Abstract
The green supplier selection (GSS) problem is one of the most pressing issues that can directly affect manufacturer performance. GSS has been studied in previous literature, which is considered to be a typical multiple criteria group decision making (MCGDM) problem. The ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy MCGDM method can present the importance of each possible value, and the priority relationship among criteria has rarely been studied. In this study, we first extend the prioritized average (PA) operator to the ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy set (OWHFS) for solving the both problems. The generalized ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy prioritized weighted average operator (GOWHFPWA) is recommended, and some desirable properties are discussed. Based on this operator, a novel MCGDM method for GSS is developed. A numerical example of GSS is then given to prove the robustness of the proposed approach, and a sensitivity analysis is used to identify the robustness of the proposed method. Finally, a comparative analysis based on the MCGDM approach with the hesitant fuzzy prioritized weighted average (HFPWA) operator is illustrated to indicate the validity and advantages of the proposed approach.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, with the increasingly global awareness of environmental responsibility, green production has already become the development orientation of industrial production for most manufacturing firms. Growing environmental concerns mean that it is necessary for manufacturing companies to be more concerned about green supply chain management (GSCM) to reduce environmental pollution from industrial sectors [1]. The green supplier selection (GSS) is a critical link of GSCM, which can directly affect the sustainable development and performance of manufacturing enterprises [2]. GSS can be regarded as a multiple criteria group decision making (MCGDM) problem that involves many conflicting assessment criteria [3], such as cost, materials, recycling capacity, green competencies, green technology, and green certification. Essentially, the act of decision making is more complicated than in the traditional supplier selection since some environmental criteria need to be considered, and these criteria are qualitative in nature and the weights cannot be provided in advance [3,4]. Therefore, how to choose a suitable green supplier in GSCM has become a key strategic consideration.
Researchers have come up with and applied a range of multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) approaches for green supplier decision making problems [5,6]. To synthesize multiple qualitative or quantitative environmental criteria and obtain a clear evaluation result, some MCDM approaches based on precise information are used in green supplier decision making. Handfield et al. [7] evaluated the environmental standards of green suppliers by using the analytic hierarchy process(AHP). Likewise, Lu et al. [8] used AHP to evaluate and coordinate green suppliers. Hsu and Hu [9] applied the the analytic network process(ANP) for GSS. Kuo et al. [10] integrated artificial neural network and MCDM approaches to GSS. Bai and Sarkis [11] came up with an analytical evaluation on the basis of rough set theory. Yeh and Chuang [12] introduced an optimal mathematical planning approach for selecting a green supplier. The ANP and radial basis function neural network approaches of choosing green suppliers for China chemical industries was proposed by Zhou et al [13]. Kuo et al. [14] integrated ANP with the data envelopment analysis (DEA) to evaluate green suppliers. A mathematical model based on DEA for choosing green suppliers was proposed by Jauhar et al. [15]. Dobos and Vörösmarty [16] used a DEA approach towards environmental issues. Freeman and Chen [17] designed an approach for GSS by combining technique for order preferenceby similarity to ideal solution (TOPSIS), the AHP model, and entropy approach. Hashemi et al. [18] combined the GSS approach with the ANP method. Yazdani et al. [19] recommended a novel integrated MCDM basis of selecting most suitable green suppliers. Liu et al. [20] expanded a linguistic group decision-making method in assessing big projects.
