Biocultural Diversity at Risk Amidst and Beyond Overtourism: The Decline in Wild Green Foraging in Corfu over the Past 50 Years
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
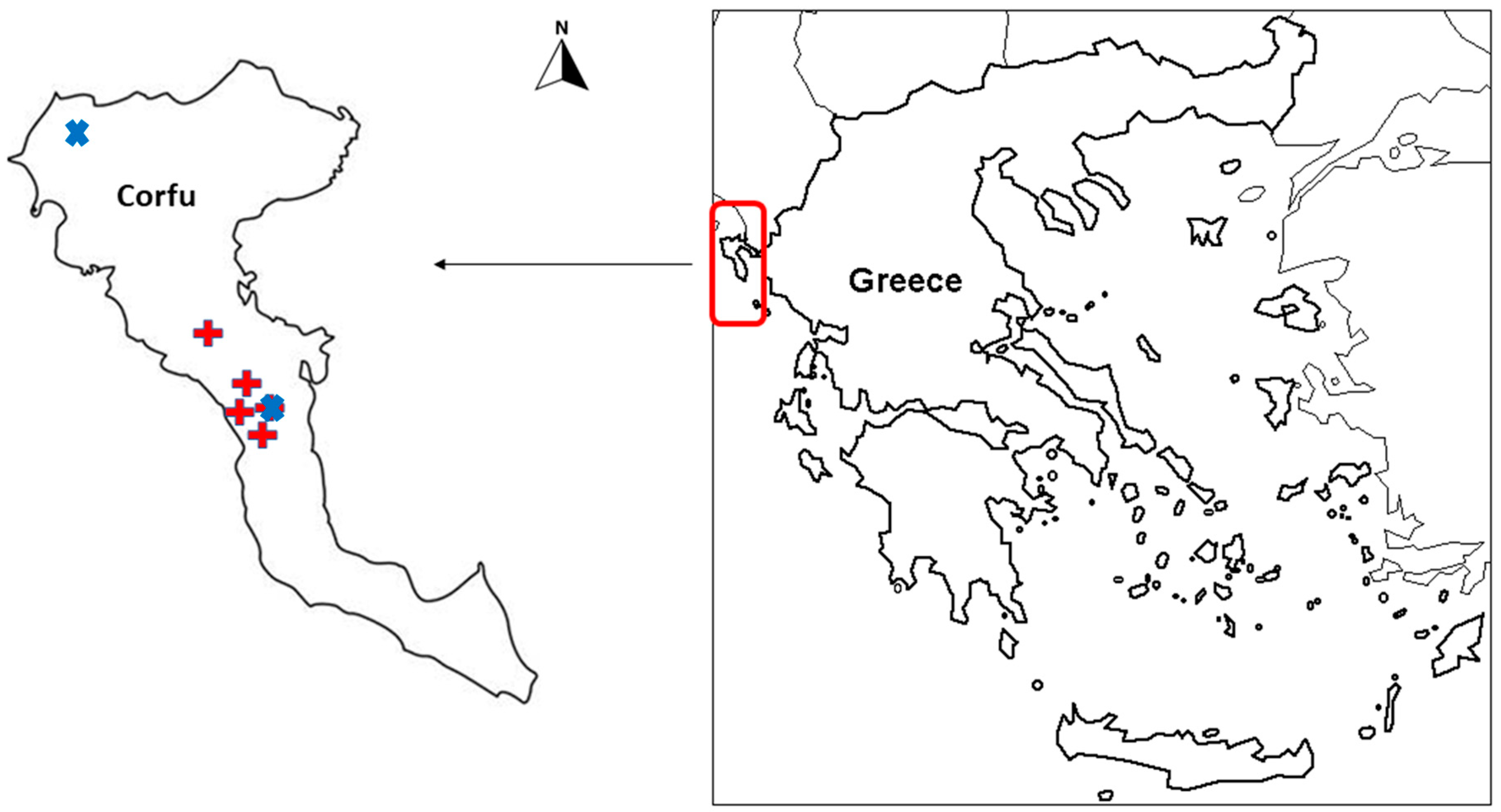
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Ethnographic and Socio-Economic Variables of Corfu Island
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Data Analysis
- Transcription and Cleaning: Interview recordings were transcribed verbatim. Non-relevant content (such as filler words and off-topic discussions) was removed while ensuring the preservation of meaningful phrases related to plant use, cultural traditions, and environmental concerns.
- Tokenisation: The text was split into individual words (tokens) to analyse specific terms.
- Lowercasing: All words were converted to lowercase to ensure uniformity and avoid duplication of terms (e.g., “Wild Plants” and “wild plants” were treated as the same term).
