Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Land Use Carbon Emissions (LUCE) in Coastal Areas—A Case Study of Hainan Island
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
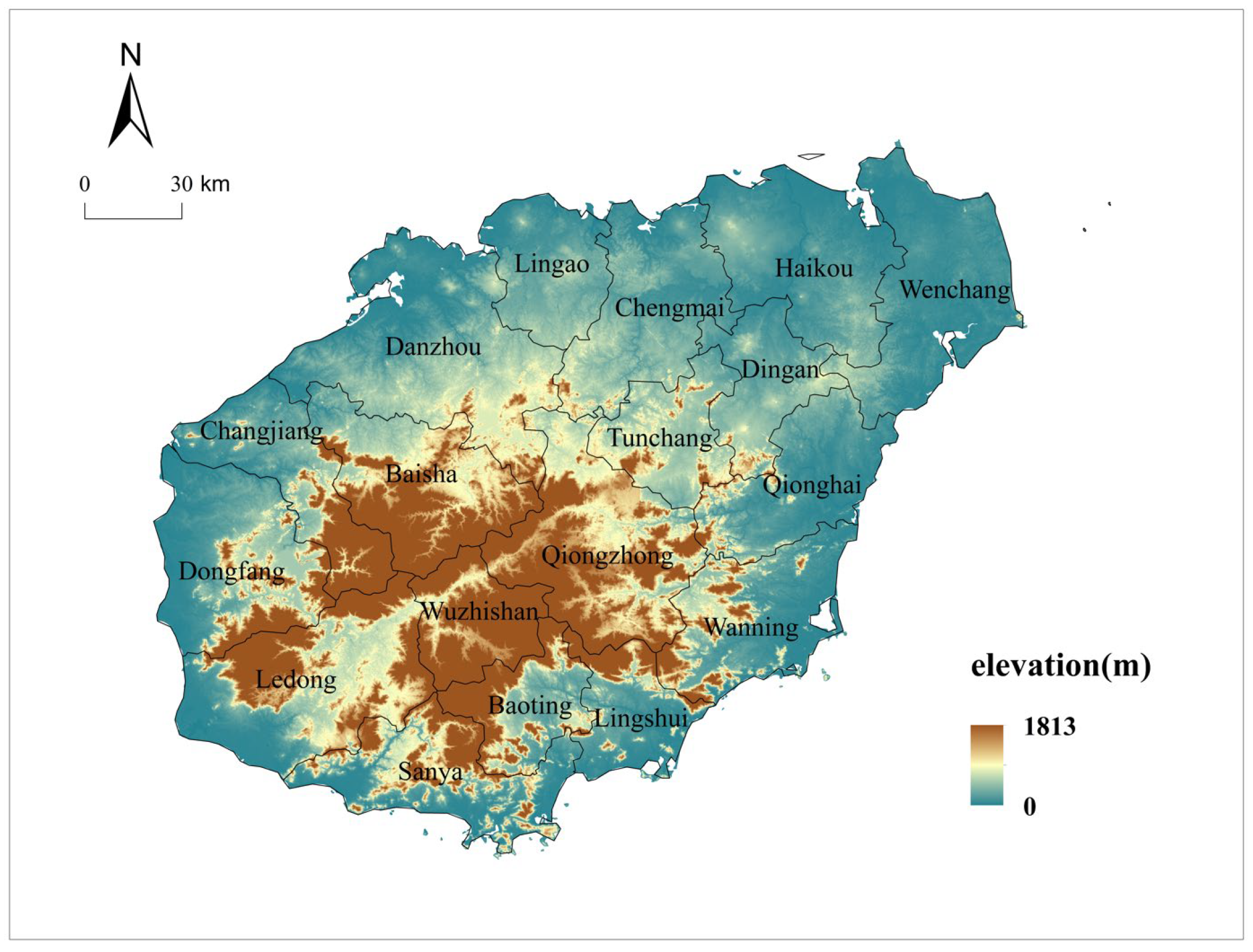
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. LUCC Calculation
2.3.2. LUCE Calculation
2.3.3. Kaya-LMDI Model
3. Results
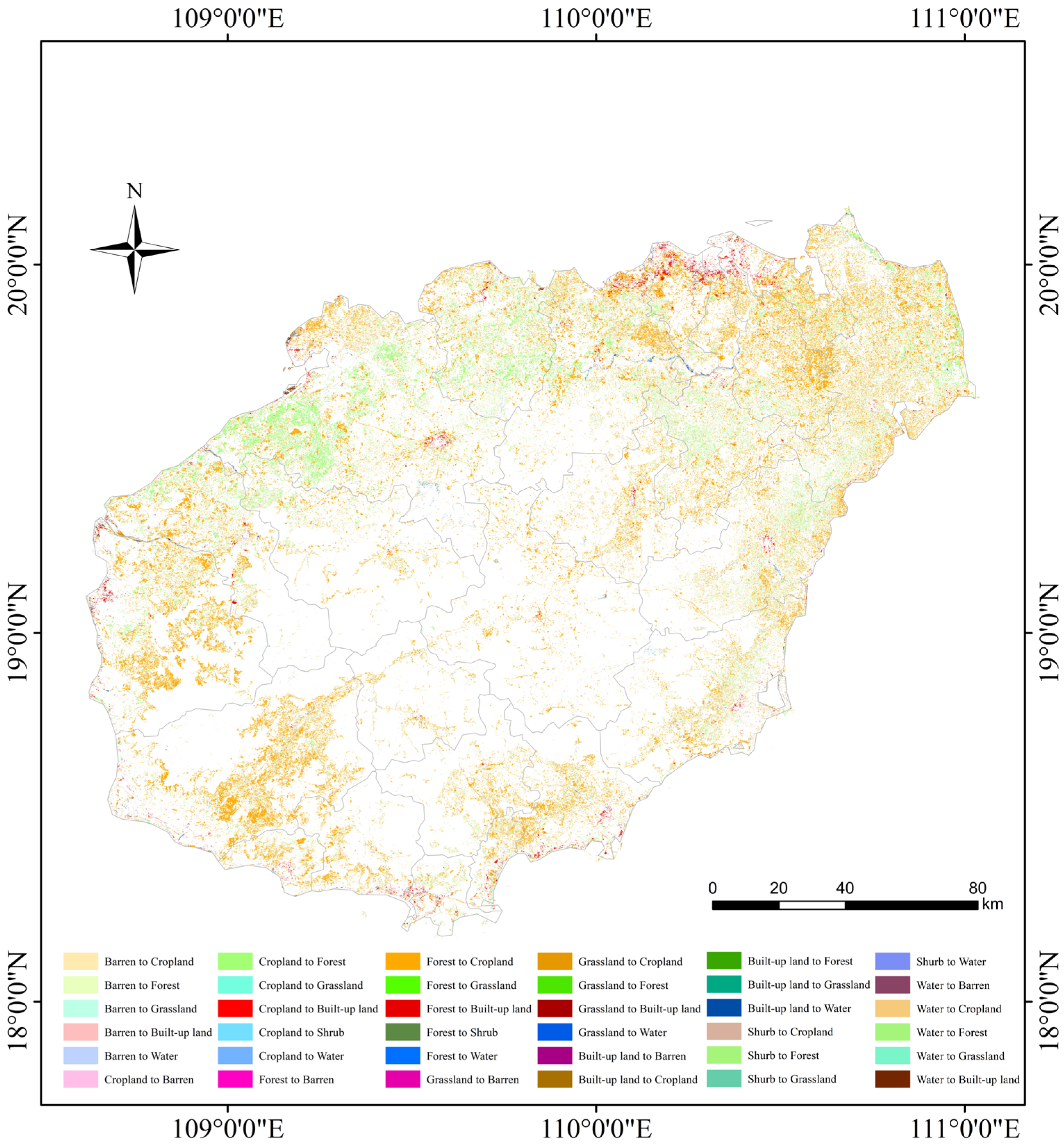
3.1. Characteristics of LUCC
3.2. Characteristics of LUCE
3.2.1. LUCE in Hainan Island
3.2.2. Spatial Variations in LUCE on Hainan Island
3.2.3. Spatial Autocorrelation of LUCE in Hainan Island
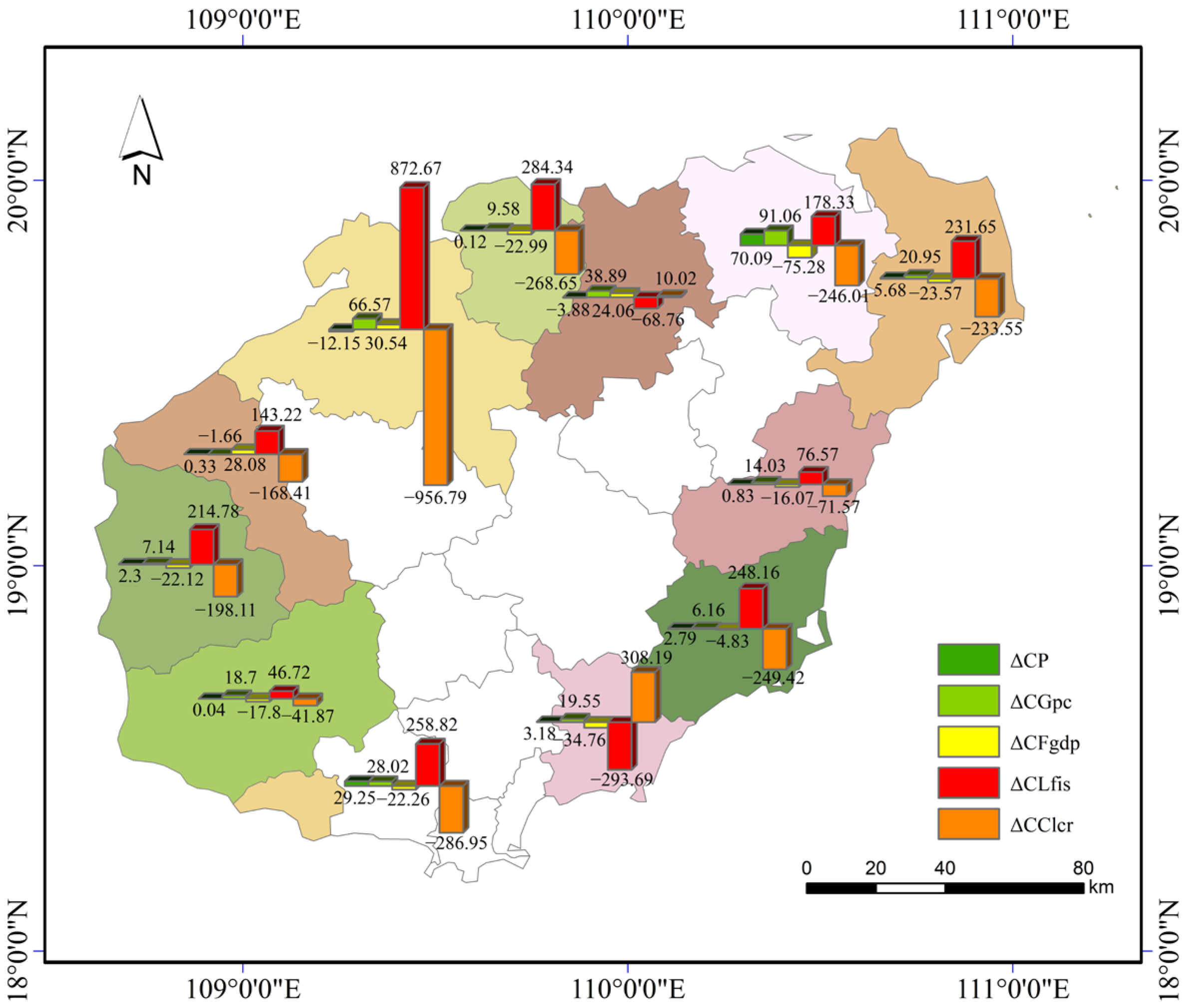
3.3. Analysis on Driving Factors of LUCE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rong, T.; Qin, M.; Zhang, P.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Spatiotemporal evolution of land use carbon emissions and multi scenario simulation in the future—Based on carbon emission fair model and PLUS model. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 38, 104087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, X.; Ma, S.; Zuo, J.; Goodsite, M. Clear skies after the haze: How the climate policy uncertainty impacts urban resilience in China. J. Asian Public Policy 2025, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Fan, C.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.; Zhou, X. Assessing the impact of land use changes on urban heat risk under different development scenarios: A case study of Guangzhou in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 130, 106532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, X.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, S.; Zuo, J.; Goodsite, M. Facilitating urban green innovative efficiency from intergovernmental perspective in China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 22751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, E.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Sha, M. Spatiotemporal coupling analysis of land urbanization and carbon emissions: A case study of Zhejiang Province, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 4594–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Qu, Y.; Shu, B.; Huang, T. Decoupling relationship between urban land use morphology and carbon emissions: Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Peng, C.; Liu, G.; Du, A.M.; Boateng, A. The impact of industrial land prices and regional strategical interactions on environmental pollution in China. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2025, 98, 103921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Long, H.; Gao, X.; Ma, E. Effects of land use transitions and rural aging on agricultural production in China’s farming area: A perspective from changing labor employing quantity in the planting industry. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, A.; Li, X.; Jiang, C.; Wu, J.; Omrani, H. Understanding recessive transition of cultivated land use in Jilin Province, China (1990–2020): From perspective of productive-living-ecological functions. Land 2023, 12, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, G. Local government competition and centralised urban growth management policy implementation: Evidence from China. J. Chin. Gov. 2024, 9, 348–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Geng, X.; Tian, W. Achieving low-carbon production: Impacts of land misallocation and industrial structure in urban China. Appl. Energy 2025, 378, 124791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennaio, M.; Hersperger, A.M.; Bürgi, M. Containing urban sprawl-Evaluating effectiveness of urban growth boundaries set by the Swiss Land Use Plan. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Wei, G.; Bi, M.; He, B.J. Carbon surplus or carbon deficit under land use transformation in China? Land Use Policy 2024, 143, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Xu, Y. Carbon reduction of urban form strategies: Regional heterogeneity in Yangtze River Delta, China. Land Use Policy 2024, 141, 107154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Yin, H.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Chinzorig, S.; Qin, K.; Tan, W.; Wan, Y.; Gao, Z.; Xu, C.; et al. Exploring the relationship between land use change patterns and variation in environmental factors within urban agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 108, 105447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Li, H.; Ko, K. Market-led transactions and illegal land use: Evidence from China. Land Use Policy 2019, 84, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhao, B.; Lu, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Z. Spatially explicit carbon emissions from land use change: Dynamics and scenario simulation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Land Use Policy 2025, 150, 107473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, M.; Tang, Z.; Mei, Z. Urbanization, land use change, and carbon emissions: Quantitative assessments for city-level