A Multi-Agent Simulation-Based Decision Support Tool for Sustainable Tourism Land Use Planning in Rural China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research Status and Theoretical Foundation of Tourism Land Simulation
2.2. Construction and Innovation of Multi-Agent Model for RSHTUE Land
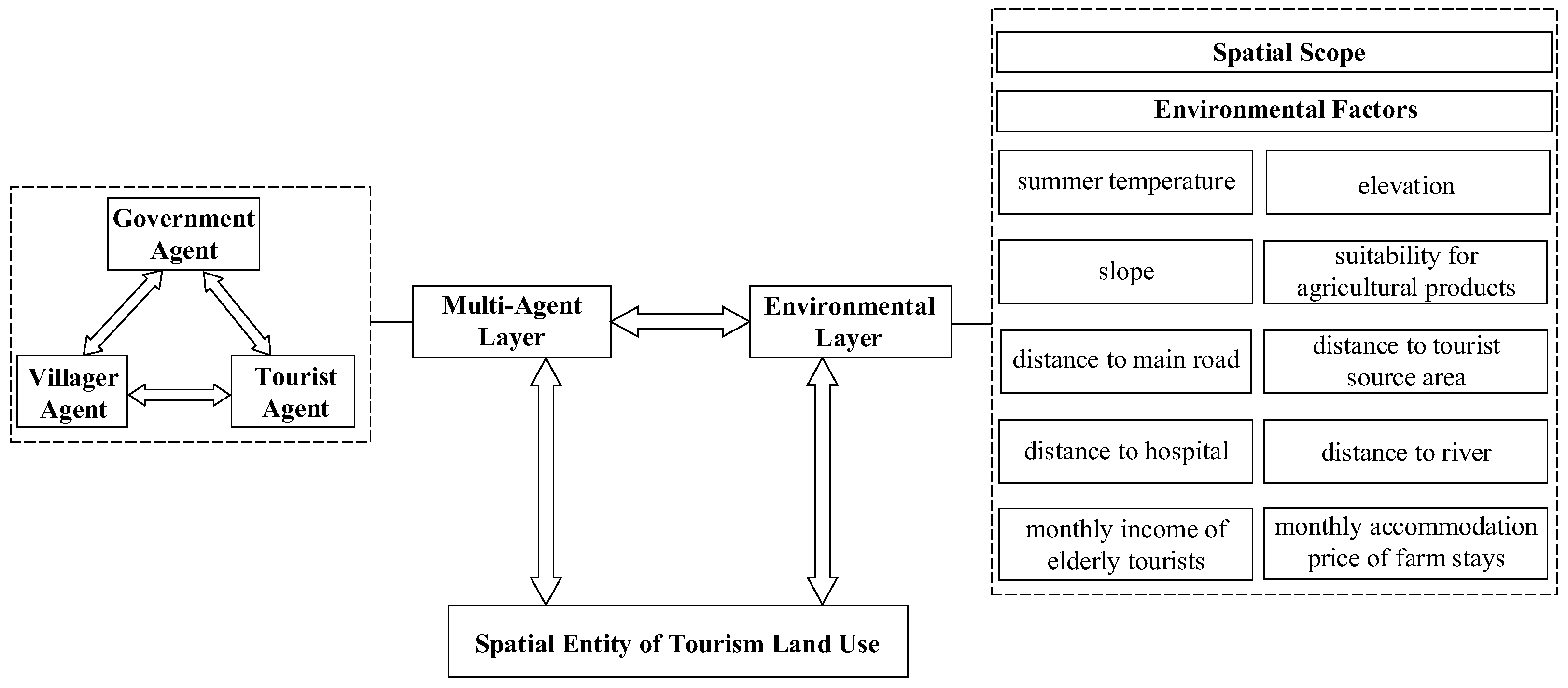
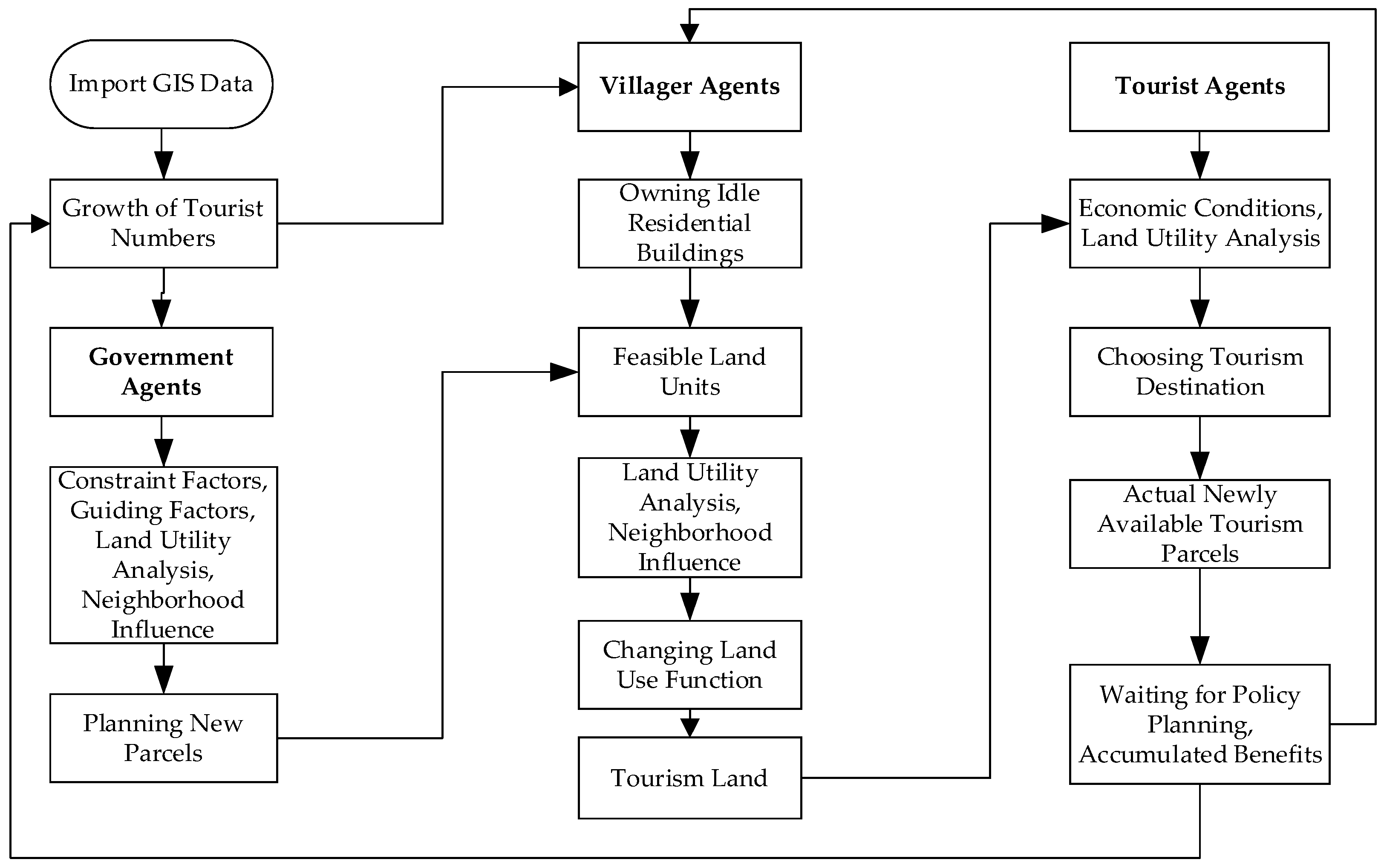
3. Multi-Agent Simulation Modeling of RSHTUE Land
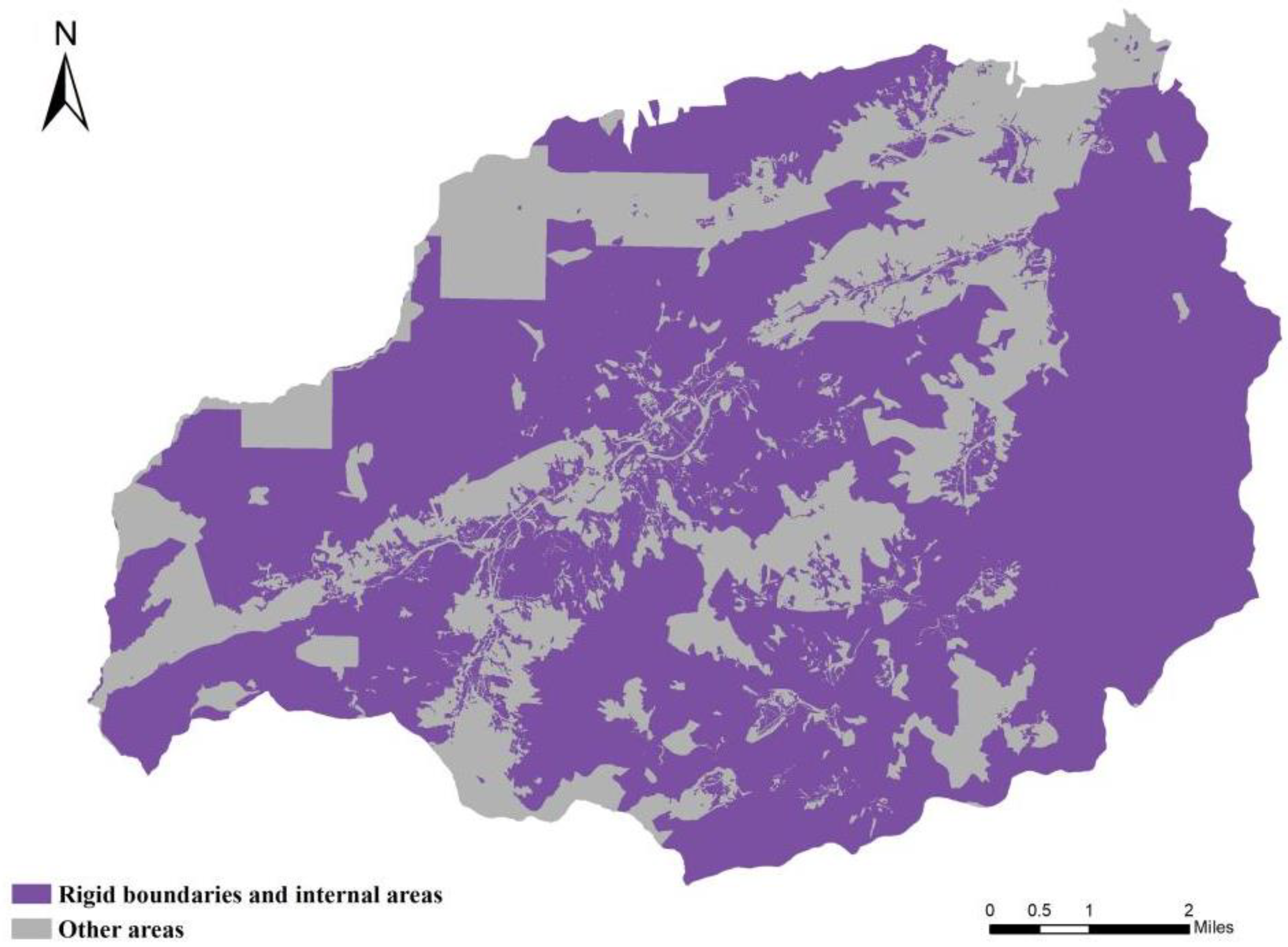
3.1. Delineation of Areas Within Rigid Boundaries
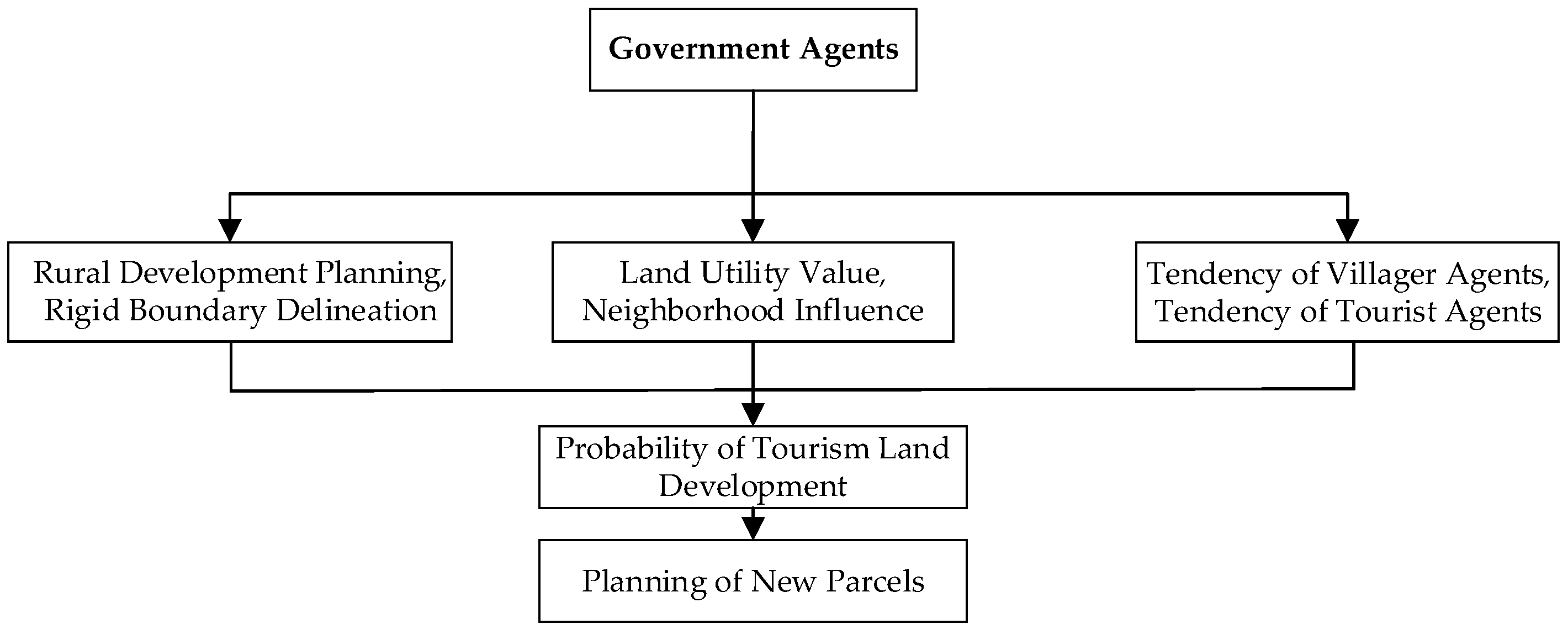
3.2. Decision-Making Rules of Government Agents
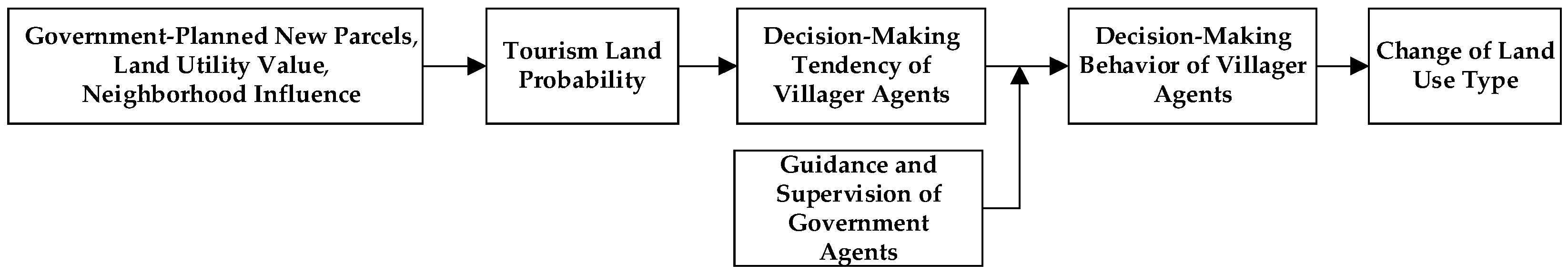
3.3. Decision-Making Rules of Villager Agents
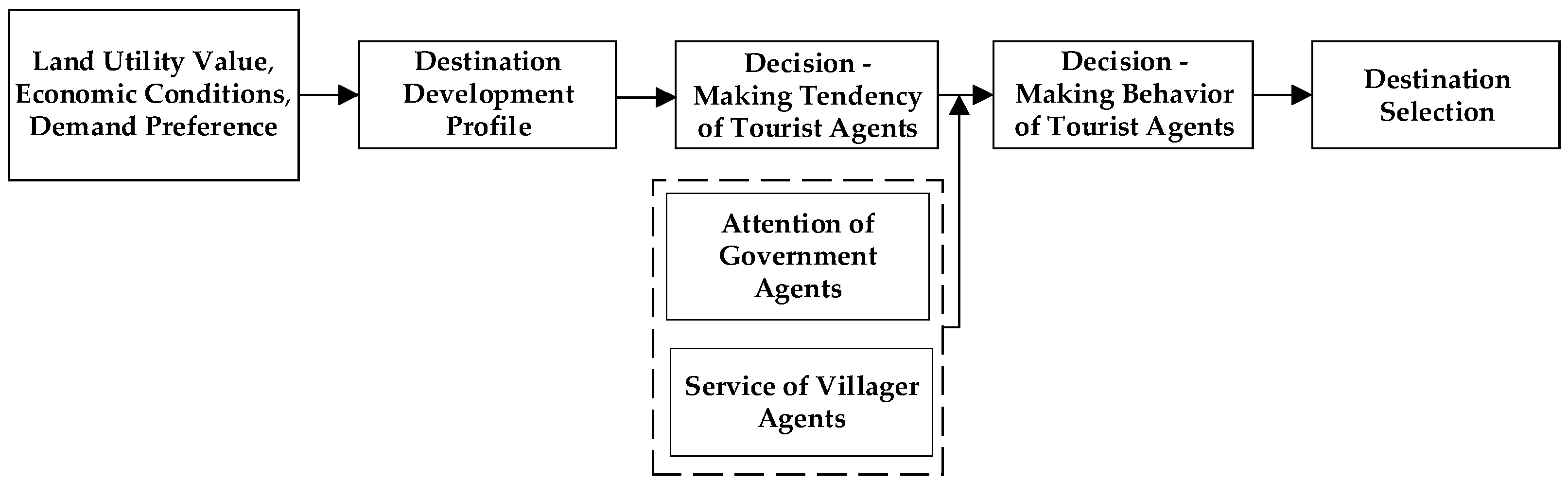
