Future of Water Supply and Demand in the Middle Drâa Valley, Morocco, under Climate and Land Use Change
Abstract
:1 Introduction
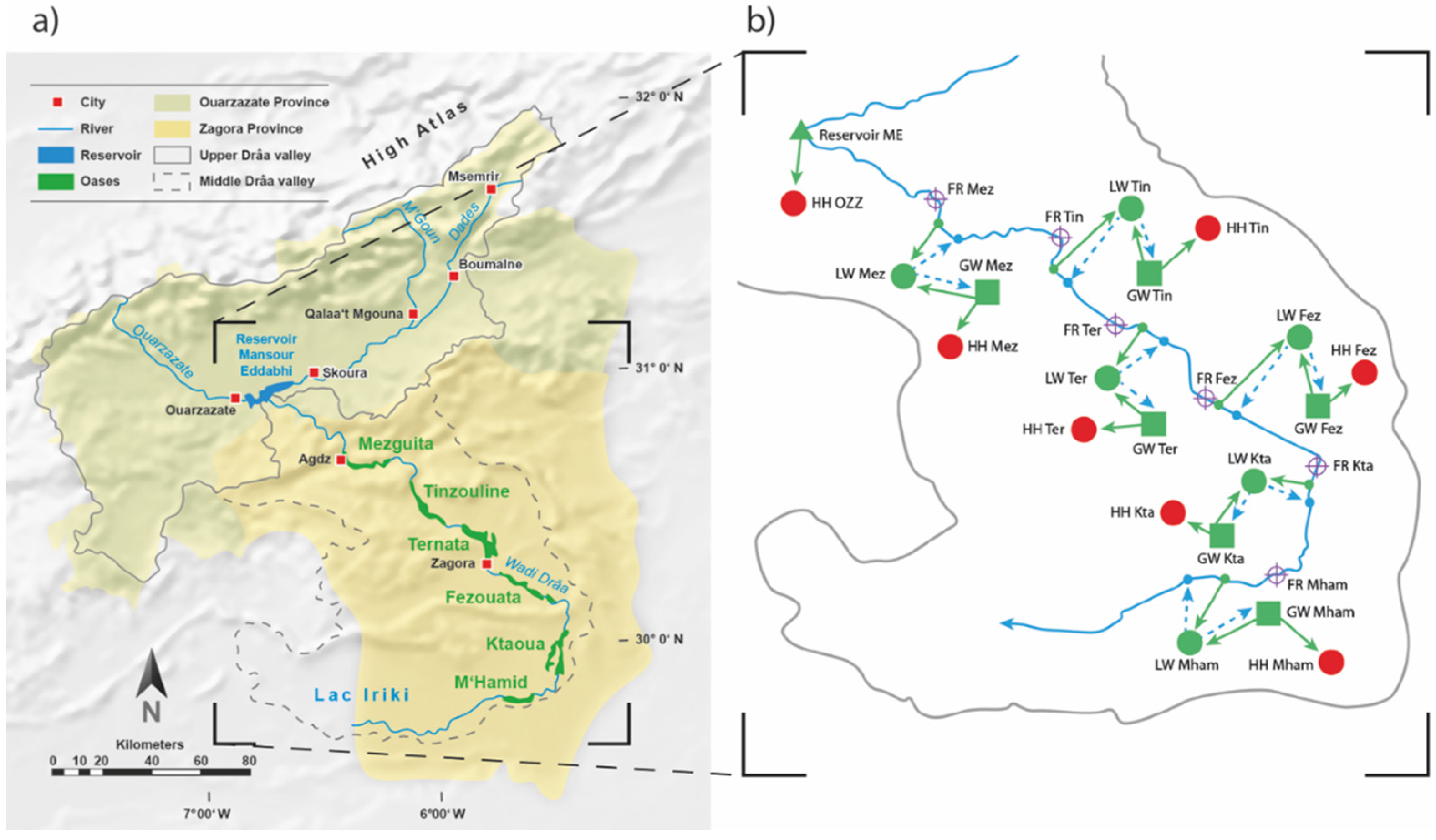
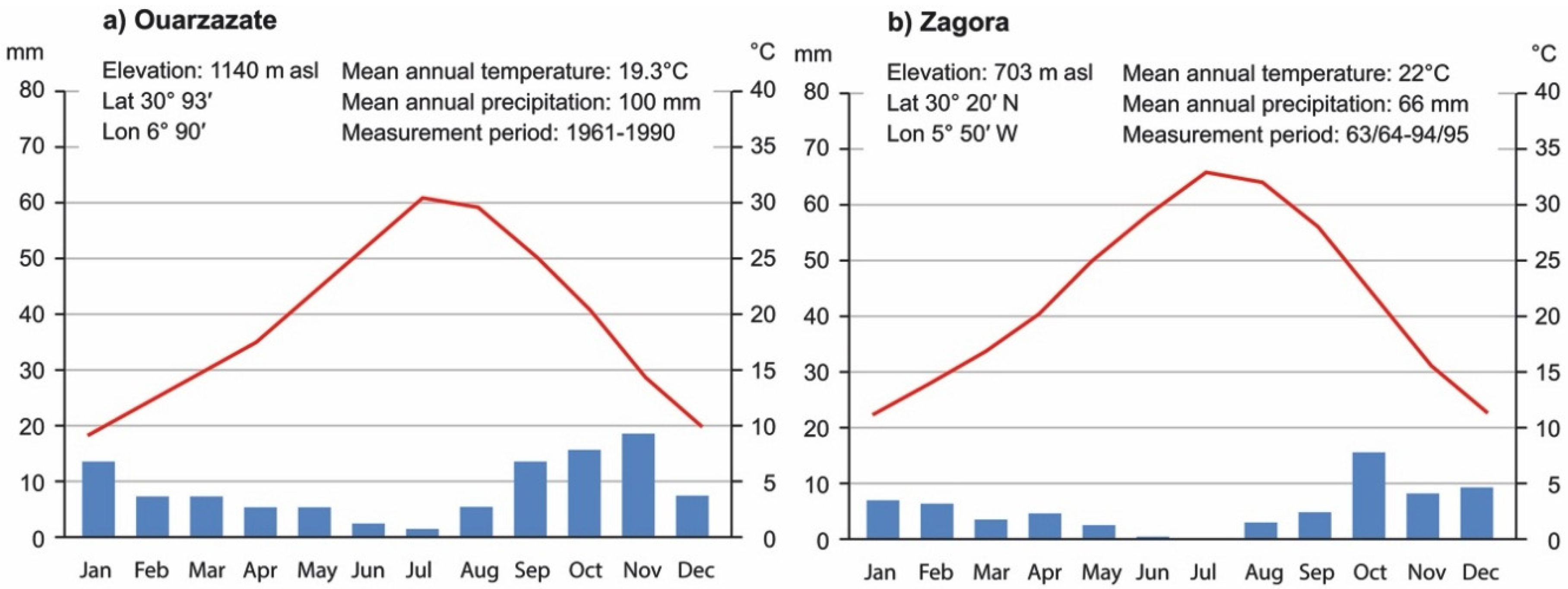
2 Study Area
3 Methods
3.1. WEAP
3.2. Input Data
3.2.1. Hydrologic Parameterization
3.2.2. Reservoir and Households
3.2.3. Agricultural Area and Irrigation Requirements
3.3. Future Scenarios
3.3.1. Climate Scenario
3.3.2. Socioeconomic Scenarios
3.3.3. M1: Marginalization—Non-Support of the Drâa Region
3.3.4. M2: Rural Development through Regional Funds
3.3.5. M3: Business as Usual
