Abstract
The development of in vitro antibody selection technologies has allowed overcoming some limitations inherent to the hybridoma technology. In most cases, large repertoires of antibody genes have been assembled to create highly diversified libraries allowing the isolation of antibodies recognizing virtually any antigen. However, these universal libraries might not allow the isolation of antibodies with specific structural properties or particular amino acid contents that are rarely found in natural repertoires. Purpose-oriented libraries specially designed to incorporate desired characteristics have been successfully used. However, the workload required for library construction has limited the attractiveness of this approach compared to the use of large universal libraries. We have developed an approach to capture synthetic or natural diversity into the complementarity determining regions 3 (CDR3) of human antibody repertoires using Type IIS restriction enzymes. In this way, we generated several libraries either biased in amino acid content or towards long CDRH3 loops. The latter were successfully used to identify antibodies inhibiting the enzymatic activity of horseradish peroxidase, whereas libraries enriched in histidines allowed for the isolation of antibodies binding to human Fc in a pH-dependent manner. These libraries indicate that tailored diversification of CDR3 is sufficient to generate purpose-oriented libraries and isolate antibodies with uncommon properties.
1. Introduction
Over the last two decades, in vitro selection technologies have matured as effective alternatives to animal immunization for the isolation of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). Since the first description that antibody fragments can be expressed on the surface of filamentous bacteriophage and selected for specific binding to a target, phage display has become one of the most widely used in vitro approaches for the generation of antibodies for research and therapeutic applications [1,2]. More recently, the display of antibodies at the surface of yeast or mammalian cells, as well as cell free systems, such as ribosome display, have complemented the panel of technologies available for the isolation and engineering of antibodies and other protein scaffolds [3,4]. Regardless of the display package used for in vitro isolation of antibodies, a collection of diversified genes encoding antibody variable regions has to be generated. The diversity and quality of such an antibody gene library is of critical importance for success and the correlation between the number and affinity of antibodies that can be isolated and the library size has been demonstrated [5]. Thus, there has been significant effort to assemble very large antibody libraries, i.e., comprising between 108 and >1011 members, so that, in principle, antibodies against any antigen can be identified [6,7,8].
Antibody libraries can be constructed either by capturing naturally rearranged immunoglobulin genes isolated from B cells or using synthetic approaches relying on mutagenesis of the complementarity determining regions (CDR) of the antibody. In addition, semi-synthetic strategies that combine both naturally occurring and synthetic sequences have also been described [9]. In most cases, naïve libraries are built as universal or ‘single pot’ source of antibodies against any antigen. However, tailor made libraries for defined purposes have also been described. These include libraries incorporating antibody variable genes derived from immunized animals or humans that had been exposed to pathogens or vaccines, thus creating a bias towards the antigen used for immunization or the pathogen [10,11]. In these cases, the frequency and affinity of specific antibodies retrieved from relatively small libraries are usually much higher. Another example is the construction of focused libraries for improved performance against a class of antigens such as haptens or peptides [12,13] or the introduction of charge-biased diversity at given positions of a target-specific library [14]. Focused libraries usually are comprised of structural features of antibodies that bind the desired class of antigen, for instance, having CDRs that form a deep pocket to accommodate a small hapten and maximize the surface of interaction [13].
Despite the benefit of increased performance, the workload and time involved in the generation of immune or focused libraries make them overall less appealing than naïve libraries. However, antibody libraries based on natural immune repertoires or incorporating synthetic diversity that mimics naturally occurring sequences might not be the best source when aiming at isolating antibodies with particular characteristics. For instance, the antibody’s paratope frequently forms a flat surface that can be ideal for interaction with protein surfaces, or form crevices of deeper pockets to accommodate peptides or small molecules. In contrast, extended loops forming protruding structures capable of inserting into concave surfaces are more rarely found. Another example is the more recent interest for antibodies having pH-dependent antigen binding properties obtained via the introduction of histidine residues within the CDR loops [15,16]. Indeed, as histidines become protonated at pH below 6, such antibodies are capable of binding their cognate antigen at pH 7.4 and releasing it in the slightly acidic environment of the endosomal compartment. This leads to the degradation of the antigen and recycling of the free antibody via binding to the neonatal Fc-receptor. As histidines are present at low frequency in natural repertoires, generation of pH-dependent binding antibodies require additional engineering steps.
We have previously described an approach to generate single-chain variable fragment (scFv) antibody libraries via the insertion into human antibody frameworks of heavy and light chain CDR3 loops using Type IIS restriction enzymes [17]. This strategy focuses the diversification to one or two CDRs located at the center of the antigen-combining site as they generally contribute the most to the interaction with the antigen (Figure 1a). Such a CDR3 cloning approach simplifies the capture of sequences from different sources. It has already been applied to the generation of synthetic or semi-synthetic naïve libraries as well as to immune libraries by capturing CDR3 from antibody variable gene repertoires that had been biased towards an antigen in vivo or in vitro [17,18]. More recently, this strategy was employed for the construction of focused libraries with heavy chain CDR3 (CDRH3) sequences enriched in histidine residues, enabling the isolation of antibodies with pH-dependent binding properties [19]. In this study, we further explored the applicability of this approach to the generation of two purpose-oriented libraries. We first incorporated long CDRH3 aiming at facilitating the isolation of antibodies capable of accessing cryptic sites such as enzyme active sites and that are difficult to obtain from standard libraries. We then expanded our work on the isolation of pH-dependent antibodies by extending histidine enrichment to both CDRH3 and CDRL3 loops. In both cases, library construction was straightforward and antibodies with the desired properties could be isolated. These examples indicate that insertion of CDR3 loops with different characteristics can be generally applied for the creation of purpose-oriented antibody libraries for the isolation of antibodies that are not easily retrieved from single pot libraries.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Long CDRH3 Libraries for the Inhibition of Enzymes
A survey of enzyme structures demonstrates that their active sites are almost systematically located in the largest cleft of the protein [20]. The large size of antibodies and the flat or concave shape of their combining sites do not favor access to these cryptic epitopes and antibodies neutralizing enzymes or viruses are difficult to generate [21]. Interestingly, camelid single-domain heavy-chain antibodies (VHH) seem to be better adapted to target buried epitopes and domain antibodies neutralizing enzymes can be more readily identified [22,23]. VHH are characterized by very long and protruding CDRH3, able to interact with the enzyme active site and therefore compete for access with their substrate [24,25]. Although very long CDRH3 sequences are not frequent in human repertoires, they can exist, as exemplified by human antibodies with CDRH3 of 23–24 amino acids that were shown to neutralize influenza virus [26,27] Moreover, Rouet and colleagues recently reported the construction of phage display libraries encoding single-domain human VH fragments which allowed the isolation of human VH against the model antigen hen egg white lysozyme [28]. Interestingly, although these VHs displayed short CDRH3 sequences, they were able to bind to the active site cleft of the lysozyme, indicating that the structure of single-domain VH fragments may be particularly suitable for the recognition of structural clefts.
