From Sources to Environmental Risks: Research Progress on Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in River and Lake Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bibliometric Overview of PFASs Research in River and Lake Environments
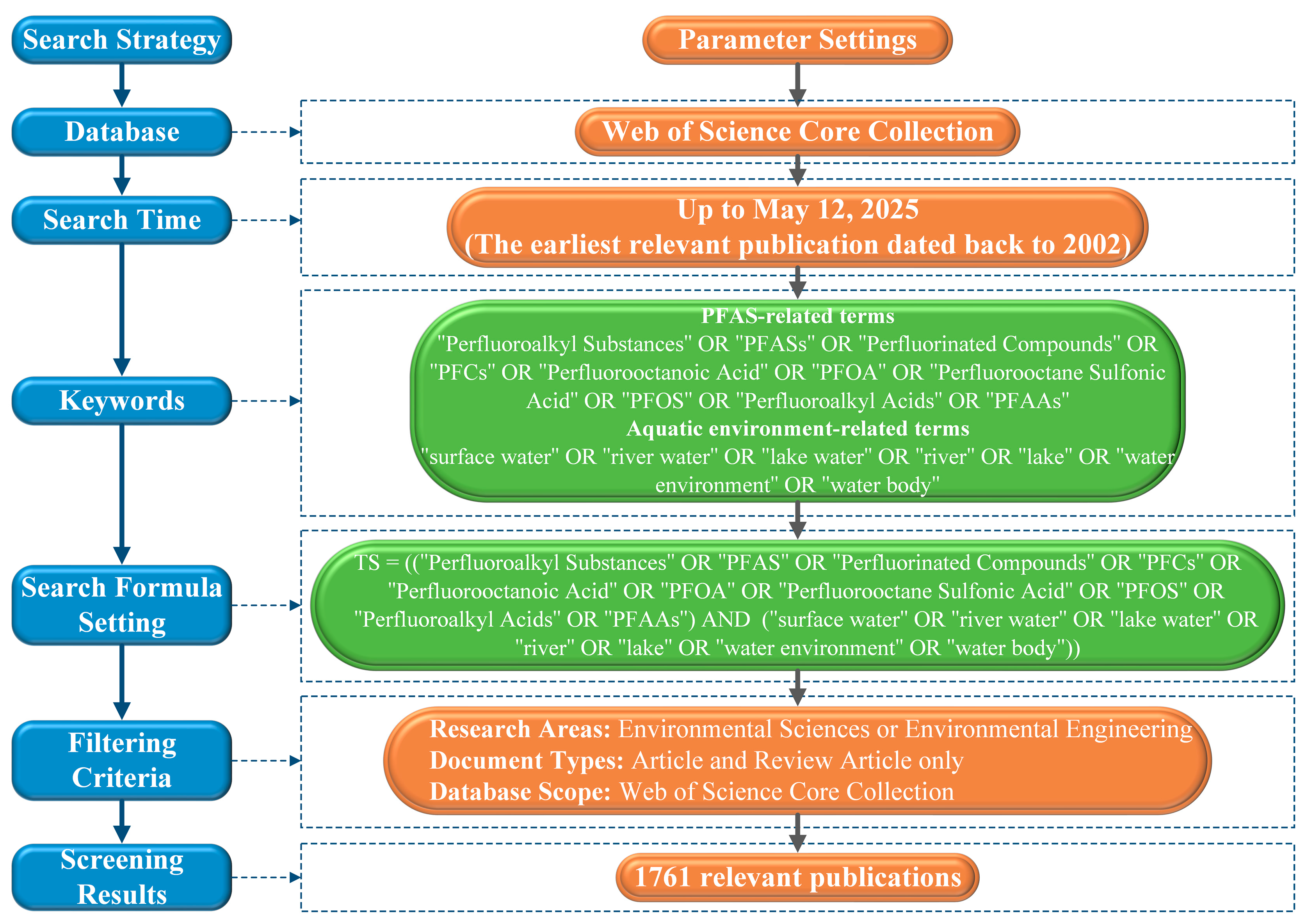
2.1. Data Sources and Analytical Methods
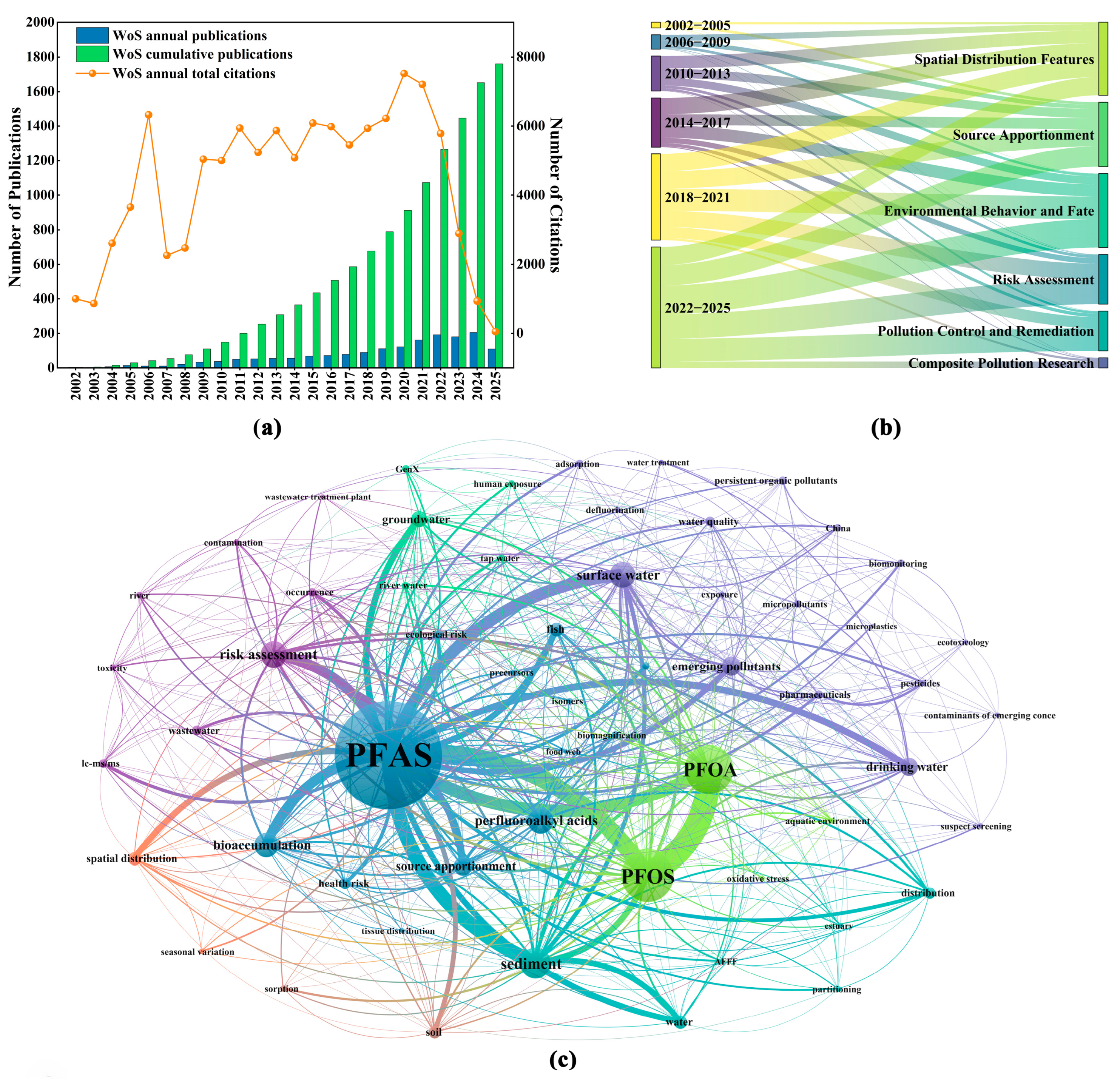
2.2. Publication Trends, Evolutionary Patterns, and Research Hotspots
3. Sources and Pollution Characteristics of PFASs in River and Lake Environments
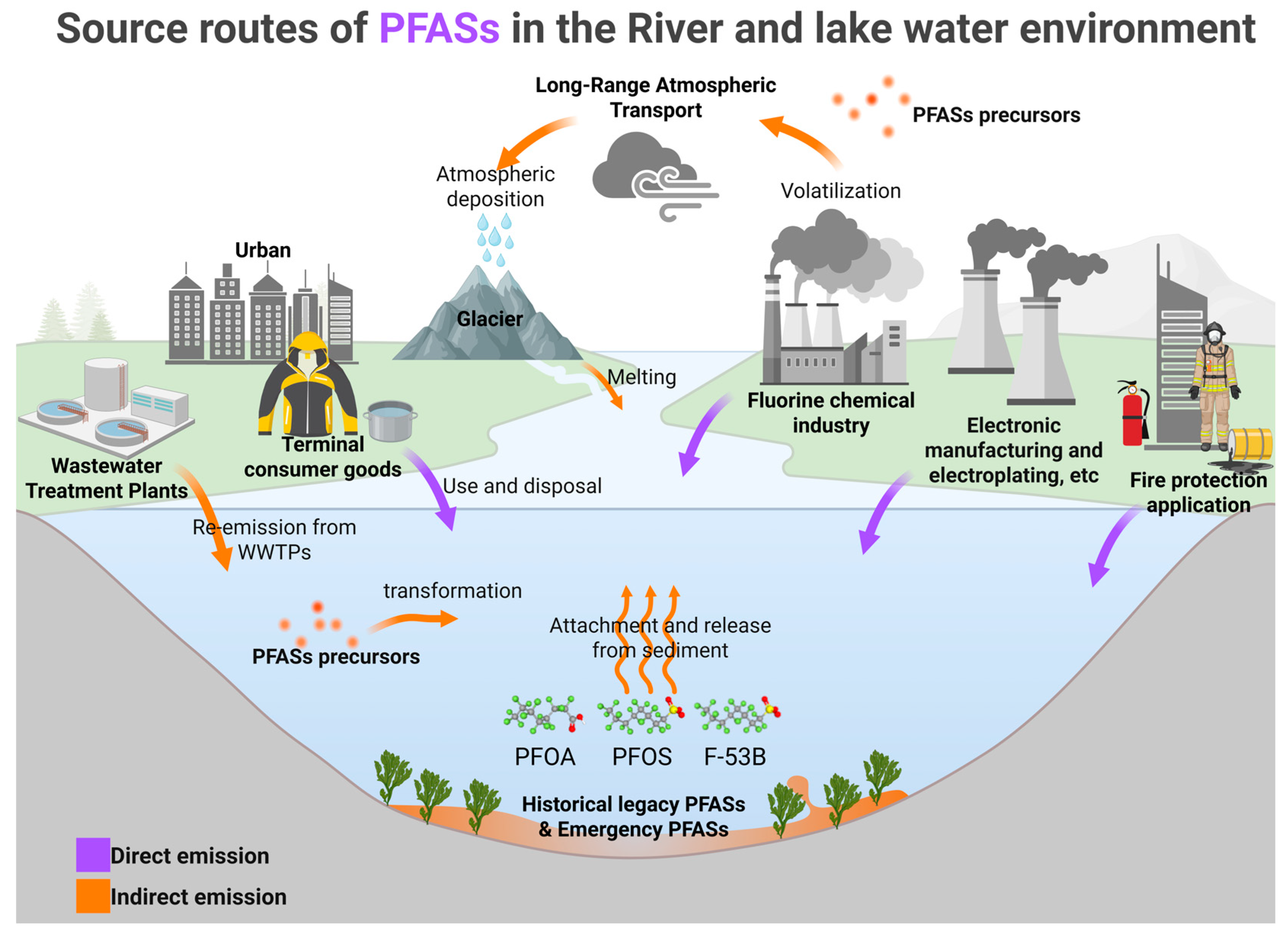
3.1. Sources of PFASs
3.1.1. Direct Input Pathways
3.1.2. Indirect Input Pathways
3.2. Pollution Characteristics of PFASs
| Country | Site | Total Concentration Range |
|---|---|---|
| China | Chongqing section of the Yangtze River [84] | 1.41~53.8 |
| Wuhan section of the Yangtze River [85] | 8.60~568 | |
| Shanghai section of the Yangtze River [10] | 113.38~362.37 | |
| Surface water in Shanghai [86] | 284~3018 | |
| Yellow River [87] | 15.57~36.42 | |
| Liao River [88] | 0.38~127.88 | |
| Xiaoqing River [82] | 25,429 | |
| Hulun Lake [70] | 3.67~8.84 | |
| Chaohu Lake [89] | 13.6~90.0 | |
| Yangzonghai Lake [68] | 14.95~26.42 | |
| America | Truckee River [90] | 441.7 |
| Las Vegas Wash [90] | 2234.3 | |
| Great Lakes [91] | 1~96 | |
| New Jersey [92] | 22.9~279.5 | |
| Korea | Asan Lake [13] | 17.7~467 |
| Changwon region [93] | 0.00~43.25 | |
| Poland | Oder River [94] | 7.62~68.01 |
| Brazil | Pampulha Lake [95] | 191~12,400 |
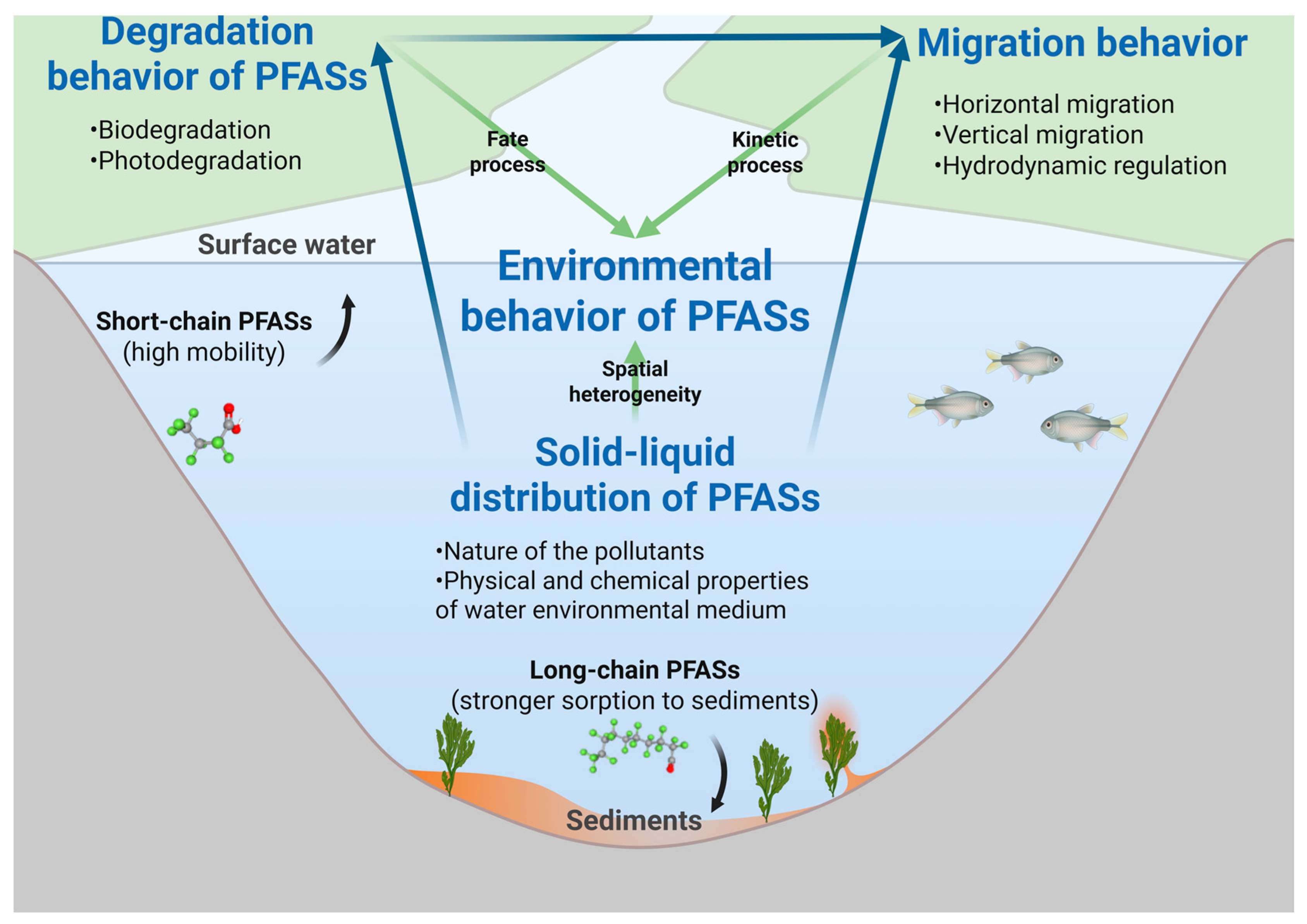
4. Environmental Behaviors and Key Influencing Factors of PFASs in River and Lake Environments
4.1. Water–Sediment Partitioning of PFASs
4.2. Biodegradation and Photodegradation of PFASs
4.3. Spatial Transport and Dynamic Release of PFASs
5. Environmental Risks of PFASs in River and Lake Environments
5.1. Ecological Risk Assessment of PFASs
5.2. Human Health Risk Assessment of PFASs
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamid, N.; Junaid, M.; Sultan, M.; Yoganandham, S.T.; Chuan, O.M. The Untold Story of PFAS Alternatives: Insights into the Occurrence, Ecotoxicological Impacts, and Removal Strategies in the Aquatic Environment. Water Res. 2024, 250, 121044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.; Anitole, K.; Hodes, C.; Lai, D.; Pfahles-Hutchens, A.; Seed, J. Perfluoroalkyl Acids: A Review of Monitoring and Toxicological Findings. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 99, 366–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gar Alalm, M.; Boffito, D.C. Mechanisms and Pathways of PFAS Degradation by Advanced Oxidation and Reduction Processes: A Critical Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Jin, R.; Qiao, Y.; Mao, J.; Wang, Z. Prevalent Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) Pollution in Freshwater Basins in China: A Short Review. Toxics 2025, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Song, B.; Zhong, H.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, D.; Lu, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G. Legacy and Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in the Bohai Sea and Its Inflow Rivers. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, J.W.; Rosal, C.G.; McCord, J.P.; Strynar, M.J.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Bergman, E.L.; Goodrow, S.M.; Tadesse, H.K.; Pilant, A.N.; Washington, B.J.; et al. Nontargeted Mass-Spectral Detection of Chloroperfluoropolyether Carboxylates in New Jersey Soils. Science 2020, 368, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Xu, S.-L.; Wang, X.-F.; Roponen, M.; Jin, N.-X.; Huang, J.-W.; Wu, Q.-Z.; Chu, C.; Sun, M.-K.; et al. Concentrations, Sources and Health Risks of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Ambient PM1 in the Pearl River Delta Region, China. Environ. Int. 2025, 198, 109439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, L.; Luo, W.; Jiang, N.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, P.; Ga, B.; Pei, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, R.; et al. Occurrence, Spatial Distribution, and Sources of PFASs in the Water and Sediment from Lakes in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Tang, B.; Cheng, X.; Fu, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, J.; Ming, D.; Xing, L.; Zhang, J. Source Apportionment and Predictable Driving Factors Contribute to Antibiotics Profiles in Changshou Lake of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wu, M.; Tang, L.; Li, J.; Qian, Z.; Han, T.; Xu, G. Perfluorinated Compounds in Surface Waters of Shanghai, China: Source Analysis and Risk Assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 149, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhuang, Y.; Dong, B.; Wu, J. Review on Per- and Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances’ (PFASs’) Pollution Characteristics and Possible Sources in Surface Water and Precipitation of China. Water 2022, 14, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Joseph, A.; Parveen, N.; Ranjan, V.P.; Goel, S.; Mandal, J.; Srivastava, P. Contamination of Per- and Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances in Agricultural Soils: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 124993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, M.-K.; Yang, H.; Lee, J.-E.; Son, Y.; Kho, Y.; Choi, K.; Zoh, K.-D. Concentration and Distribution of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in the Asan Lake Area of South Korea. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Hao, W.; Xiao, W. Emerging Perfluorinated Chemical GenX: Environmental and Biological Fates and Risks. Environ. Health 2025, 3, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endicott, D.; Silva-Wilkinson, R.; McCauley, D.; Armstrong, B. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Sediment: A Source of PFAS to the Food Web? Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2025, 21, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Pan, Y.; Qu, Y.; Ji, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, F.; Wu, B.; Xie, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Associations of Serum Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances with Hyperuricemia in Adults: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 12875–12887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, Y.; Sheng, N.; Yin, X.; Dai, J.; Li, P.; Pan, Y. Association between Serum Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Levels and Risk of Central and Peripheral Precocious Puberty in Girls. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 9140–9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Xing, Y.; Tong, J.; Lu, M.; Yan, S.; Huang, K.; Wu, X.; Tao, S.; Gao, H.; Pan, Y.; et al. Impact of Gestational Exposure to Individual and Combined Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances on a Placental Structure and Efficiency: Findings from the Ma’anshan Birth Cohort. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 6117–6127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; de Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Environment: Terminology, Classification, and Origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PFAS Technical and Regulatory Guidance Document. Available online: https://pfas-1.itrcweb.org/ (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Henry, B.J.; Carlin, J.P.; Hammerschmidt, J.A.; Buck, R.C.; Buxton, L.W.; Fiedler, H.; Seed, J.; Hernandez, O. A Critical Review of the Application of Polymer of Low Concern and Regulatory Criteria to Fluoropolymers. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2018, 14, 316–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.S.; Zhang, T.; Tao, Y.Q.; Lv, Y.G. A Review of Research Progress on Detection and Screening Techniques for Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Rock Miner. Anal. 2025, 44, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, D.; Yan, H. Advancements in Detection Techniques for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Comprehensive Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 176, 117754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhla, L.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Thamaraiselvan, C. A Comprehensive Review of Detection Techniques for PFAS Compounds in Aqueous Solution. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 77, 108569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, K.; Zulkarnain, N.A.; Niven, R.K. A Review of Analytical Methods and Technologies for Monitoring Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Water. Water 2023, 15, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Lyu, L.; Leng, J. Pretreatment and Detection of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): A Review of Current Advancements, Development Challenges, and Perspectives. Microchem. J. 2025, 213, 113789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, S.R.; Bowden, J.A.; Charest, N.; Jackson, S.R.; Koelmel, J.P.; Liberatore, H.K.; Lin, A.M.; Lowe, C.N.; Nieto, S.; Godri Pollitt, K.J.; et al. Filling the Gaps in PFAS Detection: Integrating GC-MS Non-Targeted Analysis for Comprehensive Environmental Monitoring and Exposure Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2025, 12, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Ji, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, F.; Sheng, N.; Dai, J.; Pan, Y. Unveiling Priority Emerging PFAS in Taihu Lake Using Integrated Nontarget Screening, Target Analysis, and Risk Characterization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 18980–18991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP Report of the Conference of the Parties of the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants on the Work of Its Fourth Meeting. 2009. Available online: http://chm.pops.int/portals/0/repository/cop4/unep-pops-cop.4-38.english.pdf (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- UNEP Report of the Conference of the Parties to the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants on the Work of Its Eighth Meeting. 2017. Available online: https://www.pops.int/TheConvention/ConferenceoftheParties/Meetings/COP8/tabid/5309/Default.aspx (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Liu, R.; Tian, J.; Gong, X.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Liu, Y. Partition Behavior of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Riverine Sediments. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 91, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2025 Conferences of the Parties to the Basel, Rotterdam, and Stockholm Conventions (BRS COPs). 2025. Available online: https://enb.iisd.org/sites/default/files/2025-05/enb15318e_1.pdf (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Objective for Canadian Drinking Water Quality Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. 2024. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/publications/healthy-living/objective-drinking-water-quality-per-polyfluoroalkyl-substances.html (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- ECHA Publishes Updated PFAS Restriction Proposal. 2025. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/-/echa-publishes-updated-pfas-restriction-proposal (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Addition of Certain PFAS to the TRI by the National Defense Authorization Act. 2025. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/toxics-release-inventory-tri-program/addition-certain-pfas-tri-national-defense-authorization-act (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Communication from the Commission—Guiding Criteria and Principles for the Essential Use Concept in EU Legislation Dealing with Chemicals. 2024. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/C/2024/2894/oj/eng (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Designation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid (PFOS) as CERCLA Hazardous Substances. 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/superfund/designation-perfluorooctanoic-acid-pfoa-and-perfluorooctanesulfonic-acid-pfos-cercla (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Key EPA Actions to Address PFAS. 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pfas/key-epa-actions-address-pfas (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Tao, Y.; Pang, Y.; Luo, M.; Jiang, X.; Huang, J.; Li, Z. Multi-Media Distribution and Risk Assessment of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Huai River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, X.; Hua, Z.; Xing, X.; Xue, H. Fate Variations of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Diverse Aquatic Environments: An Overlooked Influence of Hydrodynamics. Water Res. 2025, 282, 123628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Sheng, N.; Guo, Y.