The Human–Nature Paradox: Spatiotemporal Coupling and Drivers of Habitat Quality and Human Footprint in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
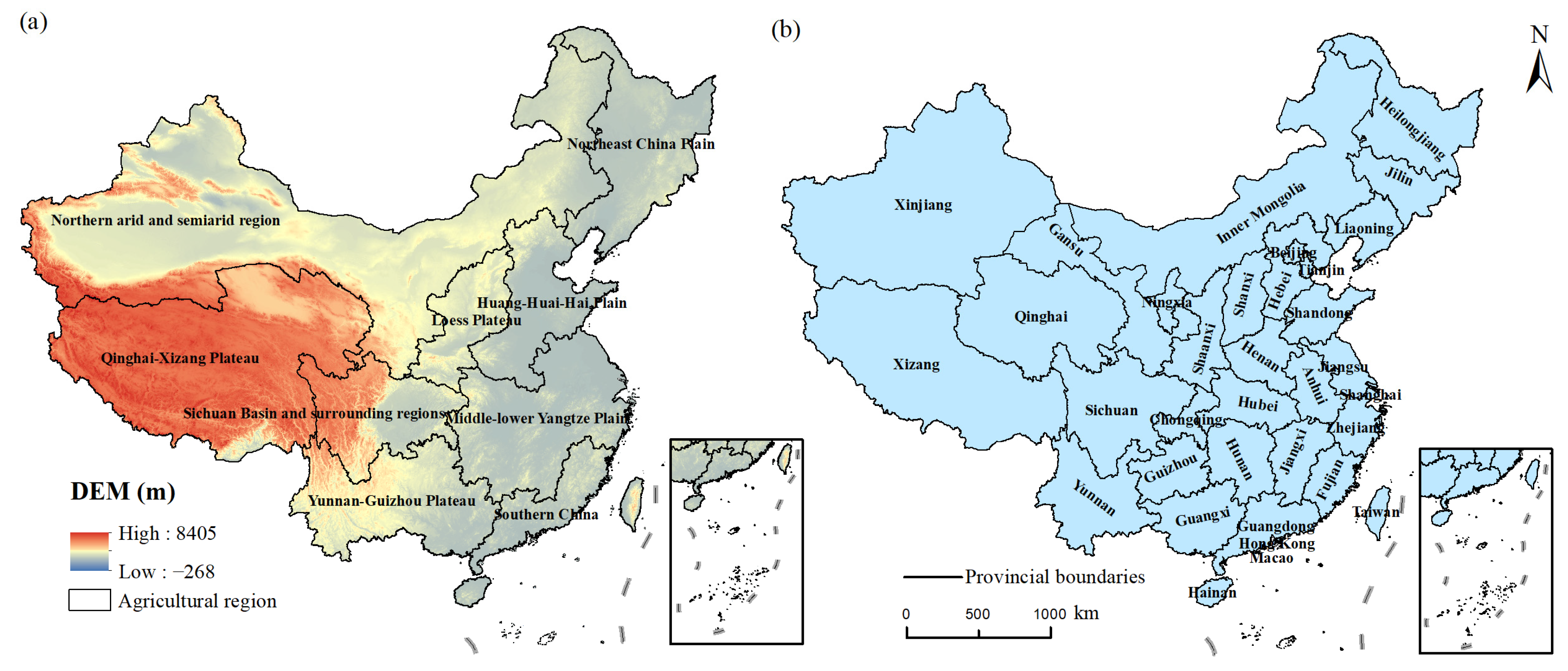
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Land Use Data
2.2.2. HFP Data
2.2.3. Driving Factor Data
| Data Type | Utilization | Data Source | Website | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land use data | Calculate HQ | National Cryosphere Desert Data Center | https://www.ncdc.ac.cn/portal/ (accessed on 15 December 2024) | 30 m |
| Human footprint Data | Calculate HFP | Urban Environmental Monitoring and Modeling (UEMM) team of China Agricultural University | https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/_b_Tracking_spatiotemporal_dynamics_of_crop-specific_areas_through_machine_learning_and_statistics_disaggregating_b_/26028769 (accessed on 15 December 2024) | 1 km |
| Natural environment data | Digital Elevation Model (DEM, X1) and slope (X2) | Geospatial Data Cloud | http://www.gscloud.cn/ (accessed on 15 December 2024) | 30 m |
| Annual average temperature (X3) and Annual average precipitation (X4) | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center | https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/ (accessed on 15 December 2024) | 1 km | |
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI, X5) | EARTHDATA | https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 15 December 2024) | 500 m | |
| Socioeconomic data | Population density (X6) | LANDSCANS | https://landscan.ornl.gov/ (accessed on 15 December 2024) | 1 km |
| Night-time lights (X7) | National Earth System Science Data Center | http://www.geodata.cn/ (accessed on 15 December 2024) | 500 m | |
| Gross domestic product (GDP, X8) | Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform | https://www.resdc.cn/Default.aspx (accessed on 15 December 2024) | 1 km | |
| Calculate land use intensity (LUI, X9) [48] | National Cryosphere Desert Data Center | https://www.ncdc.ac.cn/portal/ (accessed on 15 December 2024) | 30 m |
2.3. Evaluation Analysis Module
2.3.1. InVEST-HQ Model
2.3.2. CCD Model
2.3.3. GeoDetector
3. Results
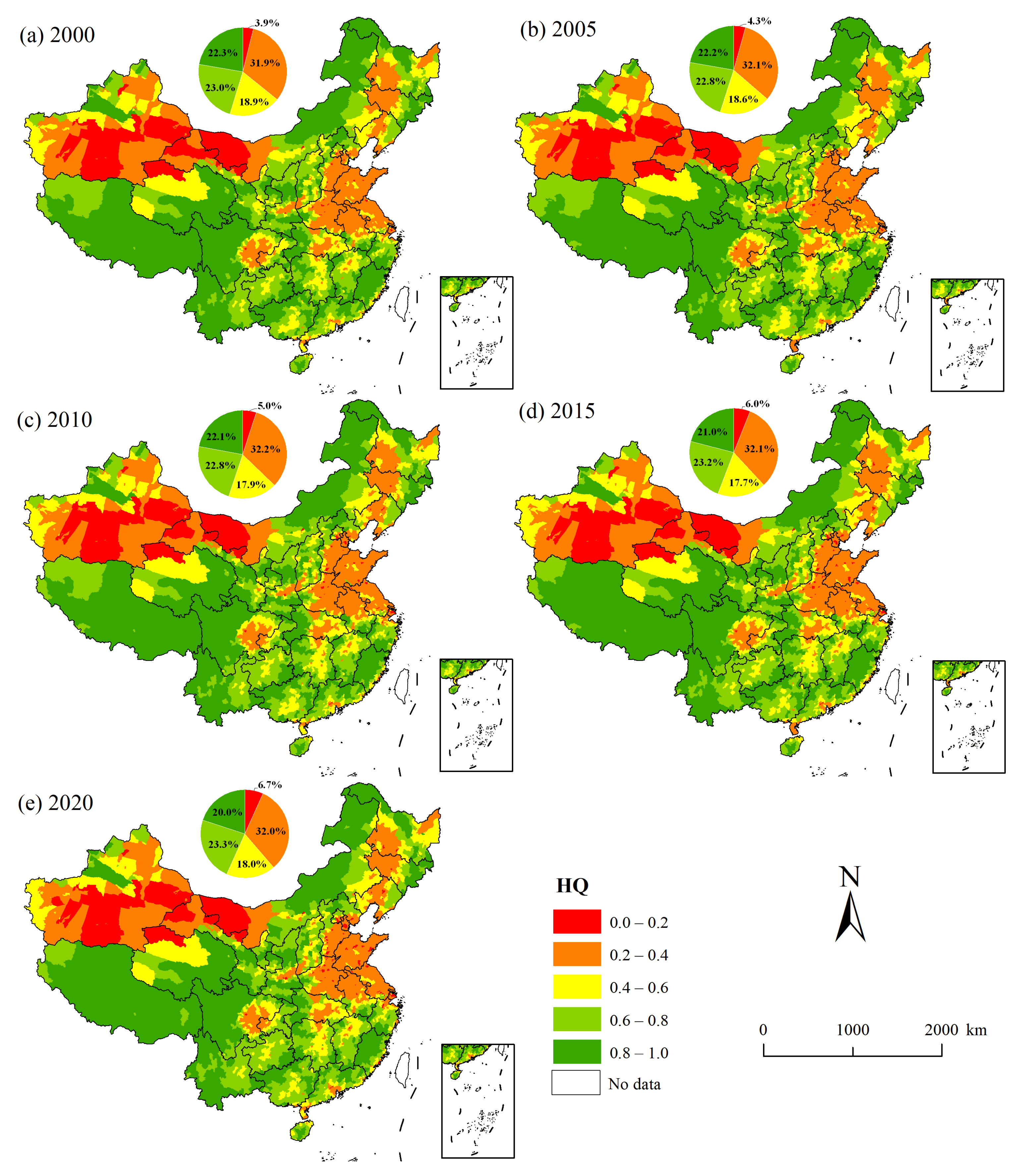
3.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of HQ in China from 2000 to 2020
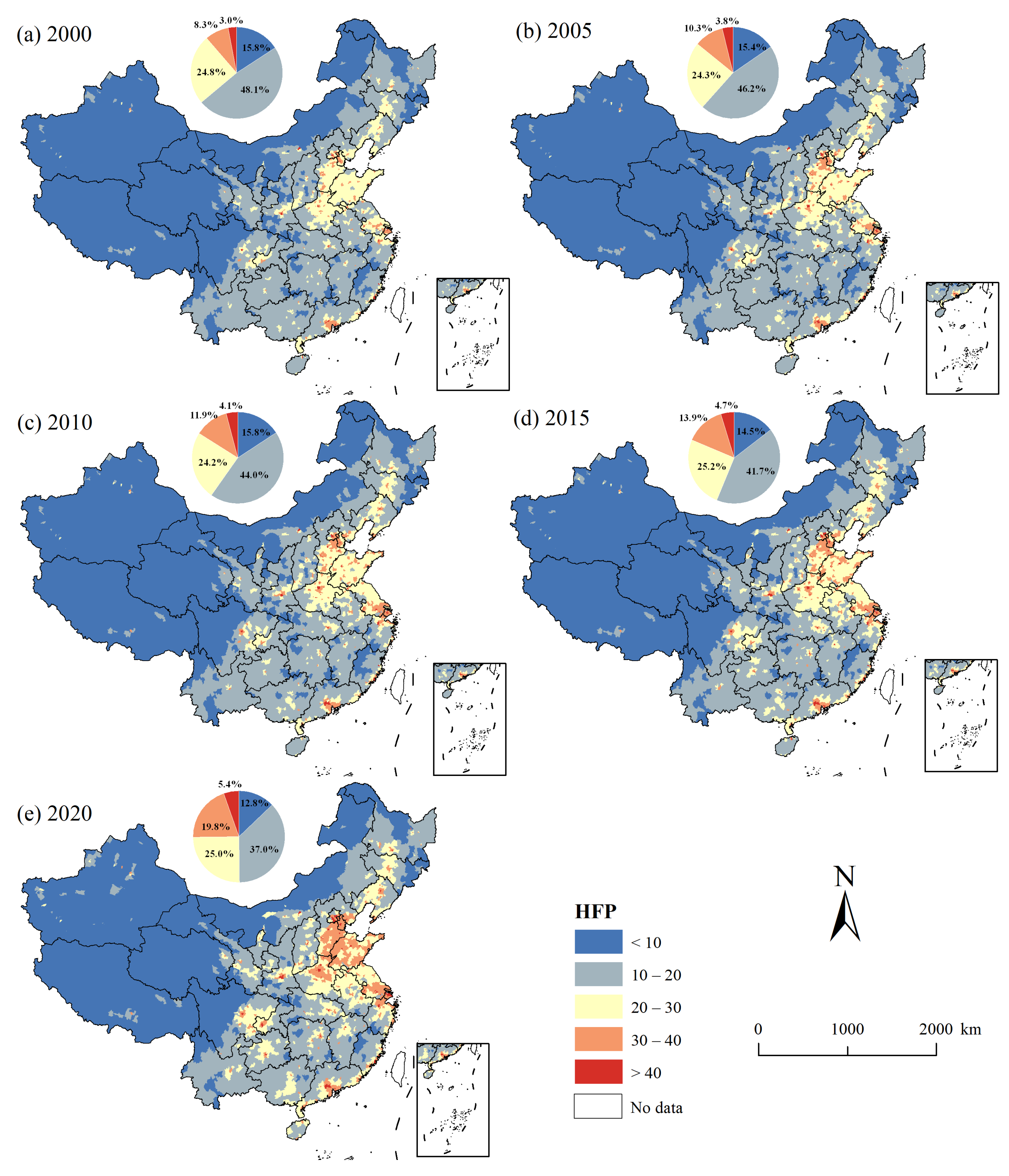
3.2. Spatiotemporal Patterns of HFP in China from 2000 to 2020
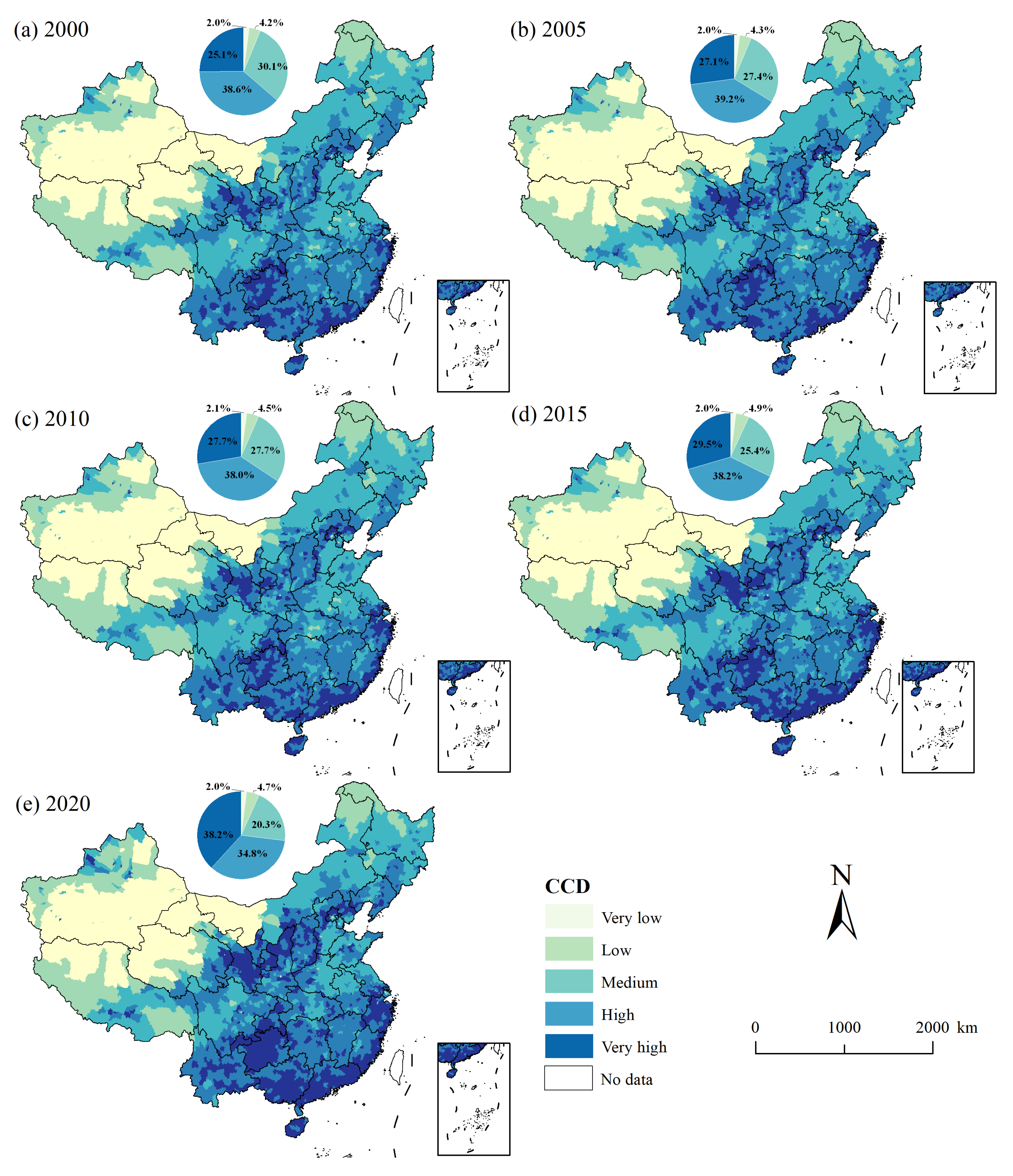
3.3. CCD Between HFP and HQ
3.4. Driving Factors of CCD Between HFP and HQ
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpretation of Findings
4.2. Spatial and Temporal Heterogeneity of Driving Factors for the CCD
4.3. Policy Implications