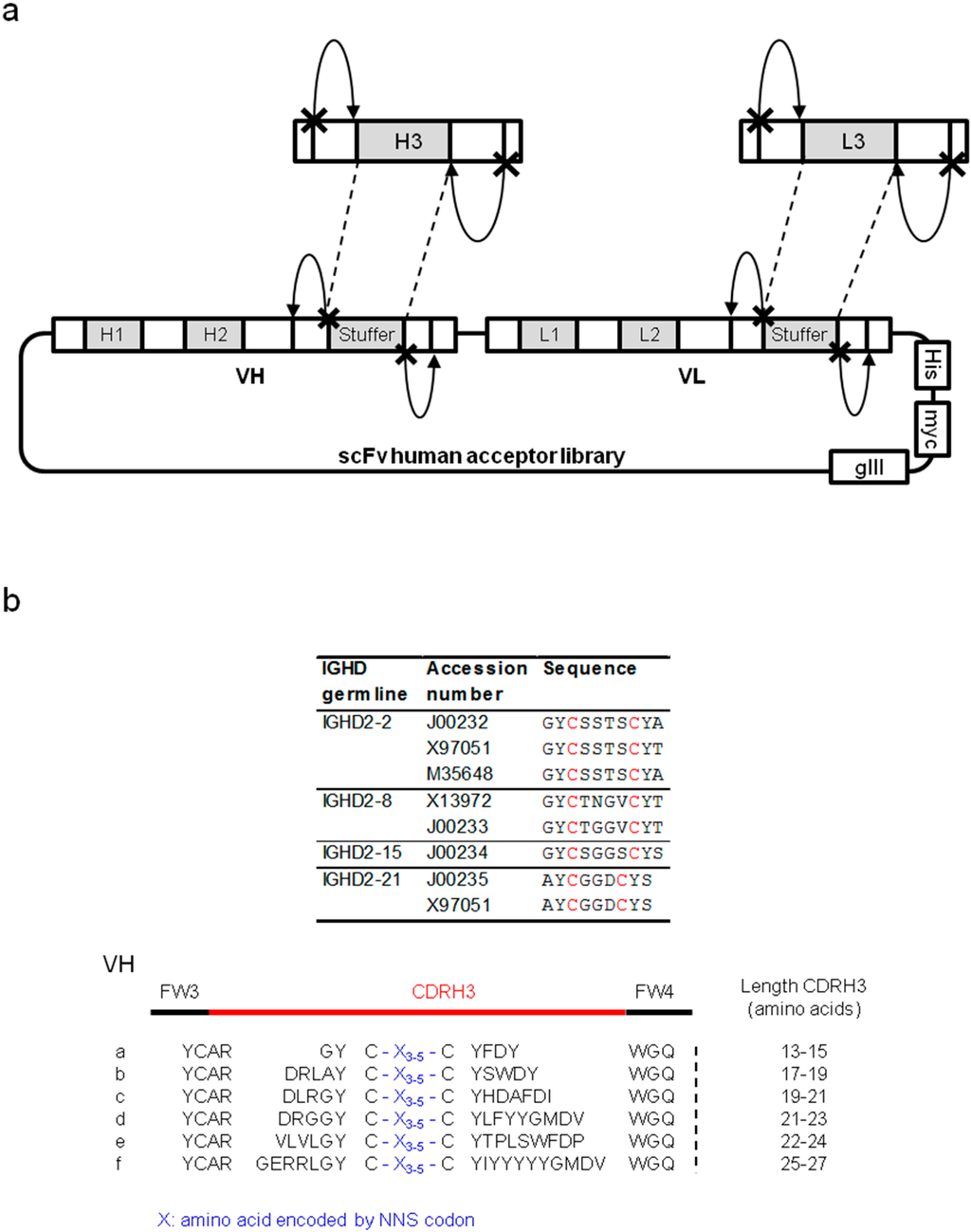
Figure 1.
Long CDRH3-biased library for the inhibition of cryptic sites. (a) Schematic representation of library construction using type IIS restriction enzymes. The site of restriction recognized by the type IIS enzyme is symbolized by a cross and the cleavage activity of the enzyme by an arrow. (b) Design of the long CDRH3 repertoire. The alignment of amino acid sequences corresponding to human D segments that include two cysteines (IMGT database) and their corresponding GenBank accession numbers are shown (top panel). The six motifs covering lengths between 13 and 27 amino acids (a–f), incorporating three, four or five randomized positions between two cysteines, are shown.
Combining these observations, a strategy was designed to integrate synthetic repertoires enriched for long sequences in libraries of human frameworks to increase the probability of generating antibodies capable of neutralizing enzymes. Synthetic, long CDRH3 sequences were designed based on naturally occurring human CDRH3 repertoires. The sequences of human D gene segments naturally containing a pair of cysteines were used to search GenBank to identify existing antibody sequences containing these motifs. Six motifs of a “long” CDRH3 were selected and used as a template to generate synthetic CDRH3 sequences, all containing two cysteines separated by three to five randomized codons (Figure 1b). The aim of this design was to generate elongated CDRH3 loops that are constrained by an intramolecular disulfide bridge. Such protruding CDRH3 sequences, carrying diversity in the constrained loop, could potentially better access and specifically interact with cryptic sites. Synthetic, long CDRH3 fragments were amplified with primers including recognition sites for a type IIS restriction enzyme (BsmBI) and then captured into a human acceptor library. This acceptor library contained sequences from seven heavy chain families and seven light chain families (both kappa and lambda). CDR1 and CDR2 sequences maintained germline sequences whereas unbiased synthetic diversity was present in the CDRL3. The newly created library was termed SL (synthetic long). Two other libraries, HnB and MnA, generated by capturing the CDRH3 repertoire from 49 human donors or spleens of naïve mice, respectively, were used as references throughout our study.
2.1.1. Characterization of Libraries by Deep Sequencing
Libraries were characterized by next generation sequencing (NGS) using the Illumina platform. As this NGS platform generates reads of 100 base pairs in length, the primers used were positioned so that the CDRH3 could be covered by the sequencing run. For subsequent analysis, only functional CDRH3 were included (sequences for which the 5' signature could be identified and therefore encode an in frame and potentially functional CDRH3). The diversity captured in each library was evaluated by counting the number of unique CDRH3 (Table 1). The libraries were also compared on the basis of their CDRH3 length profiles and amino acid compositions (Figure 2a,b).

Table 1.
Description of the libraries used in selections against horseradish peroxidase (HRP). The diversity is defined as the number of unique sequences observed analyzing a pool of one million random sequences per library. For the synthetic library, numbers marked “*” correspond to the number of unique sequences which fit the theoretical design.
| CDRH3 source | Library | Size | Unique CDRH3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | |||
| Human | HnB | 2.9 × 108 | 313'094 | 38.1% |
| Mouse | MnA | 2.5 × 108 | 70'993 | 13.0% |
| Synthetic long | SL | 5.2 × 109 | 398'124 | 43.6% |
| *185'453 | *23.3% | |||
The SL had the most diverse CDRH3 content with 43.6% of unique CDRH3 sequences (23.3% in which the expected design could be confirmed), a profile similar to HnB (38% of diversity). In comparison, the MnA library was less diverse, with only 13% of unique CDRH3 sequences. However, as the NGS focused on the CDRH3 sequences, the complete scFv of 50 randomly picked colonies was also sequenced by the Sanger method. All sequences were unique and more frequent CDRH3 sequences were combined with different light chain sequences. The characterization of CDRH3 length profiles demonstrated that, as expected from previous studies [29], CDRH3 from human origin are on average longer than the murine CDRH3 captured in the MnA library (Figure 2b). The length profile in SL showed a clear trend for longer sequences compared to both reference libraries, featuring also a high content in CDRH3 of 22 amino acids (18%). Regarding the amino acid composition, the major difference between the three libraries was an elevated content in cysteine residues (11%) in the SL library, as expected from the CDRH3 design.
