Hybrid Variational Modal Decomposition-Extreme Learning Machine-Adaptive Boosting Model for Monthly Runoff Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. VMD
2.2. ELM
2.3. AdaBoost
2.4. Modelling Process
- (1)
- Data preprocessing
- (2)
- Determination of optimal K and α values for VMD
- (3)
- Application of VMD
- (4)
- Application of hybrid ELM-AdaBoost model
- Construct the ELM model. The input features of this model consist of K modal IMF components with a lag of p months, where p is determined by the partial autocorrelation coefficient. The output features are the corresponding values of the runoff modal component for each month. Therefore, an ELM model is constructed for each IMF component and iteratively trained to create T weak ELM learners. The input layer has nodes, the hidden layer has L nodes, and the output layer has one node. Input weight matrix is randomly generated, where , with hidden layer bias vector , and each element is calculated using Equation (4) to determine the hidden layer output. The activation function of this model is a sigmoid function, i.e., , and the output weights are given by , where Y is the output matrix and H+ is the pseudoinverse matrix of H.
- Integrate AdaBoost. Given initial sample weights , each basic ELM classifier is trained using the current sample weight, the classification error is calculated as , and the sample weight is updated using Equation (5).
- (5)
- Feedback error correction
- (6)
- Denormalization and evaluation
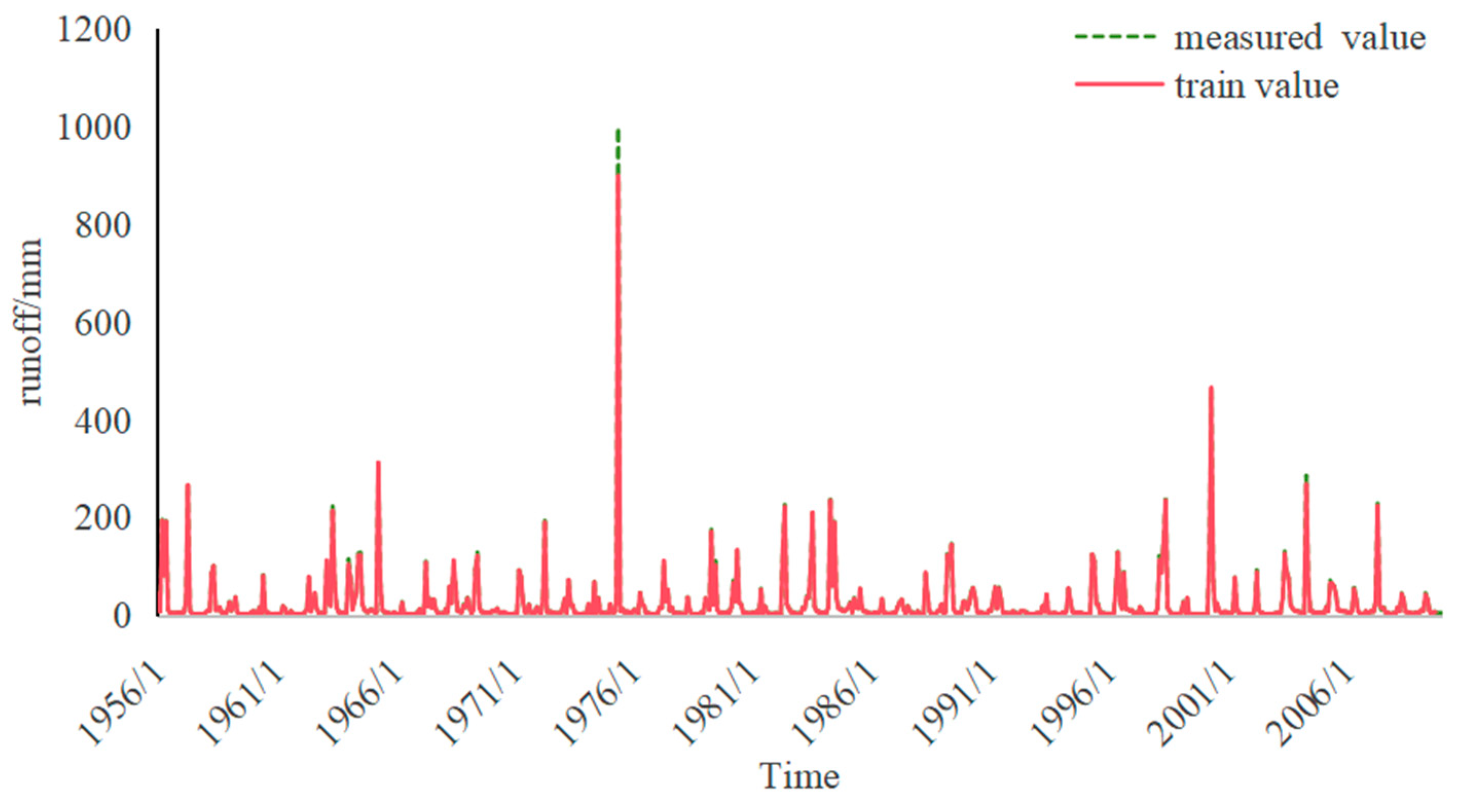
2.5. Overview of Research Area and Data Sources
3. Results
3.1. Monthly Runoff Sequence Decomposition
3.2. Model Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The VMD-ELM-AdaBoost model resolves issues of noise sensitivity and poor generalisation in nonstationary runoff prediction through “decomposition-ensemble-correction” collaborative optimisation. It outperforms all benchmark models in both deterministic accuracy and stability: on the validation set, it achieves the lowest root mean square error (RMSE = 2.5211 mm at Baiguishan Station, 2.9058 mm at Yanshan Station) and MAPE (8.56% at Baiguishan Station, 9.02% at Yanshan Station), outperforming LSTM by 77% in RMSE and VMD-TPE-LSTM by 63% in RMSE. The model also delivers lower prediction errors while avoiding the high data demand of deep learning models and the complex parameter optimisation of traditional ensemble models.
- Ablation experiments confirm the synergistic value of each component: PSO-optimised VMD effectively reduces the non-stationarity of raw runoff data, while AdaBoost significantly enhances ELM’s generalisation capability. This validates that the integrated design of the model is not a simple superposition of techniques but a targeted solution to the “non-stationarity + data scarcity” dual challenge in hydrological forecasting.
- The model only requires historical runoff data (no exogenous predictors such as precipitation or temperature) and maintains high accuracy in data-limited scenarios, making it a practical tool for monthly runoff forecasting in ungauged or poorly gauged basins. Its strong performance in predicting extreme runoff events (>100 mm) also provides reliable technical support for reservoir regulation, flood prevention, and drought early warning.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AdaBoost | Adaptive boosting |
| ELM | Extreme learning machine |
| IMF | Intrinsic modal function |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory |
| MAPE | Mean absolute percentage error |
| PACF | Partial autocorrelation function |
| PSO | Particle swarm optimisation |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| VMD | Variational modal decomposition |
| VEA | VMD-ELM-AdaBoost |
| VE | VMD-ELM |
| EA | ELM-AdaBoost |
| VTL | VMD-TPE-LSTM |
| MV | Measured value |
References