4.4. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.; Wu, N.; Lu, T. Mapping human footprint changes over Qingzang Plateau. Geo. Sus. 2025, 6, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraci, J.P.; Gaynor, K.M.; Allen, M.L.; Alexander, P.; Brashares, J.S.; Cendejas-Zarelli, S.; Crooks, K.; Elbroch, L.M.; Forrester, T.; Green, A.M.; et al. Disturbance type and species life history predict mammal responses to humans. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 3718–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, E.B.; Glidden, C.K.; MacDonald, A.J.; Mordecai, E.A. Human footprint is associated with shifts in the assemblages of major vector-borne diseases. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Lu, L.; Qin, C. Towards ecological security: Two-thirds of China’s ecoregions experienced a decline in habitat quality from 1992 to 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Tian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Bai, T.; Song, Z.; Sun, K. Human activities dominantly driven the greening of China during 2001 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.N.; Li, C.; Feng, J.M. The protected areas system policy enhances habitat quality conservation effectiveness in Dongting Lake Eco-Economic Zone. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 504, 145425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolyomi, A.; Franklin, A.; Smith, B.; Soliev, I. Ecosystem services as the silver bullet? A systematic review of how ecosystem services assessments impact biodiversity prioritisation in policy. Earth Syst. Gov. 2023, 16, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; Darge, R.C.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.E.; Naeem, S.; Oneill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.M. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, M.Y.; Zhong, Y.X.; Xiao, Z.P.; Feng, X.H.; Ma, H.Z. Spatial and temporal change of habitat quality of Poyang Lake Basin in China at small watershed scale and its multidimensional response to landscape pattern. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Xie, Y.; Cao, E.; Huang, Q.; Li, H. Integration of InVEST-habitat quality model with landscape pattern indexes to assess mountain plant biodiversity change: A case study of Bailongjiang watershed in Gansu Province. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 1193–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolcato, S.; Aplin, L. The effect of habitat health and environmental change on cultural diversity and richness in animals. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2025, 380, 20240141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, Y.; Kim, D.G.; Son, J.; Park, J.; Lee, J. The importance of the Mujechineup wetland for biodiversity: An evaluation of habitat quality and ecosystem service value. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 18, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, A.; Kim, M.; Lee, S. Analysis of priority conservation areas using habitat quality models and MaxEnt models. Animals 2024, 14, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jato-Espino, D.; Lierow, S. Spatiotemporal analysis of landscape dynamics and their use as input for the design of a habitat suitability index: A case study of in a Mediterranean region. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 82, 102731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrouse, B.C.; Semmens, D.J. Social values for Ecosystem services, version 3.0 (SolVES 3.0)—Documentation and user manual. In Open-File Report 2015–1008; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sahle, M.; Almarines, N.R.; Lahoti, S.A.; Tiburan, C.L.; Pulhin, J.M.; Saito, O. Exploring the interplay between food provision and habitat quality assessment for sustainable coexistence in the bioproduction systems of the Philippines. Resources 2025, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yang, L.; Fang, Q.; Yao, X. Impact of landscape pattern on habitat quality in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2000 to 2030. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čistý, M.; Doláková, G.; Štefunková, Z. A methodology simplifying river habitat quality assessment through regression analysis: Application in Slovakia. Environ. Process. 2025, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, M. Understanding spatiotemporal changes and influencing factors in the habitat quality of coastal waters: A case study of Jiangsu Province, China (2006–2020). Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 113125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Duan, B.; Pan, S.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y. Global urbanization and habitat quality: Interactive coercive relationships. Land 2024, 13, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohannes, H.; Soromessa, T.; Argaw, M.; Dewan, A. Spatio-temporal changes in habitat quality and linkage with landscape characteristics in the Beressa watershed, Blue Nile basin of Ethiopian highlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Tang, Z.S.; Xue, L.Y.; Zhang, W.L.; Zhang, J. Driving mechanisms of ecosystem services and their trade-offs and synergies in the transition zone between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabikandi, B.V.; Shahbazi, F.; Biswas, A. Evaluating ecosystem services under various trajectories and land use/land cover changes in a densely populated area, Iran. Earth Sci. Inform. 