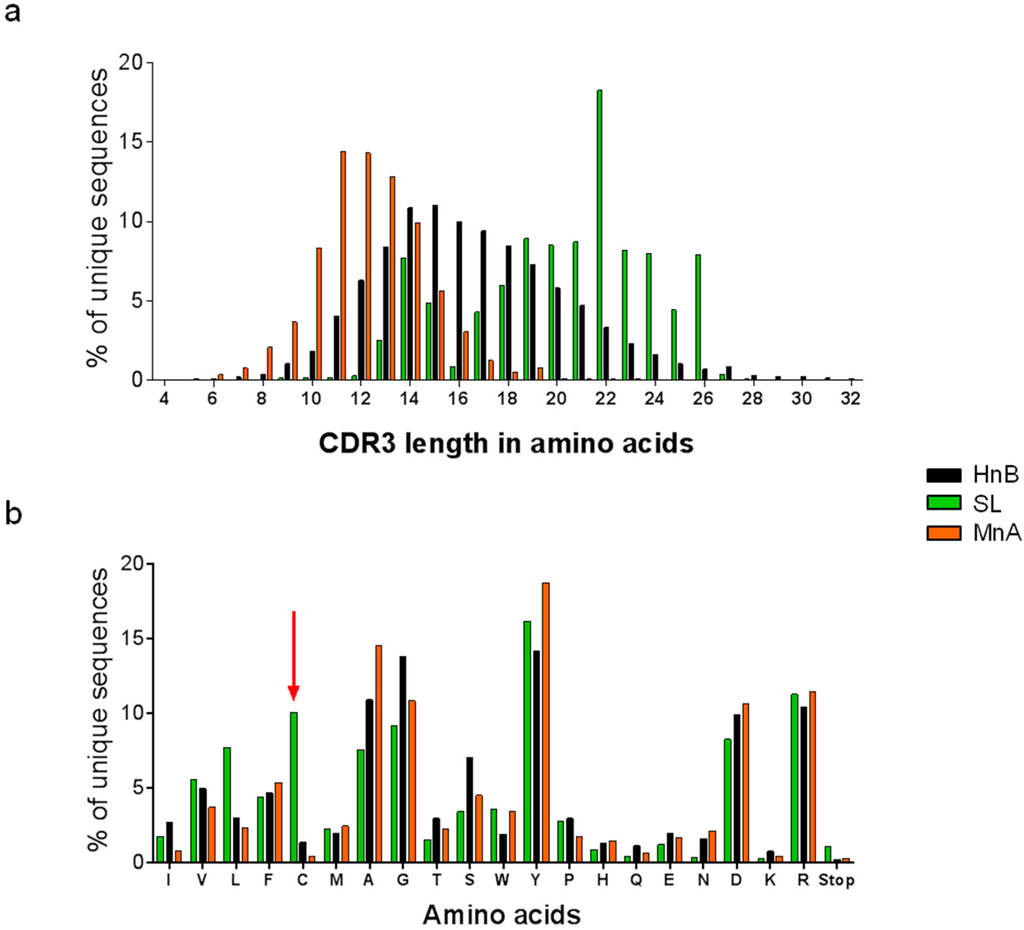
Figure 2.
Library analysis of by next generation sequencing. (a) Comparison of the length profiles of unique CDRH3 sequences in each library. (b) Amino acid composition of unique CDRH3 repertoires. As expected from the library design, the SL library has a much higher content in cysteine than MnA and HnB (red arrow). Both CDRH3 length and amino acid composition profiles were analyzed by deep sequencing.
2.1.2. Assessment of Library Performance by Phage Display Selections against HRP
The three libraries were then used for selection by phage display to assess their capacity to generate antibodies capable of neutralizing the activity of horseradish peroxidase (HRP). This enzyme contains a buried active site where the oxidization of various compounds in presence of hydrogen peroxide is catalyzed [30,31]. After three rounds of selection, the output was screened for specific binding to the target. Supernatants from randomly picked clones were individually tested by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using both scFv and phage formats for their ability to bind to HRP. In this assay, biotinylated HRP was captured on streptavidin-coated plates and individual supernatants containing secreted scFvs were added into the wells. Plates were revealed with an alkaline phosphatase-coupled antibody and an alkaline phosphatase-specific substrate to prevent the apparition of background signals that would result from the use of an HRP substrate.
The signals obtained were compared to a positive control and categorized as low, medium or high (Figure 3). Using the phage format, all the libraries gave a high frequency of binders (i.e., 88%–97%). However, phages giving rise to high signals were only obtained at high frequency from the SL and HnB libraries (73% and 41%, respectively). When performing the ELISA using soluble scFvs, a strong signal could only be obtained with candidates retrieved from the SL library. The best binders from each library were sequenced (Table 2).
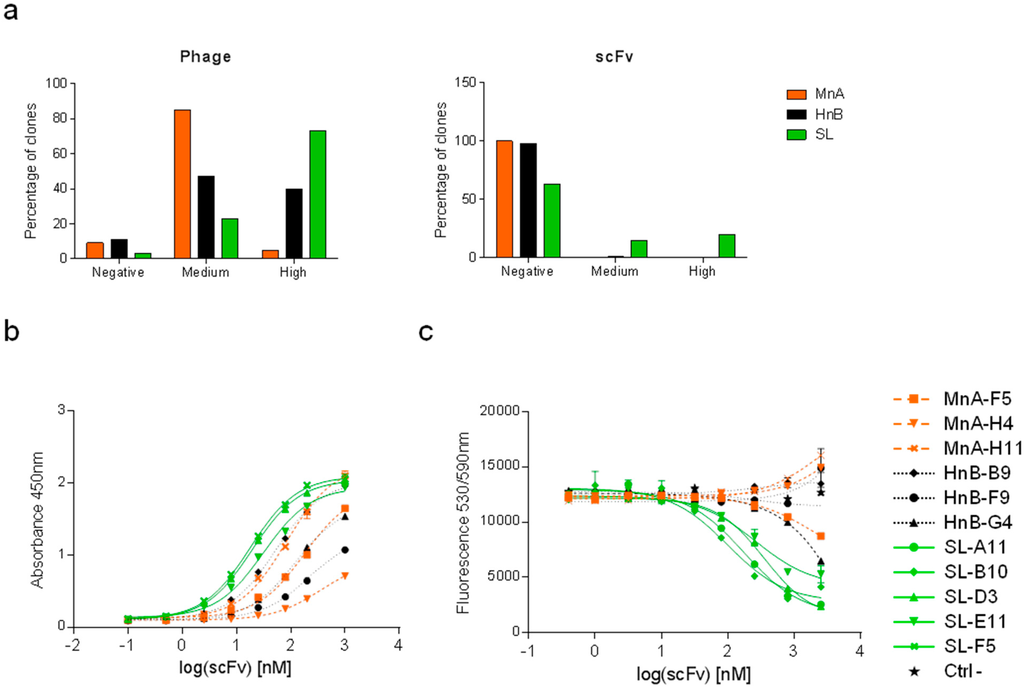
Figure 3.
Results of selections against HRP. (a) Left panel: for each library (the synthetic long library SL, the human naïve library HnB and the mouse naïve library MnA), 528 clones were expressed at the surface of the phage and tested. A commercial anti-HRP antibody was used as a positive control. Clones which displayed absorbance above 70% of the positive control signal were defined as ‘high’, clones between 10% and 70% as ‘medium’ and clones below 10% as ‘negative’. Right panel: for each library, 88 clones were tested in scFv format. Clones with absorbance above 10% of the signal given by a positive control were classified as ‘high’, clones between 5% and 10% as ‘medium’, and clones below 5% as ‘negative’ (same control as the one used for the screening in the phage format). Clones were also tested for binding to streptavidin and did not show any signal (data not shown). Purified scFvs were tested in dose-response for their capacity (b) to bind to HRP by ELISA and (c) to block the enzymatic activity of HRP. A negative control scFv was also included. Data are presented as the mean of duplicates ± SEM.

Table 2.
Characteristics of clones directed against HRP. HRP inhibition was assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; -, no inhibition.
| Clone | CDRH3 | CDRL3 | CDRH3 length | HRP inhibition IC50 [nM] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MnA-A3 | ARDAHGWYF----------DV | GTWDMPPD-VV | 11 | - |
| MnA-F5 | ARSYANYDWF---------DY | QQSVHYRP-ST | 12 | - |
| MnA-H4 | ARLGTGTGYF---------DV | GTYDVGRV-HV | 12 | - |
| MnA-H11 | ARQGNGYY-----------AY | QQSEGVP--WT | 10 | - |
| HnB-A4 | ARPQTYYYDSSGYPDAF--DI | QQREVLP--LT | 19 | - |
| HnB-B9 | ARGWGRTAT----------DY | QQPARQWP-RT | 11 | - |
| HnB-F9 | ARDPGVLWSSSSPYYF---DY | QQDLAGWP-BT | 18 | - |
| HnB-G4 | ARGLVFDSSGYYGF-----DY | QQPSPMP--PT | 16 | 3414 |
| SL-A11 | ARDLRGYC-GLV-CYHDAFDI | GTYDGATQLPV | 19 | 165 |
| SL-B10 | ARDLRGYCSWSRLCYHDAFDI | AAYDASRV-SV | 21 | 107 |
| SL-D3 | ARDLRGYCAWSRACYHDAFDI | AAWDSSPA-VV | 21 | 412 |
| SL-E11 | ARDLRGYC-GVV-CYHDAFDI | GTYDGTERVYV | 19 | 275 |
| SL-F5 | ARDLRGYCAWSRSCYHDAFDI | AAWDSRAA-LV | 21 | 495 |
| SL-G7 | ARDLRGYC-GVF-CYHDAFDI | GTYDGSASEPV | 19 | 1948 |
Soluble scFvs from selected candidates were produced at a larger scale, purified and tested in a dose response for binding to HRP and inhibition of its enzymatic activity (Figure 3b,c). Although some scFvs isolated from the MnA library could bind HRP, none of them showed neutralizing activity. The CDRH3 sequences of the MnA derived scFvs were shorter (10–12 amino acids) compared to those isolated from the HnB library (16, 18 and 19 amino acids). Despite strong binding to HRP, only one HnB derived scFv was capable of inhibiting HRP activity, albeit with a low potency (3414 nM). In contrast, the SL library provided clones displaying a range of blocking activities (107–1948 nM). Competition assays demonstrated that HRP inhibitors were competing for the binding to the antigen, supporting the hypothesis that they share a common epitope (Supplementary Figure S1). Interestingly, these CDRH3 sequences were all 19 or 21 amino acids in length and based on the same motif (i.e., motif c, Figure 1a). This motif was designed based on a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region from a cord blood B cell (GenBank - BAI52519). The observed bias could potentially also be due to a better display of this motif.