The major issue obstructing the ability to determine the right mathematical method for choosing a green supplier is the absence of the ability to handle uncertain and inadequate information which mostly happens in real-life conditions. In the practical problems of GSS, a great number of assessment detailed information is unknown, and additionally, several criteria are affected by uncertainty. Meanwhile, decision makers (DMs) usually cannot make completely reasonable judgements due to uncertain and ambiguous information. DMs judgments are usually uncertain and difficult to measure by exact numerical values, so a fuzzy set theory proposed by Zadeh [21] has become essential for solving the complications characterized by vagueness and imprecision. Recently, several studies have applied the typical MCDM methods to a range of fuzzy environments [22,23,24,25]. Chiou et al. [26] applied a fuzzy AHP for GSS in China electronic industries. Lee et al. [27] extended a fuzzy AHP decision model to identify GSS for high-tech industries. Tsai and Huang [28] came up with a fuzzy goal programming technique for GSS. Tuzkaya et al. [29] developed a hybrid fuzzy MCDM model, and Büyüközkan and Cifci [30] recommended a unique hybrid MCDM method to evaluate green suppliers base on reference [29]. Datta et al. [31] presented a VlseKriterijuska Optimizacija I Komoromisno Resenje (VIKOR) method together with the interval valued fuzzy set to choose the best green supplier. Shen et al. [32] presented a fuzzy MCDM as basis for selecting green supplier with linguistic preference. Wang and Chan [33] proposed the hierarchical fuzzy TOPSIS model to choose the green supplier. Cao et al. [34] presented a unique intuitionistic fuzzy judgment matrix integrated with the TOPSIS approach to define the subjective and objective weights in green supplier assessment and selection. Kannan et al. [35] utilized a fuzzy axiomatic design method to choose the most suitable green supplier. Hamdan and Cheaitou [36] proposed fuzzy TOPSIS and AHP methods to define preference weights of respective supplier and criterion. Guo et al. [37] developed a fuzzy MCDM method to solve the GSS in apparel manufacturing.
GSS is known as a MCGDM problem that involves both several interrelated evaluation criteria and several DMs behavior characters. Moreover, the complexity of MCGDM problems is increased when several DMs might be considered in assessment of the problems [38]. Tsui et al. [39] came up with a hybrid MCGDM method based on entropy and AHP to assess GSS problems in manufacturing enterprise. Based on group decision analysis, Darabi and Heydari [40] presented an interval-valued hesitant fuzzy ranking method for selecting green suppliers. Gitinavard et al. [41] developed a unique interval-valued hesitant fuzzy group outranking method for choosing green suppliers. Qin et al. [42] recommended a comprehensive MCGDM approach for GSS in interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Tang [43] employed the hesitant fuzzy Hamacher power weighted average operator to solve the GSS complexities with hesitant fuzzy information.
As evidently shown in the above reviewed literature, various MCDM methods for GSS have been extended to intuitionistic fuzzy sets [44], linguistic fuzzy sets [32], interval-valued fuzzy sets, and type-2 fuzzy sets [31,42]. However, little study has been done on GSS by using a hesitant fuzzy set (HFS), which was first introduced by Torra [45,46]. As a generalization of fuzzy sets, HFS can describe the situations that permit the expert’s preference judgment for a particular criterion that have few different values, which is a very suitable method for tackling uncertain information and for expressing DMs’ hesitancy in real group decision making [47,48,49]. Nowadays, to be able to solve the MCGDM problems, varieties of extensions of the HFS have been proposed by scholars, such as generalized HFS, dual hesitant fuzzy sets, hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets, the higher order HFS, and NaP-HFS [50,51,52,53,54,55,56].
However, the HFS method has its own shortcomings, because it only expresses the expert’s judgment as several probable values lack considerations of their importance. In several applied MCGDM problems, especially in GSS, experts usually come from the same field, and might often make the same judgments on a given criterion. Thus, the possible value repeated many times is more significant than that displayed only one time. For this reason, Zhang and Wu [57] developed the model of weighted hesitant fuzzy set (WHFS), in which the importance of possible values provided by DMs has been considered. Farhadinia and Xu [58] modified the definition of WHFS and proposed a new extension of HFS as the ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy set (OWHFS), in which the importance of DMs’ judgments is defined as the repetition rate of the possible values. Therefore, OWHFS can not only express the experts’ judgments as several possible values but also give the importance of each possible value.
Besides the importance of DMs’ judgments, the priority relationship among criteria of GSS selection for OWHFS is one of the most critical research topics at present. To be able to aggregate the evaluation values of criteria for an alternative, Yager [59] first presented a prioritized scoring operator and prioritized average (PA) operator. Recently, several studies have concentrated on aggregation operators for HFS and their application in MCDM. Xia and Xu [60] investigated a series of aggregation operators for hesitant fuzzy information. Wei [61] developed hesitant fuzzy prioritized operators. Qua et al. [62] examined induced generalized dual hesitant fuzzy Shapley hybrid operators. Wei et al. [63] utilized Pythagorean hesitant fuzzy Hamacher aggregation operators. Farhadinia and Xu [58] first presented several aggregation operators for OWHFS and used them for MCDM. However, as far as we know, the priority relationship among criteria for OWHFS has rarely been investigated.
