Abstract
The lurch index has recently been introduced in applied kinematics as an integral descriptor of the fluency of the motion of a rigid body in space. It may be defined in different versions, according to the component of motion under investigation. In the present paper, we analyze a rotational lurch index, which describes the fluency of the spin component of motion and whose value depends, through involved relations, on the dynamics of three canonical descriptors of the orientation of a rigid body in space. The aim of the present paper is to offer a closed-form expression of the instantaneous component of the rotational lurch, which leads to the namesake index upon integration and normalization. The closed form of the index is, then, used to evaluate its practical calculation, based on numerical approximations on a number of data sets.
1. Introduction
The kinematic state of a rigid body is described by its instantaneous position and orientation with respect to an inertial reference frame, as well as by its translational and rotational velocities [1], while its dynamic state is classically described in terms of the rates of change of these velocities (namely, its translational and rotational accelerations) and in terms of their relationships to applied forces and torques [2].
A further physical quantity, the rate of change of the acceleration of the moving body, has been recently investigated, in applied science and engineering fields [3,4,5,6], as a further descriptor of the dynamics of a rigid body which is capable of capturing more structured information (such as, e.g., information about the motion of a human body). Such descriptors are, hereafter, referred to as translational and rotational lurch. Some examples of applications are the analysis of human body movement fluency in the context of biomedical sciences [7,8,9,10] and robot arm movement planning in the context of industrial robotics [11,12].
In the present paper, we analyze the rotational lurch index, a scalar integral indicator associated with the spin component of motion. We assume that a rigid body rotates in open space and that its instantaneous orientation is described, with respect to a fixed reference frame, by three angles which are functions of time. These angles represent the three elementary three-dimensional rotations along three specific axes, which may be composed to define the instantaneous orientation (or attitude, when speaking of flying bodies [13]) of the moving object. On the basis of the instantaneous orientation, one may define, by time-derivation under appropriate geometric constraints, the angular speed of a body along the instantaneous axis of rotation, the angular acceleration, and, ultimately, the instantaneous rotational lurch.
The relationship between the angular functions that describe the orientation of a rigid body and the rotational lurch index is quite involved. Its expression, written in terms of matrix/vector multiplications, looks even more complicated when it comes to implementing it on dedicated hardware located onboard a flying drone, for example. Therefore, it is customary to approximate the value of the lurch index by resorting to numerical calculus techniques which, in turn, take as inputs the values of the angular variables acquired through dedicated hardware. A typical example is offered by inertial measurement units, mounted on electronic boards which provide power supply and read the sensors at regular intervals. The numerical calculus techniques involved are essentially formulas that allow one to approximate mathematical derivatives using finite-increment ratios. It is important to underline that the temporal spacing between successive samples cannot usually be chosen freely, as it is constrained by the capability of the hardware used to acquire orientation information (for example, some cellular-phone based acquisition apps cannot sample faster than 10 samples per second).
The present paper offers a closed-form expression of the amplitude of the rotational lurch—namely, the instantaneous rotational lurch index—which, ultimately, will lead to the value of rotational lurch upon integration and normalization. The values of the rotational lurch index, computed through the closed-form expression, will serve as a reference: The quality of the numerical approximation will be evaluated on a number of data sets acquired in different testing conditions and by different kinds of sensors.
The present paper is organized as follows: Section 2 recalls formal definitions of the rotational lurch index, in terms of the instantaneous orientation matrix and associated kinematic-dynamic indicators. Section 3 describes details of the calculations leading to the closed-form expression of the rotational lurch index, while Section 4 recalls how such an index may be calculated through numerical approximations. Section 5 compares the results obtained by numerical approximation to the corresponding results obtained through the closed-form expression on three ensembles of data sets (a group formed by three synthetic data sets, a group formed by ten data sets acquired through a dedicated inertial measurement unit, and three data sets acquired through a smartphone). Section 6 concludes the paper.
2. Rotational Lurch Index
Let us denote by the Lie group of three-dimensional rotations; namely . A rotation matrix that describes the instantaneous orientation of a rigid body with respect to a fixed inertial reference frame may be decomposed into the product of three elementary rotations, with respect to three specific rotational axes, in a number of ways, according to well-known results by Euler and Tait–Bryan [14]. The Tait–Bryan convention is largely used in aerospace applications, such that zero degrees elevation represents a horizontal attitude, and the Tait–Bryan angles represent the orientation of an aircraft with respect to the world frame. In the present paper, we chose the pitch-roll-yaw representation, as illustrated in the Figure 1. It is worth recalling that one such representation may suffer from a well-known problem, known as gimbal lock, which is briefly surveyed in the Appendix A.
