Estimating Deep Soil Salinity by Inverse Modeling of Loop–Loop Frequency Domain Electromagnetic Induction Data in a Semi-Arid Region: Merguellil (Tunisia)
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- Determine the transfer of salts from the topsoil to deeper layers by coupling the measurements of two different FD-EMI sensors (EM38 and EM31, Geonics Ltd., Mississauga, ON, Canada).
- -
- Assess the capabilities and reliability of these two devices for the detection and characterization of soil salinity by interpreting the multi-depth ECa datasets with quantitative inverse modeling methods.
- -
- Evaluate the effect of irrigation systems (e.g., drip and sprinkler) and the type of crop on the soil salinity.
- -
- Reveal temporal variation in soil salinity using time-lapse FD-EMI surveys.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Devices Used for ECa Measurements
2.3. Procedure of Data Acquisition
Number of Measurements Recovered
2.4. Soil Sampling
2.4.1. Particle Size Analysis
2.4.2. Soil Moisture
2.4.3. Electrical Conductivity of the Paste Soil Extracts (ECe)
2.5. Irrigation Water
2.6. Quantitative Interpretation of FD-EMI Apparent Conductivity Data
3. Results
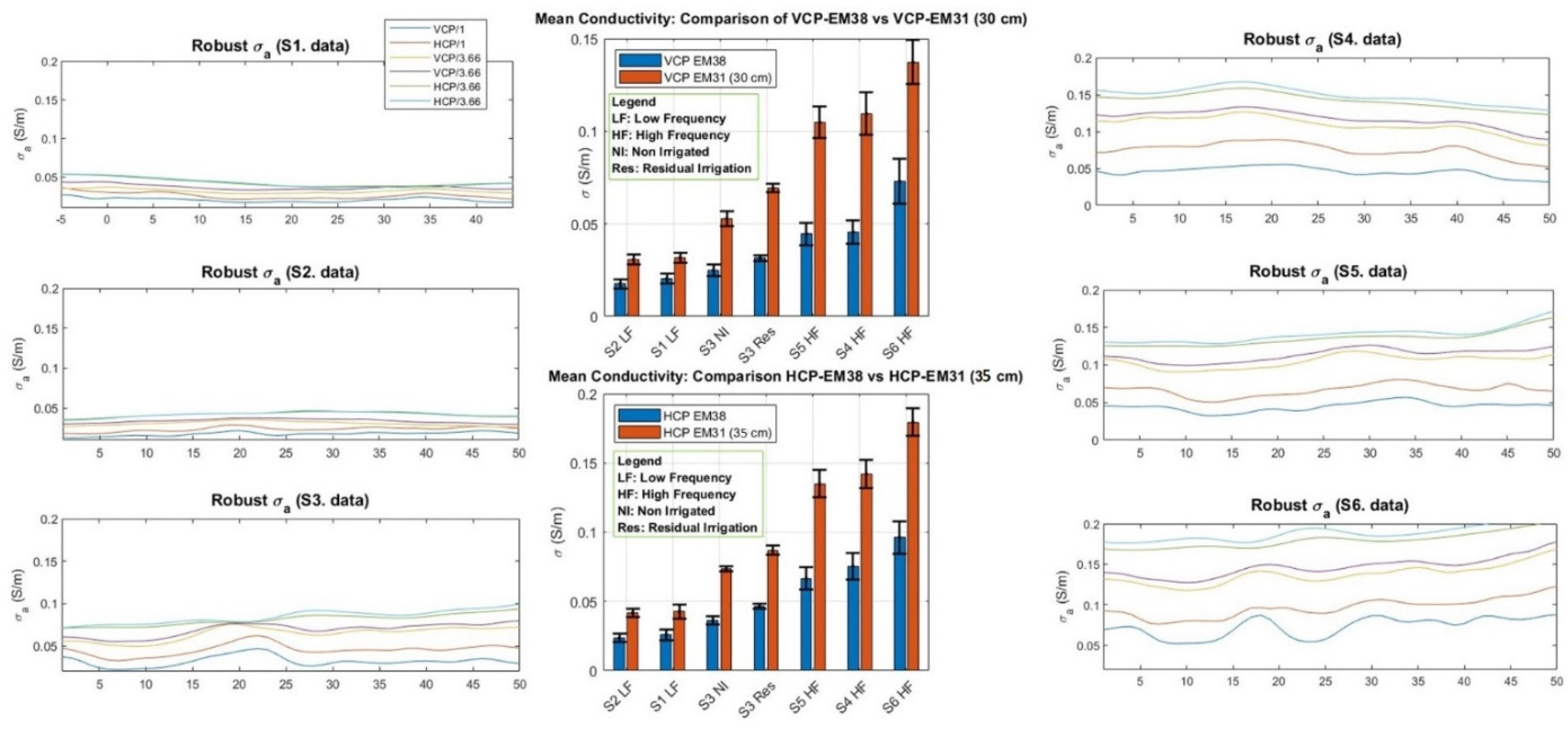
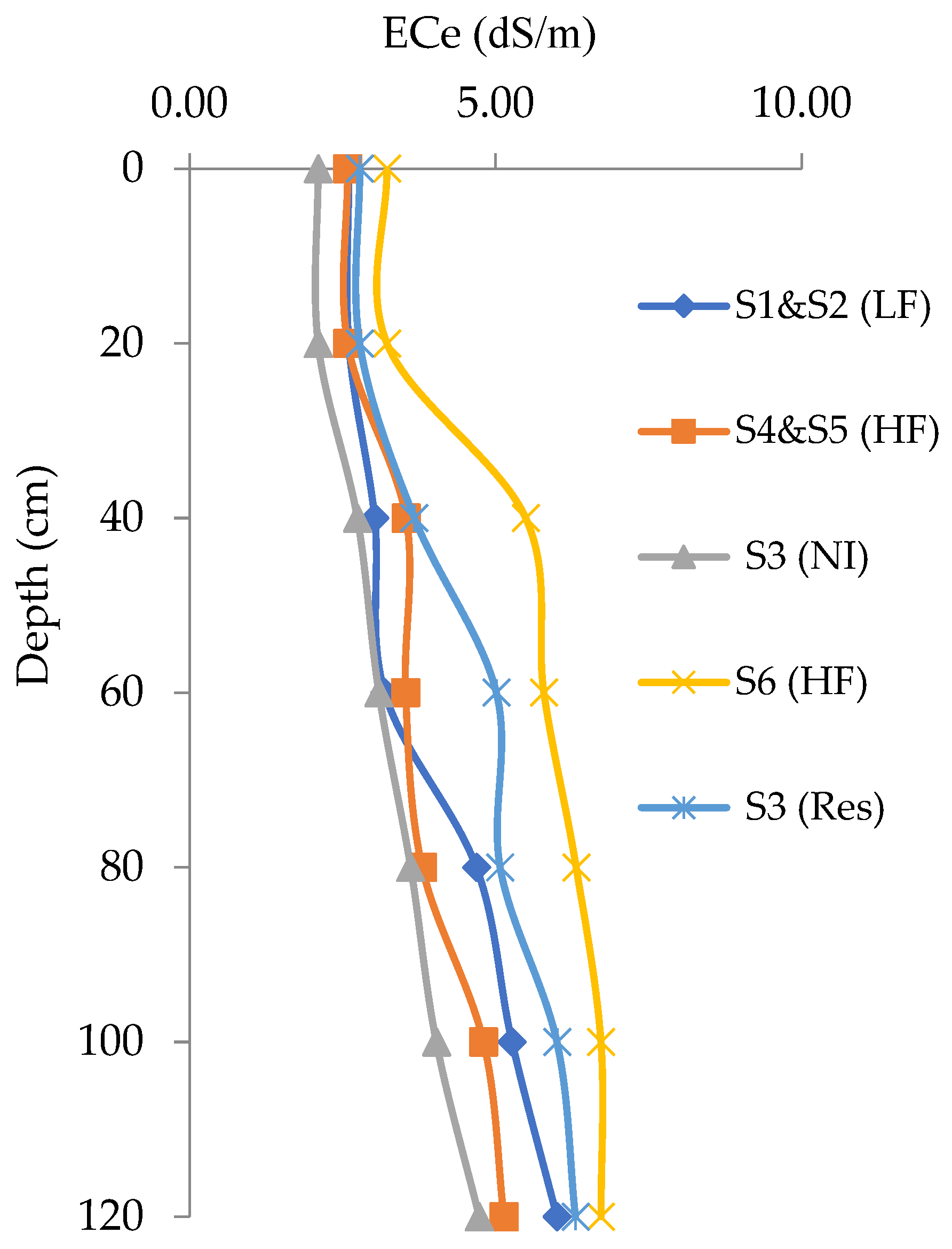
3.1. Results of Soil Sampling
3.2. Variability by Land Use and Irrigation Management
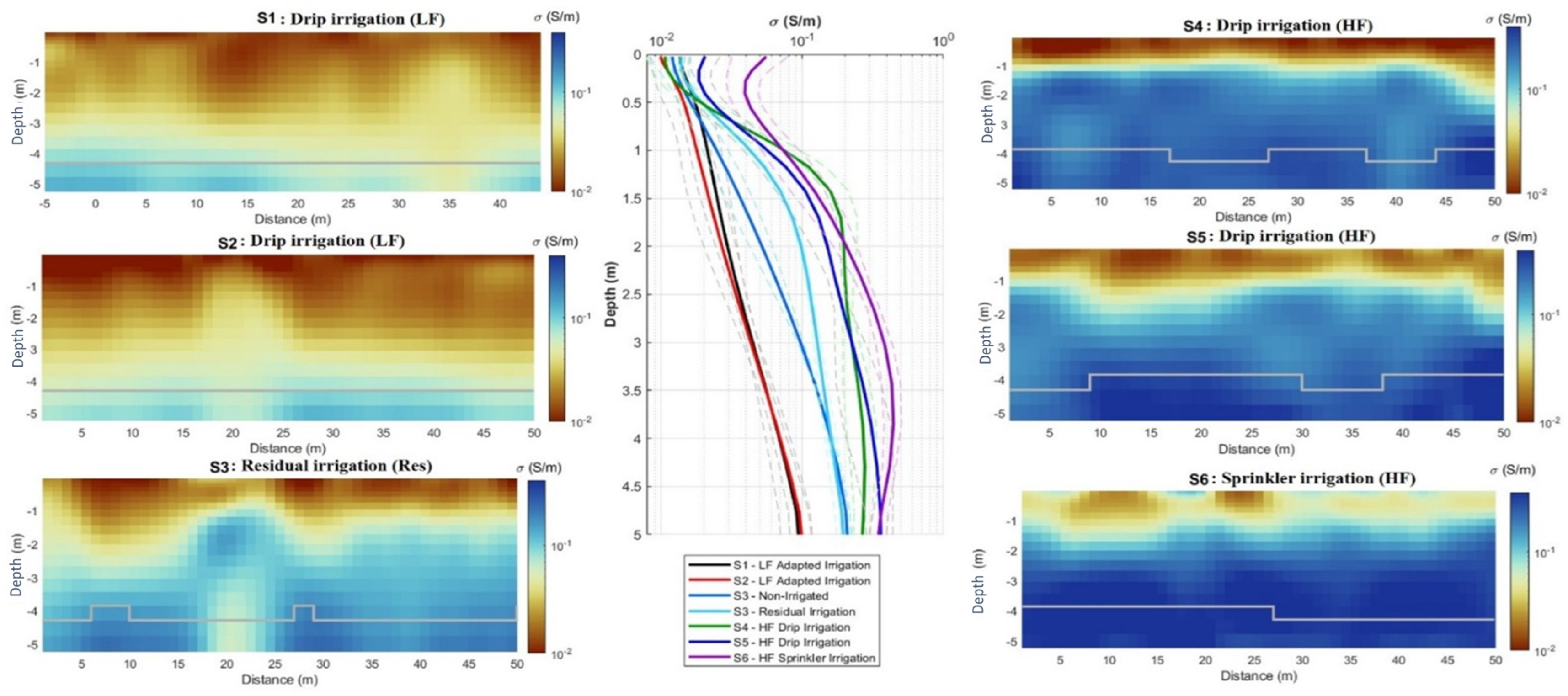
3.3. Modeling by Inversion of EMI Data
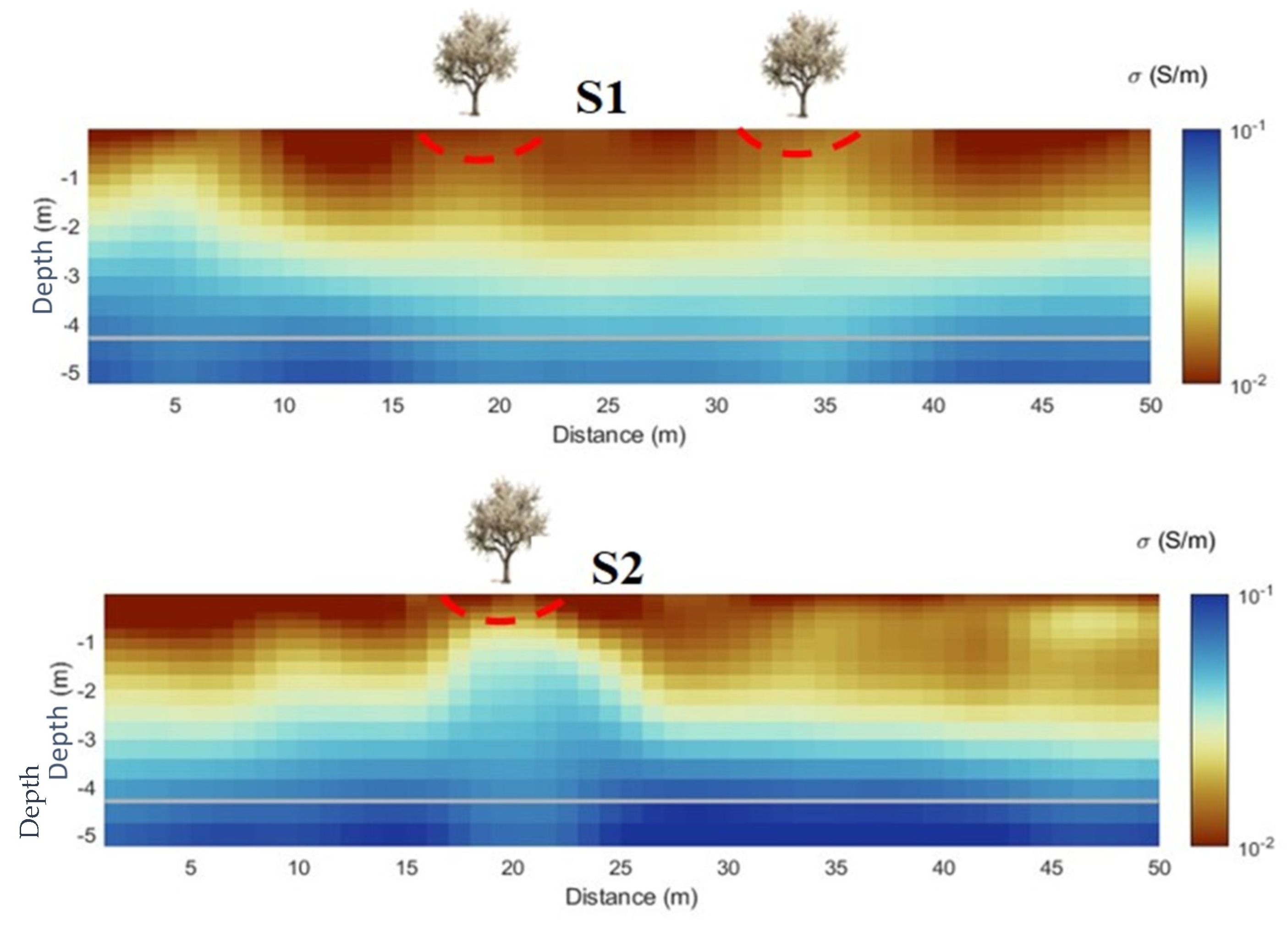
3.3.1. Long-Term Irrigation
3.3.2. Short-Term Irrigation Variation
3.3.3. Response of Soil Salinity Under Low-Frequency Drip Irrigation vs. High Frequency Drip Irrigation
3.3.4. Residual Soil Salinity
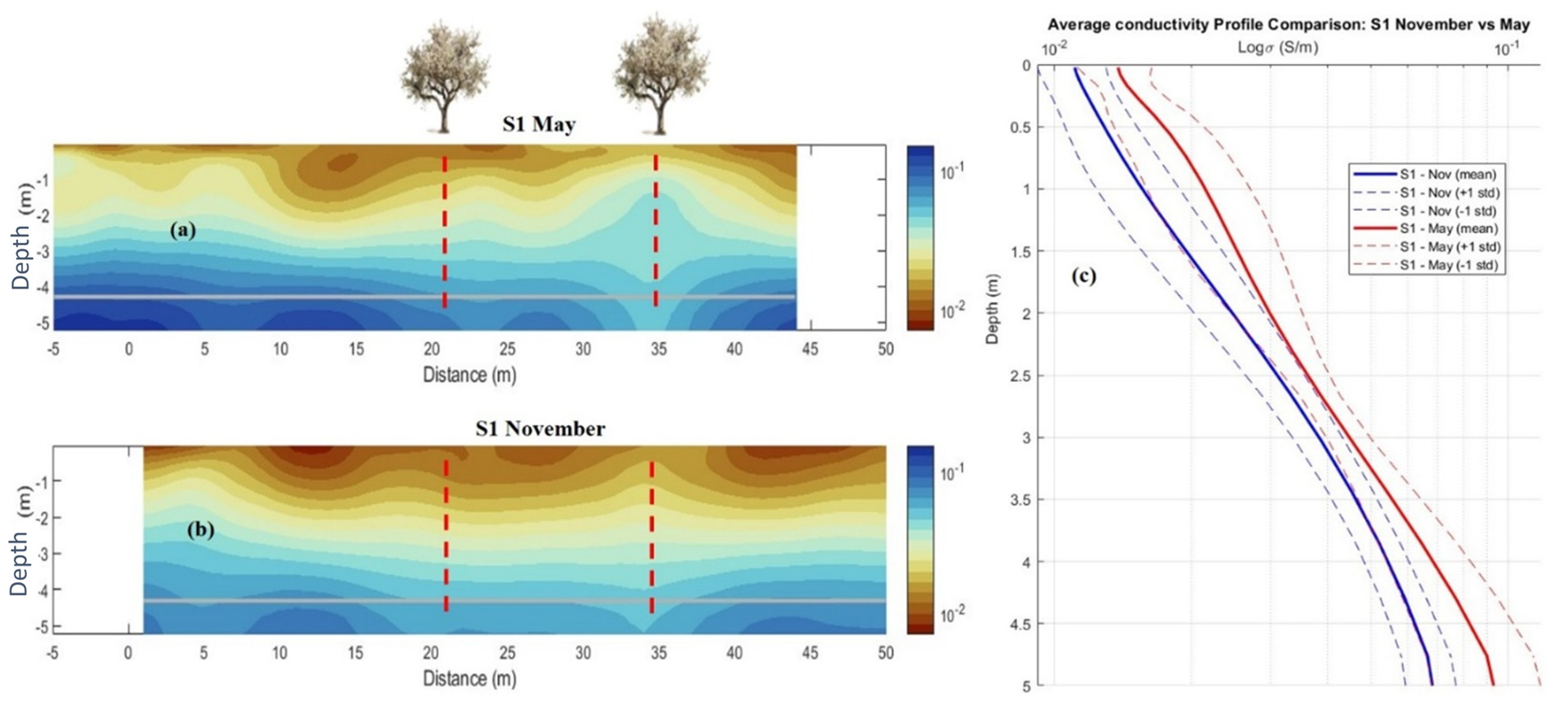
3.3.5. Modeling of Seasonal Soil Salinity Variation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture—Systems at Breaking Point. Main Report. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/cb9910en/cb9910en.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Hachicha, M. Les sols salés et leur mise en valeur en Tunisie. Sécheresse 2007, 18, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Tunisia Country Report on the State of Plant Resources for Food and Agriculture. 2019. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ca5345en/ca5345en.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Weil, R.; Brady, N. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 15th ed.; Fox, D., Ed.