3. Results
3.1. Wild Greens and Their Diversity
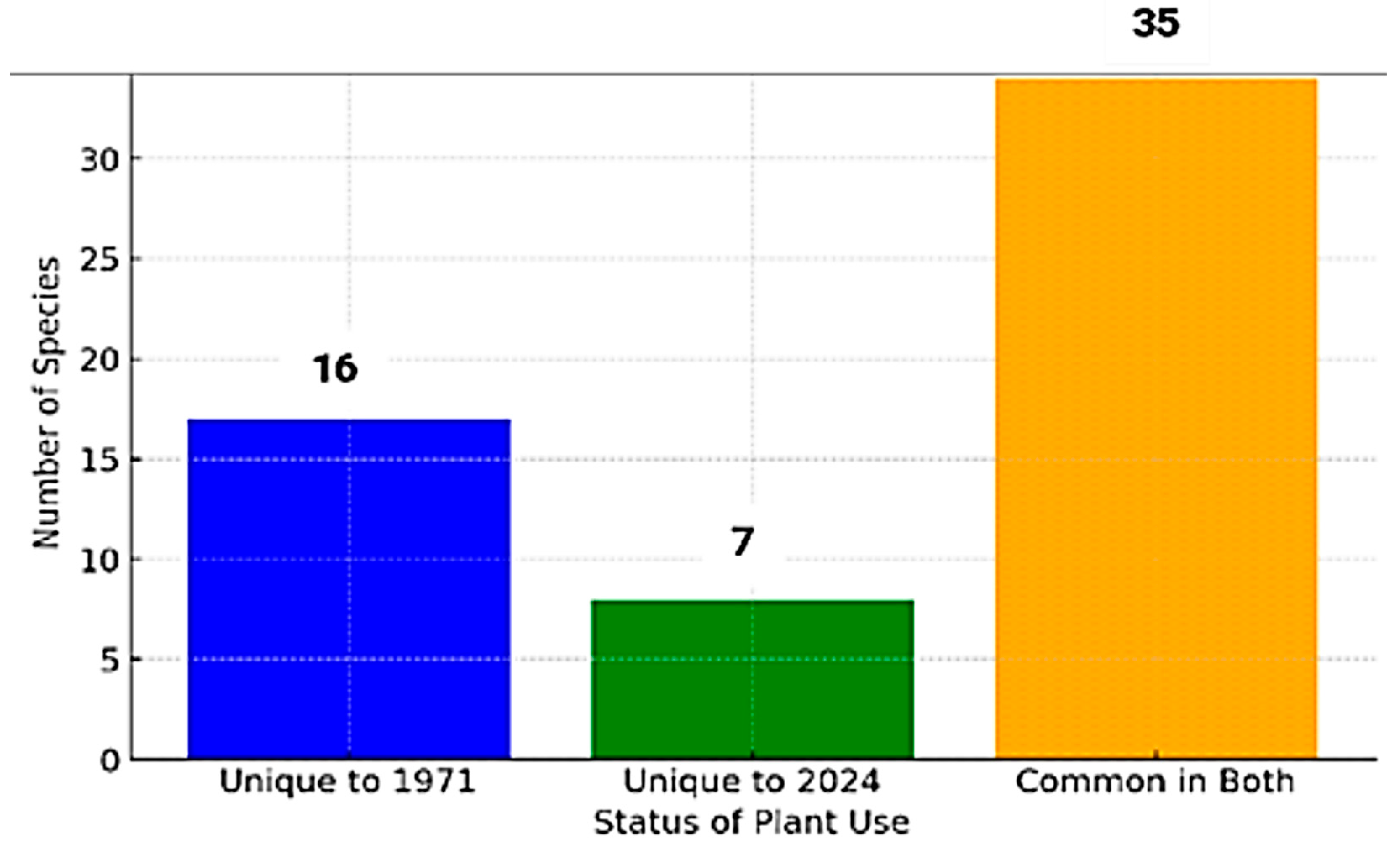
3.2. Changes in the Number of Species and Families: A Comparison of 1971 and 2024
3.3. Used Plant Parts Comparison
3.4. Textual Data Analysis and Word Cloud Visualisation
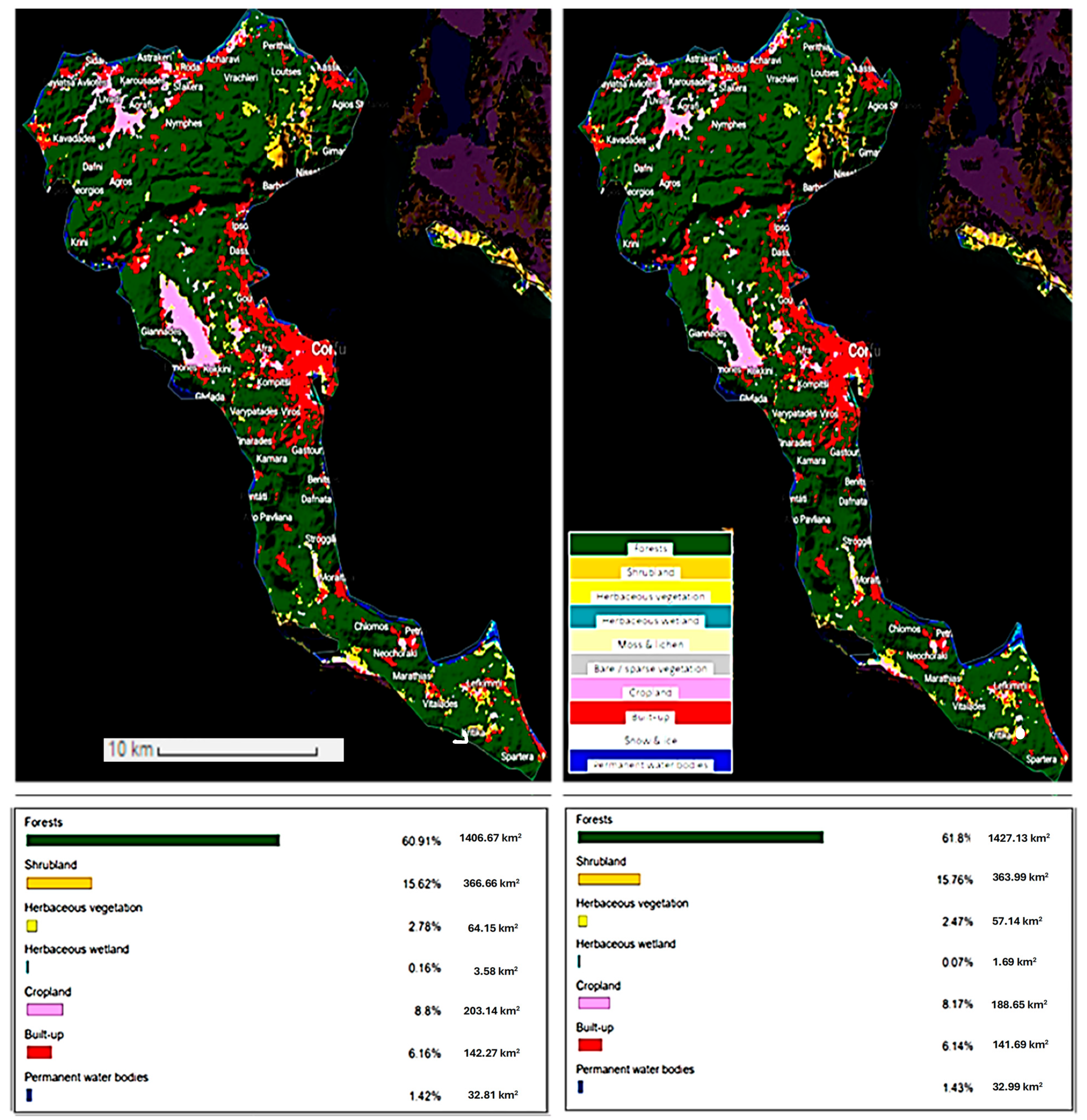
3.5. Land Use Change Analysis (Maps and Satellite Imagery)
3.6. Impact of Socio-Ecological and Developmental Changes on the Intergenerational Dynamics of Ethnobotanical Knowledge in Corfu
4. Discussion
4.1. The Decline in Wild Greens in Corfu: Ecological, Demographic, and Cultural Drivers
4.2. Climatic and Ecological Factors
4.3. Developmental Factors
4.4. Limitations and Challenges
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azam, F.M.S.; Biswas, A.; Mannan, A.; Afsana, N.A.; Jahan, R.; Rahmatullah, M. Are Famine Food Plants Also Ethnomedicinal Plants? An Ethnomedicinal Appraisal of Famine Food Plants of Two Districts of Bangladesh. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014, 2014, 741712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwajombe, A.R.; Liwenga, E.T.; Mwiturubani, D. Contribution of Wild Edible Plants to Household Livelihood in a Semiarid Kondoa District, Tanzania. World Food Policy 2022, 8, 276–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, N.; Aziz, M.A.; Stryamets, N.; Mattalia, G.; Zocchi, D.M.; Ahmed, H.M.; Manduzai, A.K.; Shah, A.A.; Faiz, A.; Sõukand, R.; et al. The Importance of Becoming Tamed: Wild Food Plants as Possible Novel Crops in Selected Food-Insecure Regions. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrhmoun, M.; Romano, A.; Sulaiman, N.; Pieroni, A. Old Plants for New Food Products? The Diachronic Human Ecology of Wild Herbs in the Western Alps. Plants 2025, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, N.; Verner, V.; Polesny, Z. Socioeconomic Dimensions of Wild Food Plant Use During the Conflict in Syria. Econ. Bot. 2023, 77, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gockowski, J.; Mbazo’o, J.; Mbah, G.; Fouda Moulende, T. African Traditional Leafy Vegetables and the Urban and Peri-Urban Poor. Food Policy 2003, 28, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, D. Some Contributions to the Wall Flora in Corfu. Braunschweiger Geobot. Arb. 2022, 14, 107–134. [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque, U.P.; Cantalice, A.S.; Oliveira, D.V.; Oliveira, E.S.; dos Santos, E.B.; dos Santos, F.I.R.; Soldati, G.T.; da Silva Lima, I.; Silva, J.V.M.; Abreu, M.B.; et al. Why Is Traditional Ecological Knowledge (TEK) Maintained? An Answer to Hartel et al. (2023). Biodivers. Conserv. 