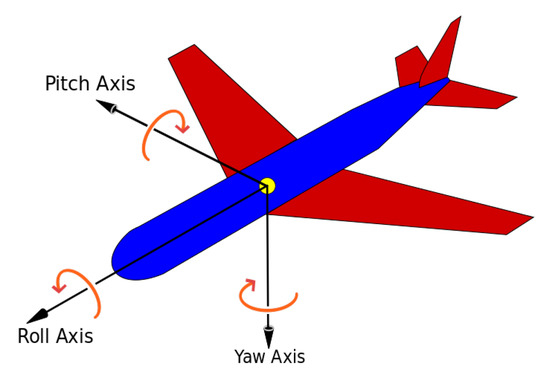
Figure 1.
Schematics of the Tait–Bryan pitch-roll-yaw representation of the orientation of a rigid body with respect to a fixed reference frame (the world frame). Reproduced from Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aircraft_principal_axes).
WHO CONFIRMED THAT IT IS FINE TO USE IN-TEXT URLs.
Section 2.1 presents a definition of the rotational lurch index, while Section 2.2 illustrates its relationships with a Cartesian lurch index and a so-called total absolute torsion index.
2.1. Definition of Rotational Lurch Index
Let us denote by the yaw angle, by the pitch angle, and by the roll angle. The ranges taken by these angles depend on the software design. Typically, the roll and yaw span a -wide range (for example, or ), while the pitch angle spans a -wide range (for example ). Also, note that the yaw axis may be oriented upside-down as well as upside-up, depending on the context.
The rotation matrix R corresponding to the ordered triple may be written as:
where the functions , , and denote standard rotation functions about the canonical axes [15]. In particular, the matrix may be written as
the matrix may be expressed as
and the matrix may be written as
The full rotation matrix R takes the form
During the motion of a rigid body, the angles change with the time ; therefore, we can consider the -valued function as a shorthand for . Within the present paper, an over-dot denotes first-order derivation with respect to t, while two over-dots and three over-dots denote second- and third-order derivation with respect to t, respectively.
The rate of change of the orientation of a rigid body varies, according to the law
The entries of the matrix , denoted by , with , have been calculated to be:
From the structure of the Lie group , it is known that such a change rate obeys the rule
where the matrix is termed the angular velocity matrix and is skew-symmetric. The symbol denotes the Lie algebra associated to the Lie group and is defined by . The angular velocity matrix takes the form
The three independent components of the angular velocity matrix may be computed by the inverse relationship , and relate to the rate of change of the yaw-pitch-roll angular co-ordinates by
The angular velocities , and are, in fact, the Cartesian components of the angular velocity vector corresponding to the canonical basis of . Notation-wise, the relationship between an rotation velocity matrix and the corresponding angular velocity vector is written as through the operator ∨ (read as ‘vee’). The direction of the angular velocity represents the orientation of the rotation axis of the rigid body and its amplitude represents the actual rotation speed. The vector field is a tangent vector field in the trivialized tangent bundle of the Lie group of three-dimensional rotations and, as such, obeys the rules of calculus prescribed by differential geometry, upon metrization of the tangent bundle. The paper [12] describes the mathematical structure of such a space and the related calculations in detail. Such calculations are based on the notion of a covariant derivative ∇ that, in summary, affords evaluating the rate of change of a vector field in a direction specified by a second vector field.
In order to evaluate the spinning fluency of a rigid body’s motion, a specific vector field is calculated; namely, the rotational lurch associated to a velocity field. The rotational lurch is defined as the second time-derivative of the speed (i.e., as the derivative of the acceleration). According to the calculations explained in [12], while the instantaneous acceleration associated to a field is simply , its second-order derivative takes the form ([12], Proposition 4.2):
where the symbol × denotes the standard three-dimensional vector cross product and where the vector field ℓ is termed the instantaneous rotational lurch. The scalar rotational lurch is the amplitude of the second covariant derivative (11), , where the symbol denotes the standard Euclidean norm in .
If we denote by the time interval that the variable t belongs to, an index of the rigid body’s spinning fluency may be defined as the time-integral of the scalar rotational lurch appropriately normalized, by:
where the constant in front of the integral is defined in a way that makes the index (12) independent of the time-interval width T and of the accumulated angular speed
The normalization introduced in (12) has the purpose of making the values of the index (12) computed for different motions comparable to one another. As an illustrative example, we remark the case, reported in [8], of three indoor wall climbers, each with different skills and experience levels, that completed the same wall in different times and using different body movement schemes and whose performances, in terms of body fluency, can be successfully compared only upon normalization of their total lurch.
2.2. Relationship with Cartesian Lurch and Total Absolute Torsion
The rotational lurch differs substantially from the Cartesian lurch used in other applications [8,16]. Given an angular speed field , the norm of its second-order time-derivative is
Conversely, the squared scalar rotational lurch reads:
Apparently, the scalar rotational lurch differs greatly from the scalar Cartesian lurch. For example, if the Cartesian lurch is negligible at a point of a trajectory (i.e., ), the rotational lurch may still differ considerably from zero, because its squared value would approximately equal . In fact, the main difference between the Cartesian lurch and the rotational lurch is given by the term , which may be thought of as an analogue of the Coriolis force in a rotating frame of reference.
