Spatiotemporal Variations of Cropland Quality and Morphology Under the Requisition–Compensation Balance Policy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
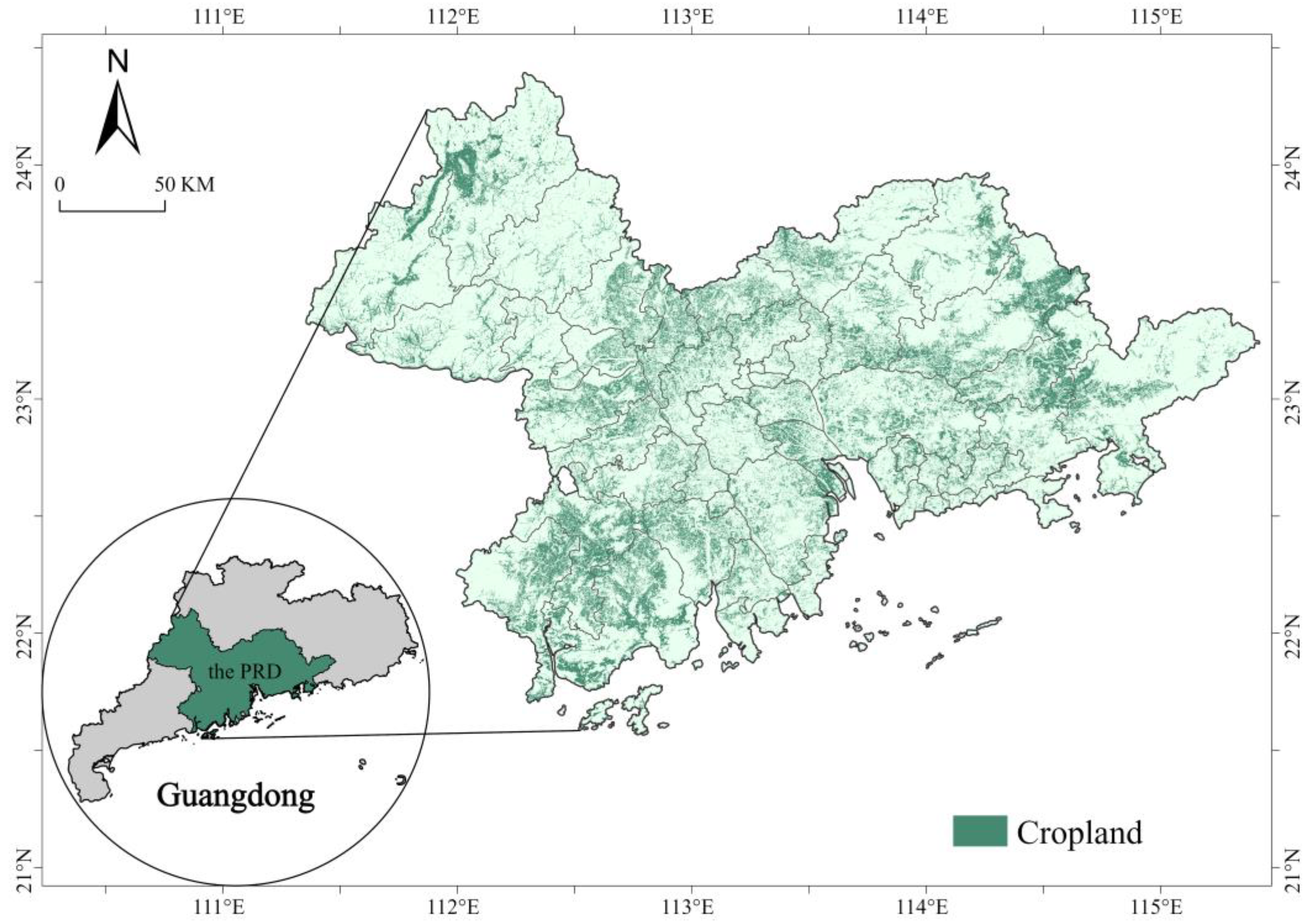
2.1. Study Area
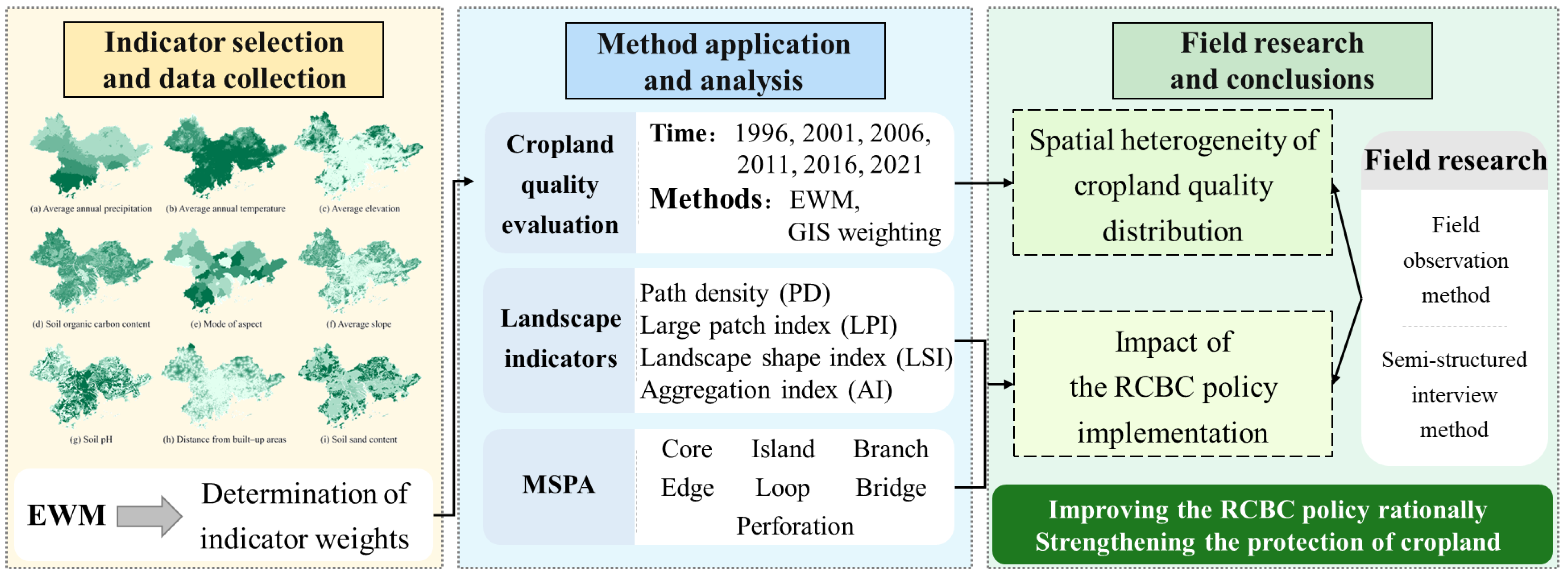
2.2. Research Framework
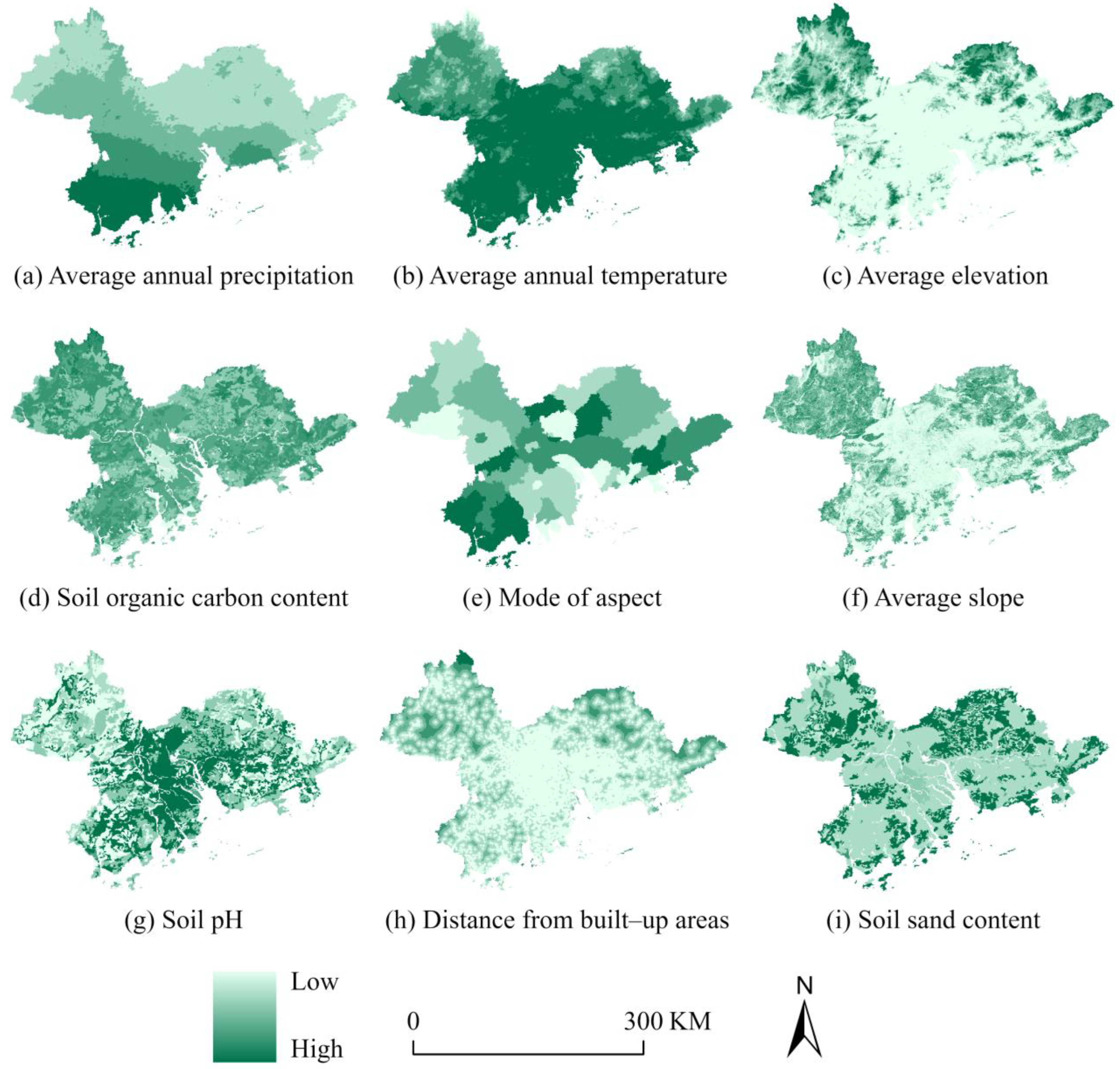
2.3. Data Sources and Processing
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Landscape Indicators
2.4.2. MSPA
2.4.3. Field Research
3. Results
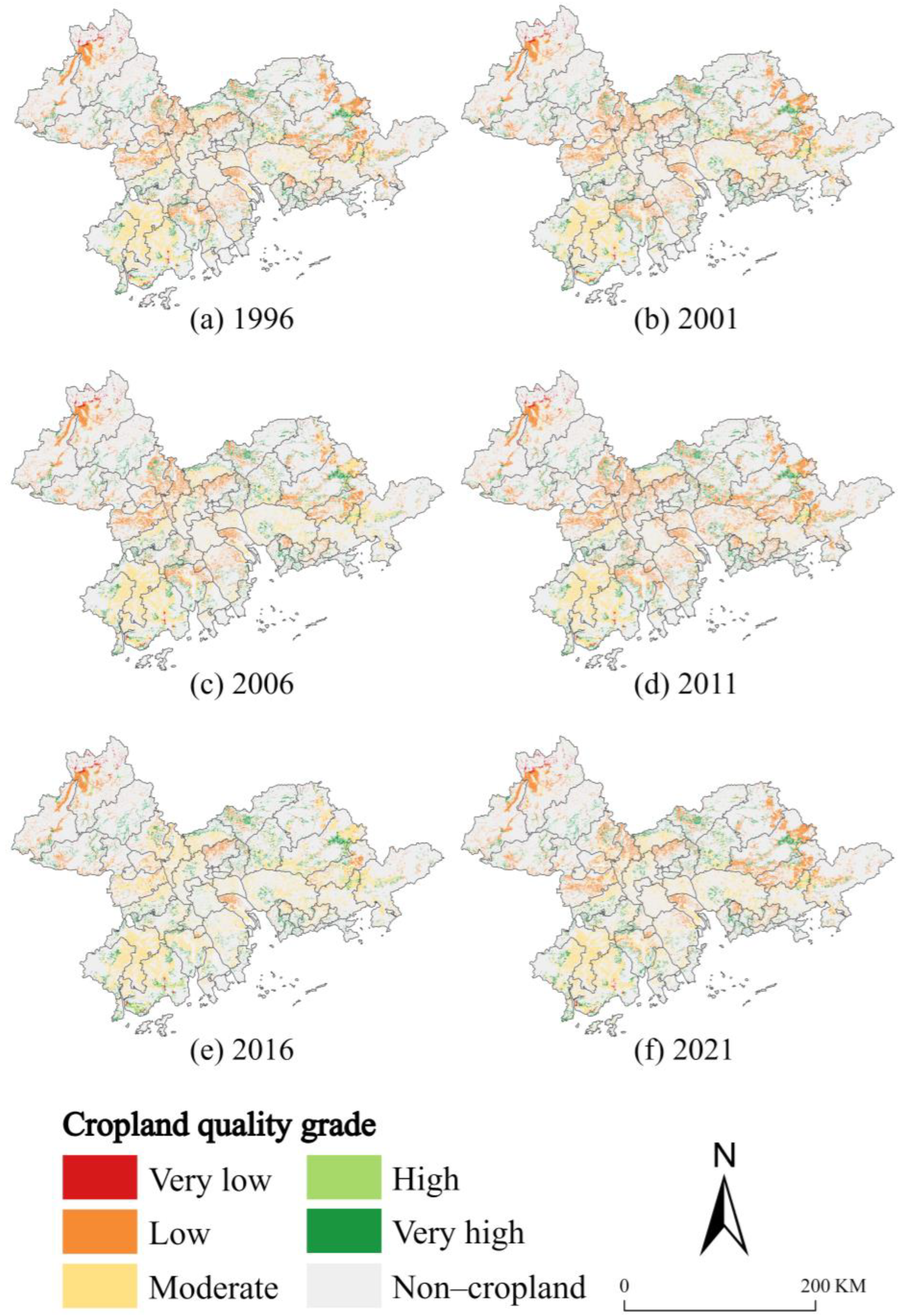
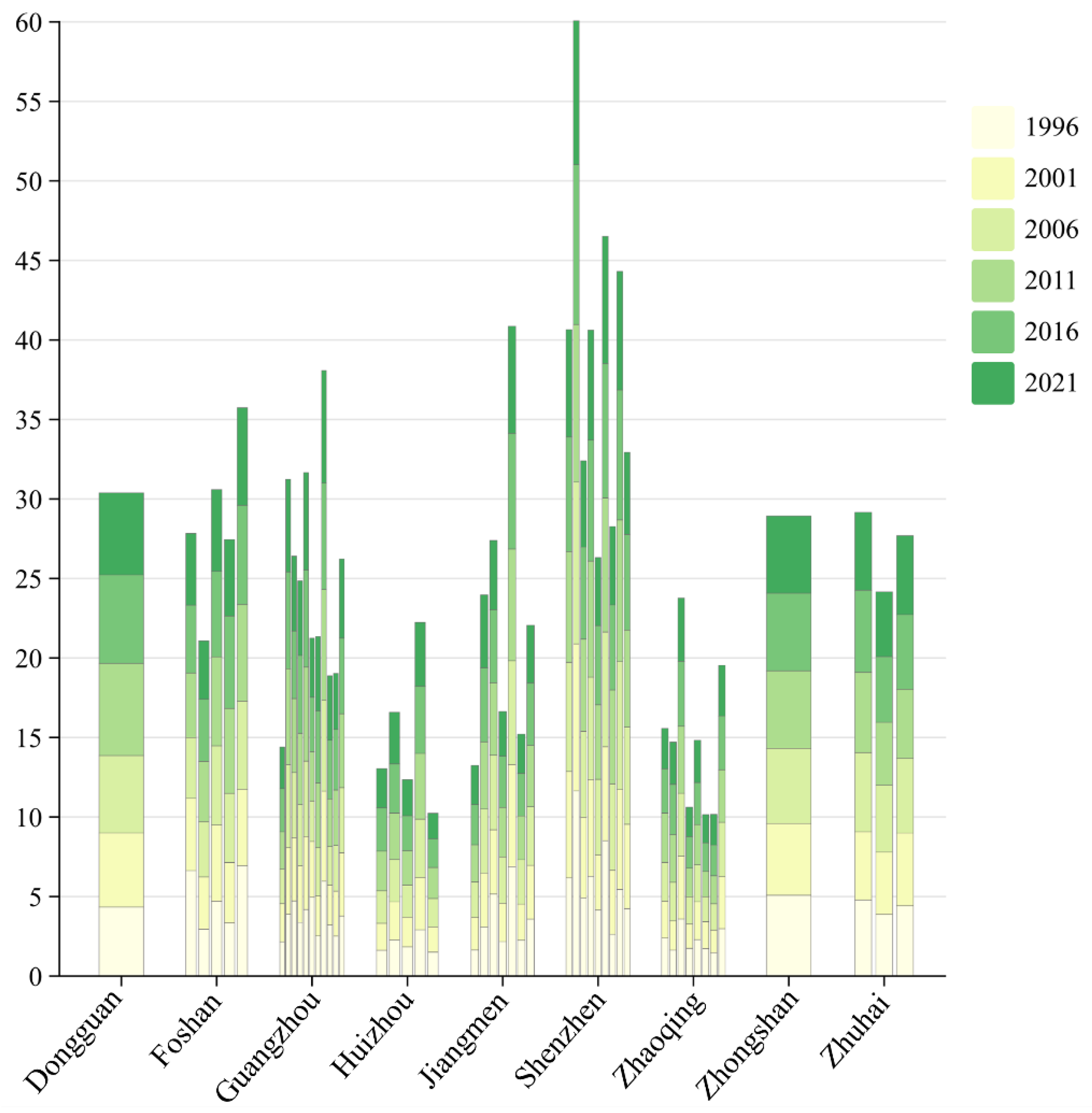
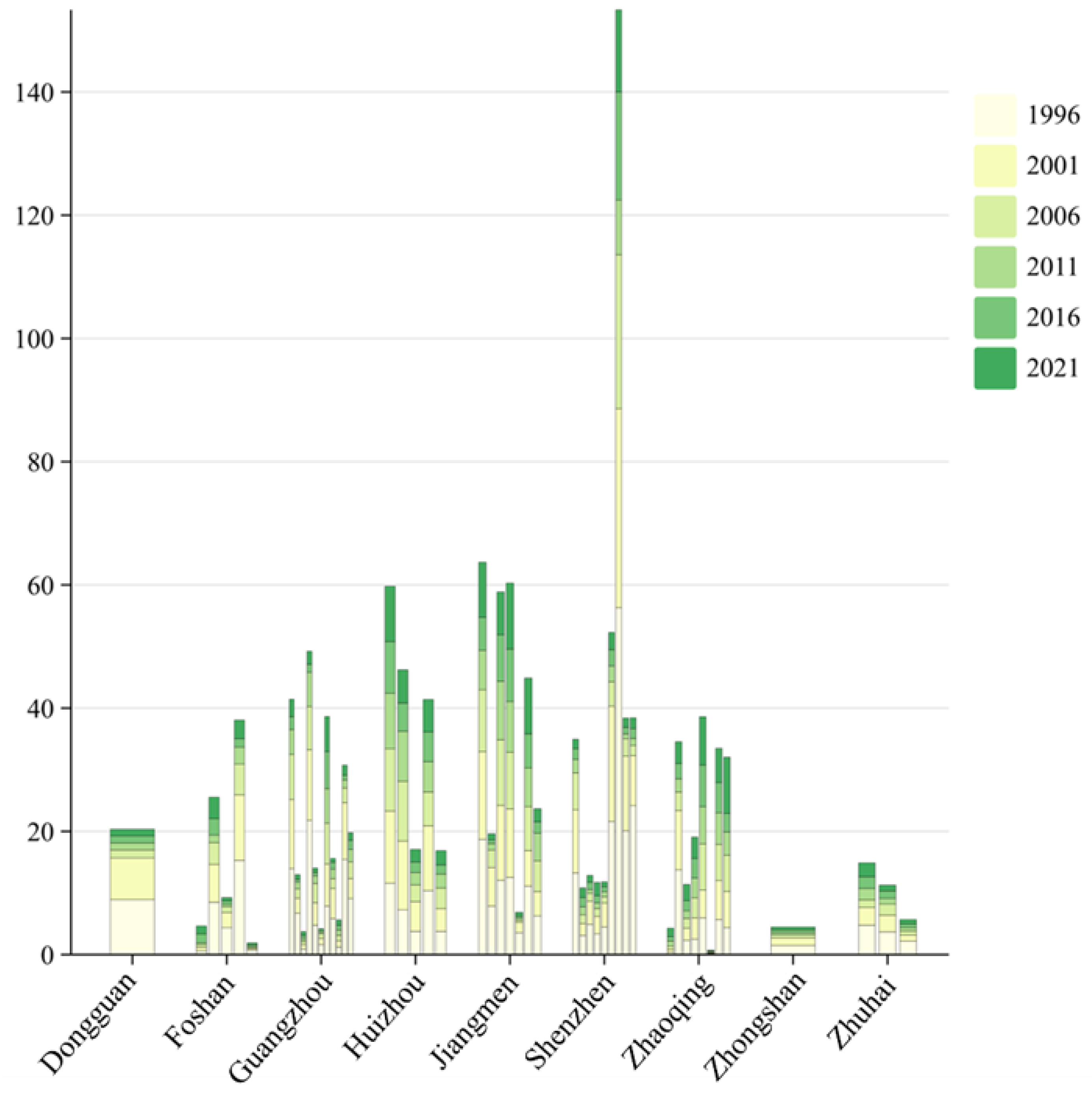
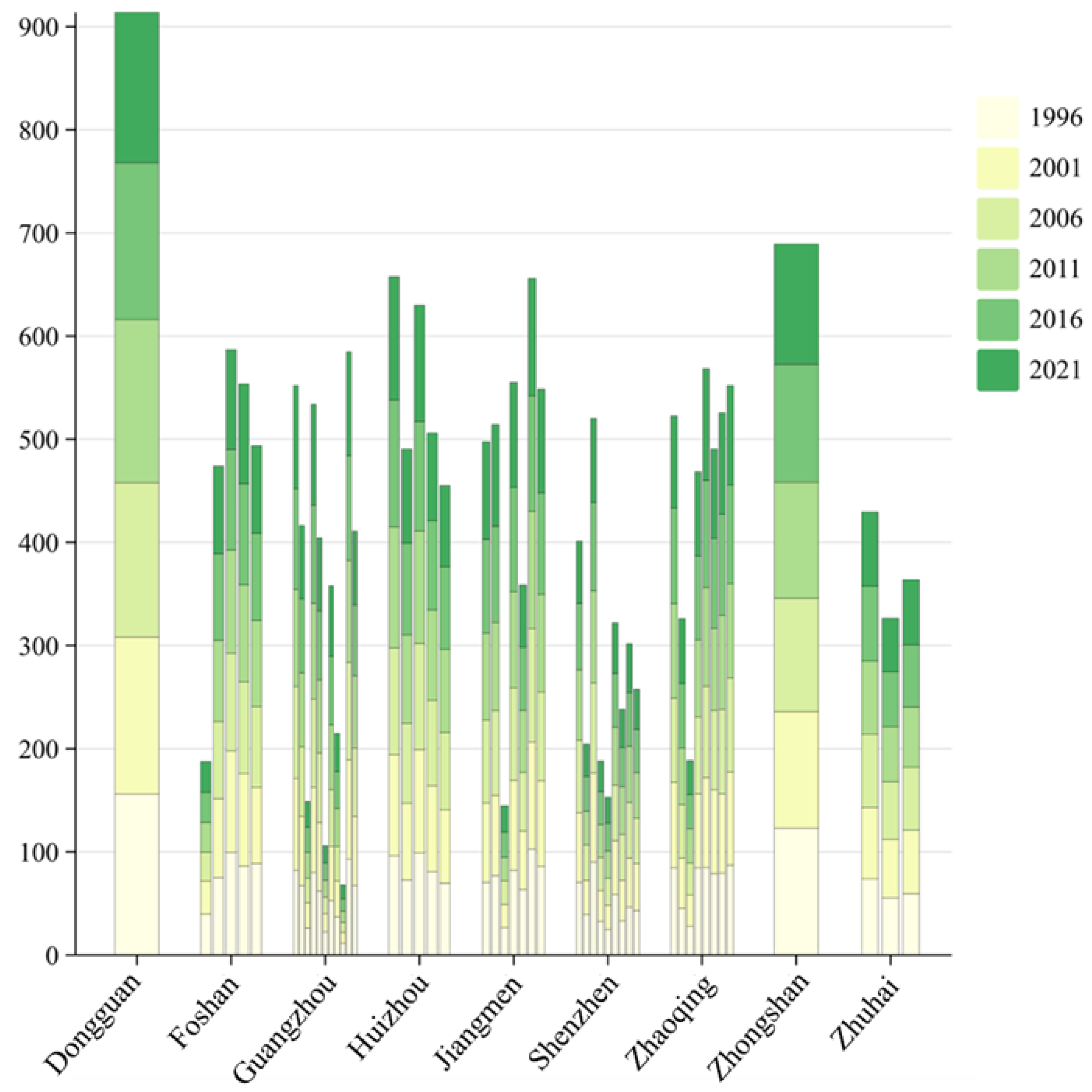
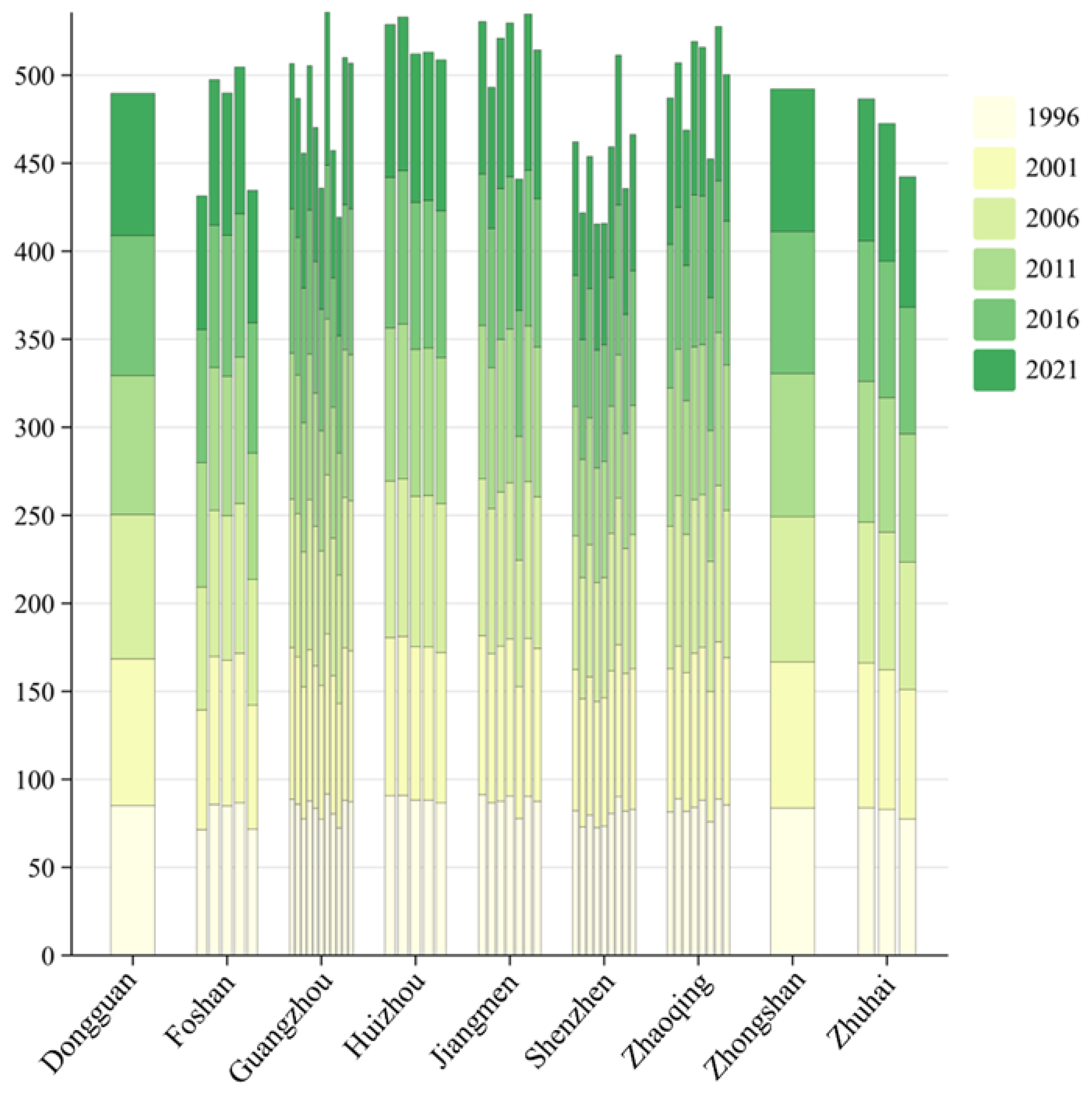
3.1. Changes in Cropland Quality
3.2. Changes in the Landscape Pattern of Cropland
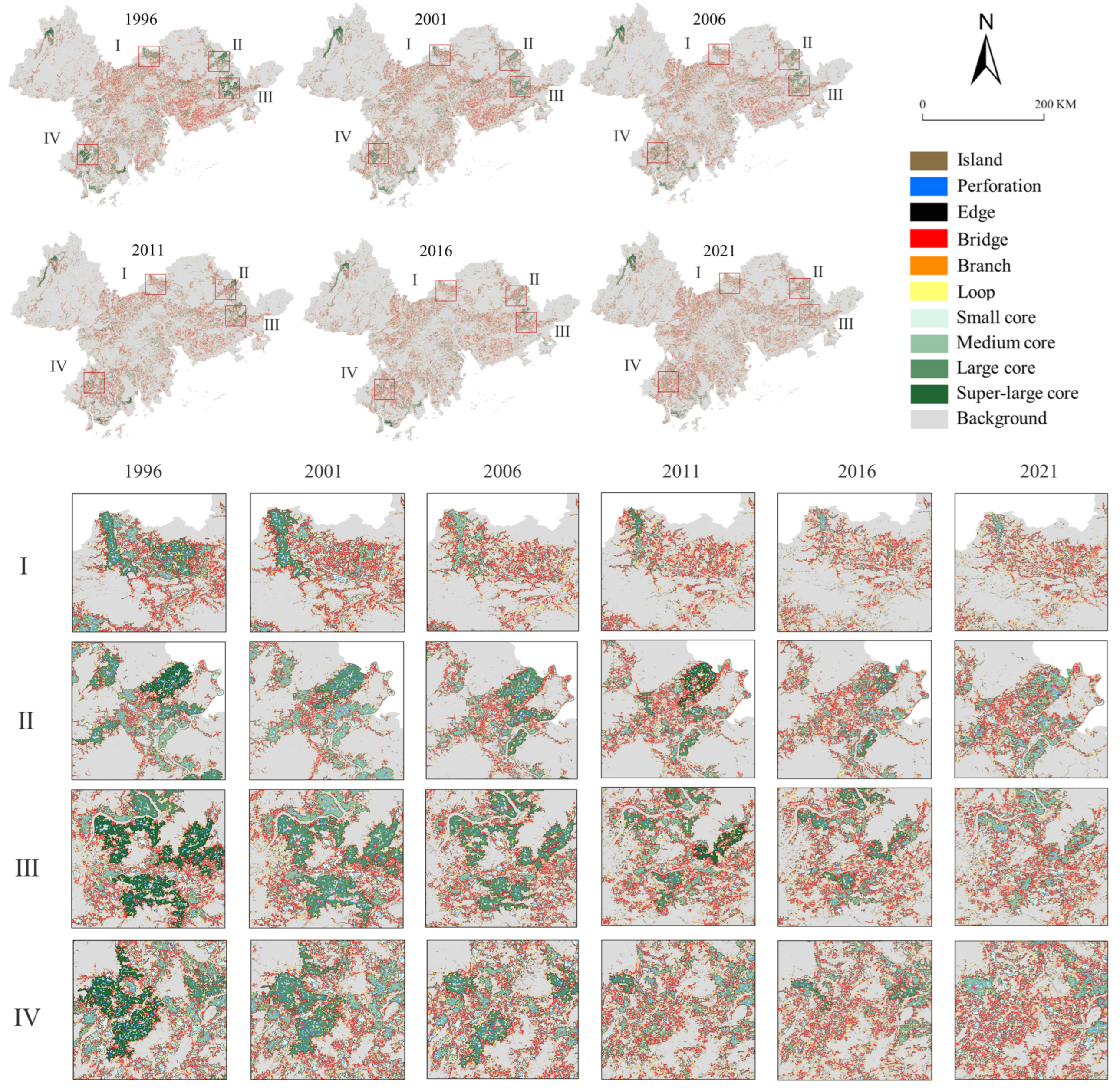
3.3. Changes in the MSPA of Cropland
4. Discussion
4.1. Verification of Results Through Field Research
4.2. Recommendations for the RCBC Policy
4.3. Key Contributions of This Study
4.4. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akbari, M.; Foroudi, P.; Shahmoradi, M.; Padash, H.; Parizi, Z.S.; Khosravani, A.; Ataei, P.; Cuomo, M.T. The Evolution of Food Security: Where Are We Now, Where Should We Go Next? Sustainability 2022, 14, 3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaf, L.; Buonocore, E.; Dumontet, S.; Capone, R.; Franzese, P.P. Applying network analysis to explore the global scientific literature on food security. Ecol. Inform. 2020, 56, 101062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X.; Yin, M.M. Change of urban and rural construction land and driving factors of arable land occupation. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Lin, J. Projecting Future Land Use Evolution and Its Effect on Spatiotemporal Patterns of Habitat Quality in China. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Xin, L.J. Assessment of the Efficiency of Cultivated Land Occupied by Urban and Rural Construction Land in China from 1990 to 2020. Land 2022, 11, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.W.; Meng, F.H.; Prishchepov, A.V. How is urbanization shaping agricultural land-use? Unraveling the nexus between farmland abandonment and urbanization in China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 214, 104170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; Wang, D.Y.; Liu, S.H.; Zhu, Y.L.; Yan, Z.R. Reclamation of Cultivated Land Reserves in Northeast China: Indigenous Ecological Insecurity Underlying National Food Security. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y. The Gains and Losses of Cultivated Land Requisition–Compensation Balance: Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Trade-Offs and Synergies in Ecosystem Services Using Hubei Province as a Case Study. Land 2024, 13, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Lijie, P.; Pengfei, T.; Rongjuan, L.; Sihua, H.; Fei, X.; Taiyang, Z. Gains and losses of farmland associated with farmland protection policy and urbanization in China: An integrated perspective based on goal orientation. Land Use Policy 2023, 129, 106643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Pijanowski, B.C. The effects of China’s cultivated land balance program on potential land productivity at a national scale. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 46, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Anna, H.; Zhang, L.Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, J.G.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Spatial and Temporal Changes of Arable Land Driven by Urbanization and Ecological Restoration in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.H.; Liu, J.Y.; Tian, H.Q.; Shi, H.; Dong, J.W.; Song, C.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Du, G.M.; Hou, Y.L.; Lu, D.S.; et al. Cropland redistribution to marginal lands undermines environmental sustainability. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwab091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.D.; Zhang, Z.C.; Ma, L.G.; Gu, Q.; Wang, K.; Xu, Z.H. Assessment on the Impact of Arable Land Protection Policies in a Rapidly Developing Region. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, Z.; Lin, J.; Wu, D. Investigating the Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of Non-Grain Production of Farmland in South China Based on MaxEnt Modeling and Multisource Earth Observation Data. Foods 2024, 13, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Jiang, C.; Yao, R.B. Cropland compensation in mountainous areas in China aggravates non-grain production: Evidence from Fujian Province. Land Use Policy 2024, 138, 107026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.L.; Liang, Y.F.; Hu, X.D.; Bai, M.D.; Wen, Q. A multidimensional