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi, M.; Sukchan, S.; Wichaidit, P.; Srisuk, K.; Kaneko, F. Hydrological and geochemical behavior of saline groundwater in Phra Yun, Northeast Thailand. In Development of Sustainable Agricultural System in Northeast Thailand Through Local Resource Utilization and Technology Improvement; Ito, O., Matsumoto, N., Eds.; Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences: Tsukuba, Japan, 2002; pp. 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soilsalinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrasek, G.; Rengel, Z.; Veres, S. Soilsalinisation and salt stress in crop production. In Abiotic Stress in Plants—Mechanisms and Adaptations; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 171–190. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. A simplified regional-scale electromagnetic induction—Salinity calibration model using ANOCOVA modeling techniques. Geoderma 2014, 230, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdnyakova, L.A.; Trubin, A.Y.; Orunbaev, S.; Mansteind, Y.A.; Umarova, A.B. In-field Assessment of Soil Salinity and Water Content with Electrical Geophysics. Mosc. Univ. Soil Sci. Bull. 2023, 78, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Scudiero, E. Review of soil salinity assessment for agriculture across multiple scales using proximal and/or remote sensors. Adv. Agron. 2019, 158, 1–130. [Google Scholar]
- McBratney, A.B.; Santos, M.M.; Minasny, B. On digital soil mapping. Geoderma 2003, 117, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R. Digital Soil Mapping: An Introductory Perspective; Lagacherie, P., McBratney, A.B., Voltz, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1217–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L.; Feng, L.I.U. Recent progress and future prospect of digital soil mapping: A review. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2871–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabas, M.; Tabbagh, A. A comparison of EMI and DC methods used in soil mapping-theoretical considerations for precision agriculture. In Precision Agriculture; Wageningen Academic: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Sudduth, K.A.; Kitchen, N.R.; Bollero, G.A.; Bullock, D.G.; Wiebold, W.J. Comparison of electromagnetic induction and direct sensing of soil electrical conductivity. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garré, S.; Hyndman, D.; Mary, B.; Werban, U. Geophysics conquering new territories: The rise of “agrogeophysics”. Vadose Zone J. 2021, 20, e20115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.M.; Franz, T.E.; Ge, Y.; Luck, J.D.; Heeren, D.M. Geophysical tools for agricultural management: Trends, challenges, and opportunities. Vadose Zone J. 2025, 24, e70029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, H.; Robinson, D.A.; Jones, S.B. Comparing bulk soil electrical conductivity determination using the DUALEM-1S and EM38-DD electromagnetic induction instruments. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedetto, D.; Castrignanò, A.; Rinaldi, M.; Ruggieri, S.; Santoro, F.; Figorito, B.; Gualano, S.; Diacono, M.; Tamborrino, R. An approach for delineating homogeneous zones by using multi-sensor data. Geoderma 2013, 199, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemoteau, J.; Tronicke, J. Evaluation of a rapid hybrid spectral-spatial domain 3D forward-modeling approach for loop-loop electromagnetic induction quadrature data acquired in low-induction-number environments. Geophysics 2016, 81, E447–E458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaga, J. The use of FDEM in hydrogeophysics: A review. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 139, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, D.; Brogi, C.; Brown, C.; Tuohy, P.; Daly, E. Linking electromagnetic induction data to soil properties at field scale aided by neural network clustering. Front. Soil Sci. 2024, 4, 1346028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, C.; Huisman, J.A.; Pätzold, S.; Von Hebel, C.; Weihermüller, L.; Kaufmann, M.S.; van der Kruk, J.; Vereecken, H. Large-scale soil mapping using multi-configuration EMI and supervised image classification. Geoderma 2019, 335, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Li, N.; Zare, E.; Wang, J.; Triantafilis, J. Mapping cation exchange capacity using a quasi-3d joint inversion of EM38 and EM31 data. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 200, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lück, E.; Guillemoteau, J.; Tronicke, J.; Klose, J.; Trost, B. Geophysical sensors for mapping soil layers—A comparative case study using different electrical and electromagnetic sensors. In Information and Communication Technologies for Agriculture—Theme I: Sensors; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 267–287. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, L.; Metcalfe, J. Assessingthe Causes, Impacts, Costs and Management of Dryland Salinity; Land and Water Resources Research and Development Corporation: Canberra, Australia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Binley, A.; Hubbard, S.S.; Huisman, J.A.; Revil, A.; Robinson, D.A.; Singha, K.; Slater, L.D. The emergence of hydrogeophysics for improved understanding of subsurface processes over multiple scales. WaterResour. Res. 2015, 51, 3837–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doolittle, J.A.; Brevik, E.C. The use of electromagnetic induction techniques in soils studies. Geoderma 2014, 223, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garré, S.; Blanchy, G.; Caterina, D.; De Smedt, P.; Romero-Ruiz, A.; Simon, N. Geophysical methods for soil applications. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Farzamian, M.; Paz, M.C.; Paz, A.M.; Castanheira, N.L.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Monteiro Santos, F.A.; Triantafilis, J. Mapping soil salinity using electromagnetic conductivity imaging—A comparison of regional and location-specific calibrations. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, J.D. Electromagnetic Terrain Conductivity Measurements at Low Induction Numbers; Technical Note 6; Geonics Limited: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Prochazka, M.J.; Triantafilis, J. Irrigation salinity hazard assessment and risk mapping in the lower Macintyre Valley, Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, T.; Amer, A.; Farzamian, M.; Bouksila, F.; Elkiki, M.; Eltarabily, M.G. Prediction of temporal and spatial soil salinity distributions using electromagnetic conductivity imaging and regional calibration. Irrig. Sci. 2025, 43, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCarlo, L.; Farzamian, M. Assessing the Impact of Brackish Water on Soil Salinization Using Time-Lapse Electromagnetic Induction Inversion. Land 2024, 13, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzamian, M.; Bouksila, F.; Paz, A.M.; Santos, F.M.; Zemni, N.; Slama, F.; Ben Slimane, A.; Selim, T.; Triantafilis, J. Landscape-scale mapping of soil salinity with multi-height electromagnetic induction and quasi-3d inversion in Saharan Oasis, Tunisia. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 284, 108330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamchuk, V.I.; Biswas, A.; Huang, H.H.; Holland, J.E.; Taylor, J.A.; Stenberg, B.; Wetterlind, J.; Singh, K.; Minasny, B.; Fidelis, C.; et al. Soil sensing. In SensingApproaches for Precision Agriculture; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 93–132. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, H.S.; Hoogmoed, W.B.; van Henten, E.J. Sensor data fusion to predict multiple soil properties. Precis. Agric. 2012, 13, 628–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Mokhtari, A.R.; Cohen, D.R.; Santos, F.A.M.; Triantafilis, J. Modelling Soil Salinity Across a Gilgai Landscape by Inversion of EM38 and EM31 Data. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongnawang, T.; Zare, E.; Srihabun, P.; Triantafilis, J. Comparing Electromagnetic Induction Instruments to Map Soil Salinity in Two-Dimensional Cross-Sections along the Kham-rean Canal Using EM Inversion Software. Geoderma 2020, 377, 114611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajhi, M.; Dobos, E. Characterization of Soil Moisture Regime in The Kairouan Region, Tunisia. Geosci. Eng. 2022, 10, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-N.-D.; Tapas, M.R.; Do, S.K.; Etheridge, R.; Lakshmi, V. Investigating the impacts of climate change on hydroclimatic extremes in the Tar-Pamlico River Basin, North Carolina. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 363, 121375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mougou, R.; Mansour, M.; Iglesias, A.; Chebbi, R.Z.; Battaglini, A. Climate Change and Agricultural Vulnerability: A Case Study of Rain-Fed Wheat in Kairouan, Central Tunisia. Reg. Environ. Change 2011, 11 (Suppl. S1), 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerbi, H.; Massuel, S.; Leduc, C.; Tarhouni, J. Assessing Groundwater Storage in the Kairouan Plain Aquifer Using a 3D Lithology Model (Central Tunisia). Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanavelu, A.; Naganna, S.R.; Al-Ansari, N. Irrigation-Induced Salinity and Sodicity Hazards on Soil and Groundwater: An Overview of Its Causes, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies. Agriculture 2021, 11, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzari, S.; Hachicha, M.; Bouhlila, R.; Battle-Sales, J. Characterization and Modeling of Water Movement and Salts Transfer in a Semi-Arid Region of Tunisia (BouHajla, Kairouan)—Salinization Risk of Soils and Aquifers. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 86, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemoteau, J.; Simon, F.X.; Lück, E.; Tronicke, J. 1D sequential inversion of portable multi-configuration electromagnetic induction data. Near Surf. Geophys. 