The orientation of a three-dimensional object in the space may be described in terms of a Frenet–Serret frame [17]. Let us consider a curve . To each point of this curve, we may attach an orthogonal frame described by three unit vectors; namely, a tangent vector , a normal vector , and a binormal vector , where denotes a running curve length parameter ( denotes the total length of the curve). Conversely, the rotational motion of a rigid body may be described in terms of an abstract curve through the identification of its rotation matrix R with the orthogonal matrix formed by the juxtaposition of tangent, normal, and binormal (column) vectors.
By the Frenet–Serret theorem, the rates of change of the vectors in a Frenet–Serret frame satisfy the following differential equation
where denotes the curvature of the curve and denotes the torsion of the curve.
It has been noticed that the lurch (12) is related to the total absolute torsion:
3. Closed-Form Expression of the Rotational Lurch Index
In this section, we aim to calculate a closed-form expression for the instantaneous scalar rotational lurch , according to the definition (11). To this aim, we need to compute the derivatives and of the vector field (10).
The components of the vector field were calculated to be
Accordingly, the components of the vector field take the expressions
The (squared) scalar rotational lurch (15) takes, therefore the closed-form expression
which may be computed directly once the functions , , and are known.
On the same line, one might want to compute the scalar angular velocity in a closed form, whose squared expression reads
to be used in the evaluation of the accumulated angular speed (13).
4. Numerical Evaluation of the Kinematic Indexes
The expressions (18) and (19) are quite involved and difficult to implement. It is, therefore, customary to approximate these quantities by numerical rules based on temporal sampling. In particular, a valid alternative to the closed-form expression of the instantaneous rotational lurch is a numerical approximation.
Assuming that the orientation of a rigid body is described by a -valued signal , uniformly sampled in time with time-spacing , the available data to perform the calculations are given by a sequence
as acquired through an orientation sensor and a communication/acquisition software application. The time-spacing h between time-adjacent samples, termed the sampling period, is fixed as given by the hardware/software design and is a datum of the problem. Uniform subsampling (i.e., decimation) may be applied, if the sampling rate is too high.
Section 4.1 outlines the formulas used to numerically estimate the lurch index. Section 4.2 focuses on the numerical formulas to estimate the angular velocity matrix and its derivatives, discusses their numerical precision, and outlines ways to increase such precision (at the expense of additional computational burden).
4.1. Numerical Estimation Formulas
Given a rotation-matrix function , its first-order derivative may be approximated numerically by means of Newton’s difference quotient rule adapted to the geometry of the Lie group . Namely, one may use the group-exponential approximation
where ‘exp’ denotes the matrix exponential [18] and is a discrete time index. An estimation of the angular velocity matrix at the snapshot may, thus, be defined as
for , where ‘log’ denotes a principal matrix logarithm [18]. The physical meaning of the skew-symmetric matrix is that of a (small, constant) rotation speed that drives the rigid body from the orientation to the orientation within the time interval .
If sampling is not sufficiently fast, compared to the body’s spin speed, two subsequent samples might differ considerably from one another and the approximation (22) may be unreliable. This is because the matrix logarithm is defined only if its argument is sufficiently close to the identity . As a result, denoting by the matrix Frobenius norm, it is sufficient that the sampling ensures that for every . As a curiosity, it is interesting to report the fastest spin on ice skates, at the time of writing, was achieved by Olivia Oliver (Canada) with a maximum rotational velocity of 342 rotations per minute, in Warsaw, Poland on 19 January 2015 (https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/fastest-spin-ice-skating/). This value corresponds to an angular velocity of about rad/s.
The angular speed vector may, thus, be calculated by means of the ‘vee’ operator as and Newton’s difference quotient rule may be put into effect to numerically approximate the derivatives and , in order to, ultimately, approximate the values of the function (11). The time-derivatives of the angular velocity vector are approximated by
The total observation interval is a multiple of intervals of duration h each. Therefore , where N denotes the number of samples. The accumulated angular speed defined in (13) is approximated numerically by
The quantity (11) is approximated numerically by
Notice that simplifies to by (23), and so
A quick comparison reveals that the numerical approximation (27) is much simpler to implement than the closed-form expression (19). Section 5 compares the numerical approximation of the lurch index to its exact value on a number of data sets, in order to numerically evaluate the quality of the above approximations.
4.2. Remarks on the Precision of the Estimations
In order to estimate the precision of the numerical formulae used to approximate the angular velocity matrix, it is necessary to recall a few notions from numerical analysis, with special emphasis on the matrix Lie group .
