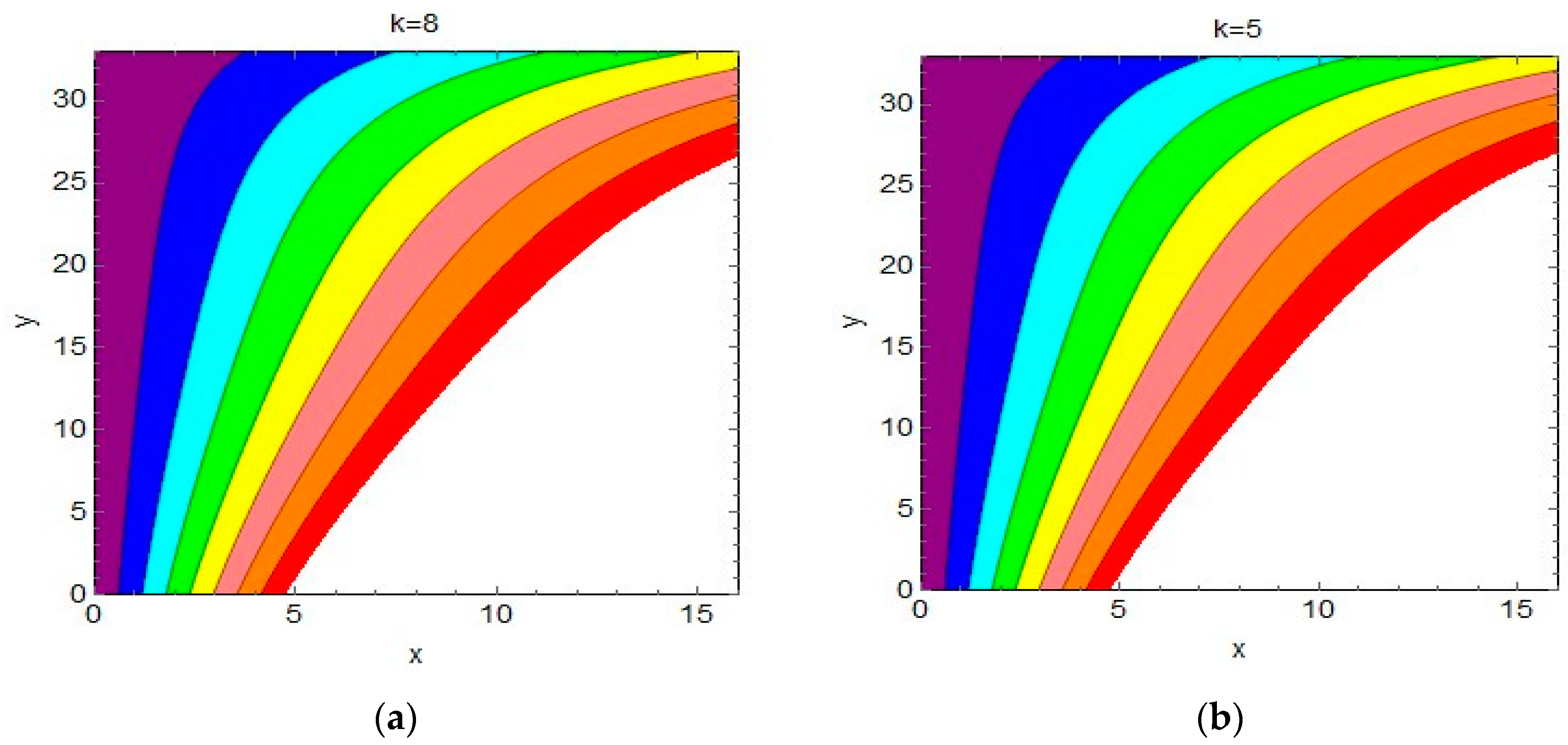
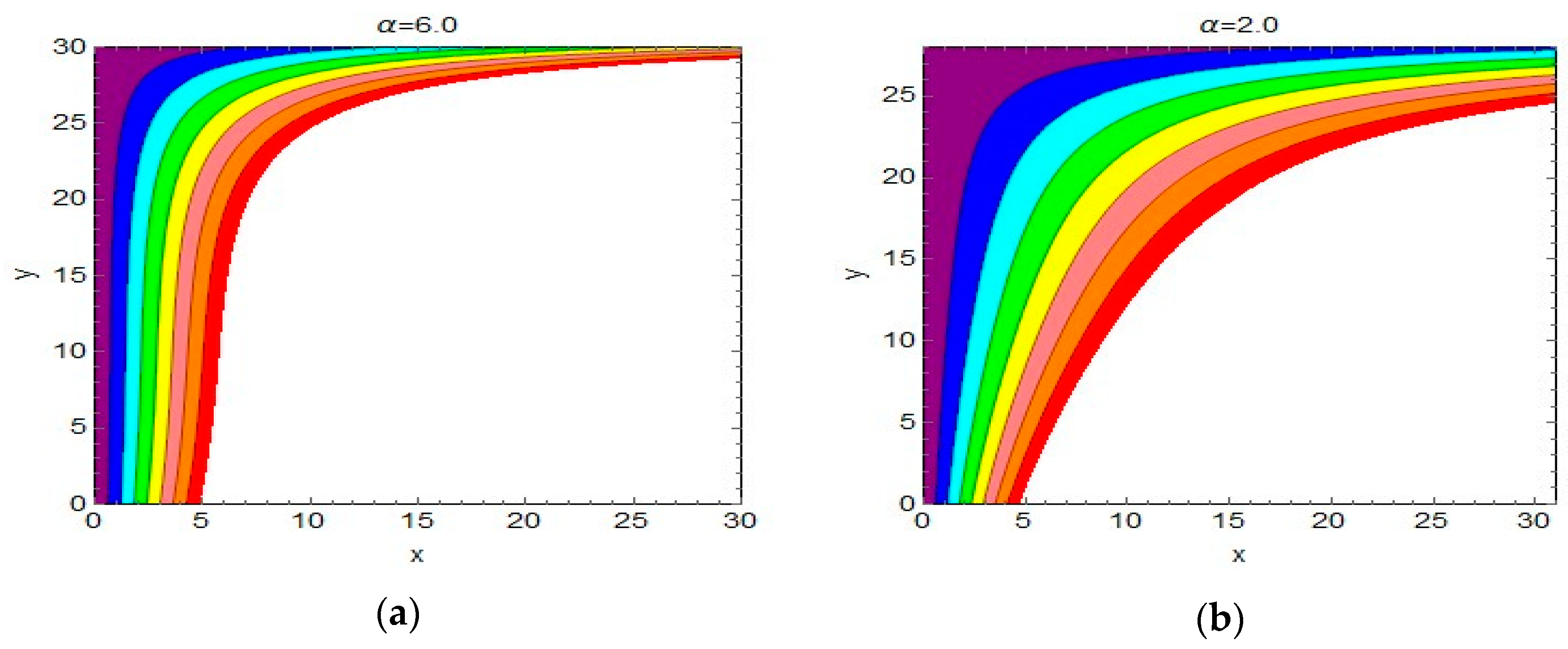
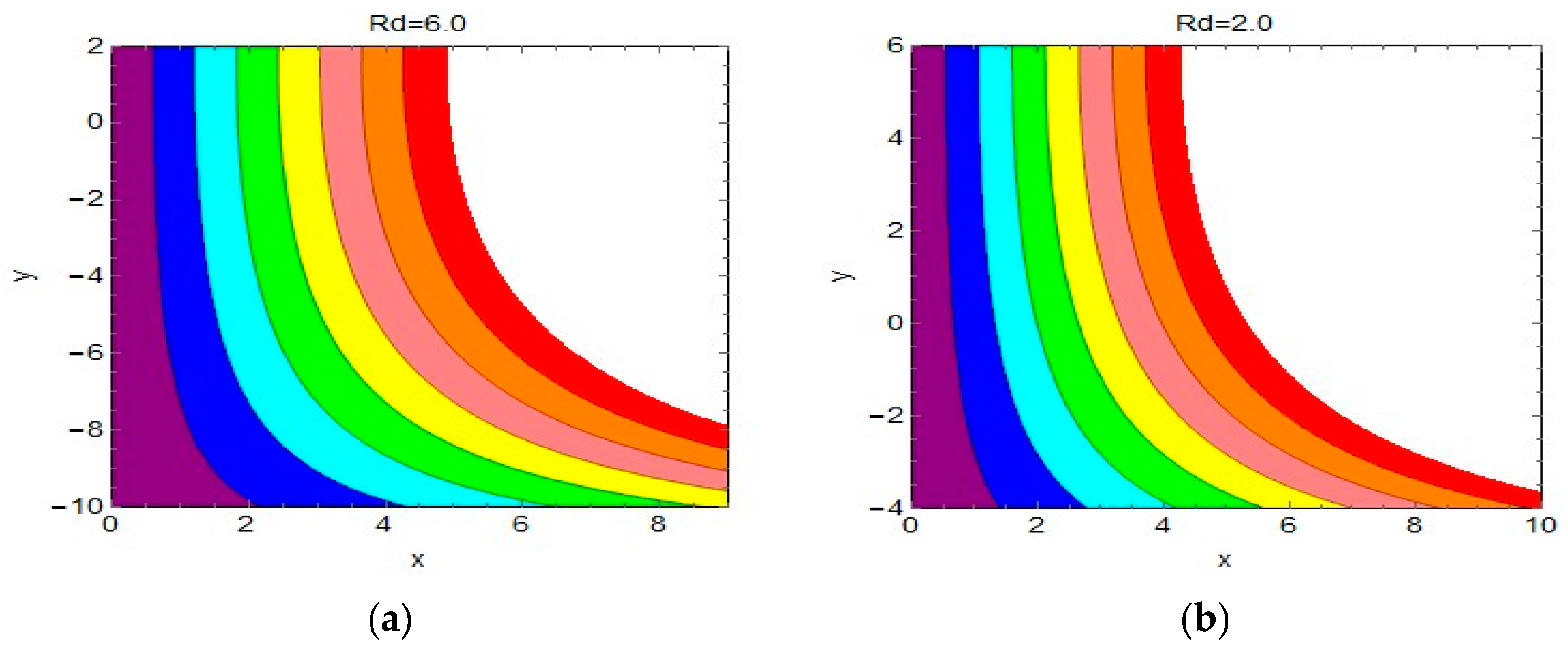
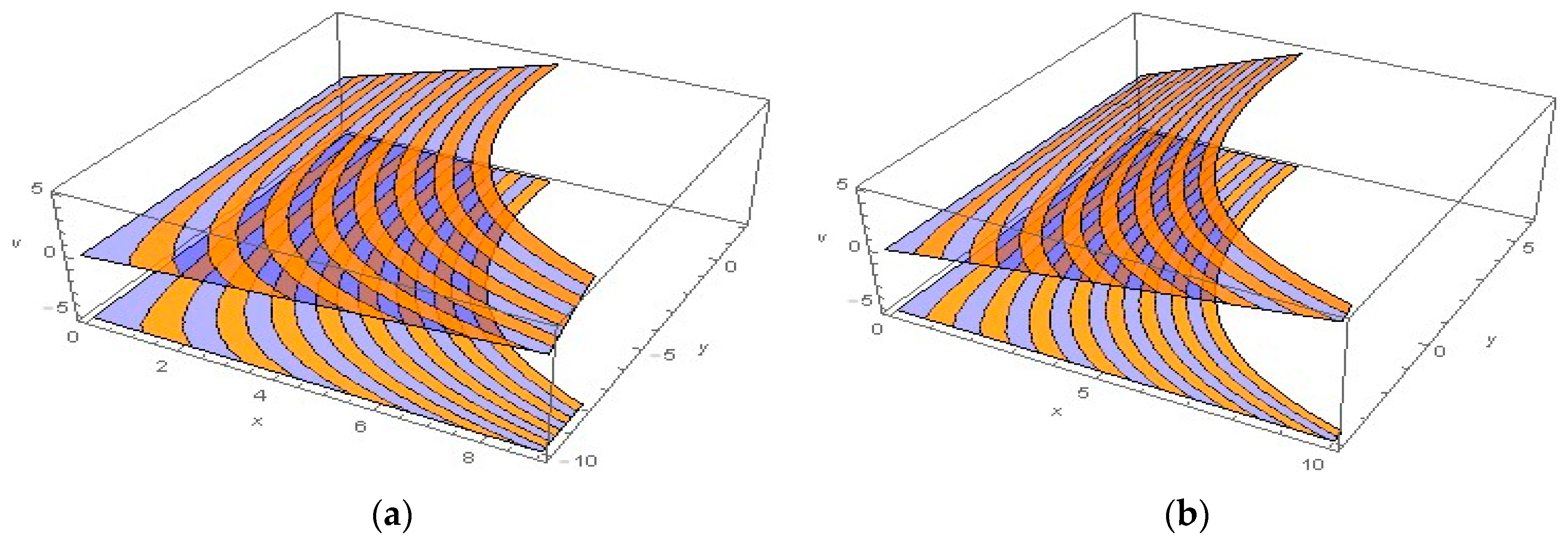
4.2. Streamlines and Isotherms
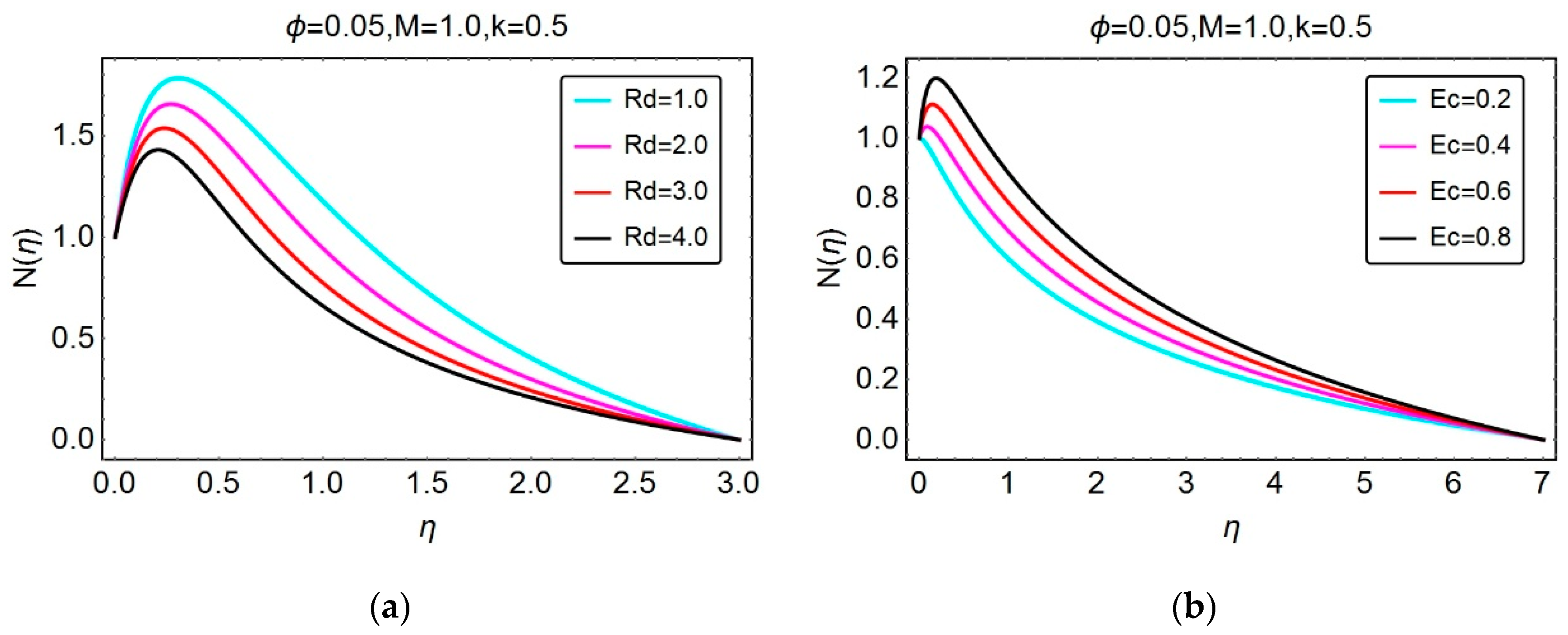
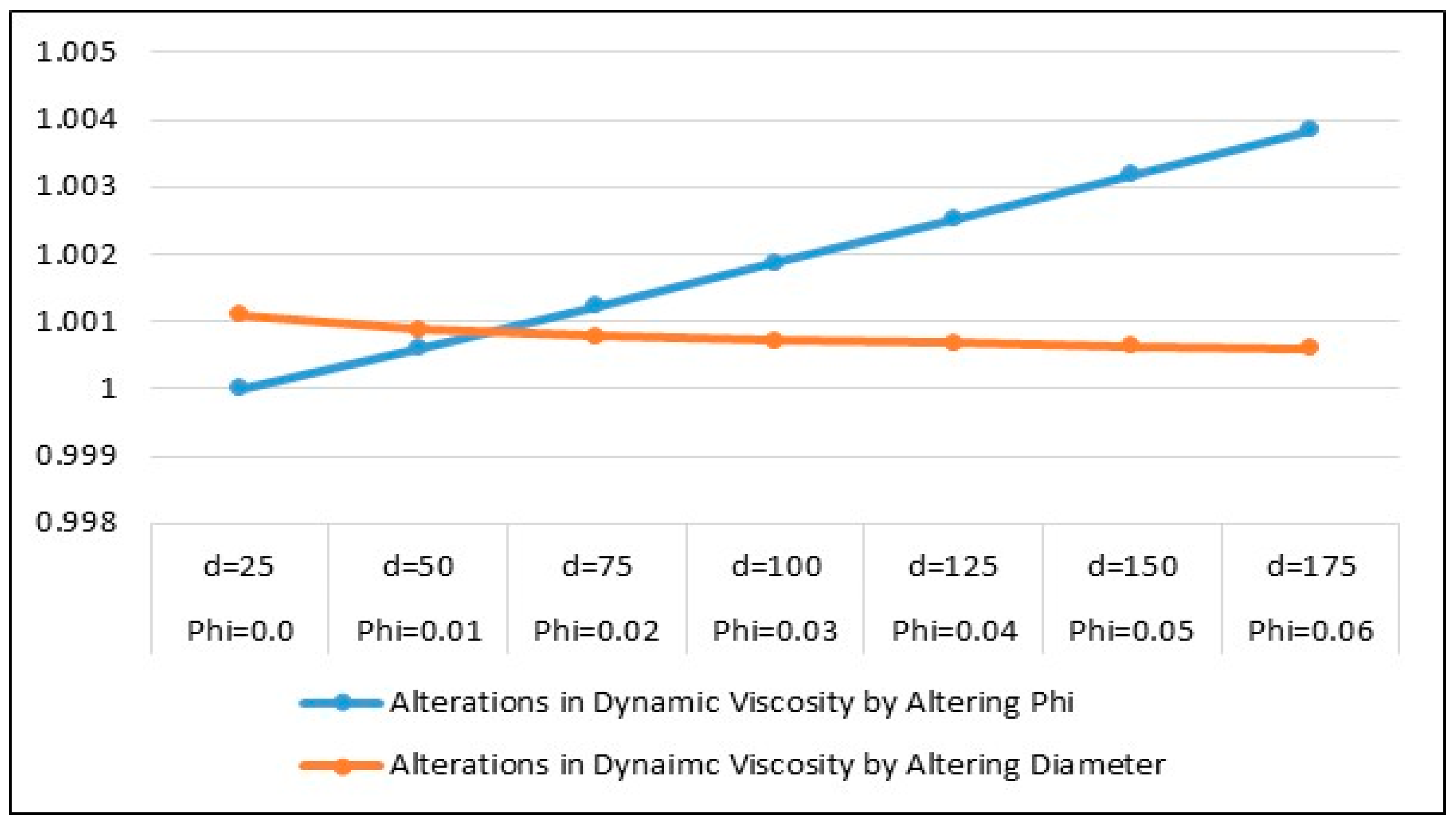
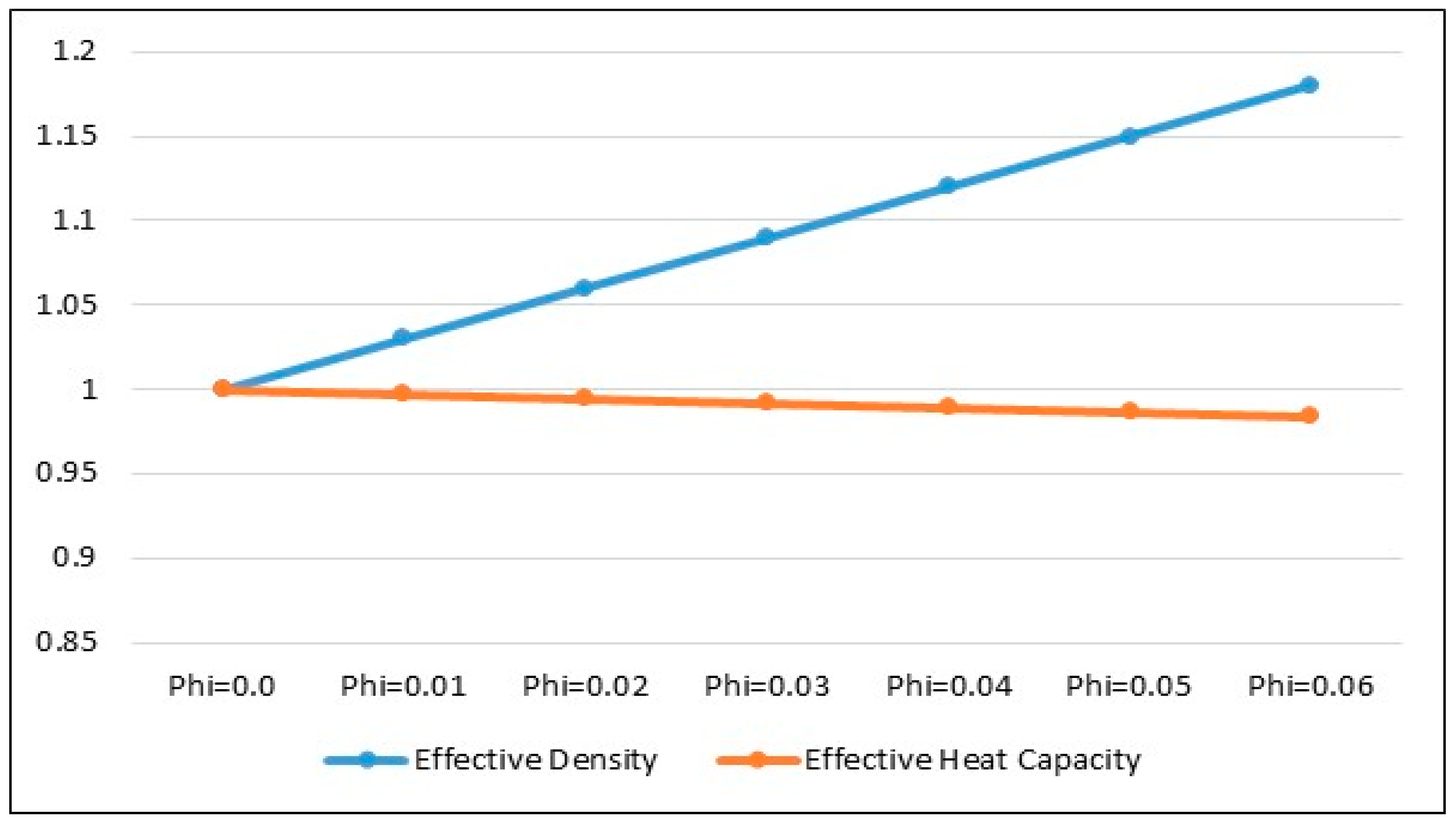
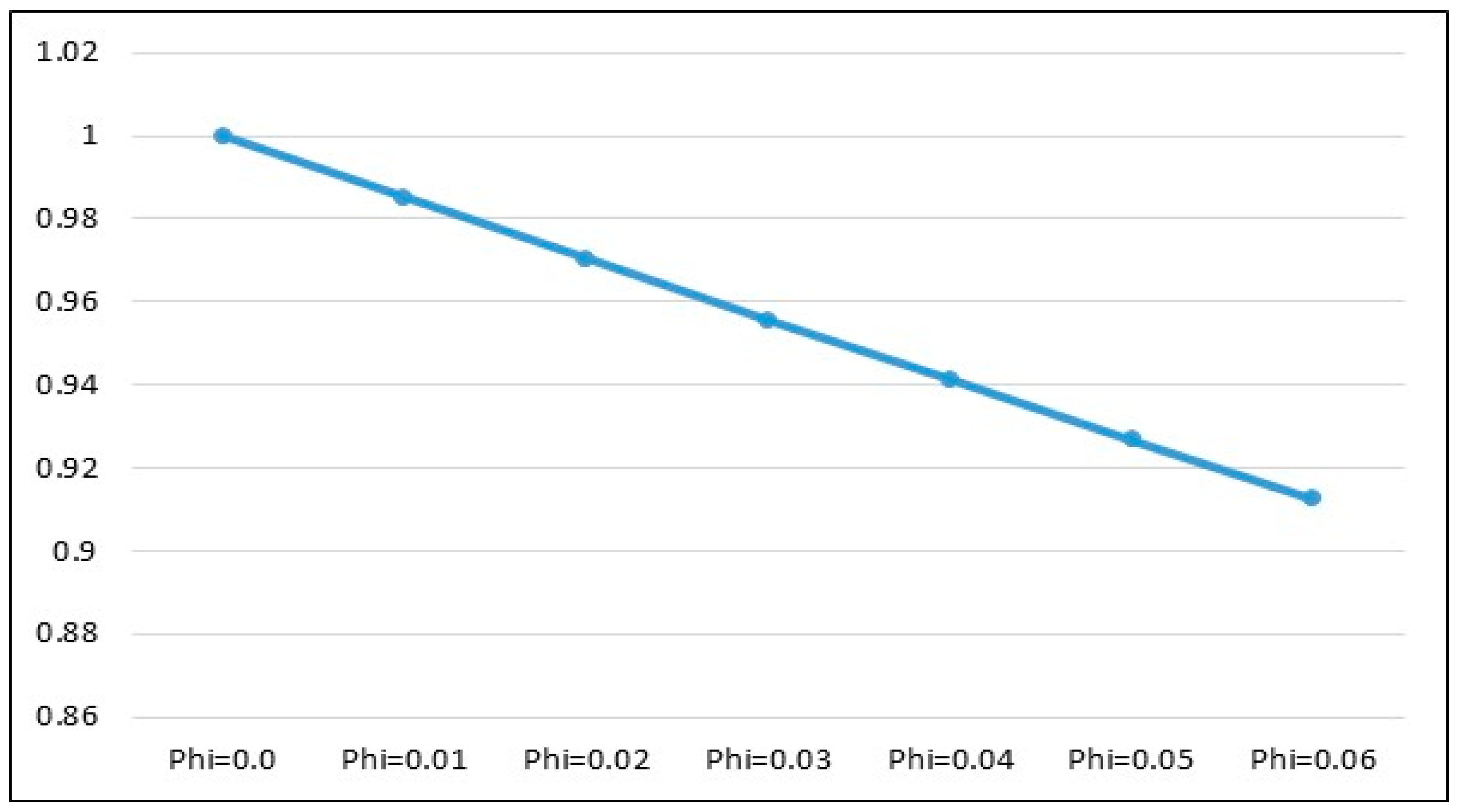
4.3. Thermophysical Characteristics
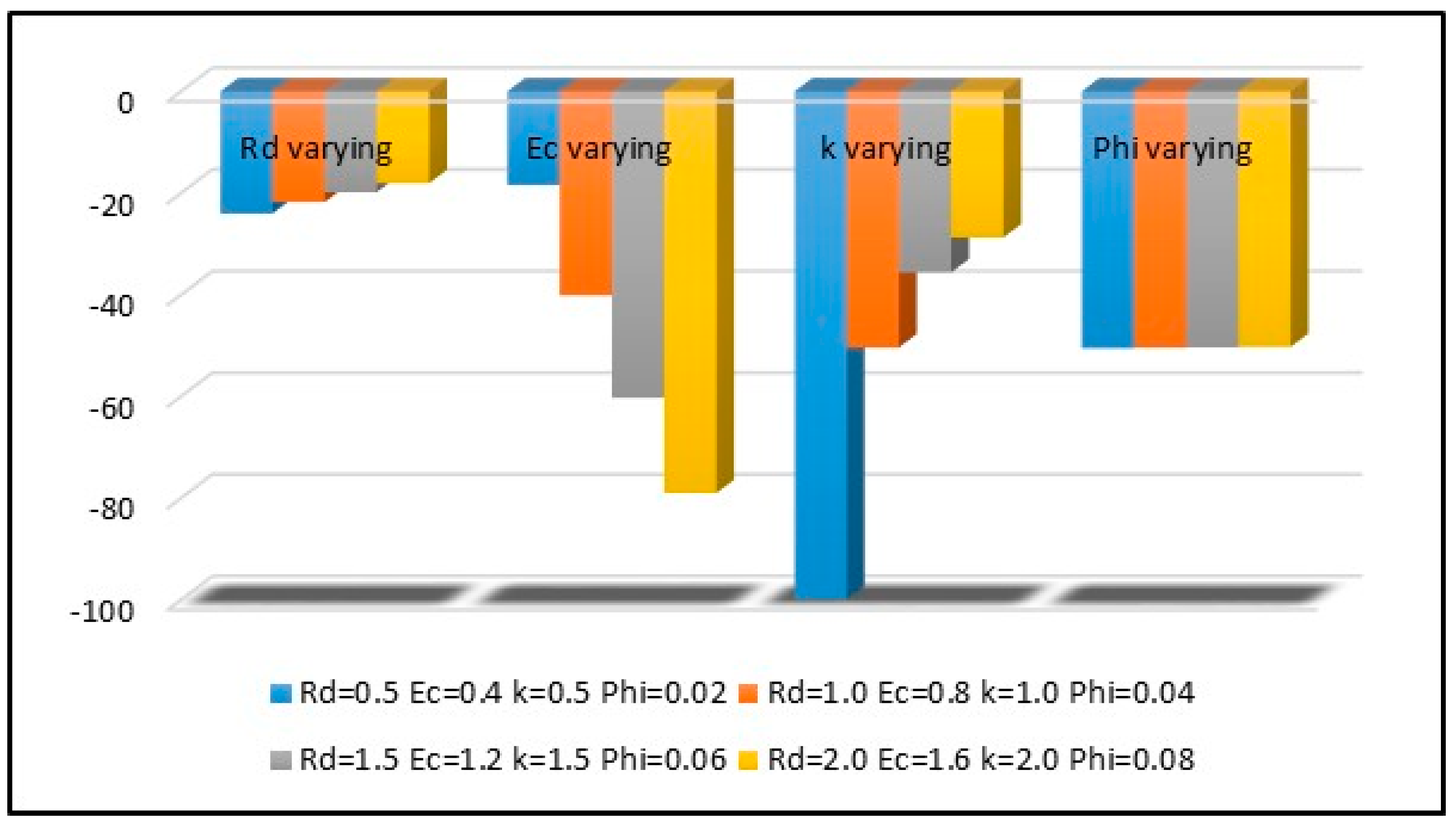
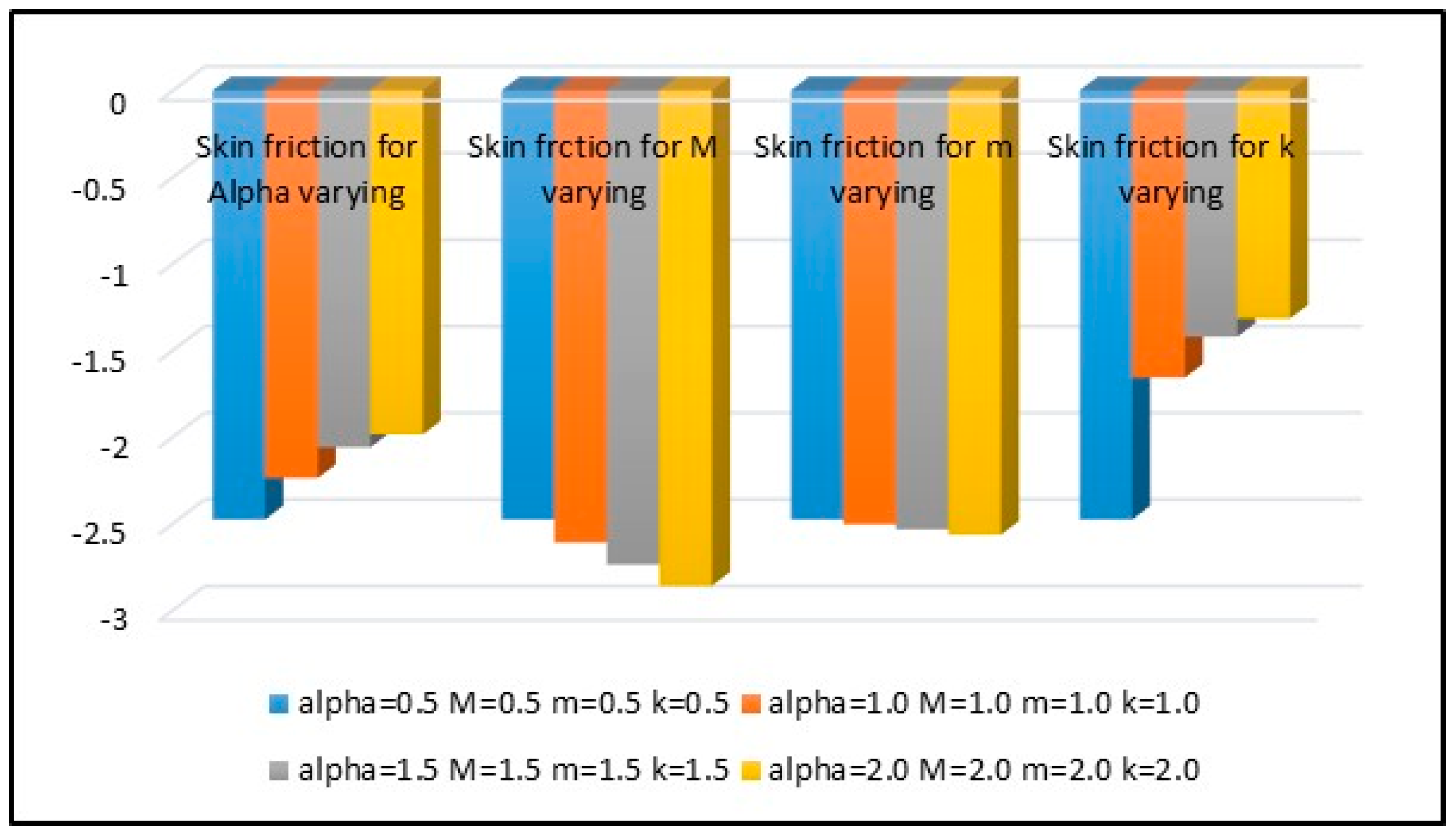
4.4. Skin Fraction and Heat Transfer Rate
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Component of the velocity | |
| Radius | |
| Temperature | |
| Temperature far from the surface | |
| Thermal conductivity of the host fluid | |
| Thermal conductivity of the nanoparticles | |
| Effective thermal conductivity of the nanofluid | |
| Heat capacity of the host fluid | |
| Electrical conductivity of the nanoparticles | |
| Electrical conductivity of the nanofluid | |
| Dynamic viscosity of the fluid | |
| Molecular weight | |
| Molecular diameter | |
| Temperature ratio parameter | |
| Prandtl number | |
