Ecological Security Patterns Based on Ecosystem Service Assessment and Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Liaoning Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. ESs Assessment
- (1)
- Water Yield
- (2)
- Habitat Quality
- (3)
- Soil Conservation
- (4)
- Carbon Storage
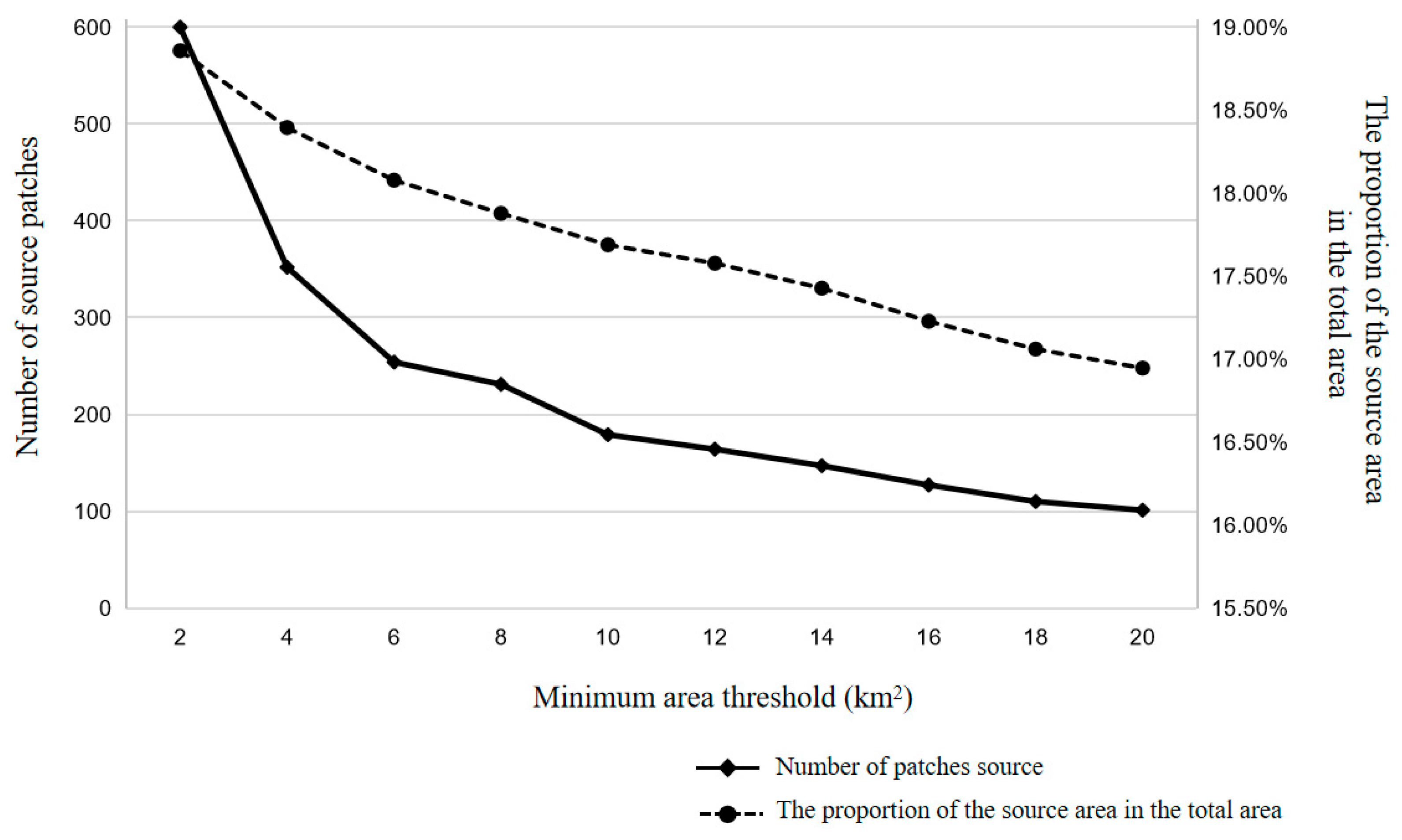
2.3.2. Selecting Ecological Sources
- (1)
- The OWA method
- (2)
- Landscape connectivity
2.3.3. Constructing Ecological Resistance Surfaces
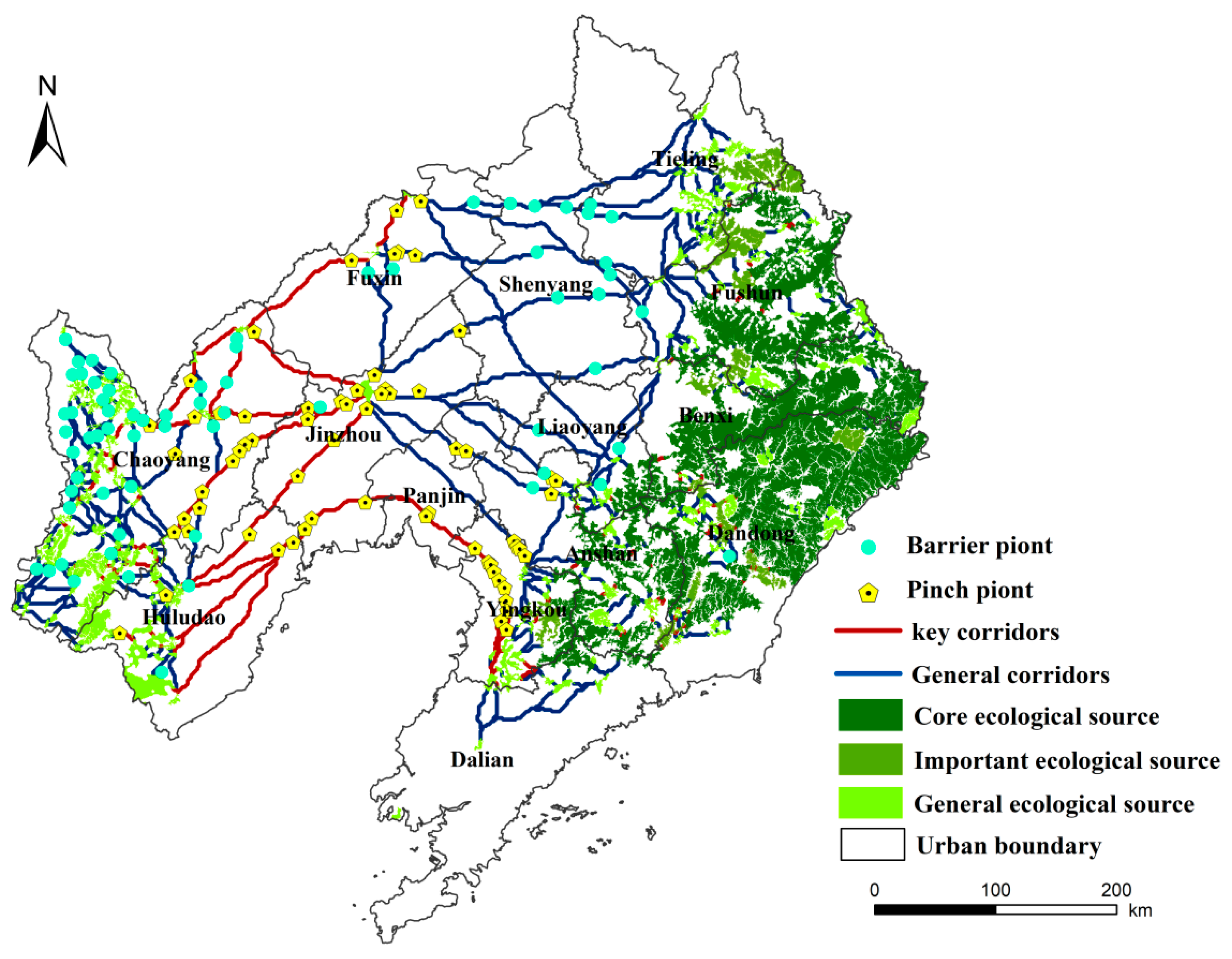
2.3.4. Extraction of Ecological Corridors, Pinch Points and Barrier Points
3. Results
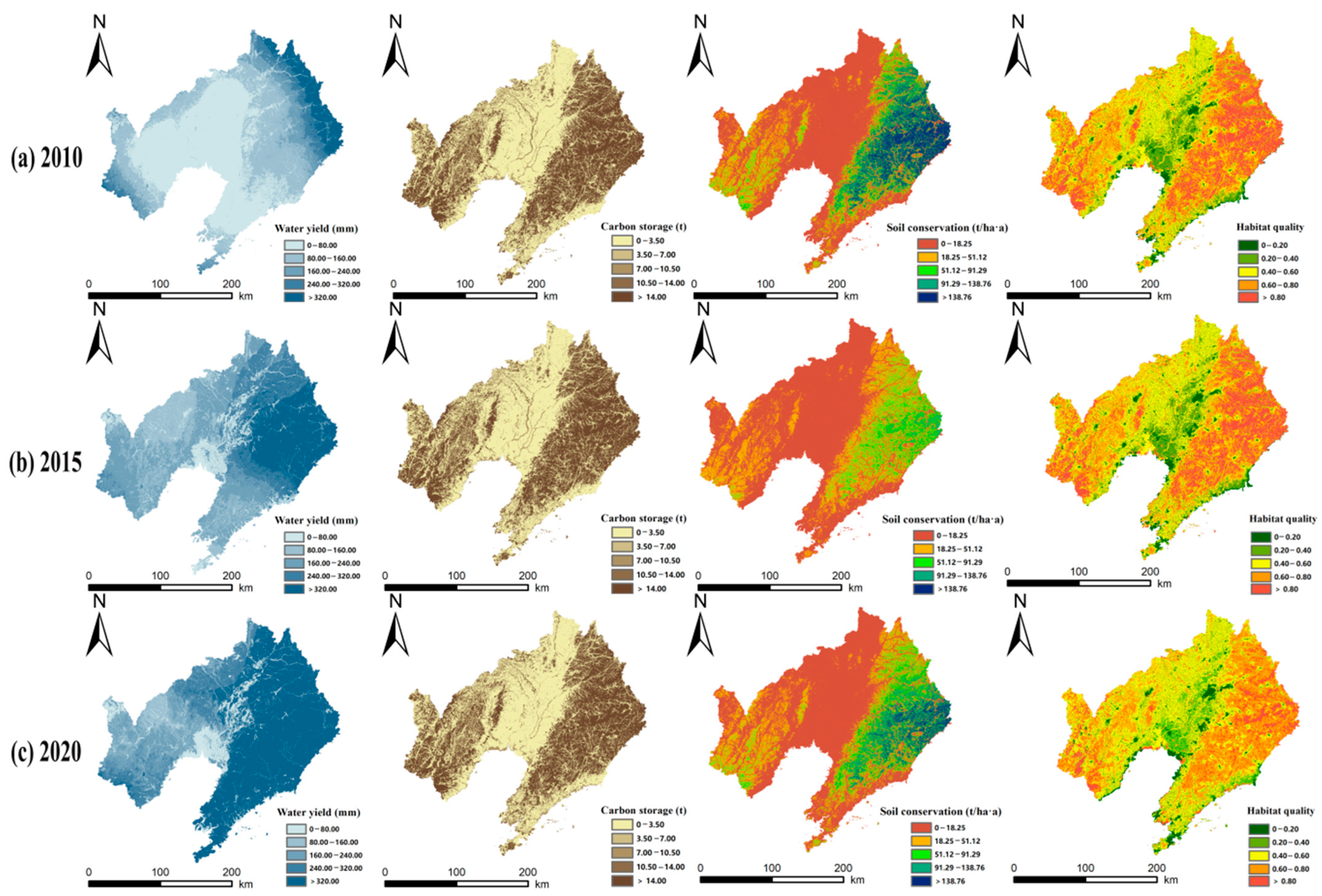
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of ESs
3.2. Construction of an ESP in Liaoning Province
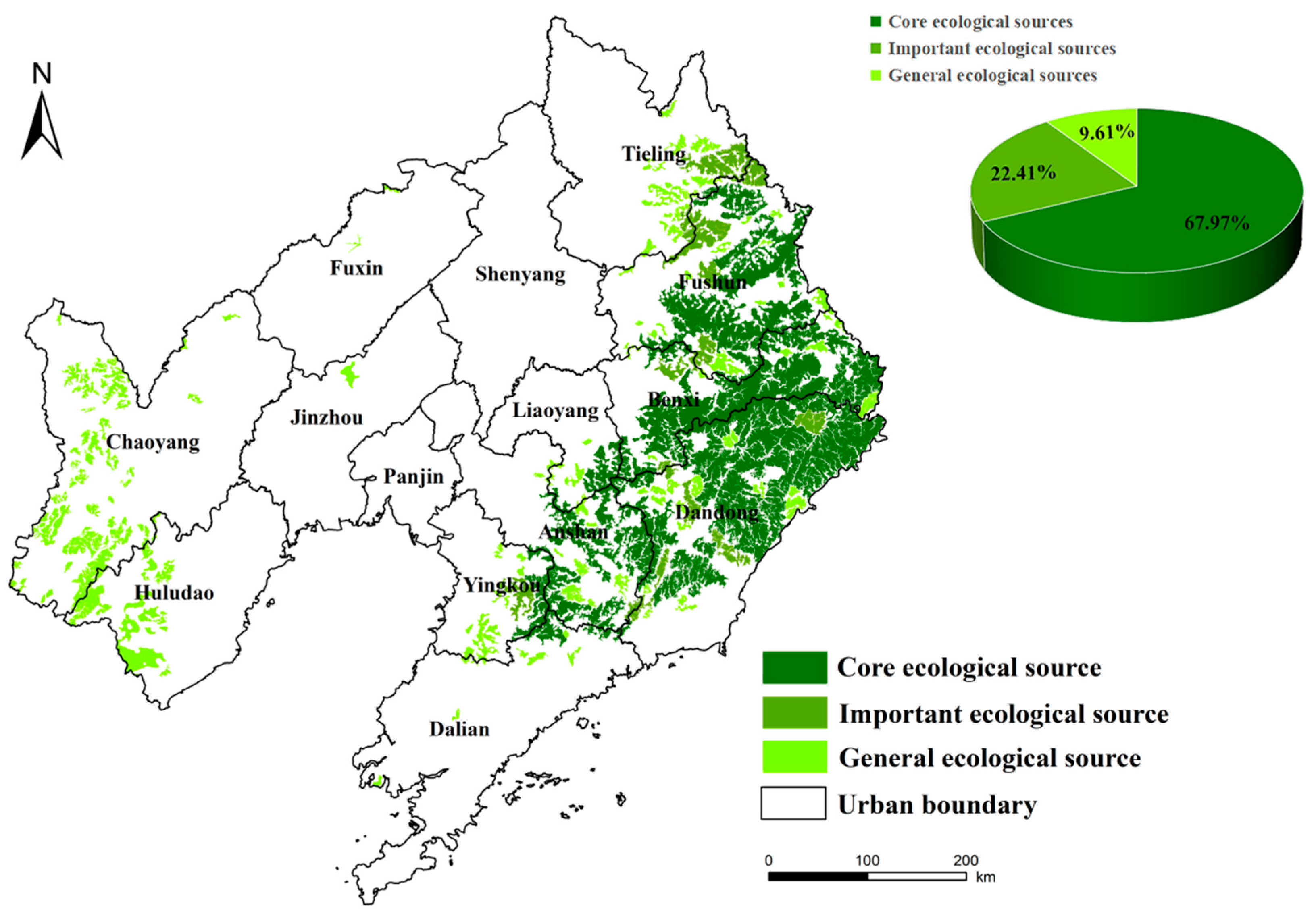
3.2.1. Identification of Ecological Sources
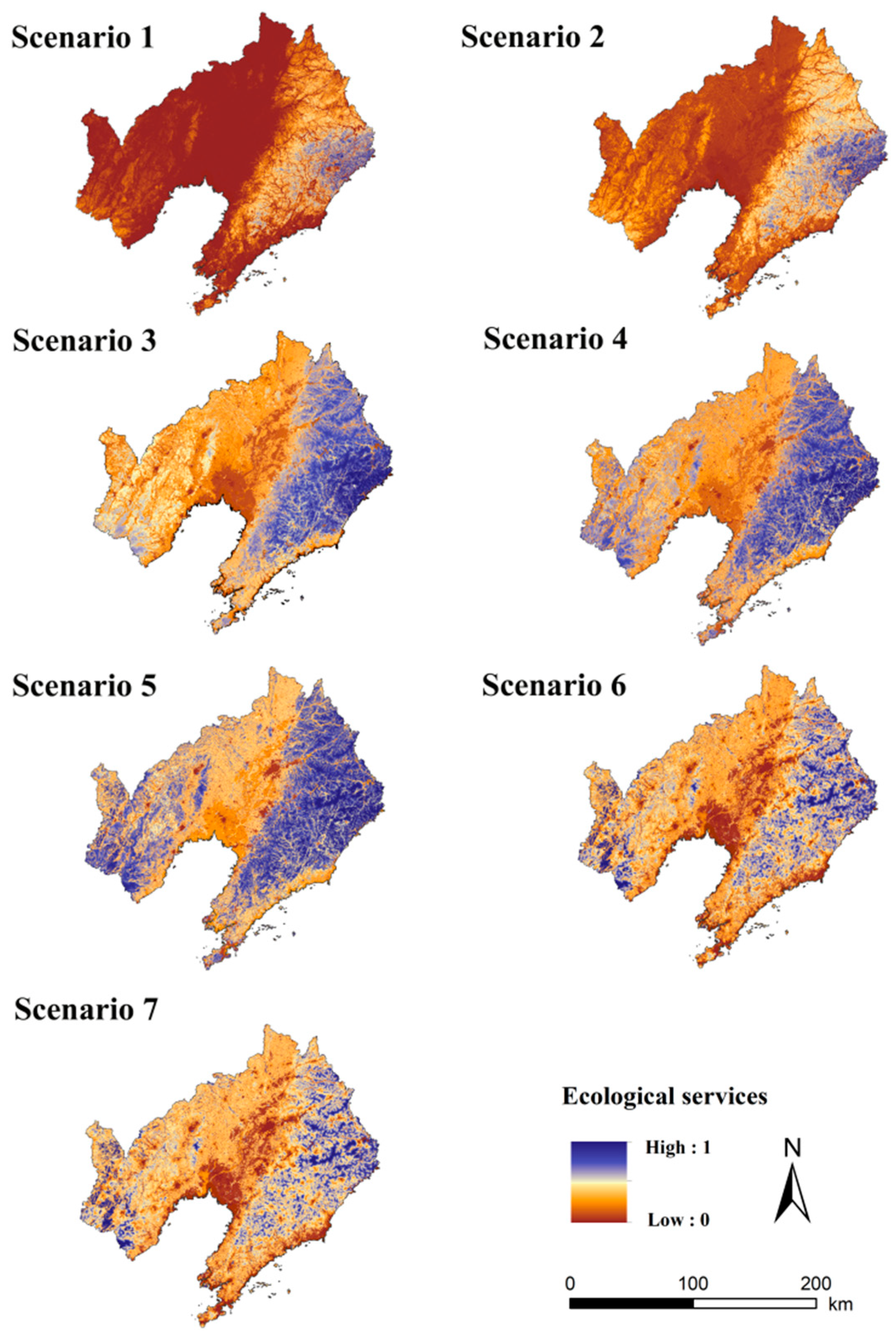
- (1)
- Ecosystem weights, risk values under different scenarios
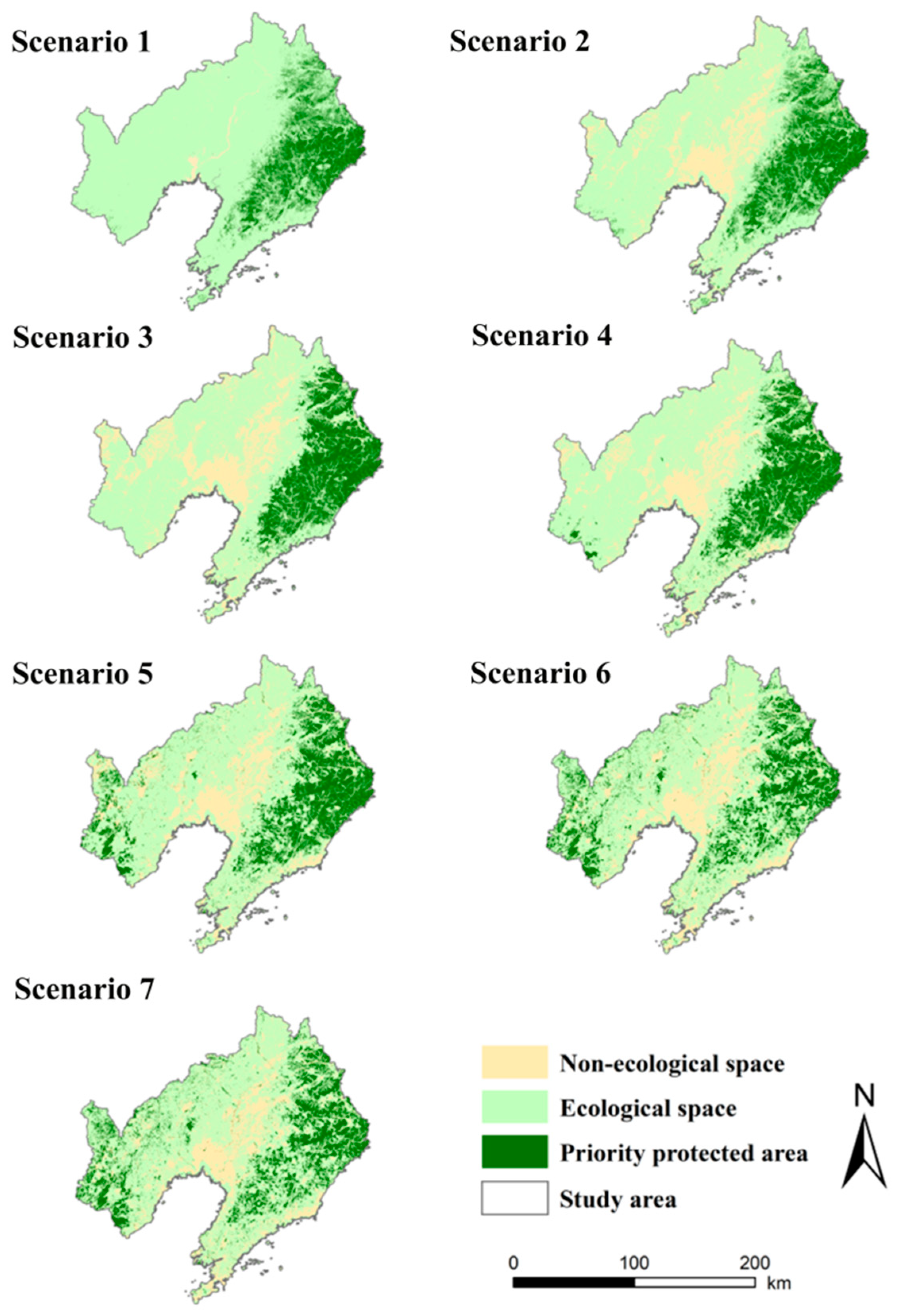
- (2)
- Determination of priority protection areas for ESs under different scenarios
- (3)
- Determine the ecological sources
3.2.2. Construction of Ecological Resistance Surface
3.2.3. Ecological Corridor Extraction
3.2.4. Identify Ecological Pinch Points and Barrier Points
3.2.5. ESP of Liaoning
4. Discussion
4.1. The Rationality of Constructing ESP
4.2. Policy Implications
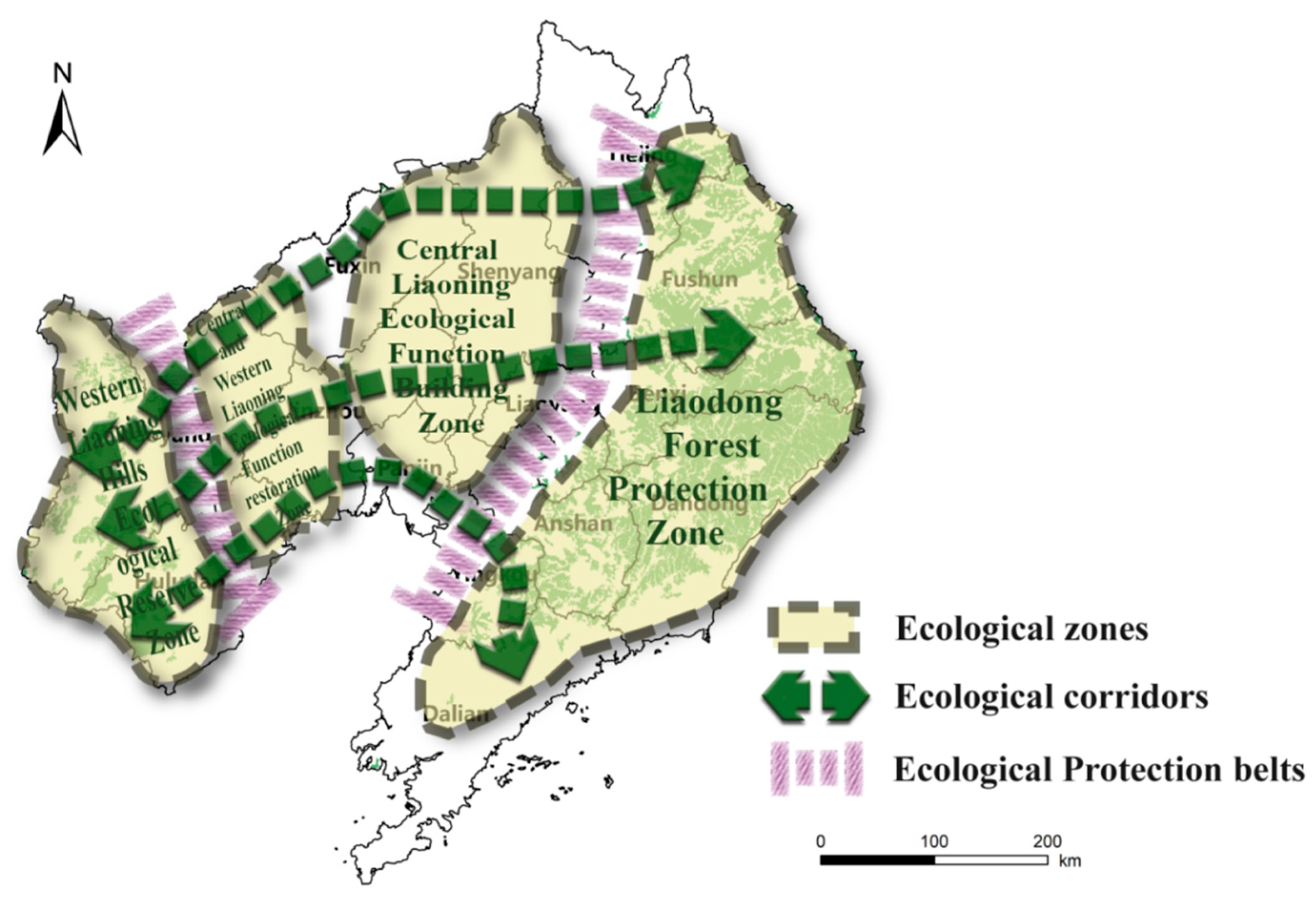
4.3. Constructing the Ecological Protection and Restoration Pattern of “Four Zones, Three Corridors and Two Belts”
4.4. Limitations and Perspectives
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Temporal and spatial differences were significant for the four ESs. In 2010, 2015, and 2020, water yield showed an increasing trend. Carbon storage increased and then decreased, soil conservation decreased and then increased, and habitat quality decreased. Spatially, the distribution of these four ESs shows a consistent pattern, with high-value areas primarily concentrated in the eastern and western woodlands.
- (2)
- The ESP of Liaoning Province is primarily composed of 179 ecological sources, 435 ecological corridors, 65 ecological pinch points, 67 barrier points, and resistance surfaces categorized into 5 levels. The ecological corridors within Liaoning Province are distributed in a network configuration. Ecological pinch points are primarily located along key corridors, while ecological barrier points are concentrated primarily in the northwestern part.
- (3)
- Based on the ESP, an ecological protection and restoration pattern featuring “four zones, three corridors and two belts” has been established.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Year | Water Yield (mm) | Soil Conservation (t/ha·a) | Carbon Storage (t/ha) | Habitat Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 119.41 | 44.97 | 11.59 | 0.61 |
