The Application of CA–MLP–ANN in Assessing Urbanisation in Quaternary Catchment X22J of Mpumalanga, South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
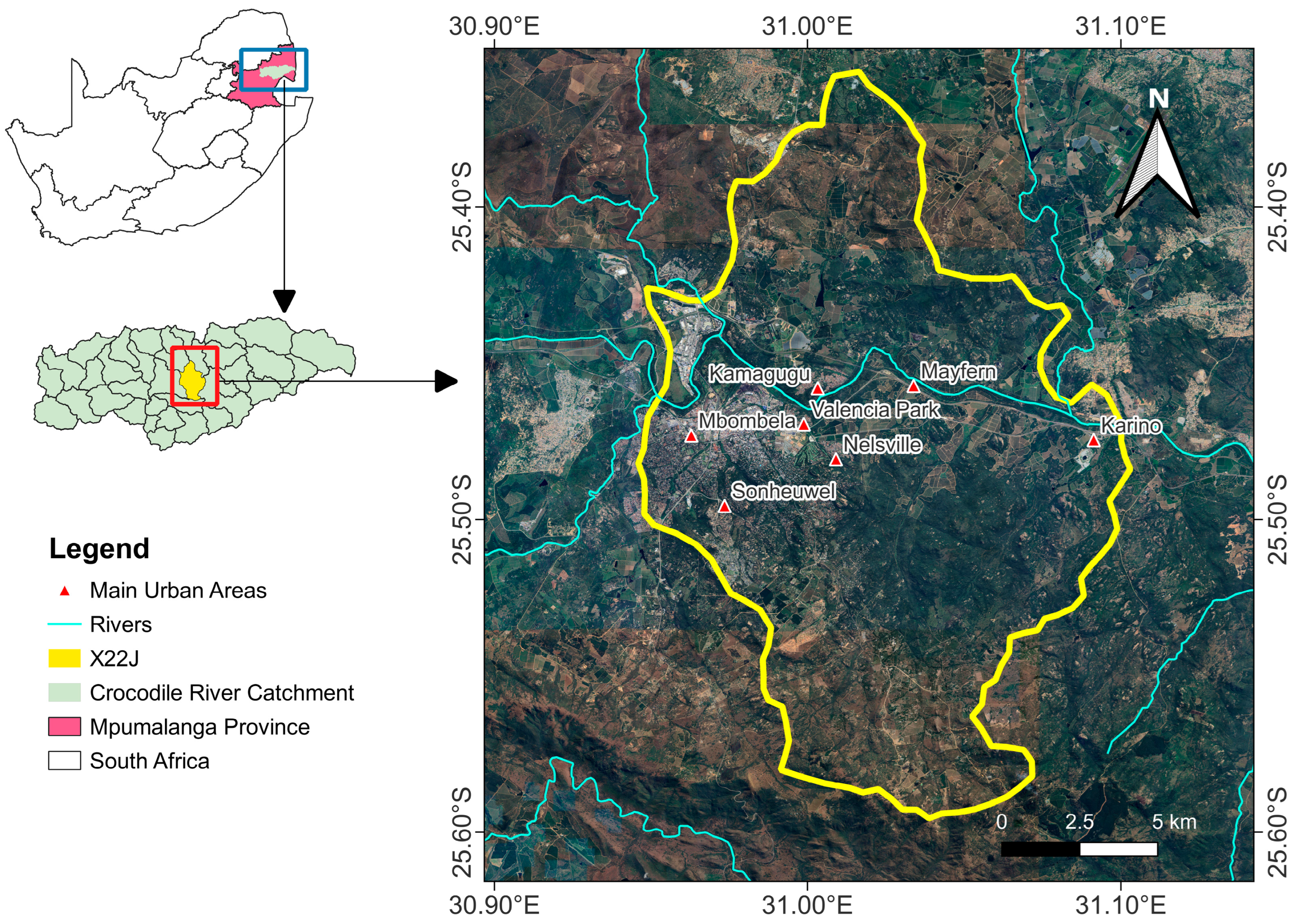
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Input Data Acquisition
2.3. LULC Classification and Analysis
2.4. Land-Use Prediction
2.4.1. Spatial Variable Data
2.4.2. The MLP–ANN Algorithm Training
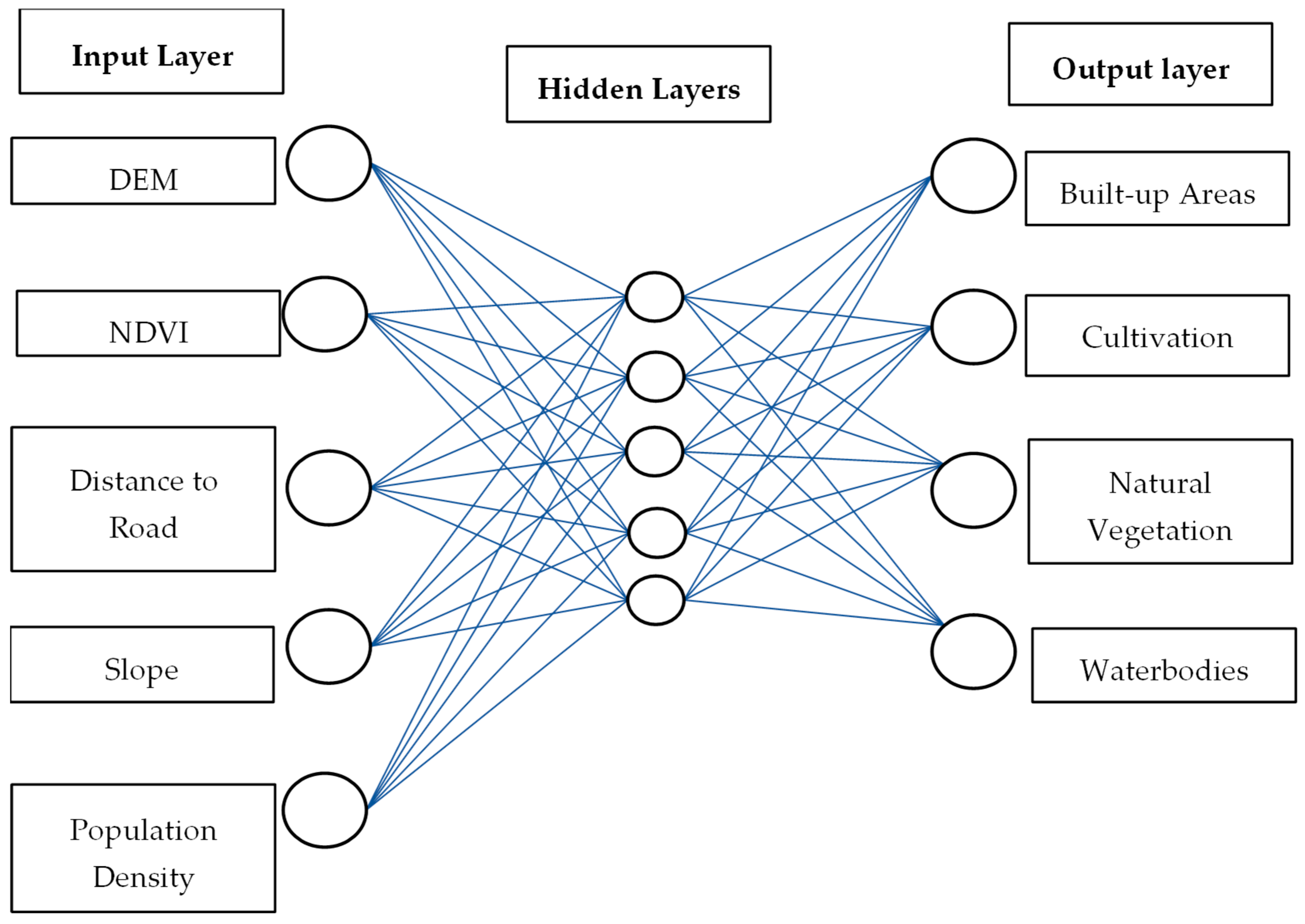
2.4.3. Accuracy Assessment and Prediction Validation
2.4.4. Magnitude of Change
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Assessment
3.1.1. Historical Land-Use Classification
3.1.2. Predicted Land-Use Classification Accuracy Assessment
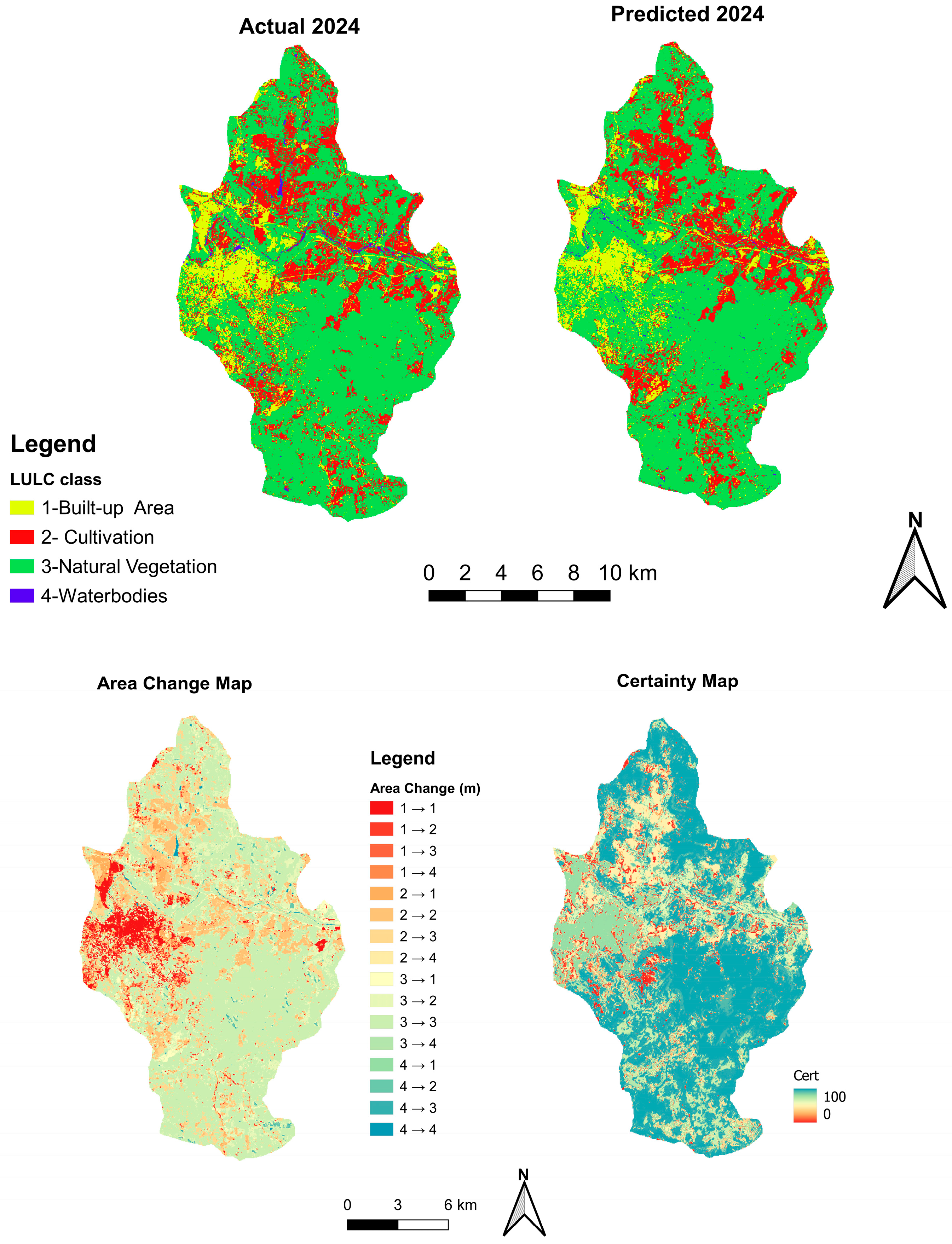
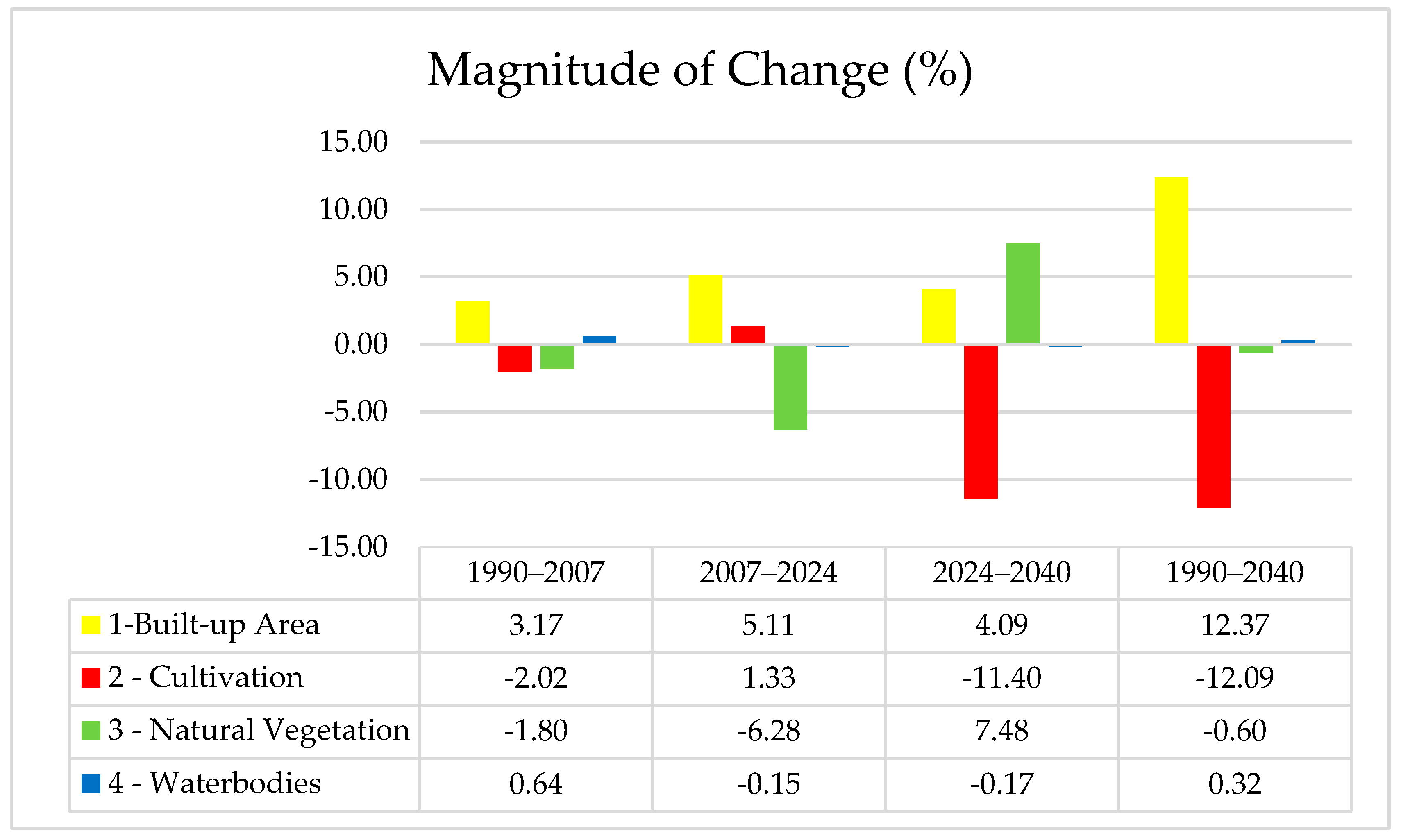
3.2. Change Detection Between 1990 and 2040
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Model
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| CA | Cellular Automation |
| COCGTA | Co-operative Governance and Traditional Affairs |