3.3.6. Sub-Scenarios for the Middle Drâa Region
3.3.7. L1—Pro Dates
3.3.8. L2—Fallow Land
4 Results and Discussion
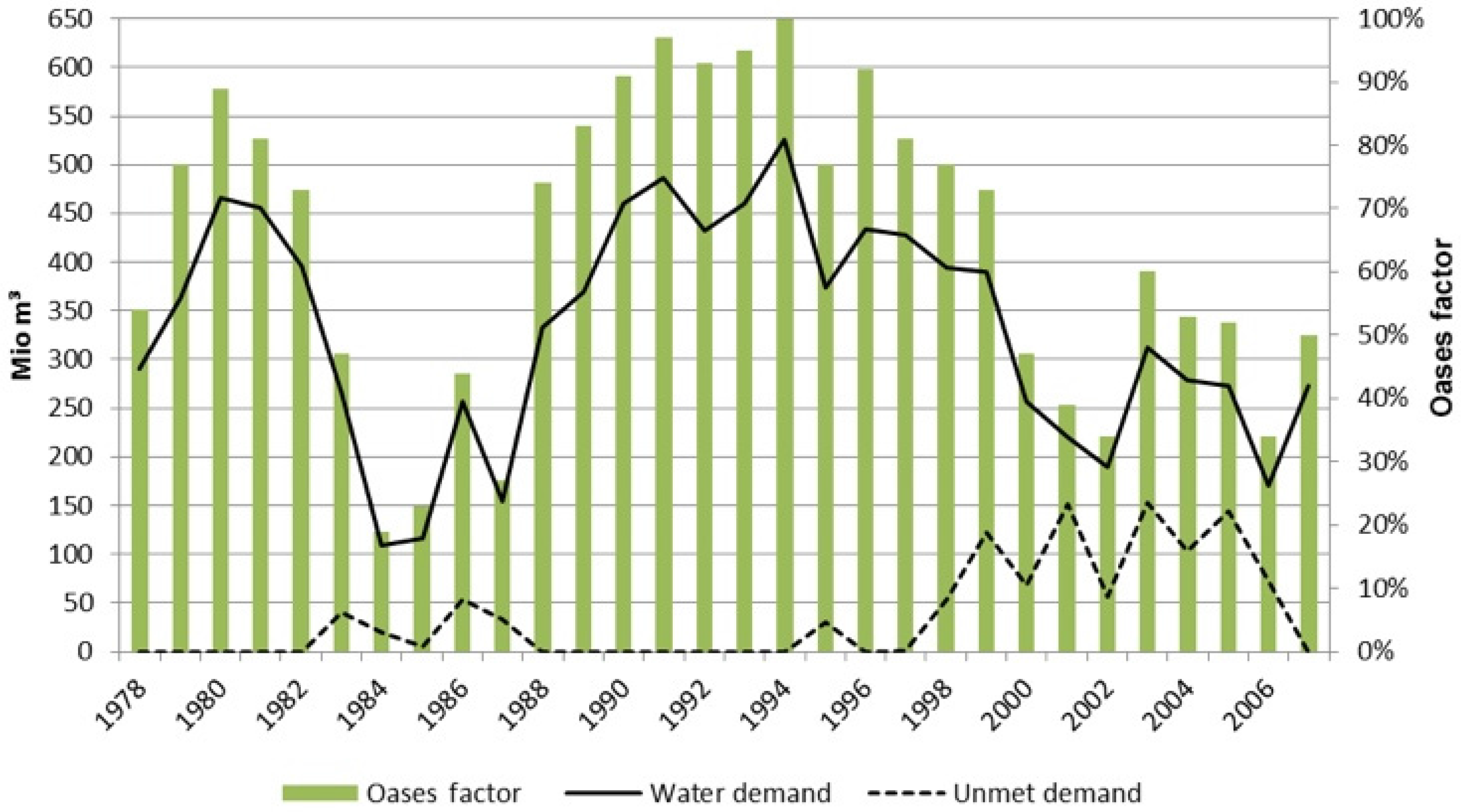
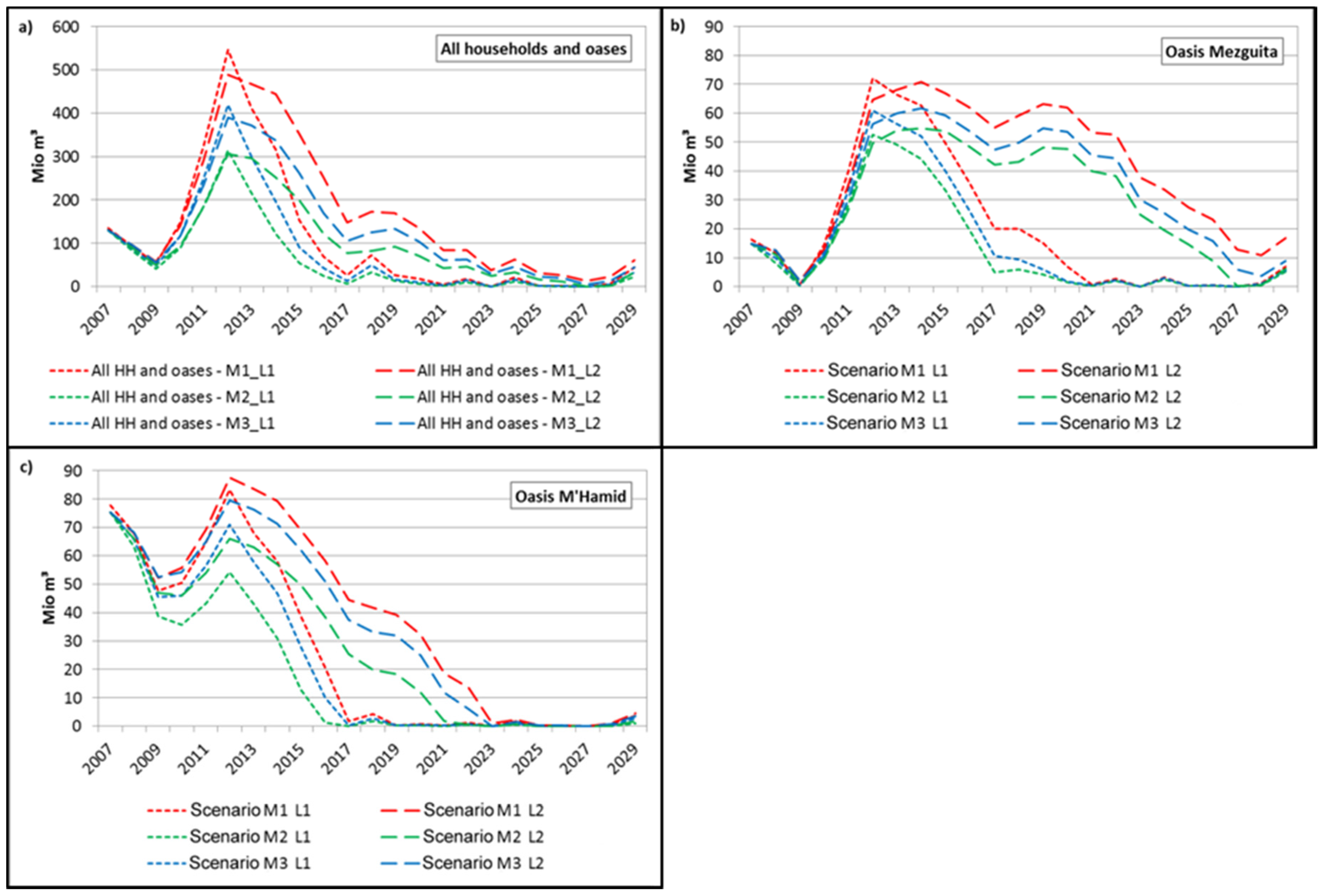
4.1. Water Demand
4.2. Reservoir
4.3. Groundwater Storage
Groundwater Storage in the Land Use Scenarios
4.4. Unmet Demand
4.4.1. Water Demand and Unmet Demand in the Land Use Scenarios
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Droogers, P.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Terink, W.; Hoogeveen, J.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Debele, B. Water Resources Trends in Middle East and North Africa Towards 2050. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3101–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Page, M.; Berjamy, B.; Fakir, Y.; Bourgin, F.; Jarlan, L.; Abourida, A.; Benrhanem, M.; Jacob, G.; Huber, M.; Sghrer, F.; et al. An Integrated DSS for Groundwater Management Based on Remote Sensing. The Case of a Semi-arid Aquifer in Morocco. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 26, 3209–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Africa Progress Report. Grain, Fish, Money. Financing Africa’s Green and Blue Revolutions; Senegal, 2014. Available online: http://app-cdn.acwupload.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/APP_APR2014_24june.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2016).
- Busche, H.G.K. Hydrology of the Drâa Basin. In Impetus Atlas Morocco: Research Results 2000–2007, 3rd ed.; Schulz, O., Judex, M., Eds.; Department of Geography, University of Bonn: Bonn, Germany, 2008; pp. 43–44. Available online: http://www.impetus.uni-koeln.de/en/impetus-atlas/impetus-atlas-morocco.html (accessed on 14 March 2016).