Moreover, by reviewing the existing literature, the criteria of GSS can usually be classified into two categories: General and green criteria [64,65]. Generally, organizations consider criteria such as cost, quality, and delivery performance when evaluating supplier performance. However, due to enterprises facing double pressures of environmental laws and regulations and the increasing demands of environmental protection, environmental performance is considered by many enterprises in selecting suppliers. To solve the complexity of GSS problems in practice, the criteria of green supplier evaluation were studied by scholars. For instance, Lee et al. [27] mentioned that quality, technology capability, environment management, and green competencies are the most commonly referred criteria in green supplier evaluation literature. Yeh and Chuang [12] developed assessment criteria for GSS such as green image, product recycling, green design, green supply chain management, pollution treatment cost, and environment performance assessment criteria. A summary of the most critical standards for GSS are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Key criteria for green supplier selection.
In summary, the concept of GSS is a typical MCGDM problem, of which there are two critical issues of concern. The first issue depicts the importance of DMs’ judgments. Another is mathematically expressing the priority relationship among criteria. The focus of this study is to develop a novel group decision making approach with ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy information for GSS that addresses both of the above problems.
The remainder of this study is established as follows: Section 2 briefly introduces the basic principles of OWHFS and the PA operator. Section 3 develops the generalized ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy prioritized weighted average (GOWHFPWA) operator and investigates its desirable properties. Section 4 proposes a novel MCGDM method for GSS with a GOWHFPWA operator. Section 5 presents a numerical example of GSS to demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of the proposed approach. Section 6 provides performance analysis and comparison, including sensitivity and validity analysis of the proposed approach. Finally, conclusions and recommendations are discussed in Section 7.
2. Preliminaries
In this section, some basic concepts related to ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy set (OWHFS) and PA operator are reviewed, which will be useful for later analysis.
Definition 1.
[58] Let be the universe of discourse. An ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy set (OWHFS) on is defined as:
where, , referred to as the ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy element (OWHFE), is a set of some different values in [0,1]. It denotes all possible membership degrees of the element to the set , and is the weight of such that for any .
It is worth noting that when for any , then the OWHFS will become a typical HFS. For the convenience of representation, OWHFE can be denoted by
Suppose that the membership degrees provided by experts, of the element in the set , where is given by experts, . It should be noted that every expert cannot persuade other experts to change their opinions. In such a situation, the membership degree of the element in the set has possible values , , …, and associated with weights , ,…, and respectively.
Definition 2.
[58] Let , and be three OWHFEs. Then, some operations on the OWHFEs , and are defined as follows:
- (1)
- ;
- (2)
- ;
- (3)
- ;
whereand.
Definition 3.
[59] Let , and be three OWHFEs. is called the score function of , and is called the deviation function of .
- (1)
- If, then
- (2)
- If, then
- (3)
- If, then
Definition 4.
[59] Let be a set of criteria, and there is a prioritization among the criteria expressed by the linear ordering , which indicates that criterion has a higher priority than , if . The value is the performance of any alternative under criterion , and satisfies . If
where , , . Then PA is called the prioritized average operator.
3. GOWHFPWA Operator and Its Properties
In this section, the GOWHFPWA operator is proposed to aggregate the OWHFEs, and some properties are studied.
The PA operator has been commonly used in situations where the DMs’ judgments are the exact values [59]. In this part, we shall extend the PA operator to ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy environments and define the GOWHFPWA operator.
Definition 5.
Letbe a set of OWHFEs, then the GOWHFPWA operator is defined as follows:
where,is a parameter of GOWHFPWA operator,,andis the score function of.
Theorem 1.
Letbe a set of OWHFEs, then their aggregated value by using the GOWHFPWA operator is also an OWHFE, and
where,,,is the score function of, and L is the number of basic units in.
Proof.
For n = 1, the result can be obtained easily by Definition 5. In the following, we prove the equation
by using mathematical induction for .
For n = 2, since
then
That is, Equation (7) holds when .
Suppose that Equation (3) also holds when for ,
when , the operational laws described in Definition 2 state that
That is, Equation (3) holds for .
