Saline Peatland Degradation in the Mezzano Lowland: 66 Years of Agricultural Impacts on Carbon and Soil Biogeochemistry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
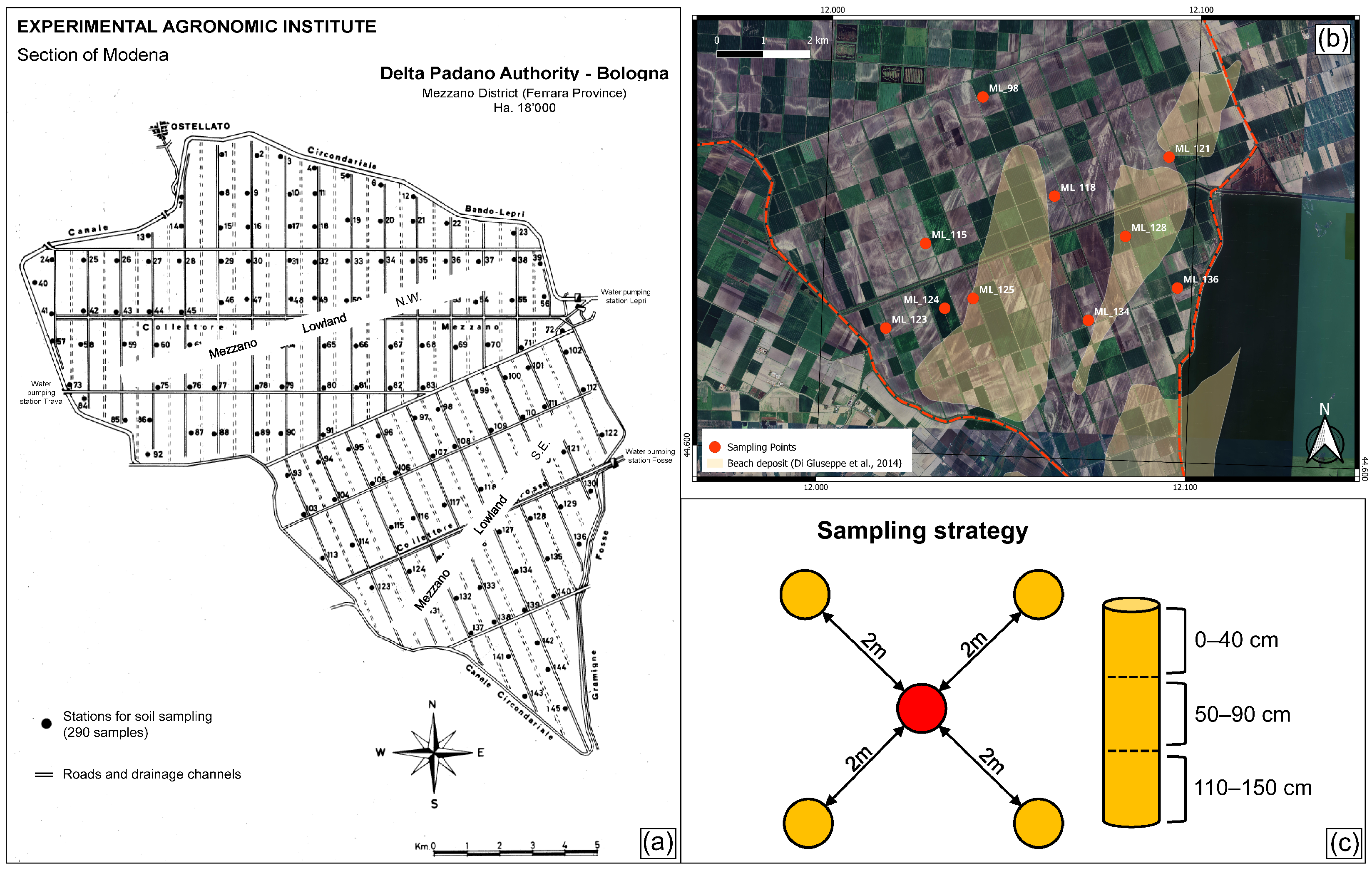
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling and Analyses—1967–1968
2.3. Soil Sampling—2023
2.4. Soil Sample Preparation and Determination of Physicochemical Parameters
2.5. Organic and Total Carbon and Nitrogen Elemental Analyses
2.6. Total Carbon Isotopic Analyses
2.7. Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR)
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
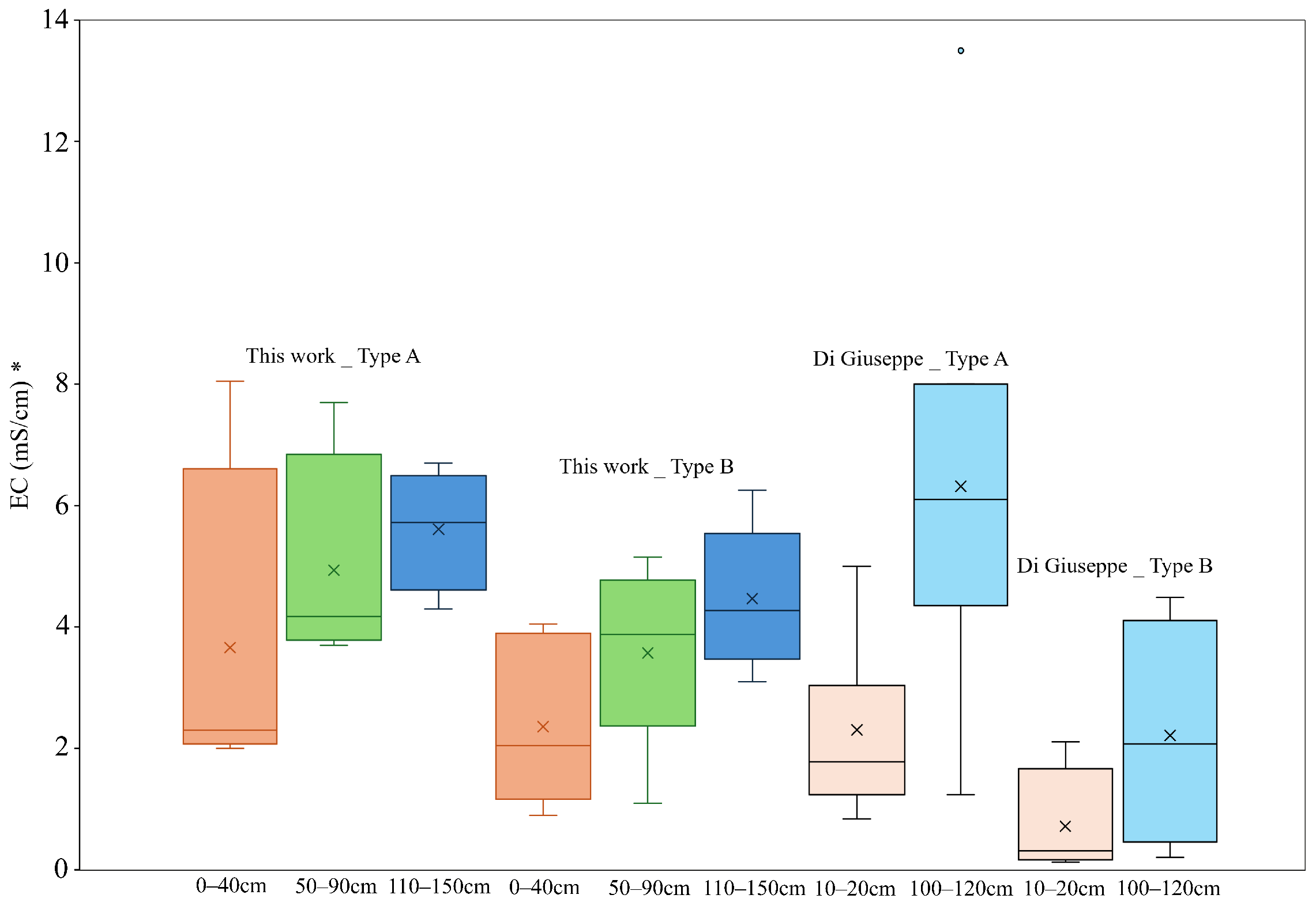
3.1. Distribution of Soil Electrical Conductivity Through Depth
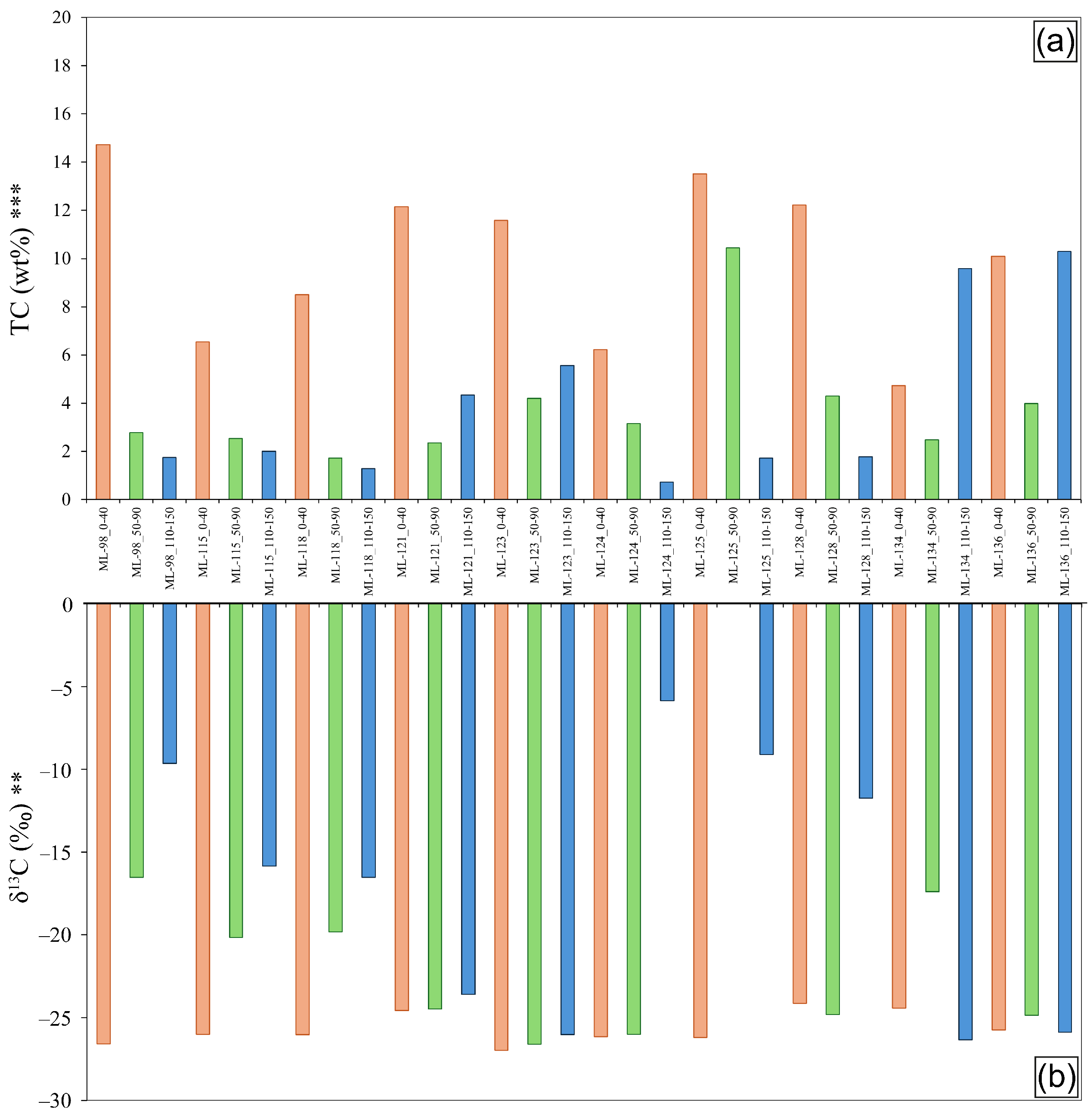
3.2. Distribution of Elemental Organic, Carbon, and Nitrogen Contents Through Depth
3.3. Distribution of Total Carbon Isotopic Signature Through Depth
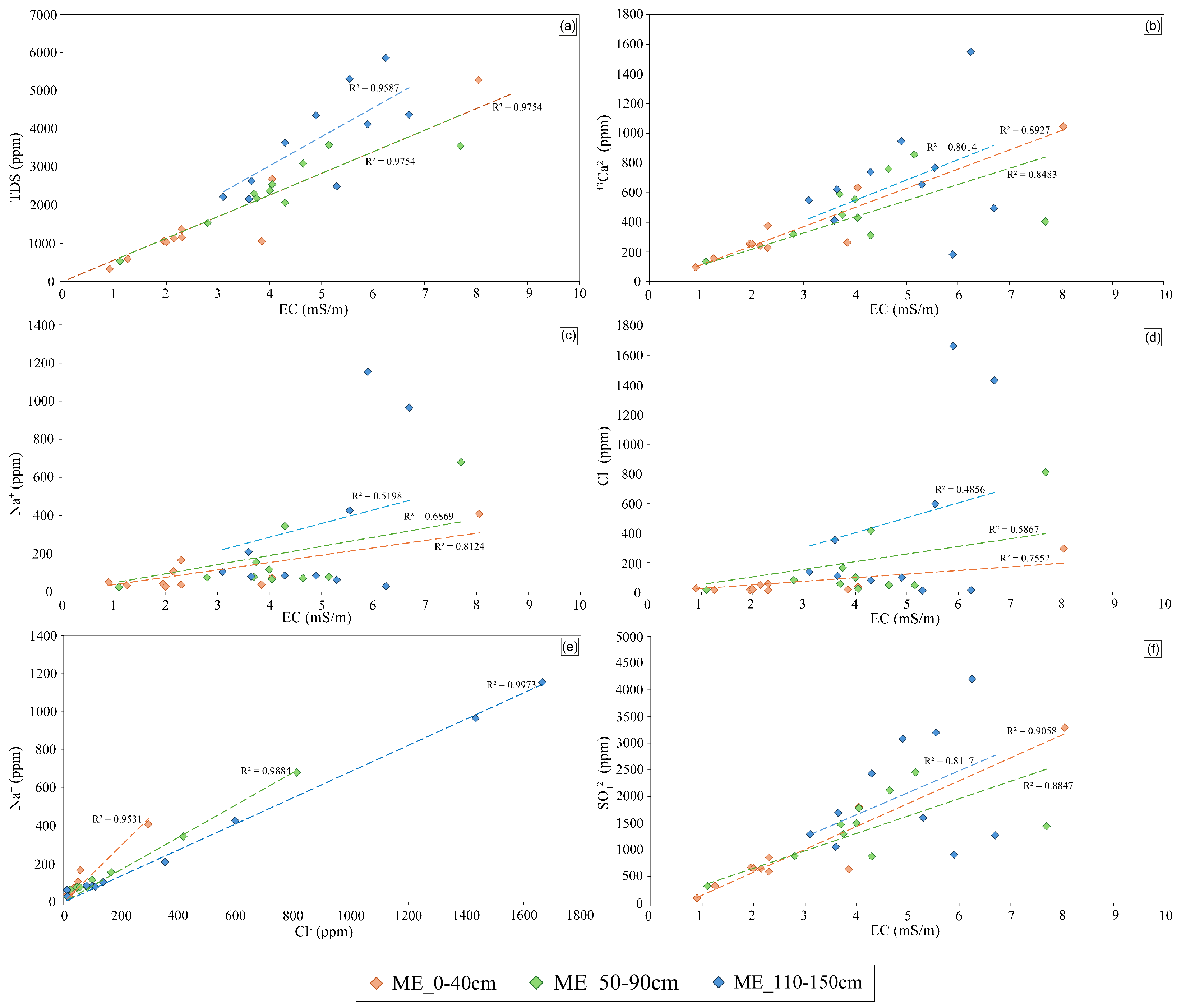
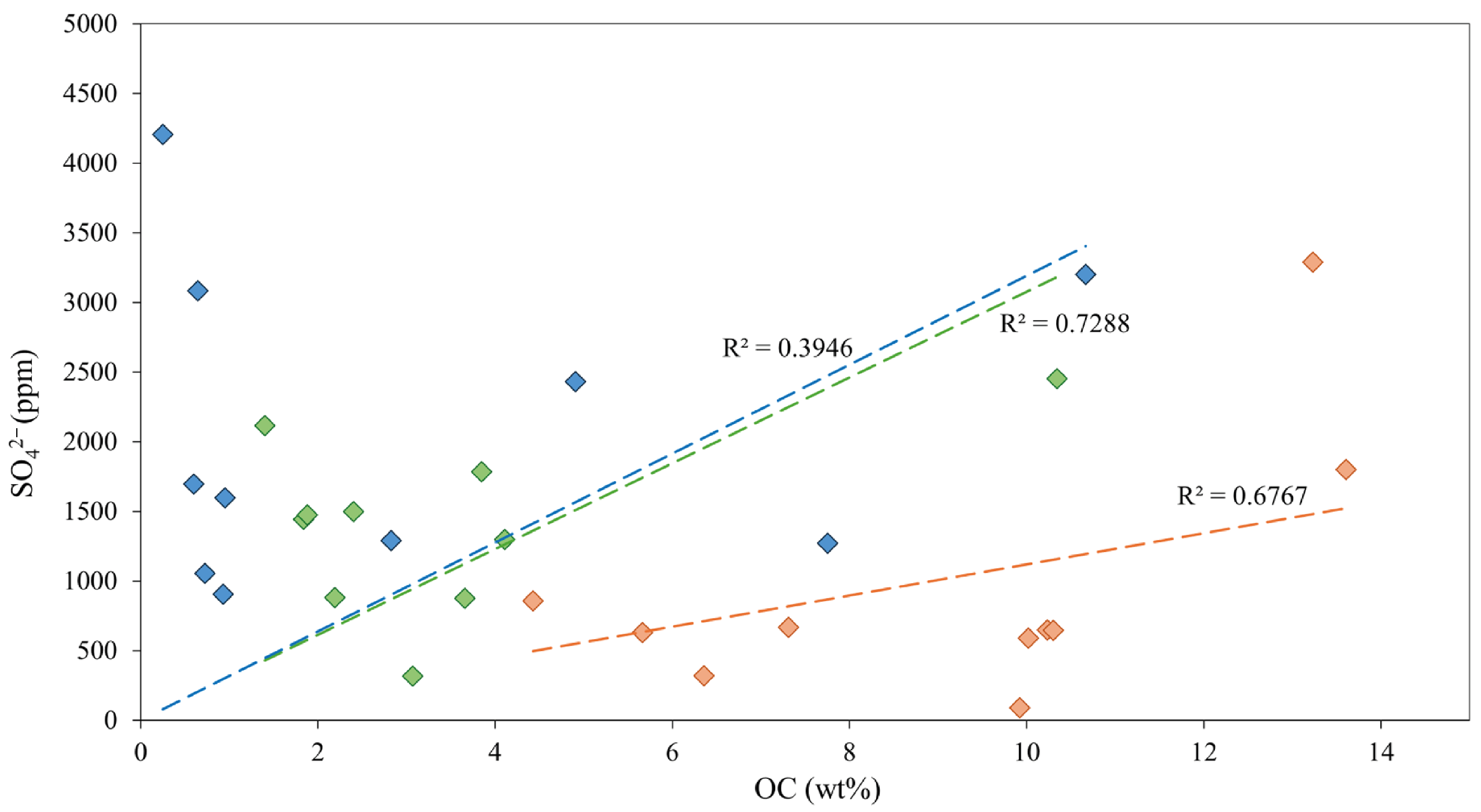
3.4. Ion Dynamics and EC Correlations in Saline Soils
3.5. Soil Stratigraphy and Peatland Thickness Analysis Through GPR Data
4. Discussion
Soil Property Data 66 Years After ML Wetland Drainage
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
| SOC | Soil Organic Carbon |
| SOM | Soil Organic Matter |
| ML | Mezzano Lowland |
References
- Ballut-Dajud, G.A.; Sandoval Herazo, L.C.; Fernández-Lambert, G.; Marín-Muñiz, J.L.; López Méndez, M.C.; Betanzo-Torres, E.A. Factors affecting wetland loss: A review. Land 2022, 11, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Carbon sequestration. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Gosselink, J.G. Wetlands; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gedan, K.B.; Silliman, B.R.; Bertness, M.D. Centuries of human-driven change in salt marsh ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Melville, D.S.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Piersma, T.; Li, B. Rethinking China’s new great wall. Science 2014, 346, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Song, Z.; Yu, B.; Fan, Y.; Tony, V.; Guo, L.; Li, Q.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Land use changes and edaphic properties control contents and isotopic compositions of soil organic carbon and nitrogen in wetlands. Catena 2024, 241, 108031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, A.; Larmola, T.; Kekkonen, H.; Saarnio, S.; Lång, K. Review of greenhouse gas emissions from rewetted agricultural soils. Wetlands 2021, 41, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.E.; Rieley, J.O.; Banks, C.J. Global and regional importance of the tropical