From Global to Local: Testing the UNEP Environmental Vulnerability Index in a Coastal Korea Context
Abstract
1. Introduction
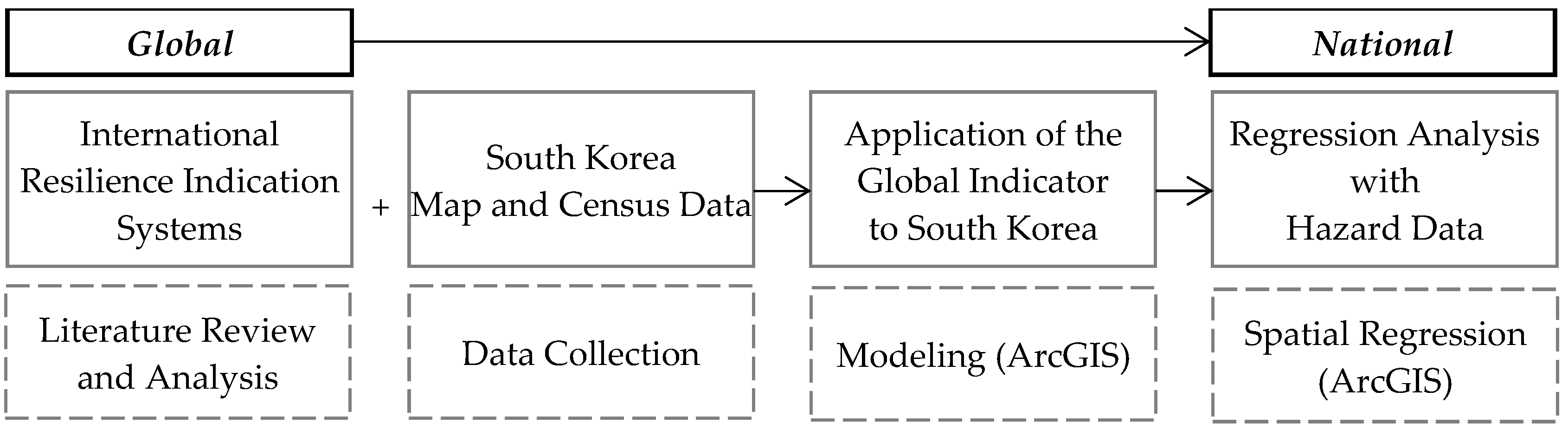
2. Material and Methods
2.1. UNEP and SOPAC Environmental Vulnerability Index
2.2. Application of the UNEP EVI to Coastal Cities in South Korea
2.3. Historical Water Disaster Data for Korean Coastal Counties
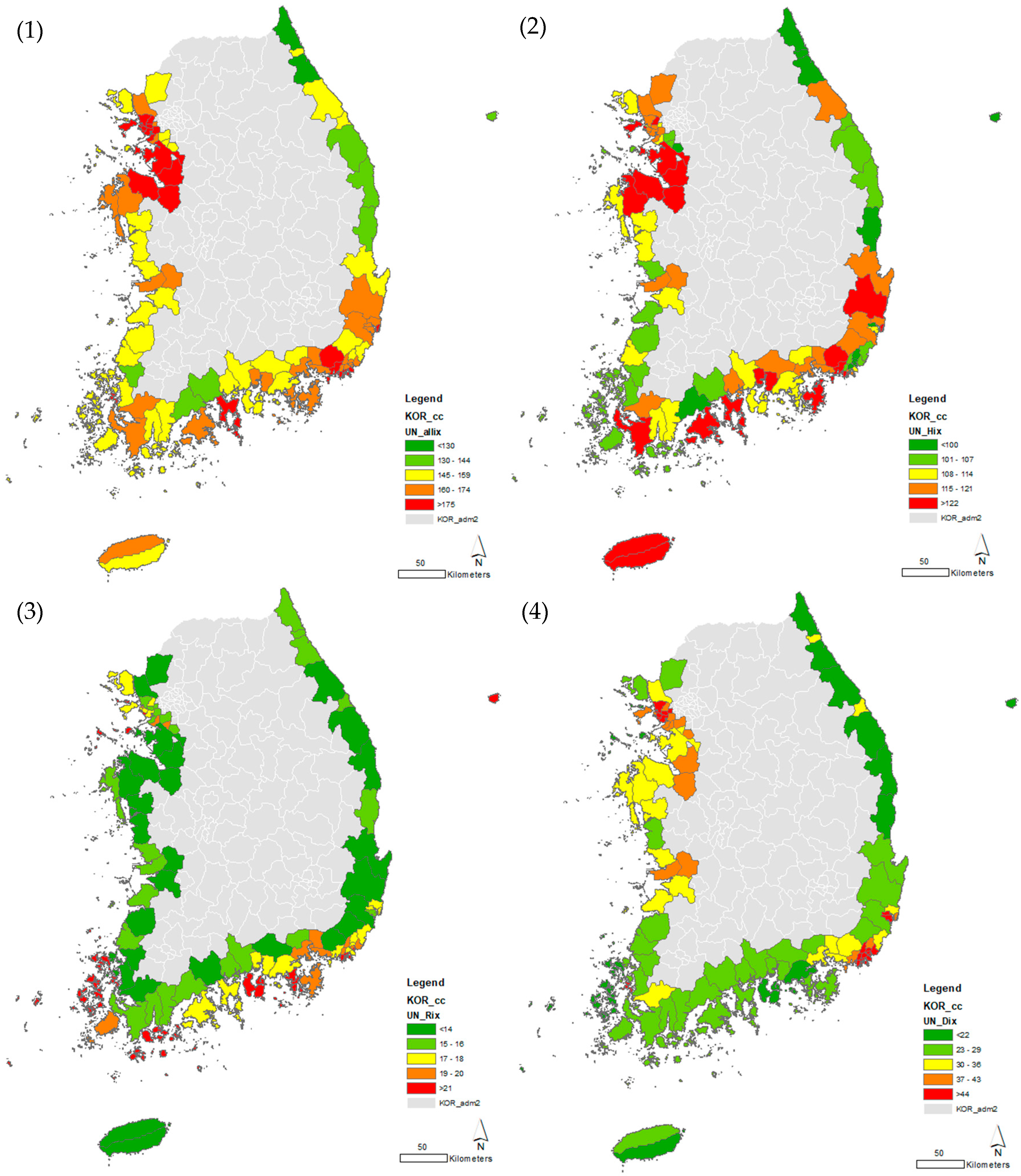
3. Results
3.1. Korean Coastal Vulnerability Index Map
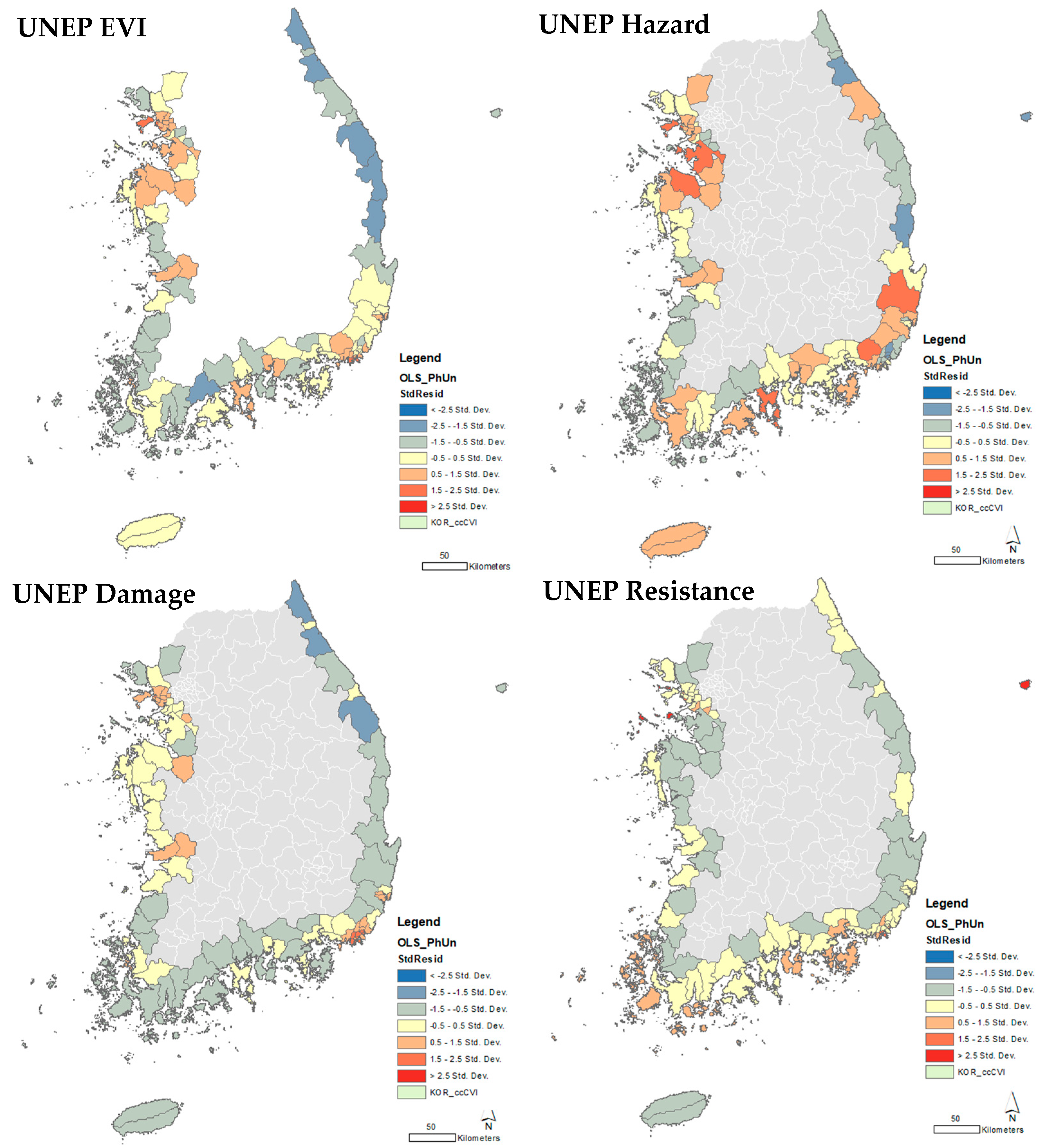
3.2. OLS Linear Regression: UNEP EVI and Previous Disaster Map
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Sixth Assessment Report, Working Group II: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kasthala, S.; Parthasarathy, D.; Narayanan, K.; Inamdar, A.B. Classification and evaluation of current climate vulnerability assessment methods. Soc. Indic. Res. 2023, 171, 605–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feenstra, I.; Burton, I.; Smith, J.B.; Tol, R.S.J. Handbook on Methods for Climate Change Impact Assessment and Adaptation Strategies; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- UNISDR & WMO. UN System Task Team on the Post-2015 UN Development Agenda: Disaster Risk and Resilience; United Nations, 2012. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/policy/untaskteam_undf/thinkpieces/3_disaster_risk_resilience.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- National Academies of Science (NAS). Disaster Resilience: A National Imperative; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Allen, M.R.; Barros, V.R.; Broome, J.; Cramer, W.; Christ, R.; Church, J.A.; Clarke, L.; Dahe, Q.; Dasgupta, P.; et al. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme and South Pacific Applied Geoscience Commission (UNEP & SOPAC). EVI: Analysis of Indicators; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo-Gonzalez, J.; Lovell, C.A.K.; Lovell, J.; Edmonds, H. Measuring climate risks: A new multidimensional index for global vulnerability and resilience. Environ. Dev. 2025, 56, 101227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Defense Fund. U.S. Climate Vulnerability Index: Fact Sheet; Environmental Defense Fund: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Available online: https://map.climatevulnerabilityindex.org/map/cvi_overall/usa?mapBoundaries=Tract&mapFilter=0&reportBoundaries=Tract&geoContext=State (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Olivares-Aguilar, I.C.; Sánchez-Dávila, G.; Wildermann, N.E.; Clark, D.; Floerl, L.; Villamizar, E.; Matteucci, S.D.; Sevilla, N.P.M.; Nagy, G.J. Methodological approaches to assess climate vulnerability and cumulative environmental impacts on coastal landscapes. Front. Clim. 2022, 4, 1018182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, D.; Park, M. Urban flood vulnerability assessment for Seoul using high-resolution rainfall scenarios. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2576. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y. Identification of flood-vulnerable areas considering demographic characteristics and regional types in South Korea. Water 2020, 12, 3451. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Nam, K.; Egawa, S. The Gaps Between Institutional and Practical Disaster Risk Management Measures on Coastal Flood Risks in South Korea’s Coastal Communities. Int. J. Disaster Risk Science. 2024, 15, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Statistical Information Service (KOSIS). 2021. Available online: https://kosis.kr/eng/statisticsList/statisticsListIndex.do (accessed on 30 January 2021).