| CRC | Crocodile River catchment |
| CSIR | Council for Scientific and Industrial Research |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| GEE | Google Earth Engine |
| GIS | Geographical Information Systems |
| LULC | Land use and land cover |
| MAP | Mean annual precipitation |
| MDC | Maputo Development Corridor |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| MOLUSCE | Modules of Land Use Change Evaluation |
| PET | Potential evapotranspiration |
| QC | Quaternary catchment |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| SANSA | South African National Space Agency |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
References
- Mthiyane, D.B.; Wissink, H.; Chiwawa, N. The impact of rural–urban migration in South Africa: A case of KwaDukuza municipality. J. Local Gov. Res. Innov. 2022, 3, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, C.; Fox, B.; Morland, L.; Samways, M.; Weaver, S.; Massey, R.; Hill, M. Patterns in macroinvertebrate taxonomic richness and community assembly among urban wetlands in Cape Town, South Africa: Implications for wetland management. Urban Ecosyst. 2021, 24, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, F.; Selepe, M. Ecostatus of the Crocodile River Catchment, Inkomati River System; Department of Water and Sanitation: Pretoria, South Africa, 2013.
- Chakwizira, J. Exploring Nelspruit as a Historical Spatial Jigsaw Corridor-Based Secondary City: A Spatial Governance Geographical Perspective. In Secondary Cities and Local Governance in Southern Africa; Matamanda, A.R., Chakwizira, J., Chatiza, K., Nel, V., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Frankson, L. Hazelmere Dam Water Level Reaches Critical Levels; IFAT Africa: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schütte, S.; Schulze, R.E. Projected impacts of urbanisation on hydrological resource flows: A case study within the uMngeni Catchment, South Africa. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelokazi, S.; Amoo, O.T.; Ikudayisi, A.; Nakin, M. Investigating Water Balance Configuration in the Urban Areas of Mthatha, South Africa. Sel. Sci. Pap. J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 19, 20240019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, R.; Zhang, W.; Abbas, Z.; Guo, F.; Gwiazdzinski, L. Spatiotemporal Change Analysis and Prediction of Future Land Use and Land Cover Changes Using QGIS MOLUSCE Plugin and Remote Sensing Big Data: A Case Study of Linyi, China. Land 2022, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, H.; Samborska, V.; Roser, M. Urbanization: The World Population Is Moving to Cities. Why Is Urbanization Happening, and What Are the Consequences? Our World in Data: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kapucu, N.; Ge, Y.; Rott, E.; Isgandar, H. Urban resilience: Multidimensional perspectives, challenges and prospects for future research. Urban Gov. 2024, 4, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SANSA. The Role of Satellite-Based Remote Sensing Technologies in Support of Urban Spatial Planning; SANSA Policy Brief: Pretoria, South Africa, 2019.