Thus, Equation (3) holds for all n.
Then,
Now, consider some desirable properties of the GOWHFPWA operator.
Theorem 2.
(Idempotency). Letbe a set of OWHFs, where, andis the score function of. If, then
Proof.
If , then . . □
Theorem 3.
(Boundedness). Letbe a collection of OWHFEs,where,,is the score function of. Let,and. Then
Proof.
Since is a decreasing function about , then, ,
thus and . □
Theorem 4.
(Monotonicity). Letandbe two sets of OWHFEs, where,,,is the score function ofandis the score function of, ifand, then
Proof.
According to the proof of Theorem 3, it is easy to prove that the GOWHFPWA operator satisfies the above monotonicity, thus the proof process is omitted. □
Theorem 5.
Letbe a set of OWHFEs, where,andis the score function of. Ifis an OWHFE. Then
Theorem 6.
Letbe a set of OWHFEs, where,andis the score function of. Then
where r is an arbitrary number greater than 0.
Theorem 7.
Letbe a set of OWHFEs, where, T = 1 and and is the score function of . If is an OWHFE. Then
where r is an arbitrary number greater than 0.
Theorem 8.
Letandbe two set of OWHFEs, where,andis the score function of. Then
Proof.
According to Definition 2, it is easy to prove that the GOWHFPWA operator satisfies Theorem 5, 6, 7, and 8, so the proof process is omitted. □
4. The MCGDM Approach with Order Weighted Hesitant Fuzzy Information
In this section, we present a novel MCGDM method based on ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy information, which utilizes the above GOWHFPWA operator to rank the alternatives of GSS. Consider a MCGDM for GSS problem, let be a set of suppliers, be a set of criteria, and be a set of DMs. In practice, there is a priority relationship among the GSS evaluation criteria. For example, if DMs believe that environmental protection is the most important criterion, they should take precedence over price, quality, and other criteria. Secondly, if price is more important than quality and other criteria, the priority of price is higher than quality, and so on. Such a prioritization among the criteria can be expressed by the ordering , in which criterion has a higher priority than if j < i.
For an alternative under a criterion, all the DMs provide their evaluated values anonymously. The evaluation values of alternative under criteria are provided by DM , which can be represented by an OWHFE . The ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy group decision matrix is constructed from all of these OWHFEs.
In view of the above analysis, the procedure of the proposed approach is described under the following steps:
Step 1. Calculate the values of based on Equation (11).
where .
Step 2. Aggregate the OWHFEs for each supplier by the GOWHFPWA operator, then we can get the overall OWHFE for the supplier as follows:
Step 3. Calculate the score functions of the OWHFE for the supplier , that is,
Step 4. Rank the score functions in ascending order. Then, the supplier with the highest priority is the most desirable green supplier.
5. Numerical Example
In light of the above discussion, we will further illustrate the procedure of the proposed method by an example of GSS. The GSCM of manufacturing enterprises is affected by its green suppliers’ performance, and GSCM is considered as a strategic decision for manufacturing enterprises to maintain a competitive advantage in the international market. Inspired by the advantages of GSCM, there is a bus manufacturing enterprise who wants to choose the most appropriate green supplier for purchasing the key components of its new bus equipment. After initial screening, five potential suppliers xi (i = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) have been determined for further assessment. In order to choose the most suitable supplier, the company established a team of six DMs from the department of purchasing, quality, and production who have abundant knowledge and experience in GSCM. Finally, four criteria are chosen from the Table 1 criteria list by experts to evaluate possible green suppliers. The four selected criteria are quality (c1), technology(c2), environment(c3), cost(c4), and the priority relationship among the criteria is in the evaluation process. For a supplier under a criterion, six DMs need to give their evaluation values. As an instance, for the supplier x1 under the criterion c1, the evaluation values 0.3, 0.5, and 0.8 are provided by two, one and three DMs, respectively, and then an OWHFE can be represented by {<0.3,2/6>,<0.5,1/6>,<0.8,3/6>}.
In the same manner, all of OWHFEs can be obtained, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy decision matrix.
Step 1. According to Equation (11), are calculated as follows:
Step 2. Aggregate by using a GOWHFPWA () operator to derive the overall OWHFEs for the supplier .
