Microtopography Governs Tidal Inundation Frequency in the Luanhe Estuarine Salt Marsh: A Decadal Assessment Integrating Sentinel Data and UAV Photogrammetry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
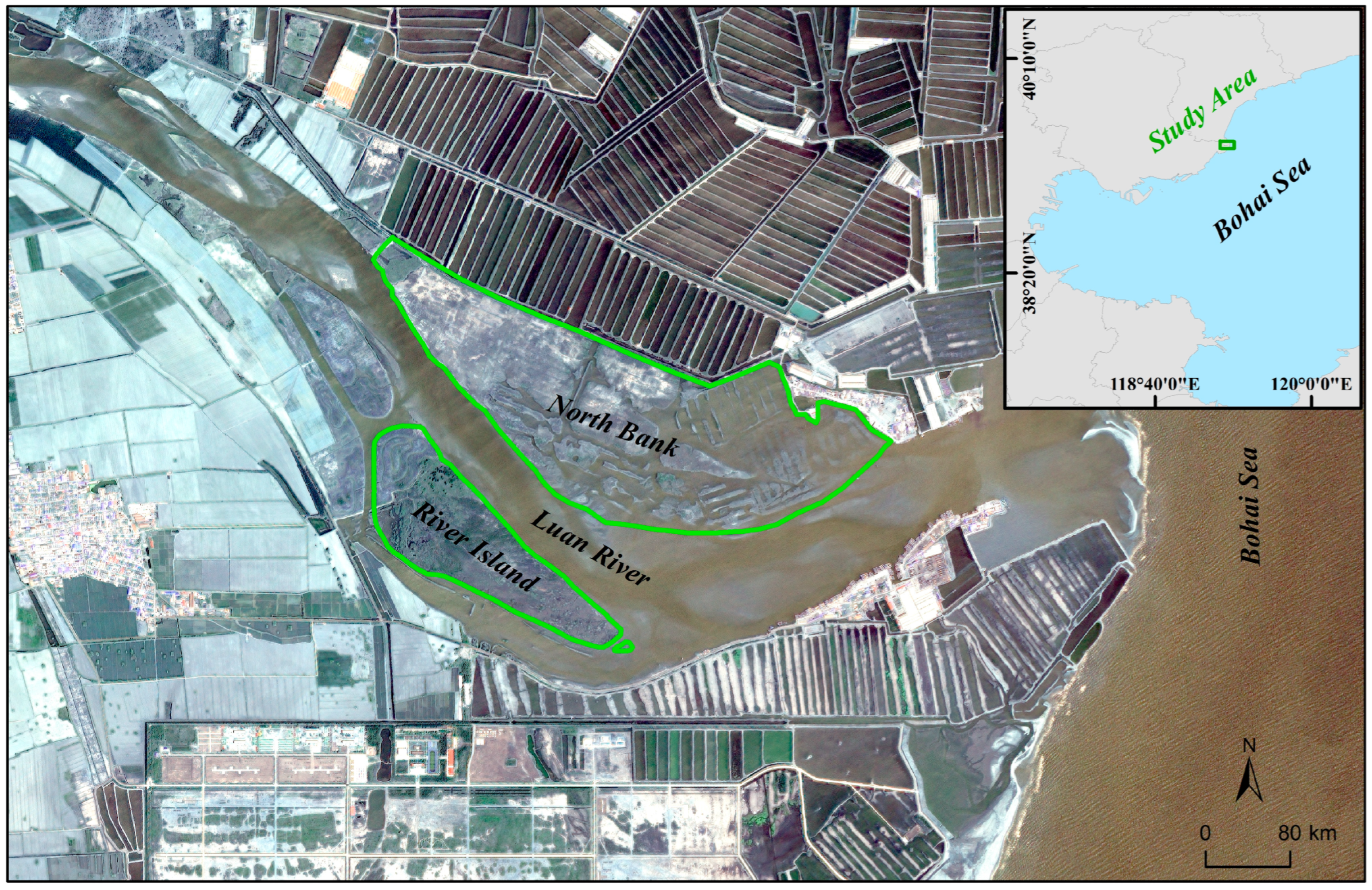
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Extraction of Inundation Water from Remote Sensing Imagery
2.3.2. Temporal Coordination and Tidal Normalization for AIF Calculation
2.3.3. Integration of Multiple Data Sources and Computation of Flood Exposure Frequency
2.3.4. Microtopography-Driven Mechanism and Long-Term Inundation Modeling
2.3.5. Critical Thresholds and Hotspot Delineation
3. Results
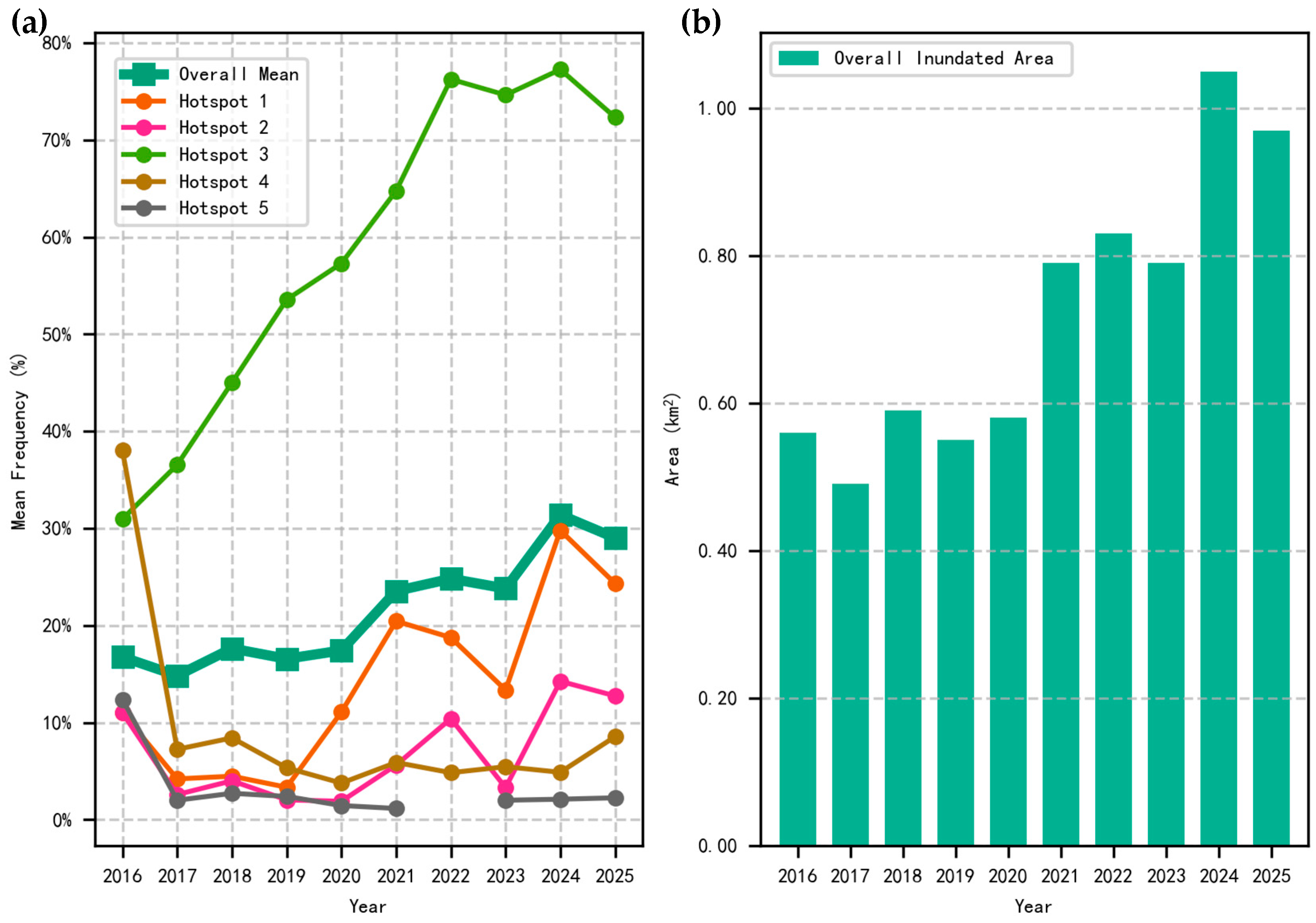
3.1. Analysis of Inundation Exposure Trend (2016–2025)
3.2. Spatial Variation and Hotspot Analysis of Saltmarsh Inundation Exposure
3.3. The Correlation Between Flooding Frequency and Microtopographical Features
3.4. Model Robustness and Prediction Accuracy Validation
4. Discussion
4.1. Evolution of Inundation Risk Under Macro Drivers and Nonlinear Accumulation
4.2. Critical Control of Microtopography and Biogeomorphological Feedback
4.3. Management Implications, Applicability, and Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pham, T.D.; Ha, N.T.; Saintilan, N.; Skidmore, A.; Phan, D.C.; Le, N.N.; Viet, H.L.; Takeuchi, W.; Friess, D.A. Advances in Earth Observation and Machine Learning for Quantifying Blue Carbon. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2023, 243, 104501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, G.; Fang, R.; Xu, S. Blue Carbon Governance for Carbon Neutrality in China: Policy Evaluation and Perspectives. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, A.; Wang, Y. Examining the Influence of Tidal Stage on Salt Marsh Mapping Using High-Spatial-Resolution Satellite Remote Sensing and Topobathymetric LiDAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5169–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, D.; Bruce, E. Examining Tidal Inundation and Salt Marsh Vegetation Distribution Patterns Using Spatial Analysis (Botany Bay, Australia). J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockelmann, A.-C.; Bakker, J.P.; Neuhaus, R.; Lage, J. The Relation between Vegetation Zonation, Elevation and Inundation Frequency in a Wadden Sea Salt Marsh. Aquat. Bot. 2002, 73, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mury, A.; Jeanson, M.; Collin, A.; James, D.; Etienne, S.; Mury, A.; Jeanson, M.; Collin, A.; James, D.; Etienne, S. High Resolution Shoreline and Shelly Ridge Monitoring over Stormy Winter Events: A Case Study in the Megatidal Bay of Mont-Saint-Michel (France). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Wang, N.; Yu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Lv, L.; Xie, Z. An Enhanced Monitoring Method for Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Salt Marsh Vegetation Using Google Earth Engine. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 298, 108658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Xu, N.; Xu, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Luan, H.; Ou, Y.; Yang, Y. Mapping Tidal Flat Topography by Combining ICESat-2 Laser Altimetry and Multi-Source Satellite Imagery. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2025, 18, 2554313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Ma, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, R. Deriving Tidal Flat Topography Using ICESat-2 Laser Altimetry and Sentinel-2 Imagery. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laengner, M.L.; van der Wal, D. Satellite-Derived Trends in Inundation Frequency Reveal the Fate of Saltmarshes. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 942719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanslow, D.J.; Fitzhenry, M.G.; Power, H.E.; Kinsela, M.A.; Hughes, M.G. Rising Tides: Tidal Inundation in South East Australian Estuaries. In Proceedings of the Australasian Coasts and Ports 2019 Conference: Future Directions from 40 °S and Beyond, Hobart, Australia, 10–13 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kumbier, K.; Rogers, K.; Hughes, M.G.; Lal, K.K.; Mogensen, L.A.; Woodroffe, C.D. An Eco-Morphodynamic Modelling Approach to Estuarine Hydrodynamics & Wetlands in Response to Sea-Level Rise. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 860910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksena, S.; Merwade, V. Incorporating the Effect of DEM Resolution and Accuracy for Improved Flood Inundation Mapping. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, H.; Stefanakis, E.; Nastev, M. DEM Fusion of Elevation REST API Data in Support of Rapid Flood Modelling. Geomatica 2016, 70, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Peng, F.; Peng, Y.; Kong, X.; Liang, H.; Li, Q. Dynamic 3D Simulation of Flood Risk Based on the Integration of Spatio-Temporal GIS and Hydrodynamic Models. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Shen, F.; Tan, K.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; Lam, N.S.N.; Ge, J. Monitoring Terrain Elevation of Intertidal Wetlands by Utilising the Spatial-Temporal Fusion of Multi-Source Satellite Data: A Case Study in the Yangtze (Changjiang) Estuary. Geomorphology 2021, 383, 107683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, E.M.; Bates, P.D.; Freer, J.E.; Mason, D.C. The Impact of Uncertainty in Satellite Data on the Assessment of Flood Inundation Models. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.M.; Izco, J.; Medrano, M. Relationships between Vegetation Zonation and Altitude in a Salt-Marsh System in Northwest Spain. J. Veg. Sci. 1996, 7, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennings, S.C.; Grant, M.