Heterogeneity and Spatial Governance of Synergy between Human Activities and Ecological Conservation in the Qinghai–Xizang Plateau, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
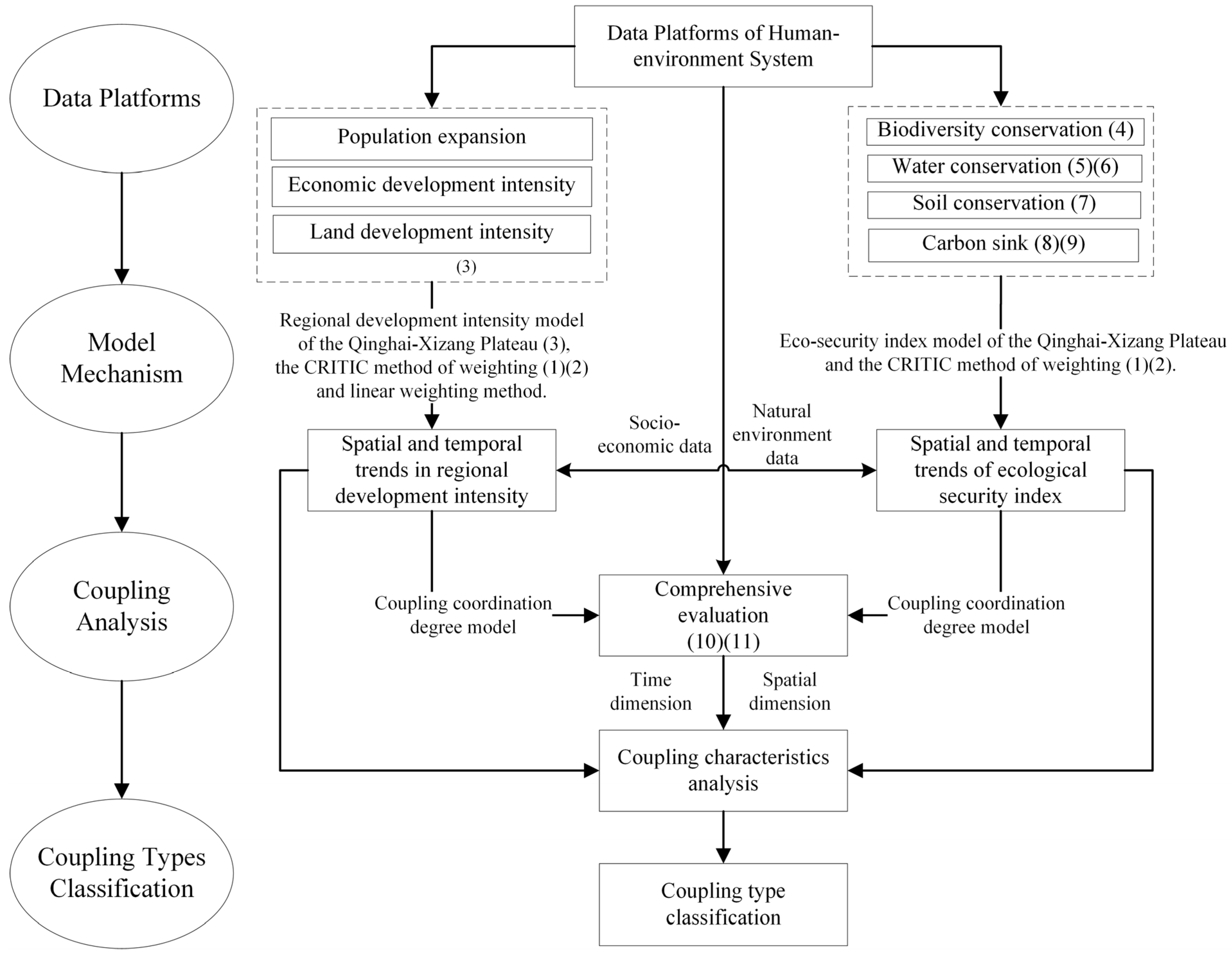
2. Theoretical Basis and Analysis Framework Construction
2.1. Theoretical Basis of “Human–Environment Coupling”
2.2. Analysis Framework Review and Selection
2.3. Analysis Framework Construction
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Research Area
3.2. Data Sources
3.3. Methodology
3.3.1. Empowerment Using CRITIC Method
3.3.2. Regional Development Intensity Model of the Qinghai–Xizang Plateau
3.3.3. Eco-Security Index Model of the Qinghai–Xizang Plateau
- (1)
- Biodiversity conservation
- (2)
- Water conservation
- (3)
- Soil conservation
- (4)
- Carbon sink
3.3.4. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
4. Results
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Trends in Regional Development Intensity
4.2. Spatial and Temporal Trends of Ecological Security Index
4.3. Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Types of Coupling between Regional Development Intensity and Ecological Security
4.3.1. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of the Coupling Coordination Degree between Regional Development Intensity and Ecological Security
4.3.2. Coupling Type Classification of Regional Development Intensity and Ecological Security
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Impact of population growth and land-use change on water resources and ecosystems of the arid Tarim River Basin in Western China. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2006, 13, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Wei, X.; Duan, Z. Coupling and coordination analysis in urban agglomerations of China: Urbanization and ecological security perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.; Watt, A.; Nowicki, P.; Alard, D.; Clitherow, J.; Henle, K.; Johnson, R.; Laczko, E.; McCracken, D.; Matouch, S.; et al. Towards sustainable land use: Identifying and managing the conflicts between human activities and biodiversity conservation in europe. Biodivers. Conserv. 2005, 14, 1641–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.S. Ecological security and multinational corporations. Environ. Chang. Secur. Proj. Rep. 1997, 3, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. Research progress and prospect on regional ecological security pattern construction. Geogr. Res. 2019, 36, 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Nan, F. Quantitative analysis of the impacts of climate change and human activities on vegetation NPP in the Qilian Mountain National Park. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 202–221. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Yu, H.; Han, D.; Zhang, G.; Wei, Y.; Huang, J.; An, L.; Liu, X.; Ren, Y. Declines in global ecological security under climate change. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Liu, J.; Jia, J.; Wang, P. Terrestrial ecological restoration in China: Identifying advances and gaps. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liao, J.; He, Y.; Chen, P. Evolution and Ecological Implications of Land Development and Conservation Patterns on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land 2022, 11, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q. Coupling coordination degree measurement and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment—Empirical evidence from tropical and subtropical regions of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Yu, D.; Qiu, J. Assessing coupling interactions in a safe and just operating space for regional sustainability. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Feng, C.-C.; Yu, Q.; Han, R.; Guo, L. Contradiction or coordination? The spatiotemporal relationship between landscape ecological risks and urbanization from coupling perspectives in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Fan, Y.; Bao, C.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Sun, S.; Ma, H. China’s improving total environmental quality and environment-economy coordination since 2000: Progress towards sustainable development goals. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 387, 135915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Ouyang, Z.; Shi, P.; Fan, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, W.; Wu, F. Current Condition and Protection Strategies of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Ecological Security Barrier. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, L. Analysis on the ecological security of the typical area in the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on landscape pattern. Chin. J. Ecol. 2022, 41, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Q.; He, L.; Yin, C.; Tian, P.; Lu, H. Spatio-temporal variation of ecological risk of agriculture and animal husbandry on the Tibetan Plateau and its regional prevention and control. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhi, X.; Song, Y. Evaluation and prediction of the cultivated land ecological security in Tibet based on PSR and GM (1,1) model. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2018, 32, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, J. Ecological security evaluation and driving force analysis of three-dimensional ecological footprint in Northwestern China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 1354–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, W.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L. Reginal differentiation of population in Tibetan Plateau: Insight from the “Hu Line”. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 255–267. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W. Human Development Assessment and Evolution Analysis on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, L. Spatio-temporal variation of human activity intensity and its driving factors on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 3995–4009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Kan, A.; Zeng, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, M.; Ci, R. Population distribution pattern and influencing factors in Tibet based on random forest model. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 664–680. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. Spatio-temporal variations of population and population distribution with data at county level in Northwest China in 1990–2010. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2013, 27, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Li, G. Interaction between urbanization and eco-environment in Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 1386–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Liu, R. Spatiotemporal Evolution of the Urban System in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 21, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wu, J.; Gong, J.; Li, S. Human footprint in Tibet: Assessing the spatial layout and effectiveness of nature reserves. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.; Wang, Z. Discovering spatio-temporal patterns of human activity on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on crowdsourcing positioning data. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Li, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, W.; Danzeng, Z.; Mima, L.; Ma, R. The Spatial Mismatch between Tourism Resources and Economic Development in Mountainous Cities Impacted by Limited Highway Accessibility: A Typical Case Study of Lhasa City, Tibet Autonomous Region, China. Land 2023, 12, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Li, J.; Wu, L.; Zhu, M.; Luo, M.; Sun, J.; Fu, W.; Ma, R.; Liang, X. Exploring Accessibility and Its Impact in the Mountain City: A Typical Case Study of Nyingchi City, Tibet Autonomous Region, China. Land 2023, 12, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Liu, L.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Luo, M.; Yuan, J. Spatio-temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Enterprises in Qinghai-Tibet Region. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 12, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, T.; Cao, X. Spatial fairness and changes in transport infrastructure in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau area from 1976 to 2016. Sustainability 2019, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Dai, T.; Song, J.; Ding, T.; Lu, W. Concept expansion, method improvement of transport superiority degree and its empirical application in Tibet. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2023, 78, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Dai, T.; Yang, X.; Song, J. Landscape fragmentation associated with the Qingzang Highway and its influencing factors—A comparison study on road sections and buffers. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, A. Fragmentation of habitat by roads and utility corridors: A review. Aust. Zool. 1990, 26, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, R.; Alexander, L. Roads and their major ecological effects. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1998, 29, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gillespie, A.; Liang, S.; Mushkin, A.; Wu, Q. Effect of the Qinghai-Tibet Railway on vegetation abundance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 5222–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C. Special thinking and green development path of urbanization in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 1907–1919. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Qi, W.; Jin, H. The settlement intention of floating population and the factors in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: An analysis from the perspective of short-distance and long-distance migrants. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 2142–2156. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, D.; Li, G. Systematically addressing the heterogeneity in the response of ecosystem services to agricultural modernization, industrialization and urbanization in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from 2000 to 2018. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 125323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Tian, L.; Ao, Y.; Wang, X. Influence of Human Disturbance on the Change of Vegetation Cover in the Tibetan Plateau. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 382–388. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Liu, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhu, J. Sustainable wildlife protection on the Qingzang plateau. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Lv, Y.; Gao, G.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Fu, B. A landscape persistence-based methodological framework for assessing ecological stability. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnology 2023, 17, 100300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. The Core of Geographical Study—Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction. Econ. Geogr. 1991, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Peng, L.; Liu, Y. Transitional geospace from the perspective of human-nature coupling: Concept, connotations, attributes, and the research framework. Geogr. Res. 2020, 39, 761–771. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Cui, X.; Liang, L. Theoretical analysis of urbanization and eco-environment coupling coil and coupler control. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 2529–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Fang, C.; Sun, S.; Bao, C.; Liu, R. Progress in local and tele-coupling relationship between urbanization and eco-environment. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 589–606. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Zheng, D.; Yao, T.; Zhang, Y. Protection and Construction of the National Ecological Security Shelter Zone on Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Wang, W.; An, B.; Piao, S.; Chen, F. The scientific expedition and research activities on the Tibetan Plateau in 1949–2017. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 1586–1602. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, C.; Qi, W. Floristic characteristics and diversity patterns of seed plants endemic to the Tibetan Plateau. Biodivers. Sci. 2018, 26, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-Q.; Duan, Y.-W.; Hao, G.; Ge, X.-J.; Sun, H. Evolutionary history and underlying adaptation of alpine plants on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Editorial. J. Syst. Evol. 2014, 52, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Tang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Su, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Relationship between plant species diversity and functional diversity in alpine grasslands. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar]
- Di, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Tang, Z. Effects of Changed Asian Water Tower on Tibetan Plateau Ecosystem; A Review. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 34, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, T.; Sun, J. Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics and Its Driving Forces of Water Conservation Function on the Tibetan Plateau from 1995 to 2014. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2021, 29, 80–92. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Xie, G.; An, K. The function and economic value of soil conservation of ecosystems in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2003, 23, 2367–2378. [Google Scholar]
- Diakoulaki, D.; Mavrotas, G.; Papayannakis, L. Determining objective weights in multiple criteria problems: The critic method. Comput. Oper. Res. 1995, 22, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tong, L. Spatio-temporal Coupling Relationship Between Development Strength and Eco-environment in the Restricted Development Zone of Northeast China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 684–694. [Google Scholar]
- Technical Specifications for the Evaluation of Ecological Environmental Conditions [For Trial Implementation] Issued by the State Envi-ronmental Protection Administration [HJ/T192-2006]; China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Khan, I.; Hou, F.; Zakari, A.; Irfan, M.; Ahmad, M. Links among energy intensity, non-linear financial development, and environmental sustainability: New evidence from Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, Z. Spatial patterns of ecosystem water conservation in China and its impact factors analysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Cao, G.; Chen, K.; Ba, D.; Liu, B.; Wang, R.; Shi, Y.E.C. Spatio-temporal Variation in Soil Conservation Service and Its Influencing Factors in the upper Reaches of the Yellow River. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Lv, K.; Qiao, Z.; Ma, F.; Jiang, O. Assessment and prediction of carbon neutrality in the eastern margin ecotone of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 9442–9455. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Fang, H.; Liang, T.; Pei, Z. Coupling relationship between resource environment and social economy development in typical regions of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2021, 41, 2510–2518. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Ma, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, W. Study on Spatial Agglomeration and Industrial Correlation of Productive Service Industries in Plateau Areas—A Case Study of the Tibet Autonomous Region. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2022, 18, 589–596. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; Guo, S.; Dan, Z.; Ciren, D. Monitoring on spatial-temporal vegetation dynamics based on Landsat time series. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2020, 11, 7–12, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Ma, R.; Liu, L.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Xu, L. Dataset of spatio-temporal Changes of Enterprises in Tibet Autonomous Region (2010–2020). Digit. J. Glob. Chang. Data Repos. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Ma, R.; Li, J. Spatial-temporal Distribution Dataset of Qinghai-Tibet Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Enterprises (2011–2021). Digit. J. Glob. Chang. Data Repos. 2022, 6, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Data | Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|
| LUCC | 30 m | CLCD of Wuhan University (80% overall accuracy) |
| Average annual precipitation | 1 km | National Earth System Science Data Center (http://www.geodata.cn/, accessed on 1 July 2023) |
| Potential evaporation | Value | Based on data from existing studies in the literature |
| Depth of root restriction layer | 1 km | Based on data from existing studies in the literature |
| Soil effective water content | 1 km | Based on the ISRIC global dataset to measure |
| NDVI | 1 km | National Aeronautics and Space Administration (https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/dataprod/mod13.php, accessed on 1 July 2023) |
| DEM | 250 m | Geospatial Data Cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn/, accessed on 1 July 2023) |
| Soil texture | 1 km | National Cryosphere Desert Data Center (http://www.ncdc.ac.cn/portal/, accessed on 1 July 2023) |
| NPP | 500 m | National Aeronautics and Space Administration (https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/dataprod/mod17.php, accessed on 1 July 2023) |
| Night light index | 1 km | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov, accessed on 1 July 2023) |
| Target Layer | Element Layer | Indicator Layer | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regional development intensity of the Qinghai–Xizang Plateau | Population expansion | Regional population density | 0.11819 |
| Urbanization rate | 0.20263 | ||
| Economic development intensity | Regional economic density | 0.20761 | |
| The ratio of non-agricultural industries | 0.15882 | ||
| Land development intensity | Night light index | 0.15362 | |
| Human activity intensity | 0.15362 |
| Target Layer | Element Layer | Indicator Layer | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ecological Security Assessment of the Qinghai–Xizang Plateau | Biodiversity | Biological abundance index | 0.38312 |
| Water conservation | Water conservation index | 0.16718 | |
| Soil conservation | Soil conservation index | 0.19159 | |
| Carbon sink | Amount of carbon sink | 0.25811 |
| Type | Coupling Coordination (D) | Subtype | Relative Size of U1 and U2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Severe imbalance | 0.0 ≤ D ≤ 0.2 | U2− U1 > 0.1 | Severe imbalance, regional development lagging behind |
| U1− U2 > 0.1 | Severe imbalance, ecological security lagging behind | ||
| 0 ≤ |U1 − U2| ≤ 0.1 | Severe imbalance | ||
| Mild imbalance | 0.2 < D ≤ 0.4 | U2− U1 > 0.1 | Mild imbalance, regional development lagging behind |
| U1− U2 > 0.1 | Mild imbalance, ecological security lagging behind | ||
| 0 ≤ |U1 − U2| ≤ 0.1 | Mild imbalance | ||
| Mild coupling coordination | 0.4 < D ≤ 0.6 | U2− U1 > 0.1 | Mild coupling, regional development lagging behind |
| U1− U2 > 0.1 | Mild coupling, ecological security lagging behind | ||
| 0 ≤ |U1 − U2| ≤ 0.1 | Mild coupling | ||
| Good coupling coordination | 0.6 < D ≤ 0.8 | U2− U1 > 0.1 | Mild coupling, regional development lagging behind |
| U1− U2 > 0.1 | Mild coupling, ecological security lagging behind | ||
| 0 ≤ |U1−U2| ≤ 0.1 | Mild coupling | ||
| Excellent coupling coordination | D > 0.8 | U2− U1 > 0.1 | Excellent coupling, regional development lagging |
| U1− U2 > 0.1 | Excellent coupling, ecological security lagging behind | ||
| 0 ≤ |U1 − U2| ≤ 0.1 | Excellent coupling |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Ma, R. Heterogeneity and Spatial Governance of Synergy between Human Activities and Ecological Conservation in the Qinghai–Xizang Plateau, China. Land 2023, 12, 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12122103
Wu L, Zhang L, Li J, Ma R. Heterogeneity and Spatial Governance of Synergy between Human Activities and Ecological Conservation in the Qinghai–Xizang Plateau, China. Land. 2023; 12(12):2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12122103
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Lingzhi, Lei Zhang, Jiaming Li, and Renfeng Ma. 2023. "Heterogeneity and Spatial Governance of Synergy between Human Activities and Ecological Conservation in the Qinghai–Xizang Plateau, China" Land 12, no. 12: 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12122103
APA StyleWu, L., Zhang, L., Li, J., & Ma, R. (2023). Heterogeneity and Spatial Governance of Synergy between Human Activities and Ecological Conservation in the Qinghai–Xizang Plateau, China. Land, 12(12), 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12122103