In summary, after three rounds of selection, all libraries generated binders against HRP. However, only HnB and SL provided scFvs inhibiting the activity of HRP. A significantly better performance was observed for the SL library both in terms of potency and diversity, as only one low potency inhibitor was isolated from the HnB library. This suggests that using libraries incorporating sequences with long CDRH3 structured by an intramolecular disulfide bond is a strategy that provides antibodies with enzyme blocking activity which may also provide access to other cryptic sites within proteins.
2.2. Anti-Fc Antibodies with pH-Dependent Binding Properties
Reagents binding to antibodies such as anti-IgG antibodies or Protein A are widely used for purification and analytical purposes. For instance, standard antibody purification protocols include a Protein A chromatography step, while biosensors used for protein-protein interaction analyses by surface plasmon resonance and bio-layer interferometry (BLI) often involve surfaces that can capture the Fc part of an antibody [32]. Such devices are often regenerated by applying low or high pH buffers that can damage the surface and limit the number of measurement cycles. The generation of pH-dependent binding reagents binding human Fc (hFc) with high affinity at pH 7.4 but rapidly releasing it at pH 6.0 or below would enable surface regeneration under milder conditions. We investigated the possibility of obtaining such anti-hFc antibodies by phage display using libraries with increased histidine content in the heavy and light chain CDR3.
2.2.1. Construction of a Synthetic Library Biased Towards Histidine
A phage display library termed CG1 was constructed by introducing histidine-biased synthetic diversity in both the CDRH3 and the CDRL3. In order to maintain enough diversity while increasing the percentage of histidine within CDR3 sequences, four to ten NAT and NNT degenerate codons were alternated into the CDRH3 to obtain sequence lengths of 9 to 15 amino acids. NNT encodes for a subset of 16 amino acids, including histidine, whereas NAT exclusively encodes for D, H, N and Y. This strategy therefore allowed for a substantial enrichment in histidine content while retaining enough diversity. The same strategy was used to diversify the CDRL3, by introducing four to eight degenerate codons within CDRL3 of 7 to 11 amino acids in length.
Synthetic oligonucleotides were amplified and cloned into VH acceptor libraries by using a Type IIS restriction enzyme ([17]). These libraries contained germline sequences from nine heavy chain families. In parallel, libraries diversified only in the VL sequence were prepared, using nine kappa light chain germline sequences. These two libraries were then combined by cloning the diversified VL repertoires into the VH library. Thus, the resulting CG1 library was diversified in both CDR3 while the CDRH1, H2, L1 and L2 maintained germline sequences. The theoretical diversity of the CG1 library is too large to be covered (more than 1018 unique sequences). We performed several rounds of electroporation to reach a final library size of 5.92 × 109 transformants. To evaluate the quality of the library, 40 randomly picked individual colonies were sequenced. The analysis indicated that CDRH3 and CDRL3 of expected length, containing between zero and three histidines, had been cloned. All sequences analyzed were unique.
2.2.2. Selections against Human Fc Fragments
To isolate pH-dependent binders against hFc, pH-dependent selections were performed using the CG1 library as well as the previously described JAB library. In the latter, diversity biased towards histidine was present only in the CDRH3 whereas diversified light chain sequences were based on kappa and lambda germlines genes [19]. Binding of phage to the appropriate target was performed at pH 7.4 and the pH decreased to 5.4 during the elution step, allowing the recovery and subsequent amplification of phage rapidly detaching from the target under these conditions. The elution pH was set to 5.4 to ensure that all histidines were protonated. To promote the emergence of Fc-specific clones, several Fc-containing proteins (i.e., human IgG and Fc-fusions) were alternated between rounds.
Following the third round, individual clones were screened to evaluate their binding to hFc. Randomly picked clones were grown in selective medium and scFvs present in periplasmic extract were then used in a pH-dependent ELISA. In this assay, two hFc-containing proteins—a human IgG1 and an Fc-tagged protein—were coated onto microwell plates and scFvs were subsequently added to the wells. Following the binding of the scFvs to the targets, an additional elution step of two hours was performed, either at pH 7.4 or 5.0. The comparison of the remaining signals obtained at pH 7.4 and pH 5.0 allowed the identification of pH-dependent binders against hFc. No unspecific binding to irrelevant proteins was observed. Hits were defined as scFvs binding to both Fc-containing proteins at pH 7.4 and losing at least 50% of binding to both proteins at pH 5.0. Among the 176 clones evaluated, 21% were positive in the screening and a panel of positive candidates showing the best differential binding was sequenced to evaluate their histidine content (Figure 4). Five out of seven candidates were derived from the JAB library. All CDRH3 sequences contained at least two histidines but, surprisingly, even in the two sequences isolated from the CG1 library, no histidine was found in CDRL3 suggesting that no pH-dependent interaction could be identified in this region. CDRL3 sequences were, however, more diverse than the CDRH3 sequences, in which histidines at positions four and ten of the CDR were frequently found. Interestingly, competition binding assay demonstrated that all tested clones compete for the binding to hFc, indicating that they share overlapping epitopes, as also expected from the analysis of the sequences (Supplementary Figure S2).
Based on library size and diversity, we expected the CG1 library to be the most successful. The bias observed could be due to the presence of lambda light chains in the JAB library whereas the CG1 library contains only kappa light chain sequences. Moreover, as the sequences retrieved from the CG1 library did not contain histidines in the CDRL3, this panel of antibodies indicates that histidine-enriched CDRH3 sequences are sufficient to obtain pH-dependent binders against hFc.
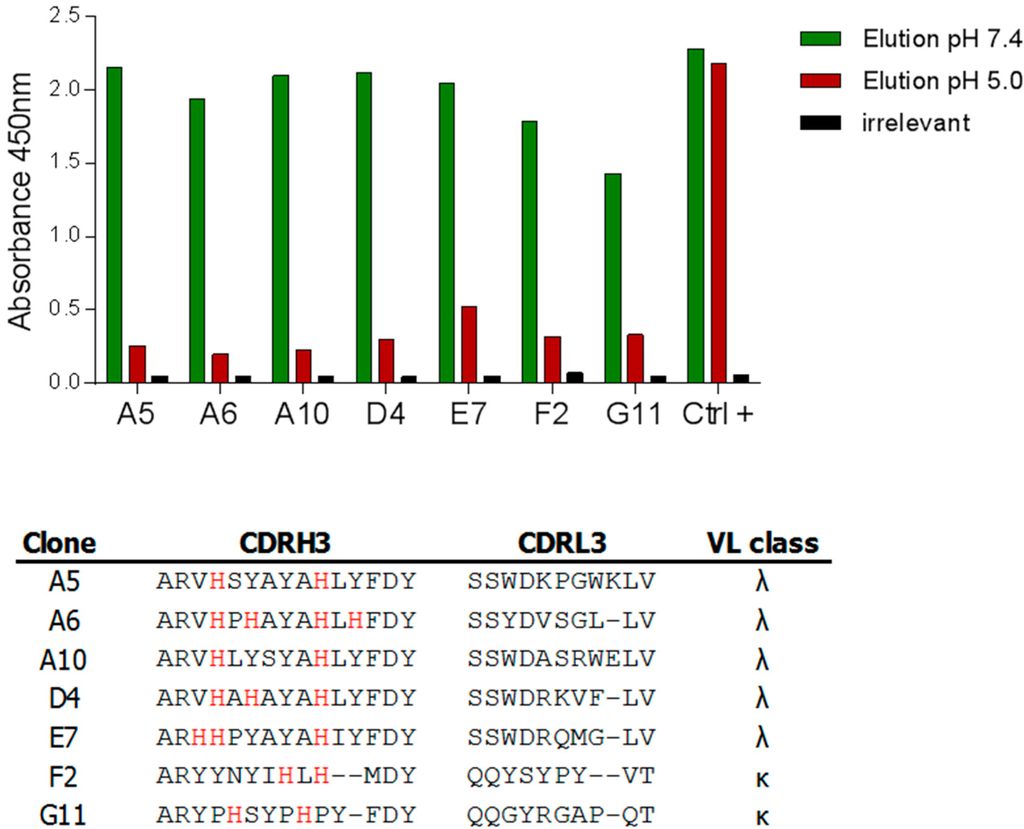
Figure 4.
