Engineered Bovine Antibodies in the Development of Novel Therapeutics, Immunomodulators and Vaccines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Designing Antibody Fragments of Desired Function
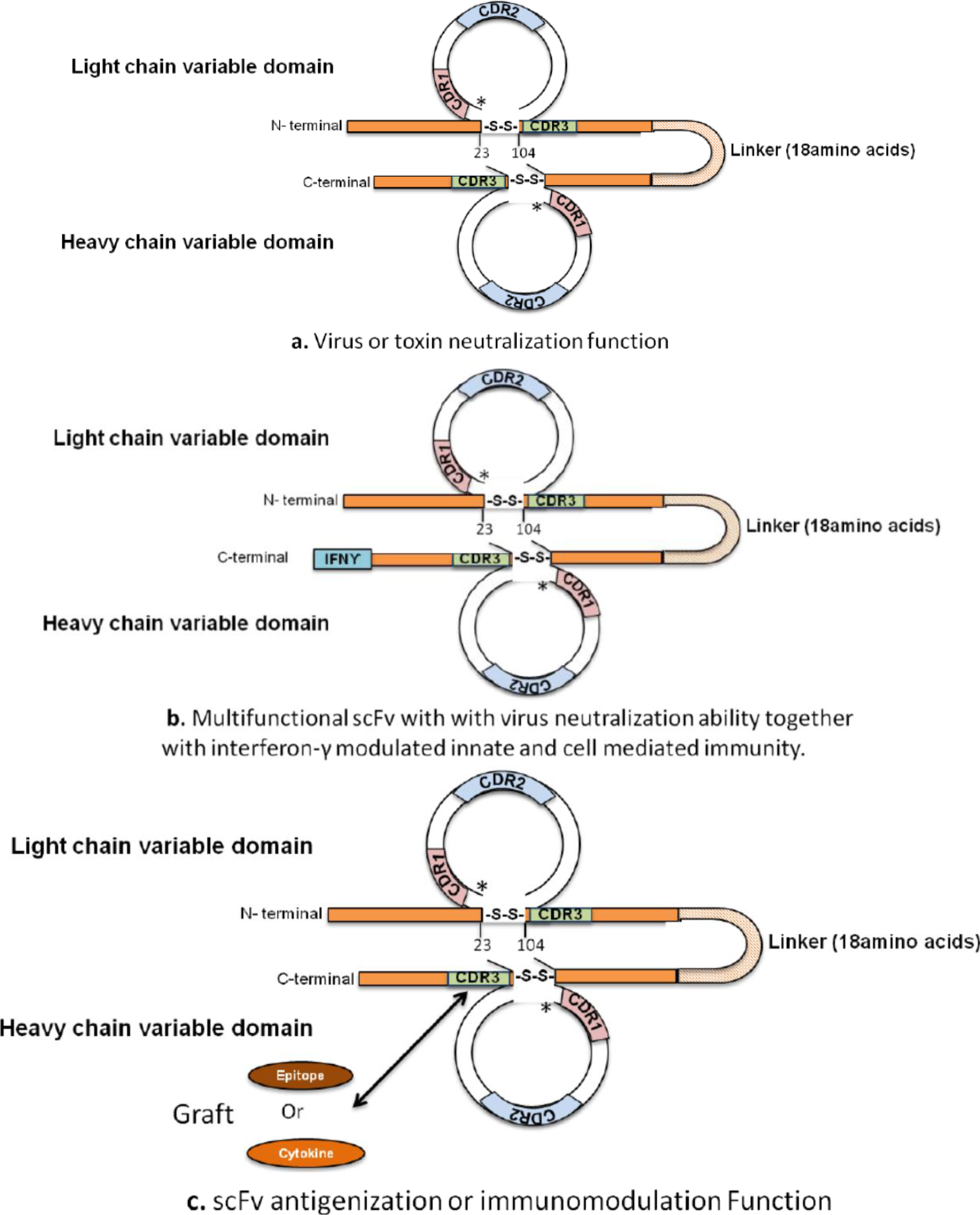
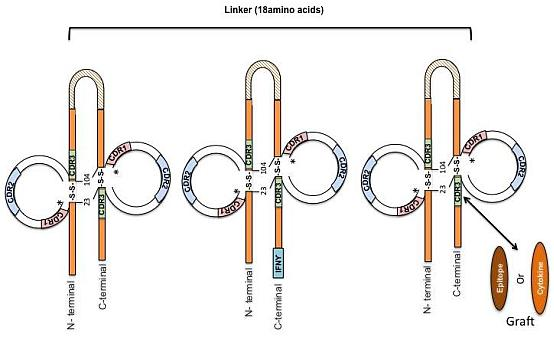
4. Development of Immunomodulating Drugs and Vaccines
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lefranc, M.-P.; Lefranc, G. The Immunoglobulin Factsbook; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, S.S.; Hein, W.R.; Kaushik, A. A single predominantly expressed polymorphic immunoglobulin VH gene family, related to mammalian group, I, clan, II, is identified in cattle. Mol. Immunol. 1997, 34, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasman, Y.; Saini, S.S.; Smith, E.; Kaushik, A.K. Organization and genomic complexity of bovine lambda-light chain gene locus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 135, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasman, Y.; Bhogal, R.; Kaushik, A.K. Novel perspective on antibody diversification from bovine immunoglobulin genetics. In Cattle: Domestication, Diseases and Environment; Liu, G., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, A.K.; Kehrli, M.E., Jr.; Kurtz, A.; Ng, S.; Koti, M.; Shojaei, F.; Saini, S.S. Somatic hypermutations and isotype restricted exceptionally long CDR3H contribute to antibody diversification in cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 127, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.S.; Allore, B.; Jacobs, R.M.; Kaushik, A. Exceptionally long CDR3H region with multiple cysteine residues in functional bovine IgM antibodies. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 2420–2426. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, S.S.; Farrugia, W.; Ramsland, P.A.; Kaushik, A.K. Bovine IgM antibodies with exceptionally long complementarity-determining region 3 of the heavy chain share unique structural properties conferring restricted VH + Vlambda pairings. Int. Immunol. 2003, 15, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.S.; Kaushik, A. Extensive CDR3H length heterogeneity exists in bovine fetal VDJ rearrangements. Scand.J. Immunol. 2002, 55, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, F.; Saini, S.S.; Kaushik, A.K. Unusually long germline DH genes contribute to large sized CDR3H in bovine antibodies. Mol. Immunol. 2003, 40, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Koti, M.; Kataeva, G.; Kaushik, A.K. Novel atypical nucleotide insertions specifically at VH-DH junction generate exceptionally long CDR3H in cattle antibodies. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 2119–2128. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, A.; Shojaei, F.; Saini, S.S. Novel insight into antibody diversification from cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2002, 87, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koti, M.; Kataeva, G.; Kaushik, A.K. Organization of D(H)-gene locus is distinct in cattle. Dev. Biol. (Basel) 2008, 132, 307–313. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, P.A.; Smith, P.L. Application of circular consensus sequencing and network analysis to characterize the bovine IgG repertoire. BMC Immunol. 2012, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, S.; Czerny, C.P.; Diesterbeck, U.S. Exceptionally long CDR3H are not isotype restricted in bovine immunoglobulins. PLoS One 2013, 8, e64234. [Google Scholar]
- Dubel, S. Handbook of Therapeutic Antibodies; Weiley-Blackwell: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; p. 1204. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Ekiert, D.C.; Ahmad, I.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bazirgan, O.; Torkamani, A.; Raudsepp, T.; Mwangi, W.; Criscitiello, M.F.; et al. Reshaping antibody diversity. Cell 2013, 153, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Wurch, T.; Bailly, C.; Corvaia, N. Strategies and challenges for the next generation of therapeutic antibodies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.L.; Dhimolea, E.; Reichert, J.M. Development trends for human monoclonal antibody therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekke, O.H.; Sandlie, I. Therapeutic antibodies for human diseases at the dawn of the twenty-first century. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.L. Antibody fragments: Hope and hype. MAbs 2010, 2, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontermann, R.E. Strategies for extended serum half-life of protein therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Dimitrov, D.S. Human monoclonal antibodies and engineered antibody domains as HIV-1 entry inhibitors. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2009, 4, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.G.; Clatworthy, M.R. FcgammaRIIB in autoimmunity and infection: Evolutionary and therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koti, M.; Farrugia, W.; Nagy, E.; Ramsland, P.A.; Kaushik, A.K. Construction of single-chain Fv with two possible CDR3H conformations but similar inter-molecular forces that neutralize bovine herpesvirus 1. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 953–960. [Google Scholar]
- Pasman, Y.; Nagy, E.; Kaushik, A.K. Enhanced bovine herpesvirus type 1 neutralization by multimerized single-chain variable antibody fragments regardless of differential glycosylation. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, L.M.; Surana, R.; Wang, S. Monoclonal antibodies: Versatile platforms for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, L.M.; Murray, J.C.; Shuptrine, C.W. Antibody-based immunotherapy of cancer. Cell 2012, 148, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyn, M.; Bremer, E.; Helfrich, W. Antibody-based fusion proteins to target death receptors in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A.C.; Carter, P.J. Therapeutic antibodies for autoimmunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, M.J.; Monroe, J.G.; Chan, A.C. B-cell targeted therapies in human autoimmune diseases: An updated perspective. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 237, 264–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefranc, M.P.; Pommié, C.; Ruiz, M.; Giudicelli, V.; Foulquier, E.; Truong, L.; Thouvenin-Contet, V.; Lefranc, G. IMGT unique numbering for immunoglobulin and T cell receptor variable domains and Ig superfamily V-like domains. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 27, 55–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kaas, Q.; Ehrenmann, F.; Lefranc, M.P. IG, TR and IgSF, MHC and MhcSF: What do we learn from the IMGT Colliers de Perles? Brief. Funct. Genomics Proteomics 2007, 6, 253–264. [Google Scholar]
- Billetta, R.; Hollingdale, M.R.; Zanetti, M. Immunogenicity of an engineered internal image antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4713–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, M.; Rossi, F.; Lanza, P.; Filaci, G.; Lee, R.H.; Billetta, R. Theoretical and practical aspects of antigenized antibodies. Immunol. Rev. 1992, 130, 125–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerne, N.K. The Nobel Lectures in Immunology. The Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine, 1984. The generative grammar of the immune system. Scand. J. Immunol. 1993, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti, M. Antigenized antibodies. Nature 1992, 355, 476–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumeanu, T.D.; Bot, A.; Bona, C.A.; Dehazya, P.; Wolf, I.; Zaghouani, H. Engineering of doubly antigenized immunoglobulins expressing T and B viral epitopes. Immunotechnology 1996, 2, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musselli, C.; Daverio-Zanetti, S.; Zanetti, M. Antigenized antibodies expressing Vbeta8.2 TCR peptides immunize against rat experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J. Immune Based Ther. Vaccines 2004, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, P.; Billetta, R.; Antonenko, S.; Zanetti, M. Active immunity against the CD4 receptor by using an antibody antigenized with residues 41–55 of the first extracellular domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11683–11687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billetta, R.; Zanetti, M. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of antigenized antibodies. Studies on B and T cells. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1993, 10, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, Y. Epitope-grafted and antigenized antibodies can be used for versatile vaccination strategies to induce epitope-specific immune responses. J. Nippon Med. Sch. 2011, 78, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechl, J.; Molnár, E.; Szekeres, Z.; Isaák, A.; Papp, K.; Balogh, P.; Erdei, A. Murine CR1/2 targeted antigenized single-chain antibody fragments induce transient low affinity antibodies and negatively influence an ongoing immune response. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 598, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.F.; Lu, P.; Suen, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.F. Construction, expression, purification, refold and activity assay of a specific scFv fragment against foot and mouth disease virus. Vet. Res. Commun. 2003, 27, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, G.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Brewster, J.D. Single-chain Fv antibody with specificity for Listeria monocytogenes. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 289, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.; Hinz, D.; Bannantine, J.P.; Griffin, J.F.T. Isolation of high-affinity single-chain antibodies against Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis surface proteins from sheep with Johne’s disease. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinale, A.; Filesi, I.; Vetrugno, V.; Pocchiari, M.; Sy, M.S.; Biocca, S. Trapping prion protein in the endoplasmic reticulum impairs PrPC maturation and prevents PrPSc accumulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 685–694. [Google Scholar]
- Donofrio, G.; Heppner, F.L.; Polymenidou, M.; Musahl, C.; Aguzzi, A. Paracrine inhibition of prion propagation by anti-PrP single-chain Fv miniantibodies. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8330–8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padiolleau-Lefevre, S.; Alexandrenne, C.; Dkhissi, F.; Clement, G.; Essono, S.; Blache, C.; Couraud, J.Y.; Wijkhuisen, A.; Boquet, D. Expression and detection strategies for an scFv fragment retaining the same high affinity than Fab and whole antibody: Implications for therapeutic use in prion diseases. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 1888–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koti, M.; Nagy, E.; Kaushik, A.K. A single point mutation in framework region 3 of heavy chain affects viral neutralization dynamics of single-chain Fv against bovine herpes virus type 1. Vaccine 2011, 29, 7905–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.M.; Aitken, R.; O’Neil, B.W.; Campo, M.S. Generation of native bovine mAbs by phage display. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 640–645. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lebreton, F.; Kaiser, C.; Crucière, C.; Rémond, M. Isolation of foot-and-mouth disease virus specific bovine antibody fragments from phage display libraries. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 286, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.-L.; Welzel, G.; Wang, Y.; Schultz, P.G.; Wang, F. An antibody CDR3-erythropoietin fusion protein. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2117–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; de Lichtervelde, L.; Sun, S.B.; Smider, V.V.; Schultz, P.G.; Wang, F. Functional antibody CDR3 fusion proteins with enhanced pharmacological properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 8295–8298. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Goswami, D.; Wang, D.; Wang, T.-S.A.; Sen, S.; Magliery, T.J.; Griffin, P.R.; Schultz, P.G.; Wang, F. An antibody with a variable-region coiled-coil “knob” domain. Angew. Chem. Int.Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Koti, M.; Saini, S.S.; Sachan, A.; Kaushik, A.K. Engineered Bovine Antibodies in the Development of Novel Therapeutics, Immunomodulators and Vaccines. Antibodies 2014, 3, 205-214. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib3020205
Koti M, Saini SS, Sachan A, Kaushik AK. Engineered Bovine Antibodies in the Development of Novel Therapeutics, Immunomodulators and Vaccines. Antibodies. 2014; 3(2):205-214. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib3020205
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoti, Madhuri, Surinder S. Saini, Ashish Sachan, and Azad K. Kaushik. 2014. "Engineered Bovine Antibodies in the Development of Novel Therapeutics, Immunomodulators and Vaccines" Antibodies 3, no. 2: 205-214. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib3020205
APA StyleKoti, M., Saini, S. S., Sachan, A., & Kaushik, A. K. (2014). Engineered Bovine Antibodies in the Development of Novel Therapeutics, Immunomodulators and Vaccines. Antibodies, 3(2), 205-214. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib3020205