- e-National Index. 2021. Available online: https://www.index.go.kr/unity/potal/eNara/main/EnaraMain.do (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA). 2021. Available online: https://www.weather.go.kr/weather/earthquake_volcano/tidalwave_02.jsp (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- South Pacific Applied Geoscience Commission (SOPAC). The Environmental Vulnerability Index (EVI); SOPAC Technical Report 384; EVI: Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, R.; Kaly, U.L.; Mitchell, J. What is Vulnerability? What is Resilience? In Environmental Vulnerability Index; UNEP and SOPAC: Suva, Fiji, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Coastal Vulnerability Assessment Scenario. Available online: https://www.noaa.gov/about-our-agency (accessed on 23 May 2021).
- Ministry of Public Administration and Security. Disaster Statistical Yearbook. Available online: http://www.mois.go.kr (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Korea Water Resources Corporation. National Water Resource Management Comprehensive Information System. Available online: https://www.wamis.go.kr (accessed on 23 May 2021).
- ESRI. Interpreting OLS Results. ArcGIS Desktop. 2021. Available online: https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.3/tools/spatial-statistics-toolbox/interpreting-ols-results.htm (accessed on 10 March 2021).


| Korea CVI | Category | Unit | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | High Winds | Hazards | day/yr | X ≤ 0.5 | 0.5 < X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 1.5 | 1.5 < X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 2.5 | 2.5 < X ≤ 3 | 3 < X |
| 2 | Dry Periods | Hazards | index | X ≤ 0 | 0 < X ≤ 0.05 | 0.05 < X ≤ 0.1 | 0.1 < X ≤ 0.15 | 0.15 < X ≤ 0.2 | 0.2 < X ≤ 0.25 | 0.25 < X |
| 3 | Wet Periods | Hazards | day/yr | X ≤ 0.15 | 0.15 < X ≤ 0.2 | 0.2 < X ≤ 0.25 | 0.25 < X ≤ 0.3 | 0.3 < X ≤ 0.35 | 0.35 < X ≤ 0.4 | 0.4 < X |
| 4 | Hot Periods | Hazards | day/yr | X ≤ 5 | 5 < X ≤ 10 | 10 < X ≤ 20 | 20 < X ≤ 30 | 30 < X ≤ 40 | 40 < X ≤ 50 | 50 < X |
| 5 | Cold Periods | Hazards | day/yr | X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 5 | 5 < X ≤ 10 | 10 < X ≤ 15 | 15 < X ≤ 20 | 20 < X ≤ 25 | 6 < X |
| 6 | Sea Temperatures | Hazards | % | X < −0.01 | −0.01 ≤ X < 0 | 0 ≤ X < 0.01 | 0.01 ≤ X < 0.02 | 0.02 ≤ X < 0.03 | 0.03 ≤ X < 0.04 | 0.04 ≤ X |
| 7 | Volcanos | Hazards | VEI/km2 | X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 3 | 3 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 5 | 5 < X ≤ 6 | 6 < X ≤ 7 | 7 < X |
| 8 | Earthquakes | Hazards | number | X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 3 | 3 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 5 | 5 < X ≤ 6 | 6 < X |