assessment and analysis of farmland fragmentation in the southeast coastal area of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 4021–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, S. National-scale connectivity analysis and construction of forest networks based on graph theory: A case study of China. Ecological Engineering 2025, 216, 107639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.X.; Ye, X.Y.; Li, J.F.; Fan, X.; Liu, Q.S.; Dong, W.C. Analyzing requisition-compensation balance of farmland policy in China through telecoupling: A case study in the middle reaches of Yangtze River Urban Agglomerations. Land Use Policy 2019, 83, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.Z.; Ye, G.B. Differences of Soil Fertility in Farmland Occupation and Supplement Areas in the Taihu Lake Watershed during 1985–2010. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 5598–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.W.; Li, S.M.; Ke, X.L.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, B.B. The impacts of cropland balance policy on habitat quality in China: A multiscale administrative perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strek, Z.; Len, P.; Wójcik-Len, J.; Postek, P.; Mika, M.; Dawid, L. A Proposed Land Exchange Algorithm for Eliminating the External Plot Patchwork. Land 2021, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.Y.; Jin, X.B.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.K. Impact of cultivated land fragmentation on spatial heterogeneity of agricultural agglomeration in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 1571–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, J.; Ertunç, E.; Muchová, Z.; Tomić, H. Impact of selected land fragmentation parameters and spatial rural settlement patterns on the competitiveness of agriculture: Examples of selected European and Asian countries. Habitat Int. 2023, 140, 102911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.T.; Zhu, L.J.; Jia, W.W. Contiguous planting on fragmented cultivated land and reduction of chemical pesticides and chemical fertilizers: Evidence from rice farmer in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 374, 124062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.L.; Pan, S.P.; Chen, W.X.; Li, J.F.; Zhou, T. Cultivated Land Fragmentation and Its Influencing Factors Detection: A Case Study in Huaihe River Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhou, W.