Isolation of pH-dependent anti-hFc antibodies. The output from round 3 was screened by pH-dependent scFv ELISA. The binding of clones to two different targets (one human IgG and one hFc-tagged protein) was assessed and clones were considered positive if binding to both targets was observed. An elution step at pH 7.4 or pH 5.0 was performed. Binding was considered to be pH-dependent if the signal obtained was at least twice that observed at pH 5.0. Clones were simultaneously tested on an irrelevant target to assess unspecific binding. The results obtained with a selection of pH-dependent hits against a human IgG1 antibody are displayed as well as the CDR3 sequences of these hits.
2.2.3. Characterization of pH-Dependent Anti-hFc Candidates
The specificity of six candidates was tested using purified scFv in pH-dependent ELISA for binding to hIgG1, mouse IgG1 (mIgG1), mIgG2a and mIgG2b. As expected, all candidates could bind to hIgG1 and some to mIgG2a in a pH-dependent manner whereas no binding to mIgG1 or to mIgG2b was detected (Supplementary Figure S3). To avoid generating auto-reactive antibodies, our hits had to be expressed on a backbone that they do not recognize. Based on the scFv results, the sequences of the variable domains of three hits (A5, D4 and F2) were cloned into a vector encoding the constant domains of mIgG1, expressed in mammalian cells and purified.
The three IgGs bound to hFc by ELISA, with subnanomolar EC50 for both A5 and D4. The binding of these two antibodies was also pH-dependent. A 45-fold and 100-fold increase of the EC50 was observed when the elution step was performed at pH 5.0 instead of pH 7.4 for A5 and D4, respectively (Figure 5a). In contrast, F2 displayed only a 5-fold increase of the EC50 (EC50 elution pH 7.4, 10.8 nM vs. EC50 elution pH 5.0, 53.4 nM) and was, therefore, not further characterized.
The kinetic profiles of the binding of A5 and D4 to hFc were evaluated using BLI. The mIgGs were captured on anti-murine IgG biosensors and dipped into a solution containing hIgG1 antibodies at neutral pH. Following an association phase of ten minutes, dissociation was performed either at pH 6.0 or pH 7.2 (Figure 5b). For both antibodies, the hIgG detached faster from the immobilized antibodies at pH 6.0 than at pH 7.2, with a larger difference between the two conditions observed for A5 compared to D4 (ratio kd(pH 7.2) vs kd(pH 6.0) of 8.4 and 2.4 for A5 and D4, respectively). These results indicate a faster off-rate at pH 6.0 and confirmed the pH-dependency of A5 and D4. In summary, two anti-hFc antibodies with strong pH-binding properties were isolated de novo from libraries containing histidine-enriched CDRH3 sequences.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Reagents
Restriction enzymes were purchased from New England Biolabs and primers were supplied by Mycrosynth. Escherichia coli cells were cultured in lysogeny broth (LB) or 2xTY supplemented when needed with ampicillin at 100 µg/mL (A–selection of pNDS vector) or kanamycin at 50 µg/mL (K–selection of helper phage) and glucose 2% (G).
3.2. Construction of the Synthetic Long Library and Sequencing
Human D gene segments including cysteine pairs were retrieved from the IMGT database [33]. Example antibody sequences containing these D segments were searched amongst all human sequences of GenBank using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool [34]. Six families representative of different CDRH3 lengths were selected, all containing two cysteines. Based on these families, the sequences preceding and following the cysteines were fixed, and diversity was generated by using three to five NNS codons between the two cysteines. DNA fragments were generated by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assembly of synthetic oligonucleotides and included recognition sites for BsmBI. All PCR steps for the assembly of these synthetic fragments were performed with the AccuPrime Pfx DNA polymerase (Invitrogen).
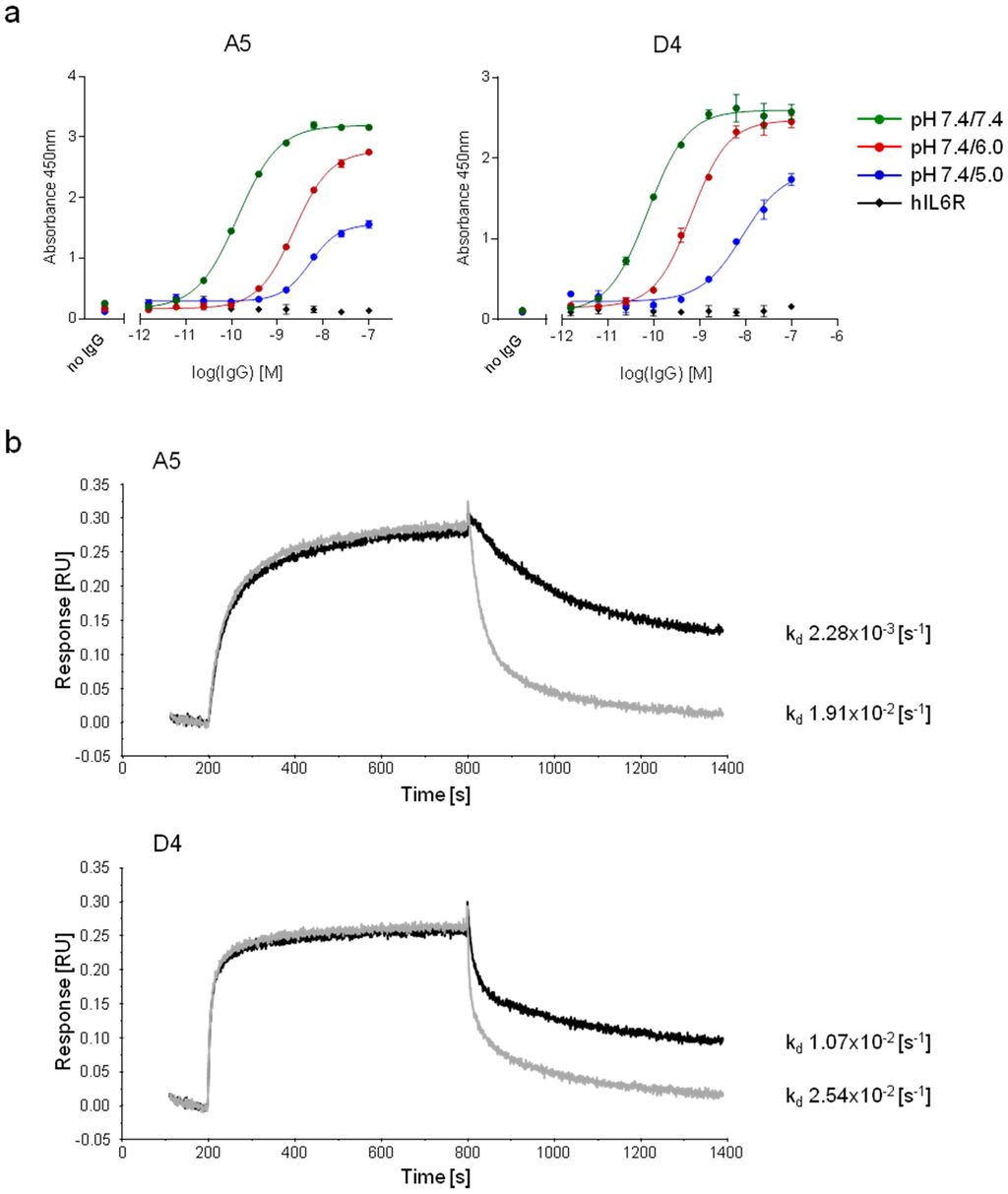
Figure 5.