| 9 | Tsunamis | Hazards | index | X ≤ 0.05 | 0.05 < X ≤ 0.1 | 0.1 < X ≤ 0.15 | 0.15 < X ≤ 0.2 | 0.2 < X ≤ 0.25 | 0.25 < X ≤ 0.3 | 0.3 < X |
| 10 | Slides | Hazards | index | X ≤ 0 | 0 < X ≤ 0.5 | 0.5 < X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 1.5 | 1.5 < X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 2.5 | 2.5 < X |
| 11 | Land Area | Resistance | LN (km2) | X > 7 | 6 < X ≤ 7 | 5 < X ≤ 6 | 4 < X ≤ 5 | 3 < X ≤ 4 | 2 < X ≤ 3 | X ≤ 3 |
| 12 | Country Dispersion | Resistance | LN (1000 km/km2) | X ≤ 5.2 | 5.2 < X ≤ 5.6 | 5.6 < X ≤ 6.2 | 6.2 < X ≤ 6.8 | 6.8 < X ≤ 7.4 | 7.4 < X ≤ 8 | 8 < X |
| 13 | Geographic Isolation | Resistance | m | X ≤ 0 | 0 < 0.X ≤ 5 | 5 < 0.X ≤ 10 | 10 < 0.X ≤ 40 | 40 < 0.X ≤ 80 | 80 < 0.X ≤ 160 | 160 < 0.X |
| 14 | Relief | Resistance | angle | X ≤ 0 | 0 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 8 | 8 < X ≤ 12 | 12 < X ≤ 16 | 16 < X ≤ 20 | 20 < X |
| 15 | Lowlands | Resistance | % | X ≤ 0 | 0 < X ≤ 0.5 | 0.5 < X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 1.5 | 1.5 < X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 2.5 | 2.5 < X |
| 16 | Shared Borders | Resistance | (NA) | X ≤ 0 | 0 < X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 6 | 6 < X ≤ 8 | 8 < X ≤ 10 | 10 < X |
| 17 | Ecosystem Imbalance | Damage | mg/L | X > 0.2 | 0 < X ≤ 0.2 | −0.2 < X ≤ 0 | −0.4 < X ≤ −0.2 | −0.6 < X ≤ −0.4 | −0.8 < X ≤ −0.6 | X < −0.8 |
| 18 | Environmental Openness | Hazards | LN (USD 100/km2) | X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 1.5 | 1.5 < X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 2.5 | 2.5 < X ≤ 3 | 3 < X ≤ 3.5 | 3.5 < X |
| 19 | Migratory Species | Resistance | Spp/km2 | X ≤ 5 | 5 < X ≤ 10 | 10 < X ≤ 15 | 15 < X ≤ 20 | 20 < X ≤ 25 | 25 < X ≤ 30 | 30 < X |
| 20 | Endemic Species | Resistance | Spp/km2 | X ≤ 5 | 5 < X ≤ 10 | 10 < X ≤ 15 | 15 < X ≤ 20 | 20 < X ≤ 25 | 25 < X ≤ 30 | 30 < X |
| 21 | Introductions | Damage | number | X ≤ 0 | 0 < X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 3 | 3 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 5 | 5 < X |
| 22 | Endangered Species | Damage | number | X > 60 | 50 < X ≤ 60 | 40 < X ≤ 50 | 30 < X ≤ 40 | 20 < X ≤ 30 | 10 < X ≤ 20 | X < 10 |
| 23 | Extinctions | Damage | number | X ≤ 0 | 0 < X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 3 | 3 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 5 | 5 < X |
| 24 | Vegetation Cover | Damage | % | X > 80 | 60 < X ≤ 80 | 40 < X ≤ 60 | 20 < X ≤ 40 | 10 < X ≤ 20 | 0 < X ≤ 10 | X ≤ 0 |
| 25 | Loss of Vegetation Cover | Hazards | % | X > 0 | X = 0 | −1 < X < 0 | −2 < X≤ −1 | X ≤ −2 | ||
| 26 | Habitat Fragmentation | Damage | LN (km/ha + 1) | X ≤ 0.2 | 0.2 < X ≤ 0.4 | 0.4 < X ≤ 0.6 | 0.6 < X ≤ 0.8 | 0.8 < X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 1.2 | 1.2 < X |
