Integration of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism in the Suburbs of Megacities: A Case Study of Huangpi District, Wuhan City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Theoretical Framework
2.1. Research Trajectory and Theoretical Perspectives
2.2. Theoretical Foundations and Analytical Framework
3. Methods
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Research Framework and Data Sources
3.3. Research Methods and Data Processing
3.3.1. Spatial Distribution Analysis
3.3.2. Entropy-Weighted TOPSIS Method
3.3.3. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
3.3.4. Grey Relational Analysis
3.4. Indicator System Construction
3.4.1. Construction of the Agricultural High-Quality Development Indicator System
3.4.2. Construction of the Cultural High-Quality Development Indicator System
3.4.3. Construction of the Tourism High-Quality Development Indicator System
4. Results
4.1. Foundations and Current Status of Agricultural-Cultural-Tourism Integration
4.1.1. Foundations and Current Status of Agricultural Industry Development
4.1.2. Development Foundation and Current Status of the Cultural Industry
4.1.3. Development Foundation and Current Status of the Tourism Industry
4.2. Evaluation of High-Quality Development Levels in Agriculture, Cultural Industry, and Tourism
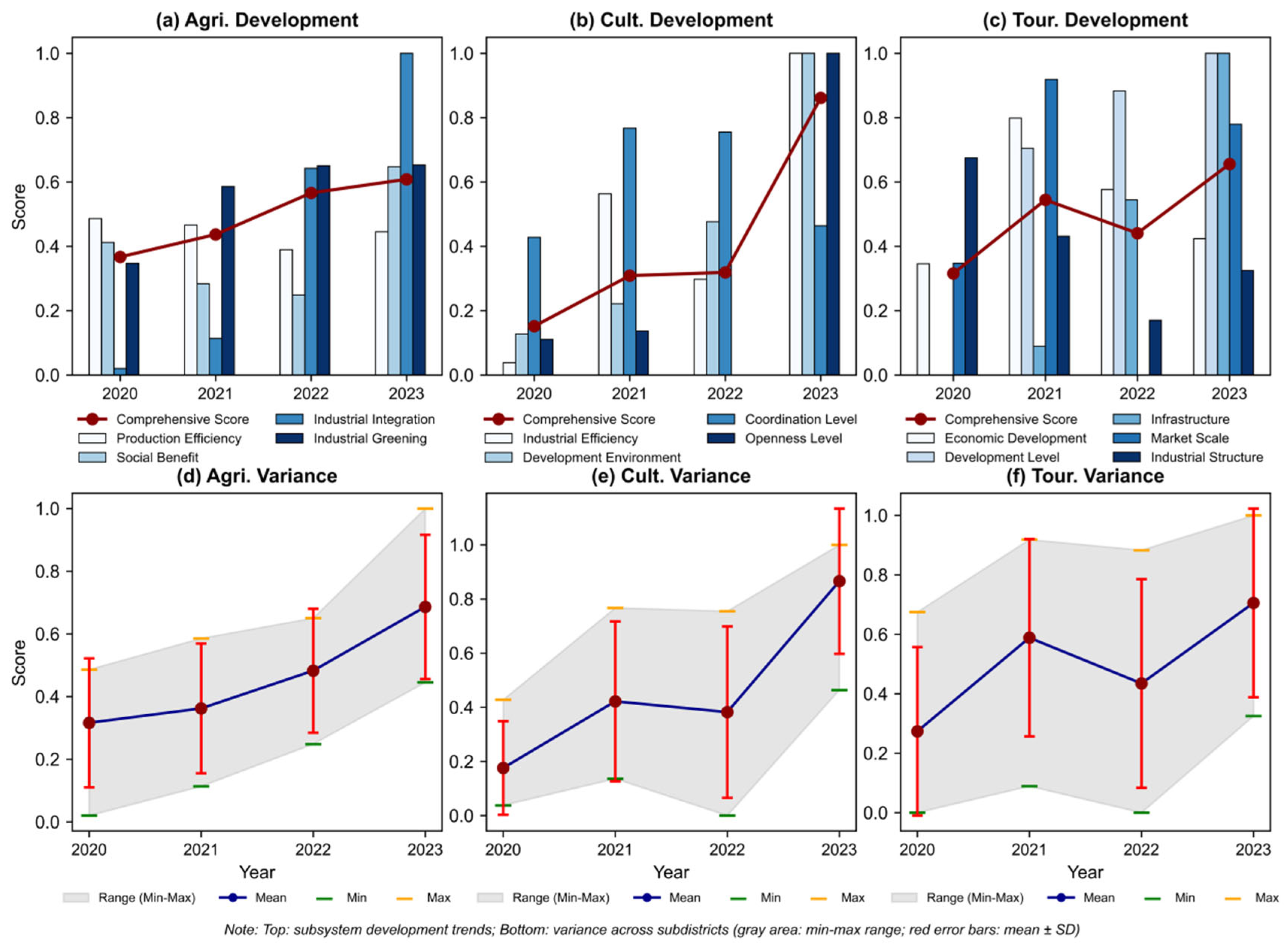
4.2.1. Evaluation of the High-Quality Development Level of the Agricultural Industry
4.2.2. Evaluation of the Cultural Industry High-Quality Development Level
- Industrial efficiency exhibited a V-shaped fluctuation, declining to 0.29 in 2021 before recovering to 1 in 2023 alongside market revival and productivity gains that were underpinned by government stabilization measures.