- Messouli, M.; Ben Salem, A.; Ghallabi, B.; Yacoubi-Khebiza, M.; Ait Boughrous, A.; El Alami El Filali, A.; Rochdane, S.; Ezzahra Hammadi, F. Ecohydrology and Groundwater Resources Management under Global Change: A Pilot Study in the Pre-Saharan Basins of Southern Morocco. Options Méditer. 2009, 88, 255d–264d. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaoui, A.; Messouli, M.; Ifaadassan, I.; Khebiza, M.Y. A Multidisciplinary Approach to Assess the Environmental Vulnerability at Local Scale in Context of Climate Change (Pilot Study in Upper Draa Valley, South Morocco). Glob. J. Technol. Optim. 2014, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busche, H.G.K. Modeling Hydrological Processes in a Semi-arid Mountainous Catchment at the Regional Scale. Dissertation, University of Bonn, Bonn, Germany, August 2012. Available online: http://hss.ulb.uni-bonn.de/2013/3173/3173.htm (accessed on 14 March 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Ghallabi, L.B.; Messouli, M.; Yacoubi, M. Integrated Approaches to the Assessment of the Impacts of Climate and Socio-economic Change on Groundwater Resources in the Tensift Basin, Morocco. Int. J. Water Resour. Arid Environ. 2011, 1, 219–225. Available online: http://www.psipw.org/attachments/article/304/IJWRAE_1%283%29219–225.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Ben Salem, A.; Messouli, M.; Yacoubi-khebiza, M. Developing an Oasis-Based Water Management Tool: Ecohydrologic Approach and Weap Software for a Large Arid Catchment in Morocco. Int. J. Water Resour. Arid Environ. 2011, 1, 387–396. [Google Scholar]
- Rochdane, S.; Reichert, B.; Messouli, M.; Babqiqi, A.; Khebiza, M.Y. Climate Change Impacts on Water Supply and Demand in Rheraya Watershed (Morocco), with Potential Adaptation Strategies. Water 2012, 4, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, S. Regional Hydrogeology and Groundwater Budget Modeling in the Arid Middle Drâa Catchment. Dissertation, University of Bonn, Bonn, Germany, November 2012. Available online: http://hss.ulb.uni-bonn.de/2013/3330/3330.htm (accessed on 14 March 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Fink, A.; Reichert, B.; Christoph, M. West Africa An Integrated Approach to the Efficient Management of Scarce Water Resources in West Africa. In Impetus Atlas Morocco: Research Results 2000–2007, 3rd ed.; Schulz, O., Judex, M., Eds.; University of Bonn: Bonn, Germany, 2008; pp. 2–4. Available online: http://www.impetus.uni-koeln.de/en/impetus-atlas/impetus-atlas-morocco.html (accessed on 14 March 2016).
- Schulz, O. Snow Cover Variability in the High Atlas Mountains. In Impetus Atlas Morocco: Research Results 2000–2007, 3rd ed.; Schulz, O., Judex, M., Eds.; University of Bonn: Bonn, Germany, 2008; pp. 22–23. Available online: http://www.impetus.uni-koeln.de/en/impetus-atlas/impetus-atlas-morocco.html (accessed on 14 March 2016).
- Hellegers, P.; Immerzeel, W.; Droogers, P. Economic Concepts to Address Future Water Supply-Demand Imbalances in Iran, Morocco and Saudi Arabia. J. Hydrol. 2013, 502, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlat, A.; Errih, M.; Guidoum, A. Simulation of Water Resources Management Scenarios in Western Algeria Watersheds Using WEAP Model. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaoui, S.O.; Snani, S.; Djebbar, Y. Management of Water Resources at Souk-Ahras Region (Algeria). In Proceedings of the 14th International Water Technology Conference, IWTC 14, Cairo, Egypt, 21–23 March 2010; pp. 599–608. Available online: http://www.iwtc.info/2010_pdf/09–05.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2016).
