Biophysical and Social Constraints of Restoring Ecosystem Services in the Border Regions of Tibet, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
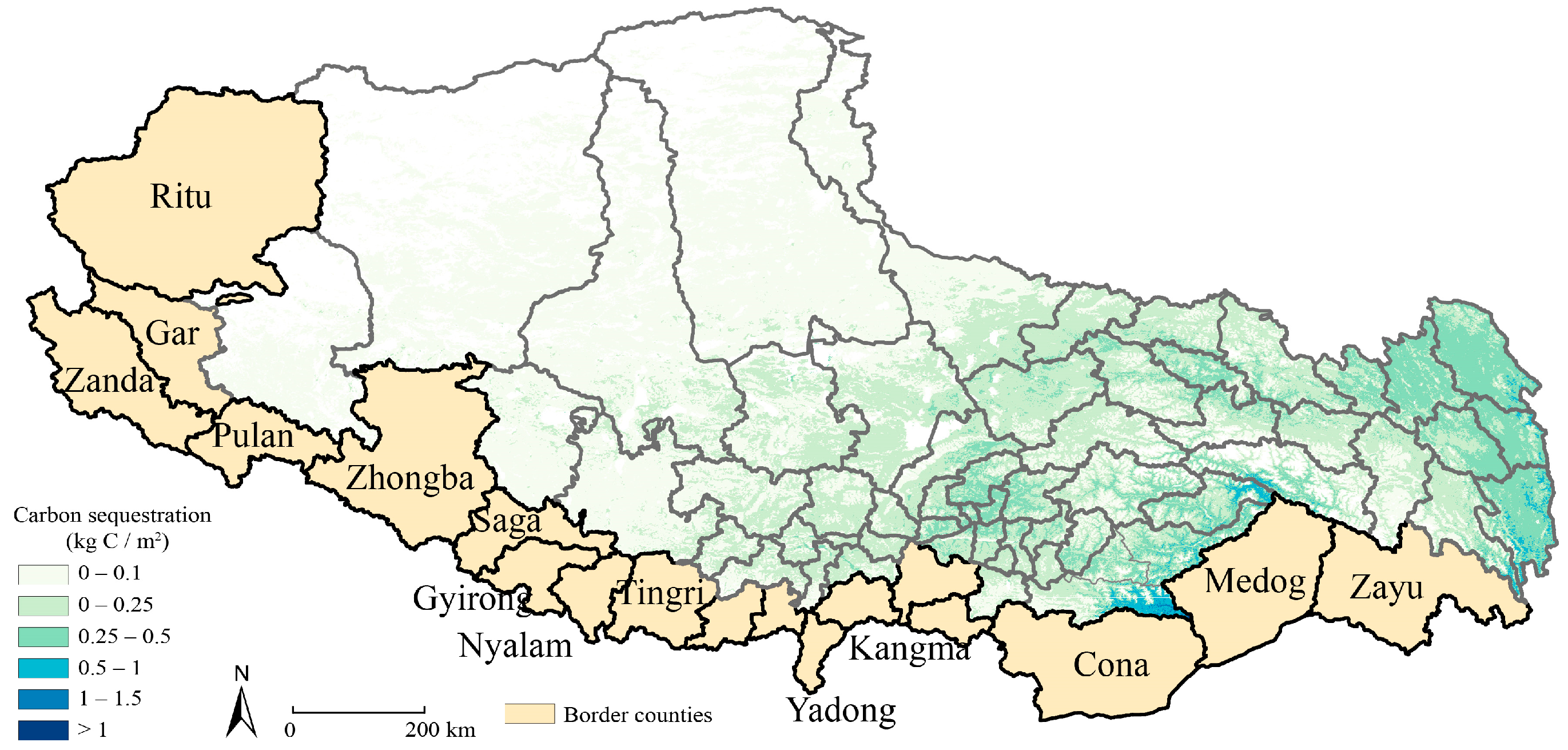
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
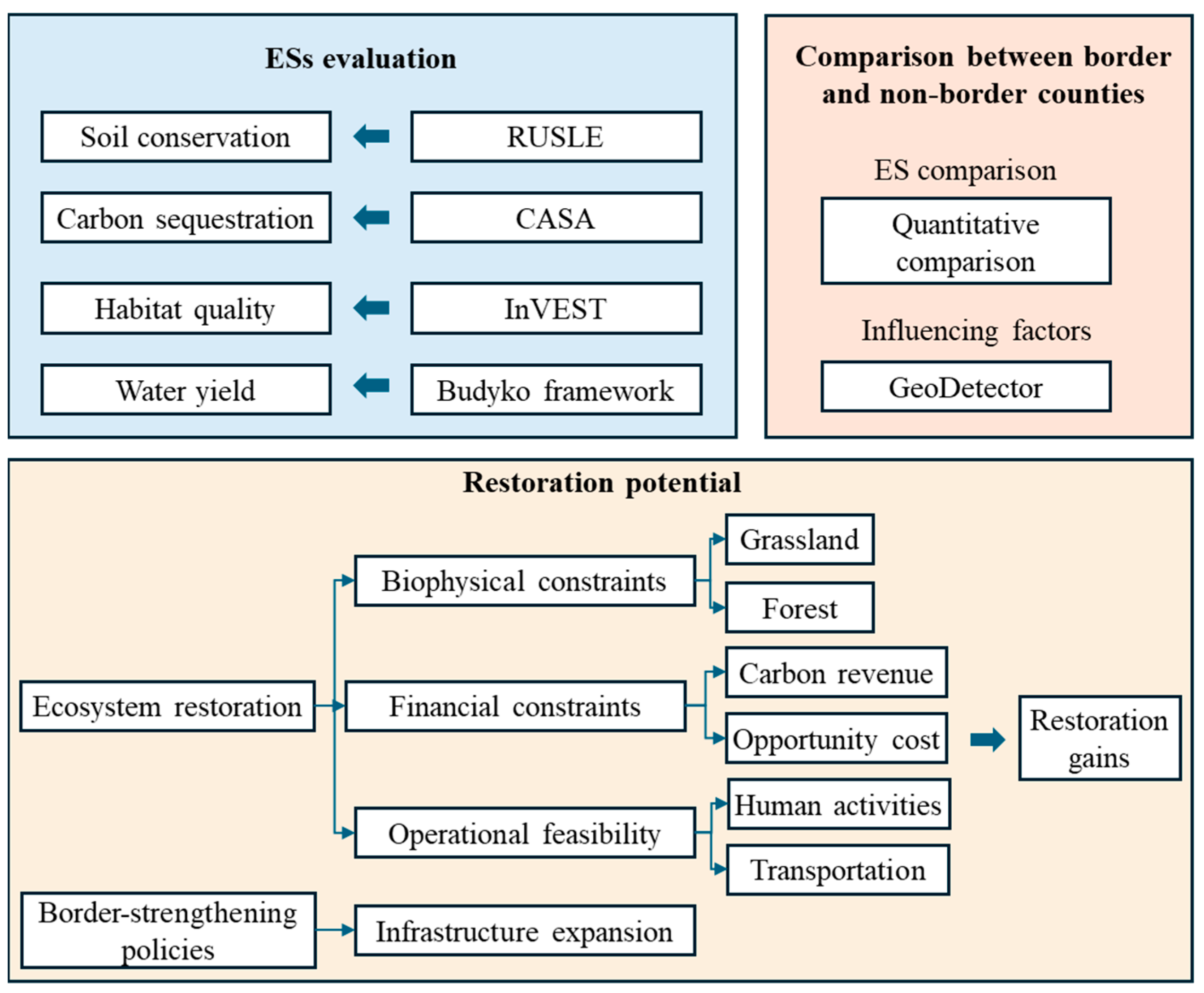
2.3. Methodological Framework
2.4. Ecosystem Services Evaluation
2.5. Influencing Factors Analysis Based on GeoDetector
2.6. Scenario Description
2.6.1. Biophysical Constraints of Ecosystem Restoration
2.6.2. Social Constraints of Ecosystem Restoration
2.6.3. Infrastructure Expansion Simulation
3. Results
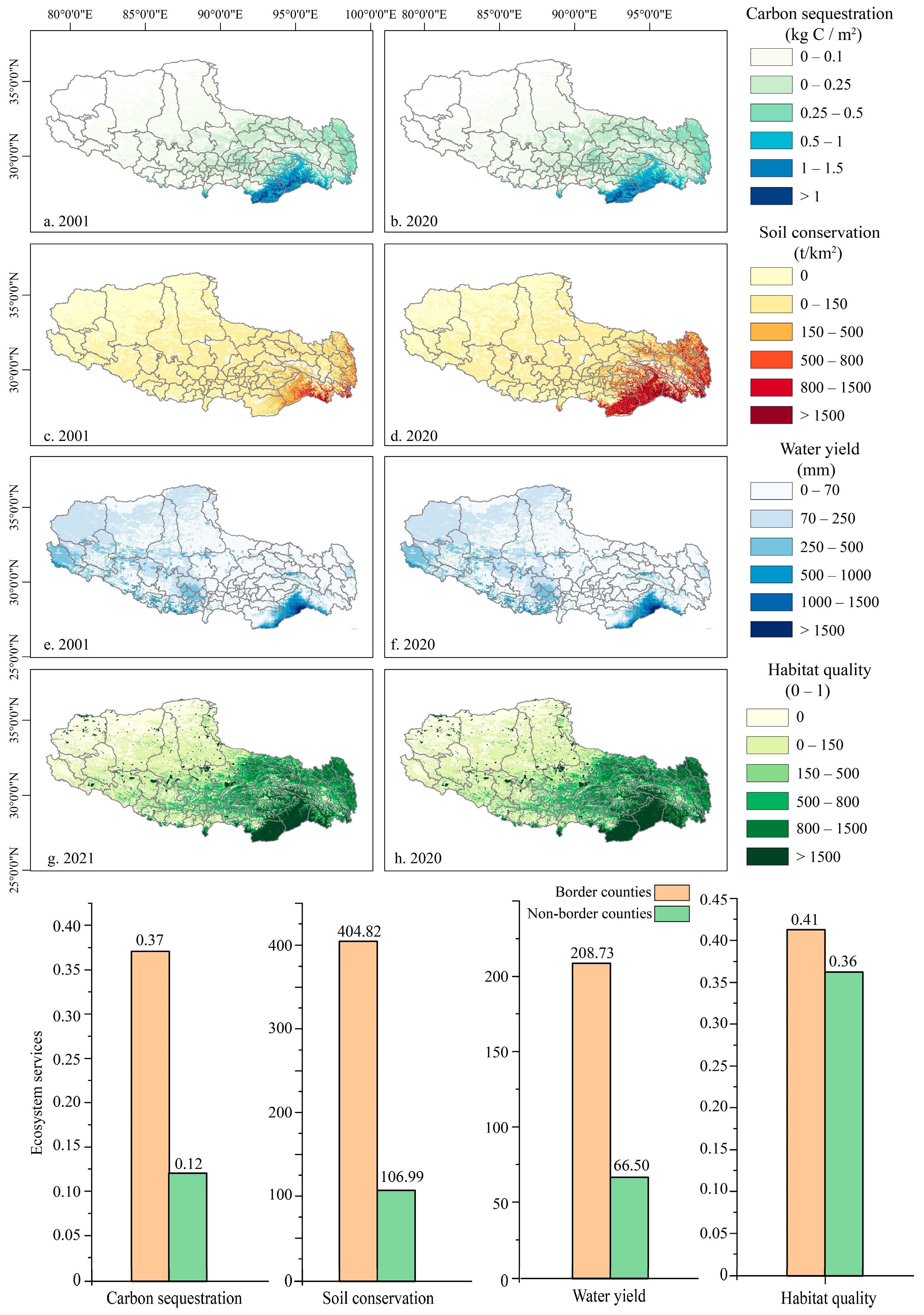