3.4. Decision-Making Rules for Tourist Agents
3.5. Scoring Rules for Environmental Factors
3.6. Model Programming and Operation
4. Empirical Study
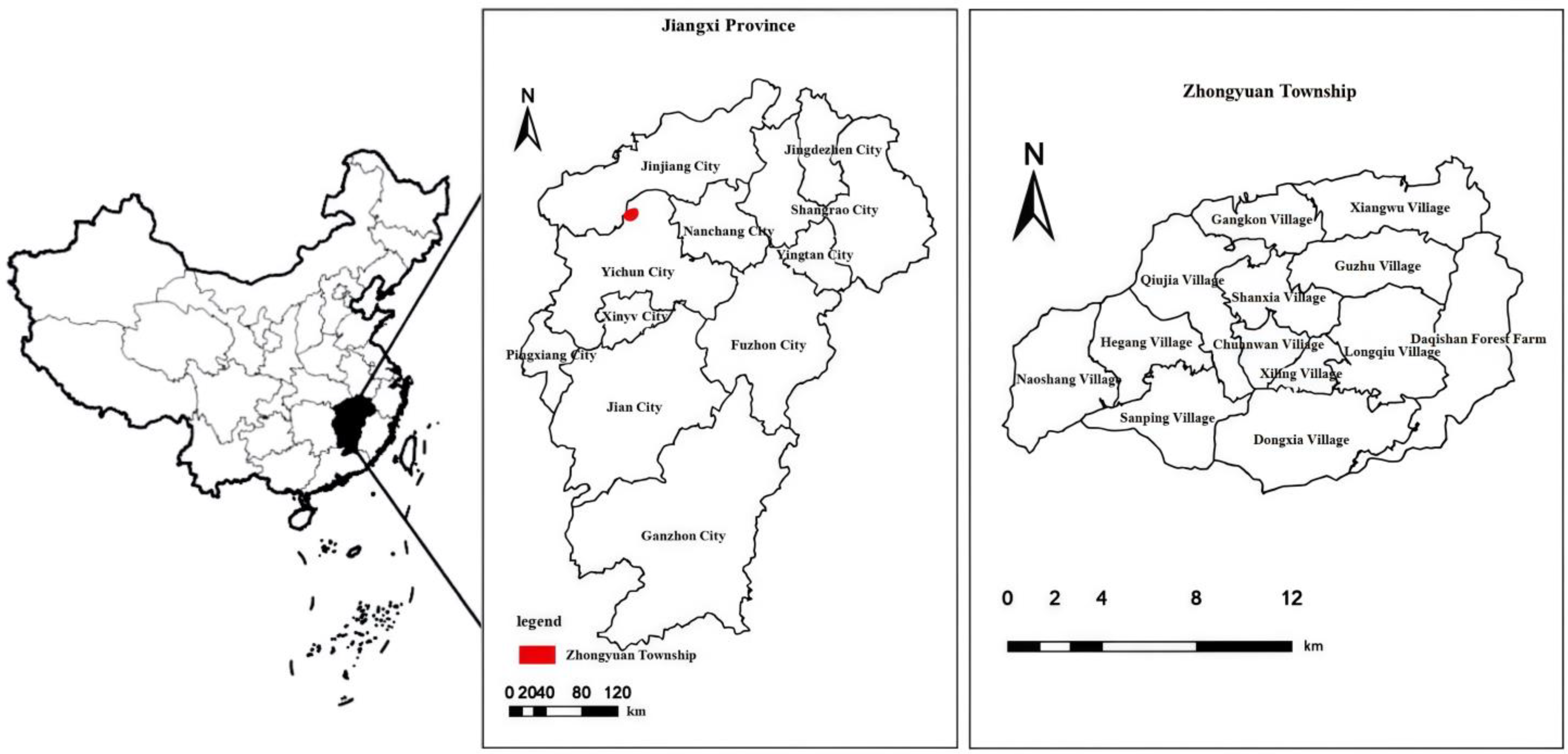
4.1. Overview of the Research Site
4.2. Data Sources and Processing
4.3. Development Scenario Planning
- (1)
- Tourism-led development scenario. It is pointed out in Yichun City’s development planning documents that efforts should be made to fully explore and leverage unique resource advantages in order to promote the vigorous growth of the emerging tourism and wellness industry [34]. The government work report of Zhongyuan Township in September 2023 also mentioned that shaping the tourism summer resort brand will be the strategic goal of the core work deployment in the future stage [61]. To achieve this, the government plans to promote and support the high-quality development of the tourism homestay industry from the aspects of planning layout and construction, infrastructure improvement and optimization, and financing channel expansion, as well as brand building and market promotion. Based on this, the study defines the first development scenario as a tourism-led development scenario, which refers to the future development model of the region guided by the tourism industry as its core.
- (2)
- Eco-protection development scenario. Under the guidance of ecological civilization and green development concepts, the comprehensive coordination of the protection of mountains, waters, forests, fields, lakes, and grasslands has become a key task [62]. Yichun City’s government emphasizes accelerating ecological zoning regulations and steadfast adherence to the principle of ecological priorities [34]. Jing’an County also clearly states that it is necessary to further strengthen the green advantages for high-quality and leapfrog development and proposes specific goals for ecological environment protection [35]. This scenario focuses on the preservation of ecological resources, takes low construction intensity and increased green coverage as its core concept, and plans regional development through strict ecological protection policies.