| 27 | Degradation | Damage | % | X ≤ 5 | 5 < X ≤ 10 | 10 < X ≤ 15 | 15 < X ≤ 20 | 20 < X ≤ 25 | 25 < X ≤ 50 | 50 < X |
| 28 | Terrestrial Reserves | Hazards | % | X > 3 | 2.5 < X ≤ 3 | 2 < X ≤ 2.5 | 1.5 < X ≤ 2 | 1 < X ≤ 1.5 | 0.5 < X ≤ 1 | X ≤ 0.5 |
| 29 | Marine Reserves | Hazards | km2 | X > 5 | 4 < X ≤ 5 | 3 < X ≤ 4 | 2 < X ≤ 3 | 1 < X ≤ 2 | 0 < X ≤ 1 | X = 0 |
| 30 | Intensive Farming | Hazards | LN (kg/km2 + 1) | X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 3 | 3 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 5 | 5 < X ≤ 6 | 6 < X ≤ 7 | 7 < X |
| 31 | Fertilizers | Hazards | % | X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 6 | 6 < X ≤ 7 | 7 < X ≤ 8 | 8 < X ≤ 9 | 9 < X ≤ 10 | 10 < X |
| 32 | Pesticides | Hazards | km2 | X ≤ 20 | 20 < X ≤ 30 | 30 < X ≤ 40 | 40 < X ≤ 50 | 50 < X ≤ 60 | 60 < X ≤ 70 | 70 < X |
| 33 | Biotechnology | Hazards | number | X ≤ 0 | None | None | None | 0 < X ≤ 20 | 20 < X ≤ 50 | 50 < X |
| 34 | Productivity Overfishing | Hazards | KRW 1000 M | X > 120 | 100 < X ≤ 120 | 80 < X ≤ 100 | 60 < X ≤ 80 | 40 < X ≤ 60 | 20 < X ≤ 40 | X ≤ 20 |
| 35 | Fish Effort | Hazards | LN (ppl + 1) | X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 4 | 2.5 < X ≤ 3 | 3 < X ≤ 3.5 | 3.5 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 4.5 | 4.5 < X |
| 36 | Renewable Water | Hazards | m³/yr/ppl | X ≤ 100 | 100 < X ≤ 200 | 200 < X ≤ 300 | 300 < X ≤ 400 | 400 < X ≤ 500 | 600 < X ≤ 700 | 700 < X |
| 37 | Sulfur Dioxide Emissions | Hazards | LN (t/km2/yr + 1) | X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 3 | 3 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 5 | 5 < X ≤ 6 | 6 < X |
| 38 | Waste Production | Hazards | LN (t/km2/yr + 1) | X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 3 | 3 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 5 | 5 < X ≤ 6 | 6 < X |
| 39 | Waste Treatment | Hazards | % | X = 100 | 80 ≤ X < 100 | 60 ≤ X < 80 | 50 ≤ X < 60 | 40 ≤ X < 50 | 30 ≤ X < 40 | X < 30 |
| 40 | Industry | Hazards | 10 M kWh | 0.X ≤ 1 | 1 < 0.X ≤ 5 | 5 < 0.X ≤ 10 | 10 < 0.X ≤ 20 | 20 < 0.X ≤ 50 | 50 < 0.X ≤ 100 | 100 < 0.X |
| 41 | Spills | Hazards | number | 0.X ≤ 5 | 5 < 0.X ≤ 10 | 10 < 0.X ≤ 15 | 15 < 0.X ≤ 20 | 20 < 0.X ≤ 25 | 25 < 0.X ≤ 30 | 30 < 0.X |
| 42 | Mining | Hazards | KRW 1 M /km2/yr | X ≤ 10 | 10 < X ≤ 20 | 20 < X ≤ 50 | 50 < X ≤ 100 | 100 < X ≤ 200 | 200 < X ≤ 300 | 300 < X |
| 43 | Sanitation | Hazards | % | X = 100 | 95 ≤ X < 100 | 90 ≤ X < 95 | 80 ≤ X < 90 | 70 ≤ X < 80 | 60 ≤ X < 70 | X < 60 |
| 44 | Vehicles | Hazards | LN (number/km2 + 1) | X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 1.5 | 1.5 < X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 2.5 | 2.5 < X ≤ 3 | 3 < X ≤ 3.5 | 3.5 < X |