Step 3. Calculate the score functions of the OWHFEs for the supplier , that is,
Step 4. Rank all the suppliers in accordance with the score functions and the priority relationship of five suppliers can be obtained, that is,
Thus, the most desirable green supplier is .
6. Performance Analysis and Comparation Analysis
In this section, performance analysis is provided based on the numerical example above to prove the validation and verification of the proposed method, including sensitivity analysis and effectiveness analysis. Additionally, the proposed GOWHFPWA operator is further compared with the hesitant fuzzy prioritized weighted average (HFPWA) operator suggested by Wei [61].
The sensitivity analysis is used to identify and determine the robustness of the proposed method. In Equation (2), the parameter α may affect the final ranking result, so the sensitivity analysis can be carried out by taking different α. The score functions with different α can be calculated, and all of the results are presented in Table 3 and Figure 1.

Table 3.
The results of the generalized ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy prioritized weighted average operator (GOWHFPWA) operator with different α.
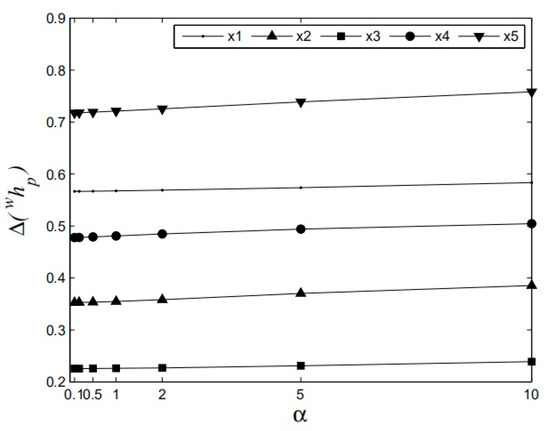
Figure 1.
The curve of the score function with different α.
It can be seen from Table 3 that as parameter α takes different values, the priority relationships of five suppliers are unchanged and the most desirable supplier is still . Therefore, the parameter α is insensitive to the proposed method and the obtained result ranking is robustness.
Meanwhile, it can be observed from Figure 1 that the values of the score function for each alternative will increase as α increases. From this point of view, the parameter α can be regarded as a DM’s risk attitude. As the DMs can select different α in accordance with their own risk preferences, the proposed GOWHFPWA operator can offer more choice opportunities for the DMs in the actual GSS problems.
Additionally, since we proposed the GOWHFPWA operator based on the HFPWA operator [61], a comparative analysis was conducted in order to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed GOWHFPWA operator. For convenience of comparison, we apply the HFPWA operator to the above numerical example in this paper. The hesitant fuzzy decision matrix is shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Hesitant fuzzy decision matrix.
Then are calculated as follows:
We aggregate all hesitant fuzzy elements by using the HFPWA operator to derive the overall hesitant fuzzy elements of the suppliers . Taking supplier x1 as an example, we have = {0.3083,0.3179,0.3295,0.3620,0.3709,0.3816,0.3879,0.3965,0.4067,0.4055,0.4138,0.4238,0.4517,0.4593,0.4685,0.4740,0.4813,0.4902,0.4501,0.4578,0.4670,0.4928,0.4998,0.5084,0.5134,0.5202,0.5284,0.4169,0.4250,0.4348,0.4622,0.4697,0.4787,0.4841,0.4912,0.4999,0.4989,0.5059,0.5143,0.5378,0.5442,0.5520,0.5566,0.5628,0.5702,0.5365,0.5429,0.5507,0.5724,0.5784,0.5856,0.5898,0.5956,0.6024,0.6338,0.6389,0.6451,0.6623,0.6670,0.6727,0.6760,0.6805,0.6860,0.6853,0.6897,0.6950,0.7098,0.7138,0.7187,0.7216,0.7255,0.7301,0.7089,0.7130,0.7179,0.7315,0.7353,0.7398,0.7424,0.7460,0.7504}.
The scores of the suppliers are obtained as the following: , , , , . Finally, ranking all the suppliers according to the scores , we can get the priority relationship of six suppliers, that is,
Thus, the most desirable supplier by using the HFPWA operator proposed by Wei [61] is also . The comparative results can be shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
The result of different approaches.