2016, 14, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssens, D.; Delefortrie, S.; Bobe, C.; Hermans, T.; De Smedt, P. Improving the reliability of soil EC-mapping: Robust apparent electrical conductivity (rECa) estimation in ground-based frequency domain electromagnetics. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.L.; George, R.; Ryder, A. Soil Salinity Assessment Using the EM38: Field Operating Instructions and Data Interpretation; Department of Agriculture, Government of Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- McNeill, J.D. Rapid, Accuratee Mapping of Soil Salinity Using Electromagnetic Ground Conductivity Meters; Technical Note TN-18; Geonics Limited: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hanssens, D.; Delefortrie, S.; De Pue, J.; Van Meirvenne, M.; De Smedt, P. Frequency-domain electromagnetic forward and sensitivity modeling: Practical aspects of modeling a magnetic dipole in a multilayered half-space. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.W. A new method for the mechanical analysis of soils and other dispersions. J. Agric. Sci. 1922, 12, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staff, U.S.L. Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Agric. Handb. 1954, 60, 83–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, S.H.; Hohmann, G.W.; Nabighian, M.N. Electromagnetic Methods in Applied Geophysics; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1988; Volume 1, pp. 131–312. [Google Scholar]
- Guillemoteau, J.; Sailhac, P.; Boulanger, C.; Trules, J. Inversion of ground constant offset loop-loop electromagnetic data for a large range of induction numbers. Geophysics 2015, 80, E11–E21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, T.; Guillemoteau, J.; Vignoli, G.; Tronicke, J. Laterally constrained inversion (LCI) of multi-configuration EMI data with tunable sharpness. J. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 196, 104519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, W. Drip irrigation in agricultural saline-alkali land controls soil salinity and improves crop yield: Evidence from a global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Qiao, X.; Zuo, Q.; Shi, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, L.; Ben-Gal, A. Remotely sensed estimation of root-zone salinity in salinized farmland based on soil-crop water relations. Sci. Remote Sens. 2023, 8, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Yang, J. Quantitative evaluation of soil salinity and its spatial distribution using electromagnetic induction method. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantaravikorn, Y.; Ongsomwang, S. Soil Salinity Prediction and Its Severity Mapping Using a Suitable Interpolation Method on Data Collected by Electromagnetic Induction Method. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmans, J.W.; Qureshi, A.S.; Kisekka, I.; Munns, R.; Grattan, S.R.; Rengasamy, P.; Ben-Gal, A.; Assouline, S.; Javaux, M.; Minhas, P.S.; et al. Critical knowledge gaps and research priorities in global soil salinity. Adv. Agron. 2021, 169, 1–191. [Google Scholar]
- Karimzadeh, S.; Hartman, S.; Chiarelli, D.D.; Rulli, M.C.; D’Odorico, P. The tradeoff between water savings and salinization prevention in dryland irrigation. Adv. Water Resour. 2024, 183, 104604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casterad, M.A.; Herrero, J.; Betrán, J.A.; Ritchie, G. Sensor-based assessment of soil salinity during the first years of transition from flood to sprinkler irrigation. Sensors 2018, 18, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltarabily, M.G.; Amer, A.; Farzamian, M.; Bouksila, F.; Elkiki, M.; Selim, T. Time-Lapse Electromagnetic Conductivity Imaging for Soil Salinity Monitoring in Salt-Affected Agricultural Regions. Land 2024, 13, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakak, H.; Huang, J.; Zouahri, A.; Douaik, A.; Triantafilis, J. Mapping soil salinity in 3-dimensions using an EM38 and EM4Soil inversion modelling at the reconnaissance scale in central Morocco. Soil Use Manag. 2017, 33, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongnawang, T.; Zare, E.; Srihabun, P.; Khunthong, I.; Triantafilis, J. Digital soil mapping of soil salinity using EM38 and quasi-3d modeling software (EM4Soil). Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, R.; Timms, W.; Rengasamy, P.; Arshad, M.; Cresswell, R. Soil and Aquifer Salinization: Toward an Integrated Approach for Salinity Management of Groundwater. In Integrated Groundwater Management; Jakeman, A.J., Barreteau, O., Hunt, R.J., Rinaudo, J.D., Ross, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 377–412. [Google Scholar]
- Triantafilis, J.; Santos, F.M. Resolving the spatial distribution of the true electrical conductivity with depth using EM38 and EM31 signal data and a laterally constrained inversion model. Soil Res. 2010, 48, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, K.; Schmidhalter, U. Theory and Guidelines for the Application of the Geophysical Sensor EM38. Sensors 2019, 19, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsetidi, P.A.; Kargas, G.; Sotirakoglou, K. Investigation of Topsoil Salinity and Soil Texture Using the EM38-MK2 and the WET-2 Sensors in Greece. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
