Abstract
This study focuses on the flow of stagnation region and heat transfer of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) over an exponentially stretching/shrinked sheet in the presence of homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions. Kerosene and water are considered base fluids in both single-wall and multi-wall carbon nanotubes. After employing the appropriate similarity variables, the system of partial differential equations is transformed to a system of nonlinear ordinary differential equations. Solution of the problems is obtained numerically using the bvp4c solver in MATLAB software. The impact of physical parameters, such as solid volume fraction, stretching/shrinking parameter, homogeneous and heterogeneous reaction rate, Schmidt number on the velocity, temperature and concentration profiles, skin friction, and heat transfer rate are discussed graphically and interpreted physically. The results indicate that for an exponentially shrinking sheet, dual solutions exist for a certain range. It is clear from figures that the concentration profile increases for increasing values of heterogeneous parameter and decreasing values of homogeneous parameter. Heat transfer and skin friction were observed to have a greater impact for single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) compared to multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). A stability analysis has been performed to show which solutions are linearly stable.
1. Introduction
In the last decades, the development of technology has undergone a considerable evolution in all different sectors of industry. Almost all researchers have noticed the importance of nanotechnology in their respective fields of research. This is due to the fact that nanotechnology has a great contribution in numerous fields of study, from improving thermal characteristics of conventional fluids to creation of a productive drug delivery system. Thereby, heat transfer is a very important issue that has to be taken into account for most present industrial developments, such as in the generation of power, and chemical, physical, and biological processes. Nanofluids are fluids that consist of nanometer-sized particles, called nanoparticles. Dispersion of nanomaterials are employed to overwhelm the poor thermal conductivity of base fluids such as water, kerosene, ethylene glycol, and engine oil. Carbon can be used to form nanoparticles because of its unique electrical and mechanical properties, including high thermal conductivity [1,2,3]. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are made by rolling up a sheet of graphene into a cylindrical shape with a diameter between 1 and 50 nm. Single-wall CNTs consist of a single layer of graphene in the cylinder, while multi-wall CNTs have many layers [4]. Many numerical investigations have been made to study the heat transfer of nanofluids [5,6]. However, there is still a lack of research on carbon nanotubes.
The investigation of stagnation point flow past a stretching/shrinking surface has gained the attention of researchers. The boundary layer flow due to a stretching surface is important in extrusion processes, such as metal sheet extrusion, polymer extrusion, and other industrial processes, while the shrinking issue is applicable in the research of environmental management strategies, shrink swell behavior, and the capillary effects in smaller pores and hydraulic properties of agricultural clay soils which are important for agricultural development [7]. The phenomena of shrinking sheets can also be found in rising and shrinking balloons. The flow of heat transfer over an exponentially shrinking sheet was first studied by Magyari and Keller [8]. More studies regarding flow over an exponentially stretching surface can be found in the literature [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. Hiemenz [17] was one of the first who considered the flow of the stagnation region and solved the governing Navier–Stokes equations using a similarity solution. Thus, Bhattacharya and Vajravellu [18] came up with the idea of an exponential shrinking sheet on the flow of stagnation region. Later, Bachok et al. [19] extended their problems by considering in nanofluids.
The natural process of chemical reactions that occurs in biochemical, combustion, and catalysis mechanisms involves both homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions. A fraction of the reactions has the capacity to either progress gradually or do not progress at all unless a catalyst is present. It should be noted that a homogeneous reaction persists during the whole process, whereas heterogeneous reactions take place in a confined region or within the boundary of a phase. A simple isothermal model for homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions in boundary layer flow is studied by Merkin [20]. Later, Bachok et al. [21] investigated the problem of stagnation point flow towards a stretching sheet in the existence of homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions. Hayat et al. [22] extended the idea of stagnation region by considering the problem in carbon nanotubes with Newton heating. Afterwards, Hayat et al. [23] examined the impact of homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions and melting heat transfer in boundary layer flow with carbon nanotubes saturated in porous medium. In addition, some of the related studies can be found in these articles [24,25,26,27].