- Yates, D.N.; Sieber, J.; Purkey, D.R.; Huber-Lee, A. WEAP21—A Demand-, Priority-, and Preference-Driven Water Planning Model. Part 1: Model Characteristics. Water Int. 2005, 30, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, B.; Vicuña, S.; Dale, L.; Dracup, J.; Hanemann, M.; Purkey, D.; Yates, D. Climate Change Impacts on Water for Agriculture in California: A Case Study in the Sacramento Valley; California Climate Change Center: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Purkey, D.; Joyce, B.; Vicuna, S.; Hanemann, M.; Dale, L.; Yates, D.; Dracup, J. Robust Analysis of Future Climate Change Impacts on Water for Agriculture and Other Sectors: A Case Study in the Sacramento Valley. Clim. Chang. 2008, 87, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höllermann, B.; Giertz, S.; Diekkrüger, B. Benin 2025—Balancing Future Water Availability and Demand Using the WEAP ‘Water Evaluation and Planning’ System. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 3591–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, H.; Bonzi, C.; Joyce, B.; Tielbörger, K. A Water Resources Planning Tool for the Jordan River Basin. Water 2011, 3, 718–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speth, P.; Christoph, M.; Diekkrüger, B. (Eds.) Impacts of Global Change on the Hydrological Cycle in West and Northwest Africa; Springer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010.
- Schulz, O.; Judex, M. (Eds.) IMPETUS Atlas Marocco: Research Results 2000–2007, 3rd ed.; Department of Geography, University of Bonn: Bonn, Germany, 2008.
- Klose, A. Soil Characteristics and Soil Erosion by Water in a Semi-arid Catchment (Wadi Drâa, South Morocco) under the Pressure of Global Change. Dissertation, University of Bonn, Bonn, Germany, August 2009. Available online: http://hss.ulb.uni-bonn.de/2009/1959/1959.htm (accessed on 14 December 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Diekkrüger, B.; Busche, H.; Giertz, S.; Steup, G. Hydrology. In Impacts of Global Change on the Hydrological Cycle in West and Northwest Africa; Speth, P., Christoph, M., Diekkrüger, B., Eds.; Springer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Heidecke, C. Economic Analysis of Water Use and Management in the Middle Drâa Valley in Morocco. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bonn, Bonn, Germany, September 2009. Available online: http://hss.ulb.uni-bonn.de/2010/2022/2022.pdf (accessed 14 December 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Platt, S. Current Development of the Population in the Provinces of Ouarzazate and Zagora. In Impetus Atlas Morocco: Research Results 2000–2007, 3rd ed.; Schulz, O., Judex, M., Eds.; University of Bonn: Bonn, Germany, 2008; pp. 59–60. Available online: http://www.impetus.uni-koeln.de/en/impetus-atlas/impetus-atlas-morocco.html (accessed on 14 March 2016).
- Heidecke, C.; Schmidt, T. Agricultural Land Use. In Impetus Atlas Morocco: Research Results 2000–2007, 3rd ed.; Schulz, O., Judex, M., Eds.; University of Bonn: Bonn, Germany, 2008; pp. 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, V.K.; Haden, V.R.; Joyce, B.A.; Purkey, D.R.; Jackson, L.E. Irrigation Demand and Supply, Given Projections of Climate and Land-use Change, in Yolo County, California. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 117, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. ETc—Single Crop Coefficient (Kc). Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/x0490e/x0490e0b.htm (accessed on 25 September 2015).
- Reichert, B.; Jaeger, A. Socio-economic Scenarios. In Impacts of Global Change on the Hydrological Cycle in West and Northwest Africa; Speth, P., Christoph, M., Diekkrüger, B., Eds.; Springer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 426–441. [Google Scholar]
- Rössler, M.; Kirscht, H.; Rademacher, C.; Platt, S.; Kemmerling, B.; Linstädter, A. Migration and Resource Management in the Drâa Valley, Southern Morocco. In Impacts of Global Change on the Hydrological Cycle in West and Northwest Africa; Speth, P., Christoph, M., Diekkrüger, B., Eds.; Springer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 584–597. [Google Scholar]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. A Global Assessment of the Water Footprint of Farm Animal Products. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.M. Livestock Water Needs in Pastoral Africa in Relation to Climate and Forage; International Livestock Centre for Africa: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Descheemaeker, K.; Amede, T.; Haileslassie, A. Improving Water Productivity in Mixed Crop-Livestock Farming Systems of Sub-Saharan Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, A.; Busche, H.; Klose, S.; Schulz, O.; Diekkrüger, B.; Reichert, B.; Winiger, M. Hydrological Processes and Soil Degradation in Southern Morocco. In Impacts of Global Change on the Hydrological Cycle in West and Northwest Africa; Speth, P., Christoph, M., Diekkrüger, B., Eds.; Springer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 198–253. [Google Scholar]
- Heidecke, C.; Kuhn, A.; Liebelt, C. Hydro-economic Processes and Institutions in Southern Morocco. In Impacts of Global Change on the Hydrological Cycle in West and Northwest Africa; Speth, P., Christoph, M., Diekkrüger, B., Eds.; Springer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 329–341. [Google Scholar]
- Tsur, Y. The Stabilization Role of Groundwater When Surface Water Supplies are Uncertain: The Implications for Groundwater Development. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, J.; Purkey, D. WEAP Water Evaluation and Planning System: User Guide; Stockholm Environment Institute: Somerville, MA, USA, 2008; Available online: http://www.weap21.org/downloads/WEAP_User_Guide.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2016).
