Spatial Morphological Characteristics of Ethnic Villages in the Dadu River Basin, a Sino-Tibetan Area of Sichuan, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
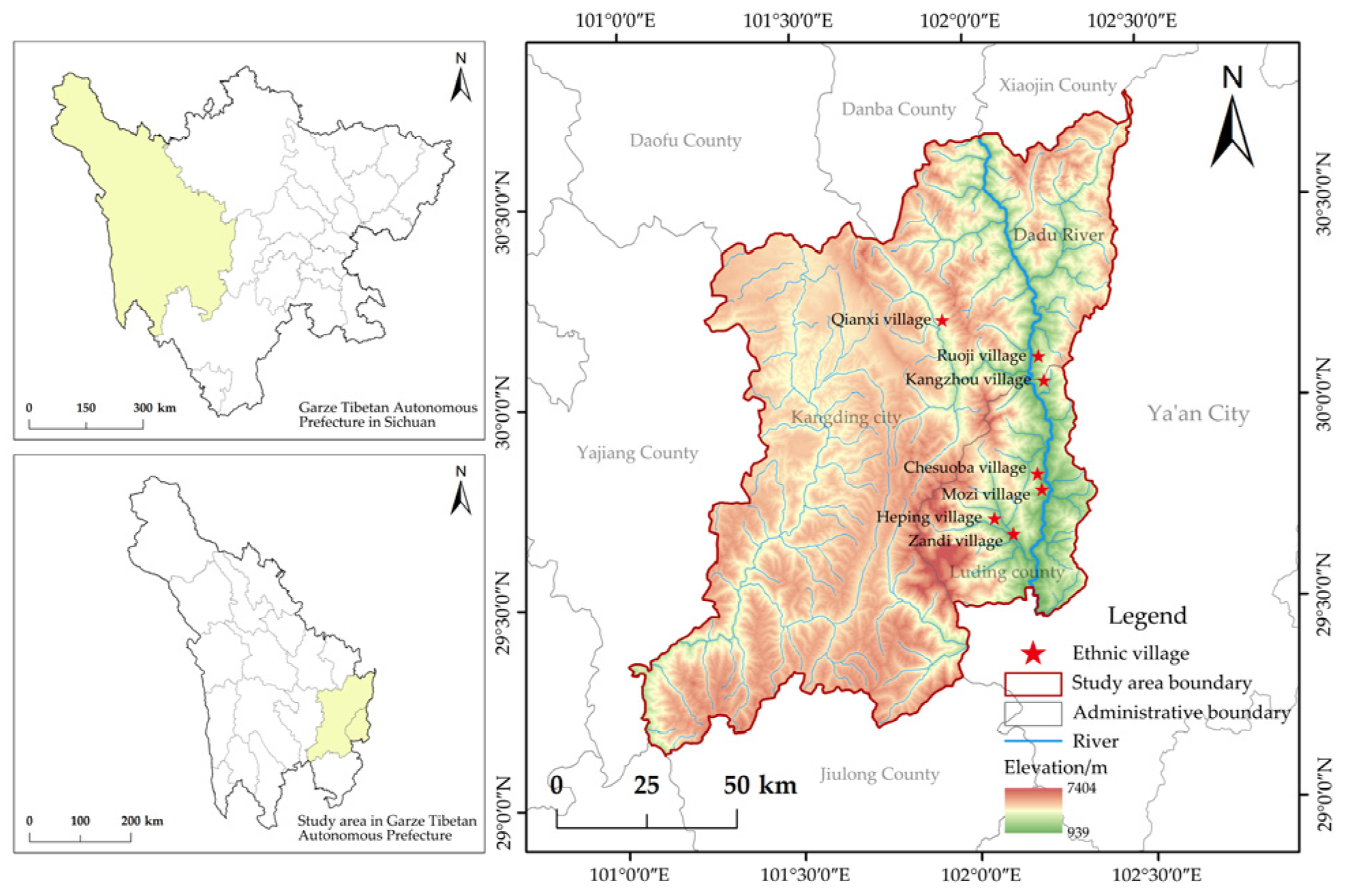
2. Study Area and Method
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Research Method
3. Results
3.1. Figure–Ground Relationship Analysis
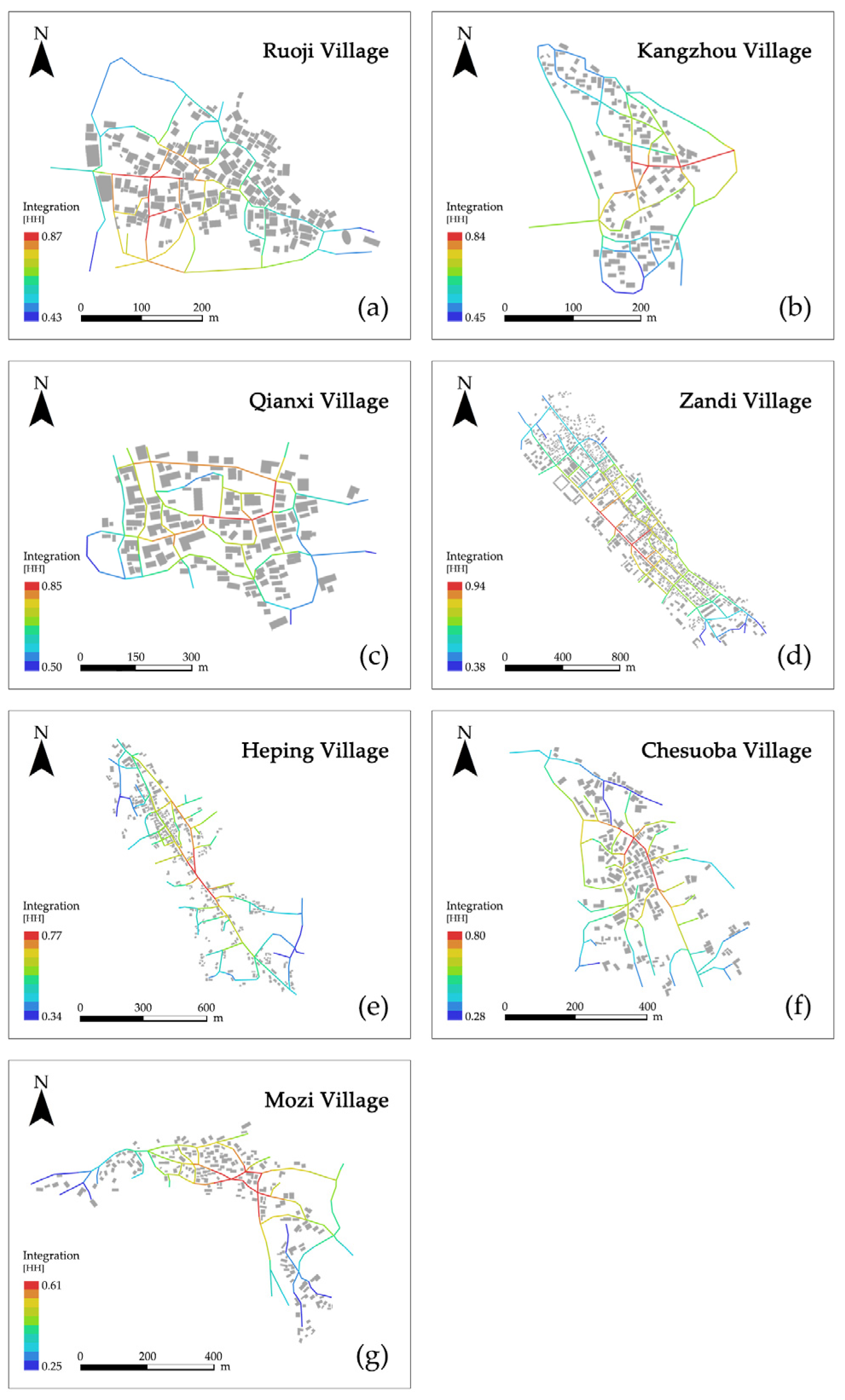
3.2. Space Syntax Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z. The Protection and Inheritance of the Village Culture with Chinese Minorities’ Characteristics from the Perspective of Cultural Ecology. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Culture, Education and Economic Development of Modern Society (ICCESE 2020), Moscow, Russia, 19 March 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.; Nisbet, A. Theatre and Performance Design, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2020; pp. 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Aronoff, M.; Fudeman, K. What Is Morphology? 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Oxford, UK, 2023; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Li, X. The Changing Settlements in Rural Areas under Urban Pressure in China: Patterns, Driving Forces and Policy Implications. Urban Plan. 2013, 120, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.J.; Leung, H.H. Becoming a Traditional Village: Heritage Protection and Livelihood Transformation of a Chinese Village. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Aimar, F. How Are Historical Villages Changed? A Systematic Literature Review on European and Chinese Cultural Heritage Preservation Practices in Rural Areas. Land 2022, 11, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P. Walter, Christaller: Hierarchical patterns of urbanization. Cent. Spat. Integr. Soc. Sci. 2007, 36. Available online: http://www-personal.umich.edu/~copyrght/image/books/Spatial%20Synthesis2/CSISS%20Classics%20-%20Walter%20Christaller%20Hierarchical%20Patterns%20of%20Urbanization.htm (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Shuang, W.; Hao, J. Zoning and Mode of Rural Residential Land Consoli-Dation Based on Location Potential Theory. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- Tamás, C.; Tibor, L. Settlement Morphology of Budapest, 1st ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, R.; Sidaway, J.D. Geography and Geographers: Anglo-American Human Geography since 1945, 7th ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2015; pp. 37–98. [Google Scholar]
- Dovring, F. Land and Labor in Europe 1900–1950: A Comparative Survey of Recent Agrarian History, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 37–131. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, S.S.; Zhou, X.Y. Research Progress and Prospect of Spatial Evolution and Optimization of Rural Settlements. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; He, Y. Dynamic Mechanism and Present Situation of Rural Settlement Evolution in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Long, Y. Spatio-temporal pattern of China’s rural development: A rurality index perspective. J. Rural. Stud. 2015, 38, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. The Change of Rural Settlements and Their Future Development Patterns. Econ. Geogr. 2017, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jiang, G. Differentiation of Spatial Morphology of Rural Settlements from an Ethnic Cultural Perspective on the Northeast Tibetan Plateau, China. Habitat Int. 2018, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Henneberry, S. Socio-Cultural Roots of Rural Settlement Dispersion in Sichuan Basin: The Perspective of Chinese Lineage. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, Z. Quantitative Research on the Boundary Pattern of the Rural Settlement in the High and Cold Minority Area—A Case Study of Xiahe County in Gannan Prefecture. J. Northwest Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2019, 55, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhou, H. Analysis on Spatial Characteristics and the Adaptation Mechanism of Miao Traditional Settlement in Qiandongnan, China. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jia, Z. Sustainable Mountain Village Construction Adapted to Livelihood, Topography, and Hydrology: A Case of Dong Villages in Southeast Guizhou, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, Q. Spatial Morphology Evolution of Rural Settlements in the Lower Yellow River Plain: The Case of Menggang Town in Changyuan City, China. Land 2023, 12, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, F. The Causes and the Spatial Morphological Characteristics of Traditional Villages of Qiannan Shui Ethnic Group. Huazhong Archit. 2023, 41, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanu-Rizfa, H.; Amos, S. Bali Traditional Settlement Morphology Analysis Penglipuran, Kubu Village, Bangli Regency, Bali Province. J. Archit. Built Environ. 2016, 43, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Yan, Y. Construction of Spatial Gene Map of Traditional Villages, Anhui Province. Planners 2022, 38, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Elzeni, M.M.; ELMokadem, A.A. Impact of Urban Morphology on Pedestrians: A Review of Urban Approaches. Cities 2022, 129, 103840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Tang, C. Research on The Relationship between The Settlement Built Environment for Rural and The Villagers’ Behavior of Spatial—A Case Study in Hunan. Archit. J. 2017, S2, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, D.; Cao, A. Analysis of the Heterogeneity of Landscape Risk Evolution and Driving Factors Based on a Combined GeoDa and Geodetector Model. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. Protection of Ethnic Cultural Value: A Case Study of VR Scene Construction in Basha Village. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zeng, C. Environmental Adaptation of Traditional Chinese Settlement Patterns and Its Landscape Gene Mapping. Habitat Int. 2023, 2013, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, A. Art and Visual Perception: A Psychology of the Creative Eye, 3rd ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1960; pp. 27–65. [Google Scholar]
- Eizenberg, E.; Sasson, O. Urban Morphology and Qualitative Topology: Open Green Spaces in High-Rise Residential Developments. Urban Plan. 2019, 4, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, B.; Leaman, A. Space Syntax. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1976, 3, 147–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölscher, C.; Brösamle, M. Challenges in Multilevel Wayfinding: A Case Study with the Space Syntax Technique. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2012, 39, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, A.; Kleinschmidt, T. Wayfinding: A simple concept, a complex process. Transp. Rev. 2012, 32, 715–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A. The ingredients of an exosomatic cognitive map: Isovists, agents and axial lines? Univ. Brem. 2007, 2007, 163–180. [Google Scholar]
- Ariza-Villaverde, A.B.; Jiménez-Hornero, F.J. Multifractal analysis of axial maps applied to the study of urban morphology. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2013, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendjedidi, S.; Bada, Y. International Review for Spatial Planning and Sustainable Development. Spat. Distrib. Pedestr. Space Cent. Tokyo 2019, 7, 108–124. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, W.; Zhou, Y.J. The Religious Culture about Jiarong Tibetan Nationality of Village Community: From Shen Village of Dadu River. Tibet. Stud. 2015, 3, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L. Feasibility Study on Poverty Alleviation and Development through Tourism in the Dadu River Basin. J. Leshan Teach. Coll. 2015, 30, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D. Introduction of Related Theories to Space Syntax. J. World Archit. 2015, 11, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Dettlaff, W. Space Syntax Analysis–Methodology of Understanding the Space. PhD Interdiscip. J. 2014, 1, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Du, X. Spatial Evolution Analysis and Spatial Optimization Strategy of Rural Tourism Based on Spatial Syntax Model. A Case Study of Matao Village in Shandong Province, China. Land 2023, 12, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelkou, L.R.; Chougui, A. Structural qualities of urban space revealed by spatial representation and intelligibility readings: The case of Setif City, Algeria. Rev. Bras. Gest. Urbana 2022, 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safizadeh, M.; Maghsoodi-Tilaki, M.J. Smart city and spatial configuration: Assessing accessibility and intelligibility to increase mobility in the George Town heritage site, Malaysia. Open House Intern. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Lu, X. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Traditional Villages in Northern Guangxi Based on Spatiotemporal Big Data and Spatial Syntax. J. Landsc. Res. 2022, 14, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Optimization Strategies of Commercial Layout of Traditional Villages Based on Space Syntax and Space. Resistance Model: A Case Study of Anhui Longchuan Village in China. Buildings 2023, 13, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Chen, W. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Traditional Villages in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pub. Health 2022, 19, 4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, Q. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Optimized Reconstruction Analysis of China’s Rural Settlements during the Process of Rapid Urbanization. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 47, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kong, Z. Research on the Spatial Pattern of Traditional Villages Based on Spatial Syntax: A Case Study of Baishe Village. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Serie: Earth Environment Science, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12 April 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, L. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Traditional Villages in the Yangtze River Basin: A Geodetector Model. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
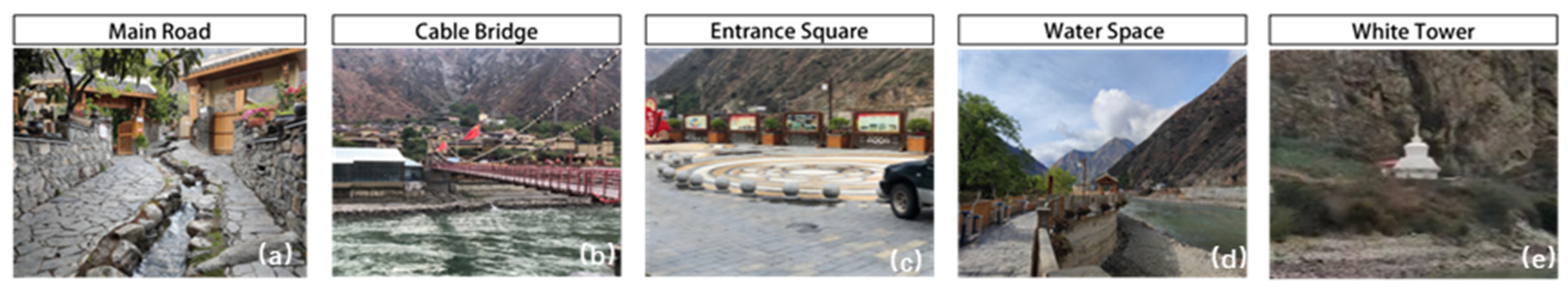
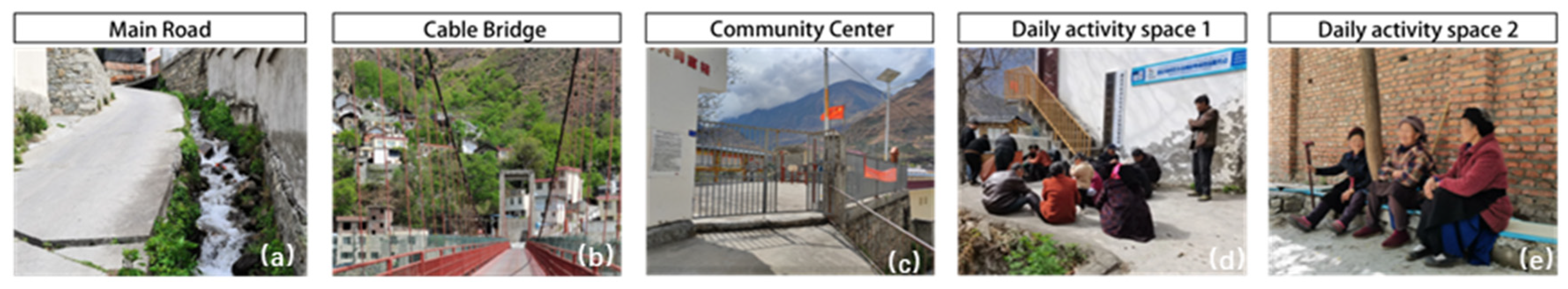
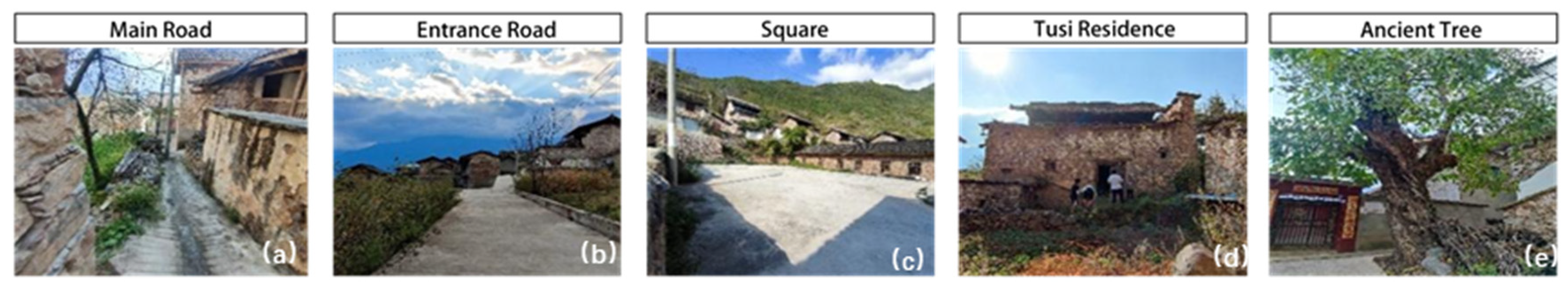
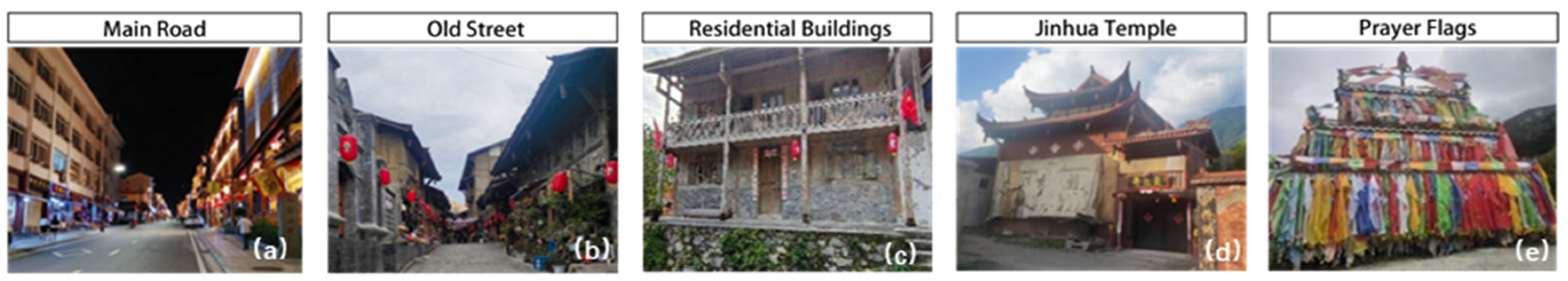
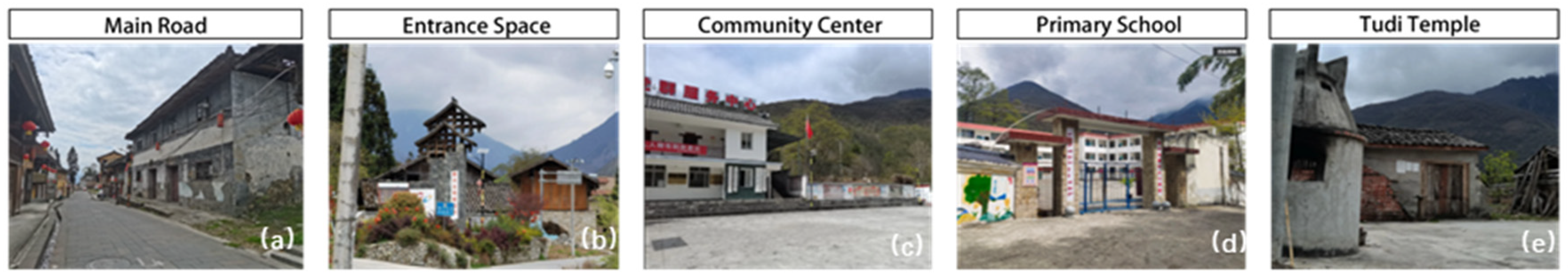








| Name | Natural Environment | Spatial Morphology | Altitude (Meters) | Economic Function | Ethnic Composition | Religious Beliefs/Iconic Venues |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ruoji | Back mountain face water, alluvial fan type | 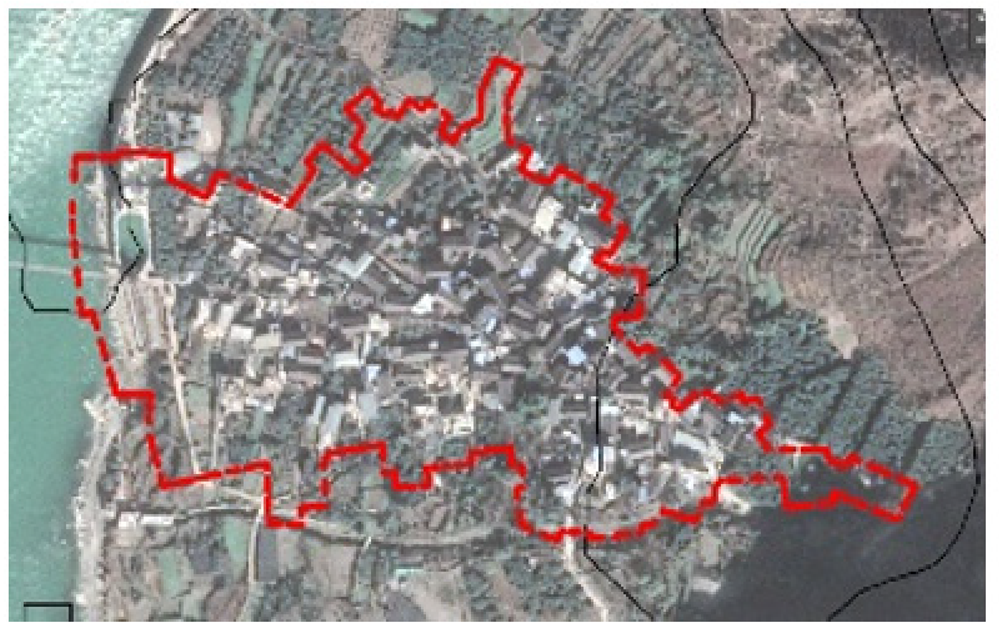 | 1520 | Tourism, Agriculture, Business | Han/Tibetan | Tibetan Buddhists, Mountain Temple, Dragon King Temple, Guanyin Temple |
| Kangzhou | Back mountain face water, alluvial fan type | 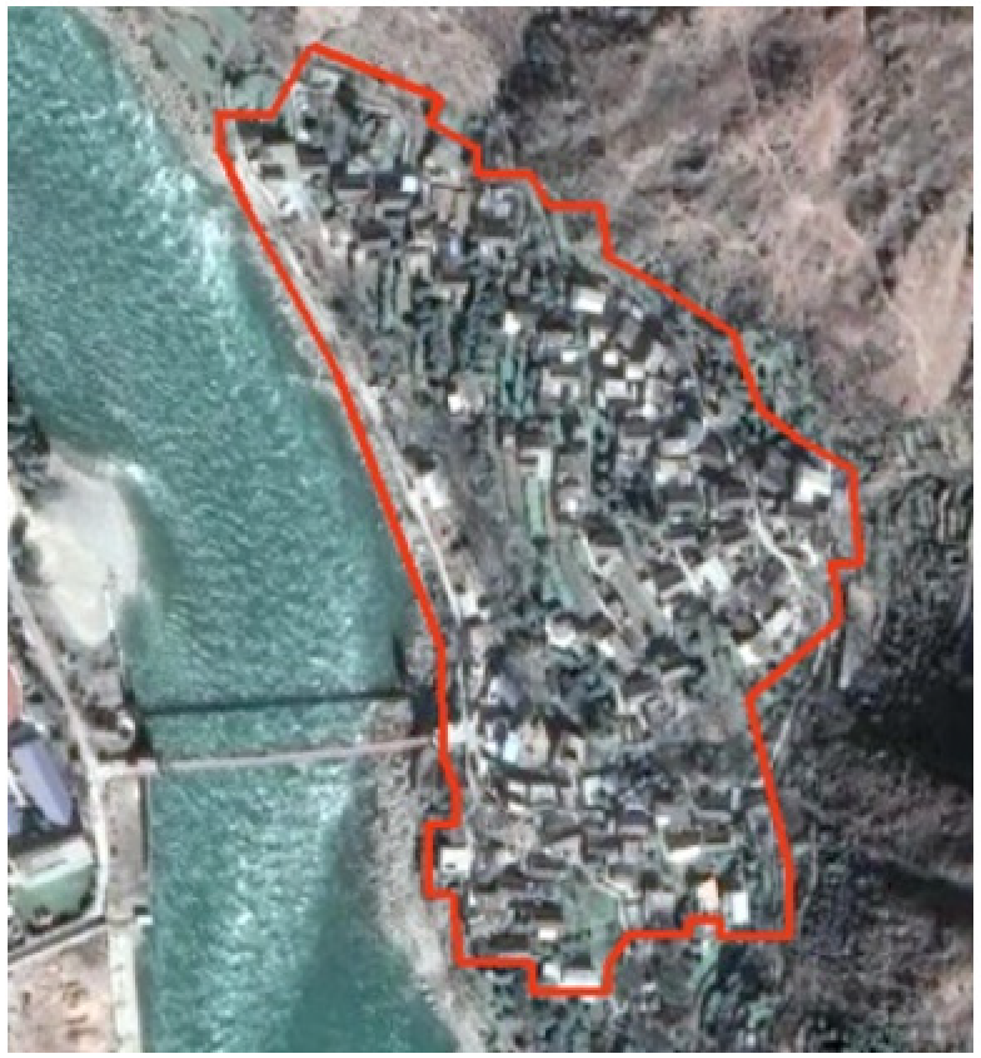 | 1550 | Agriculture, Business | Han/Tibetan | Tibetan Buddhists, Mountain religion, White Pagoda |
