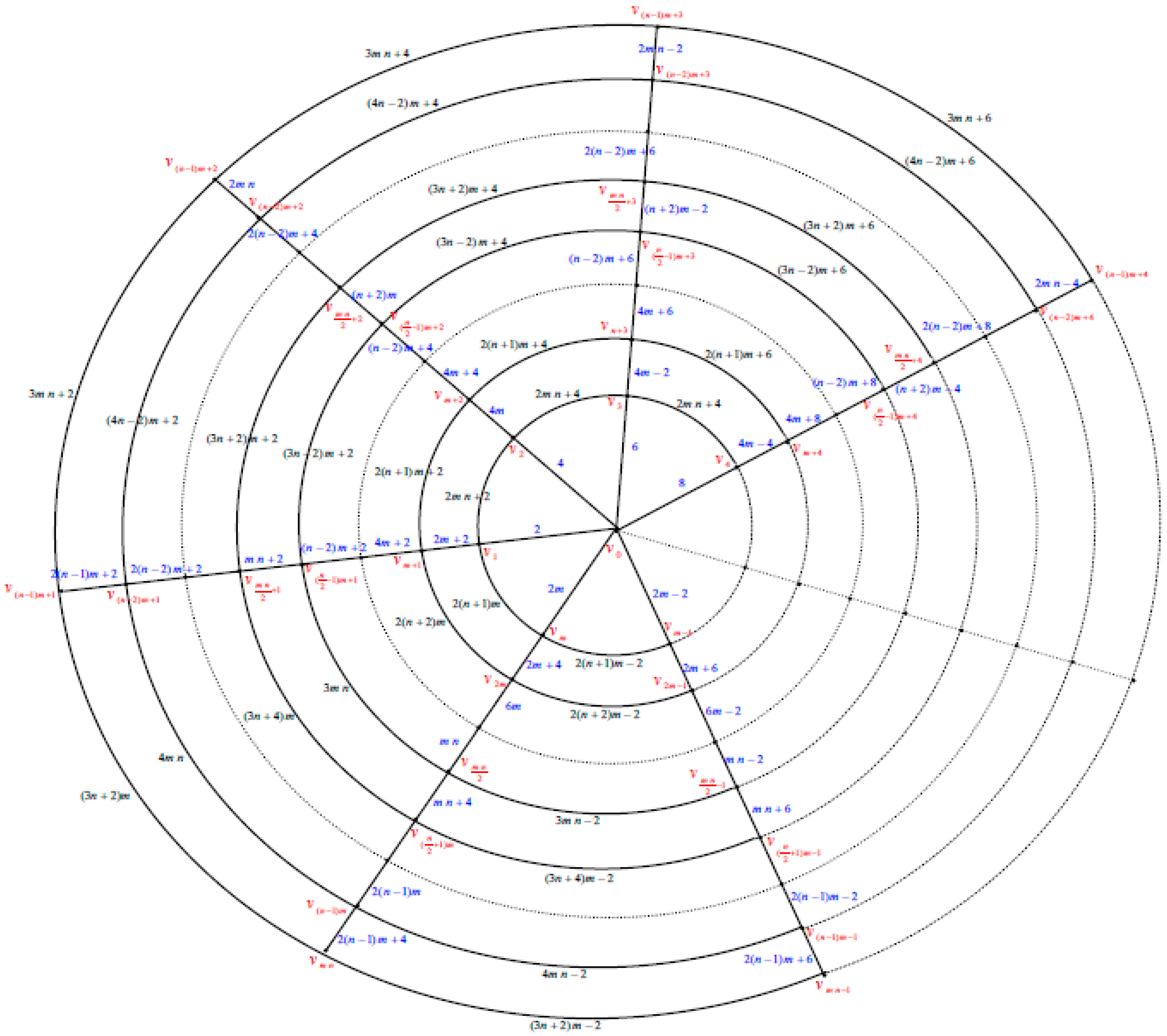
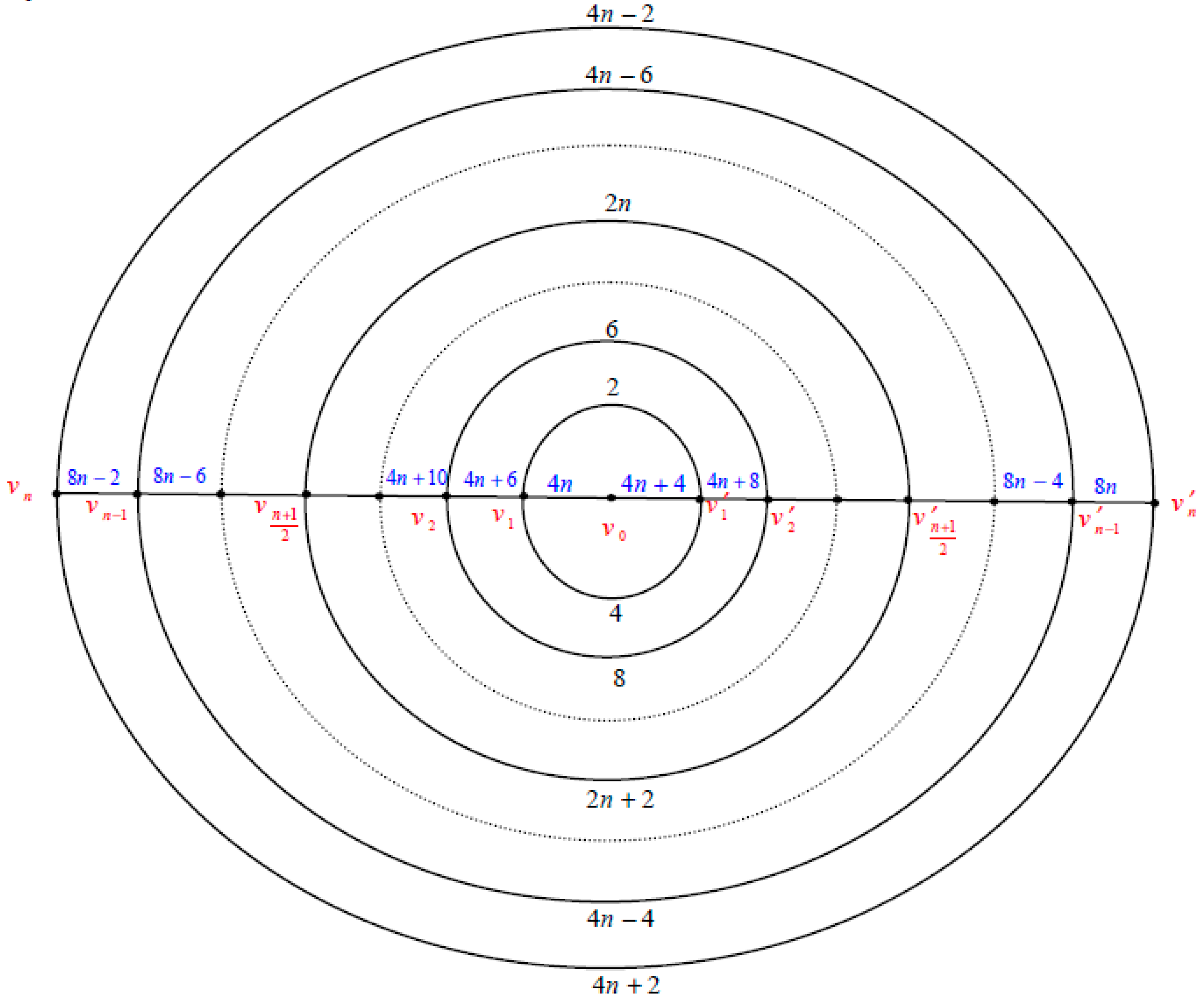
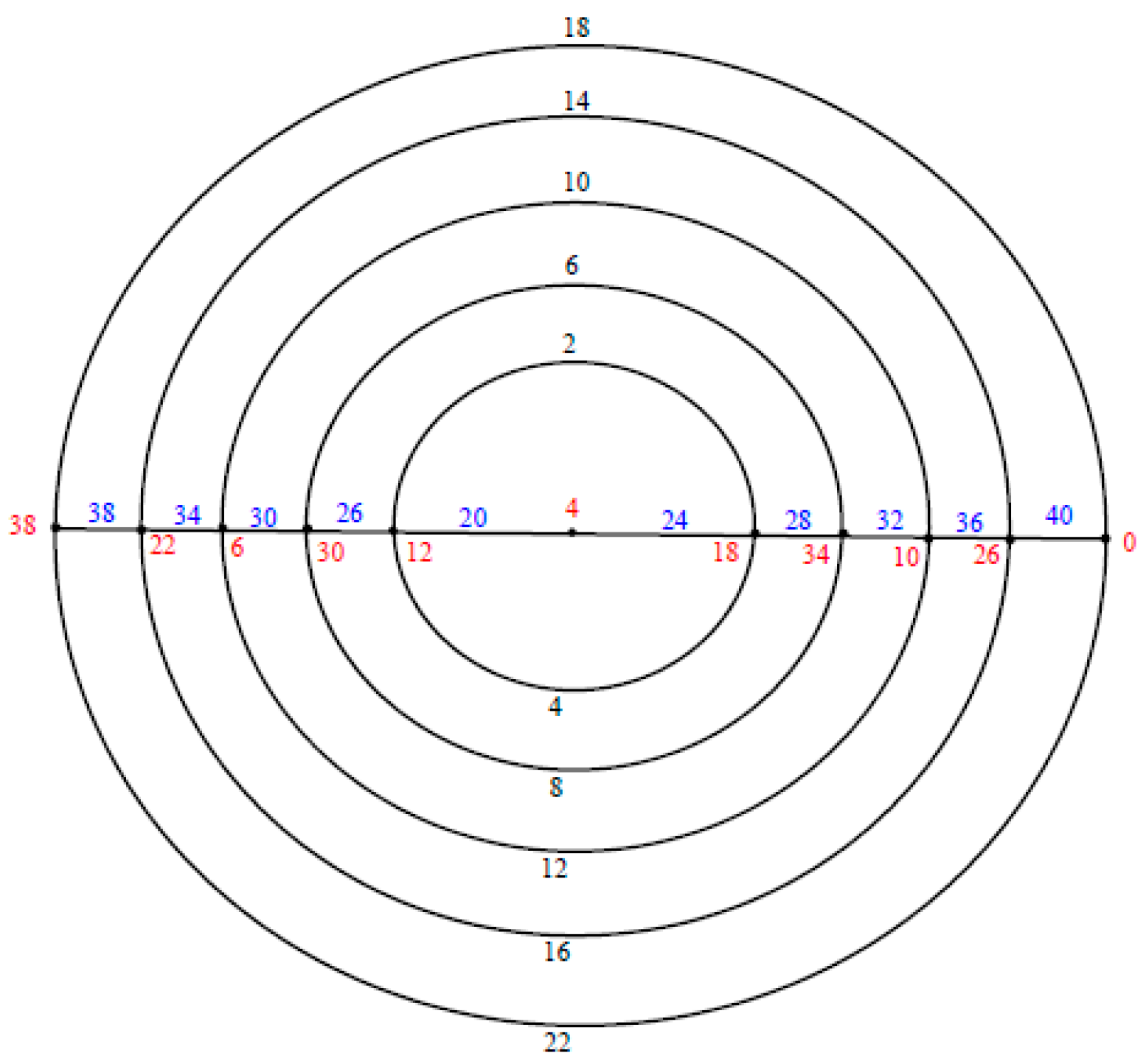
2. Polar Grid Graph
The polargrid graph
is the graph consists of
copies of circles
which will be numbered from the inner most circle to the outer circle as
and
copies of paths
intersected at the center vertex
which will be numbered as
. See
Figure 1.
