Antibodies for β2-Microglobulin and the Heavy Chains of HLA-E, HLA-F, and HLA-G Reflect the HLA-Variants on Activated Immune Cells and Phases of Disease Progression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients under Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Information on the Patient Cohort
2.2. Immunoregulatory Drugs Received by the Patient Cohort
| Chemotherapy Regimens for RA | Number of Patients with Serum IgM & IgG Antibodies Reacting to β2M, HLA-E/-F & G in Each Group | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methotrexate | Folic Acid | Chloroquine | ARAVA | Azulfidine | ACEI | Prednisone | Azathioprine | Omeprazole | Thyroid enzyme | Group 1 Table 2 14/16 | Group2 Table 3 23/24 | Group 3 Table 4 15/15 | Group 4 Table 5 6/6 | Group 5 Table 6 5/5 | Group 6 Table 7 2/3 | |
| 1 | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | |||||
| 2 | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | ||||
| 3 | [+] | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 6 | 3 | 1 | ||
| 4 | [+] | [+] | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | |||||
| 5 | [+] | [+] | [+] | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 6 | [+] | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | [+] | - | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 7 | [+] | [+] | [+] | - | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 8 | [+] | [+] | - | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | ||||
| 9 | [+] | [+] | - | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 10 | [+] | [+] | - | [+] | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 11 | [+] | [+] | - | [+] | - | - | [+] | - | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 12 | [+] | [+] | - | [+] | [+] | [+] | [+] | [+] | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 13 | [+] | [+] | - | - | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 14 | [+] | [+] | - | - | [+] | - | [+] | - | [+] | - | 1 | |||||
| 15 | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | - | [+] | [+] | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 16 | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | - | [+] | - | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 17 | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | - | [+] | - | [+] | - | 1 | |||||
| 18 | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | - | [+] | - | 1 | |||||
| 19 | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | [+] | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 20 | [+] | - | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 21 | [+] | - | [+] | - | - | - | [+] | - | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 22 | [+] | - | [+] | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 23 | [+] | - | [+] | - | - | [+] | - | - | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 24 | [+] | - | - | - | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | |||||
| 25 | [+] | - | - | - | - | [+] | - | - | - | - | 2 | |||||
| 26 | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | [+] | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | ||||
| 27 | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | [+] | - | 1 | |||||
| 28 | - | - | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | |||||
| 29 | - | - | [+] | - | - | - | - | - | [+] | - | 1 | |||||
| 30 | - | - | [+] | [+] | [+] | - | [+] | - | [+] | - | 1 | |||||
| 31 | - | - | - | [+] | - | [+] | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 32 | - | - | - | [+] | - | [+] | - | - | [+] | [+] | 1 | |||||
| Patient ID | Other Complications | Treatment at Sampling | β2M | HLA-E HLA-F HLA-G Heavy Chains | β2M | HLA-E HLA-F HLA-G Heavy Chains | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgM | IgM | IgM | IgM | IgG | IgG | IgG | IgG | ||||
| 1 | Alb-RA136F39 | Met/Chlrqn/Predns | 0 | 953 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | Alb-RA018M30 | Met/Folic/Azulf | 0 | 3721 | 1359 | 1747 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1012 | |
| 3 | Alb-RA121F60 | Met/Chlrqn/ | 0 | 771 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 585 | 0 | |
| 4 | Alb-RA112F39 | Hypertns | Met/Folic/Azat/Predns | 0 | 1172 | 553 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 585 | 0 |
| 5 | Alb-RA 106F47 | Met/Folic/ ACEI | 0 | 2286 | 1011 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 518 | 777 | |
| 6 | Alb-RA113F77 | Met/Chlrqn/ | 0 | 669 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 558 | 1227 | |
| 7 | Alb-RA082F51 | 0 | 923 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 888 | 862 | ||