| Hartmann number | |
| Dimensionless velocity | |
| Nusselt number | |
| Component of the velocity | |
| Pressure | |
| Temperature at the surface | |
| Density of the host fluid | |
| Density of the nanoparticles | |
| Effective density of the nanofluid | |
| Heat capacity of the nanoparticles | |
| Heat capacity of the nanofluid | |
| Electrical conductivity of the host fluid | |
| Effective dynamic viscosity | |
| Volume fraction of the nanoparticles | |
| Avogadro number | |
| Stefan Boltzmann constant | |
| Radiation parameter | |
| Eckert number | |
| Curvature parameter | |
| Dimensionless temperature | |
| Skin fraction coefficient |
References
- Choi, S. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles in developments and applications of non-newtonians flows. ASME J. Heat Transf. 1995, 66, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Clerk, M.J. Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1873. [Google Scholar]
- Bruggeman, D.A.G. Berechnung verschiedener physikalischer konstanten von heterogenen substanzen, I—dielektrizitatskonstanten und leitfahigkeiten der mischkorper aus isotropen substanzen. Ann. Phys. Leipz. 1935, 24, 636–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, H.L.; Crosser, O.K. Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two-component systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1962, 1, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Lin, H. Effective conductivity of composites containing aligned spherical inclusions of finite conductivity. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 6761–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.; Kleinstreuer, C. A new thermal conductivity model for nanofluids. J. Nanopart. Res. 2004, 6, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.; Kleinstreuer, C. Laminar nanofluid flow in micro-heat sinks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 48, 2652–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.Z. Model for thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube-based composites. Phys. B Phys. Condens. Matter. 2005, 368, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasher, R.; Bhattacharya, P.; Phelan, P.E. Thermal conductivity of nanoscale colloidal solutions (nanofluids). Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 92, 25901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Peterson, G.P. Experimental investigation of temperature and volume fraction variations on the effective thermal conductivity of nanoparticle suspensions (nanofluids). J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcione, M. Rayleigh–Be´nard convection heat transfer in nanoparticle suspensions. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2011, 32, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Li, Z.; Shamlooei, M. Nanofluid MHD natural convection through a porous complex shaped cavity considering thermal radiation. Phys. Lett. A 2018, 382, 1615–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Khan, A.U.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Influence of an effective prandtl number model on squeezed flow of γAl_2 O_3-H_2 O and γAl_2 O_3-C_2 H_6 O_2 nanofluids. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 238, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Zia, Q.M.Z.; Ellahi, R. Influence of induced magnetic field on free convection of nanofluid considering Koo-Kleinstreuer-Li (KKL) correlation. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadullah, A.M.; Khan, U.; Naveed, A.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Analytical and numerical investigation of thermal radiation effects on flow of viscous incompressible fluid with stretchable convergent/divergent channels. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 224, 768–775. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, U.; Naveed, A.A.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. 3D squeezed flow of γAl_2 O_3-H_2 O and γAl_2 O_3-C_2 H_6 O_2 nanofluids: A numerical study. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 24620–24633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, A.A.; Khan, U.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Influence of thermal radiation and viscous dissipation on squeezed flow of water between two riga plates saturated with carbon nanotubes. Colloids Surf. A Physciochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 522, 389–398. [Google Scholar]