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Xu, J. Spatial-temporal characteristics of cultivated land use eco-efficiency under carbon constraints and its relationship with landscape pattern dynamics. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Qiu, S.X.; Lin, Z.C.; Chen, Z.X.; Yang, Y.C.; Lin, J.Y.; Li, S.Y. Assessing the influence of green space morphological spatial pattern on urban waterlogging: A case study of a highly-urbanized city. Environ. Res. 2025, 266, 120561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickayin, S.S.; Salvati, L.; Coluzzi, R.; Lanfredi, M.; Halbac-Cotoara-Zamfir, R.; Salvia, R.; Quaranta, G.; Alhuseen, A.; Gaburova, L. What Happens in the City When Long-Term Urban Expansion and (Un)Sustainable Fringe Development Occur: The Case Study of Rome. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhang, J. Combining MSPA-MCR Model to Evaluate the Ecological Network in Wuhan, China. Land 2022, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.R.; Qiu, L.S.; Yang, D.X.; Jiang, M.X. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Correlation Analysis of Urban Land Use Patterns and Air Quality in Pearl River Delta, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 698383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.T.; Li, M.; Xia, B.C. Spatio-temporal dynamics of ecological security pattern of the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration based on LUCC simulation. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 102557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.Y.; Sun, K.Y.; Deng, B.Y.; Cheng, N.; Cao, Y. Quantification and Driving Factors of Cultivated Land Fragmentation in Rapidly Urbanizing Area: A Case Study in Guangdong Province. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.J.; Ren, S.Y.; Song, C.Q.; Cheng, C.X.; Shen, S.; Yang, J.Y.; Zhu, D.H. Spatial patterns of county-level arable land productive-capacity and its coordination with land-use intensity in mainland China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 326, 107757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Hu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, S.; Wang, W.; Wu, J. Multifunctional trade-off/synergy relationship of cultivated land in Guangdong: A long time series analysis from 2010 to 2030. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.P.; Li, F.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.L.; Chen, X.C.; Hu, D. Assessment of Land-Use/Cover Changes and Its Ecological Effect in Rapidly Urbanized Areas-Taking Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration as a Case. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Jin, X. Spatio-temporal characteristics and driving factors of cultivated land change in various agricultural regions of China: A detailed analysis based on county-level data. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Z.; Chen, H.; Lian, K.; Yu, Z.N. Comprehensive Evaluation of Cultivated Land Quality at County Scale: A Case Study of Shengzhou, Zhejiang Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, Q. Identifying spatial and temporal dynamics and driving factors of cultivated land fragmentation in Shaanxi province. Agric. Syst. 2024, 217, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, R.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Niu, B.; Li, J. Study on cultivated land quality evaluation from the perspective of farmland ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarğın, B.; Alaboz, P.; Karaca, S.; Dengiz, O. Pythagorean fuzzy SWARA weighting technique for soil quality modeling of cultivated land in semi-arid terrestrial ecosystems. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 227, 109466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Wang, X.H.; Smith, P.; Fan, J.L.; Lu, Y.L.; Emmett, B.; Li, R.; Dorling, S.; Chen, H.Q.; Liu, S.G.; et al. Soil quality both increases crop production and improves resilience to climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2022, 12, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tian, D.; Yan, F. Effectiveness of Entropy Weight Method in Decision-Making. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 3564835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, B.; Weng, Q.; Bai, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, L.; Xu, B. A 30 m annual cropland dataset of China from 1986 to 2021. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 2297–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouzhang, P. 1-km Monthly Mean Temperature Dataset for China (1901–2023); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouzhang, P. High-spatial-resolution monthly precipitation dataset over China during 1901–2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, N.; Mishra, V.N. Urban Growth Analysis Using Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Image and Landscape Metrics for Smart City Planning of Lucknow District, India. Eng. Proc. 2024, 82, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Yang, X. Landscape pattern indices for evaluating urban spatial morphology—A case study of Chinese cities. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zuo, Q.; Yi, S.Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Su, X.P.; Xu, T.; Jiang, Y. The Link between Landscape Characteristics and Soil Losses Rates over a Range of Spatiotemporal Scales: Hubei Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, M.; Hu, M.; Fan, C.; Wang, T.; Xia, B. Promoting landscape connectivity of highly urbanized area: An ecological network approach. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wei, K.; Guan, Z. Exploring the connection between morphological characteristic of built-up areas and surface heat islands based on MSPA. Urban Clim. 2024, 53, 101764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, X. The role of land use change in affecting ecosystem services and the ecological security pattern of the Hexi Regions, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Wang, Z.P.; Li, X.X.; Zhou, Y.J. Evaluation of the efficiency and drivers of complemented cropland in Southwest China over the past 30 years from the perspective of cropland abandonment. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Shangguan, S.H.; Li, W.Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.J.; Han, R.; Xu, J.W. Spatial-temporal distribution of farmland occupation and compensation and its impact on ecological service value in China from 1990 to 2021. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tan, Y.; Xiao, W.; Li, G.; Meng, F.; He, T.; Li, X. Urbanization in China drives farmland uphill under the constraint of the requisition–compensation balance. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data | Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 30 m | CACD [43] |
| Average elevation | NASA SRTM v3.0 | |
| Average slope | ||
| Mode of aspect | ||
| Distance from built-up areas | CLCD [44] | |
| Soil organic carbon content | 250 m | soilgrids.org |
| Soil pH | ||