2024, 33, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anju, T.; Kumar, A. Traditional Ecological Knowledge and Medicinal Plant Diversity Usage among the Mullu Kuruman Tribes of Wayanad District of Kerala, India and Its Implications for Biodiversity Conservation in the Face of Climate Change. Trees For. People 2024, 16, 100595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della, A.; Paraskeva-Hadjichambi, D.; Hadjichambis, A.C. An Ethnobotanical Survey of Wild Edible Plants of Paphos and Larnaca Countryside of Cyprus. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomedicine 2006, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonti, M.; Nebel, S.; Rivera, D.; Heinrich, M. Wild Gathered Food Plants in the European Mediterranean: A Comparative Analysis. Econ. Bot. 2006, 60, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraci, A.; Amato, F.; Di Noto, G.; Bazan, G.; Schicchi, R. The Wild Taxa Utilized as Vegetables in Sicily (Italy): A Traditional Component of the Mediterranean Diet. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomedicine 2018, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieroni, A.; Sulaiman, N.; Sõukand, R. Chorta (Wild Greens) in Central Crete: The Bio-Cultural Heritage of a Hidden and Resilient Ingredient of the Mediterranean Diet. Biology 2022, 11, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrhmoun, M.; Sulaiman, N.; Haq, S.M.; Abidullah, S.; Prakofjewa, J.; Krigas, N.; Pieroni, A.; Sõukand, R. Is Boiling Bitter Greens a Legacy of Ancient Crete? Contemporary Foraging in the Minoan Refugium of the Lasithi Plateau. Foods 2024, 13, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsioutsiou, E.E.; Giordani, P.; Hanlidou, E.; Biagi, M.; De Feo, V.; Cornara, L. Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used in Central Macedonia, Greece. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. ECAM 2019, 2019, 4513792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoula, M.; D’Agata, C.D.C.; Sarpaki, A. Contribution to the Ethnobotany of Crete, Greece. Bocconea 2009, 23, 479–487. [Google Scholar]
- Sordinas, A. Wild Plant Gathering for Subsistence on the Island of Corfu, Greece; Memphis State University: Memphis, TN, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Andrianou, A.-A.; Papaioannou, G. Cultural Landscapes and Botanic Gardens: The Case of Mon-Repos Garden in Corfu Island, Greece. In Cultural Sustainable Tourism; Stankov, U., Boemi, S.-N., Attia, S., Kostopoulou, S., Mohareb, N., Eds.; Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 99–108. ISBN 978-3-030-10803-8. [Google Scholar]
- Marchi, M.; Ferrara, C.; Biasi, R.; Salvia, R.; Salvati, L. Agro-Forest Management and Soil Degradation in Mediterranean Environments: Towards a Strategy for Sustainable Land Use in Vineyard and Olive Cropland. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratidis, K. Sustainable Tourism Development in the Ionian Islands. The Case of Corfu Island. In Culture and Tourism in a Smart, Globalized, and Sustainable World, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference of IACuDiT, Hydra, Greece, 17–19 June 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenic Statistical Authority Main Page ELSTAT-ELSTAT. Available online: https://www.statistics.gr/en/home/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Reina-Rodríguez, G.A.; Soriano, I. Diachronic Cartography and Spatial Pattern Assessment in Coastal Habitats: The Case of Torredembarra (Northeast Spain). J. Coast. Res. 2008, 1, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussema, S.B.F.; Allouche, F.K.; Ajmi, R.; Chaabane, B.; Gad, A.-A. Assessing and Monitoring the Effects of Land Cover Changes in Biodiversity. Case Study: Mediterranean Coastal Region, Sousse, Tunisia. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2023, 26, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.J.; Turner, K.L. “Where Our Women Used to Get the Food”: Cumulative Effects and Loss of Ethnobotanical Knowledge and Practice; Case Study from Coastal British Columbia. Botany 2008, 86, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanazaki, N. Local and Traditional Knowledge Systems, Resistance, and Socioenvironmental Justice. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomedicine 2024, 20, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borelli, T.; Hunter, D.; Powell, B.; Ulian, T.; Mattana, E.; Termote, C.; Pawera, L.; Beltrame, D.; Penafiel, D.; Tan, A.; et al. Born to Eat Wild: An Integrated Conservation Approach to Secure Wild Food Plants for Food Security and Nutrition. Plants 2020, 9, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hatmi, S.; Lupton, D.A. Documenting the Most Widely Utilized Plants and the Potential Threats Facing Ethnobotanical Practices in the Western Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman. J. Arid Environ. 2021, 189, 104484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbonias, K. Coastal Environments and Long-Term Human Practices in Corfu: A Seascape Perspective. J. Greek Archaeol. 2022, 7, 435–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, A.E.; Koukousioura, O.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Langer, M.R. Invasive Shallow-Water Foraminifera Impacts Local Biodiversity Mostly at Densities above 20%: The Case of Corfu Island. Web Ecol. 2023, 23, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogeorgis, G.; Livas, C.; Karali, N. Strategic Analysis of Mediterranean Island Destinations: The Case of Corfu. J. Environ. Manag. Tour. 2022, 13, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, E.D. Rural Tradition and Cultural Identity of the Ionian Islands. J. Bus. Manag. Econ. 2019, 7, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corfu. Wikipedia 2025. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corfu (accessed on 17 February 2024).