- Development environment demonstrated a J-shaped growth pattern, also reaching 1 in 2023, substantially supported by concrete policy measures. These included municipal-level stimuli such as the distribution of tourism consumption vouchers and travel benefit cards [95], as well as district-level relief efforts. Notably, Huangpi District implemented a loan interest subsidy program for key cultural and tourism enterprises in 2022 [96], a direct financial support measure guided by provincial-level recovery policies [97]. These multi-layered interventions helped sustain business operations during the downturn and primed the market for recovery.
- Coordination level displayed an inverted V-shape; although it slightly decreased to 0.46 in 2023, it overall maintained stable resilience.
- The openness level exhibited the most pronounced volatility, plummeting to 0 in 2022 before rebounding sharply to 1 in 2023, thereby becoming the indicator with the greatest magnitude of change. This dramatic shift is directly attributable to a surge in key underlying metrics: the number of visitors to cultural venues, which had remained between 100,000 and 120,000 from 2020 to 2022, skyrocketed to 1.248 million in 2023. Concurrently, the number of cultural and artistic performances doubled compared to the 2022 level.
4.2.3. Evaluation of the Tourism Industry High-Quality Development Level
4.2.4. Dimensional Variance in Subsystem Development
4.3. Evaluation of the Deep Integration Development Level of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism Based on the Coupling Coordination Degree Model
4.4. Grey Relational Analysis Results of Influencing Factors
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of Factors Influencing the Deep Integration Development Level of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism
5.2. Optimization Strategies for Deep Integration of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism
5.3. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, L.; Liao, X. From poverty to common prosperity: An evaluation of agricultural-cultural-tourism integration and its impact on economic growth. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1600264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Sun, D.; Wang, Z. Exploring the Rural Revitalization Effect under the Interaction of Agro-Tourism Integration and Tourism-Driven Poverty Reduction: Empirical Evidence for China. Land 2024, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Liu, Z.; Jin, C. How Does the Integration of Cultural Tourism Industry Affect Rural Revitalization? The Mediating Effect of New Urbanization. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Țicău, I.R.; Dan, M.; Hadad, S.; Nistoreanu, P. Sustainable Development in Peri-Urban Regions: A Triangulation Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-G.; Reid, B.; Meharg, A.; Banwart, S.; Fu, B. Optimizing Peri-URban Ecosystems (PURE) to re-couple urban-rural symbiosis. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahavacharin, A.; Likitswat, F.; Irvine, K.; Teang, L. Community-Based Resilience Analysis (CoBRA) to Hazard Disruption: Case Study of a Peri-Urban Agricultural Community in Thailand. Land 2024, 13, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas-Vásquez, D.; Spyra, M.; Jorquera, F.; Molina, S.; Caló, N.C. Ecosystem Services Supply from Peri-Urban Landscapes and Their Contribution to the Sustainable Development Goals: A Global Perspective. Land 2022, 11, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Díaz, P. Sustainable Land Governance for Water–Energy–Food Systems: A Framework for Rural and Peri-Urban Revitalisation. Land 2023, 12, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyra, M.; Cortinovis, C.; Ronchi, S. An overview of policy instruments for sustainable peri-urban landscapes: Towards governance mixes. Cities 2025, 156, 105508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D. Research on the Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Internal Mechanism of Cultural Industry in Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration. Master’s Thesis, Liaoning Normal University, Dalian, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qin, J.; Luo, L. Measurement and Countermeasures of the Integration Effect of Agriculture, Culture and Tourism in the Upper Reaches of the Min River. China Agric. Resour. Reg. 2023, 44, 232–246. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, E.; Lu, D.; Fang, S.; Duan, X.; Gao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, H.; Liu, Z. Analysis of Coupled and Coordinated Development of Cultivated Land Multifunction and Agricultural Mechanization in China. Land 2025, 14, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lu, F. Research on the Measurement and Influencing Factors of the Integration Level of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism in Southwest Ethnic Areas—Taking Qiandongnan Miao and Dong Autonomous Prefecture of Guizhou Province as an Example. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2025, 1–17. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3513.S.20250908.1605.033 (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China; The State Council. Opinions on Comprehensively Promoting Rural Revitalization and Accelerating Agricultural and Rural Modernization. Gaz. State Counc. People’s Repub. China 2021, 14–21. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=zE0--Q1IihR9jKyUk9xgODcxzVLMQ3meAK0Ur-_bLTbdtS-Z6VqjTnrSH_wFApE8c4H-depoaOHN8Nm8X4xkTH4OgyDyzNGjUX0oYoggnn-Gavr7qtck1mh1xI-RnhoIR8_Qv8ax19eoirQvXXOViBCrK4W70_XI5l5mWuh7eC_CLckpJMXBIg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- The State Council. Notice of the State Council on Issuing the “14th Five-Year Plan” for Tourism Development. Gaz. State Counc. People’s Repub. China 2022, 5, 28–46. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=zE0--Q1IihSfwFyAxCXziZFkvMUY30jLN-eLGo_QiuPiSpv0IHSY5LNOWb5NsKTB0d4d-uMPJH-GRrc4kCjDmiOXE1zE-_t6wMwdtHghshw2Q6DcbeQdG4lchsTsK6nu-h9qW-ct-7JjbsFkoifZb2n6k1cTCSyT8QvyVujTLWiXbF0TJc54Dw==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Ma, W.; Jiang, G.; Li, W.; Zhou, T. How do population decline, urban sprawl and industrial transformation impact land use change in rural residential areas? A comparative regional analysis at the peri-urban interface. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Dang, X.; Song, T.; Xiao, G.; Lu, Y. Agro-Tourism Integration and County-Level Sustainability: Mechanisms and Regional Heterogeneity in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, S. Exploration on the Development Path of Agricultural, Cultural and Tourism Industry Integration Under the Background of Rural Revitalization. Front. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2023, 11, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xiong, T.; Meng, D.; Gao, A.; Chen, Y. Does the Integrated Development of Agriculture and Tourism Promote Farmers’ Income Growth? Evidence from Southwestern China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Firdaus, R.; Xu, J.; Dharejo, N.; Jun, G. China’s Rural Revitalization Policy: A PRISMA 2020 Systematic Review of Poverty Alleviation, Food Security, and Sustainable Development Initiatives. Sustainability 2025, 17, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G. How Does Agro-Tourism Integration Influence the Rebound Effect of China’s Agricultural Eco-Efficiency? An Economic Development Perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 921103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Xiang, P.; Wang, H.; Xia, M. Driving Mechanisms of the Integration of Ecological Farms and Rural Tourism: A Mixed Method Study. Agriculture 2025, 15, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China; The State Council. The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council Issued the “Comprehensive Rural Revitalization Plan (2024–2027)”. People’s Daily, 23 January 2025; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.Q.; Liu, J.X. From Tradition to Innovation: The Role of Culture Tourism in Transforming Chinese Agriculture. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, J. Nonlinear Nexus between Agricultural Tourism Integration and Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity in China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, M.; Tan, Z.; Han, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Agriculture–Tourism Integration’s Impact on Agricultural Green Productivity in China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Jiang, W.; Xie, A. Can the integration of agriculture and tourism foster agricultural green development? An empirical analysis based on panel data from 30 provinces in China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1570767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Zhong, X.; Tang, L. A Study on the Integrated Development Model of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism in Guangxi: Based on a Case Study of Four Locations in Three Cities. J. Educ. Humanit. Soc. Res. 2025, 2, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M. Optimization research on the integration development path of agricultural, cultural and tourism industries in Yijun County based on data analysis. J. Comb. Math. Comb. Comput. 2025, 127a, 8169–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Qiao, W.; Hu, Y.; He, T.; Jia, K.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y. Land-Use Transition of Tourist Villages in the Metropolitan Suburbs and Its Driving Forces: A Case Study of She Village in Nanjing City, China. Land 2021, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Liu, G.; Jing, C.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Mao, W.; Shen, L.; Dai, K.; Wu, X. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Driving Factors of Cropland Abandonment in Metropolitan Suburbs: A Case Study of Chengdu Directly Administered Zone, Tianfu New Area, Sichuan Province, China. Land 2025, 14, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Q.Q.; Tang, C.C.; Liu, H.X.; Cui, M.R. Spatial characteristics and restructuring model of the agro-cultural heritage site in the context of culture and tourism integration. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuhan Municipal People’s Government. Huangpi Selected into the 2023 National Rural Revitalization Demonstration County Creation List. Official Portal of the Wuhan Municipal People’s Government. 5 September 2023. Available online: https://www.wuhan.gov.cn/sy/whyw/202309/t20230905_2258348.shtml (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Wang, W.; Xin, J.; Yang, S.; Kang, Q.; Yu, H.; Sun, P.; Cui, Y.; Wang, W.; Peng, X. Analysis of the Practical Pathway for All-for-One Tourism in Huangpi District to “Break Through and Stand Out” Under the Background of Rural Revitalization. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2024, 52, 106–108. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=zE0--Q1IihRkiNJz66UxG_hIbrBW50e_4Np0j92oKP48L8q2f7zk2dFbfZeX78Rtsdam-SyfQWK8GqruD7p_1ccp70-lKLfgxVjD8ceC9mBUxwAX-o0zs8Om94_cL2ICpi7-0ukSd23MNI8OjD5kx91LdAbsx5AUB-ASkodQjZhcG9_EdGqN23htTZgYkcY8&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Le, M. Hubei Wuhan: Exploring the Path to Agricultural and Rural Modernization in a Megacity. Farmers’ Daily, 3 June 2025; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dernoi, L.A. Farm tourism in Europe. Tour. Manag. 1983, 4, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalager, A.-M. Agricultural diversification into tourism: Evidence of a European Community development programme. Tour. Manag. 1996, 17, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, R.; Vass, A. Tourism, farming and diversification: An attitudinal study. Tour. Manag. 2006, 27, 1040–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollenburg, C.; Buckley, R. Stated Economic and Social Motivations of Farm Tourism Operators. J. Travel Res. 2007, 45, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Wu, M.; Liu, X.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y. Research on the Measurement and Improvement Strategy of Integration of Agriculture, Culture and Tourism in Hebei Province Under the Strategy of Rural Revitalization. Adv. Sustain. 2024, 13, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, X.; Yan, S.; Cui, L.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y. A Quantitative Model to Measure the Level of Culture and Tourism Integration Based on a Spatial Perspective: A Case Study of Beijing from 2000 to 2022. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Liu, J. Exploring Spatial–Temporal Coupling and Its Driving Factors of Cultural and Tourism Industry in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, W.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, X.; Mao, X.; Lan, H. Mechanism and Empirical Research on the Integrated Development of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism Based on Symbiosis Theory—A Case Study of Four Typical Tea-Producing Counties in Yunnan. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2025, 1–17. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3513.s.20250217.1135.002 (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Chen, G.; Dai, Q. The Characteristics, Mechanisms, and Impacts of Rural Homestay Development Under the Integration of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism. Soc. Sci. 2025, 3, 83–89. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/45.1008.C.20250701.1447.020 (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Fang, S.; Jiang, W.; Bu, X.; Ma, H. The Impact of Agricultural-Cultural-Tourism Integration on the Comprehensive Revitalization of Rural Areas in Border Regions. Res. Agric. Mod. 2025, 46, 916–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Du, B. A Study on the Cultural Heritage of Traditional Villages and the Integration Strategy of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism from the Perspective of Comprehensive Rural Revitalization—A Case Study of Binyang County, Guangxi. Guangxi Ethn. Stud. 2025, 1, 172–180. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=zE0--Q1IihQueTE82FNtofrEkbNyQrf0H2UK2rGwlPrBfgQNPi13YC6Z2i74FJm-JoBfY7iJm1Ed9kNc_RwgnbHj0uCGQiabw5QG1zz3yuL7nQ01b_rYj3ySPPGeZH40k4pE3d8WXSX15aT2YitQtOvT5B2EOY3ZO-Rds9r75_O93pDzSKCe4IdvdS2wKjul&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Zhao, B.; Zhan, S. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling Coordination Degree Between Agricultural-Cultural-Tourism Integration and Rural Revitalization: A Case Study of Shaanxi Province. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2025, 1–14. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3513.s.20250217.1359.016 (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Zhao, P.; Guo, J. Operational Models and Practical Pathways for Agricultural-Cultural-Tourism Integration to Empower Agricultural and Rural Modernization: A Case Study Based on Three Typical Villages. Rural Econ. 2024, 6, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Lee, S.; Ahn, Y.-J.; Kiatkawsin, K. Tourist-Perceived Quality and Loyalty Intentions towards Rural Tourism in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Li, X. Perceived Value, Place Identity, and Behavioral Intention: An Investigation on the Influence Mechanism of Sustainable Development in Rural Tourism. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y. Research on the Branding Development of Rural Tourism Destinations from the Perspective of Product Level. Front. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2022, 5, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, X. Counterurban sensibilities in the global countryside: The relational making of rurality and heritage in Xizhou Town, Southwest China. Habitat Int. 2024, 149, 103109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, B. Rural tourism in China: ‘Root-seeking’ and construction of national identity. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2024, 60, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chou, R. Rural revitalization of Xiamei: The development experiences of integrating tea tourism with ancient village preservation. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 90, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, Z. Investigating the Impact of Environmental Graphics on Local Culture in Sustainable Rural Cultural Tourism Spaces. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Xue, X. The influence of rural tourism landscape perception on tourists’ revisit intentions—A case study in Nangou village, China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. Research on Innovative Marketing Strategies of Tourism Destination Brands under the Background of Cultural Tourism Integration. SHS Web Conf. 2025, 213, 02025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, N. Technological change in the machine tool industry, 1840–1910. J. Econ. Hist. 1963, 23, 414–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R. Development of Tourism for Culture and Innovation Based on Convergence of Data in the Perspective of Industrial Integration. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 4174050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y. Research on the integration path of cultural creative industry and tourism industry based on collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 2023, 9, 00551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. Transforming China’s Tourism Industry: The Impact of Industrial Integration on Quality, Performance, and Productivity. J. Knowl. Econ. 2024, 15, 18116–18153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. Research on the Realization Mechanism of Industrial Integration Development under the Goal of Rural Common Prosperity. J. Manag. Soc. Dev. 2025, 2, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. The realistic dilemma and optimization strategy of Guangxi’s integration of culture and tourism to promote rural revitalization. Tour. Manag. Technol. Econ. 2024, 7, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y. Research on Rural Industry Integration Development Model under the Perspective of Agricultural Business Administration. Mod. Econ. Manag. Forum 2025, 6, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, R. Development of Rural Regions in China: Evidence of Industry Integration by the Residents of Yongan Village (Quanzhou City, China). Sustainability 2023, 15, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Han, M. Addressing global challenges: How does the integration of rural industries in China enhance agricultural resilience? PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0327796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.; Shan, L. Research on Financial Deepening and the Development of Industrial Integration in Poverty-eliminated Counties. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 58, 104448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Theoretical Research on Promoting the Integrated Development of Rural Industry Through the Digital Economy. Adv. Econ. Manag. Political Sci. 2025, 174, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Fang, J. Research on the Pathways of Rural Industry Integration under the Context of Rural Revitalization. Sci. J. Econ. Manag. Res. 2025, 7, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Yuan, S. Research on the Optimization and Upgrading of the Industrial Chain of Zhanjiang Diving Enterprises from the Perspective of Cultural and Tourism Integration. Econ. Bus. Manag. 2025, 2, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangpi District People’s Government. Huangpi District Overview. Available online: https://www.huangpi.gov.cn/zjhp/hpgk/hpgk_17625/ (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasiou, J.; Ploskas, N. TOPSIS. In Multiple Criteria Decision Aid Methods, Examples and Python Implementations; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.Y. Effects of the entropy weight on TOPSIS. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 168, 114186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, T.; Feng, T.; An, P. Performance evaluation and correlation analysis of land use based on entropy weight TOPSIS model. J. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Du, T.; Xie, X.; Liang, H.; Huang, A.; Han, Q. Comprehensive evaluation and spatial analysis of county-level economy in Chongqing based on entropy weight TOPSIS and GIS. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 34, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kong, W.; Ren, L.; Zhi, D.; Dai, B. Misconceptions and Correction of Domestic Coupling Coordination Model. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 793–810. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.L.; Zheng, S.Y. Coupling coordination between agriculture and tourism in the Qinba Mountain area: A case study of Shanyang County, Shanxi Province. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 31859–31878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wang, B.; Ao, Y.B.; Bahmani, H.; Chai, B.B. The coupling and coordination degree of urban resilience system: A case study of the Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 101, 107145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, L. China’s digital economy and green development coupling coordination spatiotemporal characteristics and driving mechanism. J. Geogr. 