The existence of dual or multiple solutions has gained the attention of many researchers, and most of them have attempted to run a stability analysis. However, most of them could not conclude whether the solution obtained is physically stable when using appropriate computation and analysis. The existence of the smallest eigenvalues was pioneered by Merkin [28] during his studies of mixed convection in a porous medium. He concluded that stable solutions were shown by a positive eigenvalue, while a negative eigenvalue indicates an unstable solution. Inspired by Merkin [28], the problem of stability analysis was studied by Weidman et al. [29], Merrill et al. [30], and Harris et al. [31]. Following these, numerous researchers, such as Ishak [32], Nazar et al. [33], Awaludin et al. [34], Najib et al. [35,36], and Anuar et al. [37], implemented the stability analysis for dual solutions in their works.
The majority of researchers have focused their studies of nanofluid to improve the cooling efficiency when using copper, alumina, and titania as a nanoparticle. To the best of our knowledge, the characteristics of a carbon nanotube-based nanofluid with homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions specially induced by an exponentially stretching/shrinking sheet have not been explored so far. Thus, the aim for the current paper is to investigate the behavior of the base fluids (kerosene and water) for both single-wall and multi-wall CNTs by following the governing equations proposed by Bhattacharya and Vajravellu [18] and Bachok et al. [21]. The novelty of this research is the numerical solutions obtained in the stagnation point flow region past an exponentially stretching/shrinking sheet in carbon nanotubes. The results obtained will then be examined to identify the stability of the solutions.
2. Problem Formulation
Two-dimensional, steady stagnation point flow of carbon nanotubes past over an exponentially stretching/shrinking sheet in the presence of homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions was investigated as shown in Figure 1. As depicted in Figure 1a, when the velocity on the boundary moved away from a fixed point, sheet stretching occurred, and when the velocity at the boundary moved towards a fixed point, sheet shrinking was generated, as shown in Figure 1b. Here, single-wall and multi-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs and MWCNTs, respectively) were used as nanoparticles, while water and kerosene oil were used as the base fluids. A simple homogeneous reaction can be expressed as suggested by Chaudhary and Merkin [38] in the following form:
whereas the first order of heterogeneous reactions is given by
where the concentrations of the chemical species and are denoted by and , while and are the reactions involved where and are constants. Both homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions are assumed to be isothermal. In addition, reactant A has a constant concentration ao and there is no autocatalyst B in the external flow. Then, the homogeneous reaction (l) assures that the reaction rate in the external flow and at the outer edge of the boundary layer will be zero. In this case there is a simple relation between the concentrations and , and this leads to the standard forward stagnation point boundary layer flow together with a single equation for the concentration of reactant .

Figure 1.
Physical model and coordinate system. (a) Stretching sheet; (b) shrinking sheet.
Under the foregoing assumptions, the boundary layer equations can be written as
with the boundary conditions
Here, and are the fluid velocities along the x- and y-axes. Next, , and are the dynamic viscosity, thermal diffusivity, and density of the nanofluid, respectively. , and are the temperature in the boundary layer, sheet, and free stream, respectively, while is the constant that measures the rate of temperature increase along the sheet. The mentioned term has been taken from Oztop and Abu-Nada [39]:
where is the viscosity of the base fluid; is the heat capacity of the nanoparticle, is the nanoparticle volume fraction; and , and are the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid, base fluid, and carbon nanotubes, respectively. and are the densities of the base fluid and carbon nanotubes. In addition, the effective thermal conductivity of CNTs–nanofluid, was taken from Xue [40]. Thermophysical properties for different base fluids and CNT particles are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Thermophysical properties of carbon nanotubes (CNTs)–nanofluid (Khan et al. [41]).