A function may be expanded around as
where are constant matrices in the Lie algebra . The above relationship plays the role of a Taylor series expansion formula in the matrix Lie group . As in the Taylor series, is possible to relate the matrix-coefficients to the derivatives . In order to determine such relationships, let us note that
To obtain the above expressions, it is important to recall that is a non-commutative Lie algebra. Setting t = 0 in the above derivatives and recalling that , we get:
from which it is straightforward to find that
Setting t = 0 in the last three relationships, it is readily found that
Comparing Equations (39), (40) and (41) with Equations (36), (37) and (38), respectively, the following identities are obtained:
These identities show that the coefficients in the Lie group expansion (29) are indeed the coefficients of the Taylor series expansion of the function at (as is a vector space, the Taylor series expansion of any -matrix appears as in the classical Taylor series setting).
In order to get the numerical approximation of each value used within the previous Section, one can use the expansion (29) truncated to the first term in a Newton’s difference quotient setting, namely:
where , and the notation denotes a Landau symbol. (The symbol reads “big o” and means that for any y sufficiently large [19]. A few rules-of-thumb to keep in mind are , , , and ). From the above expression, in fact, one gets:
therefore, the approximation (22) is of order 1 (i.e., the error grows linearly in h). Likewise:
On the basis of such an inaccurate estimation of the angular velocity, the estimations of its first-order and of its second-order derivatives by (23) and (24) cannot be any better, in terms of precision.
The rest of this Section explains how to obtain more precise approximations for the angular velocity matrix, as well as for its derivatives, by careful usage of the expansion (29) together with the above-noted expressions of the coefficients. Let us start by writing the expansion formula around a generic point t—namely, at points —as:
with . For the sake of conciseness, let us define
and let us drop any notational dependency from t. From the relationships (49) and (50), it is immediate that:
The matrices , as well as the time-step h, are known, while approximations for the matrices are sought.
To get an approximation of the matrix A, one may notice from (52) that
therefore, in terms of angular velocity matrix, we get the following estimation:
The above estimation, that (in analogy to the corresponding formula in ) may be referred to as a midpoint rule, is of order 2: As long as , an error may be smaller than an error ; hence, the estimation formula (54) is more accurate than the estimation formula (48). Furthermore, in the case that real-time processing of readouts must be dealt with, the above formula may be made causal by replacing each occurrence of n on the right-hand side by .
According to the identities (45), we may, thus, write
The numerical estimation obtained by dropping the remainder is of order 2.
The above setting is insufficient to get a second-order estimation of the matrix C. In fact, it is impossible to find any linear combination of the matrices and such that the terms in h, , and would vanish. In order to be able to estimate the matrix C with a precision of order 2, it is necessary to define two additional data-derived matrices, namely:
In terms of the matrix-coefficients , the above two quantities take the expressions
which were derived from the expansions (49) and (50) by replacing the increment h with . Notice that there does not exist any linear combination of the matrices , , and , nor of the matrices , , and , which results in . Conversely, there exist infinitely many linear combinations of the matrices , , , and , which results in expressions of the form , one of which is:
This, according to the identities (45), leads to the estimation
The general solution of the weighting problem of the matrices , , , and is outlined in Appendix B.
It is quite apparent how the second-order estimates (54), (56), and (61) are far more cumbersome, from a computational complexity point of view, than the first-order approximations suggested in the Section 4.1, which were tested in the numerical experiments presented in the Section 5.
Concerning the numerical approximation (25), we recall that the numerical precision of the rectangle rule (or Riemann sum) applied to a function on a uniform N-point grid with spacing h is [20]:
Therefore, the numerical quadrature formula (25) returns an approximation of the true accumulated angular speed with a precision of . Likewise, the normalized quadrature formula (28) returns an approximation L of the true lurch index with a precision of . The simple quadrature rule is, therefore, sufficiently precise to maintain the order of the estimations at the value 2.
5. Numerical Tests
Lurch has been commonly used in applied mechanics and in mechanical design [21] to minimize backlash effects, mechanical wear and tear, and to provide a smooth, stable motion profile, with clean positioning while minimizing overshoot. Kinematic lurch is a function of the mechanical stiffness of an axis, and is difficult to know prior to properly tuning the actual axis performance. As the number of applications grows, it becomes increasingly important to acquire an appropriate lurch index value for an application. The present section aims at comparing the numerical values of the lurch index, calculated through a numerical approximation with those calculated through a closed-form expression over a number of rigid-body motion data sets. In the present section, the acquired pitch-yaw-roll sequences are denoted by , , and , respectively. The angular derivatives occurring in equations (18) and (19) were evaluated numerically by a Newton’s difference quotient.
5.1. Numerical Test on Three Synthetic Data Sets
The first ensemble of data sets used to compare the numerical approximation of the rotational lurch index with the reference value calculated by its closed-form expression was composed of three synthetic orientation signals. Data set 1 consisted of three square waves, one for each orientation angle, with different phases. Data set 1 was designed to simulate non-smooth body orientation change. Data set 2 consisted of three sine waves with different phases, and was designed to simulate a smooth body movement. Data set 3 is illustrated in Figure 2: The three-dimensional representation looks quite regular for this synthetic data set, in contrast to the representation that we shall observe in a later Section pertaining to real-world human-motion-based data sets.