| 2015 | 214.73 | 20.78 | 11.61 | 0.60 |
| 2020 | 384.72 | 33.28 | 11.54 | 0.54 |
References
- Costanza, R.; De Groot, R.; Braat, L.; Kubiszewski, I.; Fioramonti, L.; Sutton, P.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M. Twenty years of ecosystem services: How far have we come and how far do we still need to go? Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X. Construction of ecological security pattern in coastal urban areas: A case study in Qingdao, China. Ecol. Ind. 2023, 154, 110754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisos, C.H.; Merow, C.; Pigot, A.L. The projected timing of abrupt ecological disruption from climate change. Nature 2020, 580, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Voogt, J.; Ren, C.; Ng, E. Spatial-temporal variations of surface urban heat island: An application of local climate zone into large Chinese cities. Build. Environ. 2022, 222, 109378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.; Lin, C. Impacts of future climate change and different management scenarios on water-related ecosystem services: A case study in the Jianghuai ecological economic Zone, China. Ecol. Ind. 2021, 127, 107732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPBES. Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services; Brondízio, E.S., Settele, J., Díaz, S., Ngo, H.T., Eds.; IPBES Secretariat: Bonn, Germany, 2019; 1148p. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.; Jiao, L.; Lian, X.; Wang, W. Linking supply-demand balance of ecosystem services to identify ecological security patterns in urban agglomerations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 92, 104497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, F. Research on recognition and protection of ecological security patterns based on circuit theory: A case study of Jinan City. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12414–12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.-L.; Shi, P.-J. Using ecosystem service supply and ecosystem sensitivity toidentify landscape ecology security patterns in the Lanzhou-Xining urban agglomeration, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 2758–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tulder, R.; Rodrigues, S.B.; Mirza, H.; Sexsmith, K. The UN’s Sustainable Development Goals: Can multinational enterprises lead the Decade of Action? J. Int. Bus. Policy 2021, 4, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Deng, W.; Yang, J.; Huang, W.; de Vries, W.T. Construction and optimization of ecological security patterns based on social equity perspective: A case study in Wuhan, China. Ecol. Ind. 2022, 136, 108714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liang, D.; Lu, N. Landscape ecology: Coupling of pattern, process, and scale. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Liu, J.; Jia, J.; Wang, P. Terrestrial ecological restoration in China: Identifying advances and gaps. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Fu, B.; Ma, R.; Yang, Y.; Lü, Y.; Wu, X. Identifying ecological security patterns based on the supply, demand and sensitivity of ecosystem service: A case study in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, C.; Marques, J.C.; Cunha, P.P.; Teixeira, Z. Ecosystem services as a resilience descriptor in habitat risk assessment using the InVEST model. Ecol. Ind. 2020, 115, 106426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Dang, G. Construction of Ecological Security Pattern of Tao River Basin Based on MCR Model and ant Colony Algorithm. Ecol. Environ. 2023, 32, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Shi, X.; He, J.; Yuan, Y.; Qu, L. Identification and optimization strategy of county ecological security pattern: A case study in the Loess Plateau. China Ecol. Ind. 2020, 112, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Li, Y.L.; Jia, H.F. Evaluation of Landscape Ecological Security Pattern in Mentougou District of Yongding River Basin. Arid Land Geogr. 2013, 36, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, M.; Hu, M.; Xia, B. Integrating ecosystem services and landscape connectivity into the optimization of ecological security pattern: A case study of the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 76051–76065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wei, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y. Construction of ecological security pattern based on the importance of ecosystem service functions and ecological sensitivity assessment: A case study in Fengxian County of Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 563–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Liang, J.; Zhao, C. Identification and optimization of ecological security pattern in the arid inland basin based on ordered weighted average and ant colony algorithm: A case study of Shule River basin, NW China. Ecol. Ind. 2023, 154, 110588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Cong, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, M.J.; Wang, L.J.; Gong, J.W.; Ma, S. Integrating the ordered weighted averaging method to establish an ecological security pattern for the jianghuai ecological economic zone in China: Synergistic intraregional development. Ecol. Ind. 2022, 135, 108543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Wu, X.; Wen, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, F.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, J. Ecological security pattern based on XGBoost-MCR model: A case study of the three gorges reservoir region. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 470, 143252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yi, S. An integrated approach to constructing ecological security patterns and identifying ecological restoration and protection areas: A case study of Jingmen, China. Ecol. Ind. 2022, 137, 108723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.R.; Dai, L.M.; Qi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.M.; Zhou, L.; Yu, D.P.; Zhao, F.Q. Constructing ecological security pattern based on ecosystem services: A case study in Liaohe River Basin, Liaoning Province, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 6486–6494. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Peng, J.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Meersmans, J. Linking ecological background and demand to identify ecological security patterns across the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area in China. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2135–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.J. Security patterns and surface model in landscape ecological planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1996, 36, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gong, X.; Han, G.; Zhao, Y. An improved ant colony algorithm for path planning in one scenic area with many spots. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 13260–13269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.T.; Sunter, E.J.; Fauvelle, C.; Bradshaw, J.L.; Ford, B.; Hutchen, J.; Phillipow, N.; Teichman, K.J. Effective corridor width: Linking the spatial ecology of wildlife with land use policy. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2020, 66, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Wang, H.; Yan, X.; Yi, S.; Wang, C.; Lei, C. Integrating CVOR and circuit theory models to construct and reconstruct ecological networks: A case study from the Tacheng-Emin Basin, China. Ecol. Ind. 2024, 165, 112170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, T.; Conrad, Z.; Peters, C.; Ridberg, R.; Tyler, E.P. Regional self-reliance of the Northeast food system. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2015, 30, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, G.; Liu, Y.; Sun, G. Understanding interactions among climate, water, and vegetation with the Budyko framework. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 212, 103451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hickel, K.; Dawes, W.R.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Western, A.W.; Briggs, P.R. A rational function approach for estimating mean annual evapotranspiration. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W02502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmayer, D.; Hobbs, R.; Montague-Drake, R.; Alexandra, J.; Bennett, A.; Burgman, M.; Cae, P.; Calhoun, A.; Cramer, V.; Cullen, P. A checklist for ecological management of landscapes for conservation. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta Aneseyee, A.; Noszczyk, T.; Soromessa, T.; Elias, E. The InVEST habitat quality model associated with land use/cover changes: A qualitative case study of the Winike Watershed in the Omo-Gibe Basin, Southwest Ethiopia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.P.; Xu, J.W.; Feng, X.H.; Guo, M.; Jin, Y.H.; Gao, X.J. Research on the Impact of Land Use Change on Habitats in Northeast China Based on the InVEST Model. Ecol. Sci. 2018, 37, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Li, Z.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Zheng, S.; Yang, S. Assessing current and future soil erosion under changing land use based on InVEST and FLUS models in the Yihe River Basin, North China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 12, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, W.S.; Letcher, R.A.; Jakeman, A.J. A review of erosion and sediment transport models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2003, 18, 761–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Tang, L. Impact of cascading processes of urban expansion and cropland reclamation on the ecosystem of a carbon storage service in Hubei Province, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, S. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use/Cover Change and Terrestrial Ecosystem Carbon Reserve Response in Liaoning Province, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Q.; Liu, G.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.Q.; Miao, Q.F.; Fu, H.C. Evaluation and Multi-scenario Prediction of Ecosystem Services in Liaoning Province from 2000 to 2020. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 4137–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, R.R. Quantifier guided aggregation using OWA operators. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 1996, 11, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, L.-J.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal changes in ecosystem services in the conservation priorities of the southern hill and mountain belt, China. Ecol. Ind. 2021, 122, 107225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Han, Z.L.; Yan, X.L.; Zhong, J.Q. Construction of Ecological Security Patterns Based on Multi-scenario Trade-offs of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of Wafangdian in Dalian City. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, R.; Su, W.C.; Quan, X.Y.; Huang, X.F. Identification of ecological security pattern in FAST Quiet Zone based on Ordered Weighted Averaging and circuit theory. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 9636–9651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.C. Identification and Optimization of Ecological Security Patterns in the Shule River Basin Based on OWA and Ant Colony lgorithm. Master’s Thesis, Northwest Normal University, Lanzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, E.S.; Urban, D.L. A graph-theory framework for evaluating landscape connectivity and conservation planning. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Fu, S.; Hao, Z.; Zhen, Z. Ecological security pattern based on remote sensing ecological index and circuit theory in the Shanxi section of the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Ind. 2024, 166, 112382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Su, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S. Constructing ecological security patterns based on ecosystem services trade-offs and ecological sensitivity: A case study of Shenzhen metropolitan area, China. Ecol. Ind. 2023, 154, 110626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Du, Y.; Meersmans, J.; Qiu, S. Linking ecosystem services and circuit theory to identify ecological security patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Beier, P. Circuit theory predicts gene flow in plant and animal populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19885–19890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Hall, S.A.; Beier, P.; Theobald, D.M. Where to restore ecological connectivity? Detecting barriers and quantifying restoration benefits. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, P.B.; Duffy, E.B.; Baldwin, R.F.; McRae, B.H.; Shah, V.B.; Mohapatra, T.K. GFLOW: Software for modeling circuit theory-based connectivity at any scale. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Peng, J.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, B. Integrating regional and interregional approaches to identify ecological security patterns. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, J. Building ecological security patterns based on ecosystem services value reconstruction in an arid inland basin: A case study in Ganzhou District, NW China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Yang, W.; Zhang, S. An integrated approach to constructing ecological security pattern in an urbanization and agricultural intensification area in northeast China. Land 2023, 12, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Xu, Q.; Yi, J.; Zhong, X. Integrating CVOR-GWLR-Circuit model into construction of ecological security pattern in Yunnan Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 81520–81545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Huan, C.; Yang, F. Spatiotemporal dynamics of ecological vulnerability and its influencing factors in shenyang city of China: Based on SRP model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.W.; Jia, T.C. Construction and Optimization of the Ecological Security Pattern in Sanjiangyuan National Park Based on Ecological Sensitivity and Landscape Connectivity. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2023, 32, 1724–1735. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yin, S.H.; Wei, X. Construction of ecological security pattern: Concept, framework and prospect. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Deng, X.P.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.R.; He, D.J.; You, W.B. Identification and Construction of County-level Ecological Security Patterns Integrating Ecological Spaces: A Case Study of Wuyishan City. Chin. J. Ecol. 2023, 42, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, H.; Yu, H.; Feng, X.; Fan, M. Construction of landscape ecological network based on MCR risk assessment Model: A case study of Liaoning Province, China. Ecol. Ind. 2024, 166, 112549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewski, J. Integrating multicriteria analysis and geographic information systems: The ordered weighted averaging (OWA) approach. Int. J. Environ. Technol. Manag. 2006, 6, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fang, C. Evolution process and obstacle factors of ecological security in western China, a case study of Qinghai province. Ecol. Ind. 2020, 117, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Cao, A. Analysis of the heterogeneity of landscape risk evolution and driving factors based on a combined GeoDa and Geodetector model. Ecol. Ind. 2022, 144, 109568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

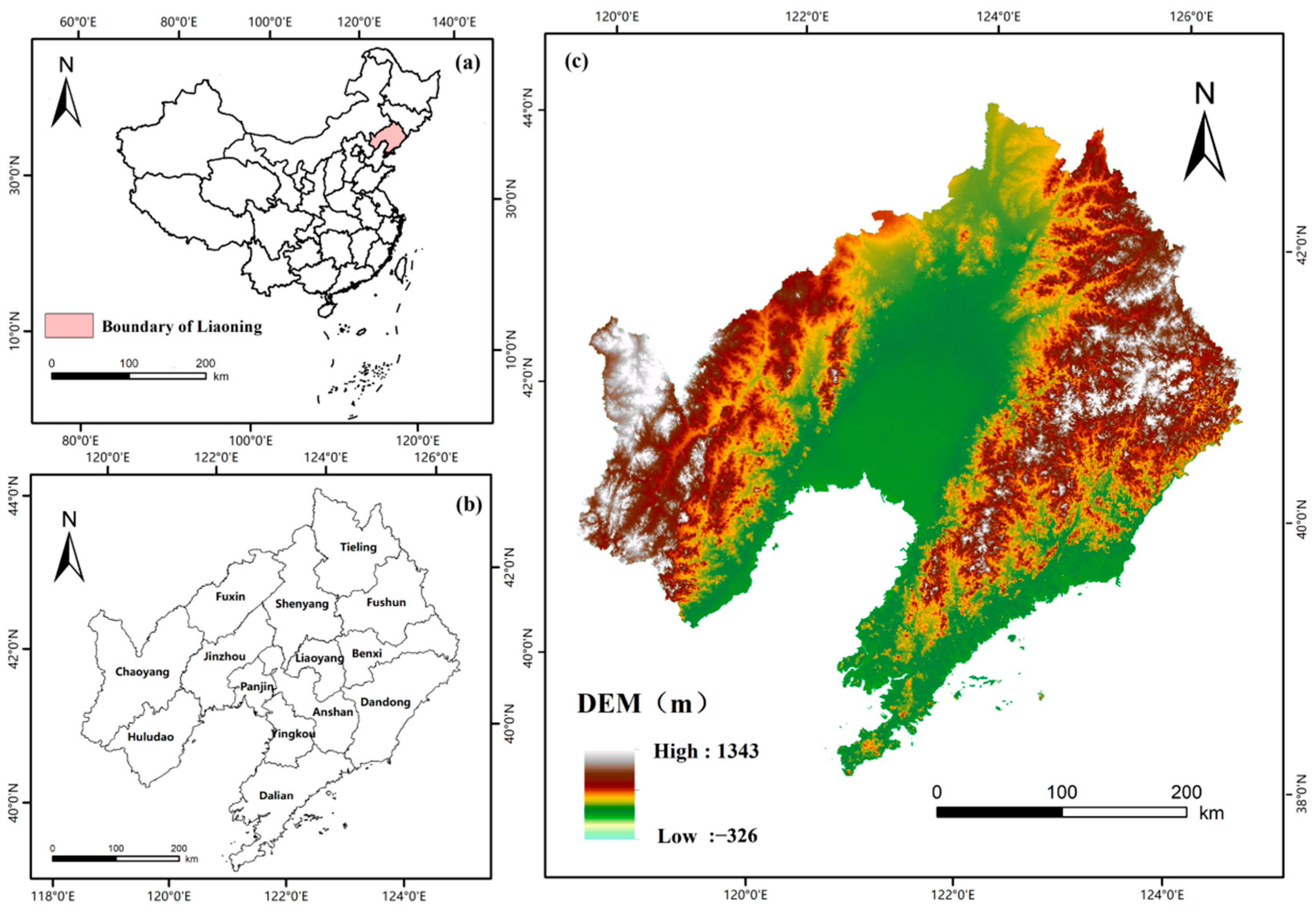
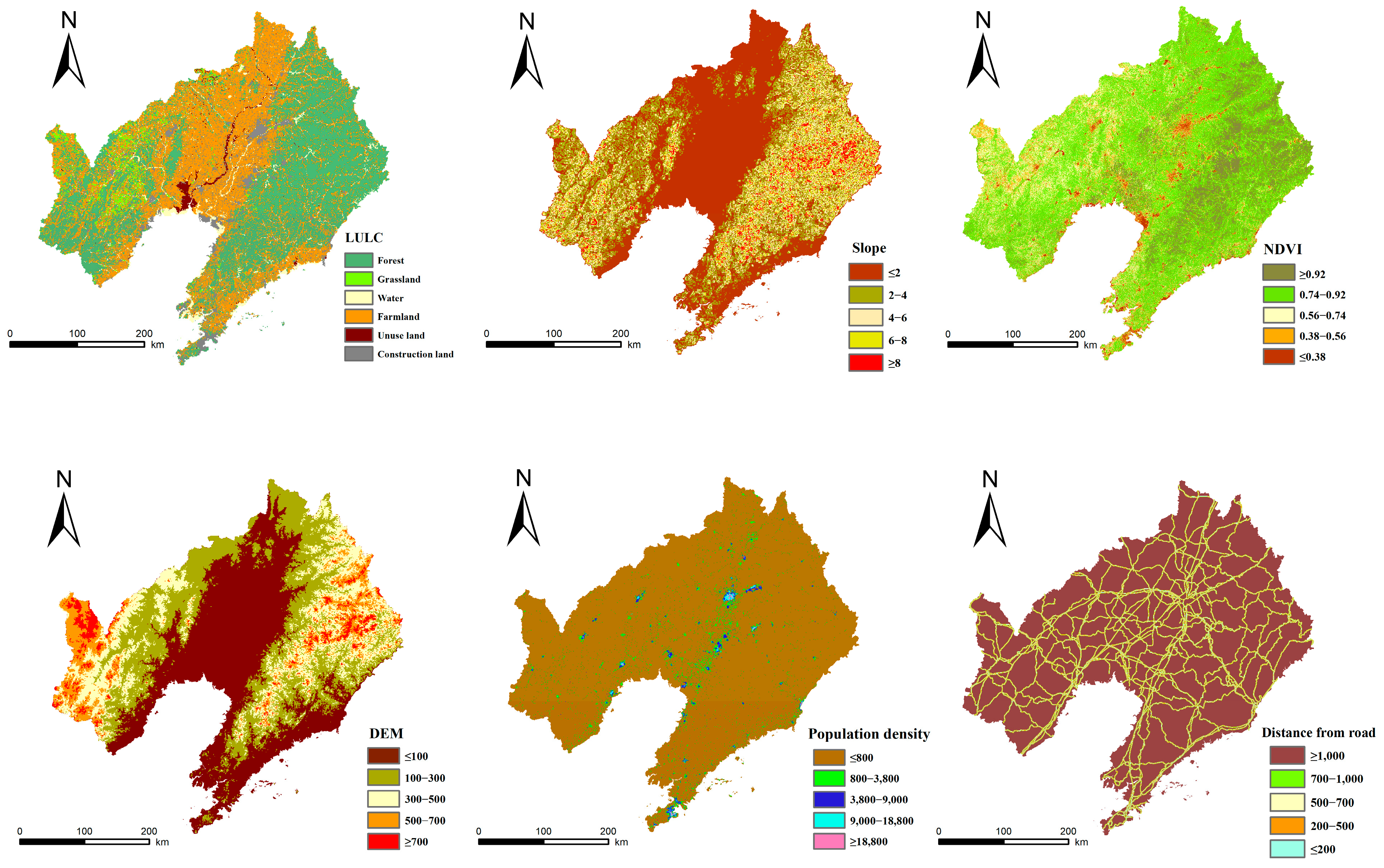


| Data | Resolution | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Land use data | 30 m | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 10 January 2025) |
| DEM | 30 m | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/, accessed on 10 January 2025) |
| Meteorological data | 1000 m | National Earth System Science Data Center (http://www.geodata.cn/, accessed on 10 January 2025) |
| Soil data | 1000 m | World Soil Database (http://www.fao.org, accessed on 10 January 2025) |
| Soil erosion factor | 300 m | Geographic Data Sharing Infrastructure (www.gis5g.com, accessed on 10 January 2025) |
| Population data | 1000 m | World Pop (https://www.worldpop.org/, accessed on 10 January 2025) |
| Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | 1000 m | MOD17A3H Data Product (https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/, accessed on 10 January 2025) |
| River data | shapefile | Open Street Map (https://www.openhistoricalmap.org/, accessed on 10 January 2025) |
| Type | Factor | Classification | Resistance Coefficient | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nature factors | Land use type | Forest | 1 | 0.2893 |
| Grassland | 3 | |||
| Water | 5 | |||
| Farmland | 7 | |||
| Unused land | 9 | |||