The velocity of stretching/shrinking, , and velocity of external flow, , are given by
where and are positive constants and is the characteristic length of a sheet. A similarity solution of Equations (3)–(8) are represented in the following form:
where is the similarity variable, refers to the kinematic viscosity of the base fluid, and represents the stream function which are defined as and Equation (3) is identically satisfied and Equations (4)–(7) are transformed to ordinary differential equations by employing similarity variables (11):
The boundary conditions take the form
where is the Prandtl number, refers to the Schmidt number, and and denote the strength of the homogeneous and heterogeneous reaction, respectively. is the ratio of the mass diffusion coefficient; is the stretching/shrinking parameter, with for stretching and for a shrinking sheet; and prime represents differentiation with respect to . These terms are defined as follows:
The diffusion coefficients of chemical species A and B are assumed to be similar in size. Therefore, we can make an additional deduction that the diffusion coefficients and are the same, i.e., (Chaudhary and Merkin [38]) and thus
Now, Equations (14) and (15) yield
with the boundary conditions
Two essential quantities of physical interest are skin friction coefficient and local Nusselt number . They are characterized as follows:
where represents the shear stress and symbolizes surface heat flux. Their mathematical expressions are as follows:
Using Equation (22) in (21), we get the following:
The local Reynolds number is represented by .
3. Stability of Solutions
To perform a stability analysis, the problem needs to be considered as an unsteady case. Following Weidman et al. [29], a variable has to be introduced. Then, Equations (4)–(7) are substituted by
subject to
where represents the time. As identified by the variable (11), the new dimensionless variable for the unsteady problem is introduced:
so that Equations (24)–(27) can be expressed as
corresponding to the boundary conditions
As discussed above, the diffusion coefficient , hence (see Equations (18), (32) and (33)) are reduced to
and the boundary conditions are
Furthermore, the stability of the steady flow solution , and comply with the boundary value problem (30), (31), and (35), and the following terms are introduced:
where , and are relatively small compared to , and , and is an unknown eigenvalue. Substitute Equation (37) into Equations (30), (31), and (35), and the following linearized problem is obtained:
along with boundary conditions
The stability of steady flow , and are investigated by setting and hence , and in Equations (38)–(40) describe the initial growth or decay of the solution (37). Therefore, the final equations are in the following form:
along with the following boundary conditions
By relaxing a boundary condition on , or as recommended by Harris et al. [31], the range of possible eigenvalues can be acquired. Therefore, the boundary condition as can be relaxed, and the system of Equations (42)–(44), subject to the boundary conditions (45) along with the new boundary condition , needs to be solved.
4. Results and Discussion
The system of nonlinear ordinary differential Equations (12), (13), and (19), together with boundary condition (16) and (20), are numerically solved using the bvp4c solver in MATLAB software for different values of homogeneous–heterogeneous parameter, nanoparticle volume fraction, and stretching/shrinking parameter on dimensionless velocity, temperature, concentration, skin friction coefficient, and Nusselt number. In addition, bvp4c is a built-in function in MATLAB software that solve a two-point boundary value problem for ordinary differential equations. The values of nanoparticle volume fraction used in this present problem were between 0 and 0.2 , where corresponds to the regular fluid. In this case, a unique solution was obtained for and dual solutions exist when with the assistance of suitable initial guesses and an appropriate value of .
Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 exhibit the influences of nanoparticle volume fraction and base fluid on the reduced skin friction and reduced heat transfer with stretching/shrinking parameter . On observing these figures, it has been concluded that reduced skin friction decreases and heat transfer increases with an increase of nanoparticle volume fraction. This is consistent with the fact that the movement of fluid tends to slow down in the presence of nanoparticles. It is further observed that by increasing the nanoparticle volume fraction, thermal conductivity of the nanofluid will also increase. The results for shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3 display similar characteristics with those found by Bhattacharya and Vajravellu [18]. It is seen that carbon nanotubes with kerosene oil as base fluid exhibit the highest skin friction coefficient and heat transfer rate. The range of stretching/shrinking parameter for the solution to exist is greater in the exponential case, i.e., compared to the range of stretching/shrinking parameter for the linear case, i.e., (see [42]). The critical value, , obtained in this research is in concurrence with those reported by Bhattacharya and Vajravellu [18]. Note that for the exponential case, the shrinking rate is faster than a linear case; the number of vorticities produced and exponential straining motion are larger and stronger for exponential shrinking compared to linear shrinking. Thus, to control the produced vorticity due to exponential shrinking sheet, the stagnation flow velocity is more definite for the exponential case in contrast with the linear case. It can be seen that for the exponential case, the second solution can be obtained, and the range of solutions widens even though the shrinking rate is low, i.e., .