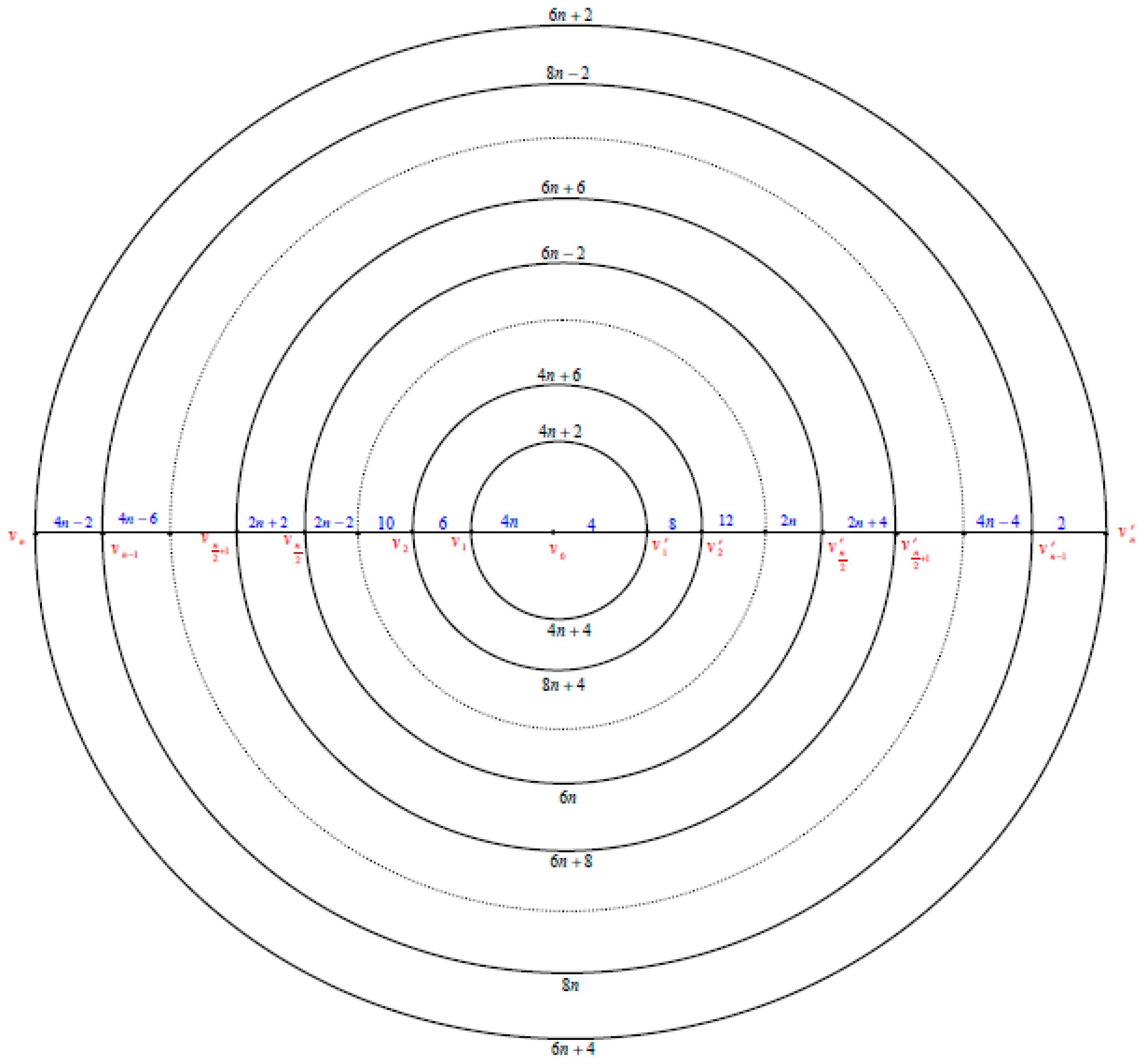
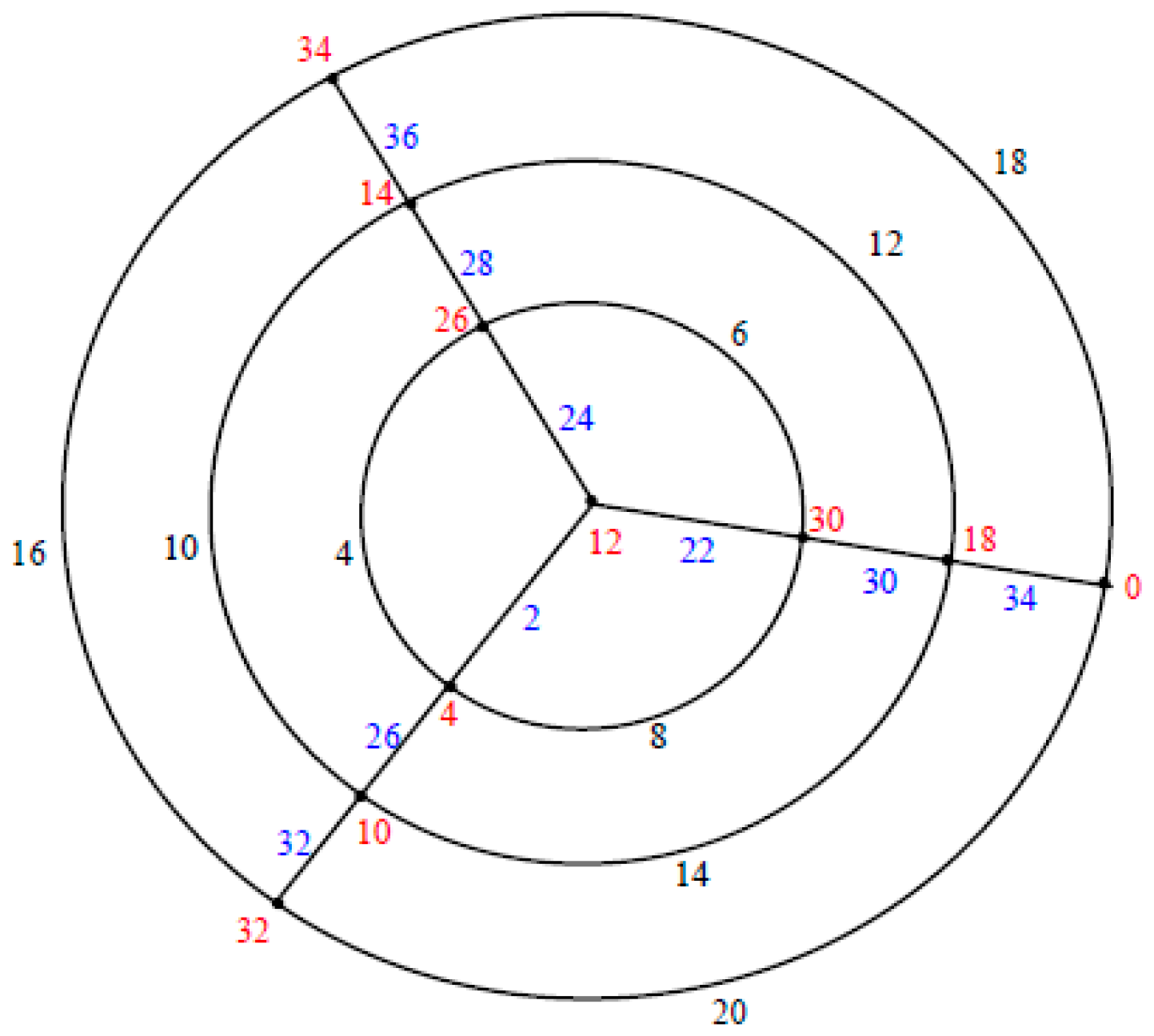
Theorem 1. If m and n are even positive integes such that and , then the polar grid graph is an edge even graceful graph.
Proof. Using standard notation
and
Let the polar grid graph
be labeled as in
Figure 2. Let
□
First we label the edges of paths begin with the edges of the path to the edges of the path as follows: Move clockwise to label the edges by then move anticlockwise to label the edges by then move clockwise to label the edges by and so on. Finally move anticlockwise to label the edges by . Second we label the edges of the circles begin with the edges of the inner most circle to the edges of the circle , then the edges of the outer circle Finally the edges of circles respectively as follows: .
Now the corresponding labels of vertices are assigned as follows:
Case (1) and
The labels of the vertices of the inner most circle to the circle are given by , the labels of the vertices of the outre circle are given by and the labels of the vertices of the circles are given by .
The label of the center vertex is assigned as follows: when , , since then , thus and when , we have .
Case (2) . In this case the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and . That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and the label of the center vertex is assigened as .The rest vertices are labeled as in case(1).
Case (3) . In this case the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and . That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and the label of the center vertex is assigened as. The rest vertices are labeled as in case(1).
Case (4) . In this case the vertex in the outer circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and . That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and and the label of the center vertex is assigened as . The rest vertices are labeled as in case (1).