- Korsic, S.A.T.; Notarnicola, C.; Quirno, M.U.; Cara, L. Assessing a data-driven approach for monthly runoff prediction in a mountain basin of the Central Andes of Argentina. Environ. Chall. 2023, 10, 100680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.-H.; Kim, H.; Do, H.X.; Beling, P.A.; Lakshmi, V. A framework on utilizing of publicly availability stream gauges datasets and deep learning in estimating monthly basin-scale runoff in ungauged regions. Adv. Water Resour. 2024, 188, 104694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, K.; Wang, C. A novel monthly runoff prediction model based on KVMD and KTCN-LSTM-SA. Water 2025, 17, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.M.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.C. An ensemble model for monthly runoff prediction using least squares support vector machine based on variational modal decomposition with dung beetle optimization algorithm and error correction strategy. J. Hydrol. 2024, 629, 130558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.J.; Miller, S.N. Using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) to assess land use impact on water resources in an East African watershed. J. Hydrol. 2013, 486, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagena, M.B.; Goering, D.; Collick, A.S.; Bock, E.; Fuka, D.R.; Buda, A.; Easton, Z. Comparison of short-term streamflow forecasting using stochastic time series, neural networks, process-based, and Bayesian models. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2020, 126, 104669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, R.; Ansley, C. Estimation, Prediction, and Interpolation for ARIMA Models with Missing Data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1986, 81, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, R.M.; Mostafa, R.R.; Elbeltagi, A.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Shahid, S.; Kisi, O. Development of new machine learning model for streamflow prediction: Case studies in Pakistan. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 999–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Tao, S.; Dong, J.; Tsakiris, G. Runoff forecasting using convolutional neural networks and optimized Bi–directional Long Short-term Memory. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 937–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, K.C.; Ball, J.E.; Sharma, A. An application of artificial neural networks for rainfall forecasting. Math. Comput. Model. 2001, 33, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabbussum, R.; Dar, A.Q. Performance evaluation of artificial intelligence paradigms—Artificial neural networks, fuzzy logic, and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for flood prediction. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 25265–25282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Goel, N.K. Streamflow prediction using support vector regression machine learning model for Tehri Dam. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Liu, X.; Shen, Y.J. Applicability of the random forest model in quantifying the attribution of runoff changes. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2022, 30, 864–874. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papacharalampous, G.; Tyralis, H.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Comparison of stochastic and machine learning methods for multi-step ahead forecasting of hydrological processes. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2019, 33, 481–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzert, F.; Klotz, D.; Brenner, C.; Schulz, K.; Herrnegger, M. Rainfall–runoff modelling using long short-term memory (LSTM) networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6005–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lv, H.; Lv, S.; Sang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, X. Enhancing robustness of monthly streamflow forecasting model using gated recurrent unit based on improved grey wolf optimizer. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fila, R.J.J.B.; Attri, S.H.; Sharma, V. Mitigating overfitting in deep learning: Insights from Bayesian regularization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP), New Delhi, India, 27–29 September 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyükşahin, Ü.