| Soil sand content | ||
| Average annual precipitation | 1 km | National Tibetan Plateau Data [45,46] |
| Average annual temperature |
| Data | Weight |
|---|---|
| Average annual precipitation | 0.106797397 |
| Average annual temperature | 0.138212732 |
| Average elevation | 0.028354329 |
| Soil organic carbon content | 0.157631204 |
| Mode of aspect | 0.11605875 |
| Average slope | 0.060333843 |
| Soil pH | 0.149299092 |
| Distance from built-up areas | 0.120892324 |
| Soil sand content | 0.122420329 |
| Indicator | Definition | Mathematical Expression |
|---|---|---|
| PD | It measures the number of patches per unit area. | |
| LPI | It measures the percentage of the landscape area occupied by the largest patch. | |
| LSI | It quantifies the complexity of patch shapes, standardized by landscape area. | |
| AI | It measures the degree of spatial clustering of patches of the same type. | (Pij: probability that patch, i is adjacent to patch j) |
| Element | Definition |
|---|---|
| Core | Interior part excluding perimeter |
| Island | Disjoint and too small to become the core |
| Perforation | Internal perimeter |
| Edge | External perimeter |
| Loop | Connected to the same core |
| Bridge | Connected to different cores |
| Branch | Connected at one end to the edge, perforation, bridge, or loop |
| Interviewee Categories | Interview Focus |
|---|---|
| Farmers | Policy awareness, current farming status, development expectations |
| Retired farmers | Historical review, policy changes, and social impacts |
| Village officials | Policy implementation and impacts, resource management, responses to challenges |
| Agricultural technicians | Professional assessment, technical applications, policy recommendations |
| 1996 | 2001 | 2006 | 2011 | 2016 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core | 4289.19 | 726.61 | 2885.28 | 2198.25 | 2020.67 | 2425.41 |
| Change | −83% | 297% | −24% | −8% | 20% | |
| Island | 1180.86 | 218.91 | 1314.90 | 1478.28 | 1606.10 | 1571.60 |
| Change | −81% | 501% | 12% | 9% | −2% | |
| Perforation | 250.63 | 63.71 | 141.54 | 78.43 | 71.61 | 92.98 |
| Change | −75% | 122% | −45% | −9% | 30% | |
| Edge | 2594.14 | 382.41 | 2063.41 | 1826.75 | 1858.22 | 2146.32 |
| Change | −85% | 440% | −11% | 2% | 16% | |
| Loop | 625.99 | 108.31 | 473.44 | 407.30 | 348.89 | 385.84 |
| Change | −83% | 337% | −14% | −14% | 11% | |