- Storm, H. Willigness to Pay for Irrigation Water in the Drâa Valley in Morocco—An Application of the Contingent Valuation Method and the MIVAD Model. Unpublished Diploma Thesis, University of Bonn, Bonn, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Askri, B.; Ahmed, A.T.; Abichou, T.; Bouhlila, R. Effects of Shallow Water Table, Salinity and Frequency of Irrigation Water on the Date Palm Water Use. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]




| Oasis Name | Aquifer Size/Storage Capacity (Million m3) | Aquifer’s Specific Yield | Aquifer’s Initial Storage (Million m3 in the Year 1978 | Max. Total Field Size (ha) | Share on Total Water Release from Reservoir |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mezguita | 119 | 19% | 46.4 | 2419 | 8% |
| Tinzouline | 254 | 22% | 74.5 | 4015 | 8% |
| Ternata | 166 | 15% | 42.6 | 5858 | 30% |
| Fezouata | 156 | 10% | 101.5 | 3825 | 14% |
| Ktaoua | 5201 | 13% | 363.8 | 7770 | 28% |
| M’Hamid | 333 | 15% | 264.0 | 2231 | 12% |
| Topic | M1—Marginalization | M2—Rural Development | M3—Business as Usual |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population | OZZ: 6% increase | OZZ: 3% increase | OZZ: 4% increase |
| Oasis: 6% decrease | Oasis: constant growth | Oasis: 3% decrease | |
| Siltation of the reservoir | Storage volume decrease: 206 Mm3 by 2029 | Storage volume decrease: 284 Mm3 by 2029 | Storage volume decrease: 214 Mm3 by 2029 |
| Agriculture area | Effective cultivated area do not exceed 90% of the possible agriculture area | Effective cultivated area does not fall below 60% of the possible agriculture area | Effective cultivated area follows the traditional climate adaption practices |
| Irrigation efficiency | Decrease of irrigation efficiency down to 75% | Increase of irrigation efficiency up to 95% | Constant value of 85% for irrigation efficiency |
| L1—Pro Dates | L2—Fallow Land |
|---|---|
| Dates increased by 10% | Barley set to 2% |
| Barley reduced by 3% | Alfalfa set to 2% |
| Alfalfa reduced by 7% | Henna set to 0% |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johannsen, I.M.; Hengst, J.C.; Goll, A.; Höllermann, B.; Diekkrüger, B. Future of Water Supply and Demand in the Middle Drâa Valley, Morocco, under Climate and Land Use Change. Water 2016, 8, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080313
Johannsen IM, Hengst JC, Goll A, Höllermann B, Diekkrüger B. Future of Water Supply and Demand in the Middle Drâa Valley, Morocco, under Climate and Land Use Change. Water. 2016; 8(8):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080313
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohannsen, Irene M., Jennifer C. Hengst, Alexander Goll, Britta Höllermann, and Bernd Diekkrüger. 2016. "Future of Water Supply and Demand in the Middle Drâa Valley, Morocco, under Climate and Land Use Change" Water 8, no. 8: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080313
APA StyleJohannsen, I. M., Hengst, J. C., Goll, A., Höllermann, B., & Diekkrüger, B. (2016). Future of Water Supply and Demand in the Middle Drâa Valley, Morocco, under Climate and Land Use Change. Water, 8(8), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080313