carbon emissions in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Lin, R.; Zhu, D. Impact of rising industrial land prices on land-use efficiency in China: A study of underpriced land price. Land Use Policy 2025, 151, 107490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Qian, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Z. Impact of the top-down quota-oriented farmland preservation planning on the change of urban land-use in-tensity in China. Habitat Int. 2018, 77, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hu, S.; Wu, S.; Song, J.; Li, H. County-level land use carbon emissions in China: Spatiotemporal patterns and impact factors. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 105, 105304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Gong, X.; Yang, Y.; Tang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, L. Research on spatial and temporal differences of carbon emissions and influencing factors in eight economic regions of China based on LMDI model. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, J.; Long, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. Integrated effects of land use and land cover change on carbon metabolism: Based on ecological network analysis. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 104, 107320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, J.; Liu, D.; Fu, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, J. Air pollution outcomes, land misallocation, and the transmission through urban sprawl. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Huang, Q.; Chong, Z. Analysis on the effect and mechanism of land misallocation on carbon emissions efficiency: Evidence from China. Land Use Policy 2022, 121, 106336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y. Has China completed the supply-side structural reform of construction land supply? Evidence from 335 cities. Habitat Int. 2025, 156, 103271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, E.; Deng, J.; Zhou, M.; Gan, M.; Jiang, R.; Wang, K.; Shahtahmassebi, A. Carbon emissions induced by land-use and land-cover change from 1970 to 2010 in Zhejiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuai, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, M.; Wu, C. Land use, total carbon emissions change and low carbon land management in Coastal Jiangsu, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, B.; Lu, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, D. Provincial cultivated land use efficiency in China: Empirical analysis based on the SBM-DEA model with carbon emissions considered. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 151, 119874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Xu, H.Z. Effects of land urbanization and land finance on carbon emissions: A panel data analysis for Chinese provinces. Land Use Policy 2017, 63, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W. LMDI decomposition approach: A guide for implementation. Energy Policy 2015, 86, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyr-Koller, R.; Thomas, A.; Schleussner, C.F.; Nauels, A.; Lissner, T. Loss and damage implications of sea-level rise on Small Island Developing States. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 50, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, U.; Majumdar, S. Impact of land use change and rapid urbanization on urban heat island in Kolkata city: A remote sensing based perspective. J. Urban Manag. 2022, 11, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. 30 m annual land cover and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Chen, L.Q.; Tg, H.X.; Chen, L.G.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Yuan, L.N.; Xiao, J.; Wu, R.; Bai, L.F.; et al. Spatial correlations of land-use carbon emissions in the Yangtze River Delta region: A perspective from social network analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.S.; Yu, X.F.; Zhou, L. Carbon emission efficiency growth of land use structure and its spatial correlation: A case study of Nanjing city. Geogr. Res. 2018, 37, 2177–2192. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Liang, H.M.; Chang, X.L.; Cui, Q.C.; Tao, Y. Land Use Patterns on Carbon Emission and Spatial Association in China. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 35, 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.Y.; Guo, Z.D.; Piao, S.L.; Chen, A. Terrestrial vegetation carbon sinks in China, 1981–2000. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, S.; Wu, N.; Wang, Y.F.; Luo, P.; Shi, F.S. Advance in studies on production, oxidation and emission flux of methane from wetlands. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2006, 12, 726. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, Y. Impact of Carbon Dioxide Emission Control on GNP Growth: Interpretation of Proposed Scenarios; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change/Response Strategies Working Group: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.L.; Zhang, Z.K.; Ji, X.P.; Jiang, S.N.; Wei, G.E.; Zhou, K.X.; Wang, P.Y. Research on suitability evaluation of land space development and functional space allocation in coastal zone: A case study of Hainan Island. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 862–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. Grey forecasting the impact of population and GDP on the carbon emission in a Chinese region. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 139025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Benjamin, N.I. Influencing factors on carbon emissions in China transport industry. A new evidence from quantile regression analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 150, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Land Type | Carbon Emission Factor | Reference Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.0422 | [37] |
| Woodland | −0.0644 | [38] |
| Grassland | −0.0021 | [37] |
| Water | −0.0253 | [37] |
| Wetland | −0.00006 | [39] |
| Unused land | −0.0005 | [37] |
| 2010~2020 | Cropland | Forest | Shrub | Grassland | Water | Barren | Built-Up Land | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 1104.17 | 0.02 | 8.68 | 31.02 | 0.21 | 138.88 | 1282.97 | |
| Forest | 3276.40 | 0.43 | 1.36 | 2.22 | 0.001 | 26.45 | 3306.86 | |
| Shrub | 0.22 | 2.97 | 0.003 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.21 | |
| Grassland | 31.35 | 0.67 | 0.00 | 4.31 | 0.45 | 5.83 | 42.62 | |
| Water | 103.89 | 10.08 | 0.00 | 1.87 | 0.57 | 19.71 | 136.12 | |
| Barren | 2.92 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.56 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 4.17 | |
| Built-up land | 1.16 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 7.86 | 0.002 | 9.10 | |
| Total | 3415.94 | 1118.11 | 0.45 | 12.52 | 45.60 | 1.23 | 191.20 | 4785.05 |
| 2018~2020 | Cropland | Forest | Shrub | Grassland | Water | Barren | Built-Up Land | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 603.22 | 0.014 | 4.634 | 11.526 | 0.133 | 68.322 | 687.85 | |
| Forest | 1073.03 | 0.502 | 0.080 | 11.131 | 0.002 | 3.213 | 1087.96 | |
| Shrub | 0.027 | 0.814 | 0.000 | 0.0004 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.84 | |
| Grassland | 7.678 | 0.081 | 0.000 | 0.222 | 0.189 | 1.092 | 9.263 | |
| Water | 50.545 | 12.102 | 0.001 | 0.434 | 0.085 | 5.396 | 68.56 | |
| Barren | 0.356 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.167 | 0.015 | 0.128 | 0.67 | |
| Built-up land | 39.631 | 1.525 | 0.000 | 0.648 | 2.631 | 0.051 | 44.48 | |