| 8 | Alb-RA045F32 | 0 | 651 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 867 | 1218 | 0 | ||
| 9 | Alb-RA 125F43 | Met/Folic | 0 | 500 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 736 | 2099 | 1027 | |
| 10 | Alb-RA 034F48 | Met/Chlrqn/ Folic/Azulf/ | 0 | 1695 | 0 | 622 | 0 | 987 | 774 | 1407 | |
| 11 | Alb-RA129F28 | Met/Chlrqn/ Folic | 0 | 2207 | 615 | 0 | 0 | 748 | 2330 | 1392 | |
| 12 | Alb-RA127M47 | Folic/Met/ Chlrqn/ | 0 | 2780 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 607 | 653 | 2957 | |
| 13 | Alb-RA 095F64 | Hypertns/diabet | Met/Folic | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1498 | 0 | 0 | 753 | 779 |
| 14 | Alb-RA098F64 | Hypertns | Met/Chlrqn/Folic/ | 0 | 0 | 666 | 0 | 0 | 602 | 627 | 1317 |
| 15 | Alb-RA012F57 | Met/Chlrqn/ | 0 | 0 | 1258 | 0 | 0 | 811 | 1357 | 1306 | |
| 16 | Alb-RA 021F65 | SLE/Hypertns diabetics | Azulf | 0 | 1806 | 769 | 1035 | 0 | 1175 | 1242 | 1380 |
| Patient ID | Other Complications | Treatment at Sampling | β2M | HLA-E HLA-F HLA-G Heavy Chains | β2M | HLA-E HLA-F HLA-G Heavy Chains | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgM | IgM | IgM | IgM | IgG | IgG | IgG | IgG | ||||
| 1 | Alb-RA032F54 | Met/Chlrqn | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 520 | 0 | |
| 2 | Alb-RA039M31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 682 | 0 | ||
| 3 | Alb-RA031M71 | Met | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 817 | 0 | |
| 4 | Alb-RA107F65 | Met/chlrqn | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1952 | 0 | |
| 5 | Alb-RA 096F41 | Met/Chlrqn/Folic | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 647 | 0 | |
| 6 | Alb-RA126M26 | Met/Chlrqn/Folic/ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1416 | |
| 7 | Alb-RA102F61 | Hyprtns/Thrmbss | Met/Folic/ ARAVA/Azulf/ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 668 | 547 |
| 8 | Alb-RA094M66 | Dyslipid | Met/Folic/ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 660 | 4138 |
| 9 | Alb-RA037F51 | Met/Chlrqn/Folic/ARAVA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1163 | 1763 | |
| 10 | Alb-RA049M66 | SysVasc/ Hyprtns/ dslIpid/Ren Dis | Met/Folic | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1294 | 946 |
| 11 | Alb-RA002F35 | Met/Folic/Arav | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1587 | 872 | |
| 12 | Alb-RA115M40 | Met/Omprz | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 512 | 645 | 0 | |
| 13 | Alb-RA076M60 | Hyprtns/dyslipid | Met/Chlrqn/ ACEI | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 514 | 773 | 0 |
| 14 | Alb-RA111F39 | Hyprtns | Met/ACEI | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 758 | 849 | 0 |
| 15 | Alb-RA058M32 | Met/Folic/Azulf Predns/Omprz | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 540 | 559 | 508 | |
| 16 | Alb-RA020F26 | Met | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 591 | 680 | 552 | |
| 17 | Alb-RA133F37 | Met/Chlrqn/Folic/ARAVA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 743 | 603 | 549 | |
| 18 | Alb-RA038F55 | Hyprtns Hypothyr | Met/Chlrqn/Folic | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 524 | 957 | 809 |
| 19 | Alb-RA103F72 | Hyprtns | Met/Folic/ ACEI | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 512 | 661 | 1206 |
| 20 | Alb-RA118F30 | Met/Chlrqn/Folic | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 577 | 1148 | 510 | |
| 21 | Alb-RA099M76 | Hyprtns | Met/AECI | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 561 | 1165 | 866 |
| 22 | Alb-RA132F58 | Hyprtns | Met/Chlrqn/Folic | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 651 | 1829 | 1528 |
| 23 | Alb-RA135F55 | Met/ Chlrqn/ Folic | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1563 | 1084 | 1477 | |
| 24 | Alb-RA109F50 | SLE/Hyprtns | Met/Folic/Azulf/ARAVA/Azat/ Predns/ ACEI | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1133 | 719 | 934 |
| Patient ID | Other Complications | Treatment at Sampling | β2M | HLA-E | HLA-F HLA-G | β2M | HLA-E | HLA-F HLA-G | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Chains | Heavy Chains | ||||||||||
| IgM | IgM | IgM | IgM | IgG | IgG | IgG | IgG | ||||
| 1 | Alb-RA 110F63 | Met/Chlrqn/Folic | 695 | 581 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | Alb-RA 114F61 | Met/Folic/ IECA | 2817 | 1910 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 510 | 0 | |
| 3 | Alb-RA 052F57 | Met/Folic/ Predns/Omprz | 3293 | 636 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 980 | 0 | |
| 4 | Alb-RA 092M56 | Met/Predns | 1134 | 618 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1469 | 0 | |