Characterization of the pH-dependent mIgGs, A5 and D4. (a) A pH-dependent ELISA was performed against hIgG1 using serial dilutions of A5 and D4 reformatted onto the mIgG1 backbone. The elution step occurred either at pH 7.4, 6.0 or 5.0. The binding to an irrelevant protein (hIL6R) was assessed to evaluate non-specific binding. Data are presented as the mean of duplicates ± SEM. (b) Bio-layer interferometry was performed using mIgGs. Antibodies were captured on murine specific biosensors and transferred to hIgG1-containing wells. The association (pH 7.2) and the dissociation (pH 7.2, black or 6.0, grey) were followed for ten minutes.
The amplified and purified CDRH3 pools were digested with BsmBI and purified by phenol/chlorophorm extraction. The human acceptor library was generated as previously described [17] and digested with BsmBI for stuffer removal. Digested CDRH3 were ligated into their corresponding acceptor libraries using Rapid DNA Ligation Kit (Roche). Ligation products were purified by phenol/chlorophorm extraction and electroporated into competent TG1 E. coli cells (Lucigen) to create the SL library.
Randomly picked TG1 clones were sequenced with the Sanger method (Fasteris) and libraries were subsequently analyzed by deep sequencing using the HiSeq Illumina platform (Fasteris). The reads being limited to a length of 100 bp, sequencing was performed with a primer annealing at the 3' end of the CDRH3. The runs covered the CDRH3 sequences and most of the time, enough of the framework 3 to determine its family. The large data sets generated (more than one million sequences) were analyzed with the N2GSAb software [35].
3.3. Phage Display Selections against HRP
Phage display selections against HRP were performed according to standard protocols. Briefly, 7 × 1011 viral particles of each library were blocked and deselected on streptavidin beads (Dynabeads M-280, Invitrogen). Biotinylated HRP (Thermo Scientific) was then added to the phage at a final concentration of 100 nM and the mix was incubated for two hours at room temperature. Following capture on Dynabeads and washes with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)/0.1% Tween 20 (Sigma-Aldrich), bound phage were eluted with 10 mM triethylamine (Sigma-Aldrich) and the solution was neutralized with 1 M Tris-HCl pH 7.4 (Sigma). The mix was used to infect 10 mL of fresh TG1 cells which were spread on 2xTY AG bioassay plates and incubated at 30 °C overnight. Phage rescue was then performed and the obtained phage particles were used for the following rounds of selection.
3.4. Screening ELISA on HRP
Individual clones were cultured in selective medium and scFv production was induced by isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) addition (1 mM final). For the screening scFv ELISA, Maxisorb plates (Nunc) were coated at 4 °C overnight with 50 µL of streptavidin (Roche). Plates were then blocked with milk 3% (weight/volume) and coated with 50 µL of biotinylated HRP (2 µg/mL). After washing, 50 µL of cell culture supernatants containing the scFv were added to plates. As the scFv are tagged with a c-myc motif, plates were revealed with a mouse anti-c-myc antibody (Jackson) and an anti-mouse Fc antibody coupled to alkaline phosphatase (Sigma).
To perform the screening phage ELISA, clones were grown in 2xTY AG and then infected with M13KO7 helper phage obtained from Invitrogen (multiplicity of infection of 10). The medium was replaced by 2xTY AK and plates were incubated overnight for phage production. The ELISA procedure was similar to that described for scFv except that the first detection antibody was a mouse anti-M13 g8p (Abcam). For both types of ELISA a mouse anti-HRP antibody (Abcam) was used as positive control.
A selection of clones were also produced as soluble scFv, purified via their 6His tag with Ni-NTA agarose chromatography (Qiagen) and quantified before being used in the scFv ELISA.
3.5. Dose Response Functional Assay of HRP Activity
Black maxisorb plates (Nunc) were blocked with milk 3%. HRP at 0.12 µg/mL in PBS was then added with serially diluted scFv fragments. Plates were incubated 90 min at room temperature. Amplex Ultra Red mix was added to each well and the plates were incubated 30 min at room temperature protected from light. Fluorescence was read at 530/590 nm (Synergy HT from Bio TeK). A serial dilution of concentrated H2O2 was used as a positive control.
3.6. Construction of Histidine-Enriched Libraries
The construction of the JAB library was reported elsewhere [19]. To obtain the CG1 library containing histidine-biased diversity in CDRL3 and CDRH3, libraries diversified in one of these CDRs were first individually constructed and then combined to obtain the final CG1 library. In both primary libraries, diversity was introduced by the use of synthetic oligonucleotides containing NAT and NNT degenerated codons. DNA fragments encoding CDR3 were generated by PCR, using oligonucleotides containing four to ten degenerated codons, cloned into the acceptor vector as described for the SL library and electroporated into TG1 E. coli to obtain the VH library. Nine different acceptor vectors have been used, encoding for nine germlines from various VH families (VH1, VH3, VH4, VH5 and VH6). These vectors contain a stuffer in lieu of the VL sequence. In a similar way, CDRL3 fragments were obtained from degenerate oligonucleotides encoding four to eight NAT/NNT codons and cloned into acceptor vectors containing the germline sequences of nine kappa families. DNA was then extracted from primary libraries using a QiaPrep Spin Miniprep kit (Qiagen). VL inserts were amplified from the VL primary library DNA using germline-specific primers containing SalI and NotI restriction sites and subsequently digested with these two enzymes (New England Biolabs). Vectors obtained from the VH library were digested with NotI, SalI and SexAI to remove their VL stuffer and dephosphorylated before being used in a ligation reaction with the VL inserts. The ligation product was purified by phenol/chloroform extraction and transformed into TG1 bacteria to obtain a final library of 5.92 × 109 transformants. Library rescue was performed as previously described [36].
3.7. pH-Dependent Phage Display Selections and Screening
To obtain pH-dependent binders of hFc, the strategy reported elsewhere was followed [19]. Briefly, purified phages were blocked with PBS containing 1.5% milk and 1.5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) and deselected against Immuno tubes (Nunc). Target proteins were adsorbed onto Immuno tubes and incubated with the deselected phage for two hours. Five washes were performed to remove the unspecific phage and bound phages were eluted with citric acid pH 5.4 for one hour. Except for the elution, the pH of all solutions used was adjusted to 7.4. The eluate was then neutralized with 1 M Tris-HCl pH 8.0 and used to infect TG1 cells (see [36] for detailed protocol). Three rounds of selection were performed. To ensure specificity, various targets were alternated during the different rounds of selection, i.e., an Fc-tagged protein (Round 1), a human IgG1 antibody (Round 2), and an Fc-tagged peptide (Round 3).
Clones from hFc-selections were screened by pH-dependent ELISA. The procedure mentioned elsewhere [19] was followed to obtain culture supernatants, containing the scFv of individual clones from round 3. Two Fc-containing targets, a anti-interferon γ hIgG1 antibody and the Fc-tagged protein Evasin-4-Fc [37], were passively coated on a Maxisorp plate. The plate was then blocked with PBS containing 3% of BSA and the culture supernatants were added on the plate. Following a one-hour incubation and washes with PBS/0.1% Tween 20, an elution step was performed by adding either PBS pH 7.4 or citrate buffer pH 5.0 to the plate and incubating for two hours. As scFv were tagged with six histidines, bound scFv were revealed with the PentaHis-HRP antibody (Qiagen). In parallel, the non-specific binding of scFv was assessed by ELISA against an irrelevant protein.
3.8. Expression and Purification of Antibodies
Hits from hFc screening were reformatted onto murine IgG1 backbone. The sequences encoding the variable heavy chain and variable light chains of scFv were amplified by PCR using Pfu Ultra II Hot Start polymerase (Agilent Technologies) and then cloned into a proprietary dual promoter mammalian expression vector, permitting the expression of mIgG1 [36].
