Kinetic Characterization of a Panel of High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Ricin and Recombinant Re-Formatting for Biosensor Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Production and Characterization of a Panel of Six Anti-Ricin mAbs
2.2. Epitope Binding Analysis of mAbs
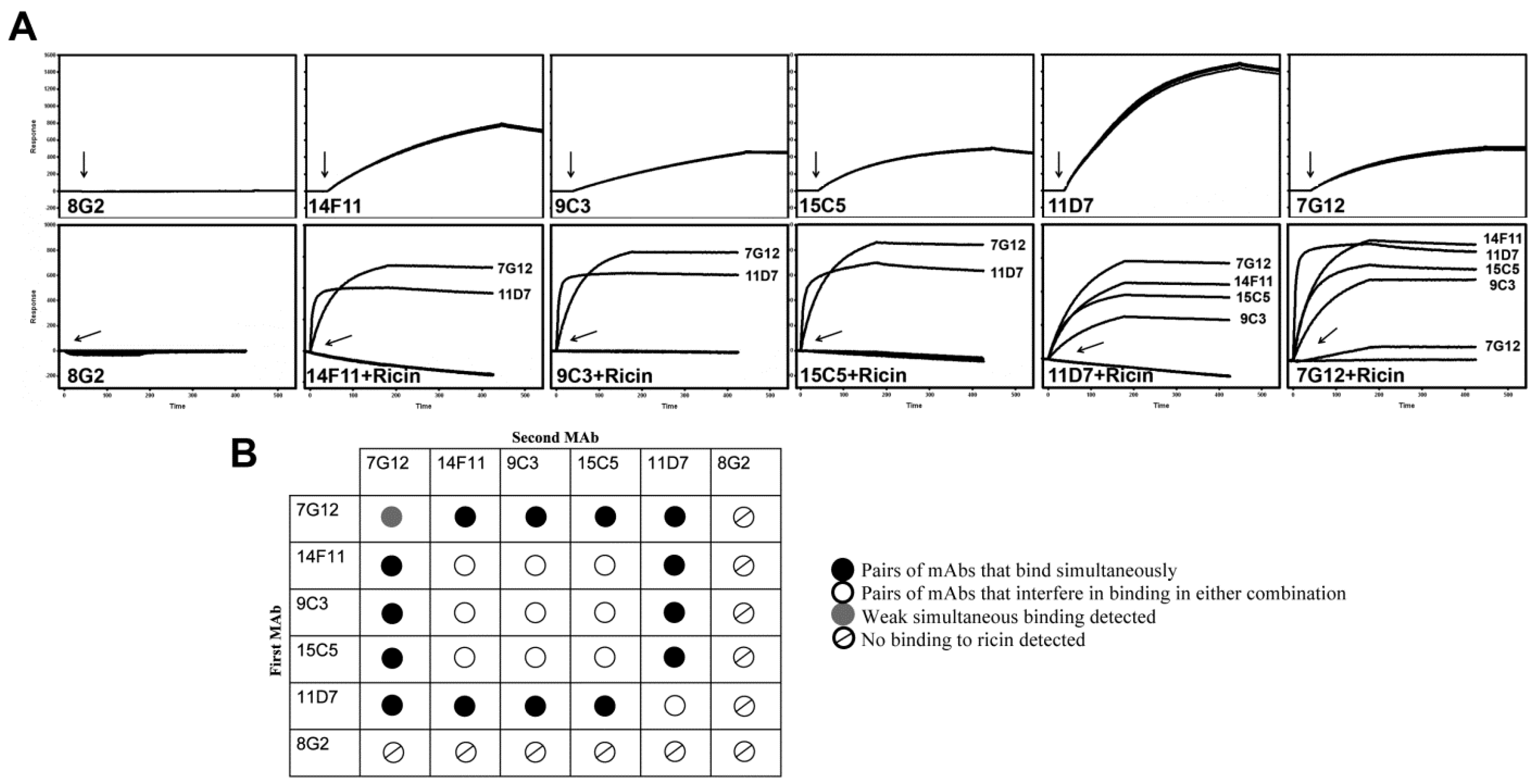
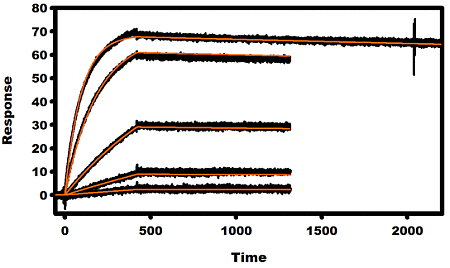
2.3. Kinetic Analysis of mAbs
| mAb | Analyte | ka × 104 (M−1 s−1) | kd × 10−4 (s−1) | KD (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7G12 | RT | 21.2 ± 0.3 | 0.30 ± 0.17 | 0.15 ± 0.08 |
| RTA | 64.7 ± 6.6 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 0.13 ± 0.2 | |
| 9C3 | RT | 11.7 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.2 |
| RTB | 14.0 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | |
| 11D7 | RT | 74.0 ± 1.8 | 9.5 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.1 |
| RTB | 94 ± 16 | 9.2 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ±0.2 | |
| 14F11 | RT | 16.5 ± 0.6 | 14.5 ± 0.9 | 8.9 ± 0.9 |
| RTB | 18.0 ± 1.3 | 11.0 ± 2.2 | 6.0 ± 0.7 | |
| 15C5 | RT | 21.3 ± 0.9 | 5.0 ± 0.3 | 2.4 ± 0.2 |
| RTB | 24.0 ± 2.8 | 4.0 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | |
| 8G2 | RT/RTA | NBD | NBD | NBD |
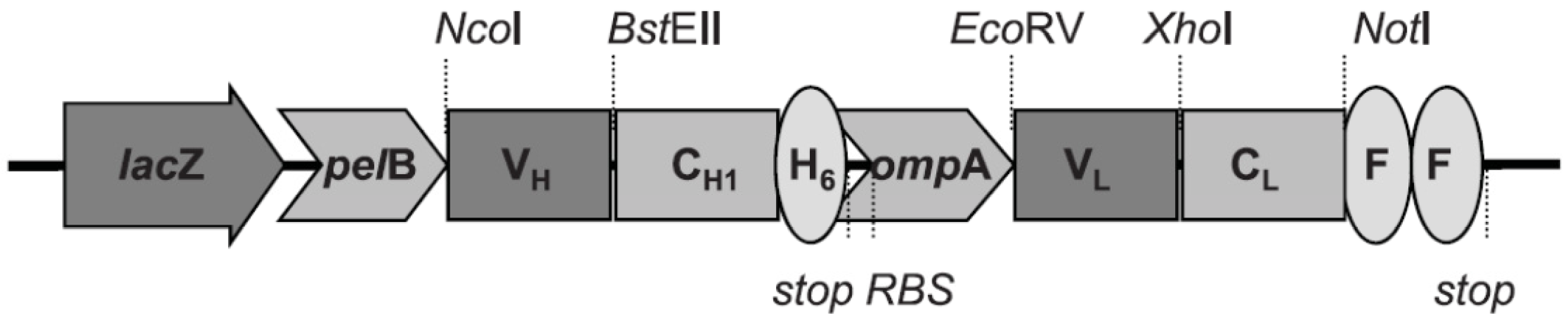
2.4. Recombinant Fab Antibody Engineering


| rFab | ka × 104 (M−1 s−1) | kd × 10−4 (s−1) | KD (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14F11 | 18.7 ± 0.8 | 50.0 ± 0.1 | 27.0 ± 0.6 |
| 9C3 | 9.9 ± 0.5 | 2.32 ± 0.02 | 2.3 ± 0.1 |
| Chained-shuffled | 23.4 ± 0.5 | 0.21 ± 0.07 | 0.13 ± 0.02 |
2.5. Antibody Neutralization of Ricin-Mediated Cytotoxicity Assays
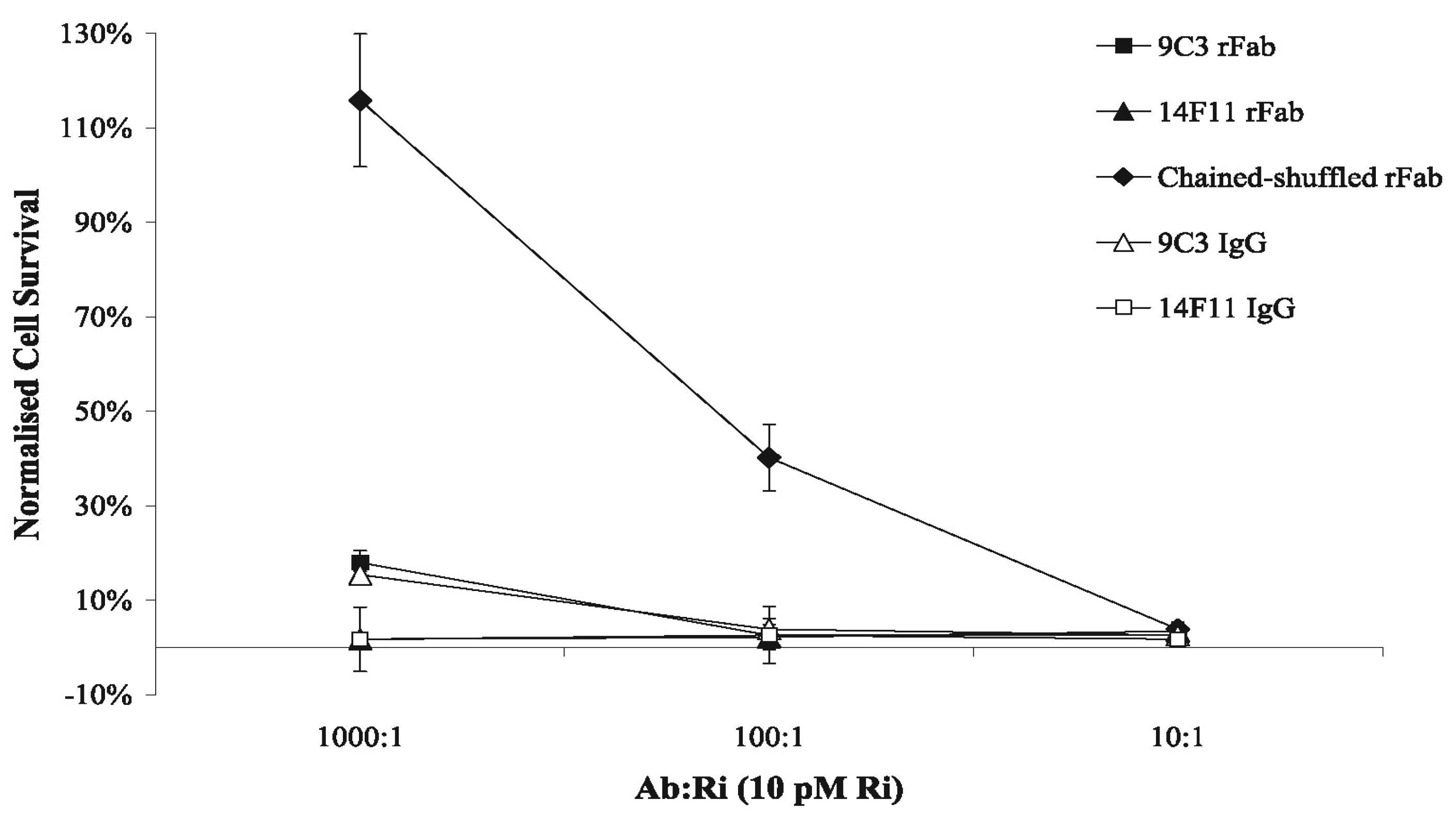
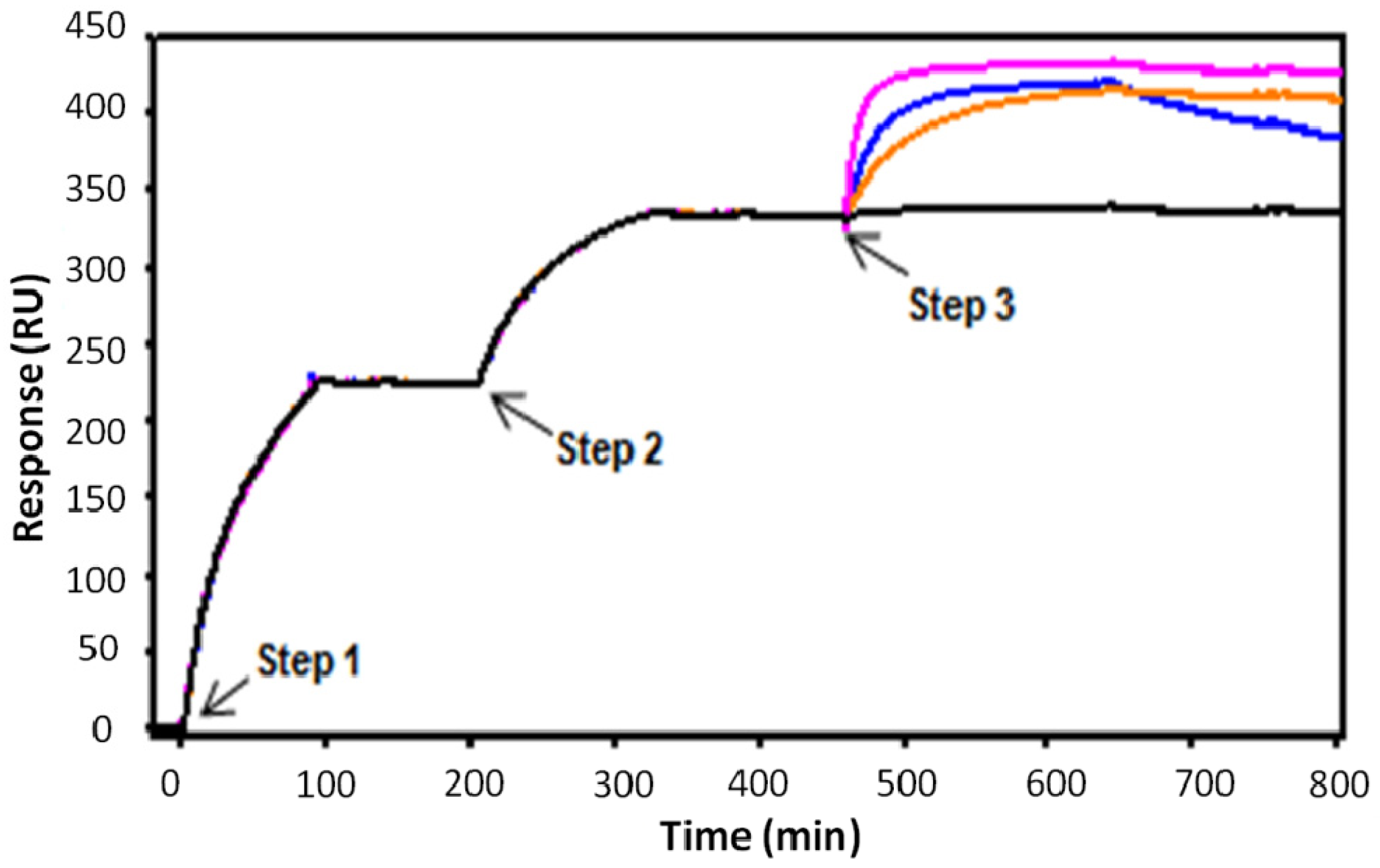
3. Experimental
3.1. Ricin and Chemical Reagents
| Primer designation | Sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| A1437 | CAGGTCACTGTCACTGGCTCAG |
| A1436 | CTTCCACTTGACATTGATGTCTTTG |
| Poly-C anchor sense | ATCGATGAATTCGGATCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC |
| A1706 | TGCAGAGACGGTGACCAGAGTCCCTTGGCCCCA |
| A1713 | CAGCCGGCCATGGCTGAGGTCCAGCTGCAGCAG |
| 9C3-K5' | GACGCCGATATCGATGACCCAAACTCCACT |
| 9C3-K3' | TTTTATCTCGAGCTTGGTCCCCCCGCCGAA |
| 15C5-K5' | CAGGCCGATATCGTGATGACCCAAACTCCA |