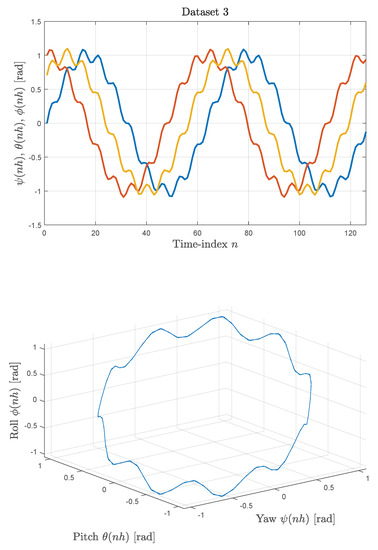
Figure 2.
Synthetic data sets: Illustration of Data set 3. Upper panel: Angular sequences , , and versus the sample index n. Lower panel: Three-dimensional representation of the angular sequences obtained by plotting the triples in for .
The numerical results obtained in the experiment are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Synthetic data sets: Summary of the numerical results obtained over the three data sets designed to exhibit different levels of motion smoothness. The sampling time used in this experiment was set to (sec). The third column’s name denotes succinctly the summation in the expression (28), while the fourth column’s name denotes succinctly the integral in the expression (12).
The numerical indices shown in the table are specified as follows: N denotes the total number of temporal samples, denotes the accumulated angular velocity computed by its closed-form expression, denotes the norm of the lurch-vector ℓ computed by a numerical approximation (27), while denotes the norm of the lurch-vector computed by its closed-form expression (19); and the symbols and denote the values of the rotational lurch index computed numerically by (28) and analytically by (12), respectively.
For Data sets 1 and 2, the values of the indices obtained numerically and obtained by their closed-form expressions were in excellent agreement. Moreover, the value of the lurch index pertaining to Data set 1 (non-smooth movement) was substantially larger than the value of the lurch index pertaining to Data set 2 (smooth movement), confirming that the lurch index is a good indicator of the fluency of the rotation of a rigid body.
The numerical values of the indices pertaining to Data set 3 showed some moderate inconsistency, in comparison to the analytic values. A detailed visualization of these results is offered in Figure 3.
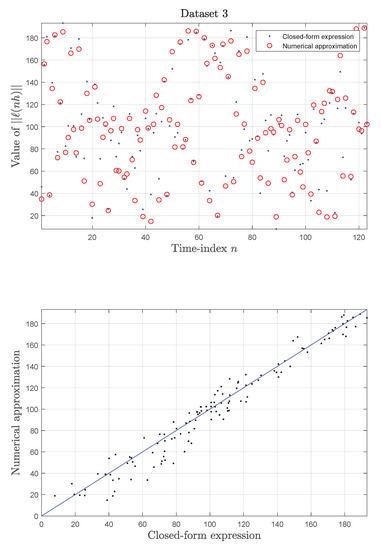
Figure 3.
Synthetic data sets: Results obtained for Data set 3. Upper panel: Sample-by-sample comparison of the values of the quantities (open circles) and (dots) versus the sample index n. Bottom panel: Scatter plot of the scalar pair (the blue line represents a secant).
From the top panel, it can be immediately noticed how several values among those calculated by a numerical approximation were out of place, compared to the reference values computed by means of the closed-form expression. The lurch-norm pairs shown in the bottom panel, which should ideally align over a secant, appear to be scattered around the blue secant. This indicates that, for this particular data set, the numerical errors were non-negligible. The net result, already observed in Table 1, is that the rotational lurch index differed from the analytically-computed index value, although this difference does not preclude the possibility of classifying the motion as one of medium-level smoothness, given the largely different values pertaining to a very smooth and non-smooth motions.
5.2. Numerical Test on Ten Data Sets Acquired by an Inertial Measurement Unit
The second ensemble of data sets was comprised of ten orientation signals acquired by an inertial measurement unit (IMU), the MPU-6050 sensor [22]. The IMU was mounted on a tilting platform that was driven manually to simulate smooth as well as non-smooth motions. The data sets were named Data set 1 through Data set 10. Dataset 4 is illustrated in Figure 4.
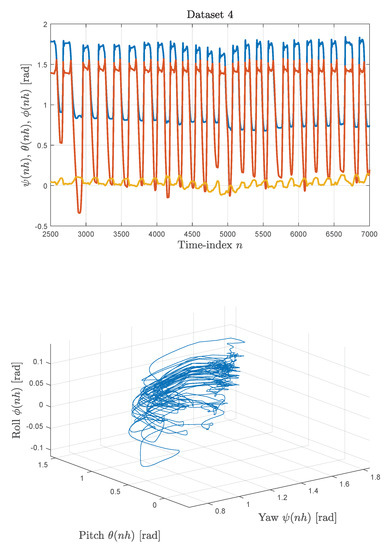
Figure 4.