IgGs were then expressed in Transformed Human Embryo Kidney epithelial cells (PEAK cells; Edge Bio). Cells were maintained in culture medium containing DMEM (Invitrogen), 10% fetal calf serum (Sigma-Aldrich) and supplemented with 2 mM glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich). Cells were transfected with DNA mix containing 30 µg of DNA and 42 µL of Lipofectamine 2000 transfection reagent (Invitrogen) in 1.5 mL of DMEM for 107 cells per T175 flask. The day after the transfection, culture medium was changed for a serum free medium containing 293SFMII (Invitrogen) and supplemented with 6 mM glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich). Seven days after transfection, culture supernatants were harvested by centrifugation. CaptureSelect IgG-Fc (ms) affinity matrix (Life Technologies) was washed with PBS and then added to the supernatant following manufacturer’s protocol. Following an overnight incubation at 4 °C, the resin was collected and washed three times with PBS. For elution, 50 mM glycine pH 2.7 was used. Different elution fractions were collected, pooled and desalted against PBS using 50 kDa Amicon Ultra Centrifugal filter units (Merck KGaA). The final product was characterized by electrophoresis in denaturing and reducing conditions using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies).
3.9. Characterization of pH-Dependent Anti-hFc IgGs
A pH-dependent ELISA was performed as described above. The elution step was performed using either PBS pH 7.4, citrate buffer 6.0 or citrate buffer 5.0 and the bound antibodies were detected with an HRP-coupled goat anti-mouse Fc IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch).
The binding of A5 and D4 to hFc was characterized by BLI on an Octet RED96 system (ForteBio) using anti-murine quantitative (AMQ) biosensors. All assays were performed at 30 °C in Kinetic Buffer (KB) with an agitation of 1000 rpm. Antibodies were diluted to 3 µg/mL and loaded on the biosensors for ten minutes. Following baseline in KB, sensors were dipped into a solution containing 150 nM of a hIgG1 protein and the association was followed for ten minutes. Sensors were then moved to wells containing either KB pH 7.2 or KB pH 6.0 (standard KB acidified with HCl). The dissociation was then followed for ten minutes and AMQ biosensors were finally regenerated according to manufacturer’s instructions. Data were fitted with a 1:1 model using the BIAEvaluation software (version 4.1.1). To obtain a correct fitting and acceptable kd values, only the initial 90 seconds of the dissociation phase were used for the fitting.
4. Conclusions
The large diversity found in natural immunoglobulin repertoires enables the immune system to produce antibodies useful to the organism against putatively any type of antigen. This formidable capacity has been successfully mimicked in vitro by the construction and use of large naïve antibody libraries. However, depending on the characteristics that are desired for an antibody for research or industrial applications, focused libraries can represent a more effective approach to generate a suitable candidate. We used a generic and straightforward cloning approach to insert CDR3 loops with different characteristics into human antibody frameworks in order to create libraries for different purposes. Several examples, including those described here, support the validity of the approach and include: (i) antigen biased libraries containing CDRH3 that were enriched in vitro or in vivo against an antigen; (ii) histidine-enriched libraries for pH-dependent binding properties and (iii) long CDRH3 libraries to access buried sites ([18,19] and Figure 6).
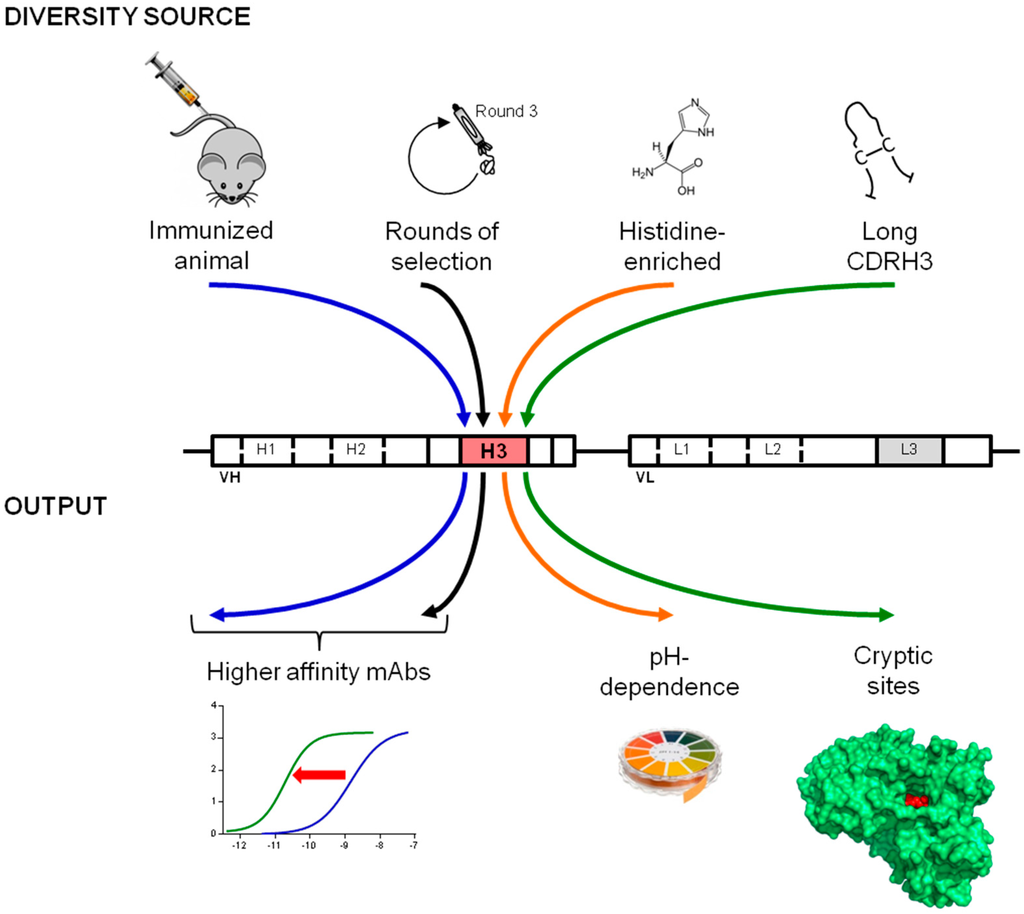
Figure 6.
Creation of purpose-oriented libraries by the introduction of tailor-made diversity into the CDRH3. A straightforward cloning strategy can be used to capture CDRH3 sequences with selected characteristics for the construction of libraries for different purposes. Several examples reported in this and previous studies are schematically depicted. In order to obtain higher affinities, libraries can incorporate antigen-biased CDRH3 sequences that are enriched in vivo or in vitro for antigen specificity [18]. The introduction of synthetic diversity biased either on amino acid content or length enables the efficient isolation of pH-dependent and enzyme neutralizing antibodies.
It is interesting that although the underlying mechanisms for diversification and maturation of immunoglobulin repertoires in mammals are identical, trends towards certain lengths and amino acid compositions have been observed between different species. For instance, murine CDRH3 tend to be shorter than human CDRH3, while camelid VHH domains are characterized by long and protruding CDRH3 [18,29]. Although the biological significance of these differences remains unclear, these repertoires represent interesting sources of CDR diversity. The approach we describe is versatile as both synthetic sequences as well as naturally occurring CDRs can be captured and their specific properties exploited. For instance, the unusual features of bovine repertoires, featuring very elongated CDRH3 containing a disulfide-linked domain at their extremity, could potentially also be harnessed [38]. Alleviating the effort required for the creation of purpose oriented or focused libraries may lead to a more generalized use of such libraries. The isolation of antibodies based on human frameworks, and therefore suitable for therapeutic applications but having properties that are beyond the reach of the human immune system, could therefore be facilitated.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be accessed at: http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4468/4/2/103/s1.
Acknowledgments
We thank G. Didelot for his help in antibody reformatting, F. Gueneau for the design of antibody libraries and P. Malinge for BLI advice.
Author Contributions
The experiments were conceived by P.B., S.V. and N.F. and performed by P.B. and S.V. All authors contributed to the analysis of the data and to the redaction of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors are current or former employees of NovImmune S.A.