2025, 18, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segan, D.B.; Murray, K.A.; Watson, J.E.M. A global assessment of current and future biodiversity vulnerability to habitat loss–climate change interactions. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2016, 5, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Chen, X.; Lu, T. Assessing the impacts of historical and future land-use/cover change on habitat quality in the urbanizing Lhasa River Basin on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, N.; Hao, Z.Z.; Sun, B.; Gao, B.T.; Gou, M.M.; Wang, P.; Pei, N.C. Urbanization intensifies the imbalance between human development and biodiversity conservation: Insights from the coupling analysis of human activities and habitat quality. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 3606–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Lu, M.; Uddin, M.; Wang, M.; Su, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Hu, J. Impacts of land use change on habitat quality and its driving mechanisms in the lake basin of Central Yunnan. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 18318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ao, Y.; Han, L.; Kang, S.Z.; Sun, Y.Y. Effects of human activity intensity on habitat quality based on nighttime light remote sensing: A case study of Northern Shaanxi, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 113148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.W. The Human Footprint and the Last of the Wild. BioScience 2002, 52, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.R.; Venter, O.; Fuller, R.A.; Allan, J.R.; Maxwell, S.L.; Negret, P.J.; Watson, J.E.M. One-third of global protected land is under intense human pressure. Science 2018, 360, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Li, X.; Wen, Y.; Huang, J.; Du, P.; Su, W.; Miao, S.; Geng, M. A global record of annual terrestrial Human Footprint dataset from 2000 to 2018. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.A.; Venter, O.; Allan, J.R.; Atkinson, S.C.; Rehbein, J.A.; Ward, M.; Di Marco, M.; Grantham, H.S.; Ervin, J.; Goetz, S.J.; et al. Change in terrestrial human footprint drives continued loss of intact ecosystems. One Earth 2020, 3, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, O.; Sanderson, E.W.; Magrach, A.; Allan, J.R.; Beher, J.; Jones, K.R.; Possingham, H.P.; Laurance, W.F.; Wood, P.; Fekete, B.M.; et al. Sixteen years of change in the global terrestrial human footprint and implications for biodiversity conservation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.Z.; Liu, Y.Q. Heterogeneous impacts of human activities and climate change on transformed vegetation dynamics on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 392, 126575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Jin, X.; Mu, H.; Yang, S.; He, R.