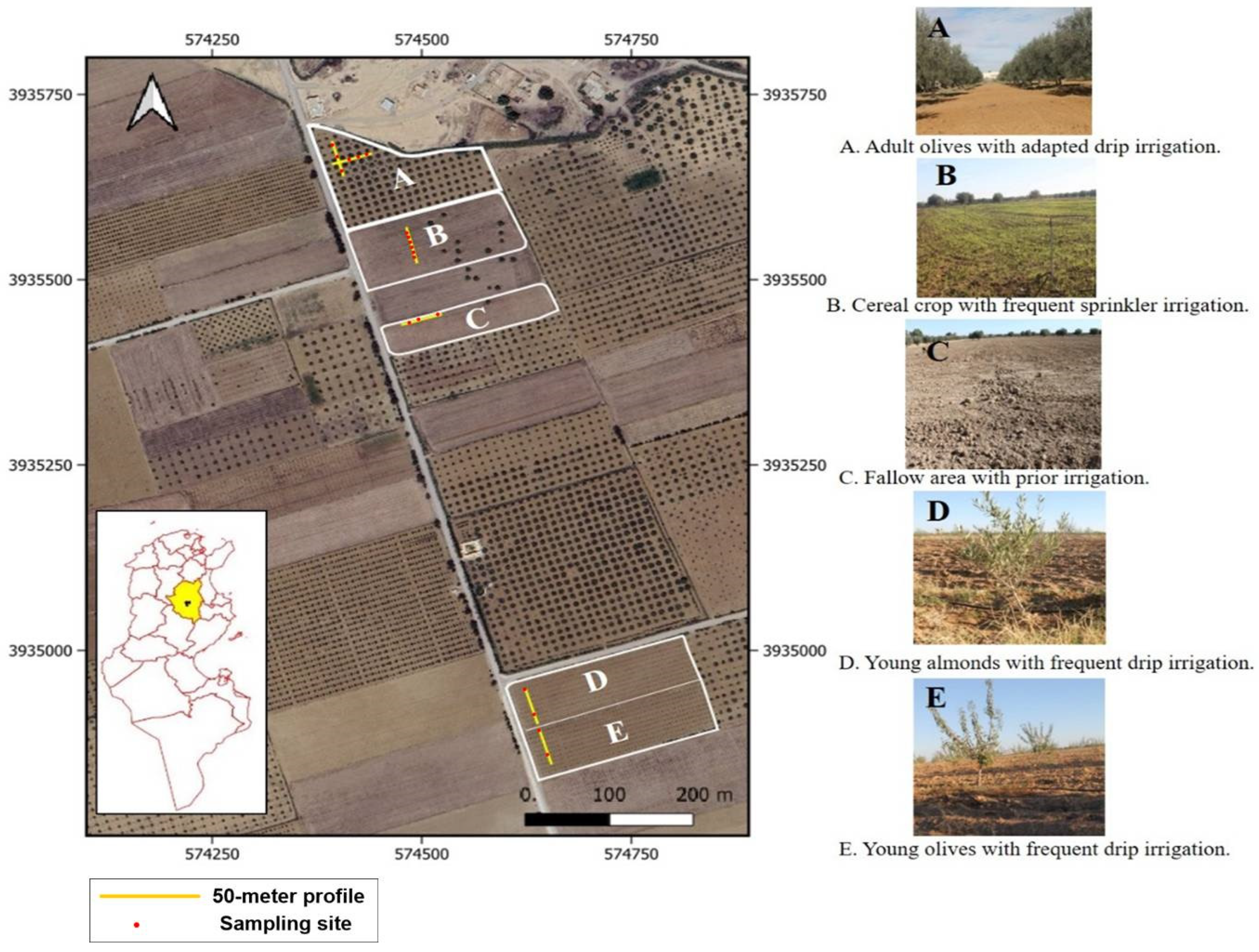
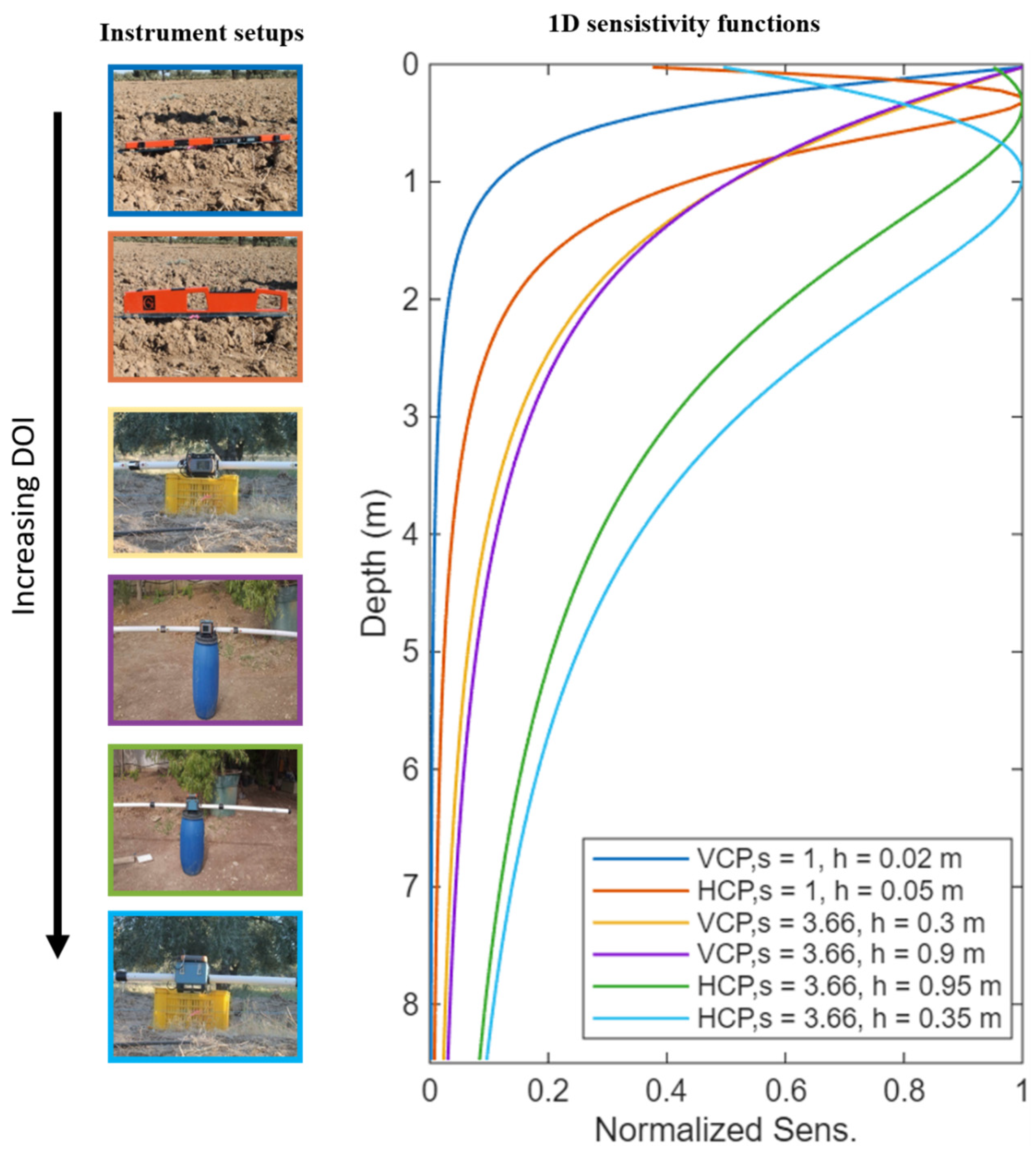
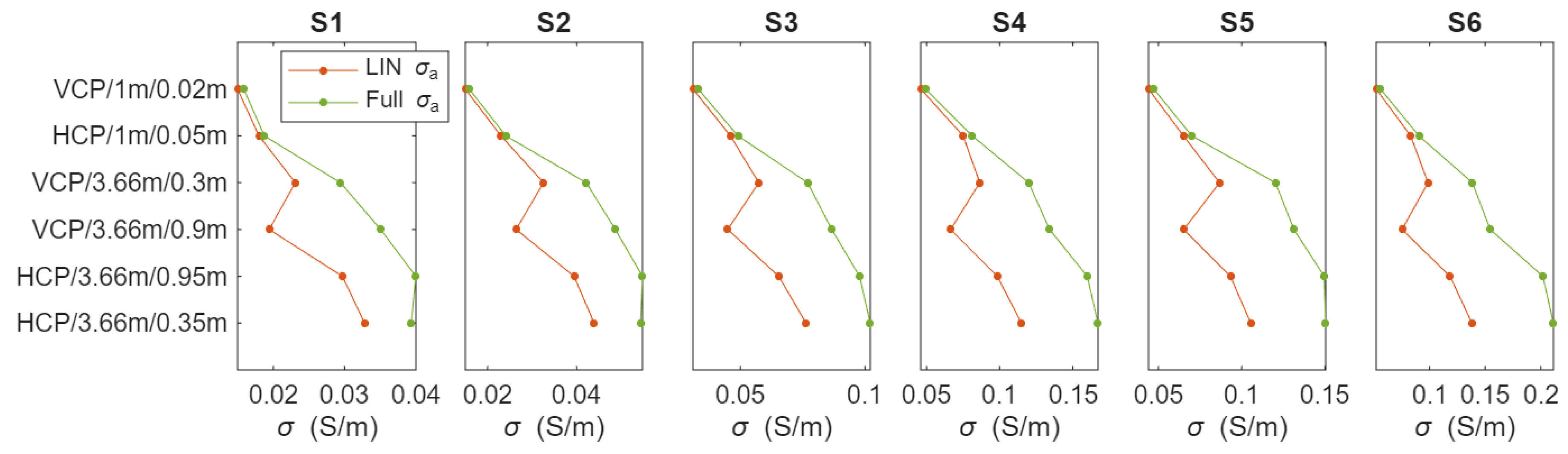
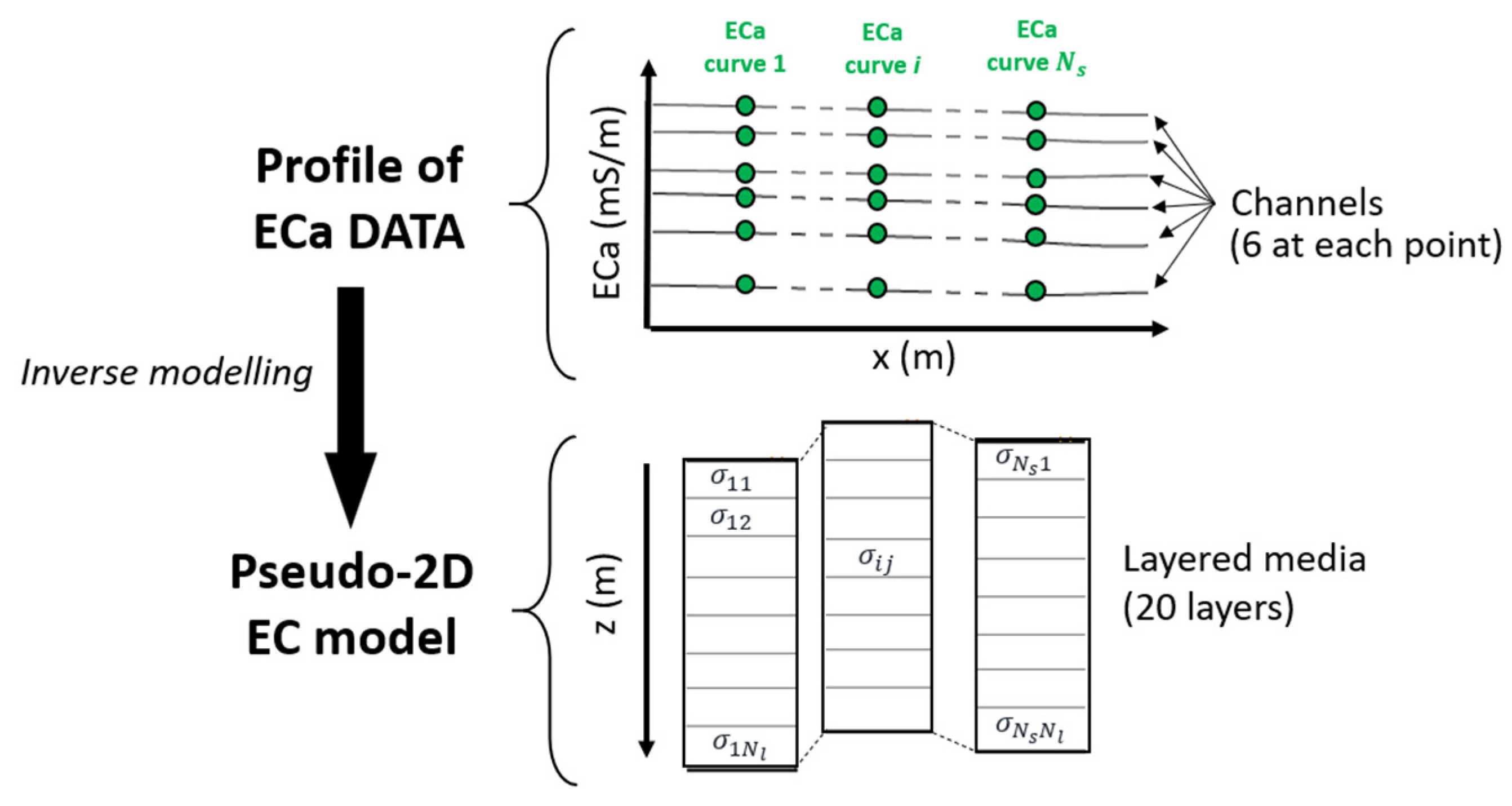
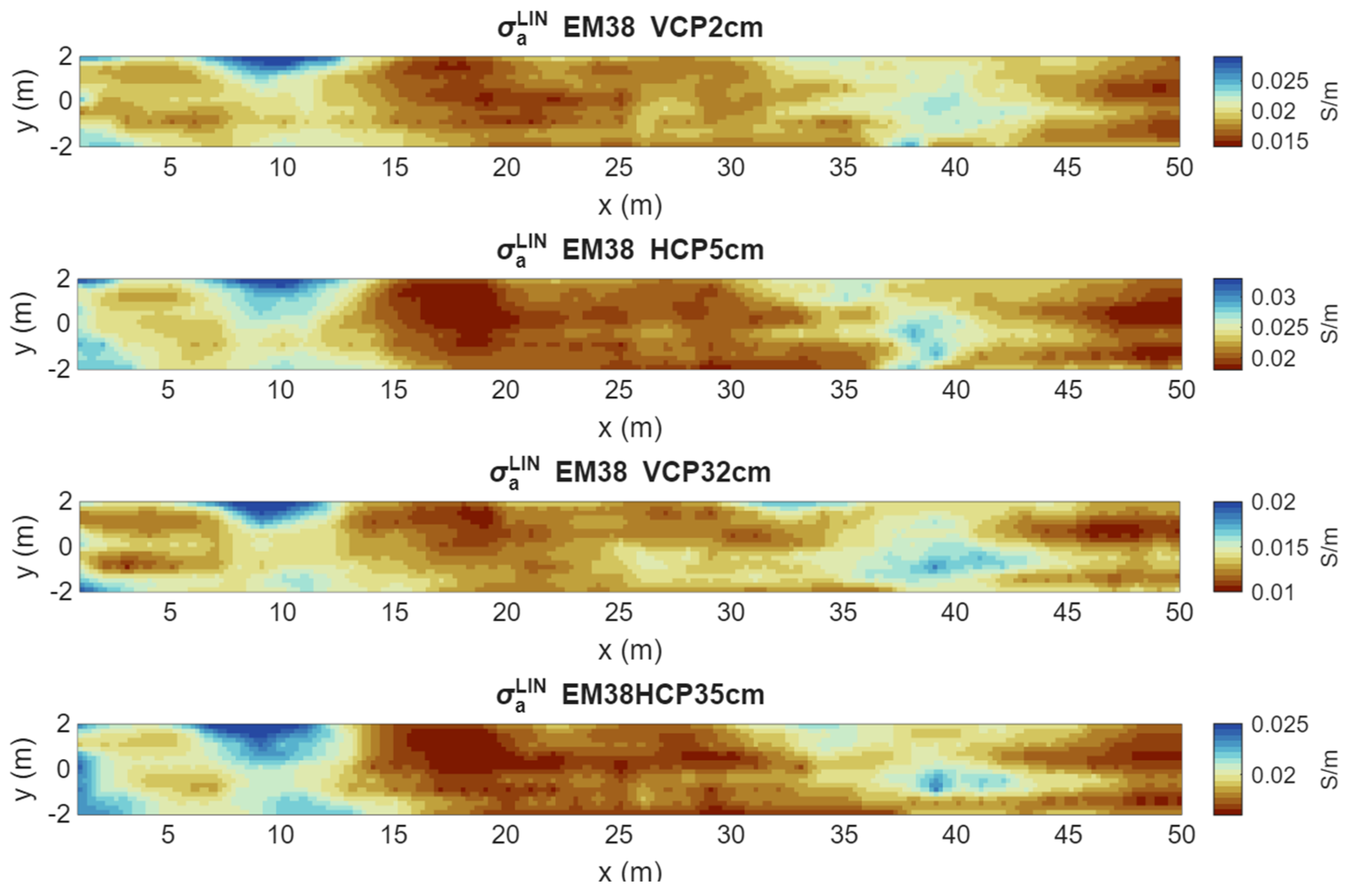
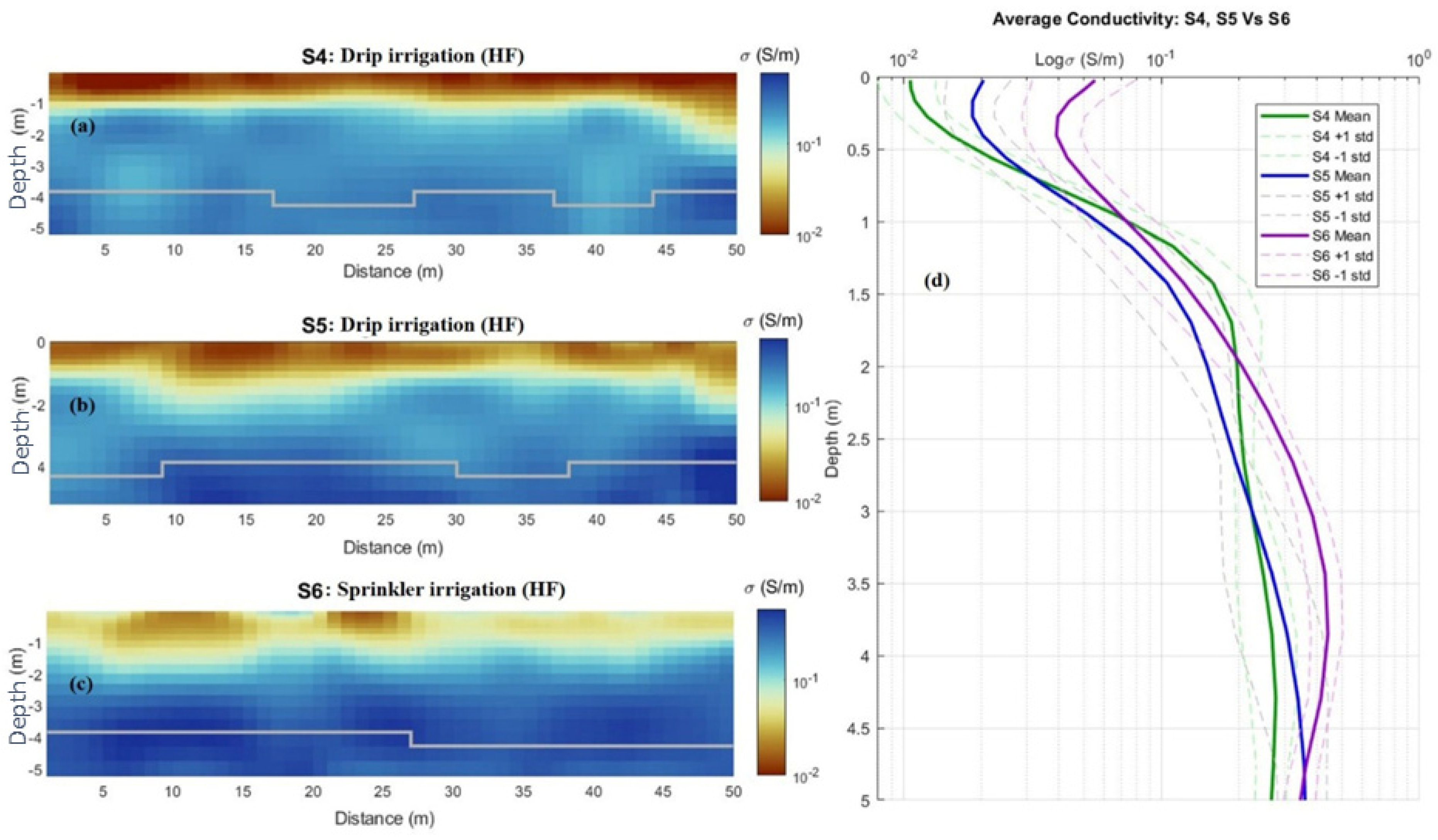
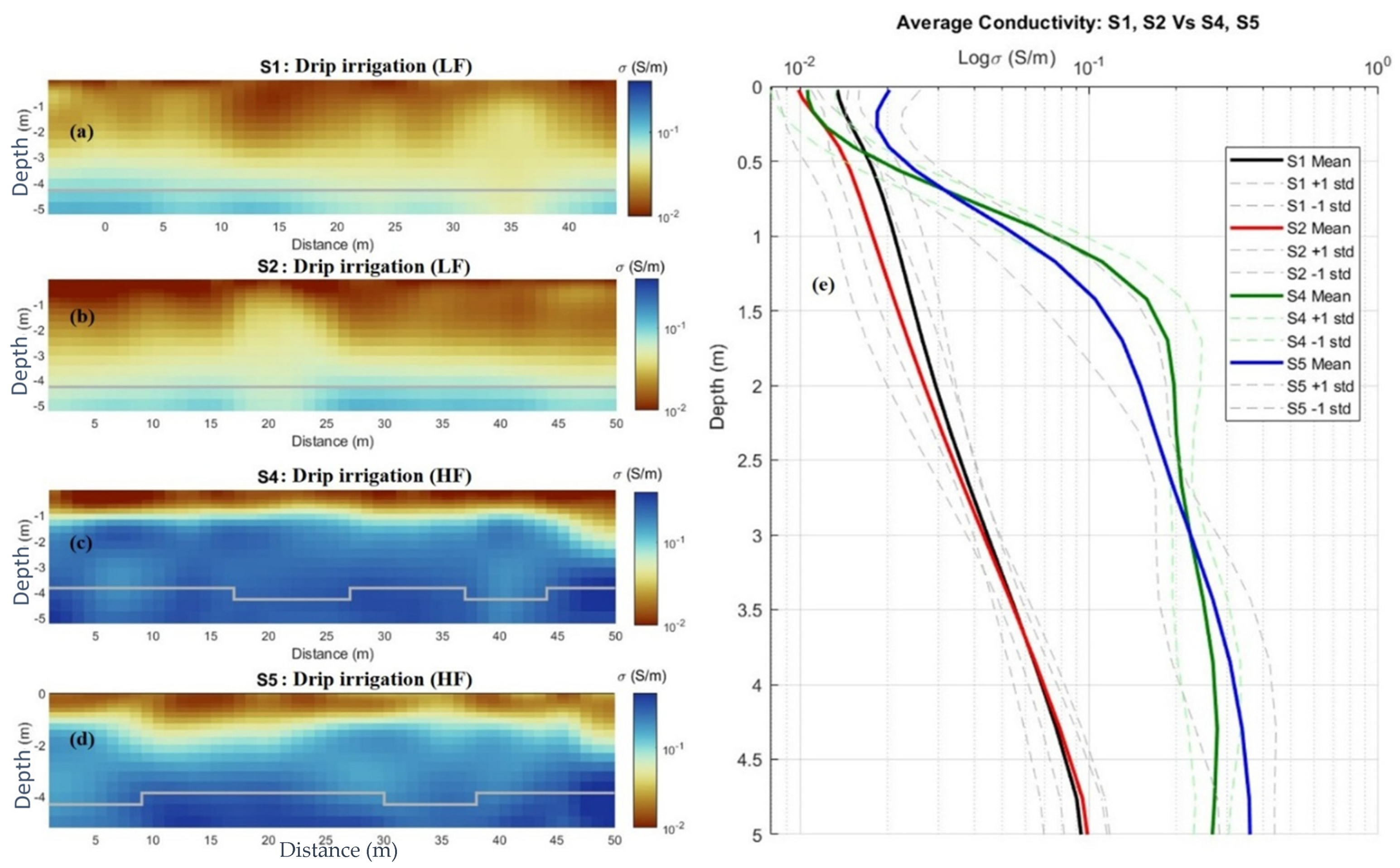
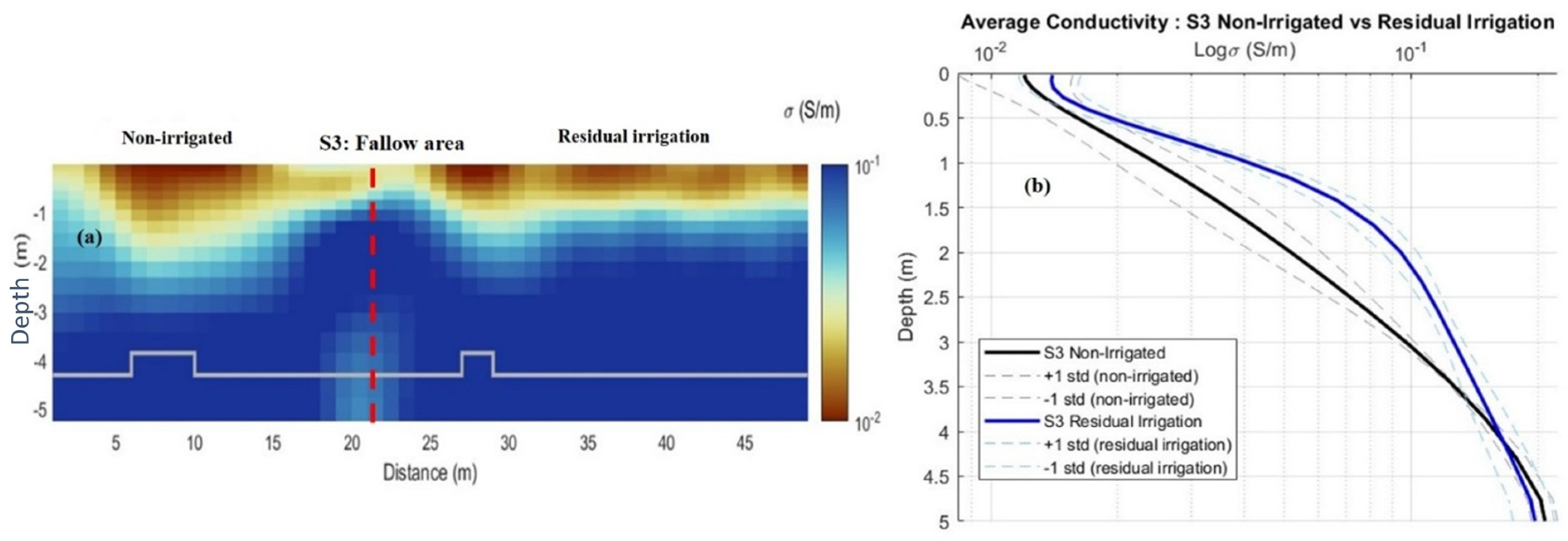
| Parameters | Moisture Content (%) | ECe (dS/m) |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | 11 | 3.99 |
| Median | 10 | 3.75 |
| Min. | 5 | 1.71 |
| Max. | 17 | 8.92 |
| CV (%) | 32 | 38 |
| Salinity | ECe | ECa (Rounded Values) |
|---|---|---|
| Low | <2 | <40 |
| Medium | 2–4 | 40–60 |
| High | >4 | >60 |
| Segments | Land Use | Irrigation System Management |
|---|---|---|
| S1 and S2 | Adult trees (Mature olive trees) | Adapted drip irrigation |
| S4 and S5 | Young trees (Young almond and olive trees) | Frequent drip irrigation |
| S6 | Irrigated Cereal (wheat) | Frequent sprinkler irrigation |
| S3 | Fallow land with irrigated antecedent | Irrigation stopped in 2019 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Allagui, D.; Guillemoteau, J.; Hachicha, M. Estimating Deep Soil Salinity by Inverse Modeling of Loop–Loop Frequency Domain Electromagnetic Induction Data in a Semi-Arid Region: Merguellil (Tunisia). Land 2026, 15, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/land15010032
Allagui D, Guillemoteau J, Hachicha M. Estimating Deep Soil Salinity by Inverse Modeling of Loop–Loop Frequency Domain Electromagnetic Induction Data in a Semi-Arid Region: Merguellil (Tunisia). Land. 2026; 15(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/land15010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleAllagui, Dorsaf, Julien Guillemoteau, and Mohamed Hachicha. 2026. "Estimating Deep Soil Salinity by Inverse Modeling of Loop–Loop Frequency Domain Electromagnetic Induction Data in a Semi-Arid Region: Merguellil (Tunisia)" Land 15, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/land15010032
APA StyleAllagui, D., Guillemoteau, J., & Hachicha, M. (2026). Estimating Deep Soil Salinity by Inverse Modeling of Loop–Loop Frequency Domain Electromagnetic Induction Data in a Semi-Arid Region: Merguellil (Tunisia). Land, 15(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/land15010032