| Qianxi | Built on the mountain, hillside type | 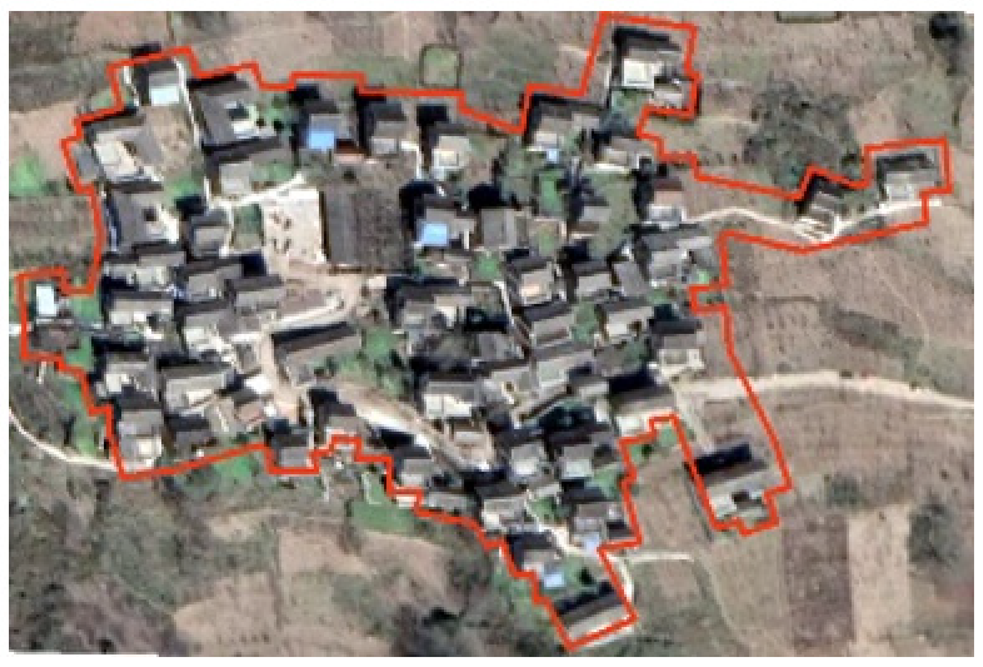 | 2300 | Agriculture, Business | Tibetan | Tibetan Buddhists, White Pagoda |
| Chesuoba | Surrounded by water, mountain gentle slope type |  | 900 | Agriculture | Han/Tibetan | Old trees |
| Mozi | Surrounded by mountains on three sides, mountain gentle slope type | 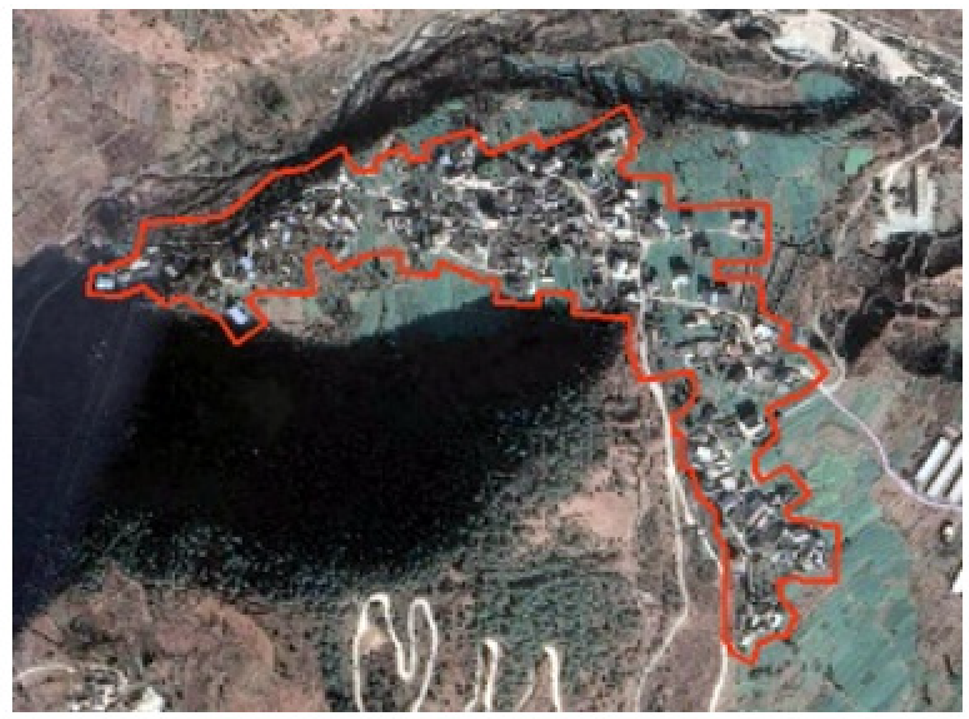 | 1100 | Agriculture | Han/Tibetan | none |
| Zandi | Surrounded by mountains and water on both sides, valley platform type | 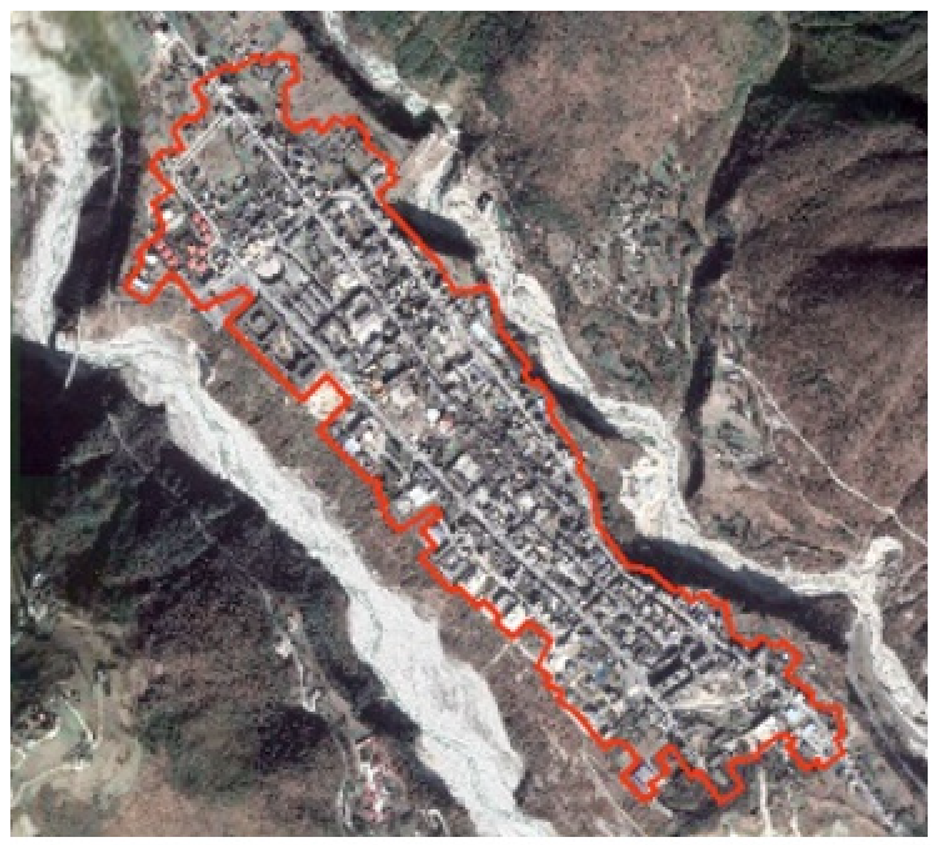 | 1520 | Tourism, Business | Han/Tibetan/Yi/Qiang | Golden Flowers Temple, Guanyin Temple |
| Heping | Surrounded by mountains and water on both sides, valley platform type | 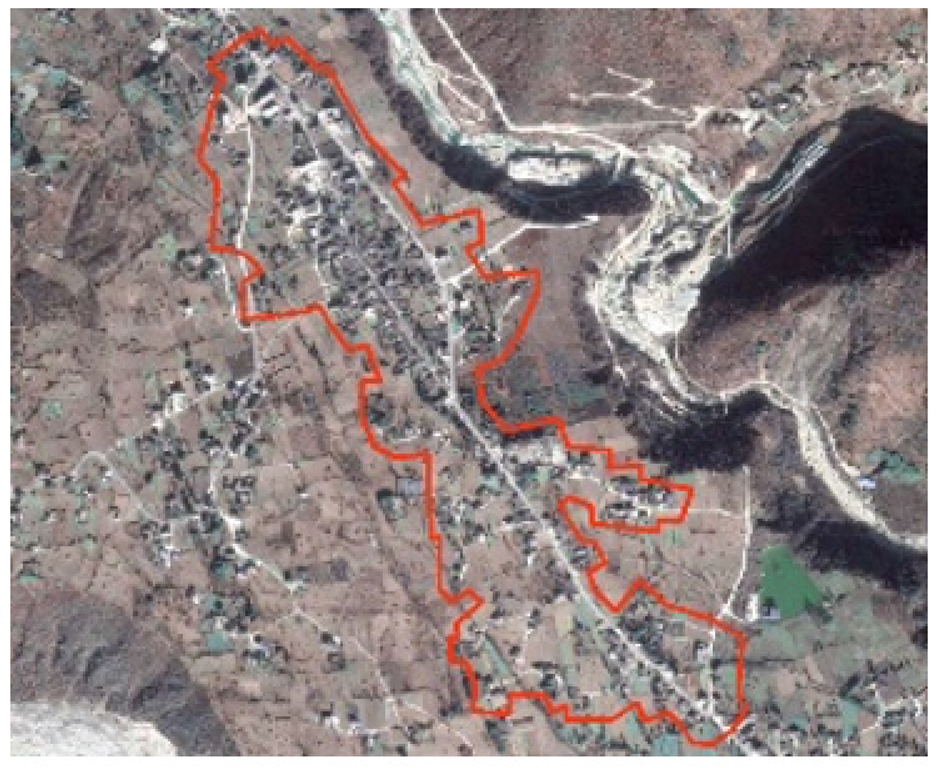 | 1950 | Agriculture, Business | Han, Tibetan, Yi | Land Temple |
| Name | Spatial Figure–Ground Relationship | Important Spatial Distribution | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ruoji | 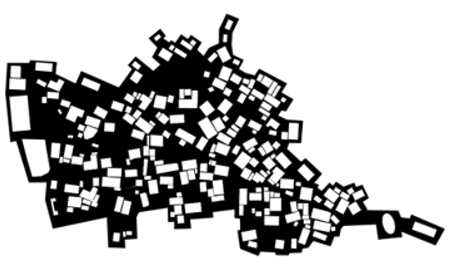 |  | Spatial hierarchy Spatial orderliness Ethnic grouping Territorial awareness Defensive Collective identity |
| Kangzhou | 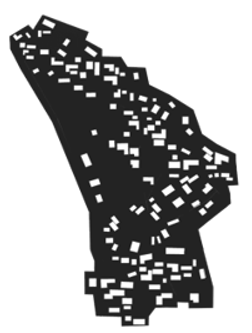 | 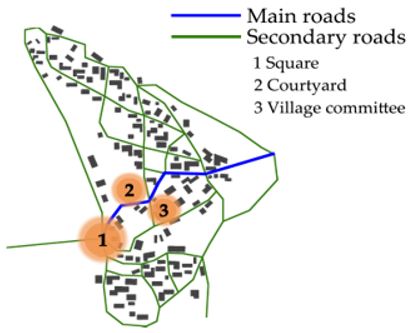 | |
| Qianxi |  | 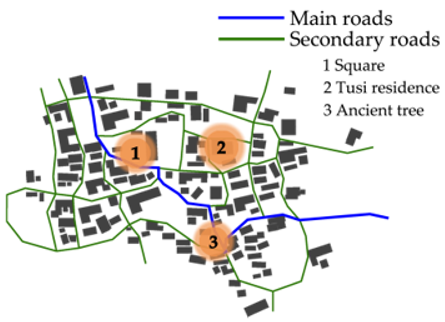 | |
| Zandi | 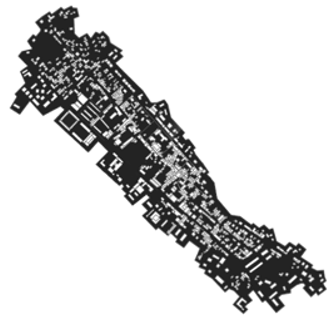 |  | Limited by lateral topography Best integration of ethnic characteristics Largest village size Abundant space carrying capacity |
| Heping |  | 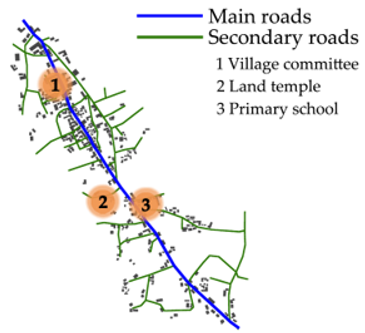 | |
| Chesuoba | 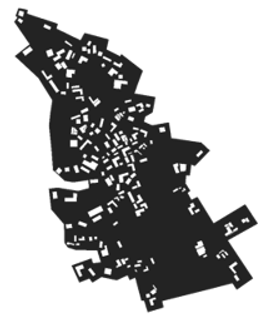 | 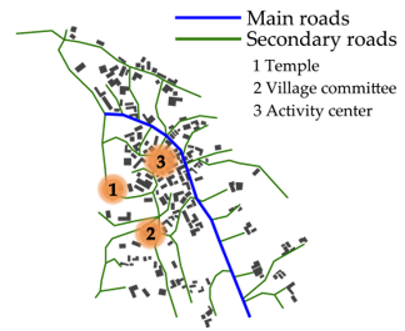 | Family lineage maintenance Spatial history memory Simple space function Dispersion continues expansion trend |
| Mozi | 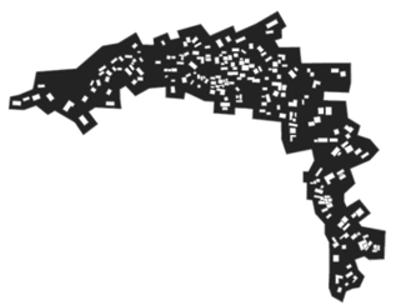 | 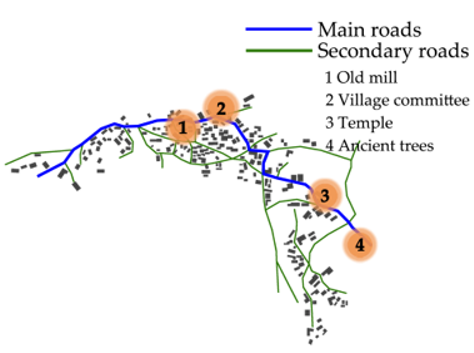 |