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, S.; Zu, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Impacts of human footprint on habitat quality and permafrost environment in Northeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 175, 113587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.; Xu, X.; Meng, J.; Wang, Z. Vulnerabilities of protected lands in the face of climate and human footprint changes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, C. Spatiotemporal evolution and coupling analysis of human footprints and habitat quality: Evidence of 21 consecutive years in China. Land 2024, 13, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, B.A.; Suraci, J.P.; Allen, M.L.; Wilmers, C.C. Human presence and human footprint have non-equivalent effects on wildlife spatiotemporal habitat use. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 241, 108383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Bian, C.; Pan, S.; Chen, W.; Zeng, J.; Xu, H.; Gu, T. Assessing the conservation effectiveness of the World’s protected areas: A habitat quality and human activities perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 431, 139772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Yao, Y.; Dang, X.; Li, X.; Hou, M.; Deng, Y.; Xiao, L.; Li, T.; Wang, T. Study on the trade-off/synergy between ecosystem services and human well-being based on land use in Weinan City, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 13549–13562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Economic growth and the environment. Q. J. Econ. 1995, 110, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Xu, Z.Q.; Chen, Y.D.; Gu, S.H.; Li, C. Impacts of landscape patterns on habitat quality in coal resource-exhausted cities: Spatial-temporal dynamics and non-stationary scale effects. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.D.; Chang, J.; Li, Z.X.; Ming, L.; Li, C.K. Influence of land use change on habitat quality: A case study of coal mining subsidence areas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Yan, K.; Wang, H.; Luo, M.; Ma, B.; Zhao, W.; Wang, W. A framework for assessing the impact of human pressure on priority core habitats of rare and endangered species. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 178, 114051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, L.; Domingos, T.; Santos, J.; Proença, V. How do bird population trends relate to human pressures compared to economic growth? Sustainability 2025, 17, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zeng, J.; Li, N. Change in land-use structure due to urbanisation in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.; Tallis, H.T.; Ricketts, T.; Guerry, A.D.; Wood, S.A.; Chaplin-Kramer, R. InVEST 3.7.0 User’s Guide; The Natural Capital Project: Standford, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Z.L.; Xiao, C.W.; Feng, Z.M.