| 5 | Alb-RA 051F44 | Met/Chlrqn/Folic | 1296 | 740 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 734 | 685 | 1106 | |
| 6 | Alb-RA 015F35 | Hypothyrd | Azulf/ ARAVA/ Chlrqn/Predns/ | 850 | 2001 | 500 | 0 | 0 | 1020 | 766 | 1251 |
| Met/Chlrqn/ | |||||||||||
| 7 | Alb-RA 105F24 | Folic/ | 593 | 4042 | 1209 | 2522 | 0 | 0 | 1022 | 829 | |
| 8 | Alb-RA 033F26 | Met/Folic/Ompraz | 603 | 632 | 1512 | 763 | 0 | 559 | 1239 | 1842 | |
| 9 | Alb-RA 014F73 | Hypertens | Met/IECA | 940 | 841 | 0 | 837 | 0 | 0 | 1207 | 1247 |
| 10 | Alb-RA 100F21 | Met/Chlrqn/ARAVA/Ompr | 1008 | 1824 | 495 | 673 | 0 | 0 | 624 | 4518 | |
| 11 | Alb-RA 019F25 | Chlrqn | 1034 | 624 | 531 | 1016 | 0 | 0 | 1234 | 1093 | |
| 12 | Alb-RA 060F44 | Met/Azulf | 1317 | 1430 | 1541 | 3545 | 0 | 2076 | 1834 | 9985 | |
| 13 | Alb-RA 047F50 | Chlrqn | 1718 | 1117 | 973 | 1441 | 0 | 1104 | 1122 | 973 | |
| 15 | Alb-RA 138F55 | Met/Folic/Azulf /Predns/ | 1728 | 786 | 0 | 2784 | 0 | 0 | 940 | 861 | |
| Patient ID | Other Complications | Treatment at Sampling | β2M | HLA-E HLA-F HLA-G | β2M | HLA-E HLA-F HLA-G | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Chains | Heavy Chains | ||||||||||
| IgM | IgM | IgM | IgM | IgG | IgG | IgG | IgG | ||||
| 1 | Alb-RA 085F47 | Dyslipid/diabet | Met/Chlrqn/ ARAVA/Statins | 596 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 540 | 1626 | 1580 |
| 2 | Alb-RA 048F41 | Hpothyr/Hyprtns | ARAVA/Ompr/ Thyrd enzys/ IECA/B-block | 638 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1267 | 1464 |
| 3 | Alb-RA 063M60 | Met/Folic/ ARAVA | 859 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 769 | 730 | 591 | |
| 4 | Alb-RA 124F29 | Met/Chlrqn/ Folic/Azulf/ | 953 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1289 | 683 | |
| 5 | Alb-RA 005M75 | Met/Folic/ ARAVA | 979 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1602 | 1771 | |
| 6 | Alb-RA 043F24 | Met/Chlrqn/ Folic/ | 1516 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1142 | 0 | |
| Patient ID | Other Complications | Treatment at Sampling | β2M | HLA-E HLA-F HLA-G Heavy Chains | β2M | HLA-E HLA-F HLA-G Heavy Chains | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgM | IgM | IgM | IgM | IgG | IgG | IgG | IgG | ||||
| 1 | Alb-RA 027F37 | Met/ ARAVA/ Predns | 0 | 0 | 1816 | 0 | 578 | 1438 | 1356 | 2580 | |
| 2 | Alb-RA084M62 | Met/Folic/ predns | 0 | 763 | 637 | 0 | 825 | 822 | 1568 | 2829 | |
| 3 | Alb-RA 137F33 | Met/Folic/azulf Chlrqn | 0 | 1381 | 0 | 0 | 500 | 1086 | 1183 | 987 | |
| 4 | Alb-RA134F45 | Met/Chlrqn/ Folic/ | 0 | 1607 | 840 | 654 | 861 | 2700 | 2763 | 3726 | |
| 5 | Alb-RA 088F34 | Diabetes | Met/Predns | 0 | 2237 | 1360 | 2799 | 754 | 1218 | 1525 | 3166 |
| Patient ID | Other Complications | Treatment at Sampling | β2M | HLA-E HLA-F HLA-G Heavy Chains | β2M | HLA-E HLA-F HLA-G Heavy Chains | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgM | IgM | IgM | IgM | IgG | IgG | IgG | IgG | ||||
| 1 | Alb-RA090F41 | Met/Chlrqn/ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 752 | 1474 | 1577 | 1104 | |
| 2 | Alb-RA030M58 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 782 | 1812 | 3138 | 1531 | ||
| 3 | Alb-RA097F47 | Thrombosis | Met/Chlrqn/ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 573 | 778 | 0 | 0 |
2.3. Antigen Source
2.4. Immunoassay with Single Antigen Beads
3. Results
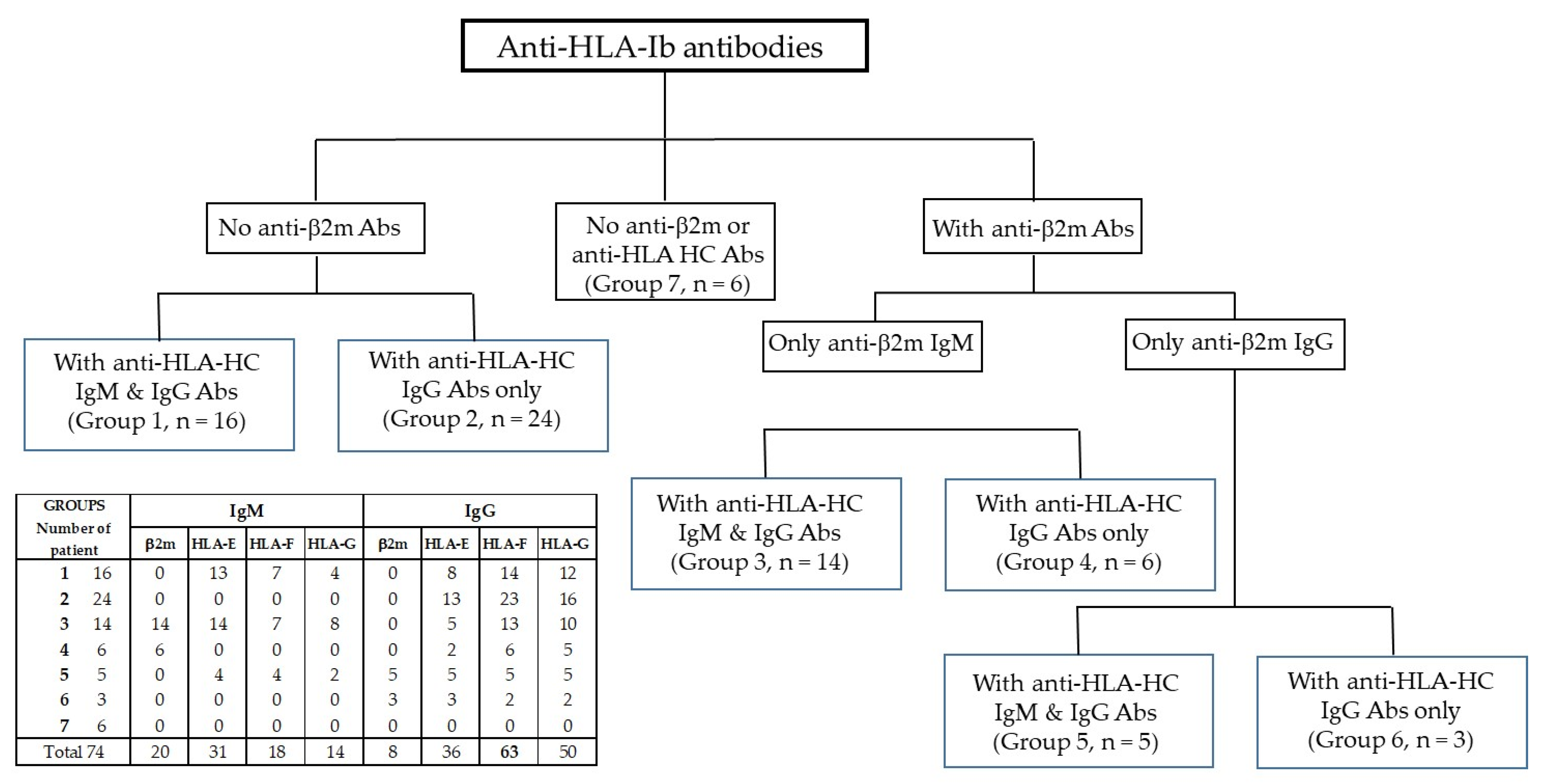
3.1. Categorization of Sera Based on the Distributions of Anti-β2m and HCs Abs
3.2. Group 1: Sera with No Anti-β2m IgM or IgG but with Anti-HLA-Ib HC IgM and IgG
3.3. Group 2: Sera with No Anti-β2m IgM or IgG but Only with Anti-HLA-Ib HC IgG
3.4. Group 3: Sera with Anti-β2m IgM Only but with Anti-HLA-Ib HC IgM and IgG
3.5. Group 4: Sera with Anti-β2m IgM Only without Anti-HLA-Ib HC IgM but with IgG
3.6. Group 5: Sera with Anti-β2m IgG but Not IgM Together with HLA-Ib HC IgM and IgG
3.7. Group 6: Sera with Anti-β2m IgG but Not IgM and with HLA-Ib HC IgG but Not IgM
3.8. Group 7: Sera with Neither Anti-β2m Nor HLA-Ib HC Abs
3.9. High Levels of Anti-HLA-Ib IgM and IgG Abs in Normal Males and Females of the Same Ethnicity as the RA Patients
4. Discussion
4.1. Anti-HLA-F IgG without Anti-β2m-IgG Is Most Prevalent in RA Patients
- (1)
- Anti-HLA-F IgG was observed in 64 of 69 patients. Only anti-HLA-F IgG was observed in 12 of 69 patients, indicating that these IgG Abs were specific for HLA-F. Thus, only anti-HLA-F IgG was observed in 2 of 16 Group 1 patients (Table 2), 5 of 24 patients in Group 2 (Table 3), 4 of 15 Group 3 patients (Table 4), and 1 of 6 Group 4 patients (Table 5).