peatland carbon pool. Glob. Change Biol. 2011, 17, 798–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijer, A.; Silvius, M.; Wösten, H.; Page, S. PEAT-CO2. Assessment of CO2 Emissions from Drained Peatlands in SE Asia; Delft Hydraulics: Delft, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wils, T.H.; van den Akker, J.J.; Korff, M.; Bakema, G.; Hegger, D.L.; Hessel, R.; van den Ende, M.A.; van Gils, M.M.; Verstand, D. Measures to reduce land subsidence and greenhouse gas emissions in peatlands: A Dutch case study. Land Use Policy 2025, 152, 107500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aben, R.C.; Van De Craats, D.; Boonman, J.; Peeters, S.H.; Vriend, B.; Boonman, C.C.; Van Der Velde, Y.; Erkens, G.; Van Den Berg, M. CO2 emissions of drained coastal peatlands in the Netherlands and potential emission reduction by water infiltration systems. Biogeosciences 2024, 21, 4099–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, D.; Manzoni, S.; Tapasco, J.; Vestin, P.; Belyazid, S. Evaluation of long-term carbon dynamics in a drained forested peatland using the ForSAFE-Peat model. Biogeosciences 2025, 22, 2023–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, K.L.; Strack, M.; Balliston, N.; Davies, M.A.; Hettinga, E.K.; Hunter, M.; Kleinke, K.; Schmidt, M.; Barreto, C.; Bird, M.; et al. Data and knowledge needs for improving science and policy for peatlands in Canada in a changing world: Insights from Global Peatlands Initiative Workshop, June 2023. FACETS 2025, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nature. The manicured wetland that sucks up more carbon than a natural marsh. Nature 2020, 577, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salani, G.; Bianchini, G.; Brombin, V.; Natali, C. Soil organic carbon data comparison after 85 years and new 13C/12C compositions: The case study of the Ferrara province (Northeastern Italy). J. Environ. Qual. 2024, 53, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeoni, U.; Corbau, C. A review of the Delta Po evolution (Italy) related to climatic changes and human impacts. Geomorphology 2009, 107, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschi, V.; Spallacci, P. Caratteristiche chimiche e agronomiche dei terreni salini della nuova bonifica del Mezzano. Ann. Dell’Istituto Sper. Agron. Bari 1974, 5, 263–363. [Google Scholar]
- GEMINA (Geomineraria Nazionale). Ligniti e Torbe dell’Italia Continentale; ILTE: Torino, Italy, 1963; p. 319. [Google Scholar]