| 45 | Human Population Density | Damage | LN (ppl/km2 + 1) | X ≤ 3 | 3 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 5 | 5 < X ≤ 6 | 6 < X ≤ 7 | 7 < X ≤ 8 | 8 < X |
| 46 | Human Population Growth | Hazards | % | X < 0 | X = 0 | 0 < X ≤ 0.5 | 0.5 < X ≤ 1 | 1 < X ≤ 1.5 | 1.5 < X ≤ 2 | 2 < X |
| 47 | Tourists | Hazards | LN (ppl/km2 + 1) | X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 6 | 6 < X ≤ 8 | 8 < X ≤ 10 | 10 < X ≤ 12 | 12 < X |
| 48 | Coastal Settlements | Damage | LN (household/km2 + 1) | X ≤ 2 | 2 < X ≤ 3 | 3 < X ≤ 4 | 4 < X ≤ 5 | 5 < X ≤ 6 | 6 < X ≤ 7 | 7 < X |
| 49 | Environmental Agreements | Hazards | ppl/100 ppl | X > 30 | 25 < X ≤ 30 | 20 < X ≤ 25 | 15 < X ≤ 20 | 10 < X ≤ 15 | 5 < X ≤ 10 | X ≤ 5 |
| 50 | Human Conflicts | Damage | index | X ≤ 50 | 50 < X ≤ 80 | 80 < X ≤ 110 | 110 < X ≤ 140 | 140 < X ≤ 170 | 170 < X ≤ 200 | 200 < X |
| City | County Level | VI | City | County Level | VI | City | County Level | VI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Busan | Saha | Gu | 196 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Sacheon | Si | 171 | Gyeonggi-do | Anyang | Si | 153 |
| Busan | Seo | Gu | 192 | Busan | Suyeong | Gu | 169 | Chungcheongnam-do | Boryeong | Si | 153 |
| Incheon | Yeonsu | Gu | 191 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Masan | Si | 168 | Jeollanam-do | Gangjin | Gun | 153 |
| Busan | Yeongdo | Gu | 189 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Geoje | Si | 167 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Haman | Gun | 153 |
| Incheon | Jung | Gu | 188 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Changwon | Si | 167 | Incheon | Ganghwa | Gun | 152 |
| Busan | Gangseo | Gu | 184 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Jinhae | Si | 167 | Gangwon-do | Gangneung | Si | 152 |
| Incheon | Gyeyang | Gu | 184 | Jeju | Jeju | Si | 167 | Gyeongsangbuk-do | Pohang | Si | 152 |
| Ulsan | Dong | Gu | 183 | Busan | Buk | Gu | 166 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Namhae | Gun | 152 |
| Busan | Dong | Gu | 181 | Jeollanam-do | Yeongam | Gun | 166 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Hadong | Gun | 152 |
| Incheon | Dong | Gu | 181 | Jeollanam-do | Goheung | Gun | 165 | Gangwon-do | Donghae | Si | 151 |
| Incheon | Namdong | Gu | 181 | Jeollanam-do | Haenam | Gun | 165 | Jeollanam-do | Jangheung | Gun | 151 |
| Incheon | Bupyeong | Gu | 181 | Busan | Busanjin | Gu | 164 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Goseong | Gun | 151 |
| Incheon | Nam | Gu | 181 | Gyeongsangbuk-do | Gyeongju | Si | 164 | Busan | Geumjeong | Gu | 150 |
| Incheon | Seo | Gu | 178 | Busan | Yeonje | Gu | 163 | Chungcheongnam-do | Seocheon | Gun | 150 |