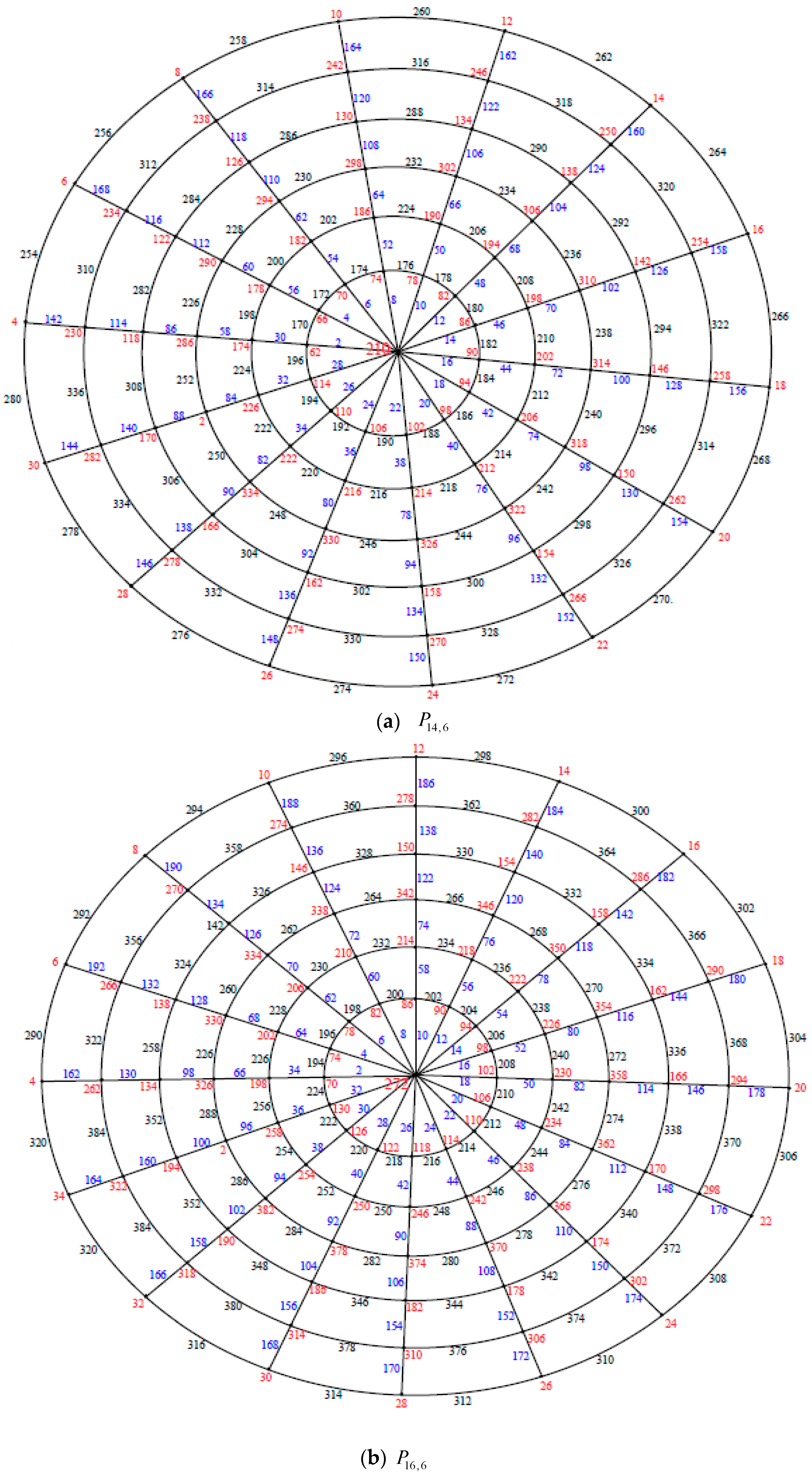
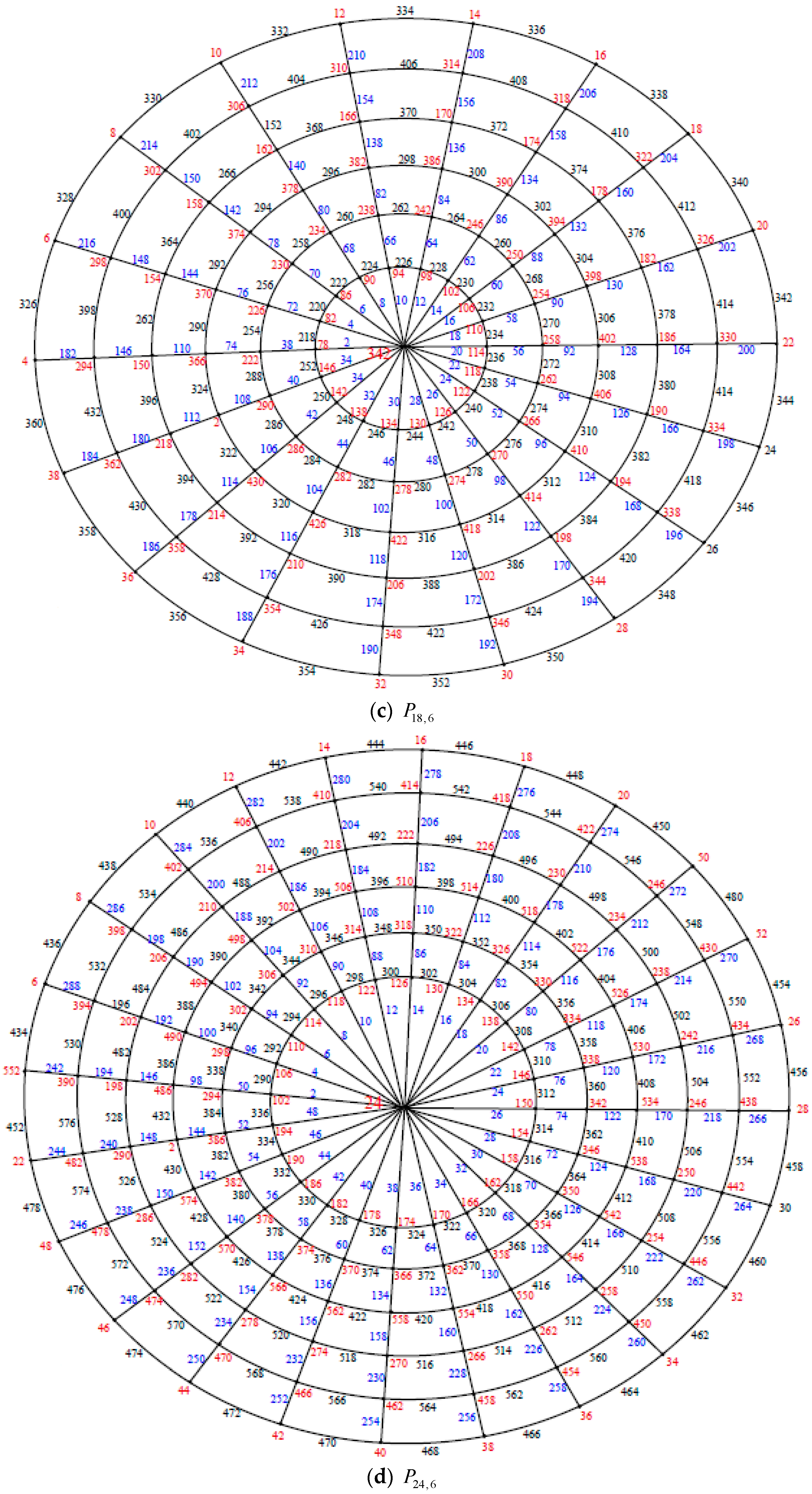
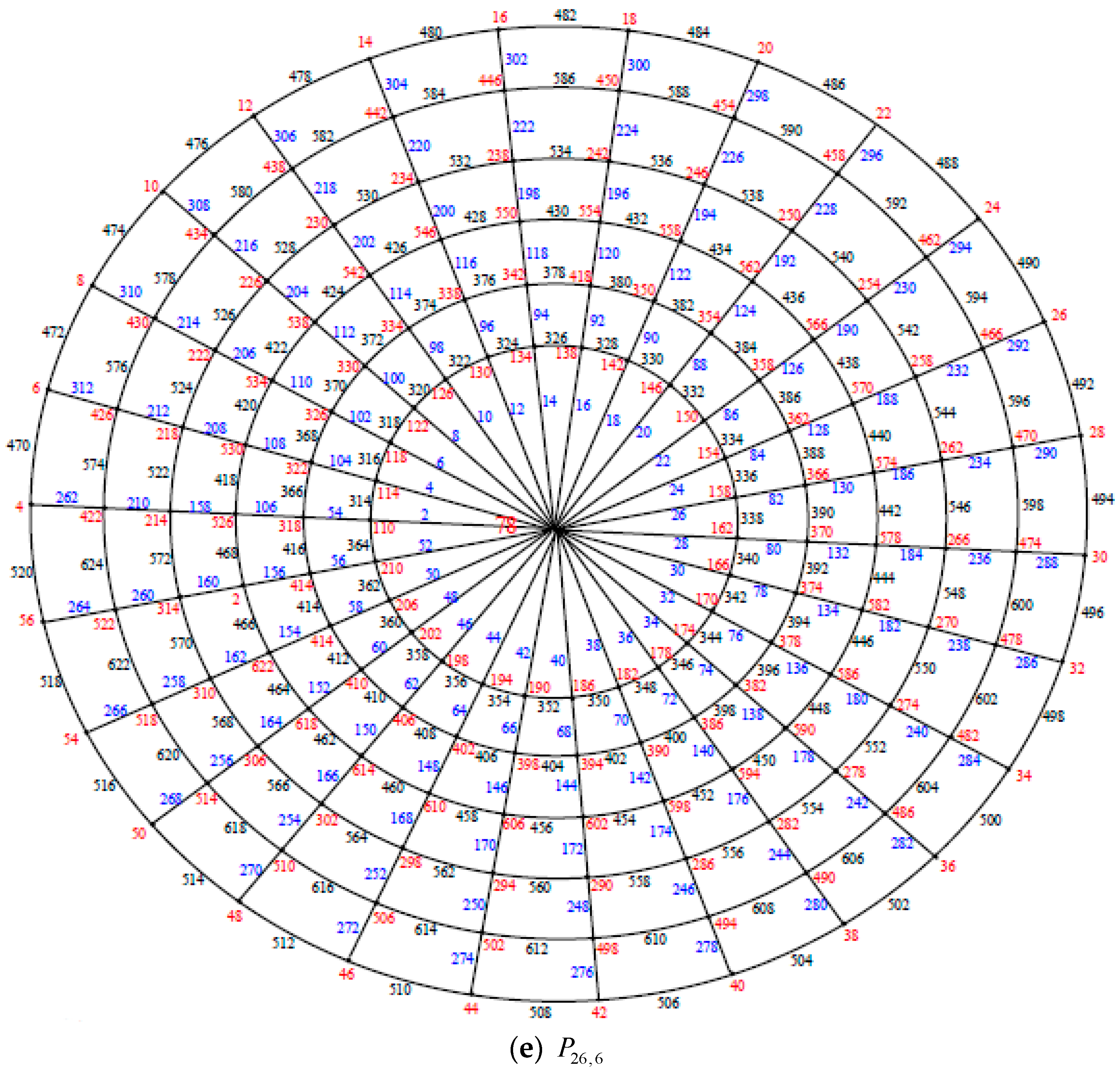
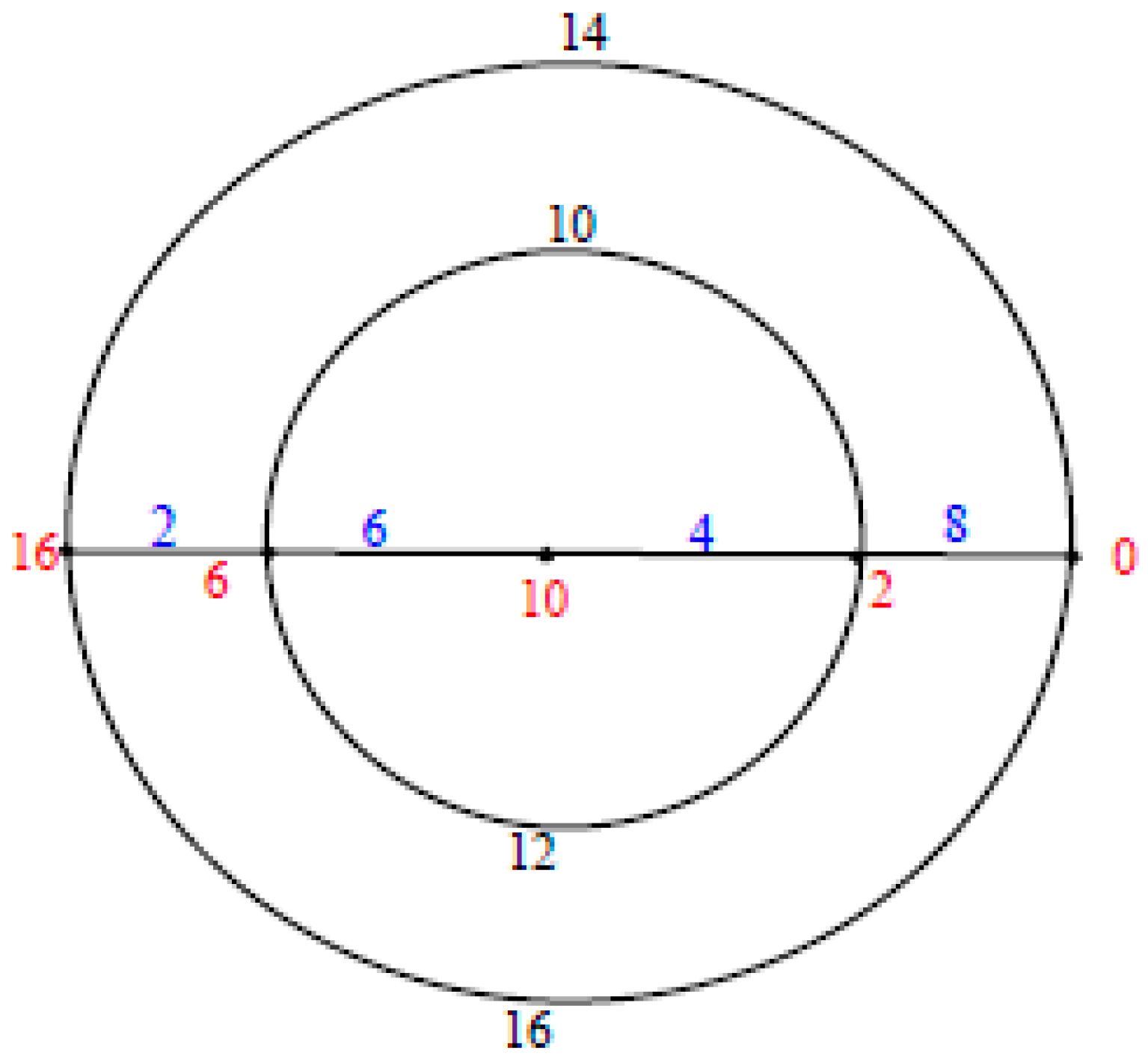