| Name | No. of Axes | Global Integration Value | Local Integration Value (R3) | Connectivity Value | Intelligibility Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | Min | Average | Average | ||
| Ruoji | 117 | 0.66 | 0.87 | 0.43 | 1.35 | 1.95 | 0.42 | 3.14 | 0.60 |
| Kangzhou | 106 | 0.62 | 0.84 | 0.45 | 1.34 | 1.96 | 0.77 | 3.09 | 0.41 |
| Qianxi | 110 | 0.68 | 0.85 | 0.50 | 1.34 | 1.89 | 0.63 | 3.07 | 0.38 |
| Zandi | 132 | 0.64 | 0.94 | 0.38 | 1.53 | 2.13 | 0.33 | 3.59 | 0.42 |
| Heping | 137 | 0.53 | 0.77 | 0.34 | 1.25 | 2.17 | 0.33 | 2.86 | 0.24 |
| Chesuoba | 123 | 0.53 | 0.80 | 0.28 | 1.15 | 1.99 | 0.33 | 2.66 | 0.42 |
| Mozi | 121 | 0.44 | 0.61 | 0.25 | 1.19 | 1.78 | 0.33 | 2.74 | 0.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, H.; Xue, C.; Yu, J.; Yu, C.; Peng, G. Spatial Morphological Characteristics of Ethnic Villages in the Dadu River Basin, a Sino-Tibetan Area of Sichuan, China. Land 2023, 12, 1662. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091662
Xiao H, Xue C, Yu J, Yu C, Peng G. Spatial Morphological Characteristics of Ethnic Villages in the Dadu River Basin, a Sino-Tibetan Area of Sichuan, China. Land. 2023; 12(9):1662. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091662
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Hai, Congli Xue, Jiahao Yu, Chuwei Yu, and Guoqiang Peng. 2023. "Spatial Morphological Characteristics of Ethnic Villages in the Dadu River Basin, a Sino-Tibetan Area of Sichuan, China" Land 12, no. 9: 1662. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091662
APA StyleXiao, H., Xue, C., Yu, J., Yu, C., & Peng, G. (2023). Spatial Morphological Characteristics of Ethnic Villages in the Dadu River Basin, a Sino-Tibetan Area of Sichuan, China. Land, 12(9), 1662. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091662