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.M. Accelerating decline of habitat quality in Chinese border areas. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 206, 107665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Zuo, D.Y.; Gong, Z.Q. How does the coupling coordination relationship between high-quality urbanization and land use evolve in China? New evidence based on exploratory spatiotemporal analyses. J. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Y.B.; Sheng, M.C.; Li, T.; Shao, J.A.; Zhao, W.X. Coupling response of ecosystem service value to human activity intensity in mountainous areas: A case study of the Three Gorges Reservoir Hinterland, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 1356–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Bai, X.; Hu, F.; Zhang, K.; Wang, S. The coupling relationship and driving mechanism between ecological environment and high-quality economic development in the Middle Yellow River Basin. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.B.; Cui, Y.Y.; Zhen, J.L.; Huang, G.H. Spatio-temporal change of habitat quality in northeast china: Driving factors exploration based on land use and land cover change. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 3742–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.; Civco, D.L.; Blei, A.; Potere, D. The dimensions of global urban expansion: Estimates and projections for all countries, 2000–2050. Prog. Plann. 2011, 75, 53–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Giineralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, G.; Huang, X. Coupling coordination analysis of urban social vulnerability and human activity intensity. Environ. Res. Commun. 2025, 7, 035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhou, L.; Dang, X.; Hu, F.; Yuan, B.; Yuan, Z.; Wei, L. Impacts and predictions of urban expansion on habitat quality in the densely populated areas: A case study of the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra dos Santos, L.C.; Frimaio, A.; Giannetti, B.F.; Agostinho, F.; Liu, G.; Almeida, C.M.V.B. Integrating environmental, social, and economic dimensions to monitor sustainability in the G20 countries. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, X.B.; Lyu, X.; Dang, D.L.; Cao, W.Y.; Du, Y.X. Unraveling the complex interconnections between food-energy-water nexus sustainability and the supply-demand of related ecosystem services. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122532. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, J. The Chinese socio-cultural sustainability approach: The impact of conservation planning on local population and residential mobility. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, W.; Fang, C.; Zeng, J. How does the coordinated development of population urbanization and land urbanization affect residents’ living standards? Empirical evidence from China. Cities 2024, 149, 104922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, Z.; Bergantino, A.S.; Intini, M.; Elia, M.; Buongiorno, A.; Giannico, V.; Sanesi, G.; Lafortezza, R. Nighttime light extent and intensity explain the dynamics of human activity in coastal zones. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yuan, Y.; Gu, T.; Ma, H.; Zeng, J. What factors drove the global cropland expansion into highlands? Earth’s Future 2025, 13, e2024EF005337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pei, F.; Wen, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, C.; Cai, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Feng, K.; et al. Global urban expansion offsets climate-driven increases in terrestrial net primary productivity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Tian, Y.; Sun, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, X.; Yin, L.; Zhang, B. Assessment of the conservation effectiveness of nature reserves on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau using human activity and habitat quality indicators. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 84, 102872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wang, T.; Chi, J. Does the South-to-North Water Diversion Project promote the growth of enterprises above designated size in the water-receiving areas?—Evidence from 31 provincial-level administrative regions in China. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0297566. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Xu, H.; Pan, S.; Chen, W.; Zeng, J. Identifying the impact of global human activities expansion on natural habitats. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Ren, Y.F.; Zhang, B.T.; Li, G.D.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, Q.N. Disentangling the intricate nexus among economic growth, urbanization, carbon emission and human well-being: The evidence from 143 countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 523, 146390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Guo, D.F.; Lu, W.T.; Xu, H. How does ecological protection redline policy affect regional land use and ecosystem services? Environ. Impact Asses. 2023, 100, 107062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Liu, S.; Ning, J.; Liu, G.