- (3)
- Rural belt joint development scenario. The integrated development of rural tourism can effectively facilitate reemployment, resource utilization, and the inheritance of rural traditional culture, making it a crucial approach to advancing rural economic revitalization [63]. To achieve sustainable tourism development, it is necessary to adopt a holistic mindset, break down administrative barriers between adjacent regions, and promote coordinated development [64]. Currently, some villages in Zhongyuan Township have been minimally positively impacted by the development of the RSHTUE industry, as they have not considered integrating their characteristic industries as extended projects in the RSHTUE industrial chain, resulting in fragmented development across regions. In order to focus on the coordinated coexistence of rural development in the new era and better meet the strategic requirements of rural revitalization, the third development scenario of Zhongyuan Township is set as the rural belt joint development scenario, which emphasizes the coordinated development of rural areas and aims to drive the development of the RSHTUE industry in relatively weak rural areas with better business development.
4.4. Scenario Prediction Results
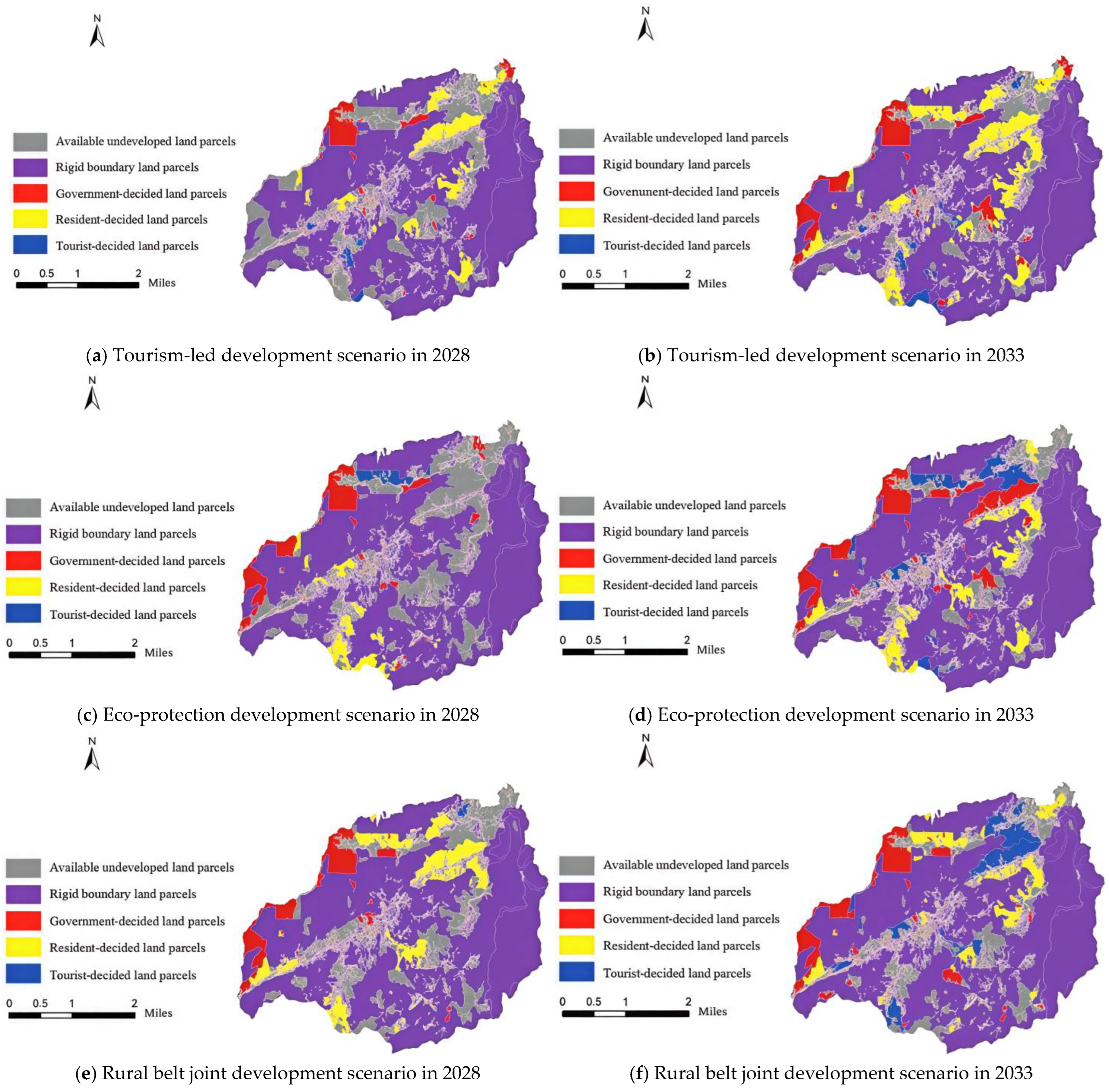
- (1)
- Under the tourism-led development scenario, the tourism land planned by the government is mainly concentrated in Qiujia Village, Naoshang Village, and Xiangwu Village. The tourism land identified by villagers is primarily distributed in Guzhu Village, Xiangwu Village, and Gangkou Village. The preferred areas for tourists are mainly Hegang Village and Sanping Village, followed by Naoshang Village, Chuanwan Village, Dongxia Village, and Xiangwu Village; these villages can be prioritized for development.
- (2)
- Under the eco-protection development scenario, the tourism land planned by the government is concentrated in Qiujia Village, Naoshang Village, and Guzhu Village. The tourism land selected by villagers is focused on Sanping Village and Guzhu Village. The areas preferred by tourists are mainly Gangkou Village, followed by Dongxia Village, Xiangwu Village, Hegang Village, and Qiujia Village; these villages have great development potential.
- (3)
- Under the rural belt joint development scenario, the key tourism lands planned by the government are located in Gangkou Village and Naoshang Village. The tourism land identified by villagers is mainly concentrated in Sanping Village, Xiangwu Village, and Guzhu Village. The areas selected by tourists are focused on Xiangwu Village, followed by Hegang Village, Sanping Village, and Chuanwan Village; these villages should be prioritized for development.