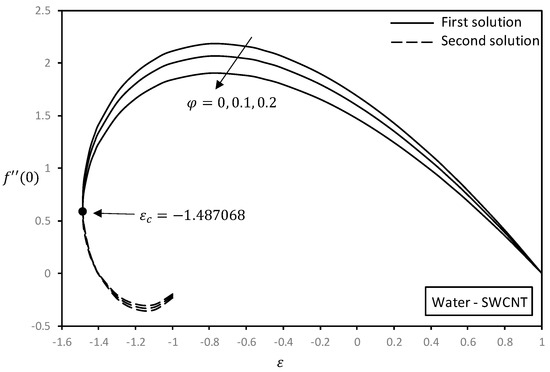
Figure 2.
Effect of on reduced skin friction with .

Figure 3.
Effect of on reduced heat transfer with .
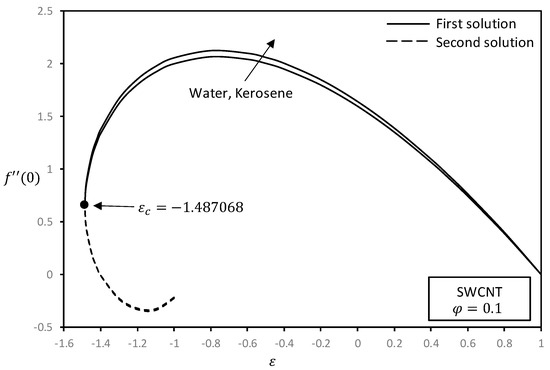
Figure 4.
Effect of base fluids on reduced skin friction with .

Figure 5.
Effect of base fluids on reduced heat transfer with .
The variations in the concentration of species A, , are presented in Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 for a variety of ranges of strength of the homogeneous reaction , heterogeneous reaction , and Schmidt number . The concentration is clearly observed to be significantly enhanced with decreasing homogeneous reaction parameter values, and reversed behavior is observed for heterogeneous parameters. It is well understood that higher values of heterogeneous parameter cause the diffusion coefficient to decrease and, thus, less diffused particles intensify the concentration field. This result coincides with preceding observations made by Bachok et al. [21]. Further, it is observed that the concentration increases for large values of Schmidt number, which is defined as the average of momentum to mass diffusivity. The concentration profile is enhanced due to the fact that the mass diffusivity is small for increasing values of Schmidt number.

Figure 6.
Effect of on concentration gradient with .
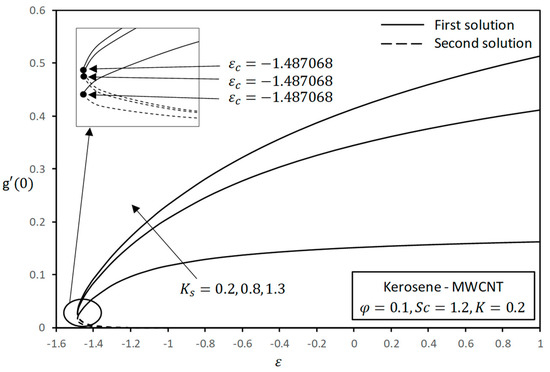
Figure 7.
Effect of on concentration gradient with .
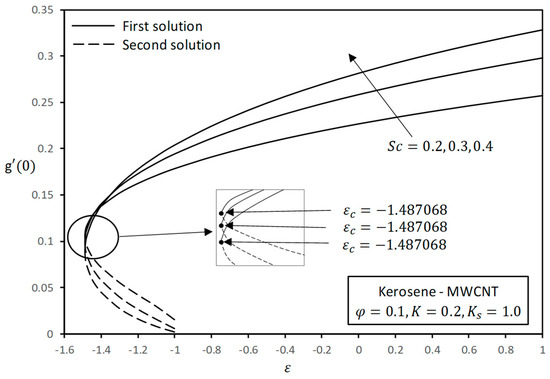
Figure 8.
Effect of on concentration gradient with .