- ISE (International Society of Ethnobiology). The ISE Code of Ethics. Available online: https://www.ethnobiology.net/what-we-do/core-programs/ise-ethics-program/code-of-ethics/ (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Stevens Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Available online: http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/ (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- The World Bank Group World Development Indicators|DataBank. Available online: https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Brandes, D. Vegetation Der Straßenränder Korfus; Tagungsbericht des Braunschweiger Kolloquiums vom. Hrsg. von Dietmar Brandes. Braunschweiger Geobotanische Arbeiten, Bd. 5. S. 247-262. Universitätsbibliothek der TU Braunschweig, 22–24. November 1996. Available online: https://www.zobodat.at/pdf/Brandes-Dietmar_7_1996_0001-0016.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Alexopoulos, J.D.; Tomara, V.; Vassilakis, E.; Papadopoulos, T.D.; Dassenakis, M.; Poulos, S.; Voulgaris, N.; Dilalos, S.; Ghionis, G.; Goumas, G.; et al. A Contribution to Environmental Research of the Korissia Coastal Wetland (Corfu Isl., Greece), with the Application of Combined Geological and Geophysical Methods Supported by Geographic Information Systems. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2007, 40, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliadou, E.; Kallimanis, A.S.; Dimopoulos, P.; Panitsa, M. Comparing the Two Greek Archipelagos Plant Species Diversity and Endemism Patterns Highlight the Importance of Isolation and Precipitation as Biodiversity Drivers. J. Biol. Res.-Thessalon. 2014, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, P.; Libralato, S.; Capezzuto, F.; D’Onghia, G.; Maiorano, P.; Sion, L.; Tursi, A.; Solidoro, C.; Carlucci, R. Ecosystem Functioning of Two Marine Food Webs in the North-Western Ionian Sea (Central Mediterranean Sea). Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 10198–10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valli, A.; Kougioumoutzis, K.; Iliadou, E.; Panitsa, M.; Trigas, P. Determinants of Alpha and Beta Vascular Plant Diversity in Mediterranean Island Systems: The Ionian Islands, Greece. Nord. J. Bot. 2019, 37, e02156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, R.C.G.; Di Gioia, F.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Petropoulos, S.A. Wild Greens Used in the Mediterranean Diet; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 209–228. [Google Scholar]
- Christoforatou, E. Plants and People on the Island of Corfu–An Ongoing Relationship; Green Corfu: Corfu, Greece, 2024; Available online: https://corfuherbs.com/en/book-chapter/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Łuczaj, Ł.; Pieroni, A.; Tardío, J.; Pardo-de-Santayana, M.; Sõukand, R.; Svanberg, I.; Kalle, R. Wild Food Plant Use in 21st Century Europe: The Disappearance of Old Traditions and the Search for New Cuisines Involving Wild Edibles. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 2012, 81, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, S.A.; Folchi, M.; Simonetti, J.A. Knowledge of Native Edible Plants in a Monoculture Plantation-Dominated Landscape. J. Ethnobiol. 2019, 39, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceló, M.; Tengö, M.; Simonetti, J.A.; Gelcich, S. Exploring Links between Local Knowledge, Values and Livelihoods in Land-Sea Interface: Insights on Emerging Tradeoffs and Change in Southern Chile. Ecosyst. People 2024, 20, 2329562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliam, F.S. The Ecological Significance of the Herbaceous Layer in Temperate Forest Ecosystems. BioScience 2007, 57, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbertsson, L. Pollinators and Insect Pollination in Changing Agricultural Landscapes. Doctoral Thesis, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ali-Shtayeh, M.S.; Jamous, R.M.; Al-Shafie’, J.H.; Elgharabah, W.A.; Kherfan, F.A.; Qarariah, K.H.; Khdair, I.S.; Soos, I.M.; Musleh, A.A.; Isa, B.A.; et al. Traditional Knowledge of Wild Edible Plants Used in Palestine (Northern West Bank): A Comparative Study. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomedicine 2008, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzuriaga-Quichimbo, C.X.; Hernández Del Barco, M.; Blanco-Salas, J.; Cerón-Martínez, C.E.; Ruiz-Téllez, T. Plant Biodiversity Knowledge Varies by Gender in Sustainable Amazonian Agricultural Systems Called Chacras. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Roque, A.; Silva-Rivera, E.; Gómez-Tolosa, M.; Pérez-Farrera, M.A.; Tejeda-Cruz, C.; López, S. Traditional Knowledge Surviving the New Millennium: Women’s Use of Wild Edible Plant Species in a Protected Natural Area. 2024. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4565461/v1 (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Ruddle, K. The Transmission of Traditional Ecological Knowledge Kenneth Ruddle. Paper presented to the Panel Session on “Traditional Ecological Knowledge”, Second Annual Meeting of the Society for the Study of Common Property, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, NB, Canada, 26-29 September 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Narváez-Elizondo, R.E.; González-Elizondo, M.; Castro-Castro, A.; González-Elizondo, S.; Tena-Flores, J.A.; Chairez-Hernández, I. Comparison of traditional knowledge about edible plants among young Southern Tepehuans of Durango, Mexico. Bot. Sci. 2021, 99, 834–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatziprokopiou, P. Immigrants’ Integration and Social Change: Greece as a Multicultural Society. In Proceedings of the 2nd LSE Symposium on Modern Greece, Current Social Science Research in Greece, Enfield Town, Middlesex, UK, 10 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Maroyi, A. Ethics in Ethnobotanical Research: Intersection of Indigenous and Scientific Knowledge Systems. J. Pharm. Nutr. Sci. 2020, 10, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda, Á.J.; Sárvári, B.; Balogh, J.M. Generation Change in Agriculture: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Economies 2023, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaroudaki, A.; Dimitropoulakis, P.; Constantinidis, T.; Katsiotis, A.; Skaracis, G.N. Ten Indigenous Edible Plants: Contemporary Use in Eastern Crete, Greece. Cult. Agric. Food Environ. 2012, 34, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurelle, D.; Thomas, S.; Albert, C.; Bally, M.; Bondeau, A.; Boudouresque, C.-F.; Cahill, A.E.; Carlotti, F.; Chenuil, A.; Cramer, W.; et al. Biodiversity, Climate Change, and Adaptation in the Mediterranean. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilescu, M. Water, Soil, and Plants Interactions in a Threatened Environment. Water 2021, 13, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, B. Impacts of Soil Salinity/Sodicity on Soil-Water Relations and Plant Growth in Dry Land Areas: A Review. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2021, 12, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gálvez Nogales, E.; Puntsagdavaa, A.; Casari, G.; Bennett, A. Linking Agriculture and Tourism to Strengthen Agrifood Systems in Asia and the Pacific; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023; ISBN 978-92-5-138026-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, G.; Wang, Z.; Maundu, P.; Hunter, D. The Role of Traditional Knowledge and Food Biodiversity to Transform Modern Food Systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 130, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Taxon | Family | Local Name (s) | Used Parts | Local Food Use | Frequency of Use | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study of 1971 | Data of 2024 | |||||
| Allium ampeloprasum L. | Amaryllidaceae | Agripraso | Whole plant | Seasoning, pies | * | |
| Allium guttatum subsp. sardoum (Moris) Stearn | Amaryllidaceae | Prassomana | Shoots | Raw, boiled | * | |
| Allium neapolitanum Cirillo | Amaryllidaceae | Agrioskordo, Agrioskortho | Bulbs | Raw, boiled | * | * |
| Allium roseum L. | Amaryllidaceae | Agrio kremydi | Bulbs | Raw, boiled | * | |