Inertial measurement unit data sets: Illustration of Data set 4. Upper panel: Angular sequences , , and versus the sample index n. Lower panel: Three-dimensional representation of the angular sequences obtained by plotting the triples in .
The three-dimensional representation for this real-world data set does not look as regular as that of a synthetic motion, but still looks quite regular.
The numerical values of the indices obtained in this experiment are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Inertial measurement unit data sets: Summary of the numerical results obtained over the ten acquired data sets. The sampling time used in this experiment was (s), which corresponds to the sampling interval of the measurement platform.
For all the data sets, the values of the indices computed by the numerical method appeared to be in excellent agreement with the values computed by the closed-form expressions. From the values of the rotational lurch index L, it is immediate that Data set 2 corresponded to the smoothest motion, that Data sets 1, 3, and 4 corresponded to less smooth motions, Data sets 8, 9, and 10 pertained to motions of a medium level of smoothness, and that Data sets 5, 6, and 7 were acquired during non-smooth tilting.
The numerical values of the indices pertaining to the Data set 4 showed some slight inconsistency, in comparison to the analytic values. In percentage, such inconsistency was evaluated as . Details of these results are made visually available in Figure 5.
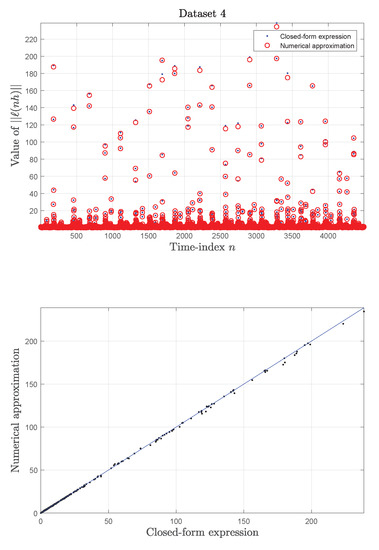
Figure 5.
Inertial measurement unit data sets: Results obtained on Data set 4. Upper panel: Sample-by-sample comparison of the values of the quantities (open circles) and (dots) versus the sample index n. Bottom panel: Scatter plot by the scalar pair (the blue line represents a secant).
From the top panel, it can be noticed how a few values among those calculated by numerical approximation were misplaced, in comparison to the reference values computed by means of the closed-form expression. The lurch-norm pairs shown in the bottom panel appear to be slightly scattered around the blue secant.
5.3. Numerical Test on Three Data Sets Acquired by a Smartphone
The third ensemble of data sets was comprised of three orientation signals acquired by a smartphone, using a software application which is able to read the sensors during motion and to store the acquired orientation values [8]. In this regard, it is interesting to recall the results of the study [23], where the authors noticed how users with smartphone input performed at least as good as those with Kinect, and most of them preferred it as a means of control.
In these experiments, the smartphone was secured to a volunteer by a belt. The volunteer performed three different kind of movements which gave rise to three data sets: Data set 1 pertained to a walking activity, Data set 2 pertaining to a running activity, and Data set 3 pertained to a jumping activity. Data set 1 is illustrated in Figure 6.
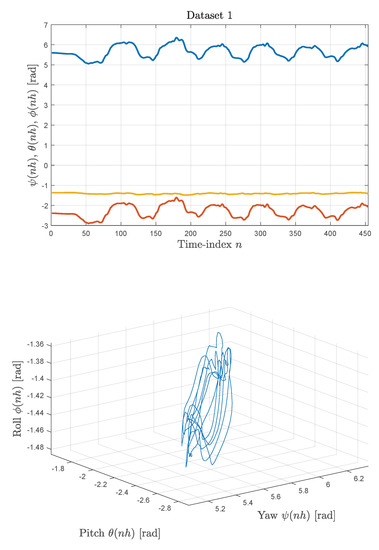
Figure 6.
Smartphone data sets: Illustration of Data set 1. Upper panel: Angular sequences , and versus the sample index n. Lower panel: Three-dimensional representation of the angular sequences obtained by plotting the triples in for .
The three-dimensional representation for this real-world data set looks chaotic, a phenomenon that has been observed in studies on human motion analysis [24].
The numerical results obtained in the experiment are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Smartphone data sets: Summary of the numerical results obtained over the three acquired data sets. The sampling time used in this experiment was (s).
For all the data sets, the values of the indices computed by the numerical method were in excellent agreement with the values computed by closed-form expressions. From the values of the rotational lurch index L reported in the Table 3, it is immediate that the computed rotational smoothness index value agreed with the intuitive understanding that a walking motion is the most fluent, while a jumping motion is the least fluent.
A detailed visualization of the comparison between the numerical and closed-form results for Data set 1 is offered in Figure 7.