2024, 79, 971–990. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, A.N.; Zhang, W.S.; Zhou, F.; Peng, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Quantitative Assessment of Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of Agricultural Development Level in China: A County-Level Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Li, X.P.; Liu, L.J.; Chen, Y.Z.; Wang, X.W.; Lu, S.H. Coupling and coordinated development of new urbanization and agro-ecological environment in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carof, M.; Colomb, B.; Aveline, A. A guide for choosing the most appropriate method for multi-criteria assessment of agricultural systems according to decision-makers’ expectations. Agric. Syst. 2013, 115, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Sun, D.S.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, X.J.; Yu, G.Q.; Zhao, X.J. An evaluation of China’s agricultural green production: 1978–2017. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Chen, X.H.; Jiang, L.S. Assessment and Improvement Strategies for Sustainable Development in China’s Cultural and Tourism Sector. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubadji, A.; Osoba, B.J.; Nijkamp, P. Culture-based development in the USA: Culture as a factor for economic welfare and social well-being at a county level. J. Cult. Econ. 2015, 39, 277–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalto, V.; Moura, C.J.T.; Langedijk, S.; Saisana, M. Culture counts: An empirical approach to measure the cultural and creative vitality of European cities. Cities 2019, 89, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, P.C.; Roders, A.R.P.; Colenbrander, B.J.F. Measuring links between cultural heritage management and sustainable urban development: An overview of global monitoring tools. Cities 2017, 60, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, D.; Huang, R.; Hu, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C. The Spatial Spillover Effects of County-Level Tourism Economic Growth in Zhejiang Province. Prog. Geogr. 2020, 39, 1512–1521. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=zE0--Q1IihSW51xDGDGswe_u-uG68l2R0vGYrSOMDWU2xHi9kdfcwXfTFXU_Rs_RgqWVE9CeIiW7Pg3yunZLjwWpFx-besz2hdrtZSqYALO-7BGAnDBgMoP-iAojOTXS7jA8LMGj8hhJUHi4JpkqBhzFrP7PJqupCpI9EMAK0qy8SN0CGBiJjbMwncrXfkP4&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 1 December 2025). [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Xiong, X. Evaluation of the coordination degree of county-level ecotourism and urban-rural integration in Chang-Zhu-Tan region. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2024, 44, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, W.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Assessment of tourism ecological carrying capacity based on multi-scale fusion: A case study of coastal counties in Jiangsu Province. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 1575–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, D.D.; Xu, D.; Yu, F.L.; Hou, B. Spatiotemporal evolution and mechanisms of tourism efficiency and its decomposition: Evidence from 63 counties in Zhejiang, China. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0297522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.R.; Chi, L.; Zhang, T.Y.; Wang, Y.J. Optimization of Tourism Management Based on Regional Tourism Competitiveness Evaluation: Evidence from Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17775-2024; Rating of Quality Levels of Tourist Attractions. State Administration for Market Regulation & Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2024.
- General Office of the People’s Government of Wuhan Municipality. Notice on Printing and Distributing the Implementation Plan for Supporting the Development of the Cultural and Tourism Industry in Wuhan in the Post-Epidemic Era (Wu Zheng Ban [2020] No. 139). Official Portal of the People’s Government of Wuhan Municipality, 24 August 2020. Available online: https://www.wuhan.gov.cn/zwgk/xxgk/zfwj/bgtwj/202008/t20200824_1432378.shtml (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Huangpi District Finance Bureau. Notice on Issuing the Budget Quota for Interest Subsidy Assistance Funds to Tourism Enterprises in 2022 (Pi Cai Yu Han [2022] No. 1515). Huangpi District People’s Government, 28 September 2022. Available online: https://www.huangpi.gov.cn/bmzl/qczj_bmzl/fdzdgknr_qczj/czzj_qczj/czzxzj_qczj/202210/t20221017_2059582.html (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Department of Culture and Tourism of Hubei Province. Notice on Printing and Distributing the Implementation Opinions on Promoting High-Quality Development of the Cultural and Tourism Industry in the Post-Epidemic Era (E Wen Fa [2022] No. 7). Official Portal of the Department of Culture and Tourism of Hubei Province, 16 June 2022. Available online: https://wlt.hubei.gov.cn/zfxxgk/zc/gfxwj/202206/t20220616_4178446.shtml (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Ma, T.; Wang, Y.N.; Zhang, L.; Hong, W.Y.; Yang, X.C. Creative assets, people, and places: Rural art action practices of US nonprofit organizations. J. Rural Stud. 2025, 113, 103476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.; Rowe, F.; Pollock, V. Creating the good life? A wellbeing perspective on cultural value in rural development. J. Rural Stud. 2018, 59, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, E.; Townsend, L. The Contribution of the Creative Economy to the Resilience of Rural Communities: Exploring Cultural and Digital Capital. Sociol. Rural. 