From Table 5, despite the evaluation result obtained by using the HFPWA operator being the same as that of the GOWHFPWA operator, the proposed method has some advantages over the previous method. Firstly, the proposed method in this paper extends a prioritized weighted average operator from HFS to OWHFS which can solve the problem of the importance of the experts’ evaluation results that the previous method cannot solve. Secondly, the computational complexity of the proposed approach is much lower than that of the previous method. Therefore, the introduced model for GSS in practice is more objective and reasonable than that obtained by using the HFPWA operator proposed by Wei [61].
7. Conclusions and Further Directions
In this paper, in order to overcome the limitation of MCGDM problems with GSS in practice, we have focused on a novel MCGDM approach with a priority relationship under the ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy environment to evaluate green suppliers, which can present the importance of each DM’s judgment. Firstly, based on the ideal of the PA operator and HFPWA operator, the OWHFPWA operator was introduced and the prominent characteristics of the propose operator were studied. Secondly, we have utilized the OWHFPWA operator to develop MCGDM approaches to solve the GSS problem. Finally, a practical example of GSS in bus manufacturing enterprise was given to verify the practicality of the proposed method, meanwhile, its feasibility and effectiveness in dealing with MCGDM problems was carried out by the performance analysis and comparative analysis.
In future research, we will develop another hesitant fuzzy prioritized aggregation operator to solve the ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy MCGDM for GSS problems, namely, the generalized ordered weighted hesitant fuzzy prioritized weighted geometric (GOWHFPWG) operator. Moreover, we will combine the expanded hesitant fuzzy set (EHFS) [67] with the PA operator to deal with the MCDGM for GSS problems for future research, which take into account that a single DM gives several hesitant fuzzy elements in MCDGM problems.
Author Contributions
Authors Y.L. and L.J. conceived and designed the model for research, pre-processed and analyzed the data and the obtained inference. Anthors F.Z. and L.J. processed the data collected and wrote the paper. The final manuscript has been read and approved by all authors.
Funding
The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Projects 71672182, 71711540309, U1604262 and 71272207.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the editors and the anonymous reviewers for providing us with insightful comments and suggestions throughout the revision process.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Guo, S.; Shen, B.; Choi, T.M.; Jung, S. A review on supply chain contracts in reverse logistics: Supply chain structures and channel leaderships. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 144, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blome, C.; Hollos, D.; Paulraj, A. Green procurement and green supplier development: Antecedents and effects on supplier performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 124, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Xu, X.; Dey, P.K. Multi-criteria decision making approaches for supplier evaluation and selection: A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 202, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Liu, J.N.; Ngai, E.W. Application of decision-making techniques in supplier selection: A systematic review of literature. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 3872–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Hu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Mahadevan, S. Supplier selection using AHP methodology extended by D numbers. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Rajendran, S.; Sarkis, J.; Murugesan, P. Multi criteria decision making approaches for green supplier evaluation and selection: A literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 98, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handfield, R.; Walton, S.V.; Sroufe, R.; Melnyk, S.A. Applying environmental criteria to supplier assessment: A study in the application of the analytical hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 141, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.Y.Y.; Wu, C.H.; Kuo, T.C. Environmental principles applicable to green supplier evaluation by using multi-objective decision analysis. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2007, 45, 4317–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.W.; Hu, A.H. Applying hazardous substance management to supplier selection using analytic network process. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, R.J.; Wang, Y.C.; Tien, F.C. Integration of artificial neural network and MAMD methods for green supplier selection. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Sarkis, J. Green supplier development: Analytical evaluation using rough set theory. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.C.; Chuang, M.C. Using multi-objective genetic algorithm for partner selection in green supply chain problems. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 4244–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Ma, X.; Li, S.; Li, J. The green supplier selection method for chemical industry with analytic network process and radial basis function neural network. Adv. Inf. Sci. Serv. Sci. 2012, 4, 147–158. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, R.J.; Lin, Y.J. Supplier selection using analytic network process and data envelopment analysis. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2012, 50, 2852–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhar, S.K.; Pant, M.; Deep, A. An approach to solve multi-criteria supplier selection while considering environmental aspects using differential evolution. In Proceedings of Swarm, Evolutionary, and Memetic Computing; Springer International Publishing: Switzerland, 2013; Volume 8297, pp. 