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Niu, L.; Huang, H.; Fan, J.; Liu, J. Remote sensing assessment of the ecological benefits provided by national key ecological projects in China during 2000–2019. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 1587–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Kaufmann, R.K.; Woodcock, C.E. Landsat reveals China’s farmland reserves, but they’re vanishing fast. Nature 2000, 406, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y. Human and natural factors affect habitat quality in ecologically fragile areas: Evidence from Songnen Plain, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1444163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.X.; Liu, W.X.; Allechy, F.B.; Zheng, Z.W.; Liu, R.; Kouadio, K.L. Machine learning-based techniques for land subsidence simulation in an urban area. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouzols, F.M.; Toivonen, T.; Di Minin, E.; Kukkala, A.S.; Kullberg, P.; Kuusterä, J.; Lehtomäki, J.; Tenkanen, H.; Verburg, P.H.; Moilanen, A. Global protected area expansion is compromised by projected land-use and parochialism. Nature 2014, 516, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Threat Factors | Maximum Stress Distance/km | Weight | Decay |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 3 | 0.3 | Linear |
| Construction land | 8 | 1 | Exponential |
| Barran land | 5 | 0.75 | Exponential |
| Land Use Type | Habitat Suitability | Cropland | Construction Land | Barren Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.3 | 0 | 0.3 | 0 |
| Forest land | 1 | 0.65 | 0.75 | 0.6 |
| Grassland | 1 | 0.6 | 0.65 | 0.5 |
| Wetland | 1 | 0.55 | 0.7 | 0.55 |
| Water | 1 | 0.35 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
| Construction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Barren land | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, M.; Chen, W. The Human–Nature Paradox: Spatiotemporal Coupling and Drivers of Habitat Quality and Human Footprint in China. Land 2025, 14, 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102089
Zhong M, Chen W. The Human–Nature Paradox: Spatiotemporal Coupling and Drivers of Habitat Quality and Human Footprint in China. Land. 2025; 14(10):2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102089
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Mingxing, and Wanxu Chen. 2025. "The Human–Nature Paradox: Spatiotemporal Coupling and Drivers of Habitat Quality and Human Footprint in China" Land 14, no. 10: 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102089
APA StyleZhong, M., & Chen, W. (2025). The Human–Nature Paradox: Spatiotemporal Coupling and Drivers of Habitat Quality and Human Footprint in China. Land, 14(10), 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102089