3.1. Ecosystem Services, Trends, and Influencing Factors: Comparison Between Border and Non-Border Counties
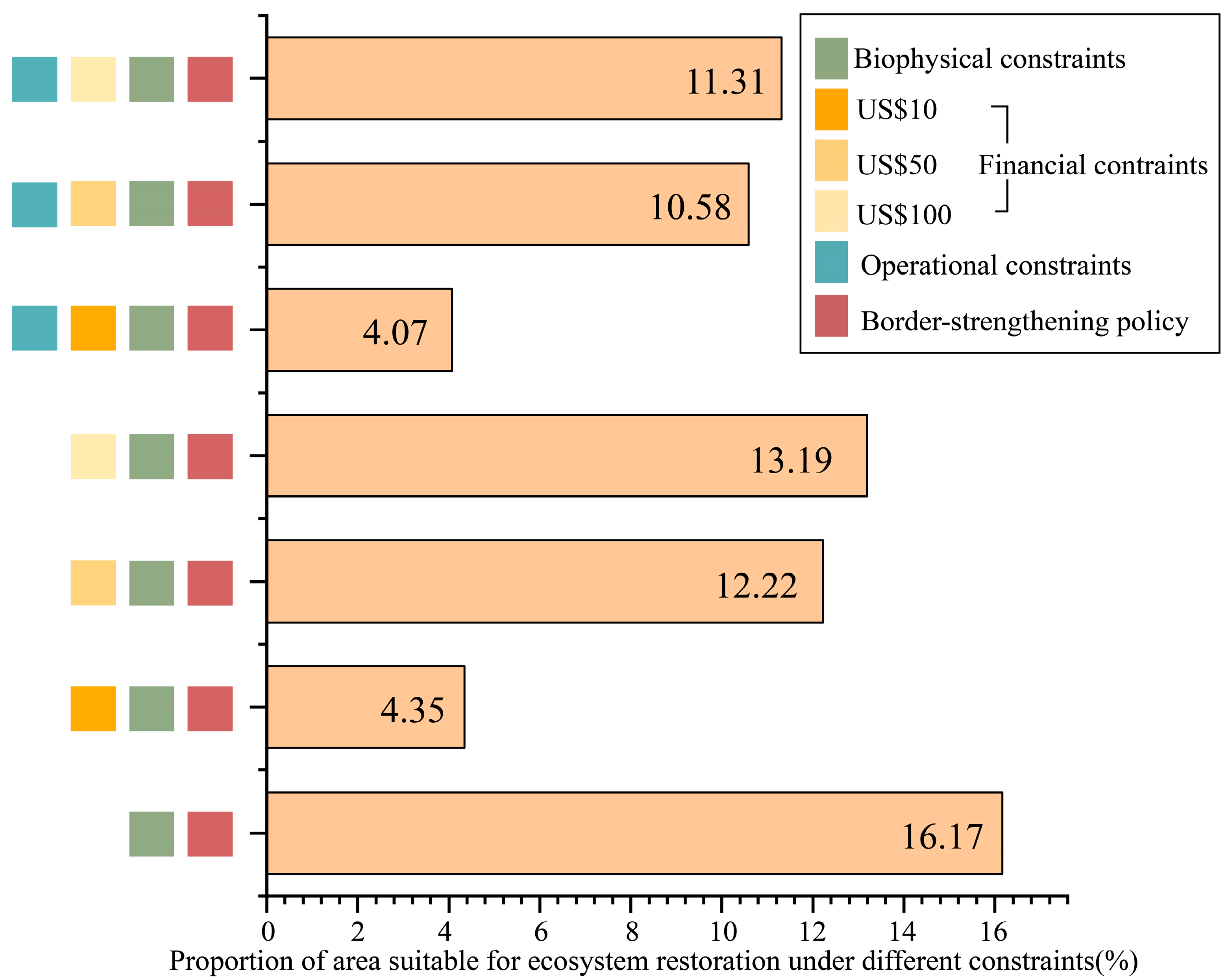
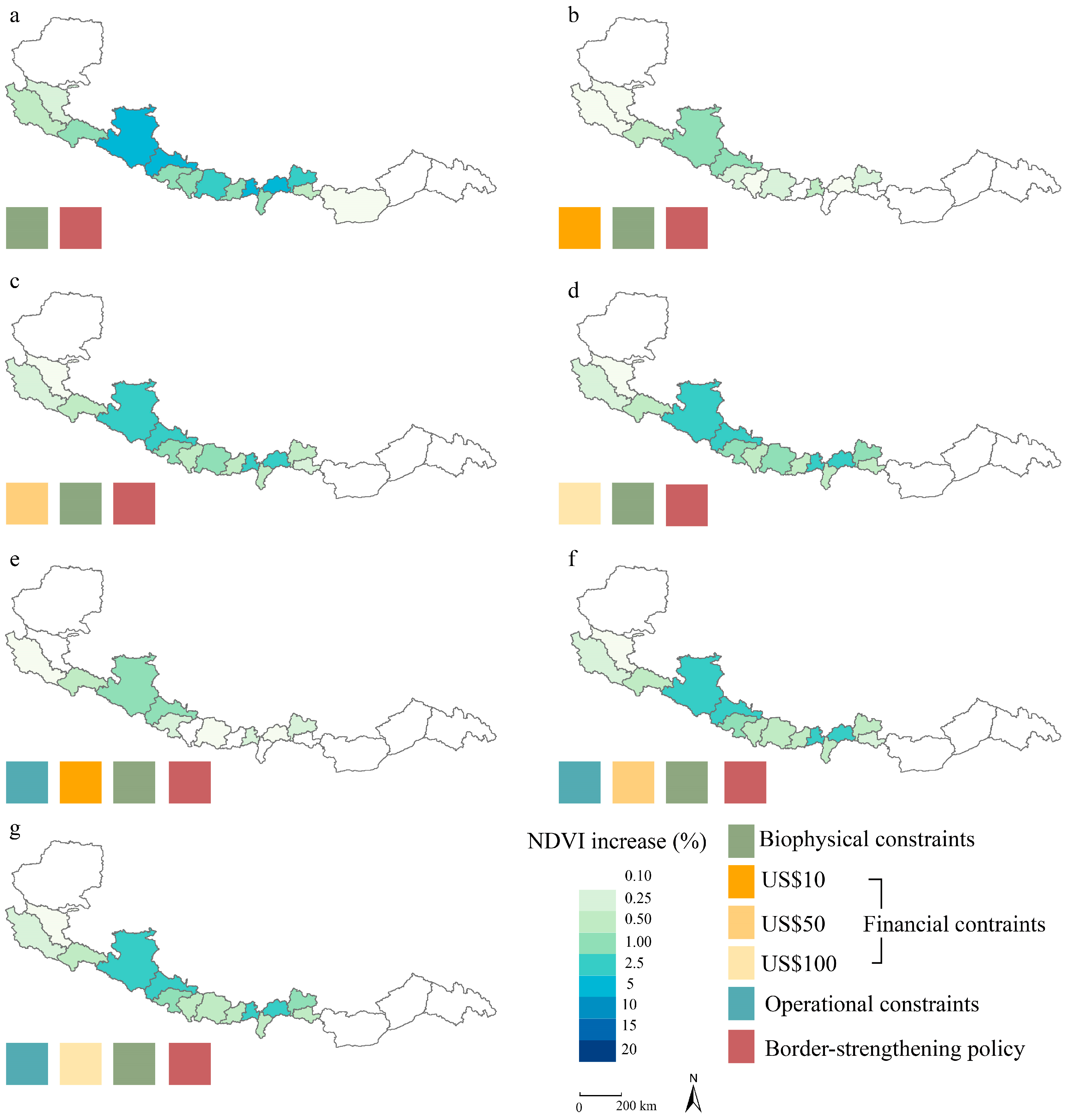
3.2. Constraints of Biophysical and Social Constraints on Available Ecosystem Restoration Regions
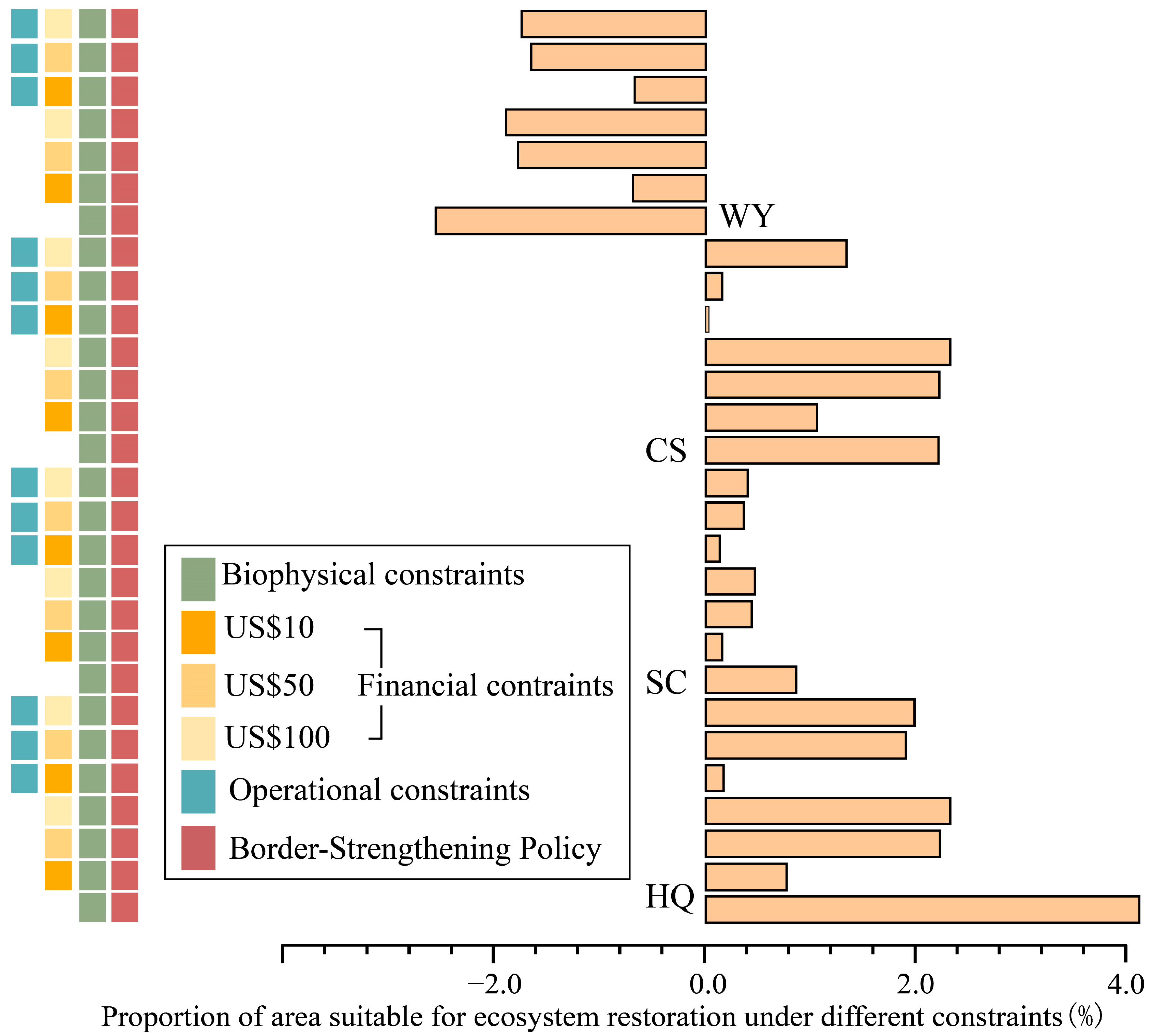
3.3. Potential Impact of Ecosystem Restoration on Ecosystem Services
4. Discussion
4.1. Restoration Importance in Tibet’s Border Areas
4.2. Biophysical and Social Constraints on Ecosystem Restoration
4.3. Policy Implications for Restoration and Rural Development