References
- Geyer, C.R.; McCafferty, J.; Dubel, S.; Bradbury, A.R.; Sidhu, S.S. Recombinant antibodies and in vitro selection technologies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 901, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCafferty, J.; Griffiths, A.D.; Winter, G.; Chiswell, D.J. Phage antibodies: Filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains. Nature 1990, 348, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binz, H.K.; Amstutz, P.; Pluckthun, A. Engineering novel binding proteins from nonimmunoglobulin domains. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, A.R.; Sidhu, S.; Dubel, S.; McCafferty, J. Beyond natural antibodies: The power of in vitro display technologies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Haard, H.J.; van, N.N.; Reurs, A.; Hufton, S.E.; Roovers, R.C.; Henderikx, P.; de Bruine, A.P.; Arends, J.W.; Hoogenboom, H.R. A large non-immunized human Fab fragment phage library that permits rapid isolation and kinetic analysis of high affinity antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 18218–18230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, C.; Lowe, D.; Edwards, B.; Welsh, F.; Dilks, T.; Hardman, C.; Vaughan, T. Modelling the human immune response: Performance of a 1011 human antibody repertoire against a broad panel of therapeutically relevant antigens. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2009, 22, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissim, A.; Hoogenboom, H.R.; Tomlinson, I.M.; Flynn, G.; Midgley, C.; Lane, D.; Winter, G. Antibody fragments from a 'single pot' phage display library as immunochemical reagents. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prassler, J.; Thiel, S.; Pracht, C.; Polzer, A.; Peters, S.; Bauer, M.; Norenberg, S.; Stark, Y.; Kolln, J.; Popp, A.; et al. HuCAL PLATINUM, a synthetic Fab library optimized for sequence diversity and superior performance in mammalian expression systems. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 413, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hust, M.; Dubel, S. Mating antibody phage display with proteomics. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, M.A.; Caothien, R.H.; Burton, D.R. Generation of diverse high-affinity human monoclonal antibodies by repertoire cloning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2432–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikunova, N.; Dubrovskaya, V.; Morozova, V.; Yun, T.; Khlusevich, Y.; Bormotov, N.; Laman, A.; Brovko, F.; Shvalov, A.; Belanov, E. The neutralizing human recombinant antibodies to pathogenic Orthopoxviruses derived from a phage display immune library. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobaugh, C.W.; Almagro, J.C.; Pogson, M.; Iverson, B.; Georgiou, G. Synthetic antibody libraries focused towards peptide ligands. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 378, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, H.; Lantto, J.; Ohlin, M. A focused antibody library for improved hapten recognition. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 357, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkham, P.M.; Neri, D.; Winter, G. Towards the design of an antibody that recognises a given protein epitope. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 285, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro-Riggers, J.; Liang, H.; DeVay, R.M.; Bai, L.; Sutton, J.E.; Chen, W.; Geng, T.; Lindquist, K.; Casas, M.G.; Boustany, L.M.; et al. Increasing serum half-life and extending cholesterol lowering in vivo by engineering antibody with pH-sensitive binding to PCSK9. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11090–11097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igawa, T.; Mimoto, F.; Hattori, K. pH-dependent antigen-binding antibodies as a novel therapeutic modality. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1844, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravn, U.; Gueneau, F.; Baerlocher, L.; Osteras, M.; Desmurs, M.; Malinge, P.; Magistrelli, G.; Farinelli, L.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.H.; Fischer, N. By-passing in vitro screening--next generation sequencing technologies applied to antibody display and in silico candidate selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venet, S.; Ravn, U.; Buatois, V.; Gueneau, F.; Calloud, S.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.; Fischer, N. Transferring the characteristics of naturally occurring and biased antibody repertoires to human antibody libraries by trapping CDRH3 sequences. PLoS One 2012, 7, e43471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonvin, P.; Venet, S.; Fontaine, G.; Ravn, U.; Gueneau, F.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.; Proudfoot, A.E.; Fischer, N. De novo isolation of antibodies with pH-dependent binding properties. MAbs 2015, 7, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Luscombe, N.M.; Swindells, M.B.; Thornton, J.M. Protein clefts in molecular recognition and function. Protein Sci. 1996, 5, 2438–2452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cope, P.A.; Mooser, G. Antibodies against active-site peptides common to glucosyltransferases of mutans streptococci. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 4814–4817. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Conrath, K.E.; Lauwereys, M.; Galleni, M.; Matagne, A.; Frere, J.M.; Kinne, J.; Wyns, L.; Muyldermans, S. Beta-lactamase inhibitors derived from single-domain antibody fragments elicited in the camelidae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 2807–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmyter, A.; Transue, T.R.; Ghahroudi, M.A.; Thi, M.H.; Poortmans, F.; Hamers, R.; Muyldermans, S.; Wyns, L. Crystal structure of a camel single-domain VH antibody fragment in complex with lysozyme. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1996, 3, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Genst, E.; Silence, K.; Decanniere, K.; Conrath, K.; Loris, R.; Kinne, J.; Muyldermans, S.; Wyns, L. Molecular basis for the preferential cleft recognition by dromedary heavy-chain antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4586–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauwereys, M.; Arbabi, G.M.; Desmyter, A.; Kinne, J.; Holzer, W.; De, G.E.; Wyns, L.; Muyldermans, S. Potent enzyme inhibitors derived from dromedary heavy-chain antibodies. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3512–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekiert, D.C.; Kashyap, A.K.; Steel, J.; Rubrum, A.; Bhabha, G.; Khayat, R.; Lee, J.H.; Dillon, M.A.; O'Neil, R.E.; Faynboym, A.M.; et al. Cross-neutralization of influenza A viruses mediated by a single antibody loop. Nature 2012, 489, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.S.; Ohshima, N.; Stanfield, R.L.; Yu, W.; Iba, Y.; Okuno, Y.; Kurosawa, Y.; Wilson, I.A. Receptor mimicry by antibody F045-092 facilitates universal binding to the H3 subtype of influenza virus. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3614. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rouet, R.; Dudgeon, K.; Christie, M.; Langley, D.; Christ, D. Fully human VH single domains that rival the stability and cleft recognition of camelid antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 11905–11917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemlin, M.; Klinger, M.; Link, J.; Zemlin, C.; Bauer, K.; Engler, J.A.; Schroeder, H.W., Jr.; Kirkham, P.M. Expressed murine and human CDR-H3 intervals of equal length exhibit distinct repertoires that differ in their amino acid composition and predicted range of structures. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 334, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, G.I.; Carlsson, G.H.; Smith, A.T.; Szoke, H.; Henriksen, A.; Hajdu, J. The catalytic pathway of horseradish peroxidase at high resolution. Nature 2002, 417, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veitch, N.C. Horseradish peroxidase: a modern view of a classic enzyme. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.F.; Ma, J.; Winter, C.; Bayer, R. Recovery and purification process development for monoclonal antibody production. MAbs 2010, 2, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, M.P.; Giudicelli, V.; Ginestoux, C.; Bodmer, J.; Muller, W.; Bontrop, R.; Lemaitre, M.; Malik, A.; Barbie, V.; Chaume, D. IMGT, the international ImMunoGeneTics database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madden, T. The BLAST Sequence Analysis Tool. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK153387/ (accessed on 12 May 2015).
- Ravn, U.; Didelot, G.; Venet, S.; Ng, K.T.; Gueneau, F.; Rousseau, F.; Calloud, S.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.; Fischer, N. Deep sequencing of phage display libraries to support antibody discovery. Methods 2013, 60, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, N.; Elson, G.; Magistrelli, G.; Dheilly, E.; Fouque, N.; Laurendon, A.; Gueneau, F.; Ravn, U.; Depoisier, J.F.; Moine, V.; et al. Exploiting light chains for the scalable generation and platform purification of native human bispecific IgG. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deruaz, M.; Bonvin, P.; Severin, I.C.; Johnson, Z.; Krohn, S.; Power, C.A.; Proudfoot, A.E. Evasin-4, a tick-derived chemokine-binding protein with broad selectivity can be modified for use in preclinical disease models. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4876–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Ekiert, D.C.; Ahmad, I.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bazirgan, O.; Torkamani, A.; Raudsepp, T.; Mwangi, W.; Criscitiello, M.F.; et al. Reshaping antibody diversity. Cell 2013, 153, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).