| Bridge | 2737.23 | 360.70 | 1949.08 | 1815.77 | 1742.76 | 2010.96 |
| Change | −87% | 440% | −7% | −4% | 15% | |
| Branch | 1359.81 | 200.61 | 1192.74 | 1179.28 | 1287.15 | 1437.91 |
| Change | −85% | 495% | −1% | 9% | 12% |
| 1996 | 2001 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Area | Area (%) | Number | Area | Area (%) | |
| Small core | 56,700 | 1991.32 | 46.43 | 53,141 | 1906.18 | 48.10 |
| Medium core | 431 | 1146.60 | 26.73 | 380 | 980.39 | 24.74 |
| Large core | 43 | 565.15 | 13.18 | 33 | 409.32 | 10.33 |
| Super-large core | 13 | 586.12 | 13.67 | 13 | 666.97 | 16.83 |
| 2006 | 2011 | |||||
| Number | Area | Area (%) | Number | Area | Area (%) | |
| Small core | 47,331 | 1576.47 | 54.64 | 45,605 | 1405.38 | 63.93 |
| Medium core | 278 | 686.49 | 23.79 | 226 | 578.49 | 26.32 |
| Large core | 27 | 329.52 | 11.42 | 10 | 143.71 | 6.54 |
| Super-large core | 6 | 292.80 | 10.15 | 2 | 70.67 | 3.22 |
| 2016 | 2021 | |||||
| Number | Area | Area (%) | Number | Area | Area (%) | |
| Small core | 47,937 | 1365.17 | 67.56 | 54,638 | 1544.25 | 63.67 |
| Medium core | 170 | 412.23 | 20.40 | 205 | 499.51 | 20.60 |
| Large core | 14 | 171.96 | 8.51 | 15 | 191.09 | 7.88 |
| Super-large core | 2 | 71.31 | 3.53 | 3 | 190.56 | 7.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Liufu, Y.; Cao, L.; Lin, J. Spatiotemporal Variations of Cropland Quality and Morphology Under the Requisition–Compensation Balance Policy. Land 2025, 14, 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061235
Lin Z, Chen Z, Zhang F, Li J, Liufu Y, Cao L, Lin J. Spatiotemporal Variations of Cropland Quality and Morphology Under the Requisition–Compensation Balance Policy. Land. 2025; 14(6):1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061235
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Zhuochun, Zejia Chen, Fengyu Zhang, Jiapei Li, Yifei Liufu, Lisiren Cao, and Jinyao Lin. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Variations of Cropland Quality and Morphology Under the Requisition–Compensation Balance Policy" Land 14, no. 6: 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061235
APA StyleLin, Z., Chen, Z., Zhang, F., Li, J., Liufu, Y., Cao, L., & Lin, J. (2025). Spatiotemporal Variations of Cropland Quality and Morphology Under the Requisition–Compensation Balance Policy. Land, 14(6), 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061235