4.4. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E.M.; et al. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanza, R.; dArge, R.; deGroot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; ONeill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gourevitch, J.D.; Alonso-Rodríguez, A.M.; Aristizábal, N.; de Wit, L.A.; Kinnebrew, E.; Littlefield, C.E.; Moore, M.; Nicholson, C.C.; Schwartz, A.J.; Ricketts, T.H. Projected losses of ecosystem services in the US disproportionately affect non-white and lower-income populations. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.Q.; Wu, T.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, W.H.; Zhang, X.B.; Daily, G.C.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Natural capital investments in China undermined by reclamation for cropland. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 7, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Cui, X.Y.; Chen, W.X.; Yao, X.W. Impact of urban expansion on the supply-demand balance of ecosystem services: An analysis of prefecture-level cities in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 99, 107003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griscom, B.W.; Adams, J.; Ellis, P.W.; Houghton, R.A.; Lomax, G.; Miteva, D.A.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Shoch, D.; Siikamäki, J.V.; Smith, P.; et al. Natural climate solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11645–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, J.; Jacobs, S. Nature-Based Solutions for Europe’s Sustainable Development. Conserv. Lett. 2017, 10, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, P.W.; Page, A.M.; Wood, S.; Fargione, J.; Masuda, Y.J.; Denney, V.C.; Moore, C.; Kroeger, T.; Griscom, B.; Sanderman, J.; et al. The principles of natural climate solutions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration. Available online: https://www.unep.org/explore-topics/ecosystems-and-biodiversity/what-we-do/decade-ecosystem-restoration (accessed on 7 June 2025).