- Saba, F.; Naveed, A.; Hussain, S.; Khan, U.; Mohyud-Din, S.T.; Darus, M. Thermal analysis of nanofluid flow over a curved stretching surface suspended by carbon nanotubes with internal heat generation. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Naveed, A.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Heat transfer effects on carbon nanotubes suspended nanofluid flow in a channel with non-parallel walls under the effect of velocity slip boundary condition: A numerical study. Neural Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J.V.R.; Sugunamma, V.; Sandeep, N. Dual solutions for nanofluid flow past a curved surface with nonlinear radiation, soret and dufour effects. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1000, 12152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Qayyum, S.; Imtiaz, M.; Alsaedi, A. Double stratification in flow by curved stretching sheet with thermal radiation and joule heating. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsabery, A.I.; Sheremet, M.A.; Chamkha, A.J.; Hashim, I. MHD convective heat transfer in a discretely heated square cavity with conductive inner block using two-phase nanofuid model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcione, M. Empirical correlating equations for predicting the efective thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of nanofuids. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, A.A.; Khan, U.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Unsteady radiative flow of chemically reacting fluid over a convectively heated stretchable surface with cross-diffusion gradients. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 121, 182–191. [Google Scholar]

| Properties | (kg/m3) | (1/k) | (J/Kg K) | (kg/ms) | (W/mk) | (S/m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | |||||||
| Al2O3 | 33 | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, U.; Abbasi, A.; Ahmed, N.; Alharbi, S.O.; Noor, S.; Khan, I.; Mohyud-Din, S.T.; Khan, W.A. Modified MHD Radiative Mixed Convective Nanofluid Flow Model with Consideration of the Impact of Freezing Temperature and Molecular Diameter. Symmetry 2019, 11, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11060833
Khan U, Abbasi A, Ahmed N, Alharbi SO, Noor S, Khan I, Mohyud-Din ST, Khan WA. Modified MHD Radiative Mixed Convective Nanofluid Flow Model with Consideration of the Impact of Freezing Temperature and Molecular Diameter. Symmetry. 2019; 11(6):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11060833
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Umar, Adnan Abbasi, Naveed Ahmed, Sayer Obaid Alharbi, Saima Noor, Ilyas Khan, Syed Tauseef Mohyud-Din, and Waqar A. Khan. 2019. "Modified MHD Radiative Mixed Convective Nanofluid Flow Model with Consideration of the Impact of Freezing Temperature and Molecular Diameter" Symmetry 11, no. 6: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11060833
APA StyleKhan, U., Abbasi, A., Ahmed, N., Alharbi, S. O., Noor, S., Khan, I., Mohyud-Din, S. T., & Khan, W. A. (2019). Modified MHD Radiative Mixed Convective Nanofluid Flow Model with Consideration of the Impact of Freezing Temperature and Molecular Diameter. Symmetry, 11(6), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11060833