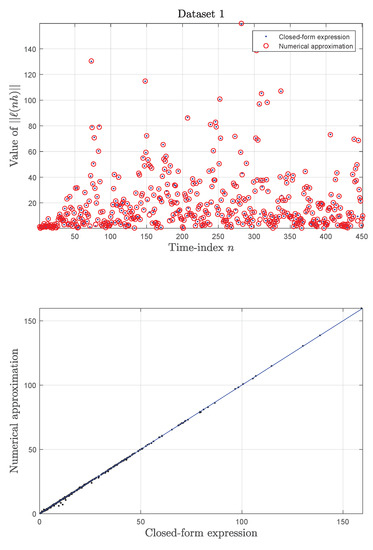
Figure 7.
Smartphone data sets: Results obtained on Data set 1. Upper panel: Sample-by-sample comparison of the values of the quantities (open circles) and (dots) versus the sample index n. Bottom panel: Scatter plot by the scalar pair (the blue line represents a secant).
Both panels show how the values obtained by the closed-form expression and by the numerical approximation were in excellent agreement.
6. Conclusions
Kinematic lurch represents the rate of change in acceleration of a body during motion. By controlling the magnitude of the kinematic lurch, it is possible to ramp the acceleration rate and to smooth the motion velocity profile, thus preventing excessive mechanical oscillation. Reducing oscillations makes it possible to maximize the acceleration and, in turn, to significantly improve machine performance in mechanics or athletic performance in sports, to name a few applications.
Upon acquiring the position and orientation of a rigid body in space with respect to an inertial reference frame, it is possible to define and compute the translation lurch index, as well as the rotational lurch index, associated to an observed motion. We have shown that the computation of the rotational lurch index, in particular, may be achieved in two ways; namely, by means of a closed-form expression, which looks involved and cumbersome, and by a numerical approximation, which is lighter computationally and easier to implement, yet untrue to the mathematical definition. The aim of the present contribution was to compare the results of these two calculation methods on a number of data sets (either generated or acquired by different devices), in order to test the accuracy of the numerical method, taking as reference the closed-form expression.
The two methods were tested on three synthetic data sets, on ten data sets acquired through an inertial measurement unit, and on three data sets acquired through a smartphone. The results of the comparisons showed that, for all data sets (with the exception of one among the synthetic data sets), the results achieved by the two methods were in excellent agreement with one another. The numerical results also confirmed that the data sets may be sorted in fluency degree order by means of their associated lurch index values, for all considered data sets.
The comparisons performed in the present paper confirmed that the numerical approximation of the rotational lurch index is suitable for evaluating the fluency of motion in a rotating rigid body. It would be interesting to apply the notions devised in the present endeavor to further data sets, such as the one made available in [25] about human body movements during physical rehabilitation exercises.
When the acceleration is not constant, the motion sensation is likely jerky (and may even snap), as there is a change in the lurch. As concrete illustrations of these concepts, the paper [21] presented, in some detail, examples for roller coasters and trampolines using authentic data. There is no agreement on the names of higher-order derivatives. The term snap is used to denote the derivative of lurch with respect to time, although another name for this fourth derivative is jounce. The fifth and sixth derivatives (with respect to time) are referred to as crackle and pop, respectively. We believe that it will be interesting to extend the present analysis to higher-order (or hyper-jerk) kinematic indices.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The author wishes to thank his former student, Nicola Sabino, for helping with the IMU-related measurements, and his former students Riccardo Genovesi, Pasquale Enrico Cortese and Dritan Progri, for helping with the Matlab codes.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Gimbal Lock
The gimbal lock is a technical issue arising from the technical solutions adopted to measure three orientation angles in space by means of a three-dimensional three-gimbal mechanism. It causes the loss of one degree of freedom, which occurs when the axes of two of the three gimbals are driven into a parallel configuration.
The gimbal lock phenomenon may occur, for example, during flight or in robotics. When a spacecraft makes a maneuver that a gyrostabilized instrument cannot follow, the gyroscope loses its reference direction and the spacecraft begins to tumble out of control. At this point, the instrument must be reset in the reference direction. This correction may take a few minutes, hours, or days, depending on the system design and on the cause of the gimbal lock. In robotics, gimbal lock is commonly referred to as wrist flip, where the three axes of the wrist (controlling yaw, pitch, and roll) all pass through a common point. An example of a wrist flip, also called a wrist singularity, is when the path through which the robot is traveling causes the first and third axes of the robot’s wrist to line up. The result of a singularity can be quite dramatic and can have adverse effects on the robot arm and on the end-effector.
Recalling the notation introduced in the Section 2, it is easy to verify that, setting the angle in , we get:
Namely, changing the values of the angle or the angle in the above matrix has the same effect: The rotation angle would change, but the rotation axis remains pointing in the same direction. The only solution for these angles to recover different roles is to move the angle from the singularity at which the gimbal lock phenomenon occurs.