- Wang, X.M.; Ge, Q.S.; Geng, X.; Wang, Z.S.; Gao, L.; Bryan, B.A.; Chen, S.Q.; Su, Y.A.; Cai, D.W.; Ye, J.S.; et al. Unintended consequences of combating desertification in China. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.Y.; Zhong, S.B.; Xi, Z.L.; Yao, S.B. Does large-scale ecological restoration threaten food security in China? A moderated mediation model. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.H.; Caldarone, G.; Duarte, T.K.; Ennaanay, D.; Hannahs, N.; Mendoza, G.; Polasky, S.; Wolny, S.; Daily, G.C. Integrating ecosystem-service tradeoffs into land-use decisions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7565–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Robinson, B.E.; Liang, Y.C.; Polasky, S.; Ma, D.C.; Wang, F.C.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Daily, G.C. Benefits, costs, and livelihood implications of a regional payment for ecosystem service program. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16681–16686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, L.J.; Peng, W.J.; Zhang, C.P.; Li, C.; Robinson, B.E.; Wu, X.C.; Kong, L.Q.; Li, R.N.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Realizing the values of natural capital for inclusive, sustainable development: Informing China’s new ecological development strategy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8623–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkema, K.K.; Verutes, G.M.; Wood, S.A.; Clarke-Samuels, C.; Rosado, S.; Canto, M.; Rosenthal, A.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Guannel, G.; Toft, J.; et al. Embedding ecosystem services in coastal planning leads to better outcomes for people and nature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7390–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N.; Tian, H.Q.; Fu, B.J.; Yu, H.Q.; Piao, S.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Li, Z.D.; et al. Biophysical and economic constraints on China’s natural climate solutions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarira, T.V.; Zeng, Y.W.; Neugarten, R.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Koh, L.P. Co-benefits of forest carbon projects in Southeast Asia. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.W.; Sarira, T.V.; Carrasco, L.R.; Chong, K.Y.; Friess, D.A.; Lee, J.S.H.; Taillardat, P.; Worthington, T.A.; Zhang, Y.C.; Koh, L.P. Economic and social constraints on reforestation for climate mitigation in Southeast Asia. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hua, T.; Chen, L.D.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Pereira, P. Divergent Changes in Vegetation Greenness, Productivity, and Rainfall Use Efficiency Are Characteristic of Ecological Restoration Towards High-Quality Development in the Yellow River Basin, China. Engineering 2024, 34, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konings, A.G.; Saatchi, S.S.; Frankenberg, C.; Keller, M.; Leshyk, V.; Anderegg, W.R.L.; Humphrey, V.; Matheny, A.M.; Trugman, A.; Sack, L.; et al. Detecting forest response to droughts with global observations of vegetation water content. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 6005–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook-Patton, S.C.; Leavitt, S.M.; Gibbs, D.; Harris, N.L.; Lister, K.; Anderson-Teixeira, K.J.; Briggs, R.D.; Chazdon, R.L.; Crowther, T.W.; Ellis, P.W.; et al. Mapping carbon accumulation potential from global natural forest regrowth. Nature 2020, 585, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, T.M.; Mittermeier, R.A.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Gerlach, J.; Hoffmann, M.; Lamoreux, J.F.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Pilgrim, J.D.; Rodrigues, A.S.L. Global biodiversity conservation priorities. Science 2006, 313, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.M.; Fu, B.J.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.H.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.Z.; Lü, Y.H.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.H.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Fu, B.J.; Wang, S.; Stringer, L.C.; Wang, Y.P.; Li, Z.D.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhou, W.X. Drivers and impacts of changes in China’s drylands. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 858–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuepper, D.; Borrelli, P.; Finger, R. Countries and the global rate of soil erosion. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.L.; Xiao, C.W.; Feng, Z.M.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.M. Accelerating decline of habitat quality in Chinese border areas. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 206, 107665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, B.A.; Gao, L.; Ye, Y.Q.; Sun, X.F.; Connor, J.D.; Crossman, N.D.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Wu, J.G.; He, C.Y.; Yu, D.Y.; et al. China’s response to a national land-system sustainability emergency. Nature 2018, 559, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Long, D.; Scanlon, B.R.; Mann, M.E.; Li, X.D.; Tian, F.Q.; Sun, Z.L.; Wang, G.Q. Climate change threatens terrestrial water storage over the Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.D.; Bolch, T.; Chen, D.L.; Gao, J.; Immerzeel, W.; Piao, S.; Su, F.G.; Thompson, L.; Wada, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. The imbalance of the Asian water tower. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Kang, S.C.; Chen, D.L.; Zhao, L.; Ji, Z.M.; Duan, K.Q.; Deng, H.J.; Tripathee, L.; Du, W.T.; Rai, M.; et al. South Asian black carbon is threatening the water sustainability of the Asian Water Tower. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; et al. High-Resolution Global Maps of 21st-Century Forest Cover Change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Zhao, W.W.; Cherubini, F.; Hu, X.P.; Pereira, P. Continuous growth of human footprint risks compromising the benefits of protected areas on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 34, e02053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.X.; Liu, S.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Dong, Y.H.; Li, M.Q.; An, Y.; Shi, F.N. Grazing intensity and human activity intensity data sets on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during 1990–2015. Geosci. Data J. 2022, 9, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogan, D.; Frolking, S.; Wisser, D.; Prusevich, A.; Glidden, S. Global gridded crop harvested area, production, yield, and monthly physical area data circa 2015. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations-a new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (Rusle); U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; Volume 703.
- Sharpley, A.N.; Williams, J.R. EPIC—Erosion/Productivity Impact Calculator: 1. Model Documentation; Technical Bulletin; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; Volume 1768.