2016, 56, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H. Impact of Investment in Tourism Infrastructure Development on Attracting International Visitors: A Nonlinear Panel ARDL Approach Using Vietnam’s Data. Economies 2021, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, A.M.; Marzouk, A.M. Memorable tourist experiences: The role of smart tourism technologies and hotel innovations. Tour. Recreat. Res. 2024, 49, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.R.; Mei, X.R.; Wang, J.D.; Huang, F.; Hao, W.P.; Li, B.G. Drip fertigation significantly increased crop yield, water productivity and nitrogen use efficiency with respect to traditional irrigation and fertilization practices: A meta-analysis in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Cheng, M.H.; Wu, L.F.; Fan, J.L.; Li, S.; Wang, H.D.; Qian, L. Review on Drip Irrigation: Impact on Crop Yield, Quality, and Water Productivity in China. Water 2023, 15, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.J.; Wang, M.S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.G.; Huang, X.J. Urban expansion and the urban-rural income gap: Empirical evidence from China. Cities 2022, 129, 103831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orîndaru, A.; Popescu, M.F.; Alexoaei, A.P.; Caescu, S.C.; Florescu, M.S.; Orzan, A.O. Tourism in a Post-COVID-19 Era: Sustainable Strategies for Industry’s Recovery. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfi, S.; Hall, C.M.; Shabani, B. COVID-19 and international travel restrictions: The geopolitics of health and tourism. Tour. Geogr. 2023, 25, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinazzi, M.; Davis, J.T.; Ajelli, M.; Gioannini, C.; Litvinova, M.; Merler, S.; Piontti, A.P.Y.; Mu, K.P.; Rossi, L.; Sun, K.Y.; et al. The effect of travel restrictions on the spread of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. Science 2020, 368, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Li, T.; Li, Y. Analyzing the impact of COVID-19 on consumption behaviors through recession and recovery patterns. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Chen, X.M.; Wang, L. A tale of two recoveries: Uncovering the imbalance between state-driven production and private consumption in post-pandemic Wuhan, China. Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2022, 15, 725–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Measurement Method | Unit | Attribute | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production Efficiency | Output Value of the Primary Industry | Output Value of the Primary Industry | Ten thousand yuan | + | 0.046 |
| Per Capita Cultivated Land Area | Cultivated Land Area/Rural Population | m2/person | + | 0.132 | |
| Land Productivity | Total Grain Output/Sown Area | Kg/mu | + | 0.080 | |
| Proportion of Primary Industry Added Value | Added Value of Primary Industry/Regional GDP | % | + | 0.056 | |
| Social Benefits | Urban–Rural Income Ratio | Urban Disposable Income per Capita/Rural Disposable Income per Capita | — | − | 0.048 |
| Urbanization Rate | Urban Permanent Population/Total Permanent Population | % | − | 0.079 | |
| Disposable Income of Rural Households Electrification Level | Disposable Income of Rural Households | Yuan | + | 0.050 | |
| Total Number of Employees | Rural Electricity Consumption/Primary Industry Labor Force | kWh/person | + | 0.050 | |
| Industrial Integration Level | Number of New Agricultural Business Entities | Number of New Agricultural Business Entities | Unit | + | 0.090 |
| Investment in Agricultural and Sideline Food Processing Industry | Investment in Agricultural and Sideline Food Processing | Ten thousand yuan | + | 0.053 | |
| Industrial Structure Optimization | Total Output Value of Farming, Forestry, Animal Husbandry, and Fishery Services/Total Output Value of Agriculture, Forestry, Animal Husbandry, and Fishery | — | + | 0.093 | |
| Industrial Greening Level | Fertilizer Application Intensity | Total Fertilizer Application/Total Sown Area | Ton/mu | − | 0.047 |
| Pesticide Application Intensity | Total Pesticide Application/Total Sown Area | Ton/mu | − | 0.052 | |
| Mulching Film Usage Rate | Total Agricultural Plastic Film Used/Total Sown Area | Ton/Hectare | − | 0.070 | |
| Effective Irrigation Rate | Effectively Irrigated Area/Total Sown Area | % | + | 0.054 |
| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Unit | Metric Attribute | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industry Efficiency | Operating Revenue of Cultural Services Enterprises Above Designated Size | Ten thousand yuan | + | 0.056 |
| Added Value of Assets in Cultural Services Enterprises Above Designated Size | Ten thousand yuan | + | 0.1 | |
| Number of Employees in Cultural Services Enterprises Above Designated Size | Person | + | 0.061 | |
| Total Assets of Cultural Services Enterprises Above Designated Size | Ten thousand yuan | + | 0.068 | |
| Development Environment | Number of Cultural Venues | Piece | + | 0.12 |
| Per Capita Cultural Consumption Expenditure of Residents | Yuan | + | 0.055 | |
| Per Capita Public Library Collections | Copy, Item | + | 0.121 | |