The influence of nanoparticles on the skin friction coefficient and the local Nusselt number given by Equation (23) when a stretching sheet is considered is presented in Figure 9 and Figure 10. These values enhanced almost linearly with nanoparticle volume fraction. Thermal conductivity of the fluid increases significantly with the presence of the nanoparticles and, therefore, enhanced the heat transfer characteristics. In this respect, skin friction coefficient and Nusselt number of SWCNTs are higher than for MWCNTs. Physically, this is because SWCNTs possess higher density and thermal conductivity compared to MWCNTs, as illustrated in Table 1. Further, it is worthwhile to mention that the skin friction and heat transfer rate near the wall are higher in kerosene oil due to more viscosity and density as compared to water. Moreover, it can be observed that CNTs have a dominant contribution in the heat transfer phenomenon and nanofluid flow motion.

Figure 9.
Effect of nanoparticles and base fluids on with .
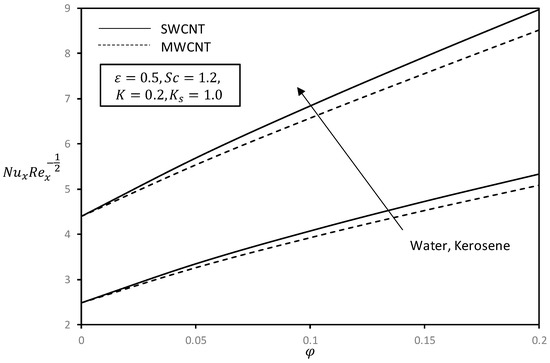
Figure 10.
Effect of different nanoparticles and base fluids on with .
Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14, Figure 15 and Figure 16 represent the effects of shrinking velocity and carbon nanotubes on the dimensionless profiles. It is observed that velocity and concentration profiles significantly decrease with shrinking velocity for the upper branch solution, while increasing for the lower branch solution except for very small . Also, it is revealed that the temperature profile increases in the first solution and decreases for the second solution with an increasing value of shrinking velocity. For these profiles, single-wall CNTs are more dominant than multi-wall CNTs. It can be seen that all these profiles asymptotically satisfied all boundary conditions. Hence, excellent convergence was achieved, and the numerical results obtained are valid. The physical importance of this problem shows that in the case of dual solutions, the flow separates from the plate, which is very important for many practical problems. An improved understanding of such flows and the application of this knowledge to new design techniques should provide substantial improvements in the performance, reliability, and cost of many fluid dynamic devices.
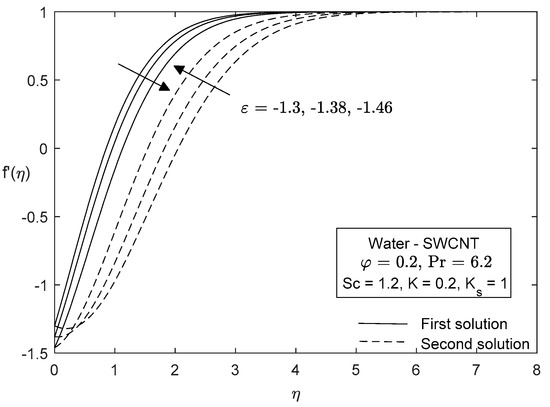
Figure 11.
Velocity profiles for different values of .
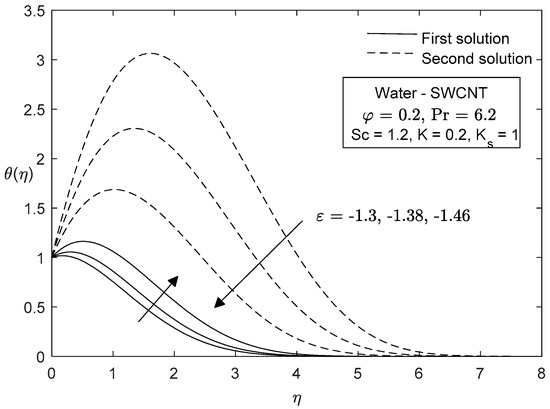
Figure 12.