- (2)
- The MFI of anti-HLA-F IgG was higher than the MFI of anti-HLA-E or anti-HLA-G in 7 of 16 patients in Group 1 (Table 2), 17 of 24 patients in Group 2 (Table 3), 8 of 15 patients in Group 3 (Table 4), 3 of 6 patients in Group 4 (Table 5), 1 of 5 patients in Group 5 (Table 6), and 2 of 3 patients in Group 6 (Table 7).
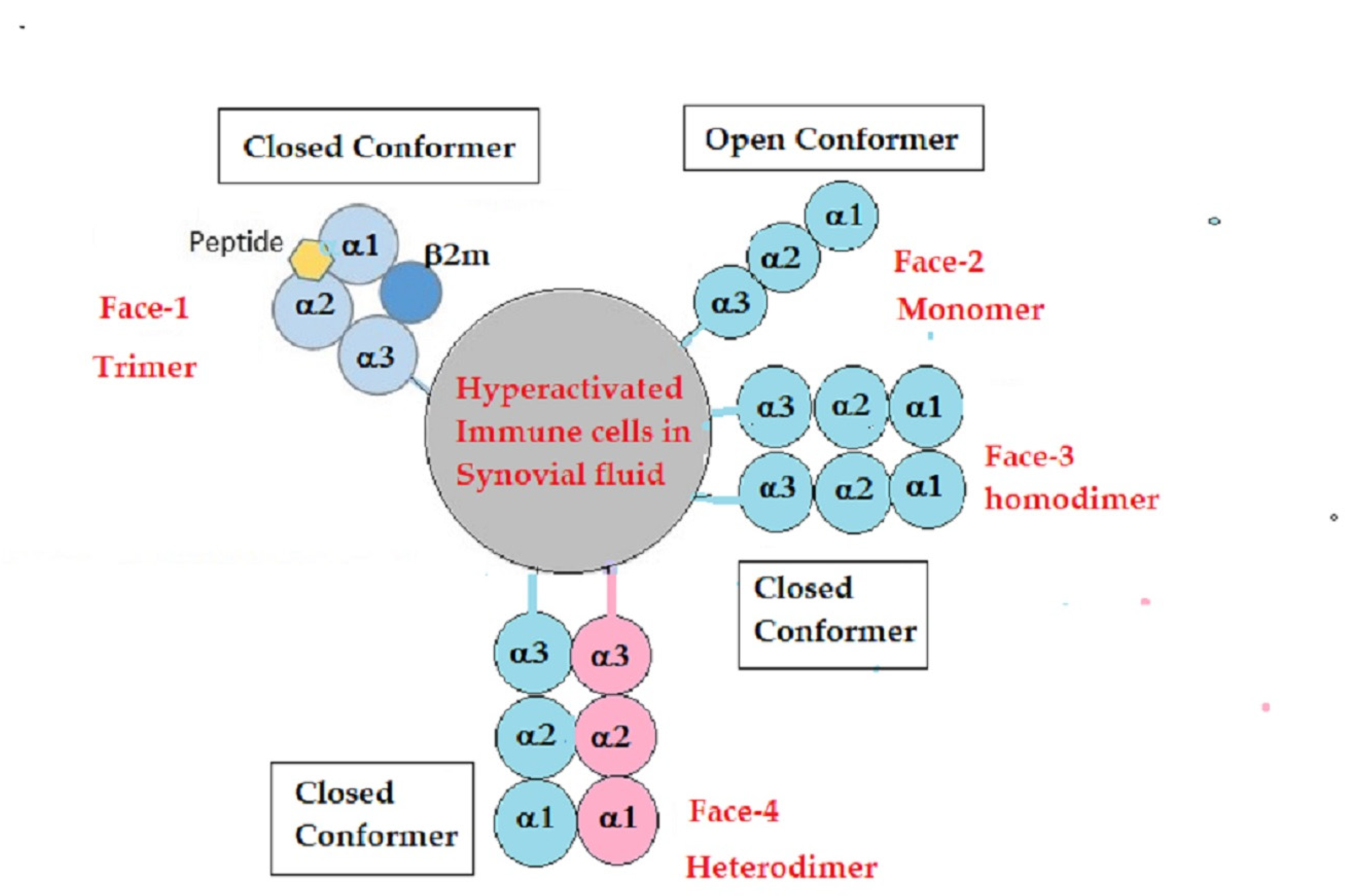
4.2. Unique Structural Variants of HLA-F on Activated Immune Cells in RA
4.3. IgM and IgG HLA-Ib Abs with and without Anti-β2m Abs May Reflect the Phases of Immunological Progression during Immunosuppressive Therapies
- (1)
- Drugs that suppress cell proliferation of activated immune cells. Methotrexate, leflunomide, and azathioprine belong to this category.
- (2)
- Drugs that inhibit IgM and IgG production. Leflunomide, prednisone, and azulfidine (sulfasalazine) belong to this category.
- (3)
- Drugs that promote apoptosis of activated human T cells and immune cells. Azulfidine (sulfasalazine) and azathioprine belong to this category.
- (4)
- Most of the drugs listed in Table 1 suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines.