| Amaranthus deflexus L. | Amaranthaceae | Agriovlyta, Vlyta, Vlythra | Leaves | Boiled | ** | *** |
| Amaranthus blitum L. (CORFU06) | Amaranthaceae | Agriovlyta, Vlyta, Vlythra | Leaves | Boiled | * | *** |
| Anacamptis palustris (Jacq.) R.M. Bateman, Pridgeon and M.W. Chase | Orchidaceae | Salepi | Tubercoles | Beverage | * | |
| Asparagus aphyllus L. | Asparagaceae | Agriasfaraghia, Agriosparaghi | Shoots | Boiled, omelettes | *** | *** |
| Capparis spinosa L. (CORFU02) | Capparaceae | Kappari | Flower buds | Pickled | ** | ** |
| Chenopodium album L. (CORFU10) | Amaranthaceae | Laboda | Leaves | Boiled | * | |
| Cichorium intybus L. | Asteraceae | Agriopikralidha, Prikalida | Young aerial parts | Boiled | ** | .. |
| Crepis vesicaria L. and possibly other Crepis spp. (CORFU01) | Asteraceae | Radiki, Rathiki | Young aerial parts | Boiled | ** | |
| Cynara cardunculus L. | Asteraceae | Agrianghinara, Agriaguluga, Agriokukuze, Angathi | Flower receptacles | Omelettes | * | ** |
| Draba verna L. | Brassicaceae | Koutsoulochorto | Young aerial parts | Boiled | ** | |
| Dioscorea communis (L.) Caddick & Wilkin | Dioscoreaceae | Ovries | Shoots | Boiled | ** | |
| Eruca sativa (L.) Mill. | Brassicaceae | Roka | Leaves | Salad | * | * |
| Foeniculum vulgare Mill. (CORFU03) | Apiaceae | Maratho, Marathro | Young aerial parts, fruits | Boiled, seasoning | ** | ** |
| Glaucium flavum Crantz | Papaveraceae | Paparouna | Young aerial parts | Pan-fried | * | |
| Helminthotheca echioides (L.) Holub | Asteraceae | Zegunas, Zochos | Young aerial parts | Boiled | * | |
| Hirschfeldia incana (L.) Lagr. -Foss. | Brassicaceae | Vrouva, Vrouves | Young aerial parts | Boiled | *** | *** |
| Laurus nobilis L. | Lauraceae | Dafni, Dafnophylla | Leaves | Seasoning | *** | *** |
| Lepidium draba L. | Brassicaceae | Agriokardamura | Young aerial parts | Boiled | * | |
| Lomelosia cretica (L.) Greuter & Burdet | Caprifoliaceae | Stravoxylo | Young aerial parts | Boiled | * | |
| Melissa officinalis L. | Lamiaceae | Melissochorto | Leaves | Seasoning soups | ** | * |
| Mentha longifolia (L.) L. | Lamiaceae | Agriodhyosmos, Dyosmos | Leaves | Seasoning | * | ** |
| Mentha pulegium L. (CORFU09) | Lamiaceae | Flisgouni, Menta | Leaves | Seasoning | * | * |
| Mentha spicata L. | Lamiaceae | Flisgouni, Menta | Leaves | Seasoning | * | * |
| Mentha × piperita L. | Lamiaceae | Agriodhyosmos, Dyosmos | Leaves | Seasoning | ** | ** |
| Leopoldia comosa (L.) Parl. | Asparagaceae | Kremydi, Volvoi | Bulbs | Raw, bioled, pickled | ** | ** |
| Myrtus communis L. | Myrtaceae | Myrtia | Fruits | Seasoning | * | |
| Nasturtium officinale R.Br. | Brassicaceae | Agriokardamura, Kardamura | Young aerial parts | Boiled | * | * |
| Nigella damascena L. | Ranunculaceae | Koutsoulochorto, Koutsulines | Leaves | Boiled | * | |
| Origanum onites L. | Lamiaceae | Rigani | Flowering tops | Seasoning | * | *** |
| Papaver rhoeas L. | Papaveraceae | Paparouna | Young aerial parts | Pan-fried | * | |
| Picris echioides L. | Asteraceae | Prikalidha | Young aerial parts | Boiled | ** | |
| Portulaca oleracea L. (C0RFU 07) | Portulacaceae | Glystridha | Young aerial parts | Salad | ** | ** |
| Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn | Dennstaedtiaceae | Fteri | Shoots | Cooked | ** | |
| Reichardia picroides (L.) Roth | Asteraceae | Lagopsomo, Pikralidha, Prikalidha | Young aerial parts | Boiled | * | |
| Rumex spp. | Polygonaceae | Lapatho | Leaves | Boiled | * | |
| Salicornia europaea L. | Amaranthaceae | Almidha, Almika, Armyricha | Aerial parts | Salads, pickled | ** | ** |
| Salsola kali L. | Amaranthaceae | Almidha, Almika, Armyricha | Aerial parts | Salads, pickled | *** | ** |
| Scandix australis L. | Apiaceae | Agriokafkalithra, Frangomaidanos, Kafkalithra, Moscholahana, Myroni, Skandix, Scanzaki, Veloni | Young aerial parts | Seasoning green mixes | * | |
| Scandix pecten-veneris L. | Apiaceae | Agriokafkalithra, Frangomaidanos, Kafkalithra, Moscholahana, Myroni, Skandix, Scanzaki, Veloni | Young aerial parts | Seasoning green mixes | *** | *** |
| Silene vulgaris (Moench) Garcke | Caryophyllaceae | Skulpit | Shoots | Boiled | ** | |