Ç.; Ertekin, Ş. Improving forecasting accuracy of time series data using a new ARIMA-ANN hybrid method and empirical mode decomposition. Neurocomputing 2019, 361, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Q.; Wu, X. A novel hybrid model by integrating TCN with TVFEMD and permutation entropy for monthly non-stationary runoff prediction. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Tang, S.; Zou, J.; Li, D.; Ge, X.; Huang, J.; Yin, X. Runoff prediction in different forecast periods via a hybrid machine learning model for Ganjiang River Basin, China. Water 2024, 16, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zou, J.; Ran, L.; Shi, R. Research on optimal selection of runoff prediction models based on coupled machine learning methods. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 32008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, R.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, X. Hydrological prediction in ungauged basins based on spatiotemporal characteristics. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0313535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Siew, C.K. Extreme learning machine: A new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 July 2004; Volume 2, pp. 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Siew, C.K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapire, R.E.; Freund, Y. Boosting: Foundations and Algorithms; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, K.; Xie, X.; Huang, Y.; Han, S.; Liu, G.; Chen, Z. VMD-ConvTSMixer: Spatiotemporal channel mixing model for non-stationary time series forecasting. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2025, 271, 126535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Babri, H.A. Upper bounds on the number of hidden neurons in feedforward networks with arbitrary bounded nonlinear activation functions. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1998, 9, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, Y.D.; Venayagamoorthy, G.K.; Mohagheghi, S.; Hernandez, J.-C.; Harley, R.G. Particle Swarm Optimization: Basic Concepts, Variants and Applications in Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2008, 12, 171–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Teng, Z.; Tian, F.; Yuan, P.; Yuan, X. Research on multi-step forecast of daily runoff based on VMD-PSO-LSTM model. Hydro-Sci. Eng. 2023, 4, 81–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, S. Research on monthly runoff forecasting method based on VMD-TPE-LSTM model. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 12, 213–225. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Site | Decompose Parameter K | Punishment Factor Parameter α |
|---|---|---|
| Yanshan Station | 4 | 458 |
| Baiguishan Station | 5 | 622 |
| Station Name | IMF | Input Step Length | Input Variable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yanshan Station | IMF1 | 5 | |
| IMF2 | 4 | ||
| IMF3 | 4 | ||
| IMF4 | 4 | ||
| Baiguishan Station | IMF1 | 4 | |
| IMF2 | 4 | ||
| IMF3 | 5 | ||
| IMF4 | 9 | ||
| IMF5 | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Tian, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y. Hybrid Variational Modal Decomposition-Extreme Learning Machine-Adaptive Boosting Model for Monthly Runoff Prediction. Water 2025, 17, 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213129
Wu L, Tian J, Jiang Z, Wang Y. Hybrid Variational Modal Decomposition-Extreme Learning Machine-Adaptive Boosting Model for Monthly Runoff Prediction. Water. 2025; 17(21):3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213129
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Li, Junfeng Tian, Zhongfeng Jiang, and Yong Wang. 2025. "Hybrid Variational Modal Decomposition-Extreme Learning Machine-Adaptive Boosting Model for Monthly Runoff Prediction" Water 17, no. 21: 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213129
APA StyleWu, L., Tian, J., Jiang, Z., & Wang, Y. (2025). Hybrid Variational Modal Decomposition-Extreme Learning Machine-Adaptive Boosting Model for Monthly Runoff Prediction. Water, 17(21), 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213129