- Rani, A.; Gupta, S.K.; Singh, S.K.; Meraj, G.; Kumar, P.; Kanga, S.; Ðurin, B.; Dogančić, D. Predicting Future Land Use Utilizing Economic and Land Surface Parameters with ANN and Markov Chain Models. Earth 2023, 4, 728–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekara, G.N.; Gupta, A.; Valeo, C.; Hasbani, J.G.; Qiao, Y.; Delaney, P.; Marceau, D.J. Assessing the impact of future land-use changes on hydrological processes in the Elbow River watershed in southern Alberta, Canada. J. Hydrol. 2012, 412–413, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Mao, H.; Dally, W.J. Deep Compression: Compressing Deep Neural Networks with Pruning, Trained Quantization and Huffman Coding. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.00149. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Farzana, K.; Papia, M.; Hasan, M. Monitoring and Prediction of Land Use/Land Cover Change using the Integration of Markov Chain Model and Cellular Automation in the Southern Tertiary Hilly Area of Bangladesh. Int. J. Sci. Basic Appl. Res. IJSBAR 2015, 24, 125–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Guan, Q.; Lin, J.; Luo, H.; Tan, Z.; Ma, Y. Simulating land use/land cover change in an arid region with the coupling models. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungai, L.M.; Messina, J.P.; Zulu, L.C.; Qi, J.; Snapp, S. Modelling Spatiotemporal Patterns of Land Use/Land Cover Change in Central Malawi Using a Neural Network Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganasri, B.P.; Raju, A.; Dwarakish, G.S. Different Approaches for Land Use Land Cover Change Detection: A Review. PRJET 2023, 2, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Basse, R.M.; Omrani, H.; Charif, O.; Gerber, P.; Bódis, K. Land use changes modelling using advanced methods: Cellular automata and artificial neural networks. The spatial and explicit representation of land cover dynamics at the cross-border region scale. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 53, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihamta, N.; Soffianian, A.; Fakheran, S.; Gholamalifard, M. Using the SLEUTH urban growth model to simulate future urban expansion of the Isfahan metropolitan area, Iran. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2015, 43, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnenfeld, Z.; Crookes, C.; Hedden, S. A Delicate Balance: Water Scarcity in South Africa; Southern Africa Report; WRC: Pretorisa, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Turok, I.; Borel-Saladin, J. Is urbanisation in South Africa on a sustainable trajectory? Dev. S. Afr. 2014, 31, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, H.; Arabi, M.; Warziniack, T.; Sharvelle, S. Effects of Urban Development Patterns on Municipal Water Shortage. Front. Water 2021, 3, 694817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambe, T.R.; Turok, I.; Visagie, J. The trajectories of urbanisation in Southern Africa: A comparative analysis. Habitat. Int. 2023, 132, 102747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpepho, L. Urbanisation and Migration in South Africa: Global Trends. Economy & Politics. 2024. Available online: https://www.meer.com/en/79655-urbanisation-and-migration-in-south-africa-global-trends (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Kafy, A.A.; Saha, M.; Faisal, A.; Rahaman, Z.A.; Rahman, M.T.; Liu, D.; Fattah, M.A.; Al Rakib, A.; AlDousari, A.E.; Rahaman, S.N.; et al. Predicting the impacts of land use/land cover changes on seasonal urban thermal characteristics using machine learning algorithms. Build. Environ. 2022, 217, 109066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdeniz, H.B.; Sag, N.S.; Inam, S. Analysis of land use/land cover changes and prediction of future changes with Land Changes Modeler: Case of Belek, Turkey. Res. Square 2022, 95, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entahabu, H.H.; Minale, A.S.; Birhane, E. Modeling and Predicting Land Use/Land Cover Change Using the Land Change Modeler in the Suluh River Basin, Northern Highlands of Ethiopia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaldah, H.A. Prediction of Future Land Use/Land Cover in Amman Area Using GIS-Based Markov Model and Remote Sensing. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2016, 8, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyemang, F.S.; Silva, E.; Poku-Boansi, M. Understanding the urban spatial structure of Sub-Saharan African cities using the case of urban development patterns of a Ghanaian city-region. Habitat Int. 2019, 85, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, G.; Clarke, K.C. The SLEUTH Land Use Change Model: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2013, 1, 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Nkosi, M. Impacts of Land Management on Water Resources in the Crocodile River Catchment, Mpumalanga. Master’s Dissertation, University of Venda, Thohoyandou, South Africa, May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- City of Mbombela. Spatial Development Framework Review-Working Document; City of Mbombela: Mbombela, South Africa, 2018.