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Dai, J.; Pan, Y. Nontargeted Identification and Temporal Trends of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in a Fluorochemical Industrial Zone and Adjacent Taihu Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 7986–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amen, R.; Ibrahim, A.; Shafqat, W.; Hassan, E.B. A Critical Review on PFAS Removal from Water: Removal Mechanism and Future Challenges. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Feng, Y.; Gao, S.; Su, M.; Feng, Q.; Chen, X. A Review on Technologies for the Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Aquatic Environments. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Bezerra de Souza, B.; Casarini, M.M.; Kewalramani, J.A. A Review of PFAS Destruction Technologies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, S.; Wyer, H.; Leapman, J.C. Addressing the Environmental and Health Impacts of Microplastics Requires Open Collaboration between Diverse Sectors. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3000932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zuo, C.; Cai, Y.; Shen, C.; Ji, B.; Wei, T. The Unheeded Inherent Connections and Overlap between Microplastics and Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances: A Comprehensive Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, C.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Yue, T.; Xing, B. Interaction and Combined Toxicity of Microplastics and Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Aquatic Environment. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shih, K.M.; Li, X.Y. The Partition Behavior of Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanesulfonamide (FOSA) on Microplastics. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorca, M.; Schirinzi, G.; Martínez, M.; Barceló, D.; Farré, M. Adsorption of Perfluoroalkyl Substances on Microplastics under Environmental Conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, J.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Photodegradation Elevated the Toxicity of Polystyrene Microplastics to Grouper (Epinephelus Moara) through Disrupting Hepatic Lipid Homeostasis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6202–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, J.; Nishimura, N.; Shimada, Y. Toxicological Interactions of Microplastics/Nanoplastics and Environmental Contaminants: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 123913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, N.J.M.; Simcik, M.F.; Novak, P.J. Perfluoroalkyl Substances Increase the Membrane Permeability and Quorum Sensing Response in Aliivibrio Fischeri. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H.-J.; Kwon, J.-H. Estimating Microplastic-Bound Intake of Hydrophobic Organic Chemicals by Fish Using Measured Desorption Rates to Artificial Gut Fluid. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, A.M.; Yolton, K.; Wang, Z.; Xie, C.; Webster, G.M.; Ye, X.; Calafat, A.M.; Braun, J.M.; Dietrich, K.N.; Lanphear, B.P.; et al. Childhood Perfluoroalkyl Substance Exposure and Executive Function in Children at 8 years. Environ. Int. 2018, 119, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, K.; Silva, M.R.; Klaper, R. Distribution and Effects of Branched versus Linear Isomers of PFOA, PFOS, and PFHxS: A Review of Recent Literature. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, N.; Li, W.; Niu, Z. Distribution, Partitioning Behavior and Positive Matrix Factorization-Based Source Analysis of Legacy and Emerging Polyfluorinated Alkyl Substances in the Dissolved Phase, Surface Sediment and Suspended Particulate Matter around Coastal Areas of Bohai Bay, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, S. The Transformation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Aquatic Environment of a Fluorochemical Industrial Park. Water 2024, 16, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, P.; Mayes, W.M.; James, A.L.; Comber, S.; Biles, E.; Riley, A.L.; Verplanck, P.L.; Bradley, L. Spatially Resolved Source Apportionment of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) within a Post-Industrial River Catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 1001, 180502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirikona, F.; Quinete, N.; Gonzalez, J.; Mutua, G.; Kimosop, S.; Orata, F. Occurrence and Distribution of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances from Multi-Industry Sources to Water, Sediments and Plants along Nairobi River Basin, Kenya. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langberg, H.A.; Arp, H.P.H.; Breedveld, G.D.; Slinde, G.A.; Høiseter, Å.; Grønning, H.M.; Jartun, M.; Rundberget, T.; Jenssen, B.M.; Hale, S.E. Paper Product Production Identified as the Main Source of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in a Norwegian Lake: Source and Historic Emission Tracking. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, A.M.; Bellona, C.; Strathmann, T.J. Rejection of PFAS and Priority Co-Contaminants in Semiconductor Fabrication Wastewater by Nanofiltration Membranes. Water Res. 2024, 262, 122111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Huo, S.; Xi, B.; Hu, S.; Zhang, J.; He, Z. Spatial Distribution and Source Apportionment of PFASs in Surface Sediments from Five Lake Regions, China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abunada, Z.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Bashir, M.J.K. An Overview of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in the Environment: Source, Fate, Risk and Regulations. Water 2020, 12, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Zhang, X.; Li, R.; Tu, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Mai, B. Spatiotemporal Distribution, Partitioning Behavior and Flux of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Surface Water and Sediment from Poyang Lake, China. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNicola, M.; Lin, Z.; Quiñones, O.; Vanderford, B.; Song, M.; Westerhoff, P.; Dickenson, E.; Hanigan, D. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Organofluorine in Lakes and Waterways of the Northwestern Great Basin and Sierra Nevada. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 166971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.C.; Pang, Y.; Chen, S.Q.; An, X.D.; Wu, J.Q.; Zhang, M.Y. Occurrence and removal effect of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in each operating unit of typical wastewater treatment processes. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2024, 14, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Pan, B.; Pan, Z.; Xu, N.; Wu, J.; Sun, W.; Hou, B.; Dong, Y. A Clustering Approach Based on High-Resolution Ecological Vulnerability Index Reveals Spatial Patterns of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Pollution in Lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Water Res. 2025, 279, 123461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Qiu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Yin, H. Targeted Screening, Characterization and Sources of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Plateau Lake Yangzonghai, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacInnis, J.; De Silva, A.O.; Lehnherr, I.; Muir, D.C.G.; St. Pierre, K.A.; St. Louis, V.L.; Spencer, C. Investigation of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Proglacial Rivers and Permafrost Seep in a High Arctic Watershed. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ren, S.; An, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G. The First Survey of Legacy and Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Hulun Lake, China: Occurrence, Sources, and Environmental Impacts. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, R.; Stubbings, W.A.; Li, F.; Wu, F.; Wang, S. Distribution, Partitioning, Source Apportionment, and Ecological Risk Assessment of Legacy and Emerging PFAS in Water and Sediment of the Pearl River Delta. ACS EST Water 2025, 5, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Jiang, J.-J.; Rodenburg, L.A.; Cai, M.; Wu, Z.; Ke, H.; Chitsaz, M. Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Sediments from the Bering Sea to the Western Arctic: Source and Pathway Analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasecnaja, E.; Zacs, D. Determination of Perfluorinated Substances (PFAS) Using LC-ORBITRAP-MS in Certain Foodstuffs of Animal Origin According to Newly Established EU Legislation. Food Anal. Methods 2024, 17, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, A.; Wojtal, P.K.; Pan, H.; Lane, C.S.; Mead, R.N. Stable Carbon and Sulfur Isotopic Compositions of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2025, 12, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.-U.; Sikder, R.; Tonmoy, T.A.; Hossain, M.M.; Ye, T.; Aich, N.; Gadhamshetty, V. Transforming PFAS Management: A Critical Review of Machine Learning Applications for Enhanced Monitoring and Treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 70, 106941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roostaei, J.; Colley, S.; Mulhern, R.; May, A.A.; Gibson, J.M. Predicting the Risk of GenX Contamination in Private Well Water Using a Machine-Learned Bayesian Network Model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonker, M.T.O. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Water (2008–2022) and Fish (2015–2022) in The Netherlands: Spatiotemporal Trends, Fingerprints, Mass Discharges, Sources, and Bioaccumulation Factors. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurwadkar, S.; Dane, J.; Kanel, S.R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Cawdrey, R.W.; Ambade, B.; Struckhoff, G.C.; Wilkin, R. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Water and Wastewater: A Critical Review of Their Global Occurrence and Distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.L.; Justice, J.R.; Elias, M.C.; Schnitker, B.; Gallagher, K. Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in US Ambient Surface Waters: A Review of Occurrence in Aquatic Environments and Comparison to Global Concentrations. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 2425–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, D.B.; Monk, J.R.; Woldetsadik, D.; Hudson, A.C.; Garner, M.C.; Lindley, K.; Piacentini, J.; Buch, A.C.; Cohu, C.; Duvall, C.S.; et al. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in the Rivers of the Western United States. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 22, 9319–9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, Y.; Ling, H.; Yi, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R. Occurrence and Human Exposure Assessment of PFAS in River and Groundwater around a Closed Fluorochemical Plant in China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 16241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, M.; Yang, D. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Chinese Surface Waters: A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulcan, R.X.S.; Yarleque, C.M.H.; Lu, X.; Yeerkenbieke, G.; Herrera, V.O.; Gunarathne, V.; Yánez-Jácome, G.S. Characterization of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Chinese River and Lake Sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 489, 137680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yan, X.; Cai, F.S.; Luo, W.K.; Zhuang, X. Pollution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Perfluorinated Compounds in the Chongqing Section of the Yangtze River Basin. In Proceedings of the 2019 Annual Conference of the Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences (Volume 4), Xi’an, China, 23–25 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Cao, M.; Zhu, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Gu, X.; Lu, X. Distribution of Perfluorinated Compounds in Surface Water from Hanjiang River in Wuhan, China. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; An, X.; Tang, C.; Tang, C.; Zhang, B.; Chen, C.; Lin, T.; Jones, K.C.; Zhao, Z. Molecular Characteristics of Emerging Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) in Surface Waters around Fluorine-Related Industries in a Chinese Megacity. Environ. Int. 2025, 198, 109444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, L. Evidences for Replacing Legacy Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances with Emerging Ones in Fen and Wei River Basins in Central and Western China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 377, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Guo, C.