| 14F11-K3' | TTTCAGCTCGAGCTTGGTCCCAGCACCGAA |
3.2. Cultivation of Hybridoma Cell Lines and Production of mAbs
3.3. Purification of mAbs
3.4. Cloning and Sequencing of Antibody Variable Regions
3.5. Plasmid Vector Construction, Expression and Purification of Anti-Ricin rFabs
3.6. Epitope Binning Experiments
3.7. Kinetic Binding Analysis of mAbs
3.8. Kinetic Binding Analysis of rFabs
3.9. Antibody Neutralization of Ricin-Mediated Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Authors Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foxwell, B.M.; Detre, S.I.; Donovan, T.A.; Thorpe, P.E. The use of anti-ricin antibodies to protect mice intoxicated with ricin. Toxicology 1985, 34, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.W.; Shen, B.F.; Feng, J.N.; Sun, Y.X.; Yu, M.; Hu, M.R. A novel neutralizing monoclonal antibody against cell-binding polypeptide of ricin. Hybridoma (Larchmt) 2005, 24, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsnes, S.; Pihl, A. Different biological properties of the two constituent peptide chains of ricin, a toxic protein inhibiting protein synthesis. Biochemistry 1973, 12, 3121–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baenziger, J.U.; Fiete, D. Structural determinants of ricinus communis agglutinin and toxin specificity for oligosaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 9795–9799. [Google Scholar]
- Alami, M.; Taupiac, M.P.; Beaumelle, B. Ricin-binding proteins along the endocytic pathway: The major endosomal ricin-binding protein is endosome-specific. Cell Biol. Int. 1997, 21, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, J.M.; Deeks, E.; Marsden, C.J.; Moore, K.; Pateman, C.; Smith, D.C.; Spooner, R.A.; Watson, P.; Roberts, L.M. Retrograde transport of toxins across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003, 31, 1260–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandvig, K.; Ryd, M.; Garred, O.; Schweda, E.; Holm, P.K.; van Deurs, B. Retrograde transport from the golgi complex to the er of both shiga toxin and the nontoxic shiga b-fragment is regulated by butyric acid and camp. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 126, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlsna, D.; Monzingo, A.F.; Katzin, B.J.; Ernst, S.; Robertus, J.D. Structure of recombinant ricin a chain at 2.3 a. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.Y.; Link, T.M.; Schramm, V.L. Ricin a-chain: Kinetics, mechanism, and rna stem-loop inhibitors. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 11605–11613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Mitsui, K.; Motizuki, M.; Tsurugi, K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 s ribosomal rna caused by the toxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 5908–5912. [Google Scholar]
- Pincus, S.H.; Smallshaw, J.E.; Song, K.; Berry, J.; Vitetta, E.S. Passive and active vaccination strategies to prevent ricin poisoning. Toxins (Basel) 2011, 3, 1163–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, C.R.; Mantis, N.J. Characterization of a novel high-affinity monoclonal immunoglobulin g antibody against the ricin b subunit. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3463–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisler, R.B.; Smith, L.A. The need for continued development of ricin countermeasures. Adv. Prev. Med. 2012, 2012, 149737. [Google Scholar]
- Smallshaw, J.E.; Vitetta, E.S. A lyophilized formulation of rivax, a recombinant ricin subunit vaccine, retains immunogenicity. Vaccine 2010, 28, 2428–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, L.M.; O'Hara, J.; Brey, R.N.; Mantis, N.J. A monoclonal immunoglobulin g antibody directed against an immunodominant linear epitope on the ricin a chain confers systemic and mucosal immunity to ricin. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigent, J.; Panigai, L.; Lamourette, P.; Sauvaire, D.; Devilliers, K.; Plaisance, M.; Volland, H.; Creminon, C.; Simon, S. Neutralising antibodies against ricin toxin. PLoS One 2011, 6, e20166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.G.; Yin, J.; Chau, D.; Negrych, L.M.; Cherwonogrodzky, J.W. Humanization and characterization of an anti-ricin neutralization monoclonal antibody. PLoS One 2012, 7, e45595. [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan, C. Fresh from the biologic pipeline-2009. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, Y.; Hong, H.J. Antibody engineering for the development of therapeutic antibodies. Mol. Cells 2005, 20, 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Pelat, T.; Hust, M.; Hale, M.; Lefranc, M.P.; Dübel, S.; Thullier, P. Isolation of a human-like antibody fragment (scfv) that neutralizes ricin biological activity. BMC Biotechnol. 2009, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.P.; Liu, J.L.; Hale, M.L.; Bernstein, R.D.; Moore, M.; Swain, M.D.; Goldman, E.R. Development of antiricin single domain antibodies toward detection and therapeutic reagents. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9604–9611. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, G.P.; Bernstein, R.D.; Swain, M.D.; Zabetakis, D.; Goldman, E.R. Binding kinetics of antiricin single domain antibodies and improved detection using a b chain specific binder. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7202–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walper, S.A.; Brozozog Lee, P.A.; Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P. Comparison of single domain antibody immobilization strategies evaluated by surface plasmon resonance. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 388, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dertzbaugh, M.T.; Rossi, C.A.; Paddle, B.M.; Hale, M.; Poretski, M.; Alderton, M.R. Monoclonal antibodies to ricin: In vitro inhibition of toxicity and utility as diagnostic reagents. Hybridoma (Larchmt) 2005, 24, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; Leong, C.; Loke, W.K.; Dogovski, C.; Liu, C.Q. Surface plasmon resonance detection of ricin and horticultural ricin variants in environmental samples. Toxicon 2008, 52, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.E.; Navarro, P.; Sun, J. Adsorption-induced antigenic changes and their significance in elisa and immunological disorders. Immunol. Invest. 1997, 26, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.P.; Glaven, R.H.; Algar, W.R.; Susumu, K.; Stewart, M.H.; Medintz, I.L.; Goldman, E.R. Single domain antibody-quantum dot conjugates for ricin detection by both fluoroimmunoassay and surface plasmon resonance. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 786, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Luo, Q.; Guo, L.; Lv, M.; Lin, Z.; Geng, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Shen, B.; Qiao, C.; et al. Structure-based affinity maturation of a chimeric anti-ricin antibody c4c13. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, D.J.; Tremblay, J.M.; Mantis, N.J.; Shoemaker, C.B. Stepwise engineering of heterodimeric single domain camelid vhh antibodies that passively protect mice from ricin toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 36538–36547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Mize, R.R.; Marrero, L.; Corti, M.; Kirk, J.M.; Pincus, S.H. Antibody to ricin a chain hinders intracellular routing of toxin and protects cells even after toxin has been internalized. PLoS One 2013, 8, e62417. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, S.C.; von Hippel, P.H. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 182, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, L.K.; Norris, N.A.; Marquardt, H.; Tsu, T.T.; Hayden, M.S.; Neubauer, M.G.; Yelton, D.E.; Mittler, R.S.; Ledbetter, J.A. Rapid and reliable cloning of antibody variable regions and generation of recombinant single chain antibody fragments. Tissue Antigens 1996, 47, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coia, G.; Ayres, A.; Lilley, G.G.; Hudson, P.J.; Irving, R.A. Use of mutator cells as a means for increasing production levels of a recombinant antibody directed against hepatitis b. Gene 1997, 201, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezal, O.; Pearce, L.A.; Lawrence, L.J.; McCoy, A.J.; Hudson, P.J.; Kortt, A.A. Scfv multimers of the anti-neuraminidase antibody nc10: Shortening of the linker in single-chain fv fragment assembled in v(l) to v(h) orientation drives the formation of dimers, trimers, tetramers and higher molecular mass multimers. Protein Eng. 2000, 13, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, R.; Streltsov, V.A.; Newman, J.; Pearce, L.A.; Wark, K.L.; Dolezal, O. Germline humanization of a murine abeta antibody and crystal structure of the humanized recombinant fab fragment. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdiche, Y.; Malashock, D.; Pinkerton, A.; Pons, J. Determining kinetics and affinities of protein interactions using a parallel real-time label-free biosensor, the octet. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 377, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravman, T.; Bronner, V.; Lavie, K.; Notcovich, A.; Papalia, G.A.; Myszka, D.G. Exploring “one-shot” kinetics and small molecule analysis using the proteon xpr36 array biosensor. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 358, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalia, G.A.; Baer, M.; Luehrsen, K.; Nordin, H.; Flynn, P.; Myszka, D.G. High-resolution characterization of antibody fragment/antigen interactions using biacore t100. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 359, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cummins, M.; Dogovski, C.; Robert, R.; Alderton, M.; Chong, D.; Proll, D.; Pontes-Braz, L.; Raicevic, A.; Hattarki, M.; Nuttall, S.; et al. Kinetic Characterization of a Panel of High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Ricin and Recombinant Re-Formatting for Biosensor Applications. Antibodies 2014, 3, 215-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib3020215
Cummins M, Dogovski C, Robert R, Alderton M, Chong D, Proll D, Pontes-Braz L, Raicevic A, Hattarki M, Nuttall S, et al. Kinetic Characterization of a Panel of High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Ricin and Recombinant Re-Formatting for Biosensor Applications. Antibodies. 2014; 3(2):215-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib3020215
Chicago/Turabian StyleCummins, Michelle, Con Dogovski, Remy Robert, Malcolm Alderton, Damien Chong, David Proll, Luisa Pontes-Braz, Anna Raicevic, Meghan Hattarki, Stewart Nuttall, and et al. 2014. "Kinetic Characterization of a Panel of High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Ricin and Recombinant Re-Formatting for Biosensor Applications" Antibodies 3, no. 2: 215-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib3020215
APA StyleCummins, M., Dogovski, C., Robert, R., Alderton, M., Chong, D., Proll, D., Pontes-Braz, L., Raicevic, A., Hattarki, M., Nuttall, S., & Dolezal, O. (2014). Kinetic Characterization of a Panel of High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Ricin and Recombinant Re-Formatting for Biosensor Applications. Antibodies, 3(2), 215-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib3020215