| Proportion of Cultural Industry | % | + | 0.051 | |
| Coordination Level | Per Capita Cultural and Entertainment Consumption Expenditure Ratio of Urban and Rural Residents | — | − | 0.051 |
| Advanced Industrial Structure | % | + | 0.052 | |
| Open to the Outside World | Number of Visitors to Cultural Venues | Ten thousand yuan | + | 0.206 |
| Number of Artistic Performance Events | Site | + | 0.06 |
| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Unit | Metric Attribute | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level of Tourism Economic Development | Total Tourism Revenue | Billion Yuan | + | 0.07 |
| Comprehensive Income from Rural Leisure Tourism | Billion Yuan | + | 0.095 | |
| Degree of Tourism Resources Development | Number of 5A Scenic Spots | Company | + | 0 |
| Number of 4A Scenic Spots | Company | + | 0.06 | |
| Number of 3A Scenic Spots | Company | + | 0.07 | |
| Provincial Demonstration Sites for Leisure Agriculture and Rural Tourism | Unit | + | 0.066 | |
| Maturity of Tourism Infrastructure | Number of Tourist Hotels | Company | + | 0.158 |
| A-Grade Tourist Restrooms | Seat | + | 0.088 | |
| Tourism Market Size | Number of Tourists | Ten Thousand People | + | 0.063 |
| Launch of Affordable Tourism Cards | Ten Thousand Sheets | + | 0.107 | |
| Industrial Structure | Proportion of the Tertiary Industry | % | + | 0.072 |
| Proportion of Tourism Expenditure in Public Finance Budget Expenditure | % | + | 0.15 |
| Number | Influencing Factor Indicator | Relevance Value | TOPSIS Weight | Number | Influencing Factor Indicator | Relevance Value | TOPSIS Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Total Assets of Cultural Services Enterprises Above Designated Size | 0.95 | 0.068 | 20 | Number of New Agricultural Business Entities | 0.77 | 0.090 |
| 2 | Number of Employees in Cultural Services Enterprises Above Designated Size | 0.93 | 0.061 | 21 | Number of Visitors to Cultural Venues | 0.76 | 0.206 |
| 3 | Proportion of the Tertiary Industry | 0.92 | 0.072 | 22 | Output Value of the Primary Industry | 0.75 | 0.046 |
| 4 | Disposable Income of Rural Households | 0.9 | 0.050 | 23 | Number of 4A Scenic Spots | 0.73 | 0.06 |
| 5 | Effective Irrigation Rate | 0.87 | 0.054 | 24 | Number of Artistic Performance Events | 0.73 | 0.06 |
| 6 | Land Productivity | 0.87 | 0.080 | 25 | Total Tourism Revenue | 0.7 | 0.07 |
| 7 | A-Grade Tourist Restrooms | 0.86 | 0.088 | 26 | Per Capita Cultural Consumption Expenditure of Residents | 0.69 | 0.055 |
| 8 | Urbanization Rate | 0.86 | 0.079 | 27 | Number of Tourists | 0.64 | 0.063 |
| 9 | Operating Revenue of Cultural Services Enterprises Above Designated Size | 0.86 | 0.056 | 28 | Launch of Affordable Tourism Cards | 0.6 | 0.107 |
| 10 | Investment in Agricultural and Sideline Food Processing Industry | 0.85 | 0.053 | 29 | Urban–Rural Income Ratio | 0.59 | 0.048 |
| 11 | Number of Tourist Hotels | 0.85 | 0.158 | 30 | Fertilizer Application Intensity | 0.55 | 0.047 |
| 12 | Provincial Demonstration Sites for Leisure Agriculture and Rural Tourism | 0.85 | 0.066 | 31 | Per Capita Cultural and Entertainment Consumption Expenditure Ratio of Urban and Rural Residents | 0.52 | 0.051 |
| 13 | Per Capita Public Library Collections | 0.84 | 0.121 | 32 | Proportion of Tourism Expenditure in Public Finance Budget Expenditure | 0.51 | 0.15 |
| 14 | Number of 3A Scenic Spots | 0.84 | 0.07 | 33 | Pesticide Application Intensity | 0.51 | 0.052 |
| 15 | Mulching Film Usage Rate | 0.83 | 0.070 | 34 | Proportion of Primary Industry Added Value | 0.51 | 0.056 |
| 16 | Industrial Structure Optimization | 0.82 | 0.093 | 35 | Per Capita Cultivated Land Area | 0.5 | 0.132 |
| 17 | Proportion of Cultural Industry | 0.81 | 0.051 | 36 | Comprehensive Income from Rural Leisure Tourism | 0.5 | 0.095 |
| 18 | Number of Cultural Venues | 0.8 | 0.12 | 37 | Advanced Industrial Structure | 0.48 | 0.052 |
| 19 | Added Value of Assets in Cultural Services Enterprises Above Designated Size | 0.79 | 0.1 | 38 | Electrification Level | 0.42 | 0.050 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Fang, S.; Luo, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, L.; Huang, E. Integration of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism in the Suburbs of Megacities: A Case Study of Huangpi District, Wuhan City, China. Land 2026, 15, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/land15010023
Liu J, Fang S, Luo Y, Qin Y, Yuan D, Zhang L, Huang E. Integration of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism in the Suburbs of Megacities: A Case Study of Huangpi District, Wuhan City, China. Land. 2026; 15(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/land15010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Junmiao, Shiming Fang, Yao Luo, Yuan Qin, Dongfang Yuan, Lihong Zhang, and Enwei Huang. 2026. "Integration of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism in the Suburbs of Megacities: A Case Study of Huangpi District, Wuhan City, China" Land 15, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/land15010023
APA StyleLiu, J., Fang, S., Luo, Y., Qin, Y., Yuan, D., Zhang, L., & Huang, E. (2026). Integration of Agriculture, Culture, and Tourism in the Suburbs of Megacities: A Case Study of Huangpi District, Wuhan City, China. Land, 15(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/land15010023