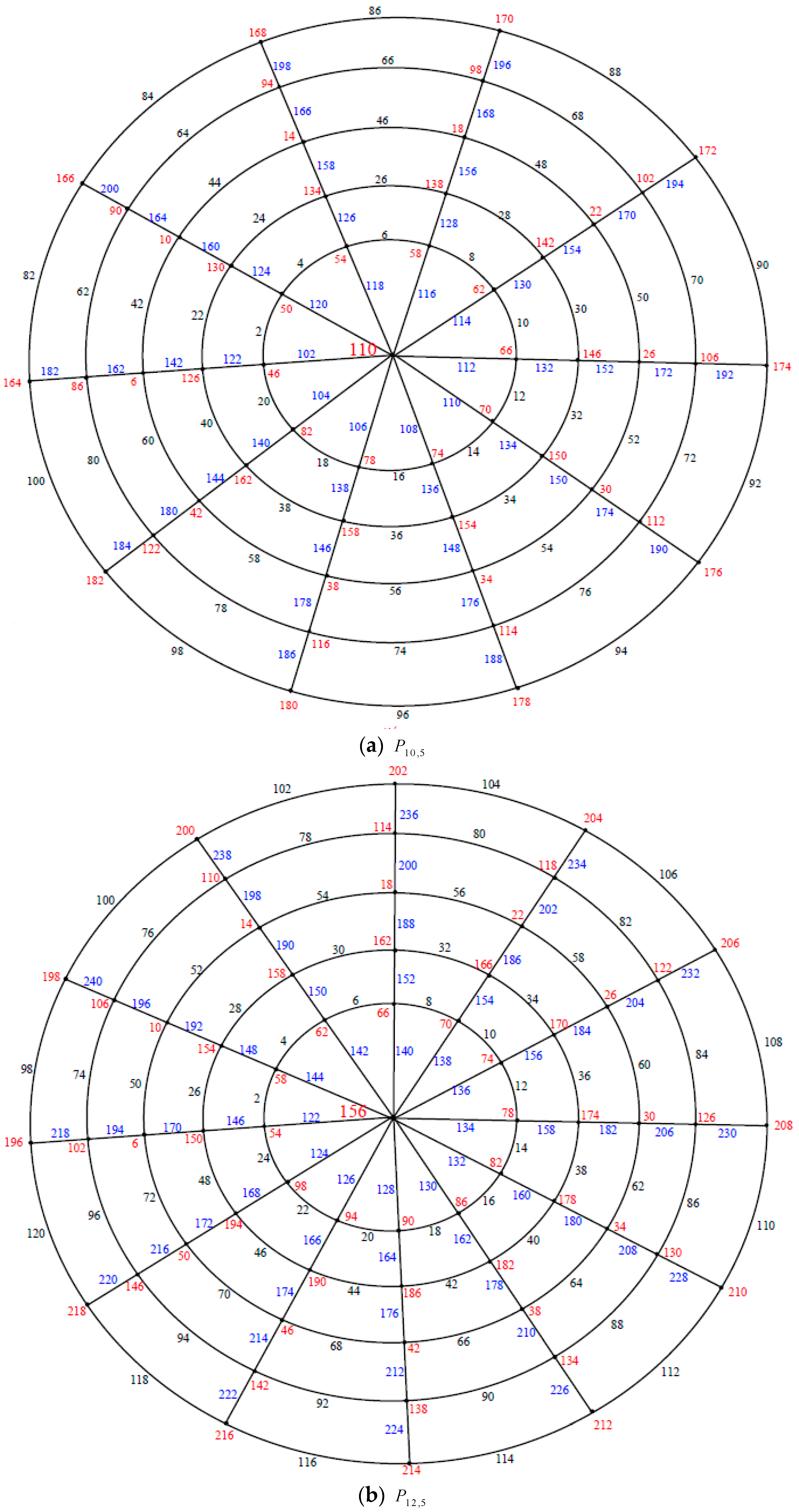
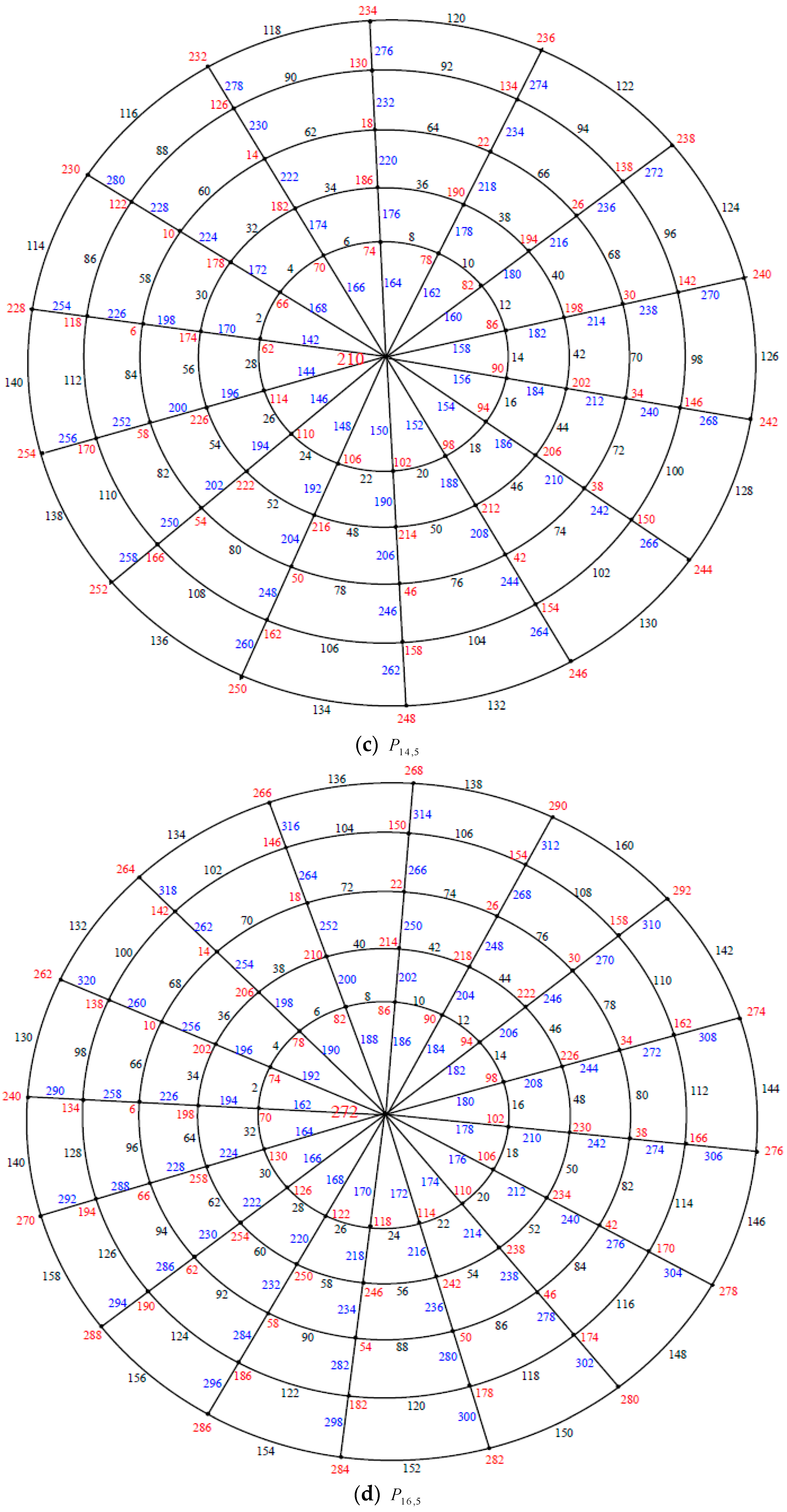
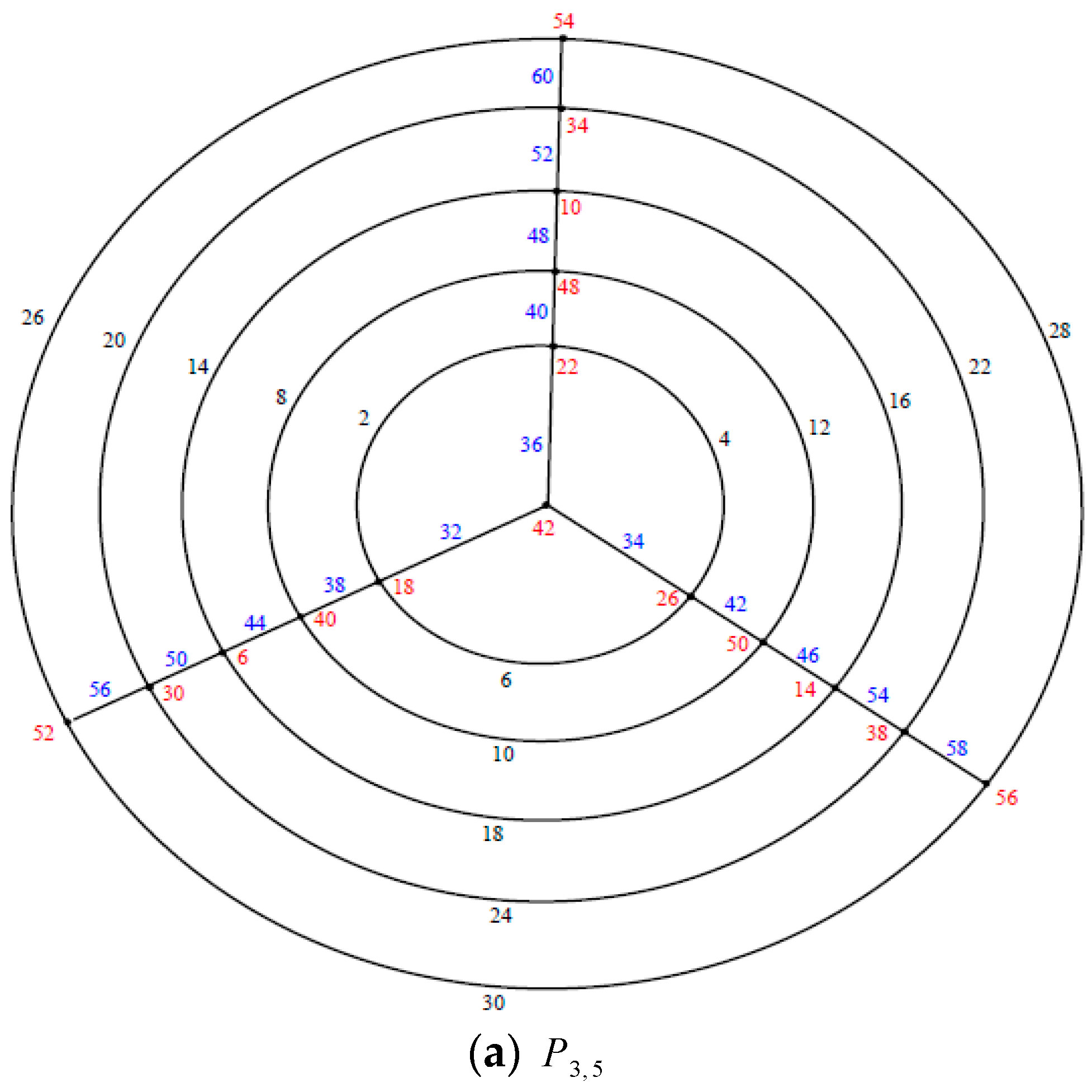
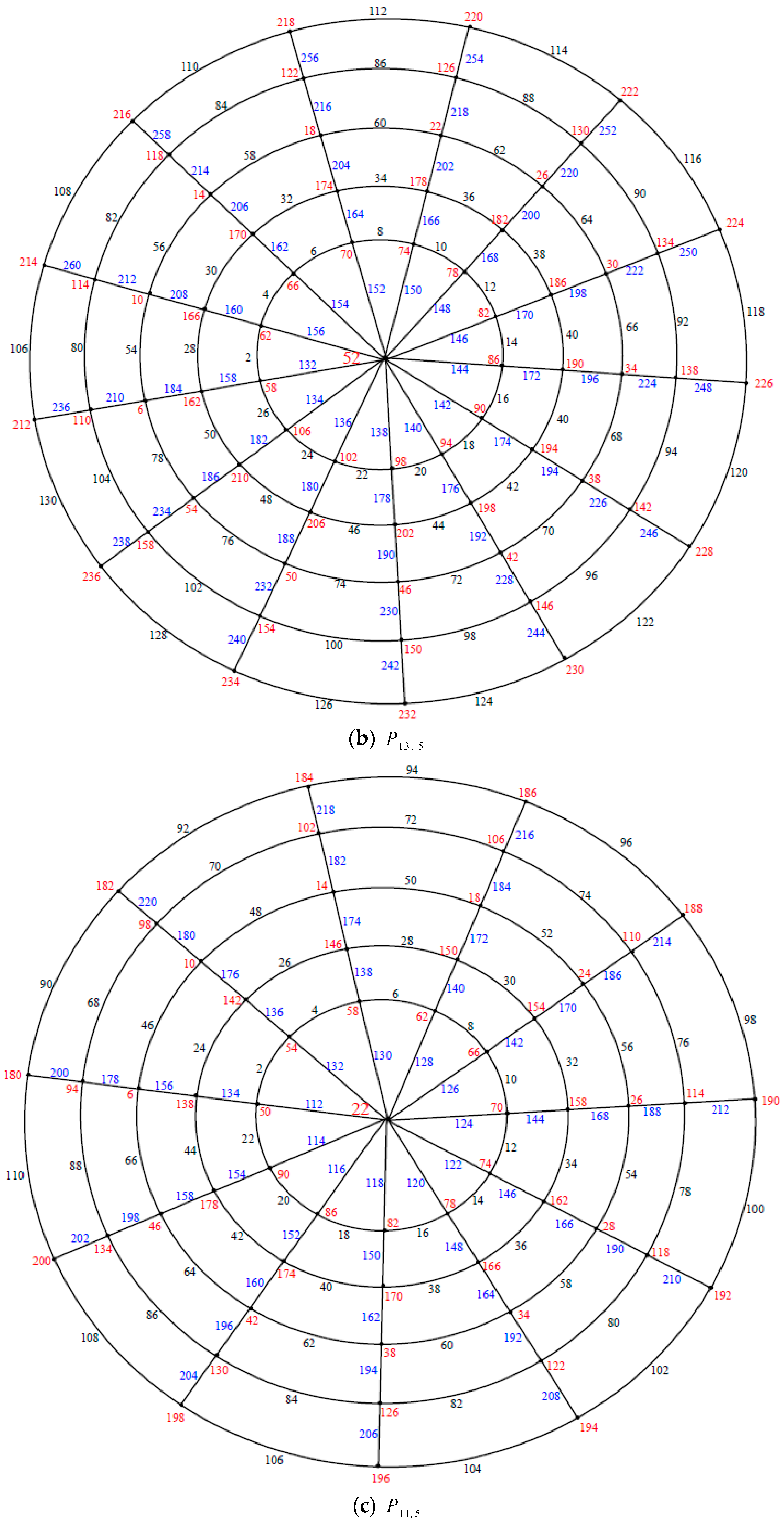