- Moore, I.D.; Burch, G.J. Physical Basis of the Length-Slope Factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Shi, P.J.; Jia, Z.W. Slope length effects on soil loss for steep slopes. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1759–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xie, G.; An, K. The function and economic value of soil conservation of ecosystems in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2003, 23, 2367–2378. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, C.S.; Randerson, J.T.; Field, C.B.; Matson, P.A.; Vitousek, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Klooster, S.A. Terrestrial Ecosystem Production—A Process Model-Based on Global Satellite and Surface Data. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1993, 7, 811–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hickel, K.; Dawes, W.R.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Western, A.W.; Briggs, P.R. A rational function approach for estimating mean annual evapotranspiration. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W02502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.M.; Lü, Y.H.; Fu, B.J.; Lü, D.; Wu, X.; Sun, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.L. A modified habitat quality model to incorporate the effects of ecological restoration. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 104029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.T.; Tallis, H.T.; Ricketts, T.; Guerry, A.D.; Wood, S.A.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Daily, G.C. Invest 3.10.2 User’s Guide. 2020. Available online: https://storage.googleapis.com/releases.naturalcapitalproject.org/invest-userguide/latest/en/index.html (accessed on 9 January 2024).
- Xu, W.H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Hull, V.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Liu, J.G.; Polasky, S.; et al. Strengthening protected areas for biodiversity and ecosystem services in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.Z.; Zhao, W.W.; Liu, Y.X.; Yang, S.Q.; Hu, X.P.; Cherubini, F. Relationships of multiple landscape services and their influencing factors on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 1987–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.F.; Liu, Y.X.; Chen, J.X.; Dong, J.Q. Scenario-based ecological security patterns to indicate landscape sustainability: A case study on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2175–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Zhao, W.W.; Cherubini, F.; Hu, X.P.; Pereira, P. Sensitivity and future exposure of ecosystem services to climate change on the Tibetan Plateau of China. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 3451–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Zhang, T.L.; Fu, B.J. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, M.; Fu, B.J.; Kemp, D.; Zhao, W.W.; Liu, G.H.; Han, G.D.; Wilkes, A.; Lu, X.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; et al. Reconsidering the efficiency of grazing exclusion using fences on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Zhao, W.W.; Cherubini, F.; Hu, X.P.; Pereira, P. Effectiveness of protected areas edges on vegetation greenness, cover and productivity on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2022, 224, 104421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargione, J.E.; Bassett, S.; Boucher, T.; Bridgham, S.D.; Conant, R.T.; Cook-Patton, S.C.; Ellis, P.W.; Falcucci, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Gopalakrishna, T.; et al. Natural climate solutions for the United States. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Luo, Y.Z.; Zheng, H.; Yang, S.S.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Luo, Y.C. Standard of payments for ecosystem services in Sanjiangyuan Natural Reserve. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 0764–0770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Cheng, C.X.; Wu, X.D. Mapping the spatial heterogeneity of global land use and land cover from 2020 to 2100 at a 1 km resolution. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wei, D.; Wang, X.D.; Hong, J.T.; Wu, J.B.; Xiong, D.H.; Liang, Y.L.; Yuan, Z.R.; Qi, Y.H.; Huang, L. Three decadal large-scale ecological restoration projects across the Tibetan Plateau. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Zhao, W.; Pereira, P. Opinionated Views on Grassland Restoration Programs on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 861200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook 2023. National Bureau of Statistics. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/2023/indexch.htm (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Bastin, J.F.; Finegold, Y.; Garcia, C.; Mollicone, D.; Rezende, M.; Routh, D.; Zohner, C.M.; Crowther, T.W. The global tree restoration potential. Science 2020, 369, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazdon, R.; Brancalion, P. Restoring forests as a means to many ends. Science 2019, 365, 24–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedeling, E.; Börner, J.; Amelung, W.; Schiffers, K.; Shepherd, K.; Rosenstock, T. Forest restoration: Overlooked constraints. Science 2019, 366, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, C.M.; Sayer, J.A. The political economy of reforestation and forest restoration in Asia-Pacific: Critical issues for REDD+. Biol. Conserv. 2012, 154, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancalion, P.H.S.; Niamir, A.; Broadbent, E.; Crouzeilles, R.; Barros, F.S.M.; Zambrano, A.M.A.; Baccini, A.; Aronson, J.; Goetz, S.; Reid, J.L.; et al. Global restoration opportunities in tropical rainforest landscapes. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.J.; Hu, Y.J.; Tang, B.J. Research on carbon market price mechanism and influencing factors: A literature review. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 761–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.L.; Chen, X.L.; Yang, Y.; He, Y. Influencing Factors and Prediction of Carbon Trading Market Prices in China via Elliptical Factor Analysis. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2024, 37, 2680–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, E.R.; Zhao, Z.X.; Jia, L.Z.; Jiang, X.T. Contribution of ecosystem services improvement on achieving Sustainable development Goals under ecological engineering projects on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 199, 107146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Jiao, L.; Che, X.C.; Wu, J.J.; Zhu, X.L.; Li, Q. Study on the water-carbon coupling coordination function on the eastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Ecol. Model. 2024, 487, 110572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Yin, L.C.; Lü, D.; Wang, X.F. Climate and scale are critical for illustrating the links between carbon and water services across Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Catena 2023, 231, 107379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lü, Y.H.; Lü, D.; Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Yin, L.C.; Wang, X.F. Carbon and water relationships change nonlinearly along elevation gradient in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Swallow, B.; Foggin, J.M.; Zhong, L.S.; Sang, W.G. Co-management for sustainable development and conservation in Sanjiangyuan National Park and the surrounding Tibetan nomadic pastoralist areas. Hum. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Swallow, B.; Foggin, J.M.; Sang, W.G.; Zhong, L.S. Developing co-management for conservation and local development in China’s national parks: Findings from focus group discussions in the Sanjiangyuan Region. Front. Conserv. Sci. 2023, 4, 903788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.B.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Avissar, R.; Roy, S.B.; Barrett, D.J.; Cook, C.W.; Farley, K.A.; le Maitre, D.C.; McCarl, B.A.; Murray, B.C. Trading water for carbon with biological sequestration. Science 2005, 310, 1944–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockerhoff, E.G.; Barbaro, L.; Castagneyrol, B.; Forrester, D.I.; Gardiner, B.; González-Olabarria, J.R.; Lyver, P.O.; Meurisse, N.; Oxbrough, A.; Taki, H.; et al. Forest biodiversity, ecosystem functioning and the provision of ecosystem services. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 3005–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jobbagy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. Trade-offs in water and carbon ecosystem services with land-use changes in grasslands. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Jia, Z.Q. Changes in soil organic carbon and nitrogen capacities of Salix cheilophila Schneid along a revegetation chronosequence in semi-arid degraded sandy land of the Gonghe Basin, Tibet Plateau. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Jia, Z.Q.; Li, Q.X.; He, L.X.Z.; Zhao, X.B.; Wang, L.; Han, D. Determine the Optimal Vegetation Type for Soil Wind Erosion Prevention and Control in the Alpine Sandy Land of the Gonghe Basin on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Forests 2023, 14, 2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Wang, G.J. Rainwater Use Process of in Semi-Arid Zone, Tibetan Plateau. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Tian, L.H.; Hasi, E.; Zhang, D.S.; Wu, W.Y. Vegetation-soil dynamics in an alpine desert ecosystem of the Qinghai Lake watershed, northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front. Env. Sci. 2023, 11, 1119605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.H.; Wu, W.Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, D.S.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, Q.Y. The Ecosystem Effects of Sand-Binding Shrub in Alpine Semi-Arid Desert in the Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land 2019, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, F.Y.; Bruijnzeel, L.A.; Meli, P.; Martin, P.A.; Zhang, J.; Nakagawa, S.; Miao, X.R.; Wang, W.Y.; McEvoy, C.; Peña-Arancibia, J.L.; et al. The biodiversity and ecosystem service contributions and trade-offs of forest restoration approaches. Science 2022, 376, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.Q.; Qi, Y.C.; Chen, D.L.; Li, D.H.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.F. Multi-scale analysis of satellite, reanalysis and muti-source precipitation estimates over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2024, 309, 107484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhan, P.; Pan, Y.Z.; Zhu, X.F.; Li, M.Y.; Zhang, D.J. Comparison of Remote Sensing Time-Series Smoothing Methods for Grassland Spring Phenology Extraction on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Zhao, W.W.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, S.; Yang, S.Q. Spatial Consistency Assessments for Global Land-Cover Datasets: A Comparison among GLC2000, CCI LC, MCD12, GLOBCOVER and GLCNMO. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.K.; Xiao, P.F.; Feng, X.Z.; Li, H.X. Accuracy assessment of seven global land cover datasets over China. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 125, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data | Time Period | Resolution | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land use | 2001–2020 | 500 m | MCD12Q1 |
| Forest cover | 2000–2020 | 30 m | Global Forest Change (GFC) dataset [32] |
| Human footprint | 2020 | 1 km | [33] |
| Grided grazing intensity | 2020 | 1 km | [34] |
| Grided population density | 2020 | 1 km | Worldpop |
| Grided crop production | 2020 | 5 min | GAEZ [35] |
| DEM | - | 90 m | SRTM3 |
| Soil | - | 1 km | ISRIS Soil Grid |
| Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | 2001–2020 | 500 m | MOD13A2 |
| Precipitation | 2000–2020 | 0.05° | CHIRPS (Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station data) [36] |
| Actual Evapotranspiration | 2001–2020 | 500 m | MOD16A3 |
| Habitat Quality | Carbon Sequestration | Soil Conservation | Water Yield | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Border | Non-Border | Border | Non-Border | Border | Non-Border | Border | Non-Border | |
| Soil organic carbon (SOC) | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.28 | 0.47 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.14 |
| NDVI | 0.81 | 0.72 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.62 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.16 |
| Population density | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.00 |
| Temperature | 0.61 | 0.37 | 0.82 | 0.50 | 0.56 | 0.26 | 0.37 | 0.02 |
| Slope | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.02 |
| Precipitation | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.33 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.14 |
| Altitude | 0.57 | 0.28 | 0.87 | 0.40 | 0.63 | 0.34 | 0.49 | 0.03 |
| Grazing intensity | 0.27 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, L.; Liu, S.; Zha, X.; Hua, T. Biophysical and Social Constraints of Restoring Ecosystem Services in the Border Regions of Tibet, China. Land 2025, 14, 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081601
Jia L, Liu S, Zha X, Hua T. Biophysical and Social Constraints of Restoring Ecosystem Services in the Border Regions of Tibet, China. Land. 2025; 14(8):1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081601
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Lizhi, Silin Liu, Xinjie Zha, and Ting Hua. 2025. "Biophysical and Social Constraints of Restoring Ecosystem Services in the Border Regions of Tibet, China" Land 14, no. 8: 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081601
APA StyleJia, L., Liu, S., Zha, X., & Hua, T. (2025). Biophysical and Social Constraints of Restoring Ecosystem Services in the Border Regions of Tibet, China. Land, 14(8), 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081601