Temperature profiles for different values of .
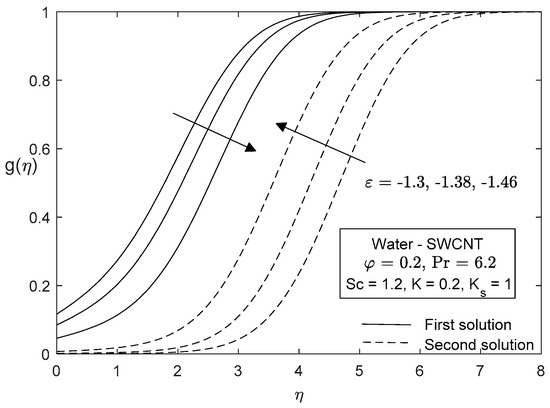
Figure 13.
Concentration profiles for different values of .

Figure 14.
Velocity profiles for different nanoparticles and base fluids.

Figure 15.
Temperature profiles for different nanoparticles and base fluids.
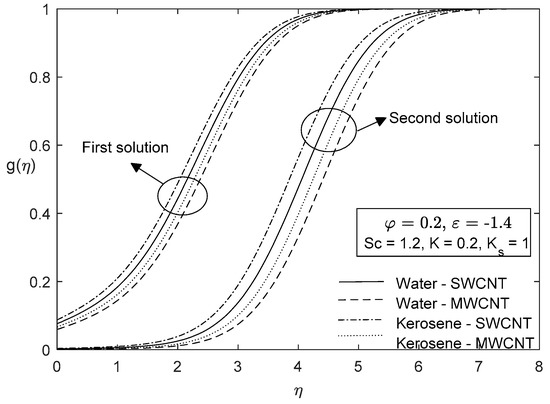
Figure 16.
Concentration profiles for different nanoparticles and base fluids.
The stability of solutions obtained in this study was conducted numerically using the bvp4c solver in MATLAB software by substituting the set of linearized Equations (42)–(44) along with the new boundary condition (45) into the codes to validate if either upper or lower solution were stable and could be physically realized. From Table 2, it was clear that the first solution bestowed a positive eigenvalue and was a stable solution (initial decay of disturbance), whereas the second solution was not (initial growth of disturbance), i.e., it had a negative eigenvalue which led to an unstable solution. It was also observed that as the stretching/shrinking parameter approached a critical point, the smallest eigenvalue also approached zero. Interestingly, the alteration from negative values to positive values of eigenvalues occurred at the critical point of the solution curve (Figure 2), that is, .

Table 2.
Smallest eigenvalues of for different values of when , and (Water–SWCNT).
5. Conclusions
The present study investigates the flow and heat transfer of carbon nanotubes over an exponentially stretching/shrinking sheet with homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions. It is concluded that:
- The skin friction and heat transfer rates increase linearly with nanoparticle volume fraction.
- Kerosene-based CNTs have higher heat transfer rates and skin friction compared to water-based CNTs.
- Single-wall CNTs show greater impact on skin friction and heat transfer rate than multi-wall CNTs in both water and kerosene.
- The concentration of species A at the surface increases with an increase in heterogeneous reaction parameter and Schmidt number , while it decreases when homogeneous reaction parameter is increased.
- The range of solutions were widely expanded for exponentially shrinking cases compared with linear cases.
- The existence of unique solutions occurs for an exponentially stretching surface , whereas dual solutions occur for an exponentially shrinking surface .
- The first solution is stable and physically realizable, while the second solution is unstable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S.A. and N.B.; Formal analysis, N.S.A.; Funding acquisition, N.B.; Methodology, N.S.A.; Supervision, N.B., N.M.A., and H.R.; Validation, N.B., N.M.A., and H.R.; Writing—original draft, N.S.A.; Writing—review & editing, N.B., N.M.A., and H.R.
Funding
This research was funded by Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS/1/2018/STG06/UPM/02/4/5540155) and MyBrainSc from the Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia.