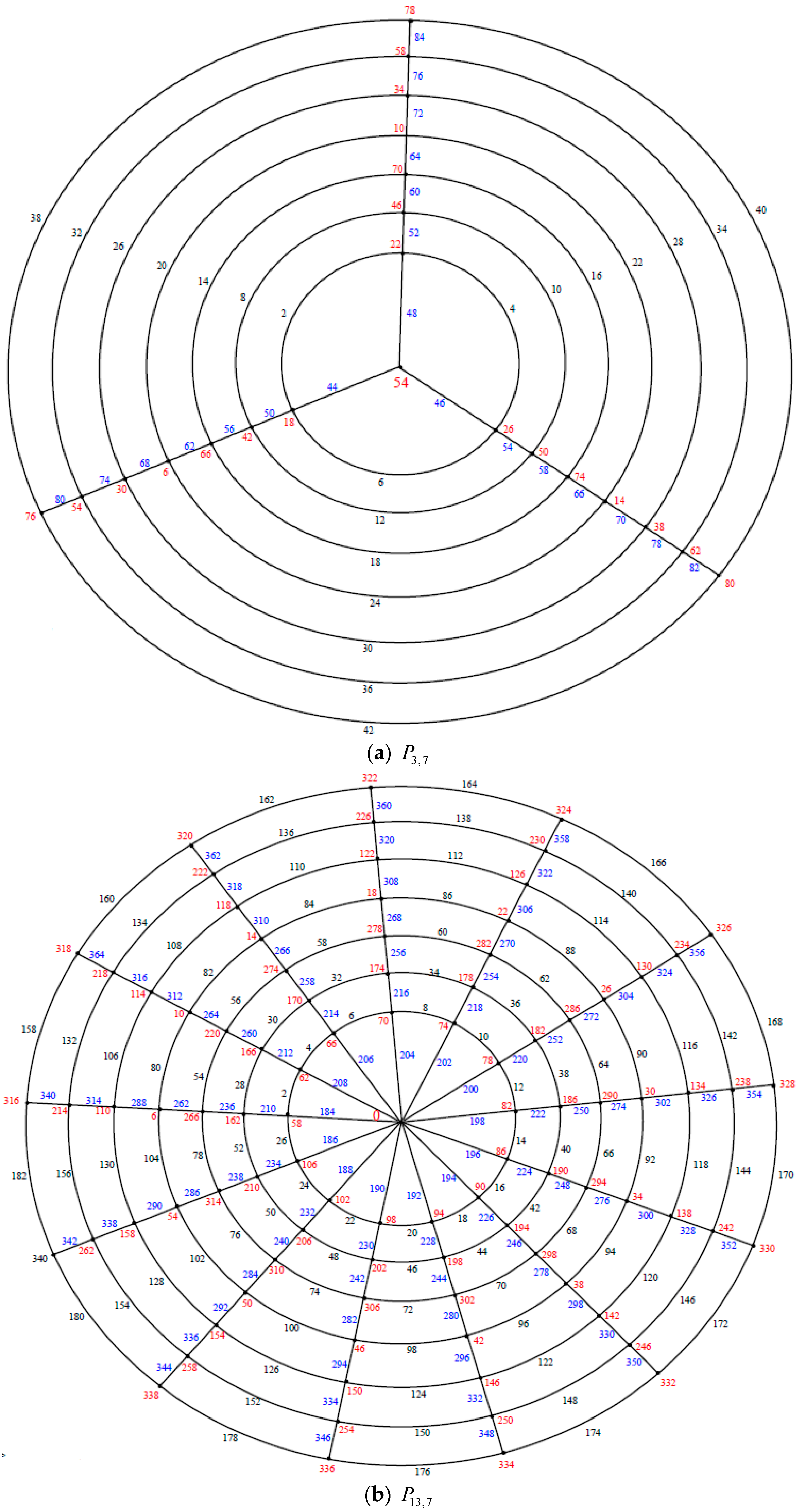
Illustration. The edge even graceful labeling of the polar grid graphs
and respectively are shown in Figure 3. Remark 1. In case and n is even, .