- CSIR. Mbombela Local Municipality: Climate Risk Profile Report. GIZ. 2023. Available online: https://greenbook.co.za/documents/GIZ_RiskProfile_MbombelaLM_Sep2023.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Buğday, E.; Erkan-Buğday, S. Modeling and simulating land use/cover change using artificial neural network from remotely sensing data. CERNE 2019, 25, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, W.; Elias, E.; Warkineh, B.; Tekalign, M.; Abebe, G. Modeling of land use and land cover changes using Google Earth Engine and machine learning approach: Implications for landscape management. Environ. Syst. Res. 2024, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negash, E.D.; Asfaw, W.; Walsh, C.L.; Mengistie, G.K.; Haile, A.T. Effects of land use land cover change on streamflow of Akaki catchment, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, Z.; Kazmi, J.H.; Shaikh, S.; Arshad, S.; Mohammed, S. Random forest-based analysis of land cover/land use LCLU dynamics associated with meteorological droughts in the desert ecosystem of Pakistan. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, H.A.; Kalakech, A.; Steiti, A. Random Forest Algorithm Overview. Babylon. J. Mach. Learn. 2024, 159, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S. Improving Land Use/Cover Classification Accuracy from Random Forest Feature Importance Selection Based on Synergistic Use of Sentinel Data and Digital Elevation Model in Agriculturally Dominated Landscape. Agriculture 2022, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahun, M.; Legesse, A. Machine learning for urban land use/cover mapping: Comparison of artificial neural network, random forest and support vector machine, a case study of Dilla town. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maithani, S. A Neural Network based Urban Growth Model of an Indian City. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2010, 37, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaraj, M.; Rangarajan, S. Predicting the Future Land Use and Land Cover Changes for Bhavani Basin, Tamil Nadu, India Using QGIS MOLUSCE Plugin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 86337–86348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkolokosa, C.; Stothard, R.; Jones, C.M. Monitoring and simulating landscape changes: How do long-term changes in land use and long-term average climate affect regional biophysical conditions in southern Malawi? Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NEXTGIS. MOLUSCE-Quick and Convenient Analysis of Landcover Changes. 2007. Available online: https://nextgis.com/blog/molusce/ (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Alshari, E.A.; Gawali, B.W. Modeling Land Use Change in Sana’a City of Yemen with MOLUSCE. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 419031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tola, B.; Deyassa, G. A modeling approach for evaluating and predicting the impacts of land use land cover changes on groundwater recharge in Walga Watershed, Upper Omo Basin, Central Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 51, 101659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramantio, B.; Hizbaron, D.R.; Khakhim, N. Prediction of the future landuse and land cover changes in the Parangtritis sand dune: A spatio-temporal analysis using QGIS MOLUSCE. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1313, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, R.; Zardari, B.A. Artificial Neural Networks: An overview. Meso. J. Comp. Sci. 2023, 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Guillén, L.A. Accuracy Assessment in Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Learning Remote Sensing Studies—Part 1: Literature Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Diego, I.M.; Redondo, A.R.; Fernández, R.R. General Performance Score for classification problems. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 12049–12063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prantl, T.; Barthel, T.; Kaiser, D.; Schwinger, M.; Bauer, A.; Kounev, S. Challenges in the evaluation of Earth observation products: Accuracy assessment case study using convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2024, 37, 101420. [Google Scholar]
- Talukdar, S.; Eibek, K.U.; Akhter, S.; Ziaul, S.; Towfiqul Islam, A.R.M.; Mallick, J. Modelling fragmentation probability of land-use and land-cover using the bagging, random forest and random subspace in the Teesta River Basin, Bangladesh. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammaboribal, P.; Triphathi, N.K. Predicting Land Use and Land Cover Change Pathumthani, Thailand: A Comprehensive Analysis from 2013–2023 Using Landsat Satellite Imagery and CA-ANN Algorithm, with Projections for 2028 and 2038. Int. J. Geoinf. 2024, 20, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Mawenda, J.; Watanabe, T.; Avtar, R. An Analysis of Urban Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Blantyre City, Southern Malawi (1994–2018). Sustainability 2019, 12, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Mubeen, M.; Nasim, W.; Mumtaz, F.; Abdo, H.G.; Mostafazadeh, R.; Fahad, S. Assessment of future prediction of urban growth and climate change in district Multan, Pakistan using CA-Markov method. Urban Clim. 2023, 53, 101766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Değermenci, A.S. Spatio-temporal change analysis and prediction of land use and land cover changes using CA-ANN model. Environ. Monit. Assess 2023, 195, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- City of Mbombela. Climate Change Response Strategy and Implementation Plan (Internal Draft); City of Mbombela: Mbombela, South Africa, 2017.