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Partitioning Behavior, Source Identification, and Risk Assessment of Perfluorinated Compounds in an Industry-Influenced River. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Xu, S.-D.; Liu, T.; Wu, L.-L.; Liu, S.-T.; Liu, G.; Sun, J.; Luo, Y.-X.; Gao, L.; Li, H.; et al. Risk Prioritization and Experimental Validation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Chaohu Lake: Based on Nontarget and Target Analyses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 492, 138179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Son, Y. Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Surface Water and Sediments from Two Urban Watersheds in Nevada, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, M.J.; Griffin, E.K.; Caspar, R.J.; Timshina, A.S.; Bowden, J.A.; Miller, C.J.; Baker, B.B.; Baker, T.R. Identification and Quantification of Novel Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Contamination in a Great Lakes Urban-Dominated Watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 941, 173325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrow, S.M.; Ruppel, B.; Lippincott, R.L.; Post, G.B.; Procopio, N.A. Investigation of Levels of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Surface Water, Sediment and Fish Tissue in New Jersey, USA. Chemosphere 2020, 729, 138839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.; Jang, H.; Jeon, J. Distribution and Seasonal Variations of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Streams within the Changwon Region. Environ. Eng. Res. 2024, 30, 240367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarębska, M.; Bajkacz, S.; Hordyjewicz-Baran, Z. Assessment of Legacy and Emerging PFAS in the Oder River: Occurrence, Distribution, and Sources. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starling, M.C.V.M.; Rodrigues, D.A.S.; Miranda, G.A.; Jo, S.; Amorim, C.C.; Ankley, G.T.; Simcik, M. Occurrence and Potential Ecological Risks of PFAS in Pampulha Lake, Brazil, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohoro, C.R.; Amaku, J.F.; Conradie, J.; Olisah, C.; Akpomie, K.G.; Malloum, A.; Akpotu, S.O.; Adegoke, K.A.; Okeke, E.S.; Omotola, E.O. Effect of Physicochemical Parameters on the Occurrence of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Aquatic Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 208, 117040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Lian, Q.; Zhang, X.; Karsili, T.K.; Holmes, W.; Chen, Y.; Zappi, M.E.; Gang, D.D. A Review of PFAS Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions: Current Approaches, Engineering Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 321, 121138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dou, Z.; Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Lin, B.-L.; et al. Occurrence and Partitioning Behavior of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Water and Sediment from the Jiulong Estuary-Xiamen Bay, China. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Ma, L.; Lin, X.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Water, Sediment, and Fish from a Subtropical River of China: Environmental Behaviors and Potential Risk. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Pan, C.-G.; Xiao, S.-K.; Wu, Q.; Tan, H.-M.; Yu, K. Insights into the Effects of Salinity on the Sorption and Desorption of Legacy and Emerging Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) on Marine Sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiu, R.-F.; Lee, H.-J.; Hsu, H.-T.; Gong, G.-C. Suspended Particulate Matter-Bound per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in a River-Coastal System: Possible Correlation with Transparent Exopolymer Particles. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Navarro, D.A.; Du, J.; Ying, G.; Yang, B.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Kookana, R.S. Increasing Ionic Strength and Valency of Cations Enhance Sorption through Hydrophobic Interactions of PFAS with Soil Surfaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Zhou, B.; Yuan, R.; Luo, S.; Gai, N.; Chen, H. Influence of Soil Composition and Environmental Factors on the Adsorption of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Pereira, H.; Kleja, D.B.; Ahrens, L.; Enell, A.; Kikuchi, J.; Pettersson, M.; Gustafsson, J.P. Effect of pH, Surface Charge and Soil Properties on the Solid–Solution Partitioning of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in a Wide Range of Temperate Soils. Chemosphere 2023, 321, 138133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, D.A.; Oliver, D.P.; Simpson, S.L.; Kookana, R.S. Organic Carbon and Salinity Affect Desorption of PFAS from Estuarine Sediments. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 1302–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Cao, H.; Pan, W.; Wang, C.; Liang, Y. The Role of Dissolved Organic Matter during Per- and Polyfluorinated Substance (PFAS) Adsorption, Degradation, and Plant Uptake: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, Q.; Huang, B.; Chen, X.; Ji, L.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, T.; Wang, J. The Complex Effect of DOM on PFOA and PFOS Transport: Considering the Interference of Solution Ionic Strength and Cation Type. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, D.; Li, X.; Jia, X.; Shi, Y.; Cai, Y. Interactive Effects of Soil Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) and Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances on Contaminated Soil Site: DOM Molecular-Level Perspective. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Kannan, K.; Lim, B.J.; An, K.G.; Kim, S.D. Effects of Salinity and Organic Matter on the Partitioning of Perfluoroalkyl Acid (PFAs) to Clay Particles. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1803–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschauzier, C.; Beerendonk, E.; Scholte-Veenendaal, P.; De Voogt, P. Impact of Treatment Processes on the Removal of Perfluoroalkyl Acids from the Drinking Water Production Chain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhu, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Distribution and Desorption of Perfluorinated Compounds in Fractionated Sediments. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smorada, C.M.; Sima, M.W.; Jaffé, P.R. Bacterial Degradation of Perfluoroalkyl Acids. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2024, 88, 103170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zheng, J.; Bai, Z.; Chen, H.; Ge, X.; Tang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Luo, H.; et al. A Review of Microbial Degradation of Perfluorinated and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) during Waste Biotransformation Processes: Influencing Factors and Alleviation Measures. Environ. Res. 2025, 279, 121795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Q.; Lin, X.; Zheng, X.; Wu, Y.; Long, M.; Chen, Y. Aerobic or Anaerobic? Microbial Degradation of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, B.A.; Zhou, J.; Clarke, B.O.; Leung, I.K.H. Enzymatic Degradation of PFAS: Current Status and Ongoing Challenges. ChemSusChem 2025, 18, e202401122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senevirathna, S.T.M.L.D.; Krishna, K.C.B.; Mahinroosta, R.; Sathasivan, A. Comparative Characterization of Microbial Communities That Inhabit PFAS-Rich Contaminated Sites: A Case-Control Study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Abbt-Braun, G.; Horn, H. Changes in the Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter during Sludge Treatment: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellerman, A.M.; Kothawala, D.N.; Dittmar, T.; Tranvik, L.J. Persistence of Dissolved Organic Matter in Lakes Related to Its Molecular Characteristics. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothawala, D.N.; Köhler, S.J.; Östlund, A.; Wiberg, K.; Ahrens, L. Influence of Dissolved Organic Matter Concentration and Composition on the Removal Efficiency of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) during Drinking Water Treatment. Water Res. 2017, 121, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lv, L.; Lan, P.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W. Effect of Effluent Organic Matter on the Adsorption of Perfluorinated Compounds onto Activated Carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 225–226, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Xiao, T.; Yu, P.-F.; Zhao, H.-M.; Mo, C.-H.; Li, Y.-W.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Zhou, D.-M.; Wong, M.-H. Mechanism and Implication of the Sorption of Perfluorooctanoic Acid by Varying Soil Size Fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11569–11579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Sun, H.; Song, M.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, W.; Ying, G.-G.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in the Soil–Plant System: Sorption, Root Uptake, and Translocation. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milinovic, J.; Lacorte, S.; Vidal, M.; Rigol, A. Sorption Behaviour of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Su, C.; Sun, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, P.; Liu, W.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Marine Food Webs from South China Sea: Trophic Transfer and Human Exposure Implication. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwayezu, J.-N.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Bäckström, M. Sorption of PFOS Isomers on Goethite as a Function of pH, Dissolved Organic Matter (Humic and Fulvic Acid) and Sulfate. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos Pereira, H.; Ullberg, M.; Kleja, D.B.; Gustafsson, J.P.; Ahrens, L. Sorption of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) to an Organic Soil Horizon—Effect of Cation Composition and pH. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Shan, X.-Q.; Zhang, S. Field Study on the Uptake and Translocation of Perfluoroalkyl Acids (PFAAs) by Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Grown in Biosolids-Amended Soils. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaalgamaa, S.; Vähätalo, A.V.; Perkola, N.; Huhtala, S. Photochemical Reactivity of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Conditions Representing Surface Water. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3043–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Mezgebe, B.; Hejase, C.A.; Sahle-Demessie, E.; Nadagouda, M.N. Photodegradation and Photocatalysis of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): A Review of Recent Progress. Next Mater. 2024, 2, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Kopinke, F.-D.; Georgi, A. Photodegradation of Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid on Fe-Zeolites in Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xue, H.; Kang, T.; Lei, Q.; Chen, J.; Zuo, Z.; Han, B.; Lu, X.; Yang, X.; Shan, X.; et al. Efficient Photodegradation of Perfluoroalkyl Substances under Visible Light by Hexagonal ZnIn2S4 Nanosheets. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 148, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta Majumdar, R.; Bliumkin, L.; Lane, D.; Soong, R.; Simpson, M.; Simpson, A.J. Analysis of DOM Phototransformation Using a Looped NMR System Integrated with a Sunlight Simulator. Water Res. 2017, 120, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, P.; Shao, T.; Zhao, S. Ferric Ion Mediated Photodecomposition of Aqueous Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) under UV Irradiation and Its Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 271, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, X.; Shan, X.; Liu, F.; Liu, D.; Feng, M.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y.; Cai, Y. Photochemical Degradation of PFAS: Mechanistic Insights and Design Strategies for Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Systems. Small 2025, 21, e06040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Cheng, J.; Yang, C.; Yang, S. Factors Influencing Aqueous Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) Photodecomposition by VUV Irradiation in the Presence of Ferric Ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 298, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Hu, S.; Huo, S.; Xi, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Spatial Distribution and Historical Deposition Behaviors of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Sediments of Lake Chaohu, a Shallow Eutrophic Lake in Eastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Chu, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Spatiotemporal Variations and Bioaccumulation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Oxidative Conversion of Precursors in Shallow Lake Water. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, L.; Gu, L.; Hua, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, H. Distribution and Release of Perfluorinated Compounds (PFCs) in Water-Sediment Systems: The Effect of Confluence Channels. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhao, D.; Peng, Z.; Zhai, X. The impact of surface water-groundwater interactions on the fate and transport of typical PFAS. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2025, 52, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Sun, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wu, J. Research progress on the pollution, adsorption, and transport of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) at the sediment-water interface. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 4147–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yan, N. Research progress on transport of PFAS coexisting with other contaminants in subsurface environment. Environ. Pollut. Control 2023, 45, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, K.; Duan, Y.; Parks, A.; Olivares, C.I.; Dixit, F.; Sedlak, D.L.; Alvarez-Cohen, L. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Release from Aqueous Film-Forming Foam Impacted Solids Exposed to Stormwater and Saltwater. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hua, Z.; Chen, Z. Impact of Long-Term Submerge-Emerge Alternation on the Fate of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Sediment-Water Systems: Insight from Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 383, 126822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, X.; Zhao, X.; Guo, R.; Wang, X.; Hao, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Distribution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Water Environment in Typical Karst Region. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 2148–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Tao, H.; Qi, G.; Guo, W.; Ge, H.; Shi, J. A QSAR–ICE–SSD Model Prediction of the PNECs for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Their Ecological Risks in an Area of Electroplating Factories. Molecules 2021, 26, 6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Trend of PFAS Concentrations and Prediction of Potential Risks in Taihu Lake of China by AQUATOX. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, W.; Huang, T.; Chen, S.; Xiang, S.; Pang, Y. Characteristics, Sources, and Risk Assessment of Perlyfluoroalkyl Substances in Surface Water and Sediment of Luoma Lake. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 3562–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, L.; She, Y.; Kang, G.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Huai, T.; Li, R.; Qi, L.; Zhang, M. Pollution Characteristics, Source Analysis and Risk Assessment of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances of Kui River. Preprint 2025, SSRN 5273330. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=5273330 (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Ankley, G.T.; Cureton, P.; Hoke, R.A.; Houde, M.; Kumar, A.; Kurias, J.; Lanno, R.; McCarthy, C.; Newsted, J.; Salice, C.J.; et al. Assessing the Ecological Risks of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Current State-of-the Science and a Proposed Path Forward. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 40, 564–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Ji, C.; Li, F.; Wu, H. Time Is Ripe for Targeting Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances-Induced Hormesis: Global Aquatic Hotspots and Implications for Ecological Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 9314–9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shen, N.; Zhang, D.; Chen, J.; He, X.; Ji, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Occurrence, Spatial Distribution, Sources and Risk Assessment of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Surface Sediments of the Yellow River Delta Wetland. J. Ocean Univ. China 2024, 23, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Li, Q.; Johnson, A.C.; Sarvajayakesavalu, S.; Sweetman, A.J. Risk Assessment and Source Identification of Perfluoroalkyl Acids in Surface and Ground Water: Spatial Distribution around a Mega-Fluorochemical Industrial Park, China. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, X.; Hua, Z. Occurrence, Distribution, and Risk Assessment of Perfluoroalkyl Acids in Drinking Water Sources from the Lower Yangtze River. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Wang, X. Occurrence, Partitioning Behavior and Risk Assessments of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Water, Sediment and Biota from the Dongshan Bay, China. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinikainen, J.; Perkola, N.; Äystö, L.; Sorvari, J. The Occurrence, Distribution, and Risks of PFAS at AFFF-Impacted Sites in Finland. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Z.; Gao, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Perfluoroalkyl Acids in the Aquatic Environment of a Fluorine Industry-Impacted Region: Spatiotemporal Distribution, Partition Behavior, Source, and Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.-E.; Zhang, D.; Tang, J. Emerging and Legacy Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Rivers of a Typical Industrialized Province of China: Spatiotemporal Variations, Mass Discharges and Ecological Risks. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 986719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Jin, Y.; Xu, H.; Qian, H.; Zheng, W.; Wu, C.; Guo, C. Assessment of contamination and health risk of perfluoroalkyl substances in drinking water in Shanghai. J. Environ. Occup. Med. 2020, 37, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettger, J.D.; DeLuca, N.M.; Zurek-Ost, M.A.; Miller, K.E.; Fuller, C.; Bradham, K.D.; Ashley, P.; Friedman, W.; Pinzer, E.A.; Cox, D.C.; et al. Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Tap Water from the American Healthy Homes Survey II. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 2686–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorakova, D.; Jurikova, M.; Svobodova, V.; Parizek, O.; Kozisek, F.; Kotal, F.; Jeligova, H.; Mayerova, L.; Pulkrabova, J. Complex Monitoring of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Tap Drinking Water in the Czech Republic. Water Res. 2023, 247, 120764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, J.; Yuan, T.; Xia, H.; Ma, Y.; Shen, Z.; Shi, R.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ding, W.; Gao, L.; et al. Characteristic and Human Exposure Risk Assessment of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Study Based on Indoor Dust and Drinking Water in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, C.; Johnson, A.C.; Sun, X.; Ding, X.; Ding, D.; Liu, S.; Liang, X. Source Apportionment and Crop Bioaccumulation of Perfluoroalkyl Acids and Novel Alternatives in an Industrial-Intensive Region with Fluorochemical Production, China: Health Implications for Human Exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groffen, T.; Wepener, V.; Malherbe, W.; Bervoets, L. Distribution of Perfluorinated Compounds (PFASs) in the Aquatic Environment of the Industrially Polluted Vaal River, South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Classification | Factor | Influence Mechanism | Typical Behavioral Characteristics | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFASs structural properties | Chemical stability | Enhances resistance to oxidation and reduces reactivity | PFASs are resistant to natural degradation and tend to accumulate in environmental media | [96,97] |
| Carbon chain length | Affects hydrophobicity and OC binding capacity | LC-PFASs tend to adsorb to sediments; SC-PFASs (e.g., PFHxA) are more mobile | [90,92] | |
| Functional group type | Influences solubility and adsorption behavior | –SO3H increases hydrophobicity and sediment deposition; –COOH favors the aqueous phase | [31] | |
| Environmental conditions | pH | Affects particle surface charge and adsorption strength | High pH promotes desorption and mobility | [96,98,99] |
| Salinity and ionic strength | Affects particle adsorption and bridging interactions | High salinity or high Ca2+ enhances PFAS accumulation in sediments | [100,101,102] | |
| Sediment properties | Influences adsorption capacity | High OC, fine particles, and iron/aluminum oxides enhance adsorption | [102,103,104,105] | |
| DOM | Competes for adsorption sites, affects desorption | DOM increases PFAS mobility; short-chain PFASs desorb more readily | [106,107,108,109,110,111] |
| Assessment Method | Principle and Features | Advantages | Limitations | Main Applicable Scenarios | Case Studies | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecological Risk Assessment | RQ | Compares environmental PFAS concentrations with ecological toxicity reference values to identify potential risk | Simple and intuitive; suitable for preliminary cumulative risk assessment | Provides only qualitative or semi-quantitative results; limited in addressing mixture pollution and long-term accumulation effects | Preliminary ecological risk screening | Ecological risk assessment of the Bohai Sea and its inflowing rivers [5]; Water environment ecological risk assessment in Southwest China karst region [144] |
| SSD | Constructs concentration–effect probability curves based on multiple toxicity data to derive predicted no-effect concentration (PNEC) | Accounts for interspecies sensitivity differences; strong capability for extrapolating risk thresholds | Limited toxicity data; applicability to emerging PFASs is insufficient | Overall risk assessment (suitable for PFOS/PFOA) | Ecological risk assessment of rivers near electroplating factories [145] | |
| EDRM | Fits dose–effect relationships to predict long-term low-dose cumulative effects; can consider hormesis effects | Captures long-term exposure and low-dose stimulation effects, enhancing risk identification | Data-intensive; interspecies sensitivity differences increase uncertainty | Long-term ecological risk assessment | – | |
| AQUATOX | Mechanistic model simulating PFAS fate, exposure, and toxic effects in aquatic ecosystems | Integrates multiple factors; suitable for long-term predictions in complex aquatic environments | Requires extensive model parameters; high workload for construction and validation | Multi-media accumulation and long-term exposure risk analysis | Ecological risk assessment of shallow lakes near fluorochemical industrial areas [146] | |
| Human Health Risk Assessment | HQ | Compares environmental concentrations with reference doses (RfD) to evaluate human exposure risk | Simple and intuitive; suitable for preliminary health risk assessment | Does not consider mixture exposure or population sensitivity differences | Preliminary human or food chain health risk assessment | Health risk assessment of regional large-scale regulated lakes [147] |
| HQmix | Aggregates cumulative exposure effects from multiple PFASs or other pollutants | Can reflect risks from multi-component mixed exposure | Data-demanding; limited treatment of synergistic or antagonistic effects | Health risk analysis under combined pollution scenarios | Mixed exposure risk assessment of PFASs in urban rivers [148] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Z.; Deng, F.; Nie, J.; Li, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y. From Sources to Environmental Risks: Research Progress on Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in River and Lake Environments. Water 2025, 17, 3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213061
Zhou Z, Deng F, Nie J, Li H, Jiang X, Wang S, Guo Y. From Sources to Environmental Risks: Research Progress on Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in River and Lake Environments. Water. 2025; 17(21):3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213061
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Zhanqi, Fuwen Deng, Jiayang Nie, He Li, Xia Jiang, Shuhang Wang, and Yunyan Guo. 2025. "From Sources to Environmental Risks: Research Progress on Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in River and Lake Environments" Water 17, no. 21: 3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213061
APA StyleZhou, Z., Deng, F., Nie, J., Li, H., Jiang, X., Wang, S., & Guo, Y. (2025). From Sources to Environmental Risks: Research Progress on Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in River and Lake Environments. Water, 17(21), 3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213061