| Sinapis alba L. | Brassicaceae | Agriosinapi, Rapanidha, Vrouves | Young aerial parts | Boiled | ** | ** |
| Sinapis arvensis L. | Brassicaceae | Agriosinapi, Rapanidha, Vrouves | Young aerial parts | Boiled | * | ** |
| Sisymbrium officinale (L.) Scop. | Brassicaceae | Skylovrouva, Vrouves | Young aerial parts | Boiled | *** | ** |
| Sisymbrium polyceratium L. | Brassicaceae | Skylovrouva, Vrouves | Young aerial parts | Boiled | * | |
| Solanum nigrum L. (CORFU05) | Solanaceae | Stafilita, Stroufolia, Styfnos, Stygmos, Strichnos | Leaves | Boiled | * | *** |
| Sonchus asper (L.) Hill. | Asteraceae | Zegunas, Zeguni, Zochos | Young aerial parts | Boiled, salads | * | *** |
| Sonchus oleraceus L. | Asteraceae | Zegunas, Zeguni, Zochos | Young aerial parts | Boiled, salads | *** | *** |
| Taraxacum officinale F.H. Wigg. | Asteraceae | Radiki, Rathiki | Young aerial parts | Boiled | ** | ** |
| Thymbra capitata (L.) Cav. | Lamiaceae | Thymari | Aerial parts | Seasoning | * | ** |
| Tordylium apulum L. | Apiaceae | Agriokafkalithra, Frangomaidanos, Kafkalithra, Moscholahana, Myroni, Skandix, Scanzaki, Veloni | Young aerial parts | Seasoning green mixes | *** | *** |
| Tordylium officinale L. (CORFUFR01) | Apiaceae | Agriokafkalithra, Frangomaidanos, Kafkalithra, Moscholahana, Myroni, Skandix, Scanzaki, Veloni | Young aerial parts | Seasoning green mixes | * | |
| Urospermum picroides (L.) Scop. ex F.W. Schmidt | Asteraceae | Zegunas, Zochos | Young aerial parts | Boiled | * | |
| Urtica dioica L. | Urticaceae | Tsunidha | Leaves | Boiled, pies | * | ** |
| Valeriana locusta L. | Caprifoliaceae | Andrakla | Young aerial parts | Salad | * | * |
| Visnaga daucoides Gaertn. | Apiaceae | Griniopodhas | Young aerial parts | Salad | * | ** |
| Variable | 1970 | 2024 | Change | β (Coefficient) | Standard Deviation | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic Factors | ||||||
| Elderly population | 30% | 20% | −10% | 0.38 | 0.12 | <0.01 |
| Women identified as wild plant experts were interviewed | 75% | 65% | −10% | −0.3 | 0.16 | 0.32 |
| Population with secondary education | 50% | 90% | +40% | 0.2 | 0.09 | 0.1 |
| Ethnic diversity (Greek) | 95% | 85% | −10% | −0.18 | 0.1 | 0.13 |
| Population density (per km2) | 100 | 200 | 100 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.04 |
| Ecological Factors | ||||||
| Average annual temperature (°C) | 20 | 21.5 | 1.5 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| Soil fertility (%) | 40% | 35% | −5% | −0.1 | 0.07 | 0.16 |
| Rainfall (mm/year) | 1200 | 1100 | −100 | −0.07 | 0.04 | 0.22 |
| Development Factors | ||||||
| Population urbanisation (%) | 20% | 50% | 30% | −0.5 | 0.14 | <0.05 |
| Tourist arrivals (annual per million) | 0.5 | 1,5 | 1 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.02 |
| Agriculture as economic driver (%) | 70% | 20% | −50% | −0.55 | 0.21 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alrhmoun, M.; Sulaiman, N.; Ullah, I.; Sõukand, R.; Pieroni, A. Biocultural Diversity at Risk Amidst and Beyond Overtourism: The Decline in Wild Green Foraging in Corfu over the Past 50 Years. Land 2025, 14, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030654
Alrhmoun M, Sulaiman N, Ullah I, Sõukand R, Pieroni A. Biocultural Diversity at Risk Amidst and Beyond Overtourism: The Decline in Wild Green Foraging in Corfu over the Past 50 Years. Land. 2025; 14(3):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030654
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlrhmoun, Mousaab, Naji Sulaiman, Irfan Ullah, Renata Sõukand, and Andrea Pieroni. 2025. "Biocultural Diversity at Risk Amidst and Beyond Overtourism: The Decline in Wild Green Foraging in Corfu over the Past 50 Years" Land 14, no. 3: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030654
APA StyleAlrhmoun, M., Sulaiman, N., Ullah, I., Sõukand, R., & Pieroni, A. (2025). Biocultural Diversity at Risk Amidst and Beyond Overtourism: The Decline in Wild Green Foraging in Corfu over the Past 50 Years. Land, 14(3), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030654