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Xue, J.; Luo, J.; Yang, A. The silver-hair economy in the new era: Political economy perspectives on its dilemmas and solutions. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, L.; Li, R. Development Drivers of Rural Summer Health Tourism for the Urban Elderly: A Demand- and Supply-Based Framework. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liang, Q.; Li, R.; Guo, S. Differentiation of rural summer health tourism for urban elderly: Tourist segmentation based on tourism experience. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2024, 59, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Zhao, M.; Ge, Q.; Kong, Q. Changes in land use of a village driven by over 25 years of tourism: The case of Gougezhuang village, China. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, X.; Pan, X.; An, J. Identification and classification of ecological restoration areas in the territorial land space of the Qaidam Basin, China. J. Arid Land 2025, 17, 1402–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y. Simulating land use change for sustainable land management in rapid urbanization regions: A research site of the Yangtze River Delta region. Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 1807–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Dong, L.; Zhang, Y. Spatiotemporal dynamic analysis and simulation prediction of land use and landscape patterns from the perspective of sustainable development in tourist cities. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cai, B.; He, J.; Kong, X. Identifying potential rural residential areas for land consolidation using a data driven agent-based model. Land Use Policy 2024, 145, 107260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Huang, J.; Guo, Y.; Ji, G. Multiscenario land use change simulation and its impact on ecosystem service function in Henan Province based on FLUS-InVEST model. Ecol. Evol. 2025, 15, e71111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Qiao, W.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Optimization of territorial ecological space under the constraint of ecosystem service externalities. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 168, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, K.; Wang, X. A hybrid cellular automaton model integrated with 3DCNN and LSTM for simulating land use/cover change. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2025, 18, 2447337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Feng, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, R. Spatial scenario projection of soil organic carbon storage loss associated with land use change. Trans. GIS 2025, 29, e70104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Liang, J.; Guo, J.; Chen, W.; Ou, M.; De Vries, W.T. Climate change-based dynamic simulation of land use and carbon storage in urban agglomerations of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. J. Geogr. Sci. 2025, 35, 1432–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, J.; Liu, R.; Lyu, P.; Han, Z.; Zhang, C. Understanding Governments, ESCOs, and Clients’ Behavioral Strategies in Public Building Energy-Efficiency Renovation Based on Evolutionary Game Theory. J. Manag. Eng. 2025, 41, 04025018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yi, X.; Qiu, H. Multi-scenario modelling of urban spatial growth under water resources and aquatic ecological environmental constraints. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 177, 113803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Gong, Q.; Liu, B.; Yu, S.; Yan, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J. Integrating linear programming and CLUE-S modeling for scenario-based land use optimization under eco-economic trade-offs in rapidly urbanizing regions. Land 2025, 14, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Hybrid CA–Deep learning model for 3D urban growth simulation. Trans. GIS 2025, 29, e70139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Q. Identification of land use conflict based on multi-scenario simulation—Taking the central yunnan urban agglomeration as an example. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Liu, H.; Hao, Z.; Gong, P.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, P. Simulating land use change for sustainability: A case study of the northern slope of Tianshan Mountains. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2025, 18, 2524055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.; Wang, P.; Zhang, G.; Shi, H.; Li, H. Ecological quality and spatial structure dynamics under future scenarios: A topological perspective from the Yellow River Basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 522, 146346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xi, J. A multi-agent model for simulation of rural settlement land use pattern: A research site of Gouge Village in Yesanpo Scenic Area. Tour. Trib. 2013, 34, 107–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cui, J.; Li, X.; Hou, X.; Li, Y.; Burgio, M.S.; Liu, H.; Yang, Q.; Liu, G. Understanding policy-volition interactions in urban ecological governance: A simulation framework based on SD-ABM coupling. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 524, 146479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, D.; Kong, X. Exploring the interaction mechanisms of behavioral options and policy regulation for construction waste and carbon reduction. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2025; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Yang, J.; Ren, J.; Yu, W.; Shi, Z.; Cong, N.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.; Qiao, Z. Enhancing urban resilience: Mitigating compound risk through multi-scenario land use optimization. Transportmetr. B Transp. Dyn. 2025, 13, 2552888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, S.; He, Z.; Huang, G.; Liang, Y. Multiscenario simulation and prediction of land use in the urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River considering urban expansion and shrinkage. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2025, 151, 04025064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; He, S.; Zeng, H.; Cao, X.; Hu, S. Modeling self-organized urban growth by incorporating stakeholders’ interactions into the neighborhood of cellular automata. Cities 2024, 149, 104976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Ni, Q.