5. HLA-Ib Antibody Profiles in the Normal Control Group
6. Limitations of This Investigation
7. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Dedication
Abbreviations
References
- Firestein, G.S.; McInnes, I.B. Immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunity 2017, 46, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmstrom, V.; Catrina, A.I.; Klareskog, L. The immunopathogenesis of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: From triggering to targeting. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellado, M.; Martínez-Muñoz, L.; Cascio, G.; Lucas, P.; Pablos, J.L.; Rodríguez-Frade, J.M. T Cell Migration in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Kwon, E.-J.; Lee, J.J. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic roles of diverse Immune cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, R.M.; Gaffen, S.L. Interleukin-17 and its target genes: Mechanisms of interleukin-17 function in disease. Immunology 2010, 129, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Gaffen, S.L. Structure-function relationships in the IL-17 receptor: Implications for signal transduction and therapy. Cytokine 2008, 41, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinne, R.W.; Brauer, R.; Stuhlmutler, B.; Palombo-Kinne, E.; Burmester, G.R. Macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthitis Res. Ther. 2000, 2, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, T.; Hasunuma, T.; Asahara, H.; Maeda, T.; Nishioka, K. Reheumatoid Arthritis and Apoptosis. Intern. Med. 1998, 37, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arosa, F.A.; Santos, S.G.; Powis, S.J. Open conformers: The hidden Face of MHC-I molecules. Trends Immunol. 2007, 28, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindranath, M.H.; Ravindranath, N.M.; Selvan, S.R.; Filippone, E.J.; Amato-Menker, C.J.; El Hilali, F. Four Faces of Cell-Surface HLA Class-I: Their Antigenic and Immunogenic Divergence Generating Novel Targets for Vaccines. Vaccines 2022, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marozzi, A.; Meneveri, R.; Bunone, G.; De Santis, C.; Lopalco, L.; Beretta, A.; Agresti, A.; Siccardi, A.G.; Della Valle, G.; Ginelli, E. Expression of beta 2m-free HLA class I heavy chains in neuroblastoma cell lines. Scand. J. Immunol. 1993, 37, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martayan, A.; Fiscella, M.; Setini, A.; Ciccarelli, G.; Gambari, R.; Feriotto, G.; Beretta, A.; Siccardi, A.G.; Appella, E.; Giacomini, P. Conformation and surface expression of free HLA-CW1 heavy chains in the absence of beta 2-microglobulin. Hum. Immunol. 1997, 53, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, P.; Beretta, A.; Nicotra, M.R.; Ciccarelli, G.; Martayan, A.; Cerboni, C.; Lopalco, L.; Bini, D.; Delfino, L.; Ferrara, G.B.; et al. HLA-C heavy chains free of beta2-microglobulin: Distribution in normal tissues and neoplastic lesions of non-lymphoid origin and interferon-y responsiveness. Tissue Antigens 1997, 50, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyson, J.E.; Erskine, R.; Whitman, M.C.; Chiu, M.; Lau, J.M.; Koopman, L.A.; Valter, M.M.; Angelisova, P.; Horejsi, V.; Strominger, J.L. Disulfide bond-mediated dimerization of HLA-G on the cell surface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16180–16185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.C.; Chen, C.J.; Yen, J.H.; Ou, T.T.; Tsai, J.J.; Liu, C.S.; Liu, H.W. Free HLA class I heavy chain-carrying monocytes—A potential role in the pathogenesis of spondyloarthropathies. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 966–972. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, Z.H.; Li, X.Y.; Wu, Z.B.; Zhu, P. Increased expression of human leucocyte antigen class I free heavy chains on monocytes of patients with spondyloarthritis and cells transfected with HLA-B27. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2015, 42, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, T.; Brown, D.; Bowness, P.; Hill Gaston, J.S.; Moffett, A.; Trowsdale, J.; Allen, R.L. Consistent patterns of expression of HLA class I free heavy chains in healthy individuals and raised expression in spondyloarthropathy patients point to physiological and pathological roles. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.L.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; McMichael, A.J.; Bowness, P. Cutting Edge: HLA-B27 Can Form a Novel b2-Microglobulin-Free Heavy Chain Homodimer Structure. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 5045–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenart, I.; Guiliano, D.B.; Burn, G.; Campbell, E.C.; Morley, K.D.; Fussell, H.; Powis, S.J.; Antoniou, A.N. The MHC Class I heavy chain structurally conserved cysteines 101 and 164 participate in HLA-B27 dimer formation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012, 16, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.G.; Lynch, S.; Campbell, E.C.; Antoniou, A.N.; Powis, S.J. Induction of HLA-B27 heavy chain homodimer formation after activation in dendritic cells. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong-Baeza, I.; Ridley, A.; Shaw, J.; Hatano, H.; Rysnik, O.; McHugh, K.; Piper, C.; Brackenbridge, S.; Fernandes, R.; Chan, A.; et al. KIR3DL2 binds to HLA-B27 dimers and free H chains more strongly than other HLA class I and promotes the expansion of T cells in ankylosing spondylitis. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3216–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.S.L.; Crostein, B.L. Molecular action of methotrexate in inflammatory diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2002, 4, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endresen, G.K.; Husby, G. Folate supplementation during methotrexate treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. An update and proposals for guidelines. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2001, 30, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, C.H.; Choi, J.H.; Byun, M.S.; Jue, D.M. Chloroquine inhibits production of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes/macrophages by different modes. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Lara, R.; Espinosa-Ortega, H.F.; Arce-Salinas, C.A.; PRECIS Study Group, All Physicians belong to Division of Internal Medicine. Hospital Central Sur de Pemex. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of leflunomide and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatol. Clin. 2019, 15, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.S.; Conn, D. The use of low-dose prednisone in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Bull. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rains, C.P.; Noble, S.; Faulds, D. Sulfasalazine: A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs 1995, 50, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKendry, R.J. Azathioprine and methotrexate as combination chemotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 1990, 25, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gigante, A.; Tagarro, I. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and gastroprotection with proton pump inhibitors: A focus on ketoprofen/omeprazole. Clin. Drug Investig. 2012, 32, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futrakul, P.; Pochanugool, C.; Poshyachinda, M.; Thamaree, S.; Yenrudi, S.; Buranasiri, K.; Saleekul, P.; Watana, D.; Sensirivatana, R.; Kingwatanakul, P.; et al. Intrarenal hemodynamic abnormality in severe form of glomerulonephritis: Therapeutic benefit with vasodilators. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 1992, 75, 375–385. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindranath, M.H.; Selvan, S.R.; Terasaki, P.I. Augmentation of anti-HLA-E Abs with concomitant HLA-Ia reactivity in IFNγ-treated autologous melanoma cell vaccine recipients. J. Immunotoxicol. 2012, 9, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindranath, M.H.; Terasaki, P.I.; Pham, T.; Jucaud, V.; Kawakita, S. Therapeutic preparations of IVIg contain naturally occurring anti-HLA-E Abs that react with HLA-Ia (HLA-A/-B/-C) alleles. Blood 2013, 21, 2013–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL Hilali, F.; Jucaud, V.; EL Hilali, H.; Bhuiyan, M.H.; Mancuso, A.; LiuSullivan, N.; Elidrissi, A.; Mazouz, H. Characterization of the Anti-HLA Class I and II IgG Abs in Moroccan IVIg Using Regular Beads and Ibeads in Luminex Multiplex Single Antigen Immunoassay. Int. J. Immunol. 2017, 5, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranath, M.; Pham, T.; El-Awar, N.; Kaneku, H.; Terasaki, P.I. Anti-HLA-E mAb 3D12 mimics MEM-E/02 in binding to HLA-B and HLA-C alleles: Web-tools validate the immunogenic epitopes of HLA-E recognized by the Abs. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranath, M.H.; El Hilali, F. Monospecific and Polyreactive Monoclonal Abs against Human Leukocyte Antigen-E: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Relevance. In Monoclonal Antibodies; Rezaei, N., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; Chapter 3; pp. 43–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindranath, M.H.; Ravindranath, N.M.; El Hilali, F.; Selvan, S.R.; Filippone, E.J. Ramifications of the HLA-I Allelic Reactivity of Anti-HLA-E*01:01 and Anti-HLA-E*01:03 Heavy Chain Monoclonal Abs in Comparison with Anti-HLA-I IgG Reactivity in Non-Alloimmunized Males, Melanoma-Vaccine Recipients, and End-Stage Renal Disease Patients. Antibodies 2022, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jucaud, V.; Ravindranath, M.H.; Terasaki, P.I. Conformational Variants of the Individual HLA-I Antigens on Luminex Single Antigen Beads Used in Monitoring HLA Antibodies: Problems and Solutions. Transplantation 2017, 101, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranath, M.H.; Flippone, E.J.; Mahowald, G.; Callender, C.; Babu, A.; Saidman, S.; Ferrone, S. Significance of the intraindividual variability of HLA IgG antibodies in renal disease patients observed with different SABs monitored with two different secondary antibodies on a Luminex platform. Immunol. Res. 2018, 66, 584–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranath, M.H.; Ravindranath, N.M.; Amato-Menker, C.J. Luminex multiplex bead assay monitoring HLA IgG antibodies in sensitized pre- and post-transplant patients: Clonality of the detection antibody impacts specificity and sensitivity. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, H.J.; Fraser, D.; Flyer, S.; Calvin, R.; Flavell, R. Beta 2microglobulin is not required for cell surface expression of the murine class I histocompatibility antigen H-213 6 or of a truncated H-213 6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 7447–7451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancet, D.; Parham, P.; Strominger, J.L. Heavy chain ofHLA-A and HLA-B antigens is conformationally labile: A possible role for beta2microglobulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 3844–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabl, E.; Stockinger, H.; Majdic, O.; Gaugitsch, H.; Lindley, I.J.; Maurer, D.; Hajek-Rosenmayr, A.; Knapp, W. Activated human T lymphocytes express MHC class I heavy chains not associated with beta 2-microglobulin. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 171, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrigal, J.A.; Belich, M.P.; Benjamin, R.J.; Little, A.M.; Hildebrand, W.H.; Mann, D.L.; Parham, P. Molecular definition of a polymorphic antigen (LA45) of free HLA-A and -B heavy chains found on the surfaces of activated B and T cells. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 174, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaria, S.; Schwab, R.; Bushkin, Y. The origin and fate of beta 2m-free MHC class I molecules induced on activated T cells. Cell. Immunol. 1992, 142, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setini, A.; Beretta, A.; De Santis, C.; Meneveri, R.; Martayan, A.; Mazzilli, M.C.; Appella, E.; Siccardi, A.G.; Natali, P.G.; Giacomini, P. Distinctive features of the alpha 1- domain alpha helix of HLA-C heavy chains free of beta 2- microglobulin. Hum. Immunol. 1996, 46, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiuti, A.; Forte, P.; Simeoni, L.; Lino, M.; Pozzi, L.; Fattorossi, A.; Giacomini, P.; Ginelli, E.; Beretta, A.; Siccardi, A.; et al. Membrane expression of HLA-Cw4 free chains in activated T cells of transgenic mice. Immunogenetics 1995, 42, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodridge, J.P.; Burian, A.; Lee, N.; Geraghty, D.E. HLA-F complex without peptide binds to MHC class I protein in the open conformer form. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 6199–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollnberger, S. The Role of HLA-Class I Heavy-Chain Interactions with Killer-Cell Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors in Immune Regulation. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 36, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremante, E.; Lo Monaco, E.; Ingegnere, T.; Sampaoli, C.; Fraioli, R.; Giacomini, P. Monoclonal Abs to HLA-E bind epitopes carried by unfolded β2m-free heavy chains. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2356–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menier, C.; Saez, B.; Horejsi, V.; Martinozzi, S.; Krawice-Radanne, I.; Bruel, S.; Le Danff, C.; Reboul, M.; Hilgert, I.; Rabreau, M.; et al. Characterization of monoclonal Abs recognizing HLA-G or HLA-E: New tools to analyze the expression of nonclassical HLA class I molecules. Hum. Immunol. 2003, 64, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Ravindranath, M.H.; Terasaki, P.I.; Freitas, M.C.; Kawakita, S.; Jucaud, V. Gastric cancer progression may involve a shift in HLA-E profile from an intact heterodimer to β2m-free monomer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonen-Gross, T.; Achdout, H.; Gazit, R.; Hanna, J.; Mizrahi, S.; Markel, G.; Goldman-Wohl, D.; Yagel, S.; Horejsí, V.; Levy, O.; et al. Complexes of HLA-G protein on the cell surface are important for leukocyte Ig-like receptor-1 function. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khare, S.D.; Hansen, J.; Luthra, H.S.; David, C.S. HLA-B27 heavy chains contribute to spontaneous inflammatory disease in B27/human β2-microglobulin (β2m) double transgenic mice with disrupted mouse β2m. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, S.D.; Bull, M.J.; Hansen, J.; Luthra, H.S.; David, C.S. Spontaneous inflammatory Disease in HLA-B27 transgenic mice is independent of MHC class II molecules: A direct role for B27 heavy chains and not B27-derived peptides. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bix, M.; Raulet, D. Functionally conformed free class I heavy chains exist on the surface of b2 microglobulin negative cells. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauli, A.; Dessole, G.; Fiorillo, M.T.; Vacca, A.; Mameli, A.; Bitti, P.; Passiu, G.; Sorrentino, R.; Mathieu, A. Increased level of HLA-B27 expression in ankylosing spondylitis patients compared with healthy HLA-B27-positive subjects: A possible further susceptibility factor for the development of disease. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauli, A.; Dessole, G.; Vacca, A.; Porru, G.; Cappai, L.; Piga, M.; Bitti, P.P.; Fiorillo, M.T.; Sorrentino, R.; Carcassi, C.; et al. Susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis but not disease outcome is influenced by the level of HLA-B27 expression, which shows moderate variability over time. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 1, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Q.; Yu, H.-C.; Gong, Y.-Z.; Lai, N.-S. Quantitative measurement of HLA-B27 mRNA in patients with ankylosing spondylitis– correlation with clinical activity. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Giles, J.; Shaw, J.; Piper, C.; Wong-Baeza, I.; McHugh, K.; Ridley, A.; Li, D.; Lenart, I.; Antoniou, A.N.; DiGleria, K.; et al. HLA-B27 homodimers and free H chains are stronger ligands for leukocyte Ig-like receptor B2 than classical HLA class I. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 6184–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindranath, M.H.; El Hilali, F.; Amato-Menker, C.J.; El Hilali, H.; Selvan, S.R.; Filippone, E.J. Role of HLA-I Structural Variants and the Polyreactive Abs They Generate in Immune Homeostasis. Antibodies 2022, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Ishitani, A.; Geraghty, D.E. HLA-F is a surface marker on activated lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 2308–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Geraghty, D.E. HLA-F surface expression on B cell and monocyte cell lines is partially independent from tapasin and completely independent from TAP. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 5264–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burian, A.; Wang, K.L.; Finton, K.A.; Lee, N.; Ishitani, A.; Strong, R.K.; Geraghty, D.E. HLA-F and MHC-I Open Conformers Bind Natural Killer Cell Ig-Like Receptor KIR3DS1. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-M.; Sugino, H.; Aoki, C.; Shimaoka, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Ochi, K.; Ochi, T.; Nishimoto, N. Abnormal networks of immune response-related molecules in bone marrow cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis as revealed by DNA microarray analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroz, A.S.; Giddaluru, J.; Vishwakarma, S.; Naz, S.; Khan, A.A.; Khan, N. A Comprehensive Gene Expression Meta-analysis Identifies Novel Immune Signatures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Wu, J.; Deng, F.Y.; Wu, L.F.; Zhang, Y.H.; Guo, Y.F.; Lei, S.F. Integrative analysis for identification of shared markers from various functional cells/tissues for rheumatoid arthritis. Immunogenetics 2017, 69, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Patient ID | Other Complications | Treatment at Sampling | β2M | HLA-E HLA-F HLA-G Heavy Chains | β2M | HLA-E HLA-F HLA-G Heavy Chains | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgM | IgM | IgM | IgM | IgG | IgG | IgG | IgG | ||||
| 1 | Alb-RA091F30 | Met | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | Alb-RA024F54 | Hpothyr | Met/Thyoid Enz | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | Alb-RA 065F59 | Hpertns/Diabet | Met/Chlrqn/Folic | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | Alb-RA104F22 | Met/Chlrqn/ Predns | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5 | Alb-RA130F51 | Met/Chlrqn/ Folic/Omprz | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 6 | Alb-RA074F37 | Met/Chlrqn/ Folic/Azul | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Males | HLA-E | HLA-F | HLA-G | Females | HLA-E | HLA-F | HLA-G | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgM | IgG | IgM | IgG | IgM | IgG | IgM | IgG | IgM | IgG | IgM | IgG | ||