-B.; Bertness, M.D. Plant Zonation in Low-Latitude Salt Marshes: Disentangling the Roles of Flooding, Salinity and Competition. J. Ecol. 2005, 93, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D. Rates of Vegetation Dynamics Along Elevation Gradients in a Backbarrier Salt Marsh of the Danish Wadden Sea. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Luo, M.; Cui, B.; Chen, C.; Xie, T.; Li, X.; Lu, F. Effects of Varied Inundation Characteristics on Early Life Stages of a Salt Marsh Plant. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1449034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuzzo, E.; Finotello, A.; D’Alpaos, A.; Marani, M. Species Competition and Dispersal Drive Vegetation Dynamics in Tidal Salt Marshes. In Proceedings of the 24th EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Wu, G.; Liang, B.; Shi, B.; Li, H. Deltaic Marsh Accretion under Episodic Sediment Supply Controlled by River Regulations and Storms: Implications for Coastal Wetlands Restoration in the Yellow River Delta. J. Hydrol. 2024, 635, 131221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Chen, S.; Ji, H.; Li, P.; Dou, S.; Fan, Y.; Yu, S.; et al. Changes of Inundation Frequency in the Yellow River Delta and Its Response to Wetland Vegetation. Land 2022, 11, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Q.; Wang, B.; Zhu, L.; Fu, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Bi, N. Rapid Change of Vegetation Cover in the Huanghe (Yellow River) Mouth Wetland and Its Biogeomorphological Feedbacks. CATENA 2024, 238, 107875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, M.; Shen, H.; Cao, Q.; Ding, X.; Xin, M.; Zhai, M.; Shen, H.; Cao, Q.; Ding, X.; Xin, M. Water Body Extraction Methods for SAR Images Fusing Sentinel-1 Dual-Polarized Water Index and Random Forest. Sensors 2025, 25, 4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.K.; Chandra, S.; Henry, P.K. Estimation of Flood Inundation in River Basins of Uttar Pradesh Using Sentinel 1A-SAR Data on Sentinel Application Platform (SNAP). Arab. J. Geosci. 2024, 17, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Ti, Y. Comparative Study on Water Extraction Based on Sentinel Image and UAV Image. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Geology, Mapping, and Remote Sensing (ICGMRS 2024), Wuhan, China, 12–14 April 2024; SPIE: Pune, India, 2024; Volume 13223, pp. 430–435. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Xiang, L.; Steffen, H.; Jia, L.; Deng, F.; Wang, W.; Hu, K.; Guo, J.; Nong, A.; Cui, H.; et al. A New and Robust Index for Water Body Extraction from Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Groth, S.; Wieland, M.; Knopp, L.; Rättich, M. Towards a Global Seasonal and Permanent Reference Water Product from Sentinel-1/2 Data for Improved Flood Mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 278, 113077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagherazzi, S.; Kirwan, M.L.; Mudd, S.M.; Guntenspergen, G.R.; Temmerman, S.; D’Alpaos, A.; van de Koppel, J.; Rybczyk, J.M.; Reyes, E.; Craft, C.; et al. Numerical Models of Salt Marsh Evolution: Ecological, Geomorphic, and Climatic Factors. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagherazzi, S.; Mariotti, G.; Leonardi, N.; Canestrelli, A.; Nardin, W.; Kearney, W.S. Salt Marsh Dynamics in a Period of Accelerated Sea Level Rise. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2020, 125, e2019JF005200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Changes of Groundwater Flow Field of Luanhe River Delta under the Human Activities and Its Impact on the Ecological Environment in the Past 30 Years. China Geol. 2021, 4, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedan, K.B.; Silliman, B.R.; Bertness, M.D. Centuries of Human-Driven Change in Salt Marsh Ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bost, M.C.; Rodriguez, A.B.; McKee, B.A. Impact of Land-Use Change on Salt Marsh Accretion. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 299, 108693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, C.; Kenney, W.F.; Patterson-Boyarski, B.; Curtis, J.H.; Vélez, M.I.; Glodzik, K.; Escobar, J.; Brenner, M. Sea-Level Changes and Paleoenvironmental Responses in a Coastal Florida Salt Marsh over the Last Three Centuries. J. Paleolimnol. 2023, 69, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, G.S.; Harding, C.; Matte, P. Changing Processes Flooding a Salt Marsh in a Microtidal Estuary with a Drying Climate. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 295, 108573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Diggelen, J. Effects of Inundation Stress on Salt Marsh Halophytes. In Ecological Responses to Environmental Stresses; Rozema, J., Verkleij, J.A.C., Eds.; Tasks for vegetation science; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; Volume 22, pp. 62–75. ISBN 978-94-010-6757-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, H.; Wittyngham, S.S.; Kirwan, M.L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y. Life-History Plasticity of Intertidal Salt Marsh in Response to Sea Level Rise: Salinity and Inundation Modulate Size-Dependent Flowering of Spartina alterniflora. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 177, 113790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, A.M.; Antler, G.; Wilkening, J.V.; Basu, A.; Bradbury, H.J.; Clegg, J.A.; Gorka, M.; Lin, C.Y.; Mills, J.V.; Pellerin, A.; et al. Creek Dynamics Determine Pond Subsurface Geochemical Heterogeneity in East Anglian (UK) Salt Marshes. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Cairns, D.M.; Bartholdy, J. Tidal Creek Morphology and Sediment Type Influence Spatial Trends in Salt Marsh Vegetation. Prof. Geogr. 