| Construction land | 10 | |||
| DEM (m) | ≤100 | 1 | 0.1812 | |
| 100–300 | 3 | |||
| 300–500 | 5 | |||
| 500–700 | 7 | |||
| ≥700 | 10 | |||
| NDVI | ≤0.38 | 10 | 0.1532 | |
| 0.38–0.56 | 7 | |||
| 0.56–0.74 | 5 | |||
| 0.74–0.92 | 3 | |||
| ≥0.92 | 1 | |||
| Slope (°) | ≤2 | 1 | 0.1263 | |
| 2–4 | 3 | |||
| 4–6 | 5 | |||
| 6–8 | 7 | |||
| ≥8 | 10 | |||
| Human factors | Population density (person/km2) | ≤800 | 1 | 0.1667 |
| 800–3800 | 3 | |||
| 3800–9000 | 5 | |||
| 9000–18,800 | 7 | |||
| ≥18,800 | 9 | |||
| Distance from road (m) | ≤200 | 1 | 0.0833 | |
| 200–500 | 3 | |||
| 500–700 | 5 | |||
| 700–1000 | 7 | |||
| ≥1000 | 9 |
| Scenarios | Risk | 1 | 2 | 3 | Trade-Off | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.001 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.0018 |
| 2 | 0.1 | 0.871 | 0.062 | 0.039 | 0.028 | 0.1721 |
| 3 | 0.5 | 0.500 | 0.207 | 0.159 | 0.134 | 0.6612 |
| 4 | 1 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 1.0000 |
| 5 | 2 | 0.063 | 0.188 | 0.313 | 0.438 | 0.6773 |
| 6 | 10 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.055 | 0.944 | 0.0736 |
| 7 | 1000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.0000 |
| Scenario | Protection Efficiency | Average Protection Efficiency | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Conservation | Water Yield | Habitat Quality | Carbon Storage | ||
| 1 | 0.31 | 1.00 | 1.01 | 1.12 | 0.86 |
| 2 | 0.35 | 0.99 | 1.09 | 1.32 | 0.94 |
| 3 | 0.39 | 0.89 | 1.14 | 1.54 | 0.99 |
| 4 | 0.40 | 0.85 | 1.18 | 1.56 | 0.99 |
| 5 | 0.45 | 0.90 | 1.33 | 1.73 | 1.10 |
| 6 | 0.49 | 1.16 | 1.04 | 1.63 | 1.08 |
| 7 | 0.51 | 1.24 | 1.12 | 1.35 | 1.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, H.; Bian, Z. Ecological Security Patterns Based on Ecosystem Service Assessment and Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Liaoning Province, China. Land 2025, 14, 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061257
Wang B, Zhang Y, Gu H, Bian Z. Ecological Security Patterns Based on Ecosystem Service Assessment and Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Liaoning Province, China. Land. 2025; 14(6):1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061257
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bingyi, Yufei Zhang, Hanlong Gu, and Zhenxing Bian. 2025. "Ecological Security Patterns Based on Ecosystem Service Assessment and Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Liaoning Province, China" Land 14, no. 6: 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061257
APA StyleWang, B., Zhang, Y., Gu, H., & Bian, Z. (2025). Ecological Security Patterns Based on Ecosystem Service Assessment and Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Liaoning Province, China. Land, 14(6), 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061257