- Natali, C.; Bianchini, G.; Cremonini, S.; Salani, G.M.; Vianello, G.; Brombin, V.; Ferrari, M.; Vittori Antisari, L. Peat soil burning in the Mezzano Lowland (Po Plain, Italy): Triggering mechanisms and environmental consequences. Geohealth 2021, 5, e2021GH000444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giuseppe, D.; Bianchini, G.; Vittori Antisari, L.; Martucci, A.; Natali, C.; Beccaluva, L. Geochemical characterization and biomonitoring of reclaimed soils in the Po River Delta (Northern Italy): Implications for the agricultural activities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2925–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, M. Soil Bio-Indicators in Different Pedoclimatic Regions of the Padana Plain (Northeast Italy). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Comas, X.; Terry, N.; Slater, L.; Warren, M.; Kolka, R.; Kristiyono, A.; Sudiana, N.; Nurjaman, D.; Darusman, T. Imaging tropical peatlands in Indonesia using ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electrical resistivity imaging (ERI): Implications for carbon stock estimates and peat soil characterization. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 2995–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, L.; West, L.; Holden, J.; Chapman, P. Evaluating approaches for estimating peat depth. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2014, 119, JG002411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, A.; Chiozzi, A.; Nikolić, Z.; Vaccaro, C.; Benvenuti, E. A PROMETHEE Multiple-Criteria Approach to Combined Seismic and Flood Risk Assessment at the Regional Scale. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giuseppe, D.; Bianchini, G.; Faccini, B.; Coltorti, M. Combination of wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence analysis and multivariate statistic for alluvial soils classification: A case study from the Padanian Plain (Northern Italy). X-Ray Spectrom. 2014, 43, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maino, A.; Alberi, M.; Barbagli, A.; Chiarelli, E.; Colonna, T.; Franceschi, M.; Gallorini, F.; Guastaldi, E.; Lopane, N.; Mantovani, F.; et al. A deep neural network for predicting soil texture using airborne radiometric data. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2024, 221, 111767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2006, First Update 2007; Number 103 in World Soil Resources Reports; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Koppen, W. Das geographische System de Klimate. In Handbuch der klimatologie; Verlag Gebrüder Borntrager: Berlin, Germany, 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Climate-Data.org. Climate Ferrara: Temperature, Climate Graph, Climate Table for Ferrara. 2025. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/europe/italy/emilia-romagna/ferrara-3207/ (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Sistema Nazionale per la Protezione Dell’Ambiente (SNPA). Il clima in Italia nel 2023; Rapporti SNPA 42/2024; Sistema Nazionale per la Protezione dell’Ambiente (SNPA): Roma, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lotti, G.; Galoppini, C. Guida Alle Analisi Chimico-Agrarie; Agricole Bologna: Bologna, Italy, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1958; 498p. [Google Scholar]
- Natali, C.; Bianchini, G. Thermally based isotopic speciation of carbon in complex matrices: A tool for environmental investigation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12162–12173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Akça, E.; Aydin, M.; Kapur, S.; Kume, T.; Nagano, T.; Watanabe, T.; Çilek, A.; Zorlu, K. Long-term monitoring of soil salinity in a semi-arid environment of Turkey. Catena 2020, 193, 104614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutton, T.W. Stable carbon isotope ratios of soil organic matter and their use as indicators of vegetation and climate change. In Mass Spectrometry of Soils; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 47–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Buchmann, N.; Flanagan, L.B. Carbon isotope ratios in belowground carbon cycle processes. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, M. Carbon Isotope Fractionation in plants. Phytochemistry 1981, 20, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, M.; Bassin, S.; Lehmann, M.F.; Johnson, M.G.; Andersen, C.P. 13C isotopic signature and C concentration of soil density fractions illustrate reduced C allocation to subalpine grassland soil under high atmospheric N deposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Wang, Y.; Dai, G.; Jia, J.; Liu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, E.; Zhang, X.; Haghipour, N.; et al. Prolonged Storage of Bound Organic Carbon in Wetland but Not Upland Soils: A 13C and 14C Perspective. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2025, 52, e2024GL112491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Apparent soil electrical conductivity measurements in agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 11–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Yemoto, K. Salinity: Electrical conductivity and total dissolved solids. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2017; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sumner, M.E. Handbook of Soil Science; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Grote, K.; Hubbard, S.; Rubin, Y. Field-scale estimation of volumetric water content using ground-penetrating radar ground wave techniques. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.; Burt, T.; Vilas, M. Application of ground-penetrating radar to the identification of subsurface piping in blanket peat. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2002, 27, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijer, A.; Page, S.; Jauhiainen, J.; Lee, W.; Lu, X.; Idris, A.; Anshari, G. Subsidence and carbon loss in drained tropical peatlands. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 1053–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezdir, V.; Čeru, T.; Horn, B.; Gosar, M. Investigating peatland stratigraphy and development of the Šijec bog (Slovenia) using near-surface geophysical methods. Catena 2021, 206, 105484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribyl, D. A critical review of the conventional SOC to SOM conversion factor. Geoderma 2010, 156, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.E.; Kuehl, R. Organic Matter Accumulation and Organic Soils; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Yan, L.; Cao, J.; Wang, K.; Luo, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Yu, R.; Pan, B.; Yu, K.; et al. Salinity significantly affects methane oxidation and methanotrophic community in Inner Mongolia lake sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1067017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Li, H.; Su, H.; Du, W.; Gao, Z.; Liu, H.; Liang, H.; Gao, D. Effects of salinity on methane emissions and methanogenic archaeal communities in different habitat of saline-alkali wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 106378–106389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poffenbarger, H.J.; Needelman, B.A.; Megonigal, J.P. Salinity influence on methane emissions from tidal marshes. Wetlands 2011, 31, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Cai, Z.; Wang, D. Preliminary budget of methane emissions from natural wetlands in China. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laanbroek, H.J. Methane emission from natural wetlands: Interplay between emergent macrophytes and soil microbial processes. A mini-review. Ann. Bot. 2010, 105, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ouyang, H.; Deng, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhou, C. Nitrogen mineralization processes of soils from natural saline-alkalined wetlands, Xianghai National Nature Reserve, China. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2005, 85, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcleod, E.; Chmura, G.L.; Bouillon, S.; Salm, R.; Björk, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Lovelock, C.E.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Silliman, B.R. A blueprint for blue carbon: Toward an improved understanding of the role of vegetated coastal habitats in sequestering CO2. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Ye, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, F.; Wen, Q.; Chen, S. Coastal blue carbon: Concept, study method, and the application to ecological restoration. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Xi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.; Wu, J.; Sun, Y. Variability in soil microbial community and activity between coastal and riparian wetlands in the Yangtze River estuary–potential impacts on carbon sequestration. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Tang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fu, X.; Sun, Y.; Tsang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Salinity influence on soil microbial respiration rate of wetland in the Yangtze River estuary through changing microbial community. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Santino, M.B.d.; Bianchini, I. Reviewing the organic matter processing by wetlands. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2023, 35, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleber, M.; Johnson, M.G. Advances in understanding the molecular structure of soil organic matter: Implications for interactions in the environment. Adv. Agron. 2010, 106, 77–142. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, K.; Guggenberger, G. The role of DOM sorption to mineral surfaces in the preservation of organic matter in soils. Org. Geochem. 2000, 31, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.W.; Torn, M.S.; Abiven, S.; Dittmar, T.; Guggenberger, G.; Janssens, I.A.; Kleber, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Manning, D.A.; et al. Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property. Nature 2011, 478, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, K.; Jackson, R.B.; Vindušková, O.; Abramoff, R.Z.; Ahlström, A.; Feng, W.; Harden, J.W.; Pellegrini, A.F.; Polley, H.W.; Soong, J.L.; et al. Global stocks and capacity of mineral-associated soil organic carbon. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brombin, V.; Salani, G.M.; De Feudis, M.; Mistri, E.; Precisvalle, N.; Bianchini, G. Soil organic carbon depletion in managed temperate forests: Two case studies from the Apennine chain in the Emilia-Romagna region (northern Italy). Environments 2023, 10, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Singh, B.; Dijkstra, F.A. Stabilisation of soil organic matter: Interactions between clay and microbes. Biogeochemistry 2022, 160, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Sarkar, B.; Sarkar, S.; Churchman, J.; Beerling, D. Stabilization of soil organic carbon as influenced by clay mineralogy. Adv. Agron. 2017, 148, 33–84. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Rao, M.P.N.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, P.D.; Lian, Z.H.; Abdugheni, R.; Jiang, H.C.; Jiao, J.Y.; Shurigin, V.; Fang, B.Z.; et al. SALINITY-Induced changes in diversity, stability, and functional profiles of microbial communities in different Saline Lakes in Arid Areas. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, E.; Yang, X.; Yang, J. Shifts in microbial community structure and Co-occurrence network along a wide soil salinity gradient. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, D.; Berben, T.; Melton, E.; Overmars, L.; Vavourakis, C.; Muyzer, G. Microbial diversity and biogeochemical cycling in soda lakes. Extremophiles 2014, 18, 791–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lu, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, D. An Analysis on the characteristics and influence factors of soil salinity in the wasteland of the Kashgar river Basin. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Schubert, S. Degradation processes and nutrient constraints in sodic soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2002, 13, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P. World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago Rosario, L.; Harms, K.; Elderd, B.; Hart, P.; Dassanayake, M. No escape: The influence of substrate sodium on plant growth and tissue sodium responses. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 14231–14249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, C.; Feng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Deo, R.C. Direct and indirect impacts of ionic components of saline water on irrigated soil chemical and microbial processes. Catena 2019, 172, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, E. Cation Binding by Humic Substances; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, R.; Petropoulos, E.; Yu, B.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X.; Gao, M.; Feng, Y. Interactive effects of salinity and SOM on the ecoenzymatic activities across coastal soils subjected to a saline gradient. Geoderma 2022, 406, 115519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pester, M.; Knorr, K.H.; Friedrich, M.W.; Wagner, M.; Loy, A. Sulfate-reducing microorganisms in wetlands-familiars but yet unknown. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Smolders, A.J.P.; Lamers, L.P.M.; Hartog, C.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Mechanisms involved in the decline of freshwater bivalves in highly anoxic conditions. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Cremonini, S.; Etiope, G.; Italiano, F.; Martinelli, G. Evidence of possible enhanced peat burning by deep-origin methane in the Po River delta plain (Italy). J. Geol. 2008, 116, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonzi, L.; Ferrari, V.; Martinelli, G.; Norelli, E.; Severi, P. Unusual geological phenomena in the Emilia-Romagna plain (Italy): Gas emissions from wells and the ground, hot water wells, geomorphological variations. A review and an update of documented reports. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2017, 58, 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Toreti, A.; Masante, D.; Acosta Navarro, J.; Bavera, D.; Cammalleri, C.; de Jager, A.; di Ciollo, C.; Hrast Essenfelder, A.; Maetens, W.; Magni, D.; et al. Drought in Europe, July 2022; Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Puppin, A.; Tognin, D.; Paccagnella, M.; Zancato, M.; Ghinassi, M.; D’Alpaos, C.; Marani, M.; D’Alpaos, A. Blue carbon assessment in the salt marshes of the Venice Lagoon: Dimensions, variability and influence of storm-surge regulation. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2024EF004715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobbe, A.; Brombin, V.; Rizzo, E.; Bianchini, G. Saline Peatland Degradation in the Mezzano Lowland: 66 Years of Agricultural Impacts on Carbon and Soil Biogeochemistry. Land 2025, 14, 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081621
Sobbe A, Brombin V, Rizzo E, Bianchini G. Saline Peatland Degradation in the Mezzano Lowland: 66 Years of Agricultural Impacts on Carbon and Soil Biogeochemistry. Land. 2025; 14(8):1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081621
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobbe, Aaron, Valentina Brombin, Enzo Rizzo, and Gianluca Bianchini. 2025. "Saline Peatland Degradation in the Mezzano Lowland: 66 Years of Agricultural Impacts on Carbon and Soil Biogeochemistry" Land 14, no. 8: 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081621
APA StyleSobbe, A., Brombin, V., Rizzo, E., & Bianchini, G. (2025). Saline Peatland Degradation in the Mezzano Lowland: 66 Years of Agricultural Impacts on Carbon and Soil Biogeochemistry. Land, 14(8), 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081621