| Total | 1171.27 | 617.75 | 0.52 | 5.96 | 25.53 | 0.46 | 78.15 | 1899.63 |
| Type\Year | 2010 | 2012 | 2014 | 2016 | 2018 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 419.7357 | 423.8717 | 469.2177 | 489.2048 | 501.7046 | 525.7439 |
| Forest | −1279.5869 | −1273.2619 | −1224.0478 | −1202.3714 | −1189.0163 | −1164.2402 |
| Shurb | −0.2671 | −0.2231 | −0.1693 | −0.1686 | −0.1388 | −0.1217 |
| Grassland | −0.1082 | −0.0894 | −0.0762 | −0.0622 | −0.0519 | −0.0450 |
| Water | −30.7648 | −31.2318 | −30.1575 | −29.2594 | −28.3412 | −26.1569 |
| Barren | −0.0030 | −0.0027 | −0.0021 | −0.0019 | −0.0016 | −0.0015 |
| Built-up land | 1781.6103 | 2118.1745 | 2317.0772 | 2715.5190 | 2828.9237 | 2864.9442 |
| LUCE | 2201.3459 | 2542.0463 | 2786.2948 | 3204.7238 | 3330.6283 | 3390.6882 |
| Land Carbon sink | −1310.7300 | −1304.8088 | −1254.4530 | −1231.8635 | −1217.5499 | −1190.5654 |
| Net LUCE | 890.6159 | 1237.2374 | 1531.8418 | 1972.8603 | 2113.0785 | 2200.1228 |
| Factors/Year | 2010–2012 | 2012–2014 | 2014–2016 | 2016–2018 | 2018–2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POP | 120.97 | 80.27 | 75.00 | 79.63 | 97.49 |
| Gpc | 618.81 | 448.03 | 340.53 | 511.06 | 348.85 |
| Fgdp | −117.39 | 276.55 | −138.26 | −127.80 | −176.30 |
| Lfis | −569.38 | −1283.29 | 351.77 | −2223.20 | 2411.26 |
| Clcr | 287.69 | 722.69 | −210.61 | 1886.24 | −2621.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, M.; Ma, Y.; Ma, H.; Cheng, M.; Li, B. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Land Use Carbon Emissions (LUCE) in Coastal Areas—A Case Study of Hainan Island. Land 2025, 14, 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122408
Jiao M, Ma Y, Ma H, Cheng M, Li B. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Land Use Carbon Emissions (LUCE) in Coastal Areas—A Case Study of Hainan Island. Land. 2025; 14(12):2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122408
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Man, Yuting Ma, Haonan Ma, Manyu Cheng, and Boqun Li. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Land Use Carbon Emissions (LUCE) in Coastal Areas—A Case Study of Hainan Island" Land 14, no. 12: 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122408
APA StyleJiao, M., Ma, Y., Ma, H., Cheng, M., & Li, B. (2025). Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Land Use Carbon Emissions (LUCE) in Coastal Areas—A Case Study of Hainan Island. Land, 14(12), 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122408