2013, 65, 544–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, G.; Zhai, J.; Cong, L.; Dai, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M. The Size and Distribution of Tidal Creeks Affects Salt Marsh Restoration. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 259, 110070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; van der Wal, D.; Li, X.; van Belzen, J.; Herman, P.M.J.; Hu, Z.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, L.; Bouma, T.J. Zooming in and out: Scale Dependence of Extrinsic and Intrinsic Factors Affecting Salt Marsh Erosion. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2017, 122, 1455–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatelli, C.; Ganju, N.K.; Zhang, X.; Fagherazzi, S.; Leonardi, N. Salt Marsh Loss Affects Tides and the Sediment Budget in Shallow Bays. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2018, 123, 2647–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Data Type | Data Source | Spatiotemporal Resolution | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-1 SAR | ESA Copernicus Hub | 10 m/6 Days | Time Series: 2016–2025; Preprocessed on GEE |
| Sentinel-2 MSI | ESA Copernicus Hub | 10 m/5 Days | Time Series: 2016–2025; Preprocessed on GEE |
| UAV DEM | DJI M350 RTK + South SA130 LiDAR | 0.5 m (Spatial) | Acquired: August 2025; Processed with Pix4D; Verified by RTK-GPS |
| UAV Multispectral Orthomosaic | DJI Mavic 3 Multispectral | 0.5 m (Spatial) | Acquired: August 2025; Serves as validation benchmark for water classification |
| Tidal Gauge Data | Temporary Tidal Station | 10 min intervals | Used for short-term water boundary calibration |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Ni, P.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Q.; Ling, Z. Microtopography Governs Tidal Inundation Frequency in the Luanhe Estuarine Salt Marsh: A Decadal Assessment Integrating Sentinel Data and UAV Photogrammetry. Water 2025, 17, 3559. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243559
Liu Y, Ni P, Ma W, Zhang Q, Hu Q, Ling Z. Microtopography Governs Tidal Inundation Frequency in the Luanhe Estuarine Salt Marsh: A Decadal Assessment Integrating Sentinel Data and UAV Photogrammetry. Water. 2025; 17(24):3559. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243559
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Youcai, Pingze Ni, Wang Ma, Qian Zhang, Qi Hu, and Ziyun Ling. 2025. "Microtopography Governs Tidal Inundation Frequency in the Luanhe Estuarine Salt Marsh: A Decadal Assessment Integrating Sentinel Data and UAV Photogrammetry" Water 17, no. 24: 3559. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243559
APA StyleLiu, Y., Ni, P., Ma, W., Zhang, Q., Hu, Q., & Ling, Z. (2025). Microtopography Governs Tidal Inundation Frequency in the Luanhe Estuarine Salt Marsh: A Decadal Assessment Integrating Sentinel Data and UAV Photogrammetry. Water, 17(24), 3559. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243559