| AT-252 | 6524 | 0 | 2334 | 1441 | 3103 | 2585 | AT-63 | 7369 | 704 | 5729 | 1396 | 7493 | 1995 |
| AT-126 | 3172 | 884 | 2139 | 1506 | 6177 | 4761 | AT-212 | 6827 | 653 | 3236 | 947 | 4835 | 1701 |
| AT-48 | 6157 | 1106 | 1743 | 2086 | 4906 | 4228 | AT-56 | 4972 | 728 | 781 | 2086 | 2209 | 2397 |
| AT-364 | 3953 | 730 | 1146 | 1511 | 1989 | 2331 | AT-343 | 4739 | 915 | 1722 | 1452 | 3086 | 1974 |
| AT-400 | 3948 | 632 | 1305 | 1002 | 2616 | 2464 | AT-372 | 4280 | 1075 | 1778 | 2199 | 5917 | 2895 |
| AT-449 | 2923 | 886 | 749 | 2069 | 1969 | 3717 | AT-1 | 3510 | 936 | 1166 | 1873 | 3738 | 2156 |
| AT-154 | 2817 | 803 | 1621 | 1728 | 1988 | 2995 | AT-323 | 3255 | 897 | 1534 | 1315 | 3715 | 2423 |
| AT-222 | 2230 | 1154 | 923 | 1387 | 1120 | 3765 | AT-253 | 3130 | 717 | 1841 | 1430 | 4206 | 3511 |
| AT-229 | 2144 | 1798 | 665 | 2002 | 1260 | 3578 | AT-362 | 2377 | 0 | 1492 | 1105 | 3773 | 1915 |
| AT-359 | 1804 | 1143 | 872 | 1982 | 2170 | 3216 | AT-38 | 2666 | 1313 | 1761 | 1823 | 2486 | 3427 |
| AT-393 | 1764 | 1115 | 919 | 1455 | 2213 | 3138 | AT-18 | 2448 | 1071 | 1994 | 1466 | 3690 | 2526 |
| AT-304 | 1623 | 0 | 980 | 1428 | 1403 | 2932 | AT-374 | 2212 | 789 | 685 | 1555 | 1483 | 3112 |
| AT-54 | 1490 | 1849 | 1469 | 2186 | 1762 | 3413 | AT-109 | 2128 | 1510 | 1004 | 2612 | 1941 | 3882 |
| AT-277 | 1360 | 1134 | 769 | 2263 | 1556 | 2487 | AT-330 | 2091 | 928 | 574 | 1927 | 2192 | 2923 |
| AT-82 | 1279 | 1028 | 875 | 1649 | 1259 | 3051 | AT-290 | 2000 | 2203 | 1060 | 2333 | 2521 | 3849 |
| AT-88 | 1227 | 834 | 0 | 1693 | 987 | 4700 | AT-150 | 1887 | 533 | 1347 | 1127 | 3287 | 3554 |
| AT-239 | 1216 | 652 | 784 | 1402 | 2019 | 3236 | AT-300 | 1866 | 1018 | 961 | 1800 | 2815 | 4152 |
| AT-338 | 1118 | 1141 | 0 | 1788 | 1009 | 3430 | AT-191 | 1663 | 1728 | 1476 | 3156 | 2788 | 2995 |
| AT-438 | 1049 | 877 | 0 | 2402 | 1005 | 2818 | AT-78 | 1621 | 685 | 823 | 1248 | 1580 | 1637 |
| AT-392 | 741 | 1314 | 1219 | 1963 | 1379 | 3477 | AT-89 | 1483 | 670 | 734 | 1404 | 2284 | 3811 |
| AT-386 | 960 | 1121 | 0 | 1945 | 1038 | 3220 | AT-200 | 1476 | 1042 | 577 | 1875 | 1362 | 2933 |
| AT-133 | 822 | 1738 | 979 | 3049 | 624 | 4756 | AT-181 | 1402 | 623 | 1052 | 1350 | 1938 | 1775 |
| AT-242 | 735 | 1206 | 554 | 1600 | 1680 | 2626 | AT-70 | 1302 | 790 | 0 | 1832 | 1225 | 2514 |
| AT-145 | 667 | 1258 | 0 | 1626 | 1263 | 2405 | AT-112 | 1137 | 0 | 995 | 935 | 1780 | 1750 |
| AT-219 | 0 | 639 | 0 | 2249 | 778 | 2321 | AT-140 | 802 | 1007 | 516 | 2083 | 1555 | 3042 |
| AT-354 | 0 | 1437 | 0 | 2778 | 641 | 3670 | AT-412 | 802 | 994 | 0 | 1794 | 1823 | 2495 |
| Mean | 1989 | 1018 | 848 | 1853 | 1843 | 3281 | Mean | 2671 | 905 | 1340 | 1697 | 2912 | 2744 |
| Median | 1425 | 1111 | 874 | 1758 | 1479 | 3218 | Median | 2110 | 906 | 1056 | 1675 | 2504 | 2711 |
| SD | 1650 | 446 | 673 | 460 | 1258.4 | 729.99 | SD | 1712 | 454 | 1123 | 520 | 1433 | 767 |
| Categories of mAbs | HLA-Ia | HLA-Ib | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-A | HLA-B | HLA-C | HLA-E | HLA-F | HLA-G | |
| Category 1 | [−] | [−] | [−] | [+] | [−] | [−] |
| Category 2 | [−] | [−] | [−] | [+] | [+] | [−] |
| Category 3 | [−] | [−] | [−] | [+] | [−] | [+] |
| Category 4 | [−] | [−] | [−] | [+] | [+] | [+] |
| Category 5 | [−] | [+] | [−] | [+] | [−] | [−] |
| Category 6 | [−] | [+] | [+] | [+] | [−] | [−] |
| Category 7 | [+] | [+] | [+] | [+] | [−] | [−] |
| Category 8 | [+] | [+] | [+] | [+] | [+] | [−] |
| Category 9 | [+] | [+] | [+] | [+] | [−] | [+] |
| Category 10 | [+] | [+] | [+] | [+] | [+] | [+] |
| Groups | Tables | β2M | Heavy Chains | Phases of Disease Progression | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-E | HLA-F | HLA-G | ||||||||
| IgM | IgG | IgM | IgG | IgM | IgG | IgM | IgG | |||
| Group 1 | Table 2 | Absent | Absent | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Phase-1 |
| Group 2 | Table 3 | Absent | Absent | Absent | Present/ Absent | Absent | Present/ Absent | Absent | Present/ Absent | Phase-2 |
| Group 3 | Table 4 | Present | Absent | Present | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Phase-3a |
| Group 4 | Table 5 | Present | Absent | Absent | Present/ Absent | Absent | Present/ Absent | Absent | Present/ Absent | Phase-3b |
| Group 5 | Table 6 | Absent | Present | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Present/ Absent | Phase-3c |
| Group 6 | Table 7 | Absent | Present | Absent | Present/ Absent | Absent | Present/ Absent | Absent | Present/ Absent | Phase-3d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ravindranath, M.H.; Ravindranath, N.M.; Amato-Menker, C.J.; El Hilali, F.; Selvan, S.R.; Filippone, E.J.; Morales-Buenrostro, L.E. Antibodies for β2-Microglobulin and the Heavy Chains of HLA-E, HLA-F, and HLA-G Reflect the HLA-Variants on Activated Immune Cells and Phases of Disease Progression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients under Treatment. Antibodies 2023, 12, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12020026
Ravindranath MH, Ravindranath NM, Amato-Menker CJ, El Hilali F, Selvan SR, Filippone EJ, Morales-Buenrostro LE. Antibodies for β2-Microglobulin and the Heavy Chains of HLA-E, HLA-F, and HLA-G Reflect the HLA-Variants on Activated Immune Cells and Phases of Disease Progression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients under Treatment. Antibodies. 2023; 12(2):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleRavindranath, Mepur H., Narendranath M. Ravindranath, Carly J. Amato-Menker, Fatiha El Hilali, Senthamil R. Selvan, Edward J. Filippone, and Luis Eduardo Morales-Buenrostro. 2023. "Antibodies for β2-Microglobulin and the Heavy Chains of HLA-E, HLA-F, and HLA-G Reflect the HLA-Variants on Activated Immune Cells and Phases of Disease Progression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients under Treatment" Antibodies 12, no. 2: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12020026
APA StyleRavindranath, M. H., Ravindranath, N. M., Amato-Menker, C. J., El Hilali, F., Selvan, S. R., Filippone, E. J., & Morales-Buenrostro, L. E. (2023). Antibodies for β2-Microglobulin and the Heavy Chains of HLA-E, HLA-F, and HLA-G Reflect the HLA-Variants on Activated Immune Cells and Phases of Disease Progression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients under Treatment. Antibodies, 12(2), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12020026