Acknowledgments
A sincere gratitude to the Universiti Putra Malaysia and Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia for the scholarship and the financial support received. The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| concentrations of the chemical species | |
| chemical species | |
| constant concentration | |
| constants | |
| skin friction coefficient | |
| specific heat at constant pressure | |
| diffusion coefficients | |
| dimensionless stream function | |
| concentration of species A | |
| concentration of species B | |
| thermal conductivity | |
| strength of the homogeneous reaction | |
| strength of the heterogeneous reaction | |
| constants | |
| constants | |
| characteristic length of a sheet | |
| local Nusselt number | |
| Prandtl number | |
| surface heat flux | |
| local Reynolds numbers | |
| Schmidt number | |
| time | |
| temperature | |
| temperature constant | |
| velocity components along the x- and y- directions, respectively | |
| stretching/shrinking velocity | |
| velocity of inviscid flow | |
| cartesian coordinates along the surface and normal to it, respectively | |
| Greek symbols | |
| thermal diffusivity | |
| ratio of the diffusion coefficient | |
| nanoparticle volume fraction | |
| dimensionless temperature | |
| unknown eigenvalues | |
| stretching/shrinking parameter | |
| kinematic viscosity | |
| dynamic viscosity | |
| fluid density | |
| heat capacity of the fluid | |
| dimensionless time variable | |
| surface shear stress | |
| stream function | |
| similarity variable | |
| Subscripts | |
| condition at the surface of the plate | |
| ambient condition | |
| carbon nanotubes | |
| fluid | |
| nanofluid | |
| Superscript | |
| differentiation with respect to | |
References
- Halelfadl, S.; Maré, T.; Estellé, P. Efficiency of carbon nanotubes water based nanofluids as coolants. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2014, 53, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javey, A.; Kong, J. (Eds.) Carbon Nanotube Electronics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.S.; Lin, M.C.C.; Huang, I.T.; Wang, C.C. Enhancement of thermal conductivity with carbon nanotube for nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 32, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biercuk, M.J.; Llaguno, M.C.; Radosavljevic, M.; Hyun, J.K.; Johnson, A.T.; Fischer, J.E. Carbon nanotube composites for thermal management. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 2767–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, M.S.; Nassab, S.A.G. Numerical investigation of forced laminar convection flow of nanofuids over a backward facing step under bleeding condition. J. Mech. 2012, 28, N7–N12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachok, N.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Unsteady boundary-layer flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 2102–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, K.; Ashraf, M. Stagnation point flow and heat transfer of a magneto-micropolar fluid towards a shrinking sheet with mass transfer and chemical reaction. J. Mech. 2013, 29, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magyari, E.; Keller, B. Heat and mass transfer in the boundary layers on an exponentially stretching continuous surface. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjayanand, E.; Khan, S.K. On heat and mass transfer in a viscoelastic boundary layer flow over an exponentially stretching sheet. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2006, 45, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidin, B.; Nazar, R. Numerical solution of the boundary layer flow over an exponentially stretching sheet with thermal radiation. Eur. J. Sci. Res 2009, 33, 710–717. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeema, S.; Hayat, T.; Malika, M.Y.; Rajputa, S.A. Thermal radiation effects on the flow by an exponentially stretching surface: A series solution. Z. Für Nat. A 2010, 65, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A. MHD boundary layer flow due to an exponentially stretching sheet with radiation effect. Sains Malaysiana 2011, 40, 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeem, S.; Zaheer, S.; Fang, T. Effects of thermal radiation on the boundary layer flow of a Jeffrey fluid over an exponentially stretching surface. Numer. Algorithms 2011, 57, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.; Lee, C. Boundary layer flow of nanofluid over an exponentially stretching surface. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaib, A.; Bhattacharyya, K.; Shafie, S. Unsteady boundary layer flow and heat transfer over an exponentially shrinking sheet with suction in a copper-water nanofluid. J. Cent. South Univ. 2015, 22, 4856–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baag, S.; Mishra, S.R.; Hoque, M.M.; Anika, N.N. Magnetohydrodynamic Boundary Layer Flow Over an Exponentially Stretching Sheet Past a Porous Medium with Uniform Heat Source. J. Nanofluids 2018, 7, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemenz, K. Die Grenzschicht an einem in den gleichformigen Flussigkeitsstrom eingetauchten geraden Kreiszylinder. Dinglers Polytech. J. 1911, 326, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, K.; Vajravelu, K. Stagnation-point flow and heat transfer over an exponentially shrinking sheet. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2012, 17, 2728–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachok, N.