Let the label of edges of the polar grid graph be as in
Figure 4. Thus we have the label of the corresponding vertices are as follows:
.
Note that
is an edge even graceful graph but not follow this rule. See
Figure 5.
Theorem 2. If is an odd positive integer greater than and an is even positive integer greater than or equal , then the polar grid graph is an edge even graceful graph.
Proof. Let the edges of the polar grid graph
be labeled as in
Figure 2. □
Now the corresponding labels of vertices are assigned as follows: There are four cases
Case (1):
The labels of the vertices of the inner most circle to the circle are given by , the labels of the vertices of the outer circle are given by and the labels of the vertices of the circles are given by .
The center vertex is labeled as , and if , we have .
Case (2): .
In this case the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and . The center vertex is labeled as . The rest vertices are labeled as in case (1).
Case (3): .
In this case the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and and in this case the center vertex is labeled as The rest vertices are labeled as in case (1).
Case (4):
In this case the vertex in the outer circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and the center vertex is labeled as The rest vertices are labeled as in case (1).
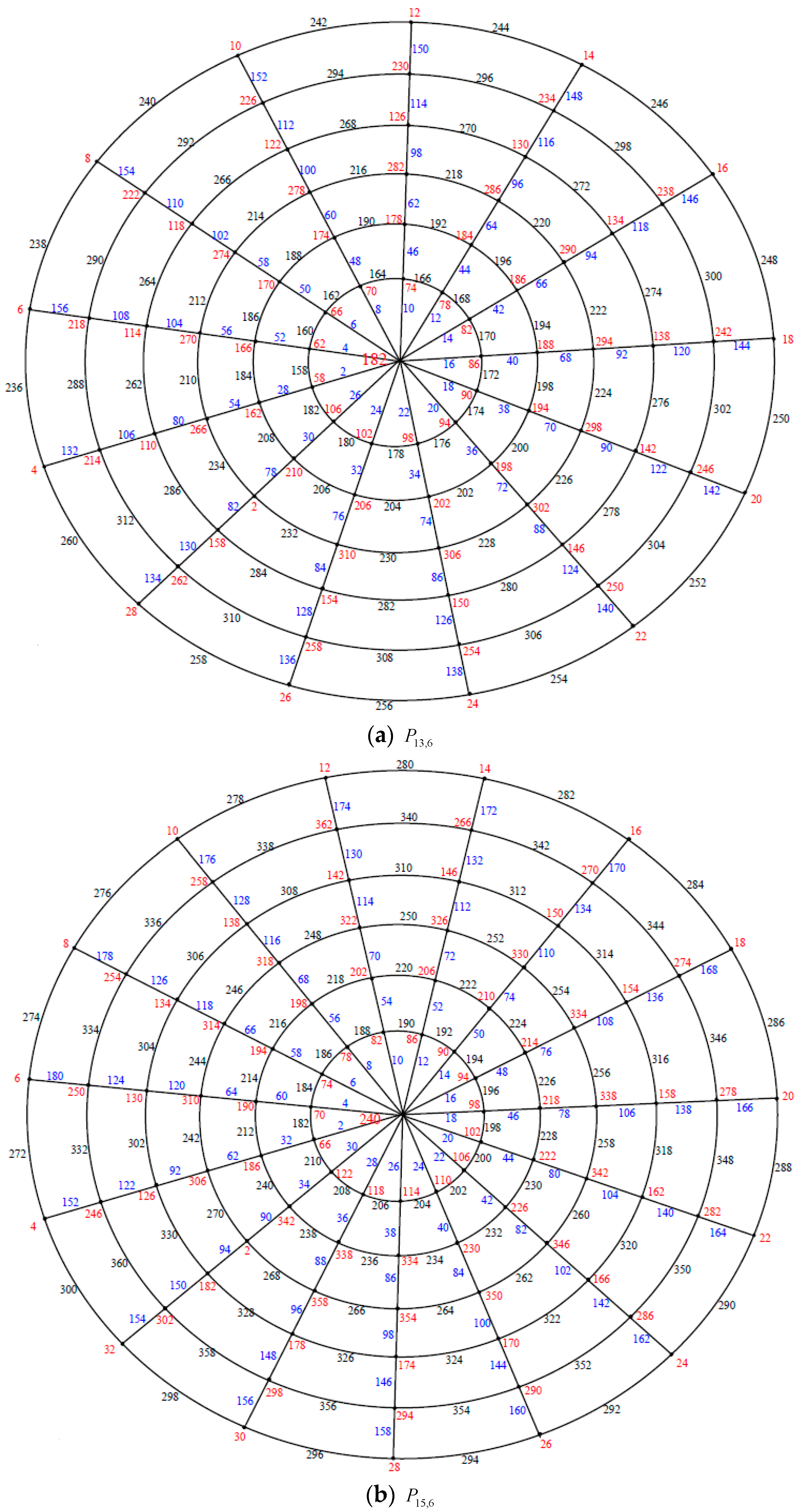
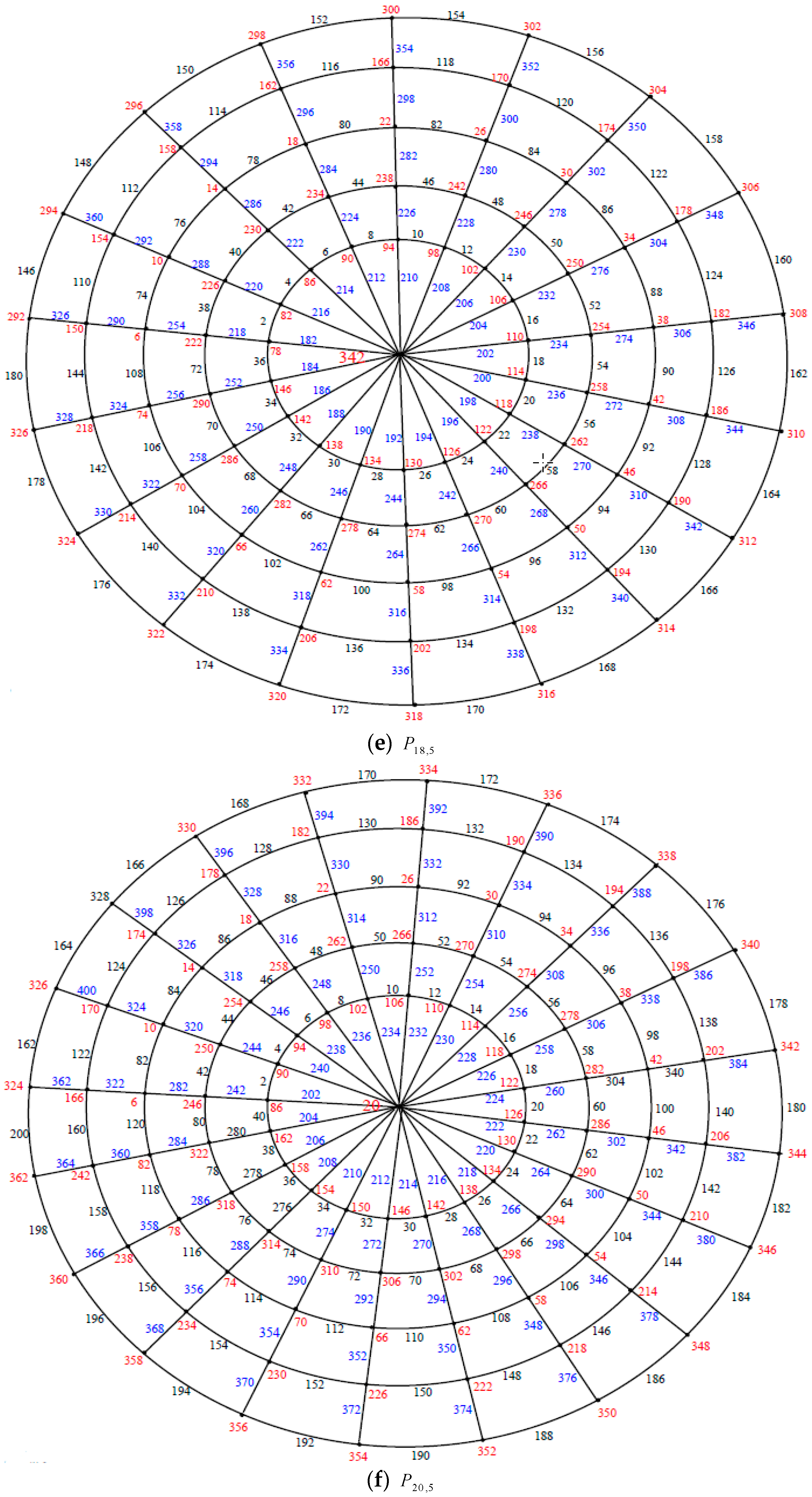
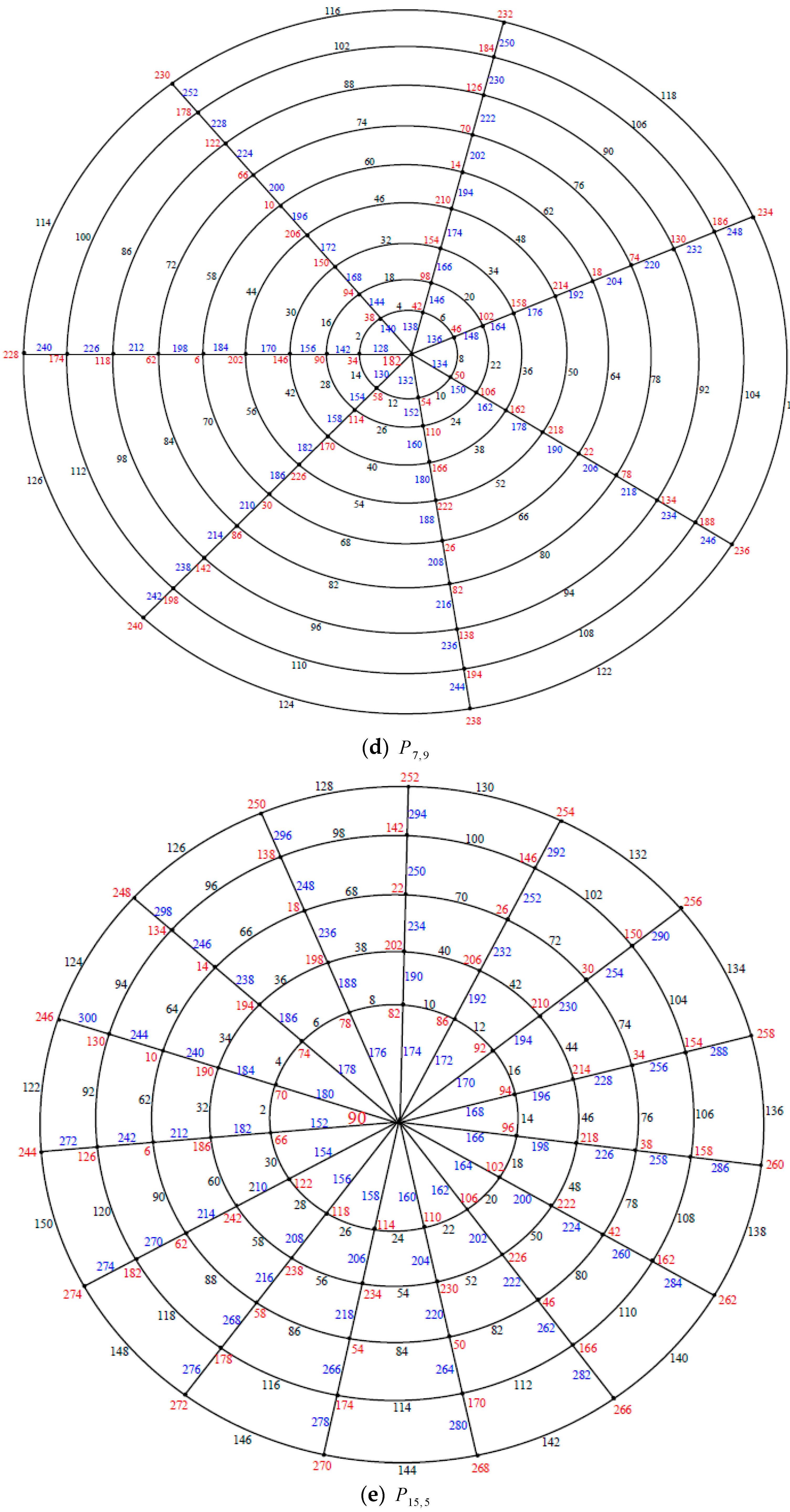
Illustration. The edge even graceful labeling of the polar grid graphs
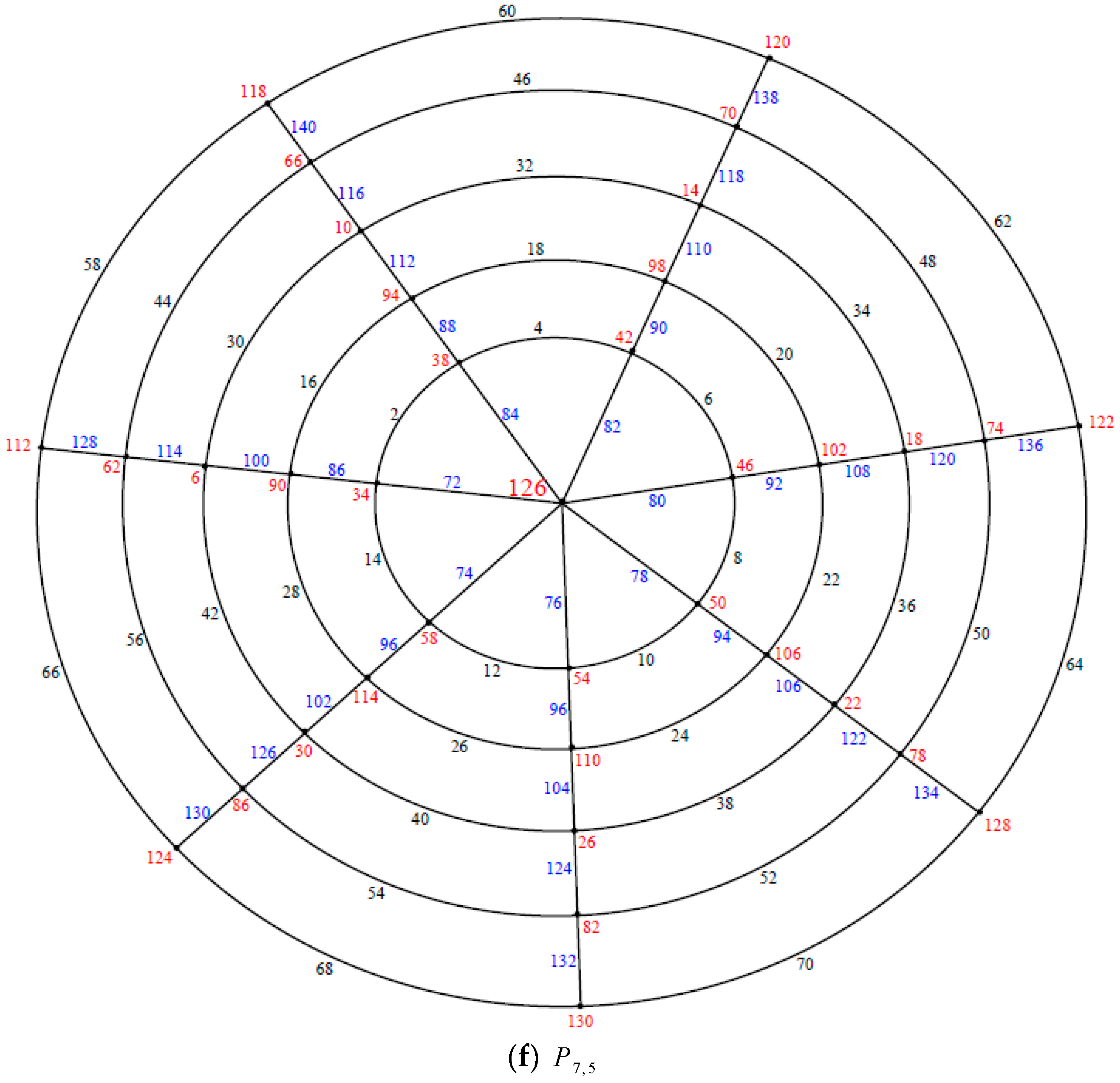
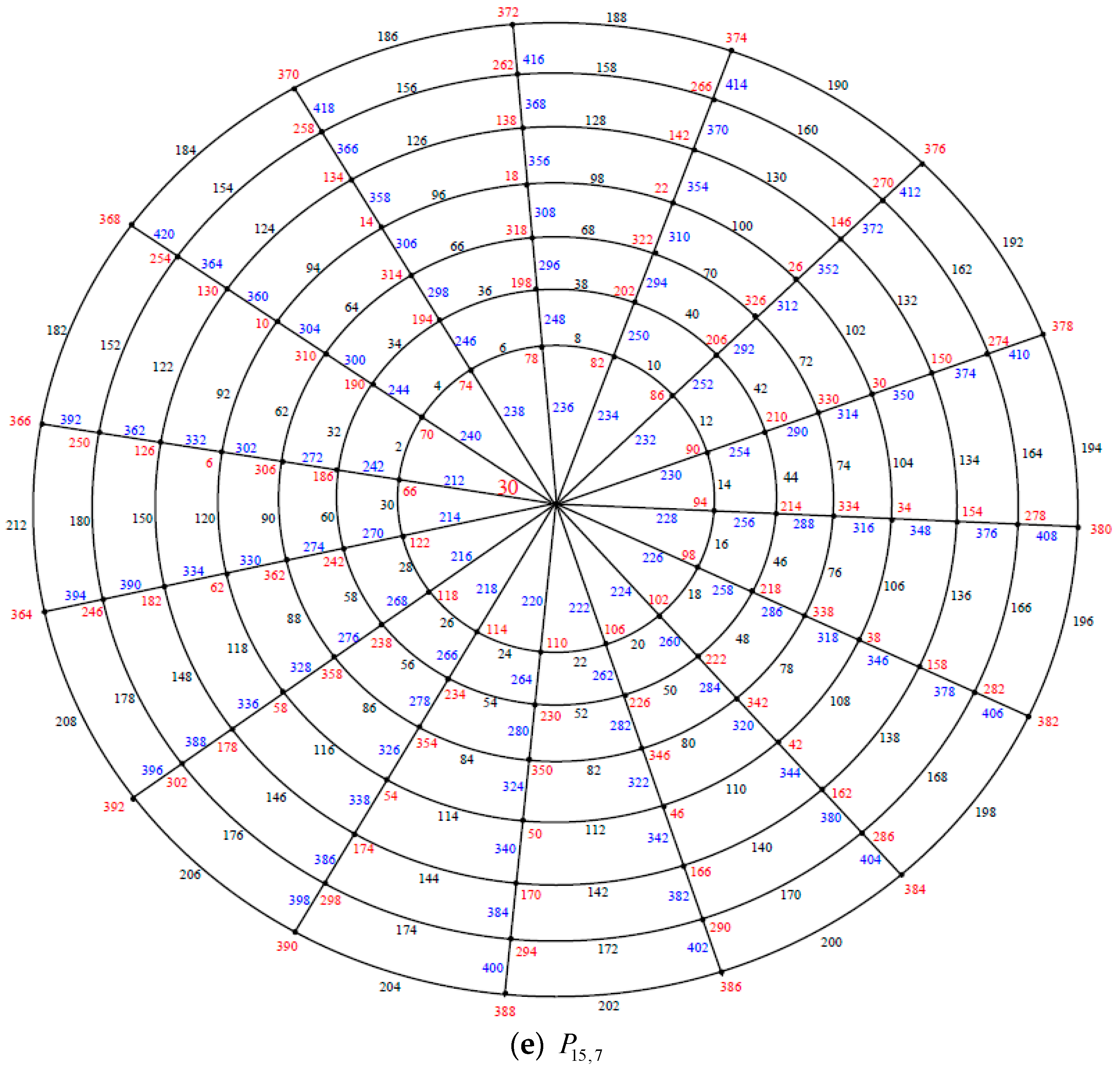
and respectively are shown in Figure 6. Theorem 3. If is an even positive integer greater than or equal and is an odd positive integer greater than or equal . Then the polar grid graph is an edge even graceful graph.