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Dobos, I.; Vörösmarty, G. Green supplier selection and evaluation using DEA-type composite indicators. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 157, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.; Chen, T. Green supplier selection using an AHP-Entropy-TOPSIS framework. Supply Chain Manag. An Int. J. 2015, 20, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.H.; Karimi, A.; Tavana, M. An integrated green supplier selection approach with analytic network process and improved Grey relational analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 159, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Chatterjee, P.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Zolfani, S.H. Integrated QFD-MCDM framework for green supplier selection. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3728–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yang, X.; Huo, T.; Shen, G.Q.; Wang, X. A linguistic group decision making framework for bid evaluation in mega public projects considering carbon dioxide emissions reduction. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control. 1965, 8, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akman, G. Evaluating suppliers to include green supplier development programs via Fuzzy c-means and VIKOR methods. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 86, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenzutti, R.; Krohling, R.A. The hellinger distance in multicriteria decision making: An illustration to the TOPSIS and TODIM methods. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 4414–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.L.; Lin, Y.H.; Tan, K.; Chen, R.H.; Chen, Y.H. Using TODIM to evaluate green supply chain practices under uncertainty. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 2983–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Khodaverdi, R.; Jafarian, A. A fuzzy multi criteria approach for measuring sustainability performance of a supplier based on triple bottom line approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 47, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.Y.; Hsu, C.W.; Hwang, W.Y. Comparative investigation on green supplier selection of the American, Japanese and Taiwanese electronics industry in China. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on IE&EM, Singapore, 8–11 December 2008; pp. 1909–1914. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.H.I.; Kang, H.Y.; Hsu, C.F.; Hung, H.C. A green supplier selection model for high-tech industry. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 7917–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.H.; Hung, S.J. A fuzzy goal programming approach for green supply chain optimization under activity-based costing and performance evaluation with a value-chain structure. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2009, 47, 4991–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzkaya, G.; Ozgen, A.; Ozgen, D.; Tuzkaya, U.R. Environmental performance evaluation of suppliers: A hybrid fuzzy multi-criteria decision approach. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 6, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyüközkan, G.; Çifçi, G. A novel hybrid MCDM approach based on fuzzy DEMATEL, fuzzy ANP and fuzzy TOPSIS to evaluate green suppliers. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 3000–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Samantra, C.; Mahapatra, S.S.; Banerjee, S.; Bandyopadhya, A. Green supplier evaluation and selection using VIKOR method embedded in fuzzy expert system with interval-valued fuzzy numbers. Int. J. Procure. Manag. 2012, 5, 647–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Olfat, L.; Govindan, K.; Khodaverdi, R.; Diabat, A. A fuzzy multi criteria approach for evaluating green supplier’s performance in green supply chain with linguistic preferences. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2013, 74, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chan, H.K. A hierarchical fuzzy TOPSIS approach to assess improvement areas when implementing green supply chain initiatives. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 3117–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.W.; Wu, J.; Liang, C.Q. An intuitionsitic fuzzy judgment matrix and TOPSIS integrated multi-criteria decision making method for green supplier selection. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 28, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, D.; Govindan, K.; Rajendran, S. Fuzzy axiomatic design approach based green supplier selection: A case study from Singapore. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 96, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, S.; Cheaitou, A. Supplier selection and order allocation with green criteria: An MCDM and multi-objective optimization approach. Comput. Oper. Res. 2016, 81, 282–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.X.; Liu, H.T.; Zhang, D.Q.; Yang, J. Green supplier evaluation and selection in apparel manufacturing using a fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making approach. Sustainability 2017, 9, 650–663. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Cabrerizo, F.J.; Herrera-Viedma, E. A consensus model for hesitant fuzzy preference relations and its application in water allocation management. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 58, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, C.W.; Tzeng, G.H.; Wen, P.U. A hybrid MCDM approach for improving the performance of green suppliers in the TFT-LCD Industry. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 6436–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, S.; Heydari, J. An interval-valued hesitant fuzzy ranking method based on group decision analysis for green supplier selection. IFAC PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitinavard, H.; Ghaderi, H.; Pishvaeeet, S.M. Green supplier evaluation in manufacturing systems: A novel interval-valued hesitant fuzzy group outranking approach. Soft Comput. 2017, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Liu, X.; Pedrycz, W. An extended todim multi-criteria group decision making method for green supplier selection in interval type-2 fuzzy environment. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 258, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.L. Green supplier selection model with hesitant fuzzy information. J. Intell Fuzzy. Syst. 2017, 32, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krohling, R.A.; Pacheco, A.G.C.; Siviero, A.L.T. IF-TODIM: An intuitionistic fuzzy TODIM to multi-criteria decision making. Knowl. Base Syst. 2013, 53, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torra, V.; Narukawa, Y. On hesitant fuzzy sets and decision. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems Fuzzy Systems, Jeju Island, South Korea, 20–24 August 2009; pp. 1378–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Torra, V. Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2010, 25, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.M.; Martínez, L.; Torra, V.; Xu, Z.S.; Herrera, F. Hesitant fuzzy sets: State of the art and future directions. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2014, 29, 495–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xu, Z.S.; Xia, M.M. Interval-valued hesitant preference relations and their applications to group decision making. Knowl. Based. Syst. 2013, 37, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.J.; Zhang, W.Y.; Xu, Y.J. Group decision making under hesitant fuzzy environment with application to personnel evaluation. Knowl. Based Syst. 2013, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.H.; Gao, C.Y.; Gao, Z.F. Generalized hesitant fuzzy synergetic weighted distance measures and their application to multiple criteria decision making. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 5837–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadinia, B. Correlation for dual hesitant fuzzy sets and dual interval-valued hesitant fuzzy sets. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2014, 29, 184–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.M.; Martínez, L.; Herrera, F. Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans. Syst. 2012, 20, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.C.; Chen, X.; Herrera, F. Minimizing adjusted simple terms in the consensus reaching process with hesitant linguistic assessments in group decision making. Inf. Sci. 2015, 297, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadinia, B. Distance and similarity measures for higher order hesitant fuzzy sets. Knowl. Based Syst. 2014, 55, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morente-Molinera, J.A.; Kou, G.; González-Crespo, R.; Corchado, J.M.; Herrera-Viedma, E. Solving multi-criteria group decision making problems under environments with a high number of alternatives using fuzzy ontologies and multi-granular linguistic modelling methods. Knowl. Syst. 2017, 137, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantud, J.C.R.; Giarlotta, A. Necessary and possible hesitant fuzzy sets: A novel model for group Decision making. Inf. Fusion 2018, 46, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, C. Weighted hesitant fuzzy sets and their application to multi-criteria decision making. British J. Math. Comput. Sci. 2014, 4, 1091–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadinia, B.; Xu, Z.S. Distance and aggregation-based methodologies for hesitant fuzzy decision making. Cogn. Comput. 2017, 9, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, R.R. Prioritized aggregation operators. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2008, 48, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Xu, Z.S. Hesitant fuzzy information aggregation in decision making. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2011, 52, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.W. Hesitant fuzzy prioritized operators and their application to multiple attribute decision making. Knowl. Based Syst. 2012, 31, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qua, G.H.; Zhang, H.P.; Qua, W.H.; Zhang, Z.H. Induced generalized dual hesitant fuzzy Shapley hybrid operators and their application in multi-attributes decision making. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 31, 633–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.W.; Lu, M.; Tang, X.Y.; Wei, Y. Pythagorean hesitant fuzzy Hamacher aggregation operators and their application to multiple attribute decision making. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2018, 33, 1197–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galankashi, M.R.; Chegeni, A.; Soleimanynanadegany, A.; Memari, A.; Anjomshoae, A.; Helmi, S.A.; Dargi, A. Prioritizing green supplier selection criteria using fuzzy analytical network process. Procedia CIRP 2015, 26, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousakhani, S.; Nazari-Shirkouhi, S.; Bozorgi-Amiri, A. A novel interval type-2 fuzzy evaluation model based group decision analysis for green supplier selection problems: A case study of battery industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omurca, S.I. An intelligent supplier evaluation, selection and development system. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantud, J.C.R.; Santos-García, G. Expanded hesitant fuzzy sets and group decision making. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Naples, Italy, 9–12 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).