- Bhatta, B. Analysis of Urban Growth and Sprawl from Remote Sensing Data; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, R.; Saleh, M.T.M. Remote Sensing and GIS-Based LULC Prediction in Shah Alam: A Strategy for Sustainable Urban Growth and Development. Bioresour. Environ. 2024, 2, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

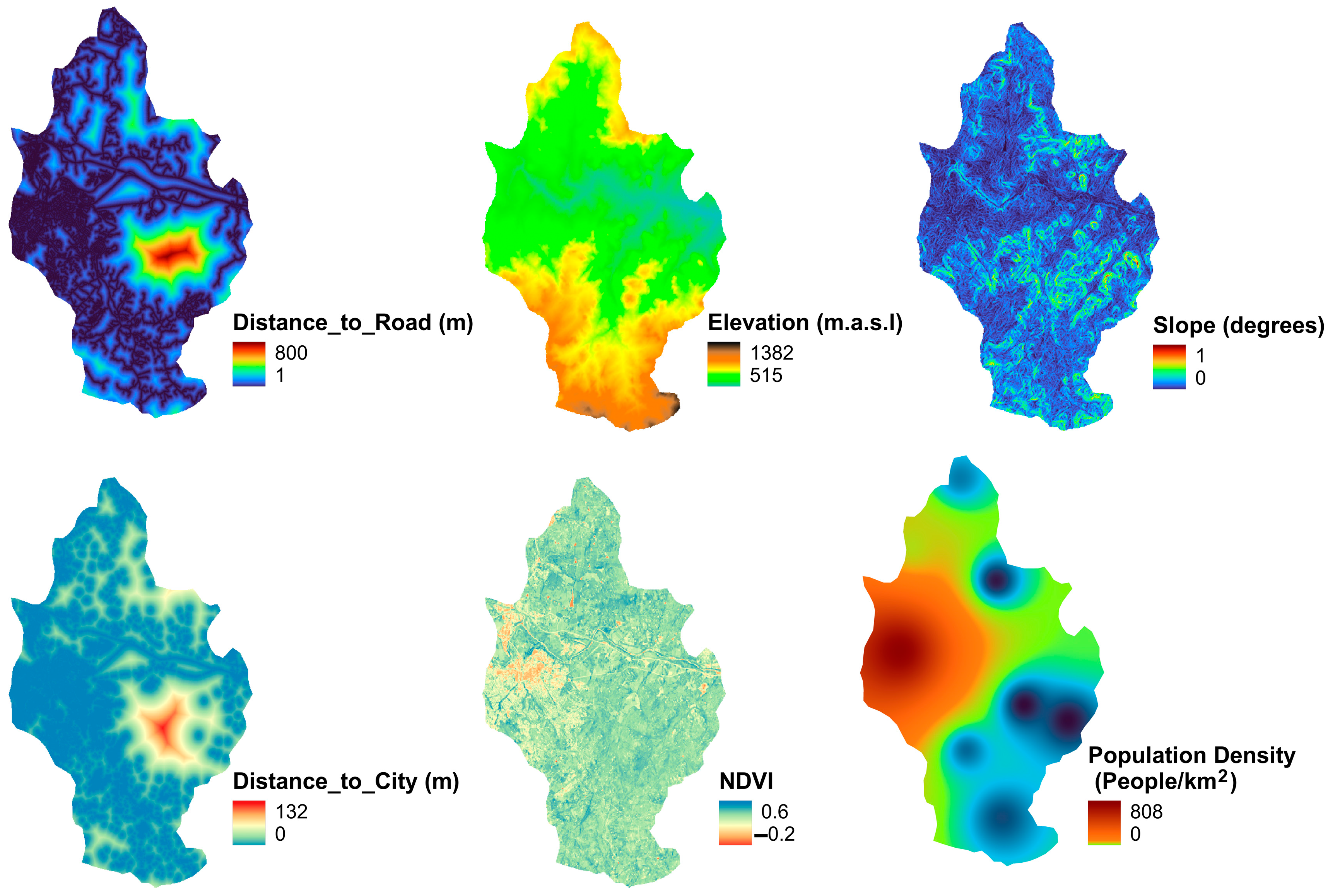


| Data Type | Description | Source | Resampled Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS) World 3D-30m Digital Surface Model (DSM) | Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) https://www.eorc.jaxa.jp/ALOS/en/dataset/aw3d30/aw3d30_e.htm (accessed on 15 April 2023) | 30 |
| Satellite Images | Landsat 4-5 TM (for 1990, 2007) Sentinel-1-2 (or 2024) | Google Earth Engine (GEE) https://code.earthengine.google.com/ (accessed on 04 May 2024) | 30 |
| Population Data | The latest population and population density data were used to create the population density variable map | Statistics of South Africa (Stats SA) https://www.statssa.gov.za/?page_id=993&id=mbombela-municipality (accessed on 16 May 2024) | 30 |
| Open Street Data | The latest open street data were used as a spatial variable for land-use prediction | Humanitarian Data Exchange https://data.humdata.org/dataset/hotosm_zaf_roads (accessed on 20 August 2023) | 30 |
| Built-up Areas | Extracted from the South African National Land Cover data | Department of Forestry, Fisheries, and Environment https://www.dffe.gov.za/egis (accessed on 20 August 2023) | 30 |
| Slope | Distance to Road | Distance to City | NDVI | DEM | Pop Density | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | 0.27 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.28 | −0.22 | |
| Distance to Road | 0.84 | 0.2 | −0.04 | −0.29 | ||
| Distance to City | 0.12 | −0.05 | −0.27 | |||
| NDVI | 0.1 | −0.4 | ||||
| DEM | −0.28 | |||||
| Population Density | ||||||
| Class | 1-Built-Up | 2-Cultivation | 3-Natural Vegetation | 4-Water | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Built-Up | 21 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 24 |
| 2-Cultivation | 2 | 25 | 1 | 0 | 28 |
| 3-Natural Vegetation | 0 | 2 | 39 | 0 | 41 |
| 4-Water | 0 | 0 | 4 | 15 | 19 |
| Total | 23 | 29 | 45 | 15 | 112 |
| Producer | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 0.79 | |
| User | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 1 |
| Class | 1-Built-Up | 2-Cultivation | 3-Natural Vegetation | 4-Water | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Built-Up | 29 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 31 |
| 2-Cultivation | 1 | 31 | 2 | 0 | 34 |
| 3-Natural Vegetation | 0 | 0 | 37 | 0 | 37 |
| 4-Water | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 20 |
| Total | 30 | 32 | 40 | 20 | 122 |
| Producer | 0.94 | 0.91 | 1 | 1.00 | |
| User | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 1.00 |
| Class | 1-Built-Up | 2-Cultivation | 3-Natural Vegetation | 4-Water | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Built-Up | 48 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 53 |
| 2-Cultivation | 1 | 49 | 5 | 0 | 55 |
| 3-Natural Vegetation | 5 | 2 | 69 | 3 | 79 |
| 4-Water | 0 | 1 | 0 | 19 | 20 |
| Total | 54 | 56 | 75 | 22 | 207 |
| Producer | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.95 | |
| User | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 1.00 |
| Land-Use Class | Simulated 2024 (%) | Predicted 2024 (%) | The Magnitude of Change (Discrepancy) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Built-Up Area | 12.52 | 12.08 | 0.44 |