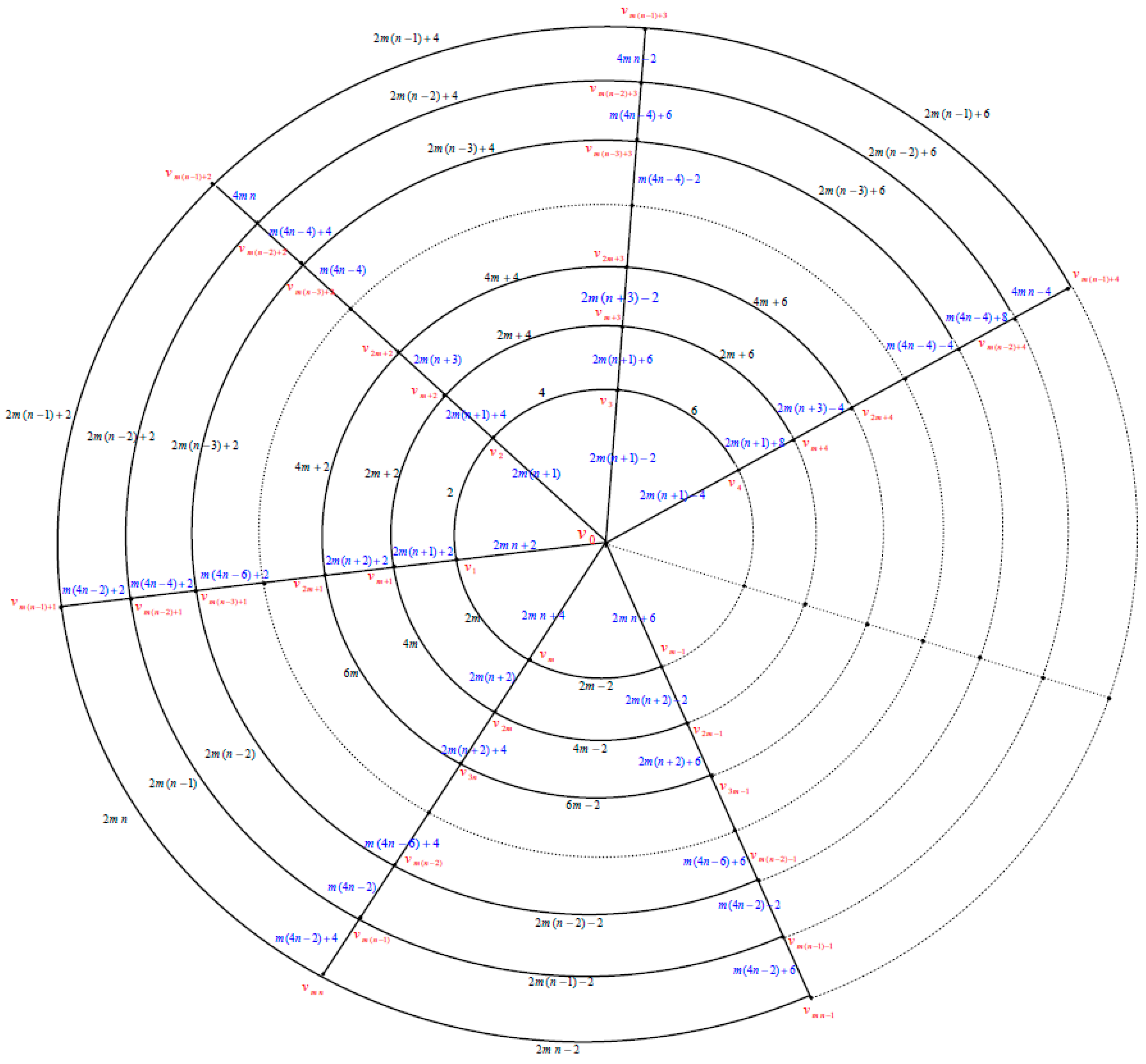
Proof. Let the polar grid graph
be labeled as in
Figure 7. Let
□
First we label the edges of the circles
begin with the edges of the inner most circle
to edges of the outer circle
as follows:
Second we label the edges of paths begin with the edges of the path as follows: Move anticlockwise to label the edges by , then move clockwise to label the edges by then move anticlockwise to label the edges by and so on. Finally move anticlockwise to label the edges by .
The corresponding labels of vertices are assigned as follows: There are four cases
Case (1) and
That is the labels of the vertices in the most inner circle are assigned by the labels of the vertices in the circle are assigned by , the labels of vertices of the circle are assigned by , the labels of vertices of the circle are assigned by , the labels of vertices of the circle are assigned by the labels of the vertices in the circle are assigned by and the labels of the vertices of the outer circle are assigned by The labels of the center vertex is assigned by when we have , when and when ,
Case (2)
In this case the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the label of two edges and . That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and . In this case the center vertex is labeled as The rest vertices are labeled as in case (1).
Case (3) . In this case the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and . That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and and in this case the center vertex is labeled as The rest vertices are labeled as in case (1).
Case (4) In this case the vertex in the outer circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and . That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and and in this case the center vertex is labeled as The rest vertices are labeled as in case (1).
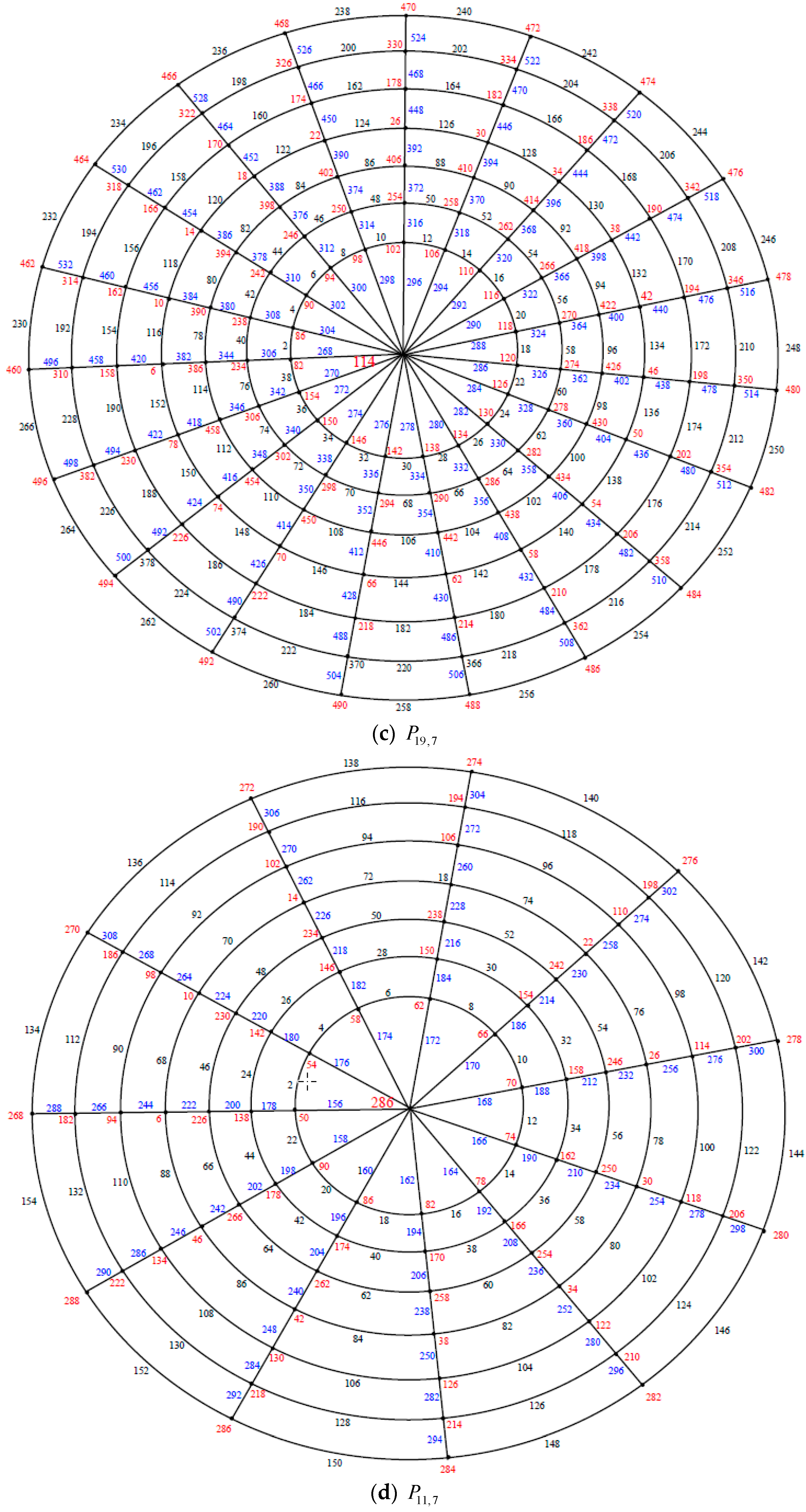
Illustration. The edge even graceful labeling of the polar grid graphs and respectively are shown in Figure 8. Remark 2. In case , is odd, .
Let the label of edges of the polar grid graph
be as in
Figure 9. Thus we have the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows:
and
.
Illustration. The edge even graceful labeling of the polar grid graphs is shown in Figure 10. Theorem 4. If and are odd positive integers greater than . Then the polar grid graph is an edge even graceful graph.
Proof. Let the polar grid graph
be labeled as in
Figure 7. Let
□
The corresponding labels of vertices are assigned as follows: There are two cases:
Case (1) , this case contains five subcases as follows:
SubCase (i)
That is the labels of vertices of the most inner circle are assigned by , the labels of vertices of the circle are assigned by , the labels of the vertices of the circle are assigned by , the labels of the vertices of the circle are assigned by , the labels of the vertices of the circle are assigned by the labels of the vertices of the circle are assigned by and the labels of the vertices of the outer circle are assigned by . The label of the center vertex is assigned by , when , we have .
SubCase (ii) , . In this subcase the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and . That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and in this case the center vertex is labeled as The rest vertices will be labeled as in subCase (i).
Remark 3. When and , in this case the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and . That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and the center vertex is labeld as .
SubCase (iii) In this subcase the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and . That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and in this case the center vertex is labeled as The rest vertices will be labeled as in subCase (i).
SubCase (iv) . In this case the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and . That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and in this case the center vertex is labeled as The rest vertices will be labeled as in subCase (i).
SubCase (v) . In this case the vertex in the outer circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and . That is and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices are as follows and , and in this case the center vertex is labeled as The rest vertices will be labeled as in subCase (i).
Illustration. The edge odd graceful labeling of the polar grid graphs and respectively are shown in Figure 11. Case (2) . This case contains also five subcases as follows:
SubCase (i)
That is the labels of vertices of the most inner circle are assigned by , the label of vertices of the circle are assigned by , the labels of vertices of the circle are assigned by , the labels of vertices of the circle are assigned by , the labels of vertices of the circle are assigned by the labels of vertices of the circle are assigned by and the labels of the vertices of the outer circle are assigned by . The label of the center vertex is assigned by , when , we have .
SubCase (ii) ,
In this subcase the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and the label of the center vertex is assigned by That rest vertices will be labeled as in subcase (i).
Remark 4. When and , we have the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and That is and and we obtain the labes of the corresponding vertices are as follows: and the label of the center vertex is assigned by .
Note that
is an edge even graceful grapg but not follow this rule. See
Figure 12.
SubCase (iii) ,
In this subcase the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows: and . The label of the center vertex is assigned by The rest vertices will be labeled as in subCase (i).
SubCase (iv)
In this subcase the vertex in the circle will repeat with the center vertex To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and That is and and we obtain the labels of the corresponding vertices as follows and the label of the center vertex is labeled as The rest vertices will be labeled as in subCase (i).
Remark 5. If we haveand the center vertex is labeled as SubCase (v)
In this subcase the vertex in the outer circle will repeat with the center vertex . To avoid this problem we replace the labels of the two edges and . That is and we obtain the labes of the corresponding vertices as follows:
and and the label of the center vertex is assigned by
The rest vertices will be labeled as in subCase (i).
Illustration. The edge odd graceful labeling of the polar grid graphs and respectively are shown in Figure 13.