Alternative representations of the orientation of a rigid body do not suffer from the gimbal lock phenomenon, such as the one based on quaternions in [26].
Appendix B. General Problem of the Weighting of P+H, P−H, P+2h, P−2h
In Section 4.2, the problem of seeking for a linear combination of the matrices , , , and was addressed, which resulted in a term of the form ; namely
Replacing the above four expressions in the condition (A2) and equating the homologous coefficients from both sides, we get the equations
and (from the terms in ). Therefore, all the solutions, parametrized in terms of , are:
Although there exist infinitely many quintuples which are solutions to the problem (A2), notice that the expression of C, as given in Section 4.2, is indeed unique. Also, notice that a coefficient being zero (for example, or ) implies that all coefficients are zero, which, in turn, implies that there does not exist any combination of only three matrices among , , and , that results in a second-order approximation of C.
References
- McCarthy, J.M. Introduction to Theoretical Kinematics; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Marion, J.B.; Thornton, S.T. Classical Dynamics of Systems and Particles, 4th ed.; Thomson Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bearee, R. New damped-jerk trajectory for vibration reduction. Control Eng. Pract. 2014, 28, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canali, F.; Guarino Lo Bianco, C.; Locatelli, M. Minimum-jerk online planning by a mathematical programming approach. Eng. Optim. 2014, 46, 763–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-S.; Shieh, R. A jerk-constrained time-optimal servo with disturbance compensation. Control Eng. Pract. 2014, 28, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzabeigy, A.; Yildirim, A. Approximate periodic solution for nonlinear jerk equation as a third-order nonlinear equation via modified differential transform method. Eng. Comput. 2014, 31, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.; Joo, S.-B.; Oh, E.; Mun, J.H. Kinematic evaluation of movement smoothness in golf: relationship between the normalized jerk cost of body joints and the clubhead. BioMed. Eng. OnLine 2014, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civita, A.; Fiori, S.; Romani, G. A mobile acquisition system and a method for hips sway fluency assessment. Information 2018, 9, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, S. Gyroscopic signals smoothness assessment by geometric jolt estimation. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2017, 40, 5893–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, L.; Orth, D.; Boulanger, J.; Dovgalecs, V.; Hérault, R.; Davids, K. Climbing skill and complexity of climbing wall design: Assessment of jerk as a novel indicator of performance fluency. J. Appl. Biomech. 2014, 30, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-I. A fast and unified method to find a minimum-jerk robot joint trajectory using particle swarm optimization. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2014, 75, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žefran, M.; Kumar, V. Planning of smooth motions on SE(3). In Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 22–28 April 1996; Volume 1, pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Scrivener, S.L.; Thompson, R.C. Survey of time-optimal attitude maneuvers. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 1994, 17, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, K.W. Euler parameters and the use of quaternion algebra in the manipulation of finite rotations: A review. Mech. Mach. Theory 1986, 21, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, Y.; Stopforth, R.; Bright, G. Quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle helicopter modelling & control. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2011, 8, 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Xueshan, Y.; Xiaozhai, Q.; Lee, G.C.; Tong, M.; Jinming, C. Jerk and jerk sensor. In Proceedings of the 14th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Beijing, China, 12–17 October 2008; Available online: http://www.iitk.ac.in/nicee/wcee/fourteenth_conf_china/ (accessed on 25 October 2015).
- Dubrovin, B.; Novikov, S.; Fomenko, A. Modern Geometry—Methods and Applications (Part I: The Geometry of Surfaces, Transformation Groups, and Fields), Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; ISBN 0387976639. [Google Scholar]
- Fiori, S.; Prifti, S. Exact low-order polynomial expressions to compute the Kolmogoroff-Nagumo mean in the affine symplectic group of optical transference matrices. Linear Multilinear Algebr. 2017, 65, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, G.H.; Wright, E.M. An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers, 5th ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1979; pp. 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Stoer, J.; Bulirsch, R. Introduction to Numerical Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Eager, D.; Pendrill, A.-M.; Reistad, N. Beyond velocity and acceleration: jerk, snap and higher derivatives. Eur. J. Phys. 2016, 37, 065008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- InvenSense Inc. MPU-6000 and MPU-6050 Product Specification, Revision 3.4; InvenSense Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vosinakis, S.; Gardeli, A. On the use of mobile devices as controllers for first-person navigation in public installations. Information 2019, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josiński, H.; Michalczuk, A.; Świtoński, A.; Mucha, R.; Wojciechowski, K. Quantifying chaotic behavior in treadmill walking. In Intelligent Information and Database Systems, Proceedings of the 2015 Asian Conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems, Bali, Indonesia, 23–25 March 2015; Lecture Notes in Computer Science Book Series (LNCS); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9012, pp. 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Vakanski, A.; Jun, H.-P.; Paul, D.; Baker, R. A data set of human body movements for physical rehabilitation exercises. Data 2018, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, S.L. Rotations, Quaternions, and Double Groups; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).