| 2-Cultivation | 23.31 | 22.26 | 1.05 |
| 3-Natural Vegetation | 63.32 | 64.98 | −1.66 |
| 4-Waterbodies | 0.85 | 0.68 | 0.17 |
| Class | 1-Built-Up | 2-Cultivation | 3-Natural Vegetation | 4-Water | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Built-Up | 22,486 | 3572 | 4986 | 875 | 31,919 |
| 2-Cultivation | 3976 | 34,322 | 20,261 | 379 | 58,938 |
| 3-Natural Vegetation | 6411 | 24,486 | 140,809 | 338 | 172,044 |
| 4-Water | 84 | 180 | 725 | 807 | 1796 |
| Total | 32,957 | 62,560 | 166,781 | 2399 | 264,697 |
| Producer | 0.70 | 0.58 | 0.82 | 0.45 | |
| User | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.84 | 0.34 |
| Class | 1990 (%) | 2007 (%) | 2024 (%) | 2040 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Built-Up | 4 | 7 | 13 | 17 |
| 2-Cultivation | 24 | 22 | 23 | 12 |
| 3-Natural Vegetation | 71 | 70 | 63 | 71 |
| 4-Water | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2007 | 2024 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | Class | 1-Built-Up | 2-Cultivation | 3-Natural Vegetation | 4-Water | 2007 | Class | 1-Built-Up | 2-Cultivation | 3-Natural Vegetation | 4-Water |
| 1-Built-Up | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0 | 1-Built-Up | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0 | ||
| 2-Cultivation | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0 | 2-Cultivation | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0 | ||
| 3-Natural Vegetation | 0 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0 | 3-Natural Vegetation | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0 | ||
| 4-Water | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 4-Water | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | ||
| 2040 | 2040 | ||||||||||
| 2024 | Class | 1-Built-up | 2-Cultivation | 3-Natural Vegetation | 4-Water | 1990 | Class | 1-Built-up | 2-Cultivation | 3-Natural Vegetation | 4-Water |
| 1-Built-Up | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0 | 1-Built-Up | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0 | ||
| 2-Cultivation | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0 | 2-Cultivation | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0 | ||
| 3-Natural Vegetation | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0 | 3-Natural Vegetation | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0 | ||
| 4-Water | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 4-Water | 0.2 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.1 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nkosi, M.; Mathivha, F.I. The Application of CA–MLP–ANN in Assessing Urbanisation in Quaternary Catchment X22J of Mpumalanga, South Africa. Land 2025, 14, 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112099
Nkosi M, Mathivha FI. The Application of CA–MLP–ANN in Assessing Urbanisation in Quaternary Catchment X22J of Mpumalanga, South Africa. Land. 2025; 14(11):2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112099
Chicago/Turabian StyleNkosi, Mary, and Fhumulani I. Mathivha. 2025. "The Application of CA–MLP–ANN in Assessing Urbanisation in Quaternary Catchment X22J of Mpumalanga, South Africa" Land 14, no. 11: 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112099
APA StyleNkosi, M., & Mathivha, F. I. (2025). The Application of CA–MLP–ANN in Assessing Urbanisation in Quaternary Catchment X22J of Mpumalanga, South Africa. Land, 14(11), 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112099