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, P.; Yuan, Z. Driving factors of rural land-use change from a multi-scale perspective: A case study of the Loess Plateau in China. Land 2025, 14, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Uncovering stakeholders’ participation to better understand land use change using multi-agent modeling approach: An example of the coal mining area of Shanxi, China. Land 2022, 11, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schück, F.; Arheimer, B.; Mazzoleni, M.; Brandimarte, L. A systematic mapping review of hydrological hazard management in agent-based systems. Environ. Res. Lett. 2025, 20, 113003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, M.; Yi, L. Study on the delimitation of the urban development boundary in a special economic zone: A case study of the central urban area of Doumen in Zhuhai, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.D.; Brottem, L.; Zaid, H.A.; Eggen, M.; Bourdjo, I.H. Connectivity and boundaries revisited: Livestock herders and parks in Central Africa. Bio. Conserv. 2025, 302, 110990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, X.; Yang, H. Scenario-based urban growth simulation by incorporating ecological-agricultural-urban suitability into a future land use simulation model. Cities 2023, 137, 104334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiangxi Provincial People’s Government. Notice of Jiangxi Provincial People’s Government on Issuing the Ecological Protection Red Line of Jiangxi Province. Available online: https://www.jiangxi.gov.cn/jxsrmzf/ndqzd217/pc/content/content_1842786463259766784.html (accessed on 26 October 2025). (In Chinese)
- Yichun Municipal People’s Government. Yichun City’s 14th Five-Year Plan for Culture and Tourism Development. Available online: https://www.yichun.gov.cn/ycsrmzf/fzgh/202112/c7da77e642704727a1d7f709572dd42d.shtml (accessed on 17 October 2025). (In Chinese)
- Jing’an County People’s Government. Land Use Master Plan of Jing'an County (2006-2020): Integration of Two Plans. Available online: http://www.jxjaxzf.gov.cn/jaxrmzf/gytdkjgh/202304/768aad994a5d4b8393e6d974c1318b5c.shtml (accessed on 18 November 2025). (In Chinese)
- Bai, X.; Yan, H.; Pan, L.; Huang, H.Q. Multi-agent modeling and simulation of farmland use change in a farming–pastoral zone: A case study of Qianjingou town in Inner Mongolia, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 14802–14833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Research on factors affecting ecosystem health in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and its multi-scenario simulation based on different spatial scales. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 45, 1–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, R.; Knowles, N.; Pöll, K.; Rutty, M. Impacts of climate change on mountain tourism: A review. J. Sustain. Tour. 2022, 32, 1984–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EI Fartassi, I.; Milne, A.E.; Metcalfe, H.; El Alami, R.; Diarra, A.; Alonso-Chavez, V.; Zawadzka, J.; Waine, T.W.; Corstanje, R. An agent-based model of farmer decision making: Application to shared water resources in arid and semi-arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 310, 109357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Song, W.; Song, C. Consolidating the layout of rural settlements using system dynamics and the multi-agent system. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 123150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streefkerk, I.N.; de Bruijn, J.; Haer, T.; Van Loon, A.F.; Quichimbo, E.A.; Wens, M.; Hassaballah, K.; Aerts, J.C. A coupled agent-based model to analyse human-drought feedbacks for agropastoralists in dryland regions. Front. Water 2023, 4, 1037971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Luo, Y.; Liu, K. The impact mechanism of social network information on tourism travel: An empirical analysis based on internet celebrity cities. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omonijo, A.G.; Olutumise, A.I.; Adeyeye, J.A. Mapping the effects of thermal sensation and climate conditions on tourism in the Ondo State, Nigeria. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2025, 156, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Romagosa, F.; Pallares-Barbera, M. Tourists’ perception of distance: A thematic review and conceptual framework. Tour. Geogr. 2025, 27, 380–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, H.; Zhou, B. Formation mechanism of tourists’ pro-environmental behavior in plateau ecotourism destination. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Mao, S.; Ma, H. The impact of the adaptability between human capital and digital technology on farmers’ choice of modern management mode. J. Agrotech. Econ. 2025, 7, 4–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Hu, J. Study of the outdoor thermal comfort threshold of elderly people in hot and humid regions in summer. South Archit. 2019, 2, 5–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Fu, L.; Wang, G.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, H. Analysis of the site selection evaluation system for rural leisure and pension projects. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2022, 4, 106–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. A Framework for Identifying Rural Summer Health Tourism Destinations Serving the Urban Elderly. Master’s Thesis, Jiangxi Normal University, Nanchang, China, 2023. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Qiu, Y. GIS-based evaluation of resort site selection in scenic areas: A research site of Nan Kun Mountain, Guangdong Province. Hum. Geogr. 2009, 24, 82–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yao, X.; Yan, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Ecological function suitability assessment and regulation division based on GIS and combination weighting method: A research site of Yannan Village. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2012, 21, 720–725. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Song, Q.; Yuan, S. Research on the site selection of endowment real estate project based on GIS—Take Tianjin City as an example. J. Tianjin Univ. Soc. Sci. 2017, 19, 204–209. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qin, T.; Cheng, L. Construction and application of Pingxiang double evaluation index system supported by GIS. Value Eng. 2023, 42, 5–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Xu, C. An empirical study on the distance choice of urban residents’ recreation around the city: A research site of Changsha City. Tour. Sci. 2008, 22, 34–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fu, G.; Wen, J. Study on relationship between consumption values and tourism consumption behavior. Enterp. Econ. 2023, 42, 121–133. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Guo, S.; Zeng, W.; Wu, L. Development of the well-being scale for urban elderly tourists who travel in the countryside for summer health. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2023, 28, 191–211. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, R.; Li, J.; Qin, Y.; Chi, M.; Zeng, P.; Wang, H.; Pan, X.; Gao, Y. Study on influential factors of surface water quality using geographic detector: A case of Lvliang City, Shanxi Province. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2023, 43, 212–222. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Guo, W.; Yang, A.; Yang, X.; Li, E.; Wang, Z. Identification and trend analysis of ecological security pattern in Mudanjiang city based on MSPA-MCR-PLUS model. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Tang, X.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Liu, K. Characteristic analyses, simulations and predictions of land use in poor mountainous cities: A case study in the central area of Chengde County, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, P.; Zhou, G.; Xing, X.; Zhang, Y. Multi-scenario simulation of land use and landscape ecological risk response based on planning control. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhongyuan Township People’s Government. Government Work Report: Delivered at the Fifth Session of the 18th People’s Congress of Zhongyuan Township. Available online: http://www.jxjaxzf.gov.cn/jaxrmzf/fzghe5/202309/4366c74b90b045799d8ba41039853812.shtml (accessed on 20 September 2025). (In Chinese)
- Sun, Q.; Wu, M.; Du, P.; Qi, W.; Yu, X. Spatial layout optimization and simulation of cultivated land based on the life community theory in a mountainous and hilly area of China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Xue, X. The influence of rural tourism landscape perception on tourists’ revisit intentions—A case study in Nangou village, China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Culture and Tourism. Guiding Opinions on Promoting the Sustainable Development of Rural Tourism. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2018-12/31/content_5433069.htm (accessed on 28 September 2025). (In Chinese)
- Richards, D.; Yabar, H.; Mizunoya, T.; Koon Koon, R.; Tran, G.H.; Esopere, Y. Balancing stakeholders’ perspectives for sustainability: GIS-MCDM for onshore wind energy planning. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Environmental Factor | Scoring Criteria | Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Summer temperature | <22.7 °C or >32.53 °C | 22.7–23.79 °C or 27.41–32.53 °C | 23.79–27.41 °C | Fang & Hu [47] |
| Elevation | <500 m or >1500 m | 500–800 m or 1000–1500 m | 800-1000 m | Zhang et al. [48]; Wang [49] |
| Slope | >27° | 14–27° | <14° | Gao & Qiu [50] |
| Distance to main road | <50 m | 50–100 m | >100 m | Zhang et al. [48] |
| Distance to river | >100 m | 50–100 m | <50 m | Chen et al. [51] |
| Distance to hospital | >800 m | 500–800 m | <500 m | Li et al. [52]; Zhang et al. [48] |
| Suitability for agricultural products | unsuitable area | moderately suitable area | suitable area | Liu et al. [53]; Field Survey Data |
| Travel time to land parcels | >3 h | 2–3 h | <2 h | Su & Xu [54] |
| Accommodation price | >2000 yuan | 2000 yuan | <2000 yuan | Xu et al. [55] |
| Tourists’ monthly income | <3000 yuan | 3000–5000 yuan | >5000 yuan | Zhang et al. [56] |
| Development Scenario | Weight of Government Agents | Weight of Villager Agents | Weight of Tourist Agents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tourism-led development scenario | 0.413 | 0.257 | 0.108 | |||
| 0.185 | 0.181 | 0.072 | ||||
| 0.123 | 0.290 | 0.085 | ||||
| 0.147 | 0.272 | 0.111 | ||||
| 0.131 | 0.215 | |||||
| 0.111 | ||||||
| 0.159 | ||||||
| 0.138 | ||||||
| Eco-protection development scenario | 0.290 | 0.223 | 0.095 | |||
| 0.170 | 0.261 | 0.086 | ||||
| 0.197 | 0.218 | 0.131 | ||||
| 0.178 | 0.298 | 0.130 | ||||
| 0.165 | 0.206 | |||||
| 0.110 | ||||||
| 0.119 | ||||||
| 0.123 | ||||||
| Rural belt joint development scenario | 0.269 | 0.282 | 0.115 | |||
| 0.139 | 0.198 | 0.085 | ||||
| 0.164 | 0.240 | 0.086 | ||||
| 0.273 | 0.280 | 0.122 | ||||
| 0.154 | 0.190 | |||||
| 0.097 | ||||||
| 0.159 | ||||||
| 0.145 | ||||||
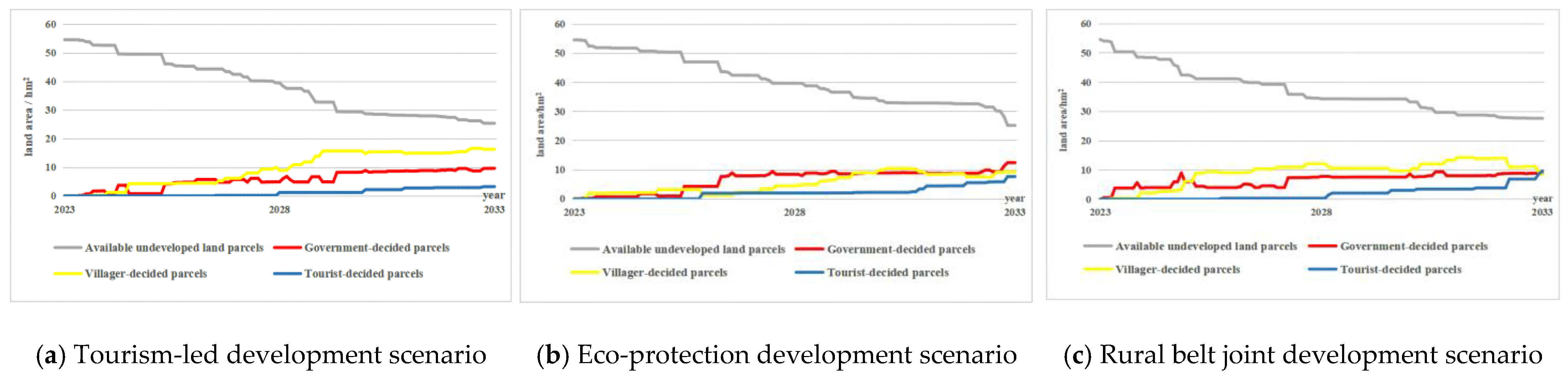
| Development Scenario | Year | Available Undeveloped Land Area/hm2 | Government-Decide Land Area/hm2 | Villager-Decide Land Area/hm2 | Tourist-Decide Land Area/hm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tourism-led development scenario | 2028 | 39.521 | 4.917 | 8.967 | 1.200 |
| 2033 | 25.392 | 9.642 | 16.322 | 3.248 | |
| Eco-protection development scenario | 2028 | 39.734 | 8.403 | 4.465 | 2.003 |
| 2033 | 25.230 | 12.447 | 9.267 | 7.660 | |
| Rural belt joint development scenario | 2028 | 34.319 | 7.803 | 12.136 | 0.346 |
| 2033 | 27.519 | 8.998 | 8.433 | 9.654 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Huang, A.; Wu, L.; Li, R.; Fu, Z. A Multi-Agent Simulation-Based Decision Support Tool for Sustainable Tourism Land Use Planning in Rural China. Land 2025, 14, 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122342
Zhang P, Huang A, Wu L, Li R, Fu Z. A Multi-Agent Simulation-Based Decision Support Tool for Sustainable Tourism Land Use Planning in Rural China. Land. 2025; 14(12):2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122342
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Puwei, Anna Huang, Li Wu, Rui Li, and Ziting Fu. 2025. "A Multi-Agent Simulation-Based Decision Support Tool for Sustainable Tourism Land Use Planning in Rural China" Land 14, no. 12: 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122342
APA StyleZhang, P., Huang, A., Wu, L., Li, R., & Fu, Z. (2025). A Multi-Agent Simulation-Based Decision Support Tool for Sustainable Tourism Land Use Planning in Rural China. Land, 14(12), 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122342