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Boundary layer stagnation-point flow and heat transfer over an exponentially stretching/shrinking sheet in a nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 8122–8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, J.H. A model for isothermal homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in boundary-layer flow. Math. Comput. Model. 1996, 24, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachok, N.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. On the stagnation-point flow towards a stretching sheet with homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions effects. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2011, 16, 4296–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Farooq, M.; Alsaedi, A. Homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in the stagnation point flow of carbon nanotubes with Newtonian heating. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 027130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Hussain, Z.; Alsaedi, A.; Ahmad, B. Heterogeneous-homogeneous reactions and melting heat transfer effects in flow with carbon nanotubes. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Hayat, T.; Khan, M.I.; Alsaedi, A. A modified homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions for MHD stagnation flow with viscous dissipation and Joule heating. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 113, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Ayub, T.; Muhammad, T.; Alsaedi, A. Three-dimensional flow with Cattaneo–Christov double diffusion and homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 2812–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Muhammad, K.; Muhammad, T.; Alsaedi, A. Melting Heat in Radiative Flow of Carbon Nanotubes with Homogeneous-Heterogeneous Reactions. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2018, 69, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.; Farooq, M.; Ahmad, S.; Anjum, A. Melting heat transfer with radiative effects and homogeneous- heterogeneous reaction in thermally stratified stagnation flow embedded in porous medium. J. Cent. South Univ. 2018, 25, 2701–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, J.H. On dual solutions occurring in mixed convection in a porous medium. J. Eng. Math. 1986, 20, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidman, P.D.; Kubitschek, D.G.; Davis, A.M.J. The effect of transpiration on self-similar boundary layer flow over moving surfaces. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2006, 44, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, K.; Beauchesne, M.; Previte, J.; Paullet, J.; Weidman, P. Final steady flow near a stagnation point on a vertical surface in a porous medium. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2006, 49, 4681–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.D.; Ingham, D.B.; Pop, I. Mixed convection boundary-layer flow near the stagnation point on a vertical surface in a porous medium: Brinkman model with slip. Transp. Porous Media 2009, 77, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A. Flow and heat transfer over a shrinking sheet: A stability analysis. Int. J. Mech. Aerosp. Ind. Mechatron. Eng. 2014, 8, 905–909. [Google Scholar]
- Nazar, R.; Noor, A.; Jafar, K.; Pop, I. Stability analysis of three-dimensional flow and heat transfer over a permeable shrinking surface in a Cu-water nanofluid. Int. J. Math. Comput. Phys. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2014, 8, 782–788. [Google Scholar]
- Awaludin, I.S.; Weidman, P.D.; Ishak, A. Stability analysis of stagnation-point flow over a stretching/shrinking sheet. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 045308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najib, N.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Senu, N. Boundary layer flow and heat transfer of nanofluids over a moving plate with partial slip and thermal convective boundary condition: Stability analysis. Int. J. Mech. 2017, 11, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Najib, N.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M. Stability of Dual Solutions in Boundary Layer Flow and Heat Transfer over an Exponentially Shrinking Cylinder. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.S.; Bachok, N.; Pop, I. A Stability Analysis of Solutions in Boundary Layer Flow and Heat Transfer of Carbon Nanotubes over a Moving Plate with Slip Effect. Energies 2018, 11, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M.A.; Merkin, J.H. A simple isothermal model for homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in boundary-layer flow. I Equal diffusivities. Fluid Dyn. Res. 1995, 16, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Nada, E. Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.Z. Model for thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube-based composites. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2005, 368, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.A.; Khan, Z.H.; Rahi, M. Fluid flow and heat transfer of carbon nanotubes along a flat plate with Navier slip boundary. Appl. Nanosci. 2014, 4, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y. Stagnation flow towards a shrinking sheet. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2008, 43, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).