| Gyeonggi-do | Siheung | Si | 178 | Gyeonggi-do | Gimpo | Si | 163 | Jeollanam-do | Wando | Gun | 150 |
| Chungcheongnam-do | Asan | Si | 177 | Ulsan | Jung | Gu | 162 | Jeollanam-do | Muan | Gun | 148 |
| Chungcheongnam-do | Dangjin | Gun | 177 | Busan | Dongnae | Gu | 161 | Jeollanam-do | Yeonggwang | Gun | 148 |
| Gyeonggi-do | Hwaseong | Si | 176 | Ulsan | Ulju | Gun | 160 | Jeollanam-do | Sinan | Gun | 148 |
| Jeollanam-do | Mokpo | Si | 176 | Chungcheongnam-do | Taean | Gun | 160 | Jeollanam-do | Jindo | Gun | 147 |
| Gyeongsangnam-do | Gimhae | Si | 176 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Tongyeong | Si | 160 | Gangwon-do | Sokcho | Si | 146 |
| Busan | Nam | Gu | 175 | Chungcheongnam-do | Hongseong | Gun | 159 | Jeollabuk-do | Gochang | Gun | 145 |
| Gyeonggi-do | Pyeongtaek | Si | 175 | Jeju | Seogwipo | Si | 159 | Jeollanam-do | Suncheon | Si | 144 |
| Jeollanam-do | Yeosu | Si | 175 | Gyeonggi-do | Gunpo | Si | 158 | Jeollanam-do | Hampyeong | Gun | 143 |
| Ulsan | Nam | Gu | 174 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Jinju | Si | 158 | Gyeongsangbuk-do | Ulleung | Gun | 140 |
| Gyeonggi-do | Bucheon | Si | 173 | Busan | Gijang | Gun | 157 | Gyeongsangbuk-do | Uljin | Gun | 136 |
| Chungcheongnam-do | Seosan | Si | 173 | Gyeonggi-do | Paju | Si | 157 | Jeollanam-do | Boseong | Gun | 135 |
| Busan | Haeundae | Gu | 172 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Yangsan | Si | 157 | Gangwon-do | Samcheok | Si | 132 |
| Gyeonggi-do | Ansan | Si | 172 | Jeollabuk-do | Buan | Gun | 156 | Gyeongsangbuk-do | Yeongdeok | Gun | 130 |
| Jeollabuk-do | Gunsan | Si | 172 | Jeollanam-do | Gwangyang | Si | 156 | Gangwon-do | Goseong | Gun | 129 |
| Busan | Sasang | Gu | 171 | Incheon | Ongjin | Gun | 155 | Gangwon-do | Yangyang | Gun | 125 |
| Ulsan | Buk | Gu | 171 | Gyeonggi-do | Suwon | Si | 154 | ||||
| Jeollabuk-do | Iksan | Si | 171 | Jeollabuk-do | Gimje | Si | 154 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S. From Global to Local: Testing the UNEP Environmental Vulnerability Index in a Coastal Korea Context. Land 2025, 14, 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061297
Han S. From Global to Local: Testing the UNEP Environmental Vulnerability Index in a Coastal Korea Context. Land. 2025; 14(6):1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061297
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, SaMin. 2025. "From Global to Local: Testing the UNEP Environmental Vulnerability Index in a Coastal Korea Context" Land 14, no. 6: 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061297
APA StyleHan, S. (2025). From Global to Local: Testing the UNEP Environmental Vulnerability Index in